Journal Description
Magnetochemistry
Magnetochemistry
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all areas of magnetism and magnetic materials published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Chemistry, Inorganic and Nuclear) / CiteScore - Q2 (Electronic, Optical and Magnetic Materials)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.5 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.6 (2024)
Latest Articles
Rare-Earth-Free Exchange-Coupled Nanocomposites Based on M-Type Hexaferrites
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(11), 99; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11110099 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
Efficient permanent magnets that are concomitantly economically viable are of paramount importance for allowing industrial stakeholders to maintain a growing and competitive advantage. This study provides a comprehensive overview of recent developments in the field of rare-earth-free nanocomposite permanent magnets based on hexaferrites.
[...] Read more.
Efficient permanent magnets that are concomitantly economically viable are of paramount importance for allowing industrial stakeholders to maintain a growing and competitive advantage. This study provides a comprehensive overview of recent developments in the field of rare-earth-free nanocomposite permanent magnets based on hexaferrites. The basic phenomenology of exchange-spring-coupled nanocomposites, comprising hard and soft magnetic components, is thoroughly explained. The use of hexaferrites as a hard phase, serving as a viable alternative to rare-earth-based permanent magnets, is extensively discussed, taking economical, accessibility-related, and environmental aspects into consideration. State-of-the-Art architectures of hard–soft magnetic nanocomposites based on hexaferrites as the hard magnetic phase, ranging from typical nanocomposites to nanowire arrays and special core–shell-like morphologies, are explored in detail. The maximum energy product (BH)max, representing the quality indicator for permanent magnets, is investigated by taking into consideration various degrees of freedom, such as substitutions, geometry, size, shape, preparation, and processing conditions (annealing), volume fraction of magnetic phases, and interfaces. Promising strategies to overcome the present challenges (e.g., size control, coercivity–remanence trade-off, and optimization for large-scale production) are provided within the framework of future permanent magnet design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fine Tuning of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanostructures)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Magnetic Susceptibility of High-Purity Molybdenum: Role of Trace Impurities and Theoretical Modeling
by
Chao Wang, Zheng Tan, Dan Jia, Xin Xin, Li Meng, Tao Liu, Likui Ning, Song Ma and Enze Liu
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(11), 98; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11110098 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study, a modified Curie–Weiss model was established for the magnetic susceptibility of high-purity molybdenum and Mo–La alloy powders. The elemental composition was analyzed by GDMS, and combined with the M–T and M–H data measured by SQUID, the
[...] Read more.
In this study, a modified Curie–Weiss model was established for the magnetic susceptibility of high-purity molybdenum and Mo–La alloy powders. The elemental composition was analyzed by GDMS, and combined with the M–T and M–H data measured by SQUID, the temperature-independent contributions of weakly magnetic elements such as La and the paramagnetic contributions of impurity ions such as Fe, Co, and Ni were distinguished. Based on the parameters obtained from the nonlinear least squares fitting, the deviation between the magnetic susceptibility at room temperature calculated by the model and the experimental value was within 5%. The results show that this model can reasonably describe the influence of trace impurities on the magnetic susceptibility of the system and provides an effective method for the magnetic prediction of high-purity metal powders.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modeling and Experimental Investigation on Rheological Characteristics of Magnetorheological Fluids and Greases Under Steady and Large-Amplitude Oscillatory Shear
by
Ran Deng, Min Sun, Zhou Zhou, Meng Zhou, Lu Han, Jiong Wang, Yiyang Bai, Limeng Peng, Junyu Chen, Guang Zhang, Min Tang and Zhong Zhang
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(11), 97; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11110097 - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study systematically investigates the complex nonlinear rheological behavior of magnetorheological fluids (MRFs) and greases (MRGs) through comparative experiments under two shear modes (steady-state shear and large-amplitude oscillatory shear) at room temperature. Results demonstrate that during steady-state shear tests, the apparent viscosity of
[...] Read more.
This study systematically investigates the complex nonlinear rheological behavior of magnetorheological fluids (MRFs) and greases (MRGs) through comparative experiments under two shear modes (steady-state shear and large-amplitude oscillatory shear) at room temperature. Results demonstrate that during steady-state shear tests, the apparent viscosity of both materials decreases with the increasing shear rate, exhibiting shear-thinning behavior at high shear rates that aligns with the Herschel–Bulkley constitutive model. Throughout the logarithmically increasing shear rate range, the viscosity and shear stress of MRF consistently exceed those of MRG. Under low-frequency, large-amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS) conditions, both materials display pronounced viscoelasticity and hysteresis. At higher current levels, the maximum shear stress of MRF surpasses MRG, but its hysteresis loops exhibit reduced smoothness. The Bouc–Wen model accurately characterizes the nonlinear hysteresis of both materials, with model parameters successfully identified via a genetic algorithm. This work establishes a universal framework for the dynamic mechanical response mechanisms of magnetorheological materials, providing theoretical guidance for designing and predicting the performance of smart damping devices.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Programmable Magnetic Navigation of Gelatin Microrobots Enhances AB4 Delivery to Inflamed Lung Epithelium
by
Yue Bu, Jianpeng Xu, Chuanhua Li, Zhixi Li, Yongjing Yu and Ziyong Yue
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(11), 96; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11110096 - 1 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Sepsis-induced acute lung injury (SALI) is characterized by dysregulated inflammation with limited therapeutic options. Although Anemoside B4 (AB4) exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, its clinical application is hindered by poor bioavailability. To address this limitation, we developed magnetically guided gelatin microrobots (MG-AB4) for targeted AB4
[...] Read more.
Sepsis-induced acute lung injury (SALI) is characterized by dysregulated inflammation with limited therapeutic options. Although Anemoside B4 (AB4) exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, its clinical application is hindered by poor bioavailability. To address this limitation, we developed magnetically guided gelatin microrobots (MG-AB4) for targeted AB4 delivery. The MG-AB4 system consists of a Fe3O4-loaded gelatin shell for enabling precise magnetic navigation (velocity: 110 μm/s), an AB4 core for rapid drug release which is advantageous for acute inflammatory responses, and surface modifications to enhance cellular uptake. Compared with free AB4, MG-AB4 significantly suppressed key inflammatory cytokines (Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α); p < 0.01), inhibited NF-κB activation (p < 0.01), and improved cell viability in an inflammatory model (p < 0.05). This study demonstrates that magnetically guided AB4 delivery using rapidly releasing microrobots is a promising strategy for SALI treatment, wherein the synergy of targeted delivery and potent anti-inflammatory action may effectively mitigate disease progression.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing the High-Frequency Performance of FeSiAl/2.25 wt.% WS2 Composites Through the Application of a Transverse Magnetic Field
by
Shoujin Zhu, Shuangjiu Feng, Xiansong Liu and Xucai Kan
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(11), 95; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11110095 - 29 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Herein, we address the challenge of high core losses in soft magnetic composites (SMCs) at high frequencies by developing a FeSiAl/WS2 composite system processed under a transverse magnetic field (TMF). In this study, 200- and 600-mesh FeSiAl powders were used as base
[...] Read more.
Herein, we address the challenge of high core losses in soft magnetic composites (SMCs) at high frequencies by developing a FeSiAl/WS2 composite system processed under a transverse magnetic field (TMF). In this study, 200- and 600-mesh FeSiAl powders were used as base materials and combined with 2.25 wt.% two-dimensional tungsten disulfide (WS2; an insulating agent) to prepare FeSiAl/2.25 wt.%WS2 soft magnetic composites via ultrasonic mixing. The evolution of soft magnetic properties under a transverse magnetic field (TMF) was systematically investigated. The novelty of this work lies in the synergistic combination of fine FeSiAl particles and WS2 nanosheets as an interparticle insulator and the application of a TMF to simultaneously suppress eddy current and hysteresis losses—a challenge that is difficult to address using conventional approaches. Morphological analysis confirmed a uniform and continuous organic coating of WS2 nanosheets on FeSiAl particle surfaces. Permeability measurements revealed a slight decrease in effective permeability after the TMF treatment; however, the high-frequency performance was markedly enhanced. Magnetic loss analysis revealed a substantial reduction in the hysteresis loss and an increase in the quality factor under the TMF. Notably, the FeSiAl (600 mesh)/2.25 wt.% WS2 composite achieved a total magnetic loss of 234 kW/m3 under a TMF of 140 kA/m, magnetic induction of 20 mT, and frequency of 1 MHz, representing a 69% reduction compared with conventional SMCs. These results not only validate the effectiveness of the proposed synergistic approach but also highlight the potential of FeSiAl (600 mesh)/2.25 wt.% WS2 for use in high-power, high-frequency magnetic devices, with improved energy efficiency and thermal performance.
Full article
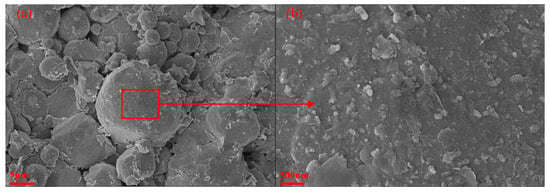
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis, Structural, and Magnetic Properties of High-Entropy (Fe0.2Co0.2Cu0.2Ni0.2Mn0.2)Nb2O6
by
Maria J. S. Lima, Fernando E. S. Silva, Matheus D. Silva, Kivia F. G. Araujo, Marco A. Morales and Uílame U. Gomes
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(11), 94; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11110094 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
In this work, we present the first report on the synthesis via the sol–gel method of a high-entropy (Fe0.2Co0.2Cu0.2Ni0.2Mn0.2)Nb2O6 with columbite–orthorhombic structure. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), ammonium niobium oxalate, and equimolar amounts
[...] Read more.
In this work, we present the first report on the synthesis via the sol–gel method of a high-entropy (Fe0.2Co0.2Cu0.2Ni0.2Mn0.2)Nb2O6 with columbite–orthorhombic structure. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), ammonium niobium oxalate, and equimolar amounts of Fe, Co, Cu, Ni, and Mn ions were used. The refinement of the XRD pattern showed the presence of niobate crystallites with an average size of 48.4 nm and a fraction of 7.6 wt% of a spinel-like phase. At temperatures below 5 K, the DC and AC magnetometry results revealed the presence of a ferromagnetic-like phase due to the niobate phase. The Mössbauer spectrum at 300 K showed a paramagnetic and two magnetically ordered components corresponding to the niobate and the spinel-like phases, respectively. The spectral components were typical of Fe3+, indicating the presence of cation vacancies. The elemental mapping obtained from EDS measurements showed compositional homogeneity. The XRF measurements confirmed a composition consistent with nominal values. These results confirm the feasibility of synthesizing entropy-stabilized columbite oxides via the sol–gel route, opening new opportunities for the design of multifunctional ceramics with tunable structural and magnetic properties for high-performance thermal barrier coatings and energy conversion applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Magnetic Materials and Composites: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
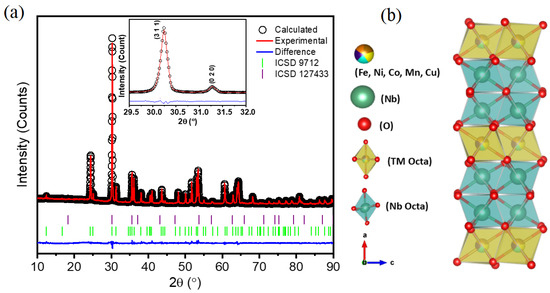
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Core Loss Prediction Model of High-Frequency Sinusoidal Excitation Based on Artificial Neural Network
by
Cunhao Lu, Fanjie Meng, Jiajie Zhang and Zeyuan Zhang
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(11), 93; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11110093 - 25 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The magnitude of core loss is a crucial factor affecting the efficiency of power converters. Due to the complex mechanism of core loss, diverse influencing factors, and the strong coupling characteristics between materials and operating conditions, traditional core loss prediction models struggle to
[...] Read more.
The magnitude of core loss is a crucial factor affecting the efficiency of power converters. Due to the complex mechanism of core loss, diverse influencing factors, and the strong coupling characteristics between materials and operating conditions, traditional core loss prediction models struggle to achieve high-precision prediction of core loss. Based on the Artificial Neural Network (ANN), this paper investigates core loss under high-frequency sinusoidal excitation. The core loss training data is processed using a logarithmic transformation method, and an ANN core loss prediction model is established with temperature, frequency, and magnetic flux density as features. The results show that, compared with non-logarithmic processing, logarithmic transformation of the data can effectively improve the prediction accuracy (PA) of the ANN model. Within the ±10% error range, the maximum PA of the ANN prediction model reaches 98.48%, and the minimum Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) can be as low as 2.58%. In addition, a comparison with the Steinmetz Equation (SE) and K-nearest neighbor (KNN) prediction models reveals that, for four materials, within the ±10% error range of the true core loss values, the minimum PA of the ANN model is 93.33% with an average of 95.38%; the minimum PA of the KNN model is 43.94% with an average of 62.07%; and the minimum PA of the SE model is 14.91% with an average of 19.83%. Furthermore, the MAPE of the ANN model is within 5%.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Magnetic Field on Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of H62 Brass Alloy
by
Hexiang Huang, Dazhao Yu, Hongjun Zhao, Aiguo Gao, Yanan Li and Jiantao Qi
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(11), 92; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11110092 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study investigates the influence of magnetic fields on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of aerospace-grade H62 brass alloy in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution and its underlying 10 mechanisms. Employing electrochemical testing techniques combined with surface characterization methods, we explored the effects of magnetic
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the influence of magnetic fields on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of aerospace-grade H62 brass alloy in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution and its underlying 10 mechanisms. Employing electrochemical testing techniques combined with surface characterization methods, we explored the effects of magnetic field intensity (25–100 mT) and orientation (parallel and perpendicular to electrode surface) on the corrosion kinetics and corrosion product evolution of H62 brass alloy. Results demonstrate that magnetic fields significantly accelerate the corrosion process of H62 brass alloy. Under parallel magnetic field (100 mT), the corrosion current density increased from 0.49 μA/cm2 to 3.66 μA/cm2, approximately 7.5 times that of the non-magnetic condition, while perpendicular magnetic field increased it to 1.73 μA/cm2, approximately 3.5 times the baseline value. The charge transfer resistance decreased from 3382 Ω·cm2 to 1335 Ω·cm2. Magnetic field orientation determines the fundamental differences in corrosion acceleration mechanisms. Parallel magnetic fields primarily enhance mass transfer processes through Lorentz force-driven magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) effects, resulting in intensified uniform corrosion; perpendicular magnetic fields alter interfacial ion distribution through magnetic gradient forces, inducing localized corrosion tendencies. Magnetic fields promote the transformation of protective Cu2O films into porous Cu2(OH)3Cl, reducing the protective capability of corrosion product layers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating Magnetic Nanoparticle–Induced Field Inhomogeneity via Monte Carlo Simulation and NMR Spectroscopy
by
Song Hu, Yapeng Zhang and Bin Zhang
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(11), 91; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11110091 - 23 Oct 2025
Abstract
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) perturb magnetic field homogeneity, influencing transverse relaxation and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra. In Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), this appears as decay of the free induction decay (FID) signal, whose relaxation rate
[...] Read more.
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) perturb magnetic field homogeneity, influencing transverse relaxation and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra. In Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), this appears as decay of the free induction decay (FID) signal, whose relaxation rate determines spectral FWHM. In D2O containing MNPs, both nanoparticles and solvent molecules undergo Brownian motion and diffusion. Under a vertical main field (
(This article belongs to the Section Magnetic Nanospecies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Skyrmion Pair Racetrack Utilizing Hall Motion
by
Shan Qiu, Tianle Zhang, Xiaotong Han, Jiahao Liu, Liang Fang and Yun Cheng
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(10), 90; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11100090 - 20 Oct 2025
Abstract
The skyrmion racetrack is a promising concept for future information technology. The primary issues with skyrmion racetrack memory are now error codes and Hall motion. Here, we propose a skyrmion pair racetrack memory. The Oersted fields generated by the non-contact current-carrying wire in
[...] Read more.
The skyrmion racetrack is a promising concept for future information technology. The primary issues with skyrmion racetrack memory are now error codes and Hall motion. Here, we propose a skyrmion pair racetrack memory. The Oersted fields generated by the non-contact current-carrying wire in the middle of the magnetic nanostrip stabilize the skyrmion pairs in the nanostrip, which are separated by a naturally formed domain wall. Through numerical models and micromagnetic simulations, we demonstrate that such a skyrmion pair can produce linear Hall motion along the nanostrip under the linear control of the Oersted field gradient. These findings offer a high-reliability method for skyrmion racetrack memory and a more efficient approach to designing devices that use the skyrmion Hall effect.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Magnetic Materials and Composites: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Magnetic Fields as Biophysical Modulators of Anticancer Drug Action
by
Xin Yu and Yue Lv
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(10), 89; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11100089 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Magnetic fields (MFs), including static (SMFs) and extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF-EMFs), have recently emerged as potential modulators of anticancer drug responses. Evidence indicates that MFs can influence membrane transport, oxidative stress, DNA damage, apoptosis, and cell cycle regulation, thereby altering the efficacy
[...] Read more.
Magnetic fields (MFs), including static (SMFs) and extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF-EMFs), have recently emerged as potential modulators of anticancer drug responses. Evidence indicates that MFs can influence membrane transport, oxidative stress, DNA damage, apoptosis, and cell cycle regulation, thereby altering the efficacy of chemotherapeutics and targeted agents. These effects are strongly dependent on MFs’ parameters and biological context, leading to synergistic, antagonistic and no-effect outcomes. However, inconsistent exposure protocols, limited reproducibility, and scarce clinical validation remain major obstacles. This review highlights current experimental findings, proposes mechanistic links between MFs and drug action, and outlines key challenges for advancing MF-based adjuvant strategies in oncology.
Full article
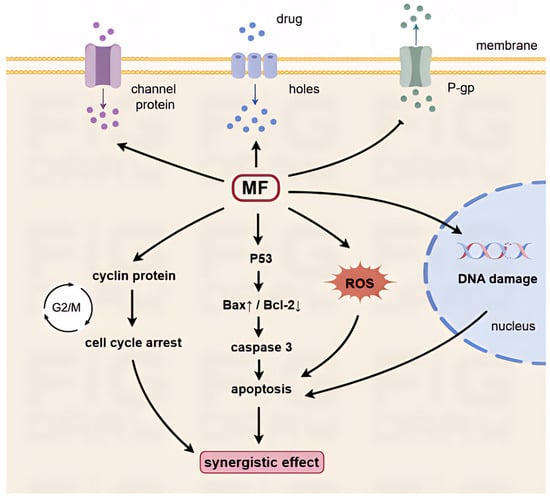
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Artificial Neural Network-Based Heat Transfer Analysis of Sutterby Magnetohydrodynamic Nanofluid with Microorganism Effects
by
Fateh Ali, Mujahid Islam, Farooq Ahmad, Muhammad Usman and Sana Ullah Asif
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(10), 88; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11100088 - 10 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The study of non-Newtonian fluids in thin channels is crucial for advancing technologies in microfluidic systems and targeted industrial coating processes. Nanofluids, which exhibit enhanced thermal properties, are of particular interest. This paper investigates the complex flow and heat transfer characteristics of
[...] Read more.
Background: The study of non-Newtonian fluids in thin channels is crucial for advancing technologies in microfluidic systems and targeted industrial coating processes. Nanofluids, which exhibit enhanced thermal properties, are of particular interest. This paper investigates the complex flow and heat transfer characteristics of a Sutterby nanofluid (SNF) within a thin channel, considering the combined effects of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD), Brownian motion, and bioconvection of microorganisms. Analyzing such systems is essential for optimizing design and performance in relevant engineering applications. Method: The governing non-linear partial differential equations (PDEs) for the flow, heat, concentration, and bioconvection are derived. Using lubrication theory and appropriate dimensionless variables, this system of PDEs is simplified into a more simplified system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). The resulting nonlinear ODEs are solved numerically using the boundary value problem (BVP) Midrich method in Maple software to ensure accuracy. Furthermore, data for the Nusselt number, extracted from the numerical solutions, are used to train an artificial neural network (ANN) model based on the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm. The performance and predictive capability of this ANN model are rigorously evaluated to confirm its robustness for capturing the system’s non-linear behavior. Results: The numerical solutions are analyzed to understand the variations in velocity, temperature, concentration, and microorganism profiles under the influence of various physical parameters. The results demonstrate that the non-Newtonian rheology of the Sutterby nanofluid is significantly influenced by Brownian motion, thermophoresis, bioconvection parameters, and magnetic field effects. The developed ANN model demonstrates strong predictive capability for the Nusselt number, validating its use for this complex system. These findings provide valuable insights for the design and optimization of microfluidic devices and specialized coating applications in industrial engineering.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Advances in Soft Magnetic Materials
by
Kaixuan Li and Zhaoyang Wu
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(10), 87; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11100087 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
Soft magnetic materials have emerged as promising candidates due to their high power density in diverse magnetic components utilized for energy conversion, filtering, resonance, and isolation [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Soft Magnetic Materials)
Open AccessArticle
Structural Color and Mueller Matrix Analysis in a Ferrocell
by
Alberto Tufaile and Adriana Pedrosa Biscaia Tufaile
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(10), 86; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11100086 - 29 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
This study investigates the magneto-optical properties of a ferrofluid using an accessible Ferrocell device. Our findings demonstrate that the ferrofluid’s behavior is critically dependent on its concentration. At high concentrations, the medium is optically dense, with inter-particle scattering and absorption dominating, which prevents
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the magneto-optical properties of a ferrofluid using an accessible Ferrocell device. Our findings demonstrate that the ferrofluid’s behavior is critically dependent on its concentration. At high concentrations, the medium is optically dense, with inter-particle scattering and absorption dominating, which prevents the formation of clear light patterns. However, with intermediate dilution, the system enters a “pattern formation zone” where the magnetic field effectively aligns the nanoparticles, creating complex, visible light patterns like horocycles. The appearance of these patterns provides evidence of field-induced ordering and structural coloration. The colors observed are not due to pigments, but result from the interaction of light with the periodic structures formed by the aligned nanoparticles. Our analysis, supported by the Mueller matrix framework, confirms that the ferrofluid acts as a retarder. The birefringence induced by the magnetic field varies across the film, leading to a chromatic dispersion that selectively suppresses certain wavelengths. This process explains how a specific color, such as blue, can be blocked at one location while others pass through, creating structural colors observed in the patterns.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Ferrofluids: Electromagnetic Properties and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
pH and Magnetic-Responsive Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Composites for Gallic Acid Delivery
by
Kun Fang, Pei Li, Hanbing Wang, Xiangrui Huang and Yihan Li
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(10), 85; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11100085 - 28 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Gallic acid (GA) exhibits a broad range of biological activities; however, its clinical application is significantly limited by poor stability, rapid degradation, and low bioavailability. Consequently, developing responsive delivery platforms to enhance GA stability and targeted release has become an important research focus.
[...] Read more.
Gallic acid (GA) exhibits a broad range of biological activities; however, its clinical application is significantly limited by poor stability, rapid degradation, and low bioavailability. Consequently, developing responsive delivery platforms to enhance GA stability and targeted release has become an important research focus. Herein, GA was encapsulated within novel composite hydrogel beads (CMC-SA-Fe3O4@GA) prepared via crosslinking carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) and sodium alginate (SA) with Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) to facilitate efficient drug delivery. The formulation was characterized and evaluated in terms of drug-loading capacity, controlled-release properties, antioxidant activity, antibacterial performance, and biocompatibility. The results indicated that the GA loading efficiency reached 31.07 ± 1.23%. Application of an external magnetic field accelerated GA release, with the observed release kinetics fitting the Ritger–Peppas model. Furthermore, antioxidant capacity, evaluated by DPPH assays, demonstrated excellent antioxidant activity of the CMC-SA-Fe3O4@GA composite beads. Antibacterial tests confirmed sustained inhibitory effects against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. In vitro, cellular assays indicated favorable biocompatibility with normal hepatic cells (HL-7702) and effective inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2). Overall, the novel pH- and magnetic field-responsive CMC-SA-Fe3O4@GA hydrogel system developed in this work offers considerable potential for controlled delivery of phenolic compounds, demonstrating promising applicability in biomedical and food-related fields.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study of the Magnetohydrodynamic Instability and a New Suppression Method in Liquid Metal Batteries
by
Jia-Jun Song, Xiao-Zhong Zuo, En-Qi Zhu, Qi-Guang Li, Bao-Zhi Chen and Ben-Wen Li
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(10), 84; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11100084 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
As a strong candidate for energy storage applications, Liquid Metal Batteries (LMBs) have the advantages of higher current density, longer cycle life, and simpler manufacturing of large-scale storage systems. Owing to the all-liquid construction, various kinds of Magnetohydrodynamic instabilities (MHDIs) are present in
[...] Read more.
As a strong candidate for energy storage applications, Liquid Metal Batteries (LMBs) have the advantages of higher current density, longer cycle life, and simpler manufacturing of large-scale storage systems. Owing to the all-liquid construction, various kinds of Magnetohydrodynamic instabilities (MHDIs) are present in LMBs. In this paper, an in-depth study of the evolution process of MHDIs within LMBs has been conducted. By analyzing the characteristic velocity, the growth rate of instabilities γ has been defined so that the critical Hartmann number at which the instability occurs can be ascertained. A new critical parameter, mixed Reynolds number Remix, has been introduced to determine the duration of stable battery operation across varying charging/discharging currents, including those that may surpass the prescribed safe limits. Finally, a method for mitigating magnetohydrodynamic instability in LMBs through the configuration of busbar current is proposed, which can be seamlessly integrated with parallel battery packs. A comparative analysis of LMBs operation with/without bus current configuration reveals that when bus current is appropriately configured, the magnetic field strength within the battery undergoes a notable reduction of 40%, leading to a significant suppression of instability. The conclusions offer theoretical underpinnings for the application of LMBs in large-scale grid-level energy storage systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Magnetic Field)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Topological Rainbow Trapping in One-Dimensional Magnetoelastic Phononic Crystal Slabs
by
Wen Xiao, Fuhao Sui, Jiujiu Chen, Hongbo Huang and Tao Luo
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(10), 83; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11100083 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
We design a one-dimensional magnetoelastic phononic crystal slab composed of the smart magnetostrictive material Terfenol-D and pure tungsten. Band inversion and topological phase transitions are achieved by modifying the geometric parameters of the non-magnetic medium within the unit cell. The emergence of topological
[...] Read more.
We design a one-dimensional magnetoelastic phononic crystal slab composed of the smart magnetostrictive material Terfenol-D and pure tungsten. Band inversion and topological phase transitions are achieved by modifying the geometric parameters of the non-magnetic medium within the unit cell. The emergence of topological interface states within overlapping bandgaps, exhibiting distinct topological properties, along with their robustness against interfacial structural defects, is confirmed. The coupling effects between adjacent topological interface states in a sandwich-like supercell configuration are investigated, and their tunability under external magnetic fields is demonstrated. A Su-Schrieffer-Heeger (SSH) phononic crystal slab system under gradient magnetic fields is proposed. Critically, and in stark contrast to previous static or structurally graded designs, we achieve reconfigurable rainbow trapping of topological interface states solely by reprogramming the gradient magnetic field, leaving the physical structure entirely unchanged. This highly localized, compact, and broadband-tunable topological rainbow trapping system design holds significant promise for applications in elastic energy harvesting, wave filtering, and multi-frequency signal processing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Low-Dimensional Magnetic Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Magnetic-Responsive Material-Mediated Magnetic Stimulation for Tissue Engineering
by
Jiayu Gu, Lijuan Gui, Dixin Yan, Xunrong Xia, Zhuoli Xie and Le Xue
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(10), 82; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11100082 - 23 Sep 2025
Abstract
Tissue repair is a significant challenge in biomedical research. Traditional treatments face limitations such as donor shortage, high costs, and immune rejection. Recently, magnetic-responsive materials, particularly magnetic nanoparticles have been introduced into tissue engineering due to their ability to respond to external magnetic
[...] Read more.
Tissue repair is a significant challenge in biomedical research. Traditional treatments face limitations such as donor shortage, high costs, and immune rejection. Recently, magnetic-responsive materials, particularly magnetic nanoparticles have been introduced into tissue engineering due to their ability to respond to external magnetic fields, generating electrical, thermal, and mechanical effects. These effects enable precise regulation of cellular behavior and promote tissue regeneration. Compared to traditional physical stimulation, magnetic-responsive material-mediated stimulation offers advantages such as non-invasiveness, deep tissue penetration, and high spatiotemporal precision. This review summarizes the classification, fabrication, magnetic effects and applications of magnetic-responsive materials, focusing on their mechanisms and therapeutic effects in neural and bone tissue engineering, and discusses future directions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Applications of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Magnetic Nanospecies: Synthesis, Properties, Physical and Biomedical Applications
by
Alexey Chubarov
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(9), 81; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090081 - 22 Sep 2025
Abstract
Magnetic nanoparticles and nanocomposites continue to garner considerable interest due to their versatility in biomedical applications, ranging from diagnostics and therapy to catalysis and sensing [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Magnetic Nanospecies: Synthesis, Properties, Physical and Biomedical Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Parahydrogen-Based Hyperpolarization for the Masses at Millitesla Fields
by
Garrett L. Wibbels, Clementinah Oladun, Tanner Y. O’Hara, Isaiah Adelabu, Joshua E. Robinson, Firoz Ahmed, Zachary T. Bender, Anna Samoilenko, Joseph Gyesi, Larisa M. Kovtunova, Oleg G. Salnikov, Igor V. Koptyug, Boyd M. Goodson, W. Michael Snow, Eduard Y. Chekmenev and Roman V. Shchepin
Magnetochemistry 2025, 11(9), 80; https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090080 - 22 Sep 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hyperpolarization (HP) techniques, such as Parahydrogen-Induced Polarization (PHIP), Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange (SABRE), and dissolution Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (d-DNP), significantly enhance the sensitivity of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy for chemical analysis and metabolic imaging. However, the high cost of equipment, ranging
[...] Read more.
Hyperpolarization (HP) techniques, such as Parahydrogen-Induced Polarization (PHIP), Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange (SABRE), and dissolution Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (d-DNP), significantly enhance the sensitivity of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy for chemical analysis and metabolic imaging. However, the high cost of equipment, ranging from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, limits accessibility of hyperpolarization for the broad scientific community. In this work, we aim to mitigate some of the challenges by developing a cost-effective solution for parahydrogen (pH2)-based PHIP and SABRE HP methods. A custom coil-winding machine was designed to fabricate solenoid magnet coils, which were then evaluated for their magnetic field profiles, demonstrating a high degree of magnetic field homogeneity. A model 1H SABRE experiment successfully implemented the constructed solenoid, achieving efficient hyperpolarization. Additionally, the solenoid magnet can be utilized for in situ detection of hyperpolarization when integrated with a low-field NMR spectrometer, reducing the total setup cost to a few thousand dollars. These findings suggest that our approach makes HP technology more affordable and accessible, potentially broadening its applications in chemical and biomedical research, as well as educational settings involving undergraduate student researchers. This work provides a practical pathway to lower the financial barriers associated with pH2 HP setups.
Full article

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Magnetochemistry Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Editorial Office
- 10th Anniversary
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Chemistry, IJMS, Molecules, Quantum Reports, Symmetry, Magnetochemistry
Theoretical, Quantum and Computational Chemistry—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Jorge Garza, Andrei L. TchougréeffDeadline: 31 July 2026
Topic in
Electronic Materials, IJMS, Magnetochemistry, Materials, Nanomaterials
Magnetic Nanoparticles and Thin Films
Topic Editors: Renat F. Sabirianov, Ahmad AlsaadDeadline: 31 December 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Magnetochemistry
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Coordination Compounds
Guest Editors: Diego Paschoal, Hélio Dos SantosDeadline: 30 November 2025
Special Issue in
Magnetochemistry
Magnetic Nano- and Microparticles in Biotechnology
Guest Editors: Ângela Leão Andrade, Rosangela María Costa SilvaDeadline: 30 December 2025
Special Issue in
Magnetochemistry
Fundamentals and Applications of Magnetic Nanospecies—Educational Aspects
Guest Editor: Evgeny KatzDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Magnetochemistry
Advances in Magnetic Metal–Organic Frameworks
Guest Editor: Jakub HrubýDeadline: 31 December 2025









