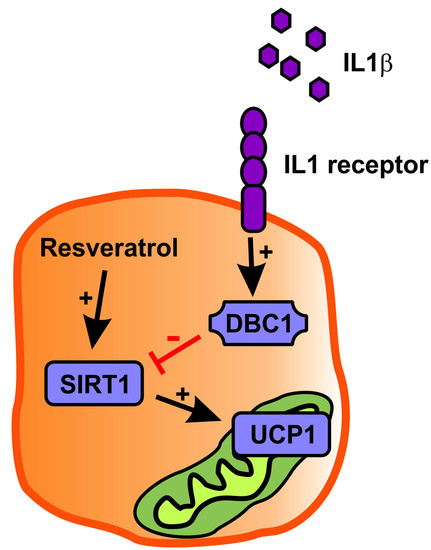
Inflammation Downregulates UCP1 Expression in Brown Adipocytes Potentially via SIRT1 and DBC1 Interaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inflammation Reduces Expression of Ucp1 in Mature Brown Adipocytes
2.2. Regulation of Ucp1 Expression (dbcAMP and SIRT1 Knock-down Experiments)
2.3. Resveratrol Partly Rescues Ucp1 Downregulation by IL1β
2.4. Effects of Chronic Inflammation on Thermogenic Genes in BAT and WAT in Mice
2.5. Expression of Tlr4 in Brown Adipocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. Gene Silencing
4.3. Animal Experiments
4.4. Gene Expression
4.5. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAT | Brown adipose tissue |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CIDEA | Cell death activator CIDE-A |
| DBC1 | Deleted in breast cancer 1 |
| dbcAMP | Dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| DIO2 | Type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase |
| IL1β | Interleukin 1 β |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor κ B |
| PGC1α | PPARγ co-activator 1 α |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| PRDM16 | PR domain containing 16 |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin-1 |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling protein 1 |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
References
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klover, P.J.; Clementi, A.H.; Mooney, R.A. Interleukin-6 depletion selectively improves hepatic insulin action in obesity. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3417–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagathu, C.; Yvan-Charvet, L.; Bastard, J.P.; Maachi, M.; Quignard-Boulange, A.; Capeau, J.; Caron, M. Long-term treatment with interleukin-1 β induces insulin resistance in murine and human adipocytes. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosogai, N.; Fukuhara, A.; Oshima, K.; Miyata, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Segawa, K.; Furukawa, S.; Tochino, Y.; Komuro, R.; Matsuda, M.; et al. Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes 2007, 56, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. Tlr4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Favelyukis, S.; Nguyen, A.K.; Reichart, D.; Scott, P.A.; Jenn, A.; Liu-Bryan, R.; Glass, C.K.; Neels, J.G.; Olefsky, J.M. A subpopulation of macrophages infiltrates hypertrophic adipose tissue and is activated by free fatty acids via toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and JNK-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35279–35292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Ricciardi, C.J.; Esposito, D.; Komarnytsky, S.; Hu, P.; Curry, B.J.; Brown, P.L.; Gao, Z.; Biggerstaff, J.P.; Chen, J.; et al. Activation of pattern recognition receptors in brown adipocytes induces inflammation and suppresses uncoupling protein 1 expression and mitochondrial respiration. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2014, 306, C918–C930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L. Chronic activation of pattern recognition receptors suppresses brown adipogenesis of multipotent mesodermal stem cells and brown pre-adipocytes. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cypess, A.M.; Lehman, S.; Williams, G.; Tal, I.; Rodman, D.; Goldfine, A.B.; Kuo, F.C.; Palmer, E.L.; Tseng, Y.H.; Doria, A.; et al. Identification and importance of brown adipose tissue in adult humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cypess, A.M.; White, A.P.; Vernochet, C.; Schulz, T.J.; Xue, R.; Sass, C.A.; Huang, T.L.; Roberts-Toler, C.; Weiner, L.S.; Sze, C.; et al. Anatomical localization, gene expression profiling and functional characterization of adult human neck brown fat. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jespersen, N.Z.; Larsen, T.J.; Peijs, L.; Daugaard, S.; Homoe, P.; Loft, A.; de Jong, J.; Mathur, N.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J.; et al. A classical brown adipose tissue mrna signature partly overlaps with brite in the supraclavicular region of adult humans. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, C.; Koza, R.A.; Yamashita, H.; Walsh, K.; Kozak, L.P. Emergence of brown adipocytes in white fat in mice is under genetic control. Effects on body weight and adiposity. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.J.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Economopoulou, M.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Alexaki, V.I.; Mitroulis, I.; Nati, M.; Gebler, J.; Ziemssen, T.; Goelz, S.E.; et al. A self-sustained loop of inflammation-driven inhibition of beige adipogenesis in obesity. Nat. Immunol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, L.; Wang, L.; Kon, N.; Zhao, W.; Lee, S.; Zhang, Y.; Rosenbaum, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, W.; Farmer, S.R.; et al. Brown remodeling of white adipose tissue by SirT1-dependent deacetylation of Pparγ. Cell 2012, 150, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, F.; Hoberg, J.E.; Ramsey, C.S.; Keller, M.D.; Jones, D.R.; Frye, R.A.; Mayo, M.W. Modulation of nf-kappab-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SirT1 deacetylase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, J.T.; Lerin, C.; Haas, W.; Gygi, S.P.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Puigserver, P. Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1α and SIRT1. Nature 2005, 434, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Kruse, J.P.; Tang, Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Qin, J.; Gu, W. Negative regulation of the deacetylase sirt1 by dbc1. Nature 2008, 451, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Chen, J.; Lou, Z. Dbc1 is a negative regulator of sirt1. Nature 2008, 451, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howitz, K.T.; Bitterman, K.J.; Cohen, H.Y.; Lamming, D.W.; Lavu, S.; Wood, J.G.; Zipkin, R.E.; Chung, P.; Kisielewski, A.; Zhang, L.L.; et al. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature 2003, 425, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, B.P.; Gomes, A.P.; Dai, H.; Li, J.; Case, A.W.; Considine, T.; Riera, T.V.; Lee, J.E.; E, S.Y.; Lamming, D.W.; et al. Evidence for a common mechanism of sirt1 regulation by allosteric activators. Science 2013, 339, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Ahmad, F.; Philp, A.; Baar, K.; Williams, T.; Luo, H.; Ke, H.; Rehmann, H.; Taussig, R.; Brown, A.L.; et al. Resveratrol ameliorates aging-related metabolic phenotypes by inhibiting camp phosphodiesterases. Cell 2012, 148, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, N.L.; Gomes, A.P.; Ling, A.J.; Duarte, F.V.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; North, B.J.; Agarwal, B.; Ye, L.; Ramadori, G.; Teodoro, J.S.; et al. Sirt1 is required for ampk activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uldry, M.; Yang, W.; St-Pierre, J.; Lin, J.; Seale, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Complementary action of the pgc-1 coactivators in mitochondrial biogenesis and brown fat differentiation. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baur, J.A.; Pearson, K.J.; Price, N.L.; Jamieson, H.A.; Lerin, C.; Kalra, A.; Prabhu, V.V.; Allard, J.S.; Lopez-Lluch, G.; Lewis, K.; et al. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 2006, 444, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nøhr, M.K.; Dudele, A.; Poulsen, M.M.; Ebbesen, L.H.; Radko, Y.; Christensen, L.P.; Jessen, N.; Richelsen, B.; Lund, S.; Pedersen, S.B. LPS-enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion is normalized by resveratrol. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flierl, M.A.; Rittirsch, D.; Nadeau, B.A.; Chen, A.J.; Sarma, J.V.; Zetoune, F.S.; McGuire, S.R.; List, R.P.; Day, D.E.; Hoesel, L.M.; et al. Phagocyte-derived catecholamines enhance acute inflammatory injury. Nature 2007, 449, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.; Ruiz, H.H.; Jhun, K.; Finan, B.; Oberlin, D.J.; van der Heide, V.; Kalinovich, A.V.; Petrovic, N.; Wolf, Y.; Clemmensen, C.; et al. Alternatively activated macrophages do not synthesize catecholamines or contribute to adipose tissue adaptive thermogenesis. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Takahashi, N.; Sawaragi, Y.; Naknukool, S.; Yu, R.; Goto, T.; Kawada, T. Inflammation induced by raw macrophages suppresses UCP1 mRNA induction via ERK activation in 10T1/2 adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 304, C729–C738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Naknukool, S.; Yoshitake, R.; Hanafusa, Y.; Tokiwa, S.; Li, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Nitta, T.; Kim, M.; Takahashi, N.; et al. Proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β suppresses cold-induced thermogenesis in adipocytes. Cytokine 2016, 77, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullberg, K.B.; Larsen, J.O.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Effects of LPS and dietary free fatty acids on MCP-1 in 3T3-l1 adipocytes and macrophages in vitro. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirumbolo, S.; Franceschetti, G.; Zoico, E.; Bambace, C.; Cominacini, L.; Zamboni, M. Lps response pattern of inflammatory adipokines in an in vitro 3T3-l1 murine adipocyte model. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagouge, M.; Argmann, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Meziane, H.; Lerin, C.; Daussin, F.; Messadeq, N.; Milne, J.; Lambert, P.; Elliott, P.; et al. Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating sirt1 and PGC-1α. Cell 2006, 127, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvidsson, S.; Kwasniewski, M.; Riano-Pachon, D.M.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Quantprime-a flexible tool for reliable high-throughput primer design for quantitative pcr. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nøhr, M.K.; Bobba, N.; Richelsen, B.; Lund, S.; Pedersen, S.B. Inflammation Downregulates UCP1 Expression in Brown Adipocytes Potentially via SIRT1 and DBC1 Interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051006
Nøhr MK, Bobba N, Richelsen B, Lund S, Pedersen SB. Inflammation Downregulates UCP1 Expression in Brown Adipocytes Potentially via SIRT1 and DBC1 Interaction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(5):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051006
Chicago/Turabian StyleNøhr, Mark K., Natalia Bobba, Bjørn Richelsen, Sten Lund, and Steen B. Pedersen. 2017. "Inflammation Downregulates UCP1 Expression in Brown Adipocytes Potentially via SIRT1 and DBC1 Interaction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 5: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051006
APA StyleNøhr, M. K., Bobba, N., Richelsen, B., Lund, S., & Pedersen, S. B. (2017). Inflammation Downregulates UCP1 Expression in Brown Adipocytes Potentially via SIRT1 and DBC1 Interaction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(5), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051006