Fungus-Based Magnetic Nanobiocomposites for Environmental Remediation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
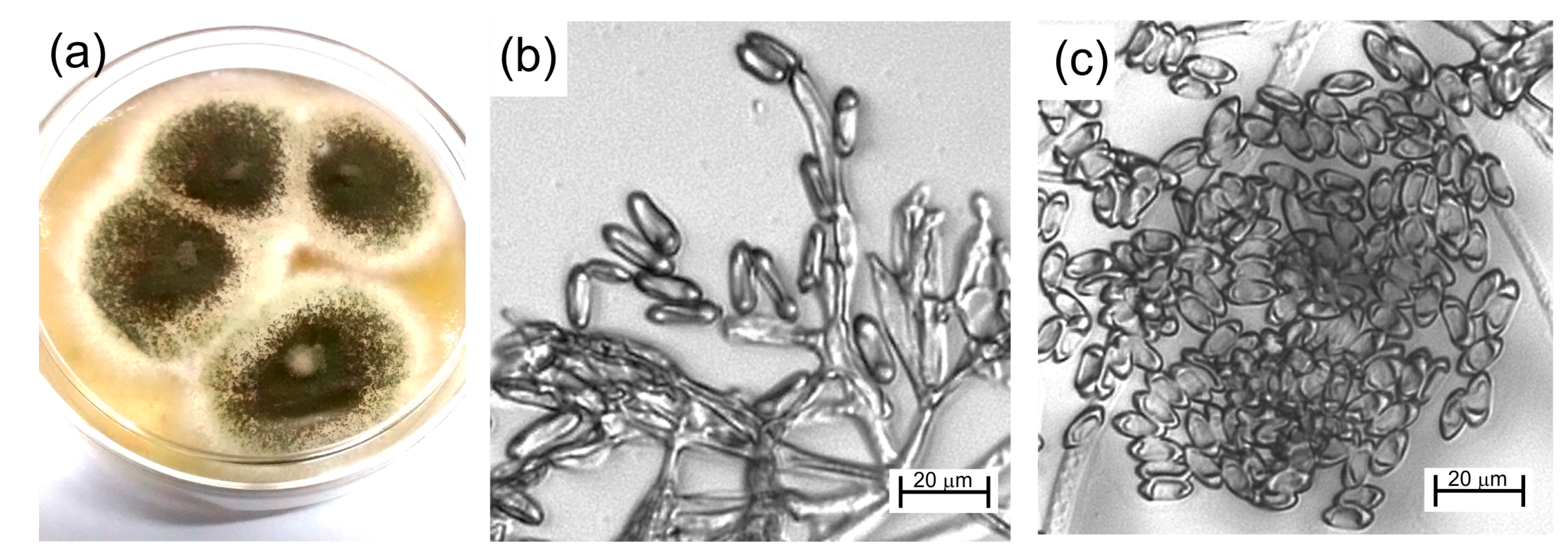
2.1. Biological Material
2.2. Magnetite Nanoparticles
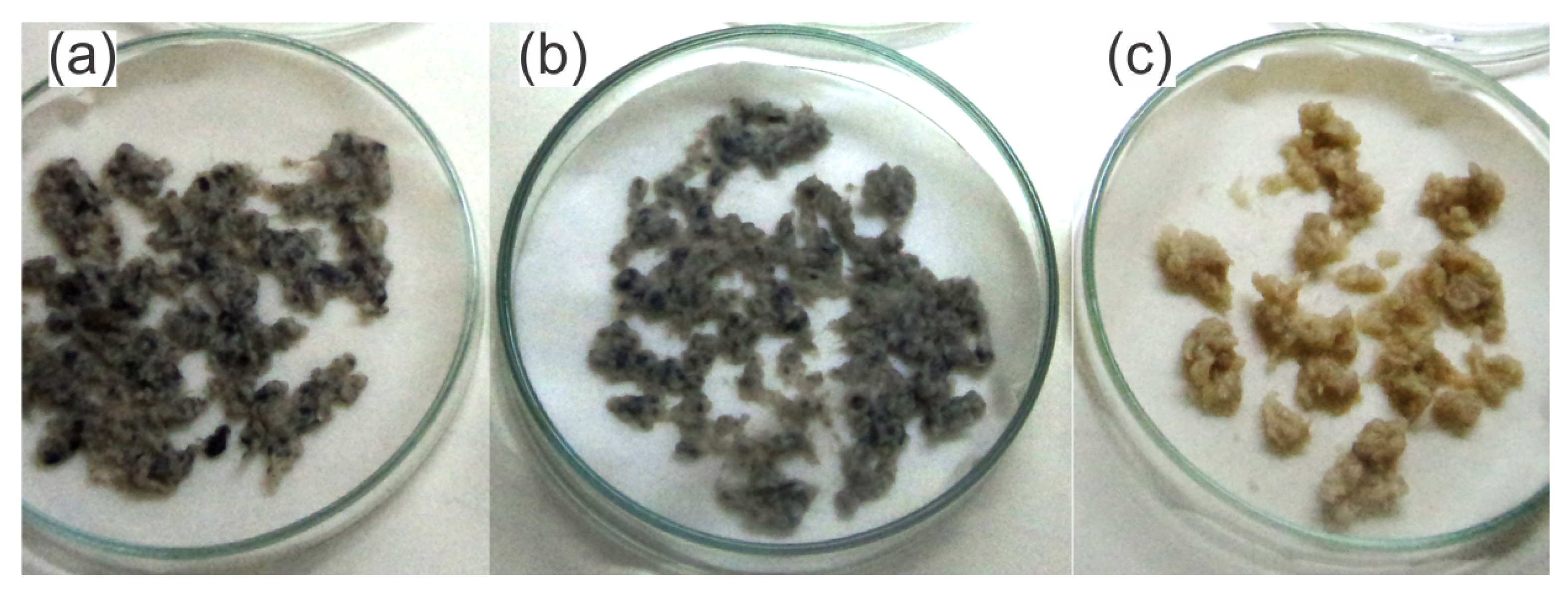
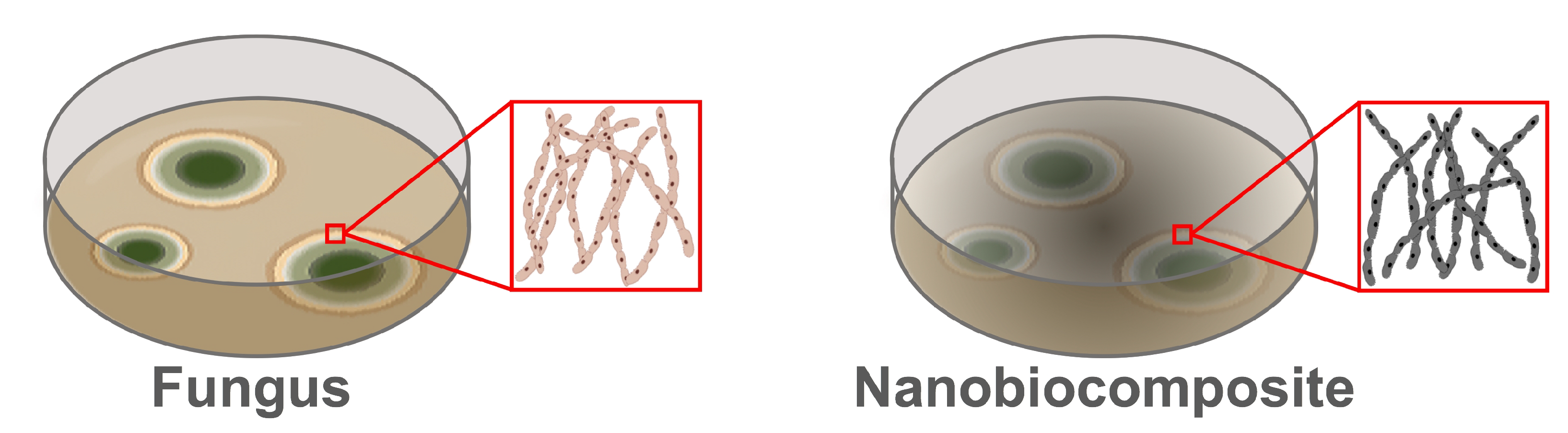
2.3. Nanobiocomposites (NBCs)
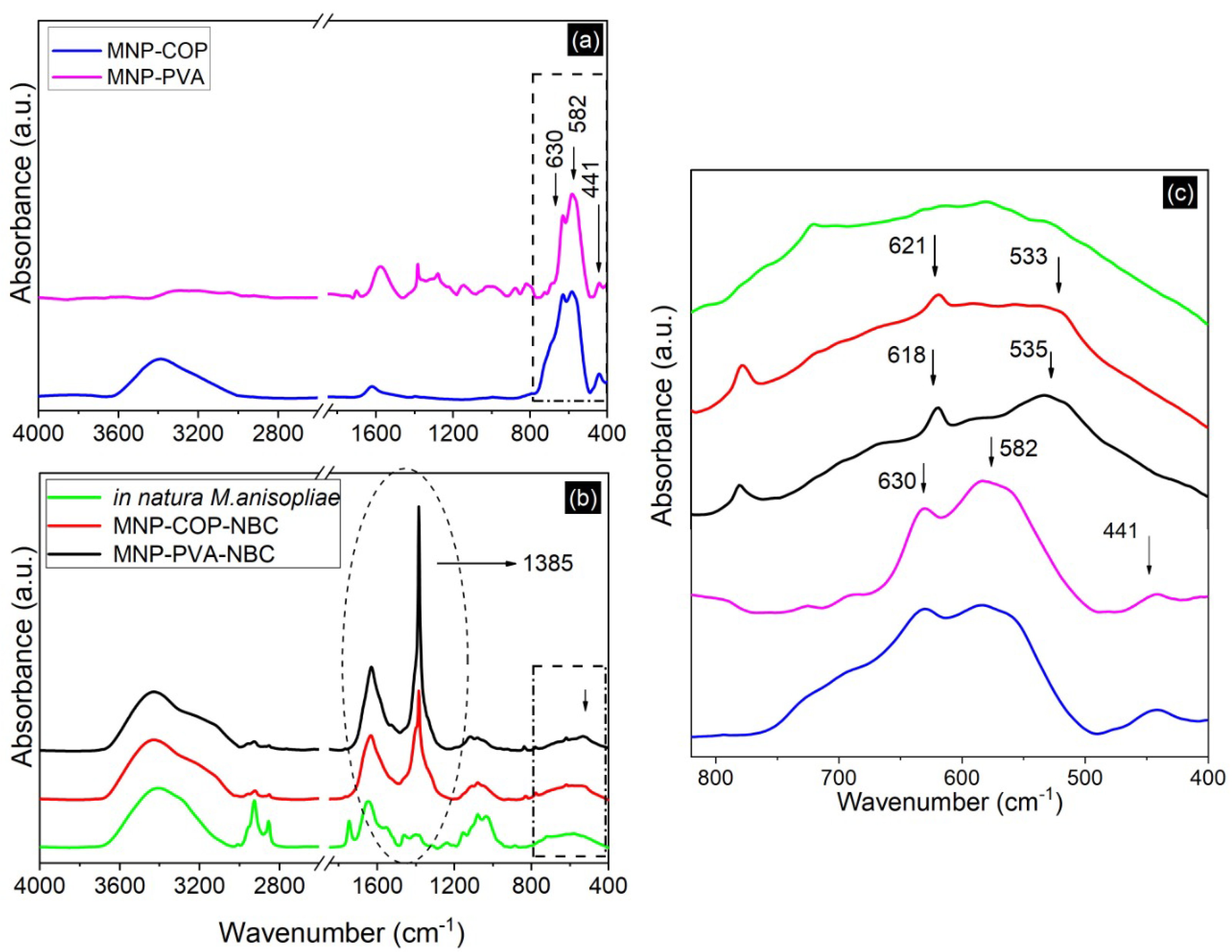
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.5. Optical Microscopy
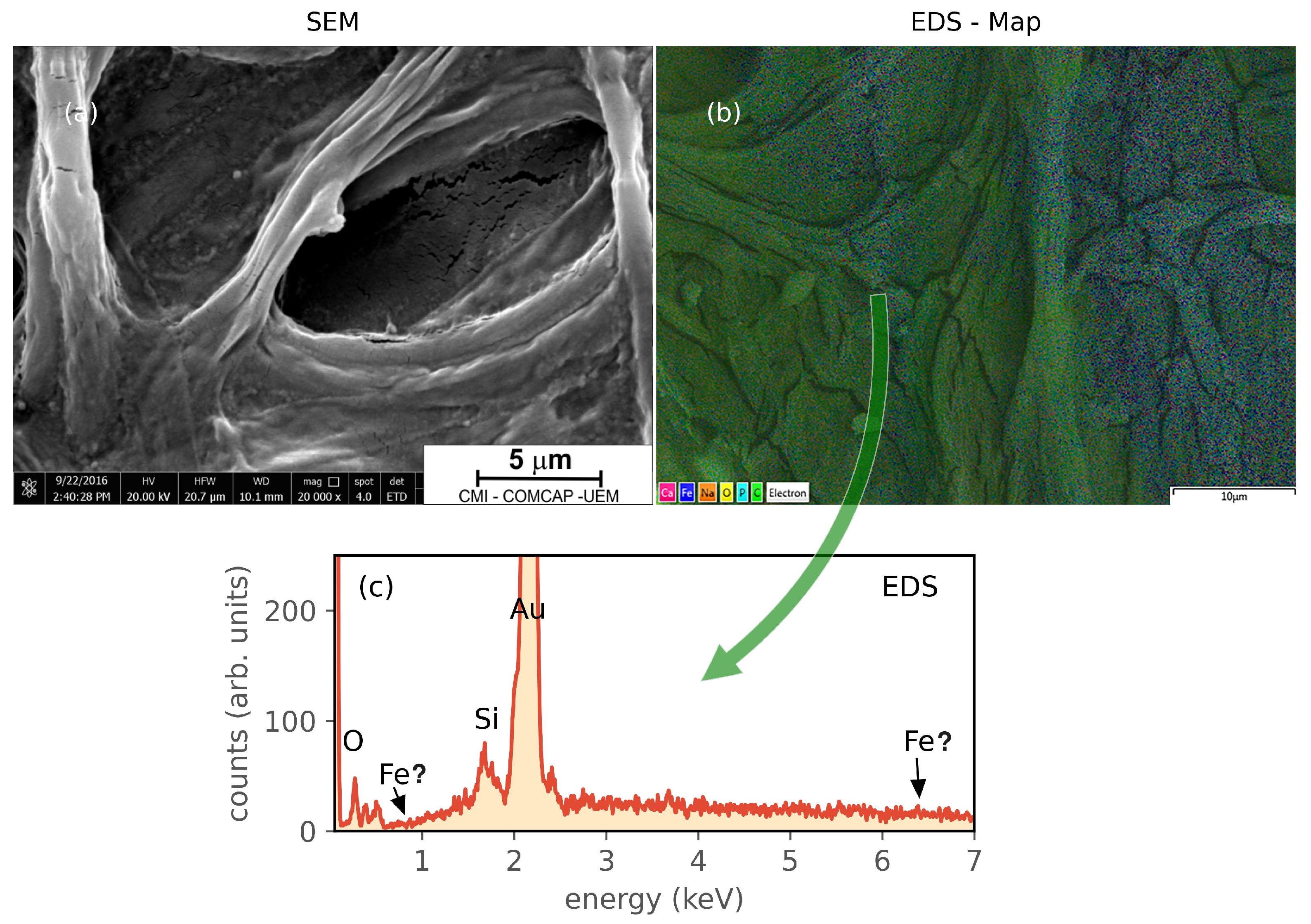
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
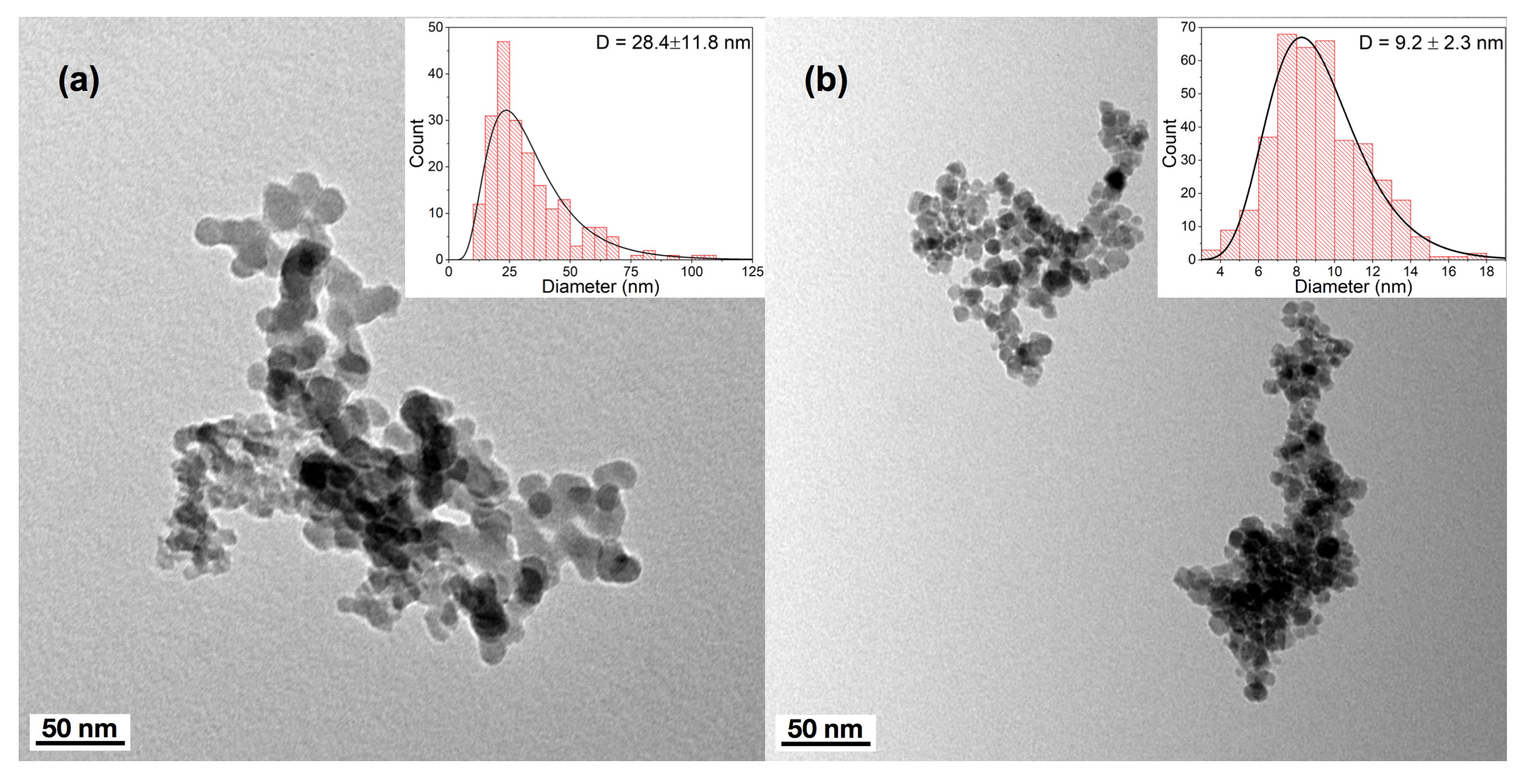
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
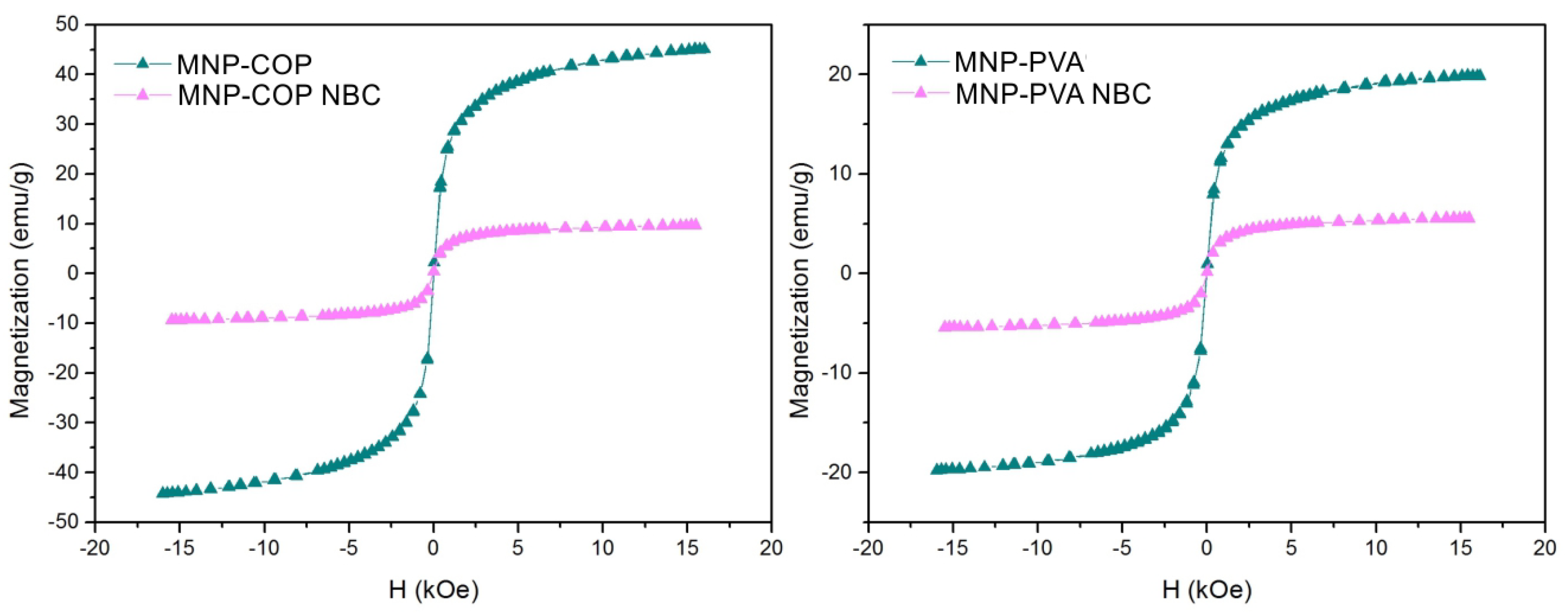
2.8. Nanobiocomposite Magnetization Test
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Yada, R. Nanotechnologies in agriculture: New tools for sustainable development. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larramendy, M.L.; Soloneski, S. Pesticides—Toxic Aspects; Soloneski, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, P.; Vivek, K.; Kumar, S.P. Nanotechnology in sustainable agriculture: Present concerns and future aspects. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A. Role of nanotechnology in agriculture with special reference to management of insect pests. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.D.; Kumbhar, B.A. Weed and its Management: A Major Threats to Crop. J. Pharm. Sci. Biosci. Res. 2016, 6, 453–758. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, K.H.J.; Waterhouse, P.M. RNAi for insect-proof plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1231–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.S.; Rao, A.N.; Singh, V.P.; Kumar, R. Weed Management in Major Field Crops. In Advances in Weed Management; Indian Society of Agronomy: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, D.K.; Behari, J.; Sen, P. Application of Nanoparticles in Waste Water Treatment. World Appl. Sci. J. 2008, 3, 417–433. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.Q.; Ashekuzzaman, S.M. Development of novel inorganic adsorbent for water treatment. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, S.; López, I.; Gámez, M.; Garay, J. A two-agent model applied to the biological control of the sugarcane borer (Diatraea saccharalis) by the egg parasitoid Trichogramma galloi and the larvae parasitoid Cotesia flavipes. Biosystems 2016, 141, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, L.; Silva, C.V.; Pamphile, J.; Conte, H. Infection, colonization and extrusion of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch) Sorokin (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) in pupae of Diatraea saccharalis F. (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). J. Entomol. Nematol. 2013, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandhu, S.S.; Sharma, A.K.; Beniwal, V.; Goel, G.; Batra, P.; Kumar, A.; Jaglan, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Malhotra, S. Myco-Biocontrol of Insect Pests: Factors Involved, Mechanism, and Regulation. J. Pathog. 2012, 2012, 126819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Dutta, J. Nanotechnology applications in pollution sensing and degradation in agriculture: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2009, 7, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhia, J.; Mandarano, G.; Ferris, N.J.; Eu, P.; Cowell, S.F. Development and use of iron oxide nanoparticles (Part 1): Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles for MRI. Biomed. Imaging Interv. J. 2010, 6, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, A.; Belhaj, H. Application of nanotechnology by means of nanoparticles and nanodispersions in oil recovery—A comprehensive review. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 34, 1284–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatkin, J.A. Assessing Nanotechnology Health and Environmental Risks. Nanotechnology: Health and Environmental Risks, 2nd ed.; Perspectives in Nanotechnology; Shatkin, J.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 5–29. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C. Environmental implications and applications of engineered nanoscale magnetite and its hybrid nanocomposites: A review of recent literature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 48–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubin, S.P. Magnetic Nanoparticles; Gubin, S.P., Ed.; Wiley–VCH: Strauss GmbH, Mörlenbach, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xu, M.; Chubik, M.; Chubik, M.V.; Gromov, A.; Wei, G.; Han, W. Entrapment of Radioactive Uranium from Wastewater by using Fungus–Fe3O4 Bio-Nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 41611–41616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groiss, S.; Selvaraj, R.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Ramesh, V. Structural characterization, antibacterial and catalytic effect of iron oxide nanoparticles synthesised using the leaf extract of Cynometra ramiflora. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1128, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, N.; Das, S.; Seth, D.; Chandra, R.; Bhattacharya, S.C.; Goswami, A. Entomotoxic effect of silica nanoparticles against Sitophilus oryzae (L.). J. Pest Sci. 2011, 84, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Galanzha, E.; Totten, D.C.; Benes, H.; Reis, R.S.; Zharov, V. Photoacoustically-guided photothermal killing of mosquitoes targeted by nanoparticles. J. Biophotonics 2014, 7, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumar, R.; Nagarajan, S.; Palanisami, T.; Naidu, R.; Mallavarapu, M. Recent advances in synthesis of inorganic nano/microstructures using microbial biotemplates and their applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52156–52169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashyap, P.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, A.; Sharma, A.K. Myconanotechnology in agriculture: A perspective. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 29, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Cheng, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X. Novel fungus-Fe3O4 bio-nanocomposites as high performance adsorbents for the removal of radionuclides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 295, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wei, G.; Liu, N.; Zhou, L.; Fu, C.; Chubik, M.; Gromov, A.; Han, W. Novel fungus–titanate bio-nanocomposites as high performance adsorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive ions from wastewater. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shora, H.M.; Khateb, A.M.; Darwish, D.B.; El-Sharkawy, R.M. Thiolation of Myco-Synthesized Fe3O4-NPs: A Novel Promising Tool for Penicillium expansium Laccase Immobilization to Decolorize Textile Dyes and as an Application for Anticancer Agent. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ince, O.K.; Aydogdu, B.; Alp, H.; Ince, M. Experimental design approach for ultra-fast nickel removal by novel bio-nanocomposite material. Adv. Nano Res. 2021, 10, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, P.N.; Bini, R.D.; Dias, G.S.; Alcouffe, P.; Santos, I.A.; David, L.; Cótica, L.F. Magnetite nanoparticles with controlled sizes via thermal degradation of optimized PVA/Fe(III) complexes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 460, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotica, L.F.; Garcia, A.; Polli, A.D.; Bini, R.D.; de Oliveira Chaves, T.; de Oliveira Junior, V.A.; Pamphile, J.A. Nanobiocomposites: Synthesis and Environmental Applications. In Fungal Nanobionics: Principles and Applications, 1st ed.; Prasad, R., Kumar, V., Kumar, M., Wang, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, C.G.S.; Beck, W.; Varanda, L.C. Multifunctional luminomagnetic FePt@Fe3O4/SiO2/Rhodamine B/SiO2 nanoparticles with high magnetic emanation for biomedical applications. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, P.N.; Moussa, A.; Milhau, N.; Bini, R.D.; Prouillac, C.; de Oliveira, B.F.; Dias, G.S.; Santos, I.A.; Morfin, I.; Sudre, G.; et al. In situ synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated by chito-oligosaccharides: Physico-chemical characterizations and cytotoxicity evaluation for biomedical applications. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 175602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, A.; Tsror, L.; Pomerantz, A.; Moreh, R.; Mordechai, S.; Huleihel, M. FTIR spectroscopy for detection and identification of fungal phytopathogenes. J. Spectrosc. 2010, 24, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukor, R.K. Vibrational Spectroscopy in the Detection of Cancer; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakesava, S.; Irudayaraj, J.M.K.; DebRoy, C. Differentiation of microorganisms by FTIR-ATR and NIR spectroscopy. Trans.-Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. Gen. Ed. 2004, 47, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.A.; Lacerda, I.C.A.; Pimentel, P.F.; Castro, H.F.D.; Rosa, C.A. Removal of heavy metals by an Aspergillus terreus strain immobilized in a polyurethane matrix. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 34, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, J. (Ed.) Nanotechnology: An Introduction; William Andrew: Kidlington, Oxford, UK, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kotrba, P.; Mackova, M.; Urbánek, V. (Eds.) Microbial Biosorption of Metals; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, E.; Baun, A.; Behra, R.; Hartmann, N.B.; Filser, J.; Miao, A.J.; Quigg, A.; Santschi, P.H.; Sigg, L. Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvadori, M.R.; Nascimento, C.A.O.; Corrêa, B. Nickel oxide nanoparticles film produced by dead biomass of filamentous fungus. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabah, A.; Dakua, I.; Kumar, P.; Mohammed, W.S.; Dutta, J. Growth of templated gold microwires by self organisation of colloids on Aspergillus niger. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2012, 7, 583–591. [Google Scholar]
- Schwegmann, H.; Feitz, A.J.; Frimmel, F.H. Influence of the zeta potential on the sorption and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles on S. cerevisiae and E. coli. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 347, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo-Neto, R.P.; Silva-Freitas, E.L.; Carvalho, J.F.; Pontes, T.R.F.; Silva, K.L.; Damasceno, I.H.M.; Egito, E.S.T.; Dantas, A.L.; Morales, M.A.; Carriço, A.S. Monodisperse sodium oleate coated magnetite high susceptibility nanoparticles for hyperthermia applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 364, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Chow, G.M. Carboxyl group (–CO2H) functionalized ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for potential bio-applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2781–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaves, T.d.O.; Bini, R.D.; Oliveira Junior, V.A.d.; Polli, A.D.; Garcia, A.; Dias, G.S.; Santos, I.A.d.; Nunes de Oliveira, P.; Pamphile, J.A.; Cotica, L.F. Fungus-Based Magnetic Nanobiocomposites for Environmental Remediation. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110139
Chaves TdO, Bini RD, Oliveira Junior VAd, Polli AD, Garcia A, Dias GS, Santos IAd, Nunes de Oliveira P, Pamphile JA, Cotica LF. Fungus-Based Magnetic Nanobiocomposites for Environmental Remediation. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(11):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110139
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaves, Thais de Oliveira, Raquel Dosciatti Bini, Verci Alves de Oliveira Junior, Andressa Domingos Polli, Adriana Garcia, Gustavo Sanguino Dias, Ivair Aparecido dos Santos, Paula Nunes de Oliveira, João Alencar Pamphile, and Luiz Fernando Cotica. 2022. "Fungus-Based Magnetic Nanobiocomposites for Environmental Remediation" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 11: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110139
APA StyleChaves, T. d. O., Bini, R. D., Oliveira Junior, V. A. d., Polli, A. D., Garcia, A., Dias, G. S., Santos, I. A. d., Nunes de Oliveira, P., Pamphile, J. A., & Cotica, L. F. (2022). Fungus-Based Magnetic Nanobiocomposites for Environmental Remediation. Magnetochemistry, 8(11), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110139







