Does Single or Combined Caffeine and Taurine Supplementation Improve Athletic and Cognitive Performance without Affecting Fatigue Level in Elite Boxers? A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Supplementation Protocol
2.4. Wingate Anaerobic Test
2.5. Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE)
2.6. Blood Lactate Levels Measured
2.7. Balance Test
2.8. Agility Test (Illinois)
2.9. Stroop Test
2.10. Familiarization
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maughan, R.J.; Murray, R. Sports Drinks: Basic Science and Practical Aspects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Leutholtz, B.; Kreider, R. Exercise and Sport Nutrition. In Nutritional Health; Wilson, T., Temple, N., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 207–239. [Google Scholar]
- Maughan, R.J.; Burke, L.M.; Dvorak, J.; Larson-Meyer, D.E.; Peeling, P.; Phillips, S.M.; Rawson, E.S.; Walsh, N.P.; Garthe, I.; Geyer, H. IOC consensus statement: Dietary supplements and the high-performance athlete. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, E.R.; Ziegenfuss, T.; Kalman, D.; Kreider, R.; Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.; Taylor, L.; Willoughby, D.; Stout, J.; Graves, B.S. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2010, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiles, J.D.; Coleman, D.; Tegerdine, M.; Swaine, I.L. The effects of caffeine ingestion on performance time, speed and power during a laboratory-based 1 km cycling time-trial. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, E. Effective nutritional ergogenic aids. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 1999, 9, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.; Dawson, B.; Schneiker, K.; Goodman, C.; Lay, B. Effect of caffeine supplementation on repeated sprint running performance. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2008, 48, 472. [Google Scholar]
- Glaister, M.; Howatson, G.; Abraham, C.S.; Lockey, R.A.; Goodwin, J.E.; Foley, P.; McInnes, G. Caffeine supplementation and multiple sprint running performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trexler, E.T.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Roelofs, E.J.; Hirsch, K.R.; Mock, M.G. Effects of coffee and caffeine anhydrous on strength and sprint performance. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2016, 16, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astorino, T.A.; Rohmann, R.L.; Firth, K. Effect of caffeine ingestion on one-repetition maximum muscular strength. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 102, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.W.; Ju Jong, C.; KC, R.; Azuma, J. Physiological roles of taurine in heart and muscle. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, L.A.; Silveira, P.C.; Ronsani, M.M.; Souza, P.S.; Scheffer, D.; Vieira, L.C.; Benetti, M.; De Souza, C.T.; Pinho, R.A. Taurine supplementation decreases oxidative stress in skeletal muscle after eccentric exercise. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2011, 29, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.C. Kidney toxicity related to herbs and dietary supplements: Online table of case reports. Part 3 of 5 series. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 502–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manore, M.M. Weight management for athletes and active individuals: A brief review. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerksick, C.M. Requirements of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats for athletes. In Nutrition and Enhanced Sports Performance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 443–459. [Google Scholar]
- Tipton, K.D. Nutritional support for exercise-induced injuries. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witard, O.C.; Wardle, S.L.; Macnaughton, L.S.; Hodgson, A.B.; Tipton, K.D. Protein considerations for optimising skeletal muscle mass in healthy young and older adults. Nutrients 2016, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon, A.A.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Wildman, R.; Kleiner, S.; VanDusseldorp, T.; Taylor, L.; Earnest, C.P.; Arciero, P.J.; Wilborn, C.; Kalman, D.S. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Diets and body composition. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.; La Bounty, P.; Taylor, L.; Nelson, M.T.; Greenwood, M.; Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Lopez, H.L.; Hoffman, J.R.; Stout, J.R. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: Energy drinks. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2013, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galloway, S.D.; Talanian, J.L.; Shoveller, A.K.; Heigenhauser, G.J.; Spriet, L.L. Seven days of oral taurine supplementation does not increase muscle taurine content or alter substrate metabolism during prolonged exercise in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 105, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milioni, F.; Malta, E.d.S.; Rocha, L.G.S.d.A.; Mesquita, C.A.A.; de Freitas, E.C.; Zagatto, A.M. Acute administration of high doses of taurine does not substantially improve high-intensity running performance and the effect on maximal accumulated oxygen deficit is unclear. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnock, R.; Jeffries, O.; Patterson, S.; Waldron, M. The effects of caffeine, taurine, or caffeine-taurine coingestion on repeat-sprint cycling performance and physiological responses. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, M.; Patterson, S.D.; Tallent, J.; Jeffries, O. The effects of an oral taurine dose and supplementation period on endurance exercise performance in humans: A meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zembron-Lacny, A.; Szyszka, K.; Szygula, Z. Effect of cysteine derivatives administration in healthy men exposed to intense resistance exercise by evaluation of pro-antioxidant ratio. J. Physiol. Sci. 2007, 57, 0711140014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Izumi, I.; Kagamimori, S.; Sokejima, S.; Yamagami, T.; Liu, Z.; Qi, B. Role of taurine supplementation to prevent exercise-induced oxidative stress in healthy young men. Amino Acids 2004, 26, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, S.C.; Candow, D.G.; Little, J.P.; Magnus, C.; Chilibeck, P.D. Effect of Red Bull energy drink on repeated Wingate cycle performance and bench-press muscle endurance. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2007, 17, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, C.; Cox, H.; Wescott, R. The effects of red bull energy drink on human performance and mood. Amino Acids 2001, 21, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coso, J.; Muñoz-Fernández, V.E.; Muñoz, G.; Fernández-Elías, V.E.; Ortega, J.F.; Hamouti, N.; Barbero, J.C.; Muñoz-Guerra, J. Effects of a caffeine-containing energy drink on simulated soccer performance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwacham, N.; Wagner, D.R. Acute effects of a caffeine-taurine energy drink on repeated sprint performance of American college football players. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2012, 22, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, M.; Chaabène, H.; Davis, P.; Franchini, E.; Cheour, F.; Chamari, K. Performance aspects and physiological responses in male amateur boxing competitions: A brief review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, D.R.; Meehan, W.P.; Loosemore, M.P.; Cummiskey, J.; von Rosenberg, J.-P.G.; McDonagh, D. Neurological tests improve after Olympic-style boxing bouts: A pretournament and post-tournament study in the 2016 Women’s World Boxing Championships. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmakci, O.; Erkmen, N.; Cakmakci, E.; Taskin, H.; Stoffregen, T.A. Postural performance while boxing with an opponent versus practice with a boxing bag. Ido Mov. Cult. J. Martial Arts Anthropol. 2020, 20, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Çetin, O.; Beyleroğlu, M.; Bağış, Y.; Suna, G. The effect of the exercises brain on boxers’ eye-hand coordination, dynamic balance and visual attention performance. Phys. Educ. Stud. 2018, 22, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sienkiewicz-Dianzenza, E.; Maszczyk, Ł. The impact of fatigue on agility and responsiveness in boxing. Biomed. Hum. Kinet. 2019, 11, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, W.B.; Dawson, B.; Henry, G.J. Agility and change-of-direction speed are independent skills: Implications for training for agility in invasion sports. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2015, 10, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarity, J.; Collie, A.; Olson, D.; Buchanan, J.; Leary, P.; McStephen, M.; McCrory, P. A prospective controlled study of cognitive function during an amateur boxing tournament. Neurology 2004, 62, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollseiffen, P.; Ghadiri, A.; Scholz, A.; Strüder, H.K.; Herpers, R.; Peters, T.; Schneider, S. Short bouts of intensive exercise during the workday have a positive effect on neuro-cognitive performance. Stress Health 2016, 32, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Rodríguez, R.; Pallarés, J.G.; López-Gullón, J.M.; López-Samanes, Á.; Fernández-Elías, V.E.; Ortega, J.F. Improvements on neuromuscular performance with caffeine ingestion depend on the time-of-day. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 18, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guest, N.S.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Nelson, M.T.; Grgic, J.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Jenkins, N.D.; Arent, S.M.; Antonio, J.; Stout, J.R.; Trexler, E.T. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraak, V.I.; Davy, B.M.; Rockwell, M.S.; Kostelnik, S.; Hedrick, V.E. Policy recommendations to address energy drink marketing and consumption by vulnerable populations in the United States. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 767–777. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries, O.; Hill, J.; Patterson, S.D.; Waldron, M. Energy drink doses of caffeine and taurine have a null or negative effect on sprint performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 3475–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Or, O. The Wingate anaerobic test an update on methodology, reliability and validity. Sports Med. 1987, 4, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulupınar, S.; Özbay, S. Energy pathway contributions during 60-second upper-body Wingate test in Greco-Roman wrestlers: Intermittent versus single forms. Res. Sports Med. 2022, 30, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekblom, B.; Golobarg, A.N. The influence of physical training and other factors on the subjective rating of perceived exertion. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1971, 83, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roozen, M. Illinois agility test. NSCA’s Perform. Train. J. 2004, 3, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Stroop, J.R. Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J. Exp. Psychol. 1935, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.T. Eta squared and partial eta squared as measures of effect size in educational research. Educ. Res. Rev. 2011, 6, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, J.A.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Doyle, J.A.; Otis, J.S. Taurine in sports and exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzdağlı, Y.; Eyipınar, C.D.; Tekin, A.; Şıktar, E.; Zydecka, K.S. Effect of Taurine Supplement on Aerobic and Anaerobic Outcomes: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Strength Cond. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balshaw, T.G.; Bampouras, T.M.; Barry, T.J.; Sparks, S.A. The effect of acute taurine ingestion on 3-km running performance in trained middle-distance runners. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Paik, I.; Park, T. Effects of dietary supplementation of taurine, carnitine or glutamine on endurance exercise performance and fatigue parameters in athletes. Korean J. Nutr. 2003, 36, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Page, L.K.; Jeffries, O.; Waldron, M. Acute taurine supplementation enhances thermoregulation and endurance cycling performance in the heat. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, F.G.; Barbieri, R.A.; Carvalho, M.B.; Dato, C.C.; Campos, E.Z.; Gobbi, R.B.; Papoti, M.; Silva, A.S.; de Freitas, E.C. Taurine supplementation can increase lipolysis and affect the contribution of energy systems during front crawl maximal effort. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Carvalho, F.G.; Brandao, C.F.C.; Batitucci, G.; de Oliveira Souza, A.; Ferrari, G.D.; Alberici, L.C.; Muñoz, V.R.; Pauli, J.R.; De Moura, L.P.; Ropelle, E.R. Taurine supplementation associated with exercise increases mitochondrial activity and fatty acid oxidation gene expression in the subcutaneous white adipose tissue of obese women. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2180–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidari, F.; Asadi, M.; Ahmadi-Angali, K. Evaluation of the effect of oral taurine supplementation on fasting levels of fibroblast growth factors, β-Klotho co-receptor, some biochemical indices and body composition in obese women on a weight-loss diet: A study protocol for a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Trials 2019, 20, 315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, S.H.; Andersen, M.L.; Cornett, C.; Gradinaru, R.; Grunnet, N. A role for taurine in mitochondrial function. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kowsari, E.; Moosavi, Z.A.; Rahimi, A.; Faramarzi, M.; Haghighi, M.M. The effect of short-term taurine amino acid supplement on neuromuscular fatigue, serum lactate level and choice reaction time after maximal athletic performance. J. Res. Med. Dent. Sci. 2018, 6, 358–364. [Google Scholar]
- Waldron, M.; Patterson, S.D.; Jeffries, O. Oral taurine improves critical power and severe-intensity exercise tolerance. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuzaki, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Miyakawa, S.; Bouscarel, B.; Ikegami, T.; Tanaka, N. Decreased taurine concentration in skeletal muscles after exercise for various durations. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takekura, H. Effects of taurine on glycolytic and oxidative enzyme activities of rat skeletal muscles. Sulfur Amino Acids 1986, 9, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Chasiotis, D.; Harris, R.; Hultman, E. The cyclic-AMP concentration in plasma and in muscle in response to exercise and beta-blockade in man. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1983, 117, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravnskjaer, K.; Madiraju, A.; Montminy, M. Role of the cAMP pathway in glucose and lipid metabolism. In Metabolic Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Raizada, M.; Murti, C.K. Binding of taurine to Hartmannella culbertsoni membranes and the synthesis of cyclic AMP. Curr. Sci. 1973, 42, 202–204. [Google Scholar]
- Karayigit, R.; Naderi, A.; Saunders, B.; Forbes, S.C.; Coso, J.D.; Berjisian, E.; Yildirim, U.C.; Suzuki, K. Combined but not isolated ingestion of caffeine and taurine improves Wingate Sprint Performance in female team-sport athletes habituated to caffeine. Sports 2021, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, C.P.; Marczinski, C.A. Taurine, caffeine, and energy drinks: Reviewing the risks to the adolescent brain. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, X.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y. Effects of taurine on alterations of neurobehavior and neurodevelopment key proteins expression in infant rats by exposure to hexabromocyclododecane. In Taurine 10; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, G.E.; Mahoney, C.R.; Brunyé, T.T.; Gardony, A.L.; Taylor, H.A.; Kanarek, R.B. Differential cognitive effects of energy drink ingredients: Caffeine, taurine, and glucose. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 102, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Idrissi, A.; Shen, C.H.; L’Amoreaux, W.J. Erratum to: Neuroprotective role of taurine during aging. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivaraj, M.C.; Marcy, G.; Low, G.; Ryu, J.R.; Zhao, X.; Rosales, F.J.; Goh, E.L. Taurine induces proliferation of neural stem cells and synapse development in the developing mouse brain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, L.M.; Muñoz, M.-D.; Martín del Río, R.; Solís, J.M. Taurine content in different brain structures during ageing: Effect on hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, R.L.; Batista, T.M.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Branco, R.; Da Silva, P.M.; Izumi, C.; Araujo, T.R.; Greene, L.J.; Boschero, A.C.; Carneiro, E.M. Taurine supplementation preserves hypothalamic leptin action in normal and protein-restricted mice fed on a high-fat diet. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2419–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Yue, M.; Chandra, D.; Keramidas, A.; Goldstein, P.A.; Homanics, G.E.; Harrison, N.L. Taurine is a potent activator of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in the thalamus. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Oja, S.S.; Saransaari, P. Regulation of taurine release in the hippocampus of developing and adult mice. In Taurine 8; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- L’Amoreaux, W.J.; Marsillo, A.; El Idrissi, A. Pharmacological characterization of GABAA receptors in taurine-fed mice. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J. Caffeine ingestion enhances Wingate performance: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.J.; Eyre, E.; Grgic, J.; Tallis, J. The effect of acute caffeine ingestion on upper and lower body anaerobic exercise performance. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, B.; Salinero, J.J.; Giráldez-Costas, V.; Del Coso, J. Similar ergogenic effect of caffeine on anaerobic performance in men and women athletes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4107–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carswell, A.T.; Howland, K.; Martinez-Gonzalez, B.; Baron, P.; Davison, G. The effect of caffeine on cognitive performance is influenced by CYP1A2 but not ADORA2A genotype, yet neither genotype affects exercise performance in healthy adults. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogervorst, E.; Bandelow, S.; Schmitt, J.; Jentjens, R.; Oliveira, M.; Allgrove, J.; Carter, T.; Gleeson, M. Caffeine improves physical and cognitive performance during exhaustive exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Childs, E.; de Wit, H. Enhanced mood and psychomotor performance by a caffeine-containing energy capsule in fatigued individuals. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2008, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.; Reynolds, N.A.; Crewther, B.T.; Cook, C.J.; Kilduff, L.P. Physiological and performance effects of caffeine gum consumed during a simulated half-time by professional academy rugby union players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Church, D.D.; Hoffman, J.R.; LaMonica, M.B.; Riffe, J.J.; Hoffman, M.W.; Baker, K.M.; Varanoske, A.N.; Wells, A.J.; Fukuda, D.H.; Stout, J.R. The effect of an acute ingestion of Turkish coffee on reaction time and time trial performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Black, C.D.; Waddell, D.E.; Gonglach, A.R. Caffeine’s Ergogenic Effects on Cycling: Neuromuscular and Perceptual Factors. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motl, R.W.; O’connor, P.J.; Tubandt, L.; Puetz, T.; Ely, M.R. Effect of caffeine on leg muscle pain during cycling exercise among females. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonglach, A.R.; Ade, C.J.; Bemben, M.G.; Larson, R.D.; Black, C.D. Muscle Pain as a Regulator of Cycling Intensity: Effect of Caffeine Ingestion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, J.D.; Farrar, A.M.; Font, L.; Patel, V.; Schlar, D.E.; Nunes, E.J.; Collins, L.E.; Sager, T.N. Differential actions of adenosine A1 and A2A antagonists on the effort-related effects of dopamine D2 antagonism. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 201, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunyé, T.T.; Mahoney, C.R.; Lieberman, H.R.; Taylor, H.A. Caffeine modulates attention network function. Brain Cogn. 2010, 72, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnopolsky, M.; Cupido, C. Caffeine potentiates low frequency skeletal muscle force in habitual and nonhabitual caffeine consumers. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiani, C. Caffeine as a tool to investigate sarcoplasmic reticulum and intracellular calcium dynamics in human skeletal muscles. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2021, 42, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Ruiz, J.; Rodríguez-Prados, M.; Delrio-Lorenzo, A.; Alonso, M.T.; García-Sancho, J. Caffeine chelates calcium in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salinero, J.J.; Lara, B.; Ruiz-Vicente, D.; Areces, F.; Puente-Torres, C.; Gallo-Salazar, C.; Pascual, T.; Del Coso, J. CYP1A2 genotype variations do not modify the benefits and drawbacks of caffeine during exercise: A pilot study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindinger, M.I.; Graham, T.E.; Spriet, L.L. Caffeine attenuates the exercise-induced increase in plasma [K+] in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993, 74, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiani, B.; Zhu, L.; Musch, B.L.; Briceno, S.; Andel, R.; Sadeq, N.; Ansari, A.Z. The neurophysiology of caffeine as a central nervous system stimulant and the resultant effects on cognitive function. Cureus 2021, 13, e15032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, M.; Nielsen, J.J.; Bangsbo, J. Caffeine intake improves intense intermittent exercise performance and reduces muscle interstitial potassium accumulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imagawa, T.; Hirano, I.; Utsuki, K.; Horie, M.; Naka, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Imagawa, S. Caffeine and taurine enhance endurance performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 2009, 30, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A.J.; Berg, H.M. Effect of taurine on sarcoplasmic reticulum function and force in skinned fast-twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the rat. J. Physiol. 2002, 538, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

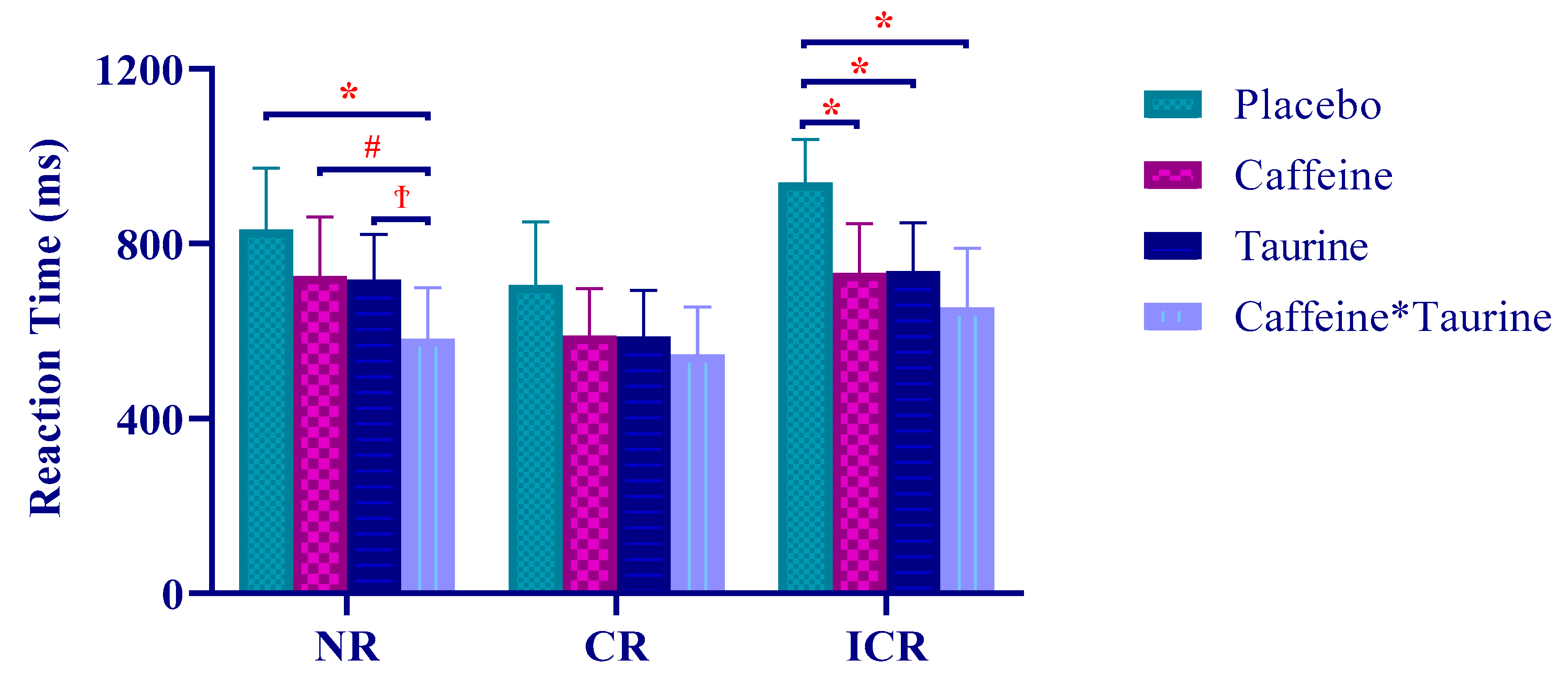
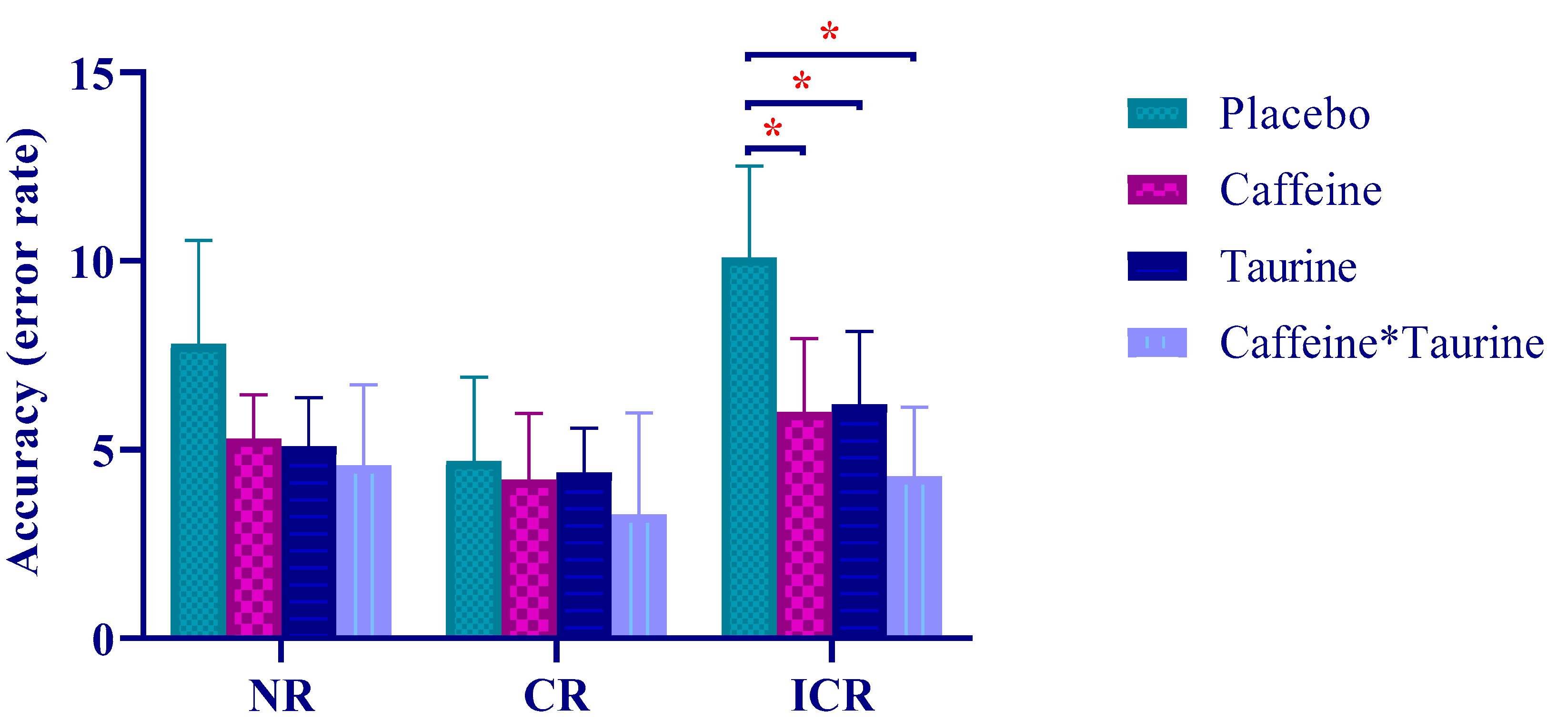
| Variables | Minimum | Maximum | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 18 | 24 | 22.14 ± 1.42 |
| Sports age (years) | 10 | 15 | 11.12 ± 1.12 |
| Height (cm) | 167 | 181 | 178 ± 6.45 |
| Body mass (kg) | 53 | 80 | 75.45 ± 8.95 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 19 | 27 | 23.67 ± 3.12 |
| Fat mass (%) | 4.7 | 20.4 | 11.01 ± 5.12 |
| Muscle mass (%) | 79.6 | 95.3 | 89.17 ± 6.23 |
| PLA Mean ± SD | CAF Mean ± SD | TAU Mean ± SD | CAF*TAU Mean ± SD | F | p | ηp2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP (W) | 633.02 ± 117.79 | 687.66 ± 125.38 * | 653.64 ± 116.8 * | 726.20 ± 144.43 *Ϯ | 1.092 | <0.001 | 0.720 |
| PP (W/kg) | 9.84 ± 1.09 | 10.65 ± 1.16 * | 10.17 ± 1.08 *# | 11.30 ± 1.42 *#Ϯ | 1.515 | <0.001 | 0.521 |
| AP (W) | 448.72 ± 82.89 | 469.52 ± 84.18 * | 459.71 ± 87.74 *# | 483.35 ± 87.20 *#Ϯ | 2.512 | <0.001 | 0.548 |
| MP (W) | 230.63 ± 34.01 | 275.18 ± 37.08 * | 263.30 ± 40.55 *# | 294.56 ± 49.25 *Ϯ | 1.873 | <0.001 | 0.641 |
| T_PP (s) | 13.90 ± 1.28 | 9.30 ± 1.20 * | 9.60 ± 1.07 * | 8.20 ± 1.03 * | 2.412 | <0.001 | 0.672 |
| RPE | 18.10 ± 1.42 | 17.20 ± 1.13 | 17.40 ± 0.84 | 16.60 ± 0.69 * | 1.424 | 0.048 | 0.345 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 10.30 ± 1.16 | 9.30 ± 1.49 | 9.10 ± 1.09 | 8.30 ± 1.33 | 2.745 | 0.125 | 0.213 |
| PLA Mean ± SD | CAF Mean ± SD | TAU Mean ± SD | CAF*TAU Mean ± SD | F | p | ηp2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static Dominant | 836.70 ± 342.06 | 733.70 ± 350.50 | 711.20 ± 351.82 | 520.70 ± 256.39 * | 2.722 | 0.030 | 0.489 |
| Static NonDominant | 825.10 ± 361.15 | 689.70 ± 314.01 | 701.50 ± 337.84 | 556.70 ± 220.95 * | 1.935 | 0.047 | 0.542 |
| Static Both Leg | 663.50 ± 297.33 | 591.10 ± 278.98 | 603.10 ± 297.04 | 515.80 ± 225.55 | 4.968 | 0.489 | 0.123 |
| Dynamic Dominant | 1165.00 ± 208.61 | 1084.40 ± 258.24 | 1106.30 ± 169.47 | 910.00 ± 238.32 * | 2.423 | 0.028 | 0.575 |
| Dynamic NonDominant | 1351.10 ± 396.55 | 1154.60 ± 350.95 | 1218.80 ± 394.61 | 918.00 ± 217.27 * | 2.145 | 0.023 | 0.622 |
| Dynamic Both Leg | 1252.30 ± 275.44 | 1119.30 ± 256.32 | 1128.40 ± 227.62 | 1043.90 ± 245.62 * | 3.834 | 0.015 | 0.660 |
| Illinois Agility Test | 18.79 ± 0.80 | 16.95 ± 0.73 * | 16.75 ± 0.47 * | 16.44 ± 0.52 * | 1.245 | <0.001 | 0.841 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozan, M.; Buzdagli, Y.; Eyipinar, C.D.; Baygutalp, N.K.; Yüce, N.; Oget, F.; Kan, E.; Baygutalp, F. Does Single or Combined Caffeine and Taurine Supplementation Improve Athletic and Cognitive Performance without Affecting Fatigue Level in Elite Boxers? A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204399
Ozan M, Buzdagli Y, Eyipinar CD, Baygutalp NK, Yüce N, Oget F, Kan E, Baygutalp F. Does Single or Combined Caffeine and Taurine Supplementation Improve Athletic and Cognitive Performance without Affecting Fatigue Level in Elite Boxers? A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(20):4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204399
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzan, Murat, Yusuf Buzdagli, Cemre Didem Eyipinar, Nurcan Kılıç Baygutalp, Neslihan Yüce, Furkan Oget, Emirhan Kan, and Fatih Baygutalp. 2022. "Does Single or Combined Caffeine and Taurine Supplementation Improve Athletic and Cognitive Performance without Affecting Fatigue Level in Elite Boxers? A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study" Nutrients 14, no. 20: 4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204399
APA StyleOzan, M., Buzdagli, Y., Eyipinar, C. D., Baygutalp, N. K., Yüce, N., Oget, F., Kan, E., & Baygutalp, F. (2022). Does Single or Combined Caffeine and Taurine Supplementation Improve Athletic and Cognitive Performance without Affecting Fatigue Level in Elite Boxers? A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients, 14(20), 4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204399









