- Article
Do LRG1–SERPINA1 Interactions Modulate Fibrotic and Inflammatory Signatures in Rheumatoid Arthritis? A Proteomic and In Silico Investigation
- Talib Hussain,
- Monika Verma and
- Sagarika Biswas
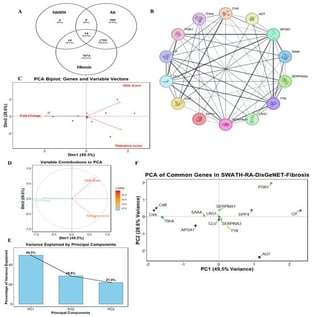
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic, pro-inflammatory, autoimmune disease that mainly affects the joints in a symmetrical manner. Differential proteomic profiling through Sequential Window Acquisition of all Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectra (SWATH-MS/MS) helps in a better understanding of the RA pathogenesis. In this study, we compared the differentially upregulated proteins with those associated with fibrosis to gain a deeper understanding of the fibrotic aspect of RA. Methods: We analyzed plasma proteomics data, previously obtained by SWATH-MS/MS. Our focus was on proteins associated with Leucine Rich Alpha2glycoprotein1 (LRG1) and we employed an in silico method. Results: We identified common proteins between RA and fibrosis. Among them, LRG1 and Serine Protease Inhibitor Clade A, Member 1 (SERPINA1) showed a high co-expression score in the gene clusters. LRG1 is both pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic, while SERPINA1 is an anti-inflammatory protein that inhibits pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic molecules (Elastase). Further, docking studies and a simulation study of the docked complexes with the analysis of Hydrogen bonds, Solvent Accessible Surface Area (SASA), Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD), Root Mean Square Fluctuation (RMSF) and Radius of gyration (Rg), suggested a strong interaction between the two partners, LRG1 and SERPINA1. Conclusions: Our study suggests that LRG1 may inhibit SERPINA1 and promote inflammation and fibrotic processes by disrupting SERPINA1’s primary function.
6 February 2026