Abstract
The aim of this systematic review was to answer the question of whether crack cocaine can induce cellular and molecular alterations and whether such alterations are somehow related to clinical lesions in the oral mucosa. The searches were undertaken in three electronic databases and conducted based on the PRISMA 2020 statement. Eleven studies published between 1994 and 2020 were analyzed. The quality of the included studies was assessed by two independent reviewers (TGP and DAR) through a confounder’s categorization methodology, in which final ratings were attributed (strong, moderate or weak) for each study. From 11 studies included, 7 evaluated the cellular/molecular impact of the addiction in a total of 492 individuals and compared to a control (non-exposure) group (n = 472). The main tests used for cellular alteration were MN and AgNORs. Cells from crack cocaine groups exhibited increased proliferation and MN counting. Only four studies evaluated the prevalence of oral lesions. All of them showed that individuals exposed to crack cocaine presented an increased number of oral lesions. Most studies showed good quality. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that crack use may induce changes at the cellular and molecular level and also exhibit an increased number of oral lesions. However, a correlation between such changes and oral mucosa lesions still needs further investigation and elucidation through other clinical studies in humans.
1. Introduction
It has been established that 243 million people between 15 and 64 years old use some form of illicit drug around the world, which adds up to approximately 5000 deaths due to drugs every year in Latin America and the Caribbean [1]. Data from the National Alcohol and Drug Use Research in Brazil show that, about 2 million Brazilians have smoked crack at least once at some point in their lives, ranking the country as the largest crack consumer in the whole world [2]. Thus, crack cocaine use is considered a serious public health problem in many places around the world, for example, Brazil, since psychosomatic injury, social exclusion, and high morbidity and mortality rates can be observed [3].
Several systemic health conditions are associated with the use of psychoactive substances (a natural or synthetic chemical taken via any route capable of acting on the central nervous system altering an individual’s behavior), especially crack cocaine (a smokable form of cocaine), with the cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological and gastrointestinal being some of the target systems [4]. In this sense, it is coherent to assume that the oral mucosa is a possible target, since the main form of crack consumption is through inhalation. The supporting mechanism to this assumption has its basis in some local effects, such as smoke heat, harmful effects of the chemical content of the drug, tissue necrosis due to gingival friction, vasoconstriction and a lower salivary flow rate [5]. Thus, cellular harmful outcomes as a result of developing oral lesions could be related to the abuse of such substances [6,7].
Even though several studies have approached the body effect of high consumption of crack cocaine [8,9,10], there is still minimal knowledge of its harmful effects on oral mucosal cells at the cellular and molecular level. In line with this limitation, this systematic review aimed to answer the following question: Are cytomorphogenetic events correlated with oral mucosal lesions induced by crack cocaine use?
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review was carried out in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement 2020 criteria. The PICOS strategy (P (oral mucosa), I (crack cocaine exposure), C (control group), O (genotoxicity), S (clinical studies)) was used as a guide.
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
Published papers were included in our systematic review if they met the following criteria: (1) studies investigating genetic damage in vivo; (2) studies published in English; (3) studies that provided data with clear scientific standards. Through our scientific search strategy, we decided to focus on some techniques used for evaluating potential alterations in the oral mucosa (at different levels), such as micronucleus, cytomorphometry, AgNOR techniques and oral clinical inspection.
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
Published papers were excluded if they met the following criteria: (1) conference abstracts, reviews, editorials and letters; (2) full text not available in English; (3) unavailable data/unextractable data; (4) multigenerational studies; (5) incomplete or unclear results; (6) in vitro; (7) in vivo not conducted in humans.
2.3. Databases and Search Strategy
Electronic searches were undertaken in January 2023 in PubMed, SCOPUS and Web of Science electronic databases without regard to publication date or geographic region with the following keywords and Boolean operators: (“Crack” OR “Crack cocaine”) AND (“Genotoxicity” OR “DNA damage” OR “genetic damage” OR “DNA breakage” OR “genetic injury” OR “DNA injury” “chromosome damage” OR “oral mucosal lesion” “cell proliferation”). In addition, manual search of articles and cited/related articles was performed to identify publications that might have been missed by the primary database searches. The search approach was applied consistently across all databases.
Duplicates were removed upon identification. After duplicate removal, full texts were read to confirm eligibility by two authors (TGP and DAR). Disagreements were resolved between the two reviewers through discussion when consensus was reached.
2.4. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
Two reviewers (TGP and DAR) independently extracted information from the included studies. The following data were extracted from the articles: authors, year and country of study, organs or cell types, time of exposure, assay, number of cells evaluated, genotoxicity assay used, blind, statistical analysis, negative control and main results. Data were tabulated and analyzed descriptively in Microsoft Office Excel 2019 (Microsoft® software, version 16, Redmond, WA, USA).
The quality assessment of chosen studies was assessed independently by two reviewers (TGP and DAR). For this purpose, all variables (confounders) were considered in the study. If the study did not control one variable (confounder), it was considered STRONG (Low Risk of Bias) at the final rating. If the study did not control two variables, it was considered MODERATE (Medium Risk of Bias) at the final rating. Finally, studies that did not control three or more variables were categorized as WEAK (Low Risk of Bias) at the final rating, as described elsewhere [11].
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
Figure 1 depicts a flowchart of the current systematic review’s study selection process. A total of 76 references were retrieved in the initial search. Full manuscripts from 11 articles composed the analysis performed in this systematic review.
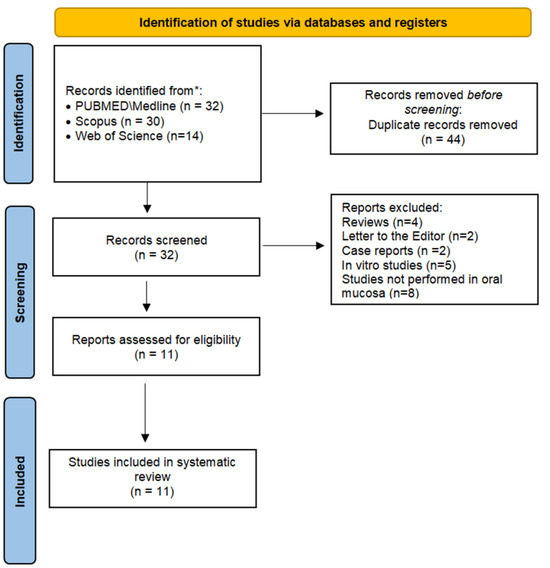
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the study investigating the cytomorphogenetic events in oral mucosa from crack cocaine users.
3.2. Study Characteristics
The included articles were published between 1994 and 2020 and were conducted in Brazil (n = 8), Germany (n = 2) and the USA (n = 1). Also, it is important to highlight that some studies only conducted oral mucosa clinical analysis (oral lesions), whilst others focused on a cellular/molecular-level evaluation.
3.3. Variables Related to Crack Use, Cytomorphogenetic Changes and Oral Lesions
Table 1 describes the main characteristics of studies that analyzed variables related to crack cocaine exposure at the cellular and molecular levels. In total, 492 individuals were evaluated in the crack cocaine group and 472 in the control (non-exposed) group. From the seven studies that evaluated the cellular and/or molecular alterations in cells, four studies used the MN test and three evaluated AgNORS. The number of counted cells evaluated in these studies varied from 50 to 1000. Table 2 shows the main characteristics of the four studies that evaluated oral mucosal lesions induced by crack cocaine. The total number of participants addicted included in the four studies was 185. In 50% of the studies, the clinical evaluation was performed by a specialist in the oral medicine field.

Table 1.
Main characteristics of studies that evaluated the effect of crack cocaine in oral mucosa cells in cellular and molecular levels.

Table 2.
Main characteristics of studies investigating oral mucosal lesions induced by crack cocaine.
3.4. Main Results
All studies (11 out of 11) showed that the abuse of this substance was associated with increased oral mucosa alterations at the cellular, molecular or clinical levels. In other words, clinical analysis for oral mucosal lesions revealed an increased prevalence of oral lesions [5,7,16,17], and cellular analysis showed positive results closely related to genotoxicity (micronucleus), proliferative activity (AgNor immunoexpression) and changes in the cytoplasmic–nucleus ratio [2,3,7,12,13,14,15]. Nonetheless, the scarcity of studies that establish a correlation between oral lesions and molecular and/or cellular changes does not allow for drawing conclusions about this potential relationship. Such findings are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Main findings of studies investigating the effects of crack cocaine in oral mucosa.
3.5. Quality Assessment
The quality assessment is described in Table 4. A total of six studies [1,2,3,6,15,16] were classified as strong, two studies [12,14] were considered as moderate and three were considered to be weak [7,13,17], according to the chosen criteria, with eight of the evaluated studies considered to be either strong or moderate.

Table 4.
Quality assessment and final rating of the studies.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to assess if, and to what level, cellular and/or molecular changes can predict oral mucosal lesions induced by crack cocaine use. For this purpose, some studies performed assays to verify the genotoxic outcomes [3,6,7,12,13,14]; two papers performed a cytomorphometric analysis [2,15], and four studies evaluated the presence of oral mucosa lesions in crack cocaine users [5,7,16,17].
Our results revealed that six articles were considered to be strong, while two were considered moderate, adding up to three studies considered as weak. Taken as a whole, we assume that most of the assessed studies had good quality for evaluating either cellular or molecular changes associated or not with clinical evaluation, confirming reliable results. To achieve these objectives, some confounders were identified in this systematic review as such assays require specific parameters to guarantee proper evaluation performances and, thus, reliable results. Many genotoxicity tests are used worldwide due to their simplicity, robustness and time- and cost-effectiveness in targeting mutagenicity and, for that, may lack academic rigidity at some level. These assays play a pivotal role in identifying possible carcinogenesis since they evaluate the initiation phase of chemical carcinogenesis.
The micronucleus assay is widely used worldwide and is considered a sensitive method to detect chromosomes or fragments inside the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. The results of this study demonstrated that there were four out of the six studies in which genotoxicity was assessed using the micronucleus assay, indicating positive genotoxicity in all four of them [7,12,13,14]. Regarding the number of cells evaluated in the micronucleus assays, all studies evaluated 1000 cells per slide, which was considered to be a confounder in the rating categorizations to properly assess studies’ quality [18]. It has been suggested that a minimum of 2000 differentiated cells for treatment should be scored per sample for a proper analysis [19].
As an increased NA/CA ratio is one of the major signs of premalignant and malignant lesions [20], such analysis is also widely used and, in this systematic review, all of the analyzed studies suggested positive morphological alterations (2 out of 2) [2,15]. Furthermore, it is known that AgNORs is abundant in cells with high proliferative activity. In this method, black-brown spots are counted and analyzed based on their distribution pattern in the nucleus by measuring the occupied area with a light microscope [3]. A total of three studies identified high proliferative activity in the oral mucosa cells of crack cocaine users [3,6,13]. Such results confirm the participation of crack cocaine in the promotion phase of carcinogenesis in the oral mucosa. Certainly, these cellular and molecular data could predict the incidence of oral lesions in crack cocaine users, especially in some places considered at high risk of oral cancer, such as the floor of the mouth and lateral border of tongue. In fact, all evaluated studies that conducted clinical analysis observed that crack/cocaine addiction was significantly associated with oral mucosa lesions [5,7,16,17]. According to Cury et al. [16], the most prevalent lesions found in crack cocaine users were traumatic ulcers and actinic cheilitis, followed by fistulae associated with a retained dental root. In a study conducted by Mitchell-Lewis et al. [17], the authors observed unusual lesions at the midline of the hard palate and candidiasis induced by crack cocaine. Antoniazzi et al. [7] suggested that the most prevalent lesions observed in oral mucosa lesions of crack cocaine users were spot/plaques followed by ulcer/fissures and papule/nodules, respectively. Also, this study suggested that oral lesions were 2.02-fold more frequent, and micronuclei were 3.54-fold more frequent in crack users, implying some association with clinical and cellular changes in the oral mucosa. However, the authors suggest that part of the impact of crack on the occurrence of lesions was influenced by tooth loss, gingivitis and dental trauma [7]. It is important to stress that the study conducted by Antoniazzi et al. [7] was the only one to evaluate both oral mucosal lesions and the incidence of micronucleus assay in buccal cells. However, these authors did not find potentially malignant disorders or oral cancer. Recognizing the significant efforts and the outstanding achievements for clarifying the incidence of oral mucosa lesions in crack cocaine users, these articles, however, were categorized as weak at final rating in the quality assessment. Particularly, a letter to the Editor was published on the basis of proper quality evaluation criteria, revealing that the manuscript did not control some important variables, such as DNA-specific stain as well as the establishment of exclusion criteria [21]. Therefore, such findings should be interpreted cautiously.
As some studies suggest that crack cocaine abusers also smoke tobacco (and even marijuana) and that their consumption (combined or not) may be harmful and induce clastogenic events in the oral mucosa as well, it is necessary to highlight that six studies formally informed that part of the experimental group smoked anything rather than crack tobacco, two studies informed that 100% also used tobacco and three studies failed to disclose or report it. Regarding alcohol use, six studies informed that part of the crack cocaine users also drank alcohol and, lastly, only three studies informed that crack cocaine users were also marijuana users (at different percentages) [12,14].
A total of five studies applied some exclusion criteria, such as patients with systemic diseases, malignant tumor history, orthodontic appliance users and medication users, among others [3,7,12,13,16]. Additionally, the description of blind analysis was seen in the methodology of six studies out of the eight, whilst the rest failed to inform on this. Finally, all the included studies adequately described the statistical test applied when performing the data analysis.
5. Conclusions
In summary, although the type of assay and sample selection criteria may have influenced the outcome, our results demonstrate that crack use may induce changes at the cellular and molecular level closely related to genotoxicity [22], proliferative activity and abnormal phenotype. Taking into account the high-vulnerability condition of this group of people, being continuously exposed to physical, chemical or biological agents, a correlation between such changes and oral mucosa lesions still needs further investigation and elucidation through other clinical studies in humans. This aspect is certainly a relevant limitation of the study. As a result, there is a need for well-structured clinical studies on this topic to elucidate if the molecular changes detected have some relation with the development of specific oral lesions or potentially oral malignant disorders. Moreover, experimental studies in rodents would be a good alternative to elucidate if, and to what extent, crack cocaine induces genotoxicity in mammalian cells.
Author Contributions
Study design: T.G.P., M.d.B.V. and D.A.R. Data search: T.G.P., M.d.B.V. and D.A.R. Data analysis: T.G.P., P.R.C., M.D.M., J.N.d.S. and D.A.R. Writing the paper: all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge research grants received from CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Grant Number #001) for a productivity fellowship to M.d.B.V., P.R.C., M.D.M., J.N.d.S. and D.A.R.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not available for this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sordi, A.O.; Pechansky, F.; Kessler, F.H.; Kapczinski, F.; Pfaffenseller, B.; Gubert, C.; de Aguiar, B.W.; de Magalhães Narvaez, J.C.; Ornell, F.; von Diemen, L. Oxidative stress and BDNF as possible markers for the severity of crack cocaine use in early withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 4031–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albini, M.B.; Malacarne, I.T.; Batista, T.B.D.; de Lima, A.A.S.; Machado, M.A.N.; Johann, A.C.B.R.; Rosa, E.A.R.; Azevedo-Alanis, L.R. Cytopathological Changes Induced by the Crack Use in Oral Mucosa. Eur. Addict. Res. 2017, 23, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabelo, R.G.; Salgueiro, A.P.; Visioli, F.; da Silva, V.P.; das Graças Alonso Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Cury, P.R.; Dos Santos, J.N. Argyrophilic nucleolar organizer regions in oral mucosa cells of crack and cocaine users: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 37920–37926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, R.J.; Henry, J.A. Clinical review: Major consequences of illicit drug consumption. Crit. Care 2008, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordi, M.B.; Massochin, R.C.; Camargo, A.R.; Lemos, T.; Munhoz, E.A. Oral health assessment for users of marijuana and cocaine/crack substances. Braz. Oral Res. 2017, 31, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, M.C.d.M.; Bohn, J.C.; Chaiben, C.L.; Grégio, A.M.; Machado, M.Â.; de Lima, A.A. Nucleolar organizer regions of oral epithelial cells in crack cocaine users. Iran. Biomed. J. 2013, 17, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniazzi, R.P.; Lago, F.B.; Jardim, L.C.; Sagrillo, M.R.; Ferrazzo, K.L.; Feldens, C.A. Impact of crack cocaine use on the occurrence of oral lesions and micronuclei. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goraya, M.H.N.; Malik, A.; Inayat, F.; Ishtiaq, R.; Zaman, M.A.; Arslan, H.M.; Tarar, Z.I. Acute pancreatitis secondary to cocaine use: A case-based systematic literature review. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, H.; Miskovic, M.; Buxton, J.A.; Holland, S.P.; Strike, C. Smoke Gets in the Eye: A systematic review of case reports of ocular complications of crack cocaine use. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2022, 41, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosário, B.D.A.; de Nazaré, M.F.S.; Estadella, D.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Viana, M.B. Behavioral and neurobiological alterations induced by chronic use of crack cocaine. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 31, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacarne, I.T.; Takeshita, W.M.; Souza, D.V.; Nagaoka, M.R.; Aguiar, O., Jr.; Renno, A.C.M.; Ribeiro, D.A. Assessment of genotoxicity of glass ionomer cements: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2022, 52, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, L.P.; Pellicioli, A.C.; Magnusson, A.S.; Danilevicz, C.K.; Bueno, C.C.; Sant’Ana Filho, M.; Rados, P.V.; Carrard, V.C. Nuclear changes in oral mucosa of alcoholics and crack cocaine users. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.D.G.A.; Dos Santos, J.N.; Cury, P.R.; da Silva, V.H.; Oliveira, N.R.; da Costa Padovani, R.; Tucci, A.M.; Ribeiro, D.A. Cytogenetic biomonitoring of oral mucosa cells of crack cocaine users. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 5760–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, T.C.; Stefanon, E.B.; Rech, V.C.; Sagrillo, M.R.; Bohrer, P.L. Analysis of oral mucosa of users of crack through micronucleus technique. Clin. Lab. 2012, 58, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woyceichoski, I.E.; de Arruda, E.P.; Resende, L.G.; Machado, M.A.; Grégio, A.M.; Azevedo, L.R.; de Lima, A.A. Cytomorphometric analysis of crack cocaine effects on the oral mucosa. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2008, 3, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cury, P.R.; Araujo, N.S.; das Graças Alonso Oliveira, M.; Dos Santos, J.N. Association between oral mucosal lesions and crack and cocaine addiction in men: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 19801–19807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell-Lewis, D.A.; Phelan, J.A.; Kelly, R.B.; Bradley, J.J.; Lamster, I.B. Identifying oral lesions associated with crack cocaine use. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1994, 125, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersesyan, A.; Kundi, M.; Fenech, M.; Stopper, H.; da Silva, J.; Bolognesi, C.; Mišík, M.; Knasmueller, S. Recommendations and quality criteria for micronucleus studies with humans. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2022, 789, 108410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, C.; Fenech, M. Micronucleus assay in human cells: Lymphocytes and buccal cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1044, 191–207. [Google Scholar]
- Seifi, S.; Feizi, F.; Mehdizadeh, M.; Khafri, S.; Ahmadi, B. Evaluation of cytological alterations of oral mucosa in smokers and waterpipe users. Cell J. 2014, 15, 302–329. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez Alpire, M.E.; Ribeiro, D.A. Regarding “Impact of crack cocaine use on the occurrence of oral lesions and micronuclei”. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malacarne, I.T.; De Souza, D.V.; Rosario, B.D.A.; Viana, M.B.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Estadella, D.; Dos Santos, J.N.; Ribeiro, D.A. Genotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response induced by crack-cocaine: Relevance to carcinogenesis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 14285–14292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).