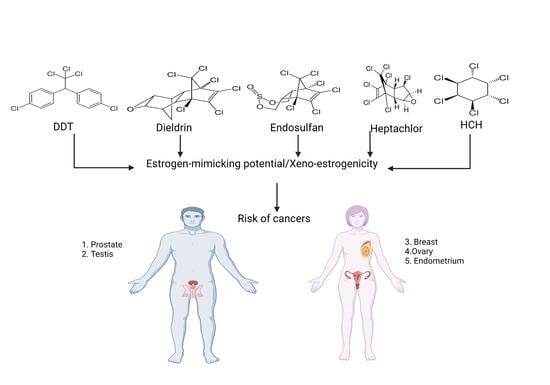
Xeno-Estrogenic Pesticides and the Risk of Related Human Cancers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Carcinogenic Effects of Organochlorine Pesticides
3. Evidence of Xeno-Estrogenicity
4. Confirmation of the Pesticide’s Xeno-Estrogenicity
- Mimicking the effect of endogenous steroidal hormones (androgens and estrogens).
- Antagonizing steroidal hormones.
- Altering the synthesis and metabolism of endogenous steroidal hormones.
- Modifying hormone receptor expression in different tissues.
5. Association of Xeno-Estrogenic Pesticides with Endocrine-Related Cancer
5.1. Xeno-Estrogenic Pesticides and Female Cancer
5.2. Xeno-Estrogenic Pesticides and Male Cancer
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rieger, P.G.; Meier, H.M.; Gerle, M.; Vogt, U.; Groth, T.; Knackmuss, H.J. Xenobiotics in the environment: Present and future strategies to obviate the problem of biological persistence. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 94, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combarnous, Y.; Nguyen, T.M.D. Membrane Hormone Receptors and Their Signaling Pathways as Targets for Endocrine Disruptors. J. Xenobiot. 2022, 12, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Chen, L.R.; Chen, K.H. In vitro and vivo identification, metabolism and action of xenoestrogens: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Lao, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Sun, X.; Zhao, M. Concentration and influence factors of organochlorine pesticides in atmospheric particles in a coastal island in Fujian, Southeast China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2982–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Mishra, M.; Verma, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, C.S. Distribution of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and hexachlorocyclohexane in urban soils and risk assessment. J. Xenobiot. 2013, 3, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mustafa, M.D.; Pathak, R.; Tripathi, A.K.; Ahmed, R.S.; Guleria, K.; Banerjee, B.D. Maternal and cord blood levels of aldrin and dieldrin in Delhi population. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 171, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.; Suke, S.G.; Ahmed, R.S.; Tripathi, A.K.; Guleria, K.; Sharma, C.S.; Ma-khijani, S.D.; Mishra, M.; Banerjee, B.D. Endosulfan and other organochlorine pesticide residues in maternal and cord blood in North Indian population. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 81, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.; Ahmed, R.S.; Tripathi, A.K.; Guleria, K.; Sharma, C.S.; Makhijani, S.D.; Banerjee, B.D. Maternal and cord blood levels of organochlorine pesticides: Association with preterm labor. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagga, D.; Anders, K.H.; Wang, H.J.; Roberts, E.; Glaspy, J.A. Organochlorine pesticide content of breast adipose tissue from women with breast cancer and control subjects. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falck, F., Jr.; Ricci, A., Jr.; Wolf, M.S.; Godbold, J.; Deckers, P. Pesticides and polychlorin-ated biphenyl residues in human breast lipids and their relation to breast cancer. Arch. Environ. Health 1992, 47, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhu, W.; Thompson, P.; Hannun, Y.A. Evaluating intrinsic and non-intrinsic cancer risk factors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamási, V.; Monostory, K.; Prough, R.A.; Falus, A. Role of xenobiotic metabolism in cancer: Involvement of transcriptional and miRNA regulation of P450s. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.K.; Sharma, T.; Banerjee, B.D. Organochlorine pesticides induce inflammation; ROS production; and DNA damage in human epithelial ovary cells: An in vitro study. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, A.C.; Chappell, V.A.; Fenton, S.E.; Flaws, J.A.; Nadal, A.; Prins, G.S.; Toppari, J.; Zoeller, R.T. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society’s Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, E1–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eve, L.; Fervers, B.; Le Romancer, M.; Etienne-Selloum, N. Exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals and risk of breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badamasi, I.; Odong, R.; Masembe, C. Threats posed by xenoestrogenic chemicals to the aquatic ecosystem, fish reproduction and humans: A review. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 45, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Fu, W.; Kiyama, R. Novel estrogen-responsive genes (ERGs) for the evaluation of estrogenic activity. PLoS ONE. 2022, 17, e0273164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.; Zappia, C.D.; Lasagna, M.; Pavicic, W.; Richard, S.; Bolzan, A.D.; Monczor, F.; Núñez, M.; Cocca, C. Effects of the pesticide chlorpyrifos on breast cancer disease. Implication of epigenetic mechanisms. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 186, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ha, D.; Yoshitake, R.; Chan, Y.S.; Sadava, D.; Chen, S. Exploring the biological activity and mechanism of xenoestrogens and phytoestrogens in cancers: Emerging methods and concepts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, M.F.F.; Pazin, M.; Pereira, L.C.; Dorta, D.J. Impact of pesticides on environmental and human health. In Toxicology Studies-Cells, Drugs and Environment; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2015; pp. 195–233. [Google Scholar]
- Stockholm Convention. The 12 Initial POPs under the Stockholm Convention; Stockholm Convention: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Poh, C.; McPherson, J.D.; Tuscano, J.; Li, Q.; Parikh-Patel, A.; Vogel, C.F.; Keegan, T. Environmental pesticide exposure and non-Hodgkin lymphoma survival: A population-based study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulou, R.; Fiste, O.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Andrikopoulou, A.; Zagouri, F.; Gav-riatopoulou, M.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Occupational exposure and multiple myeloma risk: An updated review of meta-analyses. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renier, M.; Busson, A.; Boulanger, M.; Piel, C.; Pons, R.; Tual, S.; Amadéo, B.; Meryet-Figuiere, M.; Marcotullio, E.; Clin, B.; et al. Agricultural exposure and risk of soft tissue sarcomas and gastrointestinal stromal sarcoma in the AGRIculture and CANcer (AGRICAN) cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, A.; Dubey, A.; Saini, D.; Singh, M.; Prasad, C.P.; Roy, S.; Bharati, S.J.; Rinki, M.; Singh, N.; Seth, T.; et al. Environmental and occupational determinants of lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, M.; Gasull, M.; Pumarega, J.; Kiviranta, H.; Rantakokko, P.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Sandanger, T.M.; Agudo, A.; Rylander, C.; et al. Plasma concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and pancreatic cancer risk. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrot-Applanat, M.; Pimpie, C.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Antignac, J.P.; Pocard, M. Detection of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Omental Adipose Tissue from Patients with Diffuse-Gastric Cancer: A Pilot Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VoPham, T. Environmental risk factors for liver cancer and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2019, 6, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, A.A.; Okechukwu, C.E.; Emara, S.; Sami, A.A. Occupational exposure as risk factor for kidney and bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Urol. Nephrol. Open Access J. 2019, 7, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Moreno, P.; Riquelme, I.; García, P.; Brebi, P.; Roa, J.C. Environmental and Lifestyle Risk Factors in the Carcinogenesis of Gallbladder Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. International Agency for Research on Cancer IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans; Distributed for IARC by WHO; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1980; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Madia, F.; Worth, A.; Whelan, M.; Corvi, R. Carcinogenicity assessment: Addressing the challenges of cancer and chemicals in the environment. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.G.; Shane, B.S. Xenobiotic metabolism. In Basic Environmental Toxicology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 49–105. [Google Scholar]
- Anzenbacher, P.; Anzenbacherova, E. Cytochromes P450 and metabolism of xenobiotics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2001, 58, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, F.; Rueff, J.; Kranendonk, M. The Central Role of Cytochrome P450 in Xenobiotic Metabolism—A Brief Review on a Fascinating Enzyme Family. J. Xenobiot. 2021, 11, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keswani, C.; Dilnashin, H.; Birla, H.; Roy, P.; Tyagi, R.K.; Singh, D.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Singh, S.P. Global footprints of organochlorine pesticides: A pan-global survey. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donley, N. The USA lags behind other agricultural nations in banning harmful pesticides. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, B.; Verma, V.K.; Naskar, A.K.; Chakraborty, P.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D. Human health risk from hexachlorocyclohexane and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane pesticides, through consumption of vegetables: Estimation of daily intake and hazard quotients. J. Xenobiot. 2013, 3, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ToxFAQsTM for Aldrin and Dieldrin. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR)-Toxic Substance portal. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/tsp/ToxFAQs/ToxFAQsDetails.aspx?faqid=316toxid=56 (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Owago, O.J.; Qi, S.; Xin, X.; Yuan, Z.; Sylvie, M.A. Residues of organochlorine pesticides in vegetables from Deyang and Yanting areas of the Chengdu economic region, Sichuan Province, China. J. Am. Sci. 2009, 5, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa, M.A.; Anjum, F.M.; Asi, M.R.; Ahmed, A.; Nawaz, H. Field incurred endosulfan residues in fresh and processed vegetables and dietary intake assessment. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Stathis, P.; Permuth, S.F.; Tokes, L.; Feldman, D. Bisphenol-A: An estrogenic substance is released from polycarbonate flasks during autoclaving. Endocrinology 1993, 132, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mima, M.; Greenwald, D.; Ohlander, S. Environmental toxins and male fertility. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2018, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Xu, T.; Xu, H.; Fang, H.; Yu, Y. Characterization and genome functional analysis of the DDT-degrading bacterium Ochrobactrum sp. DDT-2. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutgesell, R.M.; Tsakiridis, E.E.; Jamshed, S.; Steinberg, G.R.; Holloway, A.C. Impact of pesticide exposure on adipose tissue development and function. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 2639–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New-Aaron, M.; Naveed, Z.; Rogan, E.G. Estrogen Disrupting Pesticides in Nebraska Groundwater: Trends between Pesticide-contaminated Water and Estrogen-related Cancers in An Ecological Observational Study. Water 2021, 13, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, I.A.; Tee, K.A.M.; Unson, J.R.S.; Hallare, A.V. Organochlorine pesticide residues in surface water and groundwater along Pampanga River, Philippines. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ślósarczyk, K.; Witkowski, A.J. Preliminary Evaluation of the Possible Occurrence of Pesticides in Groundwater Contaminated with Nitrates—A Case Study from Southern Poland. Water 2021, 13, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, U.K.; Pathak, A.K.; Srivastava, S.M. Assessing organochlorine pesticide (OCP) residues in water and fish samples from a small perennial river and associated wetlands of Ganga Basin; India for sustainable management. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panis, C.; Candiotto, L.Z.P.; Gaboardi, S.C.; Gurzenda, S.; Cruz, J.; Castro, M.; Lemos, B. Widespread pesticide contamination of drinking water and impact on cancer risk in Brazil. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, K. Bioaccumulation of pesticides and its impact on biological systems. In Pesticides in Crop Production Physiological and Biochemical Action; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Gerber, R.; Smit, N.J.; Van Vuren, J.H.; Nakayama, S.M.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Ikenaka, Y.; Wepener, V. Bioaccumulation and human health risk assessment of DDT and other organochlorine pesticides in an apex aquatic predator from a premier conservation area. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisekar, U.; Shakila, R.J.; Shalini, R.; Jeyasekaran, G.; Arumugam, N.; Almansour, A.I.; Perumal, K. Bioaccumulation of organochlorine pesticide residues (OCPs) at different growth stages of pacific white leg shrimp (Penaeus vannamei): First report on ecotoxicological and human health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Pan, Z.; Bai, A.; Li, J.; Li, X. Distribution and bioaccumulation of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in food web of Nansi Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, U.; Sandal, S.; Cumbul, A.; Yildiz, S.; Aydin, M.; Yilmaz, B. Evaluation of estrogenic effects of polychlorinated biphenyls and organo-chlorinated pesticides using immature rat uterotrophic assay. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presibella, K.M.; Kita, D.H.; Carneiro, C.B.; Andrade, A.J.; Dalsenter, P.R. Re-productive evaluation of two pesticides combined (deltamethrin and endosulfan) in female rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, A.M.; Sonnenschein, C. Estrogens, xenoestrogens, and the development of neoplasms. In Endocrine Disruptors; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 175–215. [Google Scholar]
- Varayoud, J.; Monje, L.; Bernhardt, T.; Muñoz-de-Toro, M.; Luque, E.H.; Ramos, J.G. Endosulfan modulates estrogen-dependent genes like a non-uterotrophic dose of 17β-estradiol. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 26, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Najmi, A.; Mogus, J.P. Agrochemicals with estrogenic endocrine disrupting properties: Lessons Learned? Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 110860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinina, T.S.; Kononchuk, V.V.; Gulyaeva, L.F. Expression of estrogen-, progesterone-, and androgen-responsive genes in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells treated with o, pʹ-DDT, p, pʹ-DDT, or endosulfan. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA Office of Pesticide Programs, Health Effects Division, Science Information Management Branch. Chemicals Evaluated for Carcinogenic Potential; USEPA Office of Pesticide Programs, Health Effects Division, Science Information Management Branch: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Briz, V.; Molina-Molina, J.M.; Sánchez-Redondo, S.; Fernández, M.F.; Grimalt, J.O.; Olea, N.; Rodríguez-Farré, E.; Sunol, C. Differential estrogenic effects of the persistent organochlorine pesticides dieldrin, endosulfan, and lindane in primary neuronal cultures. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eze, U.A.; Huntriss, J.; Routledge, M.N.; Gong, Y.Y.; Connolly, L. The effect of individual and mixtures of mycotoxins and persistent organochloride pesticides on oestrogen receptor transcriptional activation using in vitro reporter gene assays. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 130, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, A.M.; Sonnenschein, C. Environmental causes of cancer: Endocrine disruptors as carcinogens. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alarcón, R.; Varayoud, J.; Luque, E.H.; Milesi, M.M. Effect of neonatal exposure to endosulfan on myometrial adaptation during early pregnancy and labor in rats. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 491, 110435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.; Narayan, R.; Shanker, R.; Saxena, D.K. Endosulfan-induced bio-chemical changes in the testis of rats. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1995, 37, 547–549. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, R.; Raghavan, S.C. Exposure to Endosulfan can result in male in-fertility due to testicular atrophy and reduced sperm count. Cell Death Discov. 2015, 1, 15020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katzenellenbogen, J.A. The structural pervasiveness of estrogenic activity. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C.; Ghisari, M.; Wielsøe, M.; Bjerregaard-Olesen, C.; Kjeldsen, L.S.; Long, M. Biomonitoring and hormone-disrupting effect biomarkers of persistent organic pollutants in vitro and ex vivo. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 115, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Dailey, A.B.; Talbott, E.O.; Ilacqua, V.A.; Kearney, G.; Asal, N.R. Associations of serum concentrations of organochlorine pesticides with breast cancer and prostate cancer in US adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nelles, J.L.; Hu, W.Y.; Prins, G.S. Estrogen action and prostate cancer. Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 6, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarluzea, J.M.; Fernández, M.F.; Santa-Marina, L.; Olea-Serrano, M.F.; Rivas, A.M.; Aurrekoetxea, J.J.; Expósito, J.; Lorenzo, M.; Torné, P.; Villalobos, M.; et al. Breast cancer risk and the combined effect of environmental estrogens. Cancer Causes Control 2004, 15, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, V.; Bhatnagar, P.; Sharma, R.G.; Acharya, V.; Sexana, R. Breast cancer incidence and exposure to pesticides among women originating from Jaipur. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calaf, G.M.; Ponce-Cusi, R.; Aguayo, F.; Muñoz, J.P.; Bleak, T.C. Endocrine disruptors from the environment affect breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.L.; Bradlow, H.L.; Wolff, M.; Woodruff, T.; Hoel, D.G.; Anton-Culver, H. Medical hypothesis: Xenoestrogens as preventable causes of breast cancer. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 101, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, B.A.; Wolff, M.S.; Cirillo, P.M.; Sholtz, R.I. DDT and breast cancer in young women: New data on the significance of age at exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohn, B.A.; Cirillo, P.M.; Terry, M.B. DDT and breast cancer: Prospective study of induction time and susceptibility windows. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.L.Y.; Co, V.A.; El-Nezami, H. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and breast cancer: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 6549–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; El-Zaemey, S.; Heyworth, J.; Tang, M.C. DDT exposure in early childhood and female breast cancer: Evidence from an ecological study in Taiwan. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høyer, A.P.; Grandjean, P.; Jørgensen, T.; Brock, J.W.; Hartvig, H.B. Organochlorine exposure and risk of breast cancer. Lancet 1998, 352, 1816–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, G.D. Toxicological Profile for Aldrin/Dieldrin; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2002.
- Pizzatti, L.; Kawassaki, A.C.B.; Fadel, B.; Nogueira, F.C.; Evaristo, J.A.; Woldmar, N.; Teixeira, G.T.; Da Silva, J.C.; Scandolara, T.B.; Rech, D.; et al. Toxicoproteomics disclose pesticides as downregulators of TNF-α, IL-1β and estrogen receptor pathways in breast cancer women chronically exposed. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradlow, H.L.; Davis, D.L.; Lin, G.; Sepkovic, D.; Tiwari, R. Effects of pesticides on the ratio of 16 alpha/2-hydroxyestrone: A biologic marker of breast cancer risk. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleva, R.; Manzella, N.; Gaetani, S.; Bacchetti, T.; Bracci, M.; Ciarapica, V.; Tomasetti, M. Mechanism underlying the effect of long-term exposure to low dose of pesticides on DNA integrity. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Rong, M.; Li, M.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, Q. Serum concentrations of organochlorine pesticides; biomarkers of oxidative stress, and risk of breast cancer. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiderpass, E.; Adami, H.O.; Baron, J.A.; Wicklund-Glynn, A.; Aune, M.; Atuma, S.; Persson, I. Organochlorines and endometrial cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Mallozzi, M.; Leone, C.; Manurita, F.; Bellati, F.; Caserta, D. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and endometrial cancer: An overview of recent laboratory evidence and epidemiological studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fénichel, P.; Chevalier, N. Is testicular germ cell cancer estrogen dependent? The role of endocrine disrupting chemicals. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patisaul, H.B.; Adewale, H.B. Long-term effects of environmental endocrine disruptors on reproductive physiology and behavior. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2009, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodprasert, W.; Main, K.M.; Toppari, J.; Virtanen, H.E. Associations between male reproductive health and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2019, 7, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nori, F.; Carbone, P.; Giordano, F.; Osborn, J.; Figà-Talamanca, I. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and testicular cancer: A case-control study. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2006, 61, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuner, E.V.; Lim, Y.H.; Koch, T.; Uldbjerg, C.S.; Gregersen, L.S.; Pedersen, M.K.; Frederiksen, H.; Petersen, J.H.; Coull, B.A.; Andersson, A.M.; et al. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and risk of testicular cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2021, 106, e4834–e4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, P.; Andersen, A.; Irgens, L.M.; Bye, A.S.; Sundheim, L. Cancer in offspring of parents engaged in agricultural activities in Norway: Incidence and risk factors in the farm environment. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 65, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, B.A.; Cirillo, P.M.; Christianson, R.E. Prenatal DDT exposure and testicular cancer: A nested case-control study. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2010, 65, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena-Mullor, M.; Navarro-Mena, A.; Wei, R.; López-Guarnido, O.; Lozano-Paniagua, D.; Alarcon-Rodriguez, R. Evaluation of gonadal alterations in a population environmentally exposed to a mixture of endocrine active pesticides. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: An Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of prostate cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobbs, R.W.; Malhotra, N.R.; Greenwald, D.T.; Wang, A.Y.; Prins, G.S.; Abern, M.R. Estrogens and prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019, 22, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.Y.; Shi, G.B.; Hu, D.P.; Nelles, J.L.; Prins, G.S. Actions of estrogens and endocrine disrupting chemicals on human prostate stem/progenitor cells and prostate cancer risk. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 354, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welshons, W.V.; Nagel, S.C.; Thayer, K.A.; Judy, B.M.; Vom Saal, F.S. Low-dose bioactivity of xenoestrogens in animals: Fetal exposure to low doses of methoxychlor and other xenoestrogens increases adult prostate size in mice. Toxicol. Ind. Health 1999, 15, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Yadav, C.S.; Singh, S.; Goel, S.; Ahmed, R.S.; Gupta, S.; Grover, R.K.; Banerjee, B.D. CYP 1A1 polymorphism and organochlorine pesticides levels in the etiology of prostate cancer. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Banerjee, B.D.; Datta, S.K.; Yadav, C.S.; Singh, S.; Ahmed, R.S.; Gupta, S. Association of CYP1A1, CYP1B1 and CYP17 gene polymorphisms and organochlorine pesticides with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chemosphere 2014, 108, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhananjayan, V.; Ravichandran, B. Occupational health risk of farmers exposed to pesticides in agricultural activities. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 4, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barul, C.; Parent, M.E. Occupational exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and risk of prostate cancer. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis-Mikhael, A.M.; Bueno-Cavanillas, A.; Guiron, T.O.; Olmedo-Requena, R.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Jiménez-Moleón, J.J. Occupational exposure to pesticides and prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 73, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.M.; Vial, S.L.; Fuortes, L.J.; Guo, H.; Reedy, V.E.; Smith, E.M. Organochlorines and risk of prostate cancer. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 45, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settimi, L.; Masina, A.; Andrion, A.; Axelson, O. Prostate cancer and exposure to pesticides in agricultural settings. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 104, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, N.; Chia, S.E.; Ong, C.N.; Kelly, B.C. Associations of serum organohalogen levels and prostate cancer risk: Results from a case–control study in Singapore. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, É.A.V.; Sánchez, L.E.T.; Salas, R.A.V.; Carrillo, L.L.; Cebrián, M.E. Endosulfan Exposure Is Associated with Prostate Cancer In Mexico. In Proceedings of the 2015 ISEE Conference, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 30 August–3 September 2015. [Google Scholar]


| Name of Pesticide | Commercial Name | Ban Status | Current Status | Year of Listing in Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants | Used for the Crops | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dieldrin | Hortico, Dieldrin Dust Mustex 25%, Shell Dieldrex, Yates Garden Dust | Complete | No manufacturing | 2001 | Corn, cotton, citrus cabbage, legumes | [39] |
| DDT | Cezarex, Anofex, Clorophenothane, Dicophane, Dinocide, Gesarol, Guesapon, Guesarol, Gyron, Ixodex, Neocid, Neocidol, Zerdane | Partial | For malaria control programs (countries of Africa and Asia) | 2001 | Amaranth, cabbage, lettuce, pumpkin, spinach | [40] |
| Endosulfan | Afidan, Beosit, Endocel, Hildan Cyclodan, Devisulfan, Endocide, Endosol, FMC 5462, Hex-asulfan, Hoe 2671, Insectophene, Malix, Thiodan, Thimul, Thifor, Thionex | Regulated | For certain crop–pest complexes | 2011 | Spinach, cauliflower, potato, brinjal, tomato, okra | [41] |
| Aldrin | Aldrec, Aldrex, Drinox, Octalene, Seedrin, Compound 118 | Complete | No manufacturing | 2007 | Corn, cotton, citrus, cabbage, legumes | [39] |
| HCH | Forlin, Etan 3G, Gamaphex, Isotox, GermatePlus, Gamma-Mean400, Lindagram | Complete | No manufacturing | 2008 | Amaranth, cabbage, lettuce, pumpkin, spinach | [40] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, V.; Yadav, C.S.; Banerjee, B.D. Xeno-Estrogenic Pesticides and the Risk of Related Human Cancers. J. Xenobiot. 2022, 12, 344-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox12040024
Kumar V, Yadav CS, Banerjee BD. Xeno-Estrogenic Pesticides and the Risk of Related Human Cancers. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2022; 12(4):344-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox12040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Vivek, Chandra Shekhar Yadav, and Basu Dev Banerjee. 2022. "Xeno-Estrogenic Pesticides and the Risk of Related Human Cancers" Journal of Xenobiotics 12, no. 4: 344-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox12040024
APA StyleKumar, V., Yadav, C. S., & Banerjee, B. D. (2022). Xeno-Estrogenic Pesticides and the Risk of Related Human Cancers. Journal of Xenobiotics, 12(4), 344-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox12040024