Abstract
The aim of this study was to produce several flavor esters via esterification of octanoic acid with different commercial short-chain alcohols (methanol, propanol, isoamyl alcohol, hexanol and benzyl alcohol) and fusel oil in solvent-free systems. Lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 immobilized via mechanism of interfacial activation on poly(styrenene-divinylbenzene) (PSty-DVB) beads was used as heterogeneous biocatalyst and its catalytic performance was compared with that of the soluble lipase. The heterogeneous biocatalyst was prepared by employing 5 mmol·L−1 buffer sodium acetate at pH 5.0 and 25 °C using an initial protein loading of 40 mg·g−1. The maximum amount of immobilized protein reached was 31 mg·g−1, corresponding to an immobilization yield of 80%. Mass transfer studies demonstrated that the lipase was preferentially adsorbed inside the pores of the support, which was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy analysis. Lipase immobilization can be described by a pseudo-first-order kinetic model via a physisorption process. When used as biocatalysts of the target reactions, the highest conversion percentage (between 65% and 85% of acid conversion after 60–90 min of reaction) values were achieved for esterification reactions catalyzed by immobilized lipase. Reusability tests revealed high retention of the original activity of the immobilized lipase after six successive batch reactions using isoamyl alcohol (47%) and fusel oil (72%). The proposed reaction systems can be considered green processes (EcoScale score above 80), with exception of methanol medium, classified as an acceptable green process (EcoScale score of 68). These results show that the heterogeneous biocatalyst prepared can be an economic and sustainable option for flavor esters production on an industrial scale.
1. Introduction
The global flavors and fragrances market was $25.89 billion in 2021 and it is expected to reach $36.49 billion in 2029, with a projected annual growth rate of 4.7% during the forecast period [1]. The compounds used in this market can be obtained from natural sources such as animal and plant materials (herbs, honey, fruits, flowers, and spices) or via chemical synthesis. These compounds comprise lactones, carboxylic acids, alcohols, esters, ketones, aldehydes, and terpenes [1,2]. Synthetic flavors and fragrances, such as a wide variety of esters, are currently used in several products, including food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, fine fragrances, cosmetics, personal care products, and home and floor care products [1,2,3]. They have been preferentially produced using a variety of homogeneous or heterogeneous chemical catalysts or biocatalysts. Among the latter, we can remark whole-cells from several microorganisms or isolated enzymes—lipases, cutinases, acyltransferases, lipoxygenases, hydroperoxide lyases, alcohol dehydrogenases or even multi-enzymatic systems [4]. Recently, increasing environmental and health awareness among the general public and in legislation have driven the need to seek eco-friendly and sustainable processes for producing valuable industrial esters, including flavors and fragrances. In this context, the use of environmentally friendly catalysts (biocatalysts) in industrial processes has been considered crucial to meet the requirements of some sectors, including food, cosmetics and personal care industries, that require high-quality products [3,4]. Moreover, esters produced via biocatalytic routes can be labeled as green products, with the advantages that this has in their commercialization and possible price [2,3,5].
Lipases (triacylglycerol acylhydrolases, EC 3.1.1.3) stand among the most important industrial enzymes. In nature, these enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of triacylglycerols into diacylglycerols, monoacylglycerols, free fatty acids and glycerol at the water/oil interface [6,7]. In vitro, they can be utilized for producing food-grade flavor and fragrance compounds, mainly via esterification reactions conducted in the presence or absence of organic solvents [3,4,6,7,8].
In general, the application of lipases in their free forms (soluble or powder crude extracts) in non-aqueous systems is not attractive, due to their difficult recovery from the reaction systems and their inactivation involving several phenomena such as possible distorting effects caused by the use of high temperature, organic solvents or by the effects of raw materials, such as short-chain carboxylic acids and alcohols commonly used for producing flavor and fragrance esters [9,10,11,12]. Moreover, enzyme aggregation can also drastically reduce their catalytic performances due to the generation of substrate diffusional problems [3,6,7,13]. To overcome such problems, immobilization of lipases has been an important tool in industrial processes for their application. Immobilization of lipases allows easy separation of the biocatalysts from the reaction mixtures at the end of the process, reuse for repeated reactions in batch or continuous modes (as long as the enzyme remains active). Moreover, it has been shown that immobilization may be a potent tool to improve many other enzyme features, such as stability (following different mechanisms) [10]. Immobilization can also improve enzyme selectivity, specificity or reduced inhibitions [14,15,16,17], being coupled to enzyme purification [18]. However, only a properly designed and controlled immobilization protocol can really fully benefit from the potential of these techniques, as many points that influence the final effects on the enzyme features are still under investigation [12]. Physical adsorption of lipases on hydrophobic support surfaces allows their immobilization via the mechanism of interfacial activation, enabling the immobilization of the open form of the lipase. This has been the most used method for preparing robust and versatile biocatalysts for further application in biotransformation reactions in non-aqueous systems [9,19]. This immobilization protocol provides simultaneous stabilization, hyperactivation and purification of lipases [9].
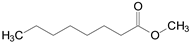
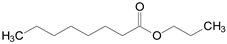
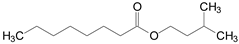
In this context, the objective of the present study is the environmentally-friendly production of food-grade flavor esters via esterification of octanoic acid with different alcohols (methanol, propanol, fusel oil, isoamyl alcohol, hexanol and benzyl alcohol) in solvent-free systems. This is a cleaner and sustainable option for enzymatic production of valuable esters, since it facilitates downstream processes and reduces environmental impacts [20]. The chemical structure and flavor profiles of the different synthetic esters produced in this study are listed in Table 1. Fusel oil, a by-product from the bioethanol production composed of a mixture of several alcohols such as ethanol, propanol, isobutanol, and isoamyl alcohol (this last being its main component) [21,22,23], was also used as a low-cost and sustainable raw material. For such a purpose, a genetically modified enzyme derived of the commercial lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus (produced by a genetically modified strain of Aspergillus oryzae) with the trade-name of Eversa® Transform 2.0 by Novozymes S.A. was utilized [24,25,26]. This enzyme has been launched as a useful one to produce biodiesel in its free form, making it among the cheapest commercial lipases [25,26]. The enzyme was immobilized via interfacial activation on poly(styrene-divinylbenzene) (PSty-DVB) beads and utilized as heterogeneous biocatalyst of the target reaction. This support was chosen due to its high surface area and pore size, high versatility for adsorbing lipases from several sources, including lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0, and its easy separation from the reaction systems via simple filtration and reuse after several batch reactions, with high retention of the original activity of lipases [27,28,29]. In this study, the enzyme’s catalytic performance in esterification reactions was compared with soluble lipase (liquid enzyme preparation). Kinetic and mass transfer studies for the adsorption process were conducted to elucidate the interaction of the lipase with the PSty-DVB surface. The catalytic performance of the lipase after successive batch esterification reactions and sustainability responsibility (EcoScale score analysis) of the process was also investigated. In consultation with the Scopus base, the production of food-grade flavor esters via esterification of octanoic acid using Eversa® Transform 2.0 as biocatalyst has not been reported in the literature to date and this bibliographic survey shows the novelty of this study.

Table 1.
Technical information of the different flavor esters from octanoic acid produced in this study.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Influence of Contact Time on the Adsorption Process: Kinetic and Mass Transfer Studies
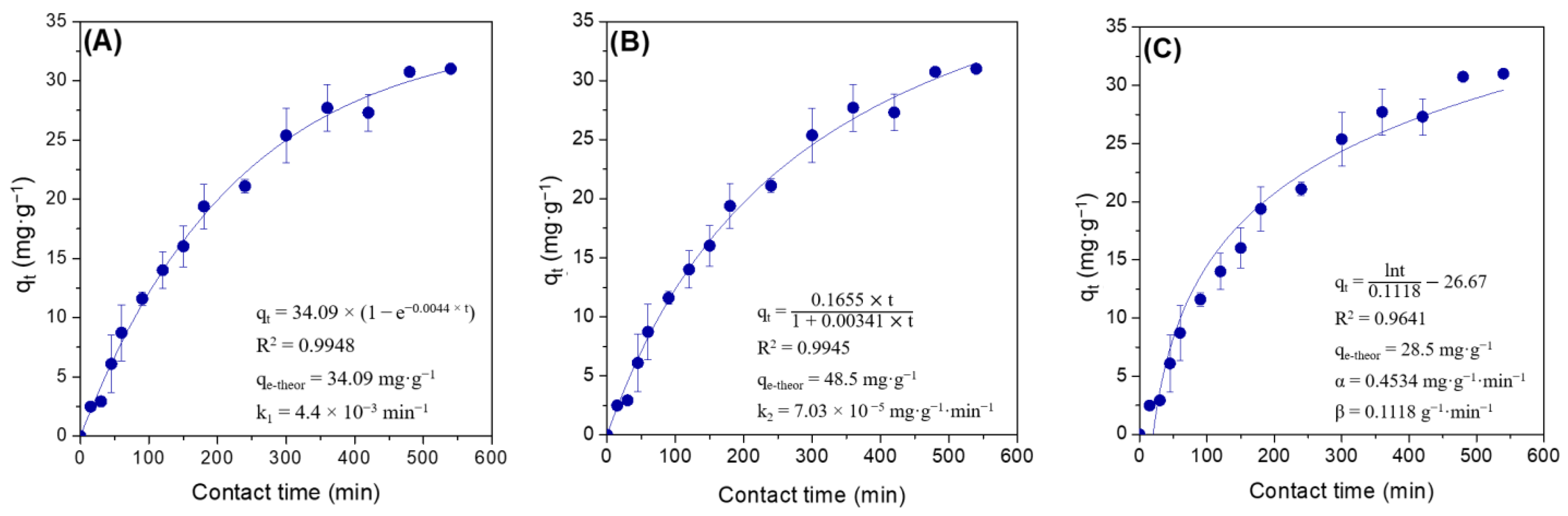
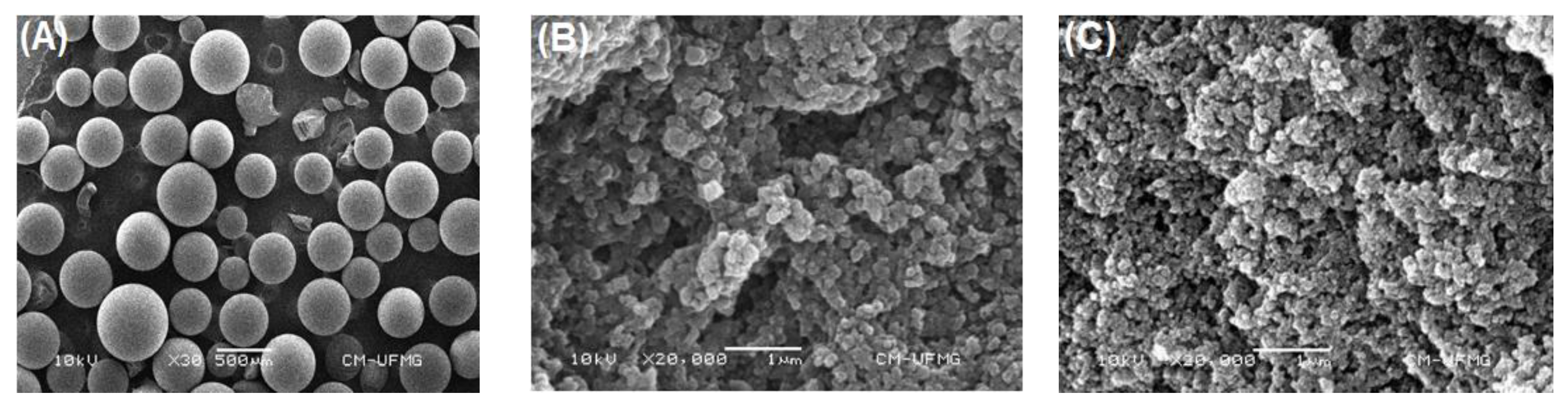
In this study, the adsorption process of lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 on PSty-DVB beads in a batch mode was performed under moderate experimental conditions—pH 5.0 at low ionic strength (5 mmol·L−1—buffer sodium acetate), 25 °C, mechanical stirring of 200 rpm and an initial protein loading of 40 mg·g−1 of support for providing a heterogeneous biocatalyst with high immobilized protein amount and, thus, catalytic performance to produce valuable industrial esters [28,29]. According to Figure 1A–C, a linear profile of lipase adsorption can be observed during the first 180 min of contact time due to the high surface area and pore size of PSty-DVB beads, followed by a slight decrease of the adsorption rate due to possible reduction of the available surface area in the support and/or restrict access of the enzyme to the internal part of the pores (reduction of the pore diameter by the previously adsorbed lipase molecules). The maximum adsorbed protein amount of 31 mg·g−1 of support was achieved after 480 min of contact time, which corresponds to 77.5% of the protein loading initially offered (40 mg·g−1 of support). The immobilization yield, based on the units of activity (hydrolytic activity) lost during the adsorption process, was very similar (80.4%), thus showing that the soluble lipase used in this study (Eversa® Transform 2.0) has few contaminant proteins in its formulation. A control test by incubating the lipase under the same experimental conditions (lipase solution in the absence of support) was also performed, and it retained all of its original activity after 540 min. These results clearly showed that all units of activity that disappeared in the supernatant were due to adsorption of the enzyme on the support surface. SEM images show that the support has a spherical geometry with non-uniform particle size distribution varying from 250 to 850 µm (magnification of 30×—Figure 2A), and large pores (magnification of 20,000×—Figure 2B). In fact, an apparent decrease of pore size and uniform distribution of the enzyme on the support surface after the adsorption process can be observed (magnification of 20,000×—Figure 2C). These images show that lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 can be immobilized on both external and internal support surfaces.
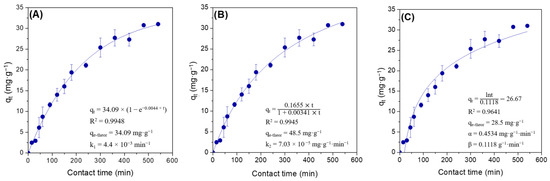
Figure 1.
Non-linear adsorption kinetic models of (A) pseudo-first-order; (B) pseudo-second-order; and (C) Elovich plots for the adsorption of lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 on PSty-DVB beads at 25 °C, 200 rpm, and pH 5.0 (buffer sodium acetate at low ionic strength—5 mmol·L−1), using an initial protein loading of 40 mg·g−1 of support.
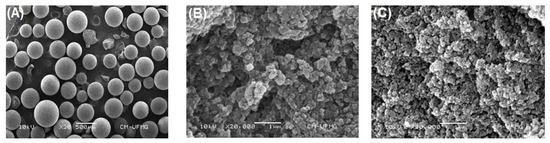
Figure 2.
SEM images of PSty-DVB beads at (A) 30× and (B) 20,000× magnification, and (C) immobilized lipase at 20,000× magnification.
Three non-linear empirical adsorption kinetic models such as pseudo-first-order (PFO), pseudo-second-order (PSO) and Elovich were used to fit these experimental adsorption data for determining of adsorption rate of the lipase on the support surface and better understanding on the adsorption process [34]. According to results in Figure 1A–C, PFO and PSO kinetic models gave the highest and very similar coefficient correlation (R2) values-0.9948 and 0.9945, respectively, followed by the Elovich kinetic model (R2 = 0.9641). However, the theoretical qe value obtained for PFO kinetic value (qe-theor = 34.09 mg·g−1 of support—Figure 1A) was consistent with the experimental value (qe-exp = 31 mg·g−1 of support). This difference around 10% between qe-theor and qe-exp values could be due to possible adsorption of stabilizing agents, e.g., polyols and salts, on the support surface that may prevent the adsorption of some lipase molecules. The theoretical qe value obtained by fitting the Elovich kinetic model was also very similar to the qe-exp value (qe-theor = 28.5 mg·g−1 of support—Figure 1C); however, this kinetic adsorption model assumes chemisorption interactions [34]. Therefore, PFO was the model that better describes the experimentally obtained data. This adsorption kinetic model has been widely applied for describing physisorption (reversible) processes [35,36,37,38]. In this case, the reversible adsorption of the lipase occurs via preferential hydrophobic interactions (mechanism of interfacial activation) [9,12,19]. These results suggest a possible regeneration and recyclability of PSty-DVB beads by desorbing lipase molecules from its surface using several chemicals such as detergents for next lipase adsorption processes and, thus, new application in biotransformation reactions [39,40]. This can be considered a crucial factor for its use as a support for preparing heterogeneous biocatalysts to be used in industrial processes.
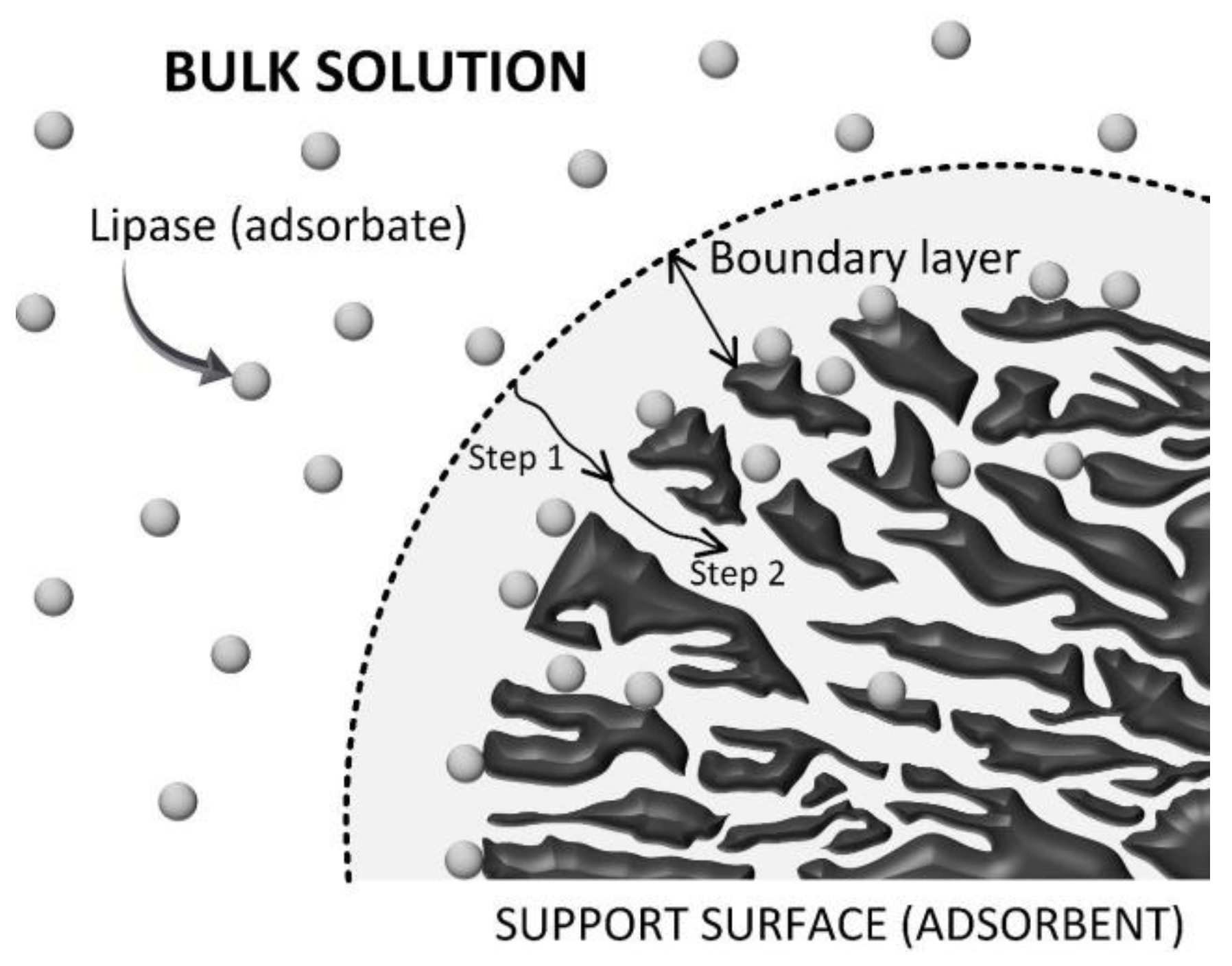
The adsorption process involves several mass transfer steps such as: (i) external mass transfer over the stagnant film formed between the liquid phase and external surface of the adsorbent (convective mass transfer); (ii) diffusional mass transfer inside the pores of the support; and (iii) interaction of the adsorbate, in this case lipase molecules, with the internal support surface via several mechanisms—physisorption and/or chemisorption [41,42,43]. An illustrative representation of mass transfer of lipase molecules from the solution to the support microenvironment (internal and/or external surfaces) is shown in Figure 3.
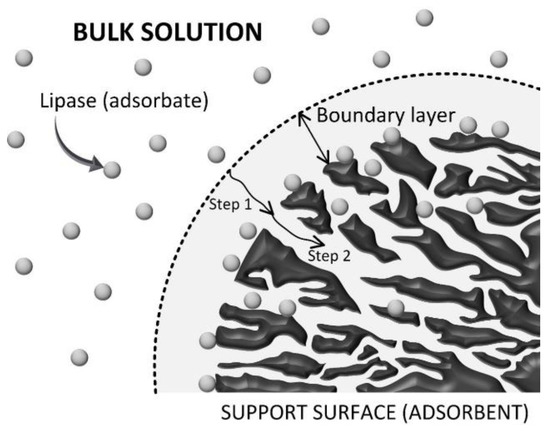
Figure 3.
Representative scheme of the mechanism of lipase adsorption on PSty-DVB beads. Step 1 is the film diffusion (boundary layer) and Step 2 is the internal diffusion (inside the pores of the support). This illustration was adapted with permission from Elsevier, Ref. [34], ON: 5425270722857.
Therefore, mass transfer studies were conducted to determine the limiting-step of the adsorption process. Firstly, it was necessary to determine some physical properties of the support and bulk solution (enzyme solution) for the calculation of mass transfer parameters at a liquid-solid interface, as shown in Table 2. Exceptionally for PSty-DVB, some properties were obtained from the supplier (Supelco® Analytical Products); however, other relevant properties for conducting the present study such as apparent specific mass (), porosity (εp), tortuosity (τ) and external surface area (SEXT) were determined based on previous reports [44,45]. According to Table 2, the calculated external surface of this support (SEXT) was 25 m2·g−1 that corresponds to only 5% of its overall surface area (500 m2·g−1). This shows that the lipase is preferentially adsorbed on the internal support surface and, thus, internal mass transfer effects plays an important role in the adsorption process [43,45], and, thus, the catalytic performance of the heterogeneous biocatalyst (immobilized lipase). In fact, SEM analysis illustrated in Figure 2B shows clearly that this support has a large internal surface required for preparing heterogeneous biocatalysts, which confirms this result of calculated SEXT.

Table 2.
Properties of the support, enzyme solution and suspension solid–liquid for the determination of fluid mechanics and mass transfer parameters of the adsorption process (preparation of the heterogeneous biocatalyst).
Dimensionless numbers in fluid mechanics and mass transfer were also calculated to determine external and internal mass transfer parameters such as the solid–liquid external mass transfer coefficient (kSL) and effective diffusivity of the enzyme inside the pores of the support (Deff.), respectively [41,43,45]. According to Table 2, the Reynolds number, a dimensionless number that describes the ratio between inertial and viscous forces, was 7692.4, thus showing that the adsorption process was conducted in a turbulent flow (Re > 4000) [46]. Under such conditions, a drastic decrease on the boundary layer thickness is expected (see Figure 3), thus indicating that the internal mass transfer is the limiting-step on the adsorption process. The Biot number, a dimensionless that gives the ratio between internal and external mass transfer resistances [42,47,48], was also determined to elucidate the controlling step on the proposed adsorption system. According to Table 2, the Biot number was 105.2, which confirms that the proposed protocol for immobilization of lipase on PSty-DVB beads was clearly controlled by the internal diffusion [47,48]. This result is in accordance with SEM analysis that shows the preferential adsorption of the enzyme on the internal support surface that corresponds to nearly 95% of all its specific surface area.
The catalytic performance of the biocatalyst (immobilized lipase) was also determined on the hydrolysis of olive oil emulsion and compared with soluble lipase. According to the results, the prepared biocatalyst exhibited a hydrolytic activity of 157.3 ± 12.3 U·g−1. The immobilization process drastically reduced the specific activity, ratio between hydrolytic activity and maximum immobilized protein amount—qe [49], of the enzyme from 560 U·mgprotein−1 (soluble lipase) to 5.05 U·mgprotein−1 (immobilized lipase). These results may be mainly due to the low solubility of oil molecules in the aqueous media and/or the restricted access of drops of substrate to the internal microenvironment of the heterogeneous biocatalyst, suggesting strong diffusive effects using olive oil emulsion, which is also a highly viscous reaction mixture. Moreover, the active center of the lipase is oriented towards the support surface without any spacer arm (in contraposition to the use of supports coated with acyl groups such as octyl or octadecyl) [9]. The objective of this study was the preparation of a heterogeneous biocatalyst to catalyze the production of several monoesters with flavor properties via direct esterification of short-chain starting materials such as octanoic acid (8 carbon atoms) and several alcohols—from 1 carbon atom (methanol) to 7 carbon atoms (benzyl alcohol). In this case, excellent external mass transfer of short-chain starting materials from the reaction mixture (warranted by a vigorous mechanical stirring-240 rpm) to the internal microenvironment of the biocatalyst is expected, thus exhibiting high catalytic performance in synthetic short-chain esters production, as follows.
2.2. Comparative Performance of Soluble or Immobilized Lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 on Flavor Esters Production via Esterification
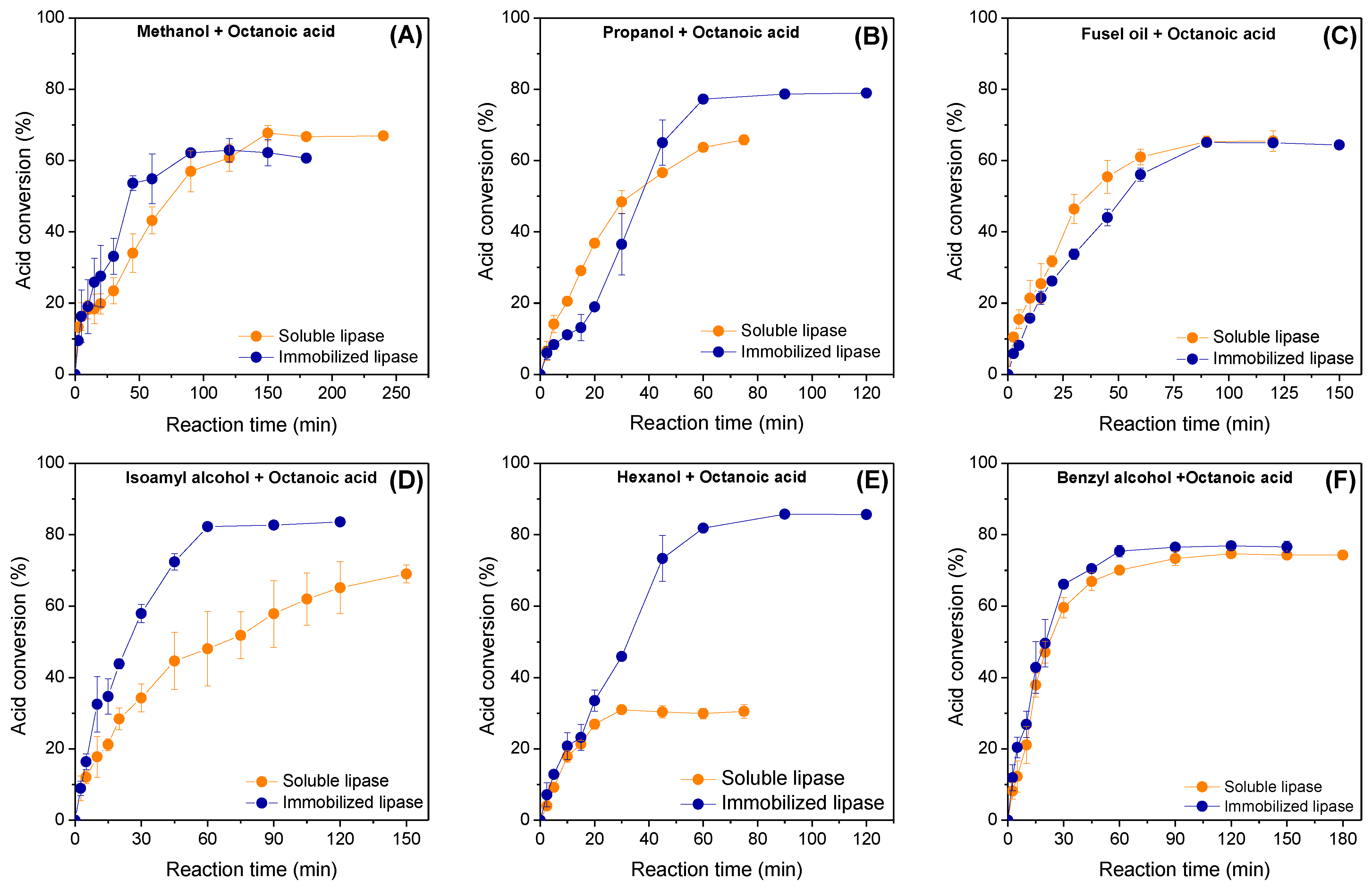
The catalytic performance of immobilized lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 on PSTy-DVB beads in the direct esterification of octanoic acid with different short-chain alcohols in solvent-free systems was evaluated and compared with its soluble form. The different chemical structures (linear, branched or aromatic chains) and polarity of short-chain alcohols, as well as different rheological properties of the reaction media, can strongly influence the mass transfer processes (external and internal mass transfer) and catalytic performance of the enzyme [50,51]. Moreover, the form of the biocatalyst (soluble or immobilized lipase) can also alter the polarity and partitioning effects that results in the distinct accessibility of starting materials to the enzyme microenvironments [50]. In this study, the polarity of the different alcohols was defined based on their Log P values, logarithm of partition coefficient in an 1-octanol/water biphasic system [8]. In fact, different catalytic performances by using different alcohols or lipase forms were achieved, as shown in Figure 4A–F. In general, a linear profile for all reaction systems using both biocatalyst forms (soluble or immobilized lipase) up to 50% of acid conversion can be observed, thus suggesting lack of diffusional problems. However, the different reaction times to achieve such acid conversion percentage values can be verified due to different properties for each reaction mixture, as expected. For reaction systems using methanol (Figure 4A), it is possible to observe that the immobilized biocatalyst gave the highest acid conversion percentage of 62.5% after the first 90 min of contact time, while soluble lipase required nearly 150 min of reaction to achieve an acid conversion of 67.7%. After replacing methanol with propanol, soluble lipase was more active than the immobilized biocatalyst during the first 30 min of reaction (Figure 4B); however, maximum acid conversion was also achieved using immobilized biocatalyst (77.5% after 60 min of reaction). Soluble lipase was also slightly more active than the heterogeneous biocatalyst up to 45 min of reaction using fusel oil; however, similar acid conversion percentages (around of 65%) can be observed after 90 min of reaction catalyzed by both biocatalyst forms (Figure 4C). Using isoamyl alcohol, a maximum acid conversion of 82.3% was obtained after 60 min of reaction for immobilized lipase, whereas soluble lipase gave only 45% in this reaction time (Figure 4D). A maximum conversion percentage into isoamyl octanoate around of 70% can be observed at 150 min of reaction for soluble lipase. Comparing commercial isoamyl alcohol and fusel oil systems, the immobilized lipase exhibited a highest preference towards isoamyl alcohol, while soluble lipase presented preference towards highly polar short-chain alcohols such as ethanol, propanol and isobutyl alcohol present in fusel oil composition.
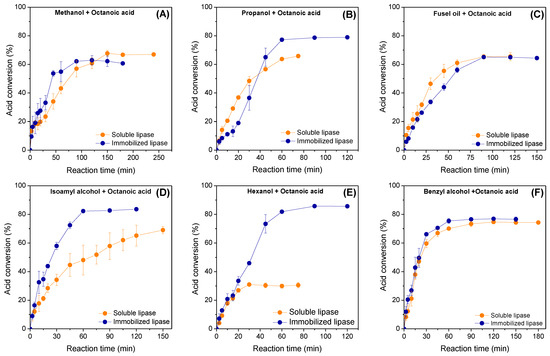
Figure 4.
Influence of reaction time on the esterification of (A) methanol; (B) propanol; (C) fusel oil; (D) isoamyl alcohol; (E) hexanol; and (F) benzyl alcohol with octanoic acid catalyzed by soluble and immobilized lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0. The reactions were performed in solvent-free systems at 40 °C, 240 rpm, stoichiometric acid:alcohol molar ratio and initial protein concentration of 3.3 mg protein per gram of reaction mixture.
This could be explained through high partition of the hydrophobic commercial isoamyl alcohol to the internal surface of the hydrophobic heterogeneous biocatalyst due to its highest hydrophobicity compared with highly polar short-chain alcohols (see Log P values in Table 3). In fact, high catalytic performance using immobilized lipase was also observed for the reaction system prepared with hexanol, the most hydrophobic alcohol tested in this study (Log P = 2.03—Table 3), due to its better diffusion and partitioning effect in the internal microenvironment of the heterogeneous biocatalyst. Thus, maximum acid conversion percentage around of 85% was achieved after 75 min of reaction, almost three-fold higher than those observed using soluble lipase, that exhibited its maximum acid conversion (only 31%) after the first 30 min of reaction, as shown in Figure 4E. A similar acid consumption profile for both homogeneous and heterogeneous biocatalysts using benzyl alcohol, an aromatic alcohol with Log P value lower than hexanol and very close to commercial isoamyl alcohol, was also observed (Figure 4F), as shown in Table 3. This indicates a possible improvement of its partition in the microenvironment of soluble lipase, yielding similar acid conversion (around of 75%) for both reaction systems after 60 min of reaction. These results suggest a better partition of hydrophobic starting materials to the microenvironment of the heterogeneous biocatalyst, thus providing the highest acid conversion values in shorter-reaction times. Exceptionally for fusel oil and benzyl alcohol, both biocatalysts presented similar acid conversion percentage values. These results confirm the strong influence of the different alcohols on the catalytic properties of soluble and immobilized lipases.

Table 3.
Estimation of productivity for the production of several octanoate esters catalyzed by soluble and immobilized lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0.
The experimental data obtained for acid conversion at equilibrium were also expressed in Table 3 to determine the productivity values for the different reaction systems evaluated in the present study using fixed initial protein concentration (20 mg of protein that corresponds to a protein concentration of 3.33 mg per gram of reaction mixture). According to these values, it is possible to note that the highest productivity values from 10.3 to 19.4 µmol·min−1·mgprot−1 were obtained for immobilized lipases due to the excellent dispersion of lipase molecules on the support surface, which can be confirmed by SEM analysis (see Figure 2). In general, soluble lipases in aqueous media have a strong tendency to form aggregates (dimers of lipase molecules in open conformation) that restrict the diffusion of some starting materials [52]. The presence of some stabilizing agents in their formulation can also strongly interfere the equilibrium between closed and open conformation of soluble lipase and, thus, their catalytic activity in non-aqueous systems [50]. In fact, soluble lipases exhibited similar performances compared to immobilized lipase in some reaction systems prepared using fusel oil and benzyl alcohol. These results are in accordance with previous reports that demonstrate the excellent catalytic performance of soluble lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 to catalyze reactions in organic media, exceptionally monoalkyl esters production (biodiesel and biolubricants) [24,25,26,53]. However, esterification reactions conducted with soluble lipase under such experimental conditions resulted in an emulsification in all reaction systems for acid conversion percentage values above 50% that indicated strongly difficult downstream processes, such as products separation (see Figure S1—Supplementary Material). This phenomenon was not observed using immobilized lipases (data not shown). Thus, further tests (reusability and environmental assessment studies) were conducted only for the heterogeneous biocatalyst (immobilized lipase).
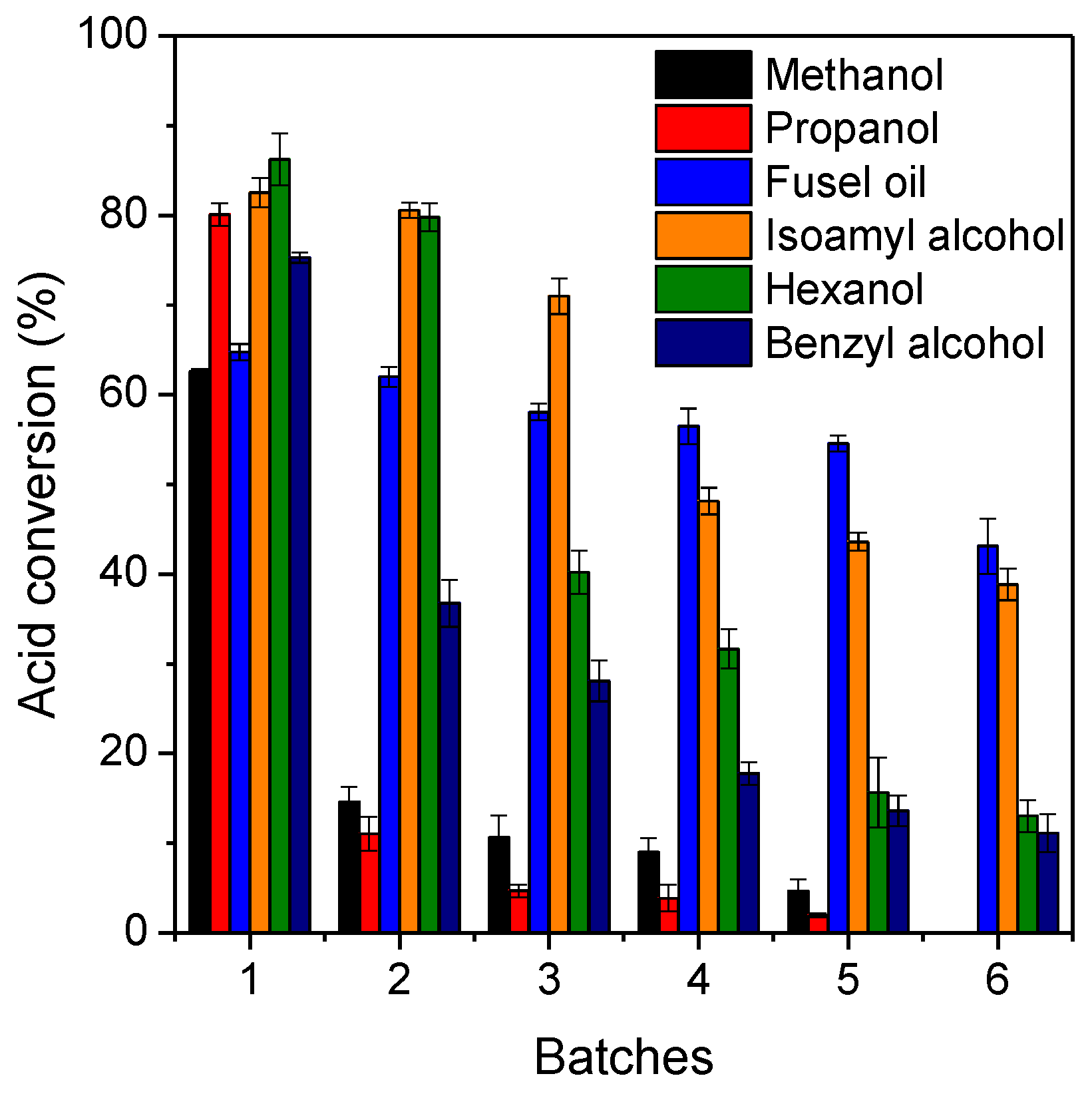
2.3. Biocatalyst Reusability Studies
The reusability of immobilized lipase after six consecutive batch esterification reactions was investigated, as shown in Figure 5. The reaction times for each reaction system were the ones required to achieve maximum acid conversion percentage at equilibrium and are summarized in Table 3. According to results, a strong decrease of the original activity of the biocatalyst using highly polar alcohols (methanol and propanol) was observed, resulting in full inhibition of its original activity at 6th batch esterification. This can be explained by a possible accumulation of water molecules on the biocatalyst surface that improves the partition/diffusion of highly polar alcohols; however, this may cause inhibitory effects on the catalytic performance of lipases in organic media [54,55]. On the other hand, the creation of a hydrophilic layer can drastically reduce the diffusion of octanoic acid in the internal biocatalyst microenvironment due to its high hydrophobicity (log P value of 3.05) [51]. In fact, esterification reactions performed with hexanol and benzyl alcohol also exhibited progressive decrease of catalytic activity due to possible water accumulation inside the pores of the biocatalyst and thus an acid conversion percentage between 10% and 12% after six esterification reactions can be observed. Interestingly, successive esterification reactions using fusel oil and its majority component (commercial isoamyl alcohol) demonstrated better preservation of the original catalytic activity of the biocatalyst, resulting in acid conversion percentage of 39% (for isoamyl alcohol) and 45% (for fusel oil) at 6th batch reaction (Figure 5).
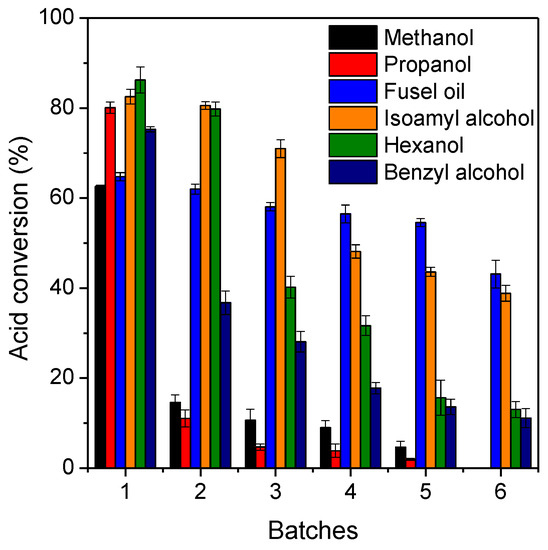
Figure 5.
Reusability tests of lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 immobilized on PSty-DVB beads after successive batch esterification reactions. The reactions were performed in solvent-free systems at 40 °C, 240 rpm, stoichiometric acid:alcohol molar ratio and 10% of mass of heterogeneous biocatalyst per gram of reaction mixture (that corresponds to an initial protein concentration of 3.3 mg protein per gram of reaction mixture).
These values correspond to a loss of the original activity of the biocatalyst of around 28% (from 62.5% in the first batch to 45% in the sixth batch) and 53% (from 82.5% in the first batch to 39% in the sixth batch) using fusel oil and commercial isoamyl alcohol, respectively. These results clearly show the promising use of fusel oil as alcohol instead of commercial isoamyl alcohol, due to its possible heterogeneous composition and, thus, peculiar physico-chemical features that provided better retention of catalytic activity of the enzyme after successive batch reactions. Our results are consistent with a recent study for isoamyl butyrate production via esterification in organic solvent systems using commercial isoamyl alcohol and fusel oil catalyzed by lipase from Rhizopus oryzae immobilized on a commercial heterofunctional support [56].
2.4. Environmental Assessment Studies
In this study, a scale for the assessment of environmental responsibility (EcoScale) for flavors esters production using immobilized lipase as biocatalyst was proposed. According to Table 4, the EcoScale scores for the different reaction systems were above 80 points, which represents excellent green processes, with an exception for the enzymatic production of methyl octanoate, which can be considered an acceptable green process (EcoScale score value = 68). This is due to partial acid conversion into ester (62.5%–19 penalty points) and high toxicity (5 penalty points) + flammability (5 penalty points) of methanol. No penalty points were observed for costs, on account of the fact that heterogeneous biocatalyst (lipase + support) and starting materials were inexpensive—final costs varying from $0.32 (hexanol + octanoic acid) to $0.77 (benzyl alcohol + octanoic acid) for producing 10 mmol of esters [57], which were based on analytical grade starting materials supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (Merck). From an economic standpoint, the application of the heterogeneous biocatalyst prepared in this study is highly interesting on an industrial scale, since its average final cost may be estimated around of $300 per Kg, and this is cheaper than a well-known commercially available immobilized biocatalyst Novozym® 435 (the cost is $700 per Kg [58]), the most used heterogeneous biocatalyst to produce flavor esters via esterification [59]. In addition, no penalty points were also observed for technical setup and workup/purification parameters due to simple experimental apparatus used to produce octanoate esters (closed stirred-tank reactors using conventional heating) and biocatalyst recovery from the reaction mixtures via simple conventional filtration, respectively. Penalty points for the parameters of temperature/time varied from 1 to 3 points due to different reaction times required to achieve chemical equilibrium from 60 min (1 penalty point) to 90 min (3 penalty points). This study shows clearly that the enzymatic production of octanoate esters in solvent-free systems is an environmentally-friendly process.

Table 4.
EcoScale score for the enzymatic production of several octanoate esters catalyzed by immobilized lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Eversa® Transform 2.0, a soluble lipase at a protein concentration of 33 mg·mL−1, was acquired from Sigma-Aldrich® (St. Louis, MO, USA). PSty-DVB beads (Diaion® HP-20) were acquired from Supelco® Analytical Products (Bellefonte, PA, USA). Their physical properties are summarized in Table 2. Octanoic acid and hexanol were also purchased from Sigma-Aldrich®. Methanol, propanol, isoamyl alcohol, and benzyl alcohol were purchased from Synth® Ltd. (São Paulo, SP, Brazil). Fusel oil was acquired from Raízen Tarumã Ltda. (Tarumã, SP, Brazil), having the following composition (% m·m−1): water (11.6%), ethanol (4.2%), propanol (3.9%), butanol (1.1%), isobutyl alcohol (11.5%) and isoamyl alcohol (67.7%), and average molecular mass of 72.5 g·mol−1. All other reagents and organic solvents were of analytical grade acquired from Synth® Ltd.
3.2. Fusel Oil Dehydration
Fusel oil was firstly dehydrated using anhydrous Na2SO4 previously pretreated at 250 °C by 4 h in a muffle furnace. The suspension containing anhydrous Na2SO4 at 20% m·v−1 was added to a closed glass flask immersed in a temperature-controlled thermostatic water-bath under continuous stirring (240 rpm) at 25 ± 1 °C by 24 h of contact. This experimental procedure was repeated twice before to be used as a starting material in esterification reactions. The water concentration was reduced from 11.6% m·m−1 to 2% m·m−1, quantified via automatic Titler Karl Fischer (Koheler Model AKF5000).
3.3. Immobilization of Lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 via Interfacial Activation: Adsorption Kinetic and Mass Transfer Studies
Initially, 10 g of the support (PSty-DVB beads) were soaked in 50 mL of hydrous ethanol solution (70% m·m−1) for 8 h under static conditions at 25 °C so as to remove air bubbles within their pores [61]. Afterwards, the wetted support was filtered in a Büchner funnel under vacuum to remove excess ethanol solution and washed with 200 mL distilled water. This wetted support was added to 190 mL of a lipase solution prepared by adding 12 mL of liquid lipase formulation (Eversa® Transform 2.0) to 178 mL of a 5 mmol·L−1 sodium acetate solution pH 5.0 (0.21 mg protein per mL of solution that corresponds to 40 mg of protein per g of support). The suspension was transferred to a 250 mL closed glass flask and immersed in a temperature-controlled thermostatic water-bath under continuous stirring (200 rpm) at 25 ± 1 °C. Finally, the heterogeneous biocatalyst was recovered via filtration in a Buchner funnel under vacuum, washed with an excess of distilled water and stored at 4 °C for 24 h in a refrigerator for further assays. The adsorption process was monitored by determining the residual protein concentration [62], and hydrolytic activity [28,49] in the supernatant solution. Immobilization yield was determined as the ratio between the units of hydrolytic activity physically adsorbed on the support surface and the initial activity [49]. The catalytic activity of the enzyme was assayed by olive oil emulsion hydrolysis method [61]. One international unit(U) of hydrolytic activity was defined as being the mass of lipase required to release 1 µmol of free fatty acids per minute at pH 8.0 (100 mmol·L−1 sodium phosphate), and 37 °C and 200 rpm [61].
3.3.1. Adsorption Kinetic Studies
Adsorption kinetic studies of lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 on PSty-DVB beads were performed by applying three traditional non-linear kinetic models to these experimental data such as pseudo-first order (Equation (1)), pseudo-second-order (Equation (2)), and Elovich (Equation (3)) models [34]:
where: qt and qe are, respectively, the concentration of adsorbed lipase at a certain time t and at maximum contact time (mg·g−1), k1 (min−1), and k2 (mg·g−1·min−1) are, respectively, the first- and second-order adsorption kinetic constants, α is the initial adsorption rate (mg·g−1·min−1), β is the desorption constant (g−1·mg−1), and t is the contact time.
3.3.2. Calculation of External and Internal Mass Transfer Parameters
In this study, mass transfer parameters were also estimated to elucidate the adsorption process. Initially, the external diffusion coefficient of lipase molecules in buffer solution (DAB) was determined using the Wilke–Chang correlation (Equation (4)) [63]:
where: DAB is the external diffusion coefficient of the enzyme in the solution (cm2·s−1); ψ is the association factor of the enzyme solution (ϕ = 2.6, dimensionless); Msolution is the molecular mass of the solvent—water (18 g·mol−1); T is the absolute temperature (298.15 K); μsuspension is the dynamic viscosity of the solid–liquid suspension (g·cm−1·s−1); and VM is the molar volume of the lipase (cm3·mol−1).
The molar volume (VM) of lipase from T. lanuginosus, a spherical enzyme with a size of 35 Å × 45 Å × 50 Å that corresponds to 7.875 × 10−20 cm3 [7], can be calculated according to Equation (5):
where: NA is the Avogrado constant (6.02 × 1023 molecules.mol−1) and Venzyme is the volume of each lipase molecule (7.875 × 10−20 cm3).
The specific mass (—g·cm−3) and dynamic viscosity (µsuspension—g·cm−1·s−1) values of the suspension solid–liquid with a solid concentration up to 20% v·v−1 were determined as described in Equations (6) and (7), respectively [64,65].
where: Cm is the concentration of support in the suspension by unit of mass (5%); is the solid specific mass of PSty-DVB beads (1.01 cm3·g−1—Supelco Technical Information); is the specific mass of the enzyme solution (1.007 cm3·g−1); μsolution is the dynamic viscosity of the enzyme solution (9.3 × 10−3 g·cm−1·s−1); Cv is the concentration of support in the suspension by unit of volume (≈5%).
Dimensionless numbers such Schmidt (Sc), Reynolds (Re), and Sherwood (Sh) were calculated according to Equations (8)–(10), respectively. The solid–liquid external mass transfer coefficient (kSL) was then determined as shown in Equation (11) [45,66,67]:
where: n is the mechanical stirring frequency (200 rpm or 3.3 revolutions per second); dT is the inner diameter of the cylindrical flasks (5 cm), kSL is the solid–liquid mass transfer coefficient (cm·s−1); and Dp is the average diameter of PSty-DVB beads (5.5 × 10−2 cm—Supelco Technical Information).
The intraparticle diffusion of molecules in porous adsorbents can be due to Fick diffusion [45,68]. Therefore, the effective diffusivity of lipase molecules inside the pores of the support (Deff.—cm2·g−1) can be estimated as follows (Equation (12)) [42,45]:
where: εp is porosity (dimensionless) and τ is the tortuosity (dimensionless) of PSty-DVB beads, respectively.
The apparent specific mass of PSty-DVB beads (—cm3·g−1) and porosity (εp) were calculated according to Equations (13) and (14), respectively [69]. The tortuosity (τ) was determined as described in Equation (15) [43,44,45]. The external surface area of the support (SEXT—m2·g−1) can be calculated according to Equation (16) [42,44]:
where: Vp is the pore volume per unit mass of PSty-DVB beads (1.3 cm3·g−1—Supelco Technical Information) and is the solid specific mass of PSty-DVB beads (1.01 cm3·g−1—Supelco Technical Information).
Finally, Biot number (Bim) was determined according to Equation (17) [42,48]:
where: C0 is the initial protein concentration in the supernatant (2.1 mg·mL−1 or 2.1 mg·cm−3); Rp is the average particle radius (2.75 × 10−2 cm); and qe is the maximum immobilized protein concentration (31 mg·g−1 of support).
3.4. SEM Analysis
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of PSty-DVB beads (magnification of 30× and of 20,000×) and immobilized Eversa® Transform 2.0 (magnification of 20,000×) were acquired on a JSM 6360 LV field-emission scanning electron microscope (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) at 10 kV accelerating voltage.
3.5. General Procedure for Enzymatic Production of Flavor Esters
The enzymatic production of flavor esters via direct esterification of octanoic acid with several short-chain alcohols (methanol, propanol, fusel oil, isoamyl alcohol, hexanol and benzyl alcohol) was conducted in closed glass flasks with a capacity of 100 mL (ratio height to diameter of ≈2) containing 6 g of reaction mixture composed of stoichiometric acid:alcohol molar ratio (1:1). The reactions were performed using a fixed biocatalyst concentration of 3.7 mg of protein per gram of reaction mixture (0.6 mL of soluble or 0.63 g immobilized lipase that corresponded to 20 mg of protein—3.33 mg protein per gram of reaction mixture). The reaction systems were immersed in a temperature-controlled thermostatic water-bath at 40 ± 1 °C under continuous stirring (240 rpm). Samples from the reaction mixtures (50 µL) were periodically withdrawn, diluted in 10 mL of hydrous ethanol solution (92.5% m·m−1) and titrated with a NaOH solution (40 mmol·L−1) using phenolphthalein as indicator. The acid conversion percentage (Y—%) was determined as shown in Equation (18) [61,70]. Esters production were performed with two replications and experimental data are represented as mean ± deviation. Blank assays were conducted with PSty-DVB beads and no acid consumption was detected under such experimental conditions, thus confirming that all consumed octanoic acid in the reaction is converted into esters.
where: A0 and At are the initial and residual octanoic acid concentration after a given reaction time t (mol·L−1), respectively.
Productivity (P—µmol·min−1·mgprot−1) was determined as follows (Equation (19)) [70]:
where: A0 is the initial octanoic acid concentration (µmol·L−1), Y is acid conversion percentage (%), V is the reaction volume (≈7.5 × 10−3 L for all reaction mixtures), t is reaction time (min), and mprot is the protein amount in the reaction mixture (mg).
3.6. Reusability Tests
Reusability tests of the immobilized lipase were conducted after six successive batch reactions under fixed experimental conditions, as described above. At the end of each batch, the heterogeneous biocatalyst was recovered via filtration in a Büchner funnel under vacuum, washed with excess of cold hexane to remove residual starting materials or products retained in its surface and maintained to dry in a freezer at 4 °C overnight. Finally, the recovered biocatalyst was re-suspended in a fresh reaction mixture to start new batches. Acid conversion percentage was determined at the end of each batch.
3.7. EcoScale Score
EcoScale score, an analytical tool commonly used for the measurement of the environmental responsibility of a process, was determined by applying penalty points to six critical parameters such as yield, price of reaction components, safety of chemicals (starting materials and products), technical setup, reaction conditions (temperature/time) and workup and purification [58]. This tool covers a scale from 0 to 100 points, where 100 represents an ideal process. An EcoScale score value above 75 represents an excellent green process, value between 50 and 75 points is an acceptable green process and lower than 50 points means an inadequate green process. The EcoScale score for each reaction mixture using either soluble or immobilized lipase was calculated as follows (Equation (20)).
4. Conclusions
Kinetic and mass transfer studies demonstrated that Eversa® Transform 2.0, a low-cost commercial liquid lipase formulation, was preferentially adsorbed via reversible interactions (based on the mechanism of interfacial activation) inside the pores of PSty-DVB beads. A maximum immobilized protein amount of 31 mg·g−1 was obtained after 480 min of contact time in a batch mode under mild experimental conditions −25 °C, 200 rpm at low ionic strength (5 mmol·L−1) pH 5.0. The catalytic performance of immobilized lipase was examined in the production of flavor esters via direct esterification of octanoic with six different alcohols and compared with its soluble form. According to results, the heterogeneous biocatalyst provided, in general, better catalytic activity than soluble lipase due to excellent partition and diffusion of starting materials in its microenvironment under the experimental conditions used to perform this study. In fact, soluble lipase also exhibited good catalytic performance for reaction mixtures composed by fusel oil and benzyl alcohol. However, all reaction systems using homogeneous catalyst (soluble lipase) led to an emulsification of the reaction systems that made downstream processes difficult (flavor esters separation). Reusability tests showed a drastic decrease of catalytic activity using highly polar alcohols (methanol and propanol) after consecutive batch reactions. On the other hand, the heterogeneous biocatalyst retained nearly 34% and 53% of its original activity after six successive batches using commercial isoamyl alcohol and fusel oil, respectively. The latter is an interesting option due to its renewable nature, low-cost and easy acquisition in several countries. Environmental assessment studies demonstrated that the production of flavor esters in solvent-free systems catalyzed by immobilized lipase is a sustainable and eco-friendly process. This study confirms the promising application of immobilized lipase to catalyze biotransformation reactions in organic media (flavor esters production). Moreover, it also raises possibilities for new industrial applications of lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0, a commercial lipase used to produce biodiesel from waste oils on an industrial scale. Further studies should be conducted using fusel oil as an alcohol source from bioethanol distilleries, evaluating the influence of relevant factors, including water molecules removal strategies that will improve the catalytic performance and operational stability of immobilized lipases on esters production in batch or continuous processes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal12111412/s1, Figure S1: Illustration of the reaction mixture at equilibrium for esterification of fusel oil and octanoic acid catalyzed by soluble lipase.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.M. and R.F.-L.; methodology, J.M.J., F.R.M., G.R.C. and A.B.R.Z.; software, A.A.M.; validation, J.M.J., F.R.M., G.R.C. and A.B.R.Z.; formal analysis, A.A.M.; investigation, J.M.J., F.R.M., G.R.C. and A.B.R.Z.; resources, J.M.J., F.R.M., G.R.C. and A.B.R.Z.; data curation, J.M.J., F.R.M., G.R.C. and A.B.R.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M.J., F.R.M., G.R.C. and A.B.R.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.A.M. and R.F.-L.; visualization, J.M.J., F.R.M., G.R.C. and A.B.R.Z.; supervision, A.A.M.; project administration, A.A.M. and R.F.-L.; funding acquisition, A.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES)—Brazil—Finance Code 001. The authors also thank the financial support of Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG)— Brazil (Process APQ-01691-21). José Miguel Júnior and Fernanda R. Mattos thank the FAPEMIG Foundation for the student fellowship. Adriano A. Mendes thanks the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for the research fellowship (PQ-2 CA EQ, Grant 310633/2020-6).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Angel Berenguer-Murcia (Universidad de Alicante, Alicante, Spain) for the kind suggestions during the writing of this paper. The authors are also grateful to UFMG Microscopy Center (Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil) by the SEM analysis and Aldo Henrique A. Mendes (Raízen Tarumã Ltda., Tarumã, SP, Brazil) for the donation of fusel oil used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Flavors and Fragrances Market Size, Share|Report [2022–2029]. Available online: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/flavors-and-fragrances-market-102329 (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Kumar Verma, D.; Thyab Gddoa Al-Sahlany, S.; Kareem Niamah, A.; Thakur, M.; Shah, N.; Singh, S.; Baranwal, D.; Patel, A.R.; Lara Utama, G.; Noe Aguilar, C. Recent Trends in Microbial Flavour Compounds: A Review on Chemistry, Synthesis Mechanism and Their Application in Food. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SÁ, A.G.A.; de Meneses, A.C.; de Araújo, P.H.H.; de Oliveira, D. A Review on Enzymatic Synthesis of Aromatic Esters Used as Flavor Ingredients for Food, Cosmetics and Pharmaceuticals Industries. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Akacha, N.; Gargouri, M. Microbial and Enzymatic Technologies Used for the Production of Natural Aroma Compounds: Synthesis, Recovery Modeling, and Bioprocesses. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 94, 675–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Wei, X. A Review on Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Geranyl Esters as Flavor Additives for Food, Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlercreutz, P. Immobilisation and Application of Lipases in Organic Media. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6406–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus: Uses and Prospects as an Industrial Biocatalyst. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 62, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, P.Y.; Foukis, A.; Filippou, M.; Koukouritaki, M.; Parapouli, M.; Theodorou, L.G.; Hatziloukas, E.; Afendra, A.; Pandey, A.; Papamichael, E.M. Advances in Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification Reactions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1846–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Alcantara, A.R.; Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Immobilization of Lipases on Hydrophobic Supports: Immobilization Mechanism, Advantages, Problems, and Solutions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 746–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Carballares, D.; Morellon-Sterling, R.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Stabilization of Enzymes via Immobilization: Multipoint Covalent Attachment and Other Stabilization Strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 52, 107821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana-Peña, S.; Carballares, D.; Morellon-Sterlling, R.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Alcántara, A.R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Enzyme Co-Immobilization: Always the Biocatalyst Designers’ Choice…or Not? Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 51, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar, J.M.; Woodley, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Is Enzyme Immobilization a Mature Discipline? Some Critical Considerations to Capitalize on the Benefits of Immobilization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 6251–6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolina, I.C.A.; Gomes, R.A.B.; Mendes, A.A. Biolubricant Production from Several Oleaginous Feedstocks Using Lipases as Catalysts: Current Scenario and Future Perspectives. BioEnergy Res. 2021, 14, 1039–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, C.; Palomo, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Improvement of Enzyme Activity, Stability and Selectivity via Immobilization Techniques. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Galan, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Rodrigues, R.C. Potential of Different Enzyme Immobilization Strategies to Improve Enzyme Performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2885–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Rocha-Martin, J.; Moreno-Gamero, D. Enzyme Immobilization Strategies for the Design of Robust and Efficient Biocatalysts. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 35, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.L.C.; Prata, A.S.; Forte, M.B.S. Enzyme Immobilization: What Have We Learned in the Past Five Years? Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2022, 16, 587–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Torres, R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Strategies for the One-Step Immobilization-Purification of Enzymes as Industrial Biocatalysts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoel, E.A.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Freire, D.M.G.; Rueda, N.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Immobilization of Lipases on Hydrophobic Supports Involves the Open Form of the Enzyme. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2015, 71, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.R.; Silva, A.S.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Ferreira-Leitão, V.S. Solvent-Free Esterifications Mediated by Immobilized Lipases: A Review from Thermodynamic and Kinetic Perspectives. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 5696–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón, A.A.; Vilas Boas, R.N.; Biaggio, F.C.; de Castro, H.F. Synthesis of Biolubricant by Transesterification of Palm Kernel Oil with Simulated Fusel Oil: Batch and Continuous Processes. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 119, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas Bôas, R.N.; de Lima, R.; Mendes, A.A.; Freitas, L.; Bento, H.B.S.; Carvalho, A.K.F.D.; de Castro, H.F. Batch and Continuous Production of Biolubricant from Fusel Oil and Oleic Acid: Lipase Screening, Reactor System Development, and Reaction Optimization. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2021, 168, 108568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mendoza-Pedroza, J.J.; Sánchez-Ramírez, E.; Segovia-Hernández, J.G.; Hernández, S.; Orjuela, A. Recovery of Alcohol Industry Wastes: Revaluation of Fusel Oil through Intensified Processes. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2021, 163, 108329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wancura, J.H.C.; Rosset, D.V.; Mazutti, M.A.; Ugalde, G.A.; de Oliveira, J.V.; Tres, M.V.; Jahn, S.L. Improving the Soluble Lipase–Catalyzed Biodiesel Production through a Two-Step Hydroesterification Reaction System. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 7805–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wancura, J.H.C.; Fantinel, A.L.; Ugalde, G.A.; Donato, F.F.; Vladimir de Oliveira, J.; Tres, M.V.; Jahn, S.L. Semi-Continuous Production of Biodiesel on Pilot Scale via Enzymatic Hydroesterification of Waste Material: Process and Economics Considerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.R.C.; Arana-Peña, S.; da Rocha, T.N.; Miranda, L.P.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Tardioli, P.W.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Liquid Lipase Preparations Designed for Industrial Production of Biodiesel. Is It Really an Optimal Solution? Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 1566–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.R.; Hernandez, K.; Barbosa, O.; Rueda, N.; Garcia-Galan, C.; dos Santos, C.S.J.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Immobilization of Proteins in Poly-Styrene-Divinylbenzene Matrices: Functional Properties and Applications. Curr. Org. Chem. 2015, 19, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, W.C.A.; Luiz, J.H.H.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Hirata, D.B.; Mendes, A.A. Eco-Friendly Production of Trimethylolpropane Triesters from Refined and Used Soybean Cooking Oils Using an Immobilized Low-Cost Lipase (Eversa® Transform 2.0) as Heterogeneous Catalyst. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 155, 106302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes Júnior, J.G.E.; Mattos, F.R.; Sabi, G.J.; Carvalho, W.C.A.; Luiz, J.H.H.; Cren, É.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Mendes, A.A. Design of a Sustainable Process for Enzymatic Production of Ethylene Glycol Diesters via Hydroesterification of Used Soybean Cooking Oil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavor Library|FEMA. Available online: https://www.femaflavor.org/flavor-library/search?fulltext=octanoate (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Propyl Octanoate|C11H22O2—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Propyl-octanoate (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Sun, J.; Yu, B.; Curran, P.; Liu, S.Q. Lipase-Catalysed Transesterification of Coconut Oil with Fusel Alcohols in a Solvent-Free System. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzyl Octanoate, 10276-85-4. Available online: http://thegoodscentscompany.com/data/rw1039491.html (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the Adsorption Kinetics Models for the Removal of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyatshe, A.; Cele, Z.E.D.; Balogun, M.O.; Nkambule, T.T.I.; Msagati, T.A.M. Chitosan Modified Sugarcane Bagasse Biochar for the Adsorption of Inorganic Phosphate Ions from Aqueous Solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Han, R.; Qu, L. Crosslinked Polyethylenimine/Polyacrylonitrile Blend Membrane for Multifunctional Adsorption of Heavy Metals and Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 365, 120124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, R.; Fan, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Peng, F.; Du, Y.; Yang, W. Flexible Self-Supporting Electrode for High Removal Performance of Arsenic by Capacitive Deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ranjbari, S.; Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Orooji, Y.; Alizadeh, M.; Karimi, F.; Salmanpour, S.; Rouhi, J.; Sillanpää, M.; et al. Novel 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Bromide Impregnated Chitosan Hydrogel Beads Nanostructure as an Efficient Nanobio-Adsorbent for Cationic Dye Removal: Kinetic Study. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana-Peña, S.; Mendez-Sanchez, C.; Rios, N.S.; Ortiz, C.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. New Applications of Glyoxyl-Octyl Agarose in Lipases Co-Immobilization: Strategies to Reuse the Most Stable Lipase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, N.S.; Mendez-Sanchez, C.; Arana-Peña, S.; Rueda, N.; Ortiz, C.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Immobilization of Lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens on Glyoxyl-Octyl-Agarose Beads: Improved Stability and Reusability. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Ramos, R.; Diaz-Flores, P.E.; Leyva-Ramos, J.; Femat-Flores, R.A. Kinetic Modeling of Pentachlorophenol Adsorption from Aqueous Solution on Activated Carbon Fibers. Carbon 2007, 45, 2280–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.P.; Alvarenga, G.; Goszczynski, A.C.F.; Rosa, G.R.; Lopes, T.J. Batch Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye Using Enterolobium contortisiliquum as Bioadsorbent: Experimental, Mathematical Modeling and Simulation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 91, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Ansari, K.B.; Danish, M.; Khatoon, A.; Ali Khan Rao, R.; Zaidi, S.; Ahmad Aftab, R. A Comprehensive Investigation of External Mass Transfer and Intraparticle Diffusion for Batch and Continuous Adsorption of Heavy Metals Using Pore Volume and Surface Diffusion Model. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 120996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.R.; Dotto, G.L.; Salau, N.P.G. Detailed Numerical Solution of Pore Volume and Surface Diffusion Model in Adsorption Systems. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 122, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.S.P.; Fagundes, J.L.S.; Georgin, J.; Salau, N.P.G.; Dotto, G.L. A Mass Transfer Study Considering Intraparticle Diffusion and Axial Dispersion for Fixed-Bed Adsorption of Crystal Violet on Pecan Pericarp (Carya Illinoensis). Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cooney, D.O. Comparison of Simple Adsorber Breakthrough Curve Method with Exact Solution. AICHE J. 1993, 39, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Balsamo, M.; Montagnaro, F. Liquid-Solid Mass Transfer in Adsorption Systems—An Overlooked Resistance? Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 22007–22016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudrant, J.; Woodley, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Parameters Necessary to Define an Immobilized Enzyme Preparation. Process Biochem. 2020, 90, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.; Mladenoska, I.; Wehtje, E.; Adlercreutz, P. Preparation of Lipases for Use in Organic Solvents. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 31, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez, B.C.; Medina, A.R.; Rubio, F.C.; Moreno, P.G.; Grima, E.M. Modeling the Effect of Free Water on Enzyme Activity in Immobilized Lipase-Catalyzed Reactions in Organic Solvents. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 33, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, J.M.; Fuentes, M.; Fernández-Lorente, G.; Mateo, C.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernández-Lafuente, R. General Trend of Lipase to Self-Assemble Giving Bimolecular Aggregates Greatly Modifies the Enzyme Functionality. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo-Silva, R.; Vieira, A.C.; de Giordano, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Tardioli, P.W. Enzymatic Synthesis of Fatty Acid Isoamyl Monoesters from Soybean Oil Deodorizer Distillate: A Renewable and Ecofriendly Base Stock for Lubricant Industries. Molecules 2022, 27, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgujar, K.C.; Bhanage, B.M. Immobilization of Lipase on Biocompatible Co-Polymer of Polyvinyl Alcohol and Chitosan for Synthesis of Laurate Compounds in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Using Response Surface Methodology. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgujar, K.C.; Badgujar, V.C.; Bhanage, B.M. Lipase as a Green and Sustainable Material for Production of Levulinate Compounds: State of the Art. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2022, 5, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fernández, J.; Benaiges, M.D.; Sebastian, X.; Bueno, J.M.; Valero, F. Producing Natural Flavours from Isoamyl Alcohol and Fusel Oil by Using Immobilised Rhizopus oryzae Lipase. Catalysts 2022, 12, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aken, K.; Strekowski, L.; Patiny, L.; Strekowski, L. EcoScale, a Semi-Quantitative Tool to Select an Organic Preparation Based on Economical and Ecological Parameters. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2006, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosney, H.; Mustafa, A. Semi-Continuous Production of 2-Ethyl Hexyl Ester in a Packed Bed Reactor: Optimization and Economic Evaluation. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.; Ferreira, M.L.; Barbosa, O.; Dos Santos, J.C.S.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Briand, L.E.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Novozym 435: The “Perfect” Lipase Immobilized Biocatalyst? Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 2380–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppini, M.; Magro, J.D.; Martello, R.; Valério, A.; Zenevicz, M.C.; de Oliveira, D.; Oliveira, J.V. Production of Methyl Esters by Enzymatic Hydroesterification of Chicken Fat Industrial Residue. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, F.A.P.; Bassi, J.J.; Corradini, M.C.C.; Todero, L.M.; Luiz, J.H.H.; Mendes, A.A. Preparation of a Biocatalyst via Physical Adsorption of Lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus on Hydrophobic Support to Catalyze Biolubricant Synthesis by Esterification Reaction in a Solvent-Free System. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 84, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, C.R.; Chang, P. Correlation of Diffusion Coefficients in Dilute Solutions. AICHE J. 1955, 1, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulnaga, B.; Abulnaga, B. Slurry Systems Handbook; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 9781260452792. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, H.; Higashitani, K.; Yoshida, H. Powder Technology Handbook, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 1–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Davis, R.J. Fundamentals of Chemical Reaction Engineering; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 184–239. [Google Scholar]
- Todero, L.M.; Bassi, J.J.; Lage, F.A.; Corradini, M.C.; Barboza, J.C.; Hirata, D.B.; Mendes, A.A. Enzymatic Synthesis of Isoamyl Butyrate Catalyzed by Immobilized Lipase on Poly-Methacrylate Particles: Optimization, Reusability and Mass Transfer Studies. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1601–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischer, W.; Kasche, V. Immobilized Enzymes: Crystals or Carriers? Trends Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Readers, P.; Search, A.; Website, P.; About, C.; Privacy, S. Adsorption Engineering-with-Cover; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 1989; ISBN 0444988025. [Google Scholar]
- Sabi, G.J.; Gama, R.S.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Cancino-Bernardi, J.; Mendes, A.A. Decyl Esters Production from Soybean-Based Oils Catalyzed by Lipase Immobilized on Differently Functionalized Rice Husk Silica and Their Characterization as Potential Biolubricants. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 157, 110019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).