A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
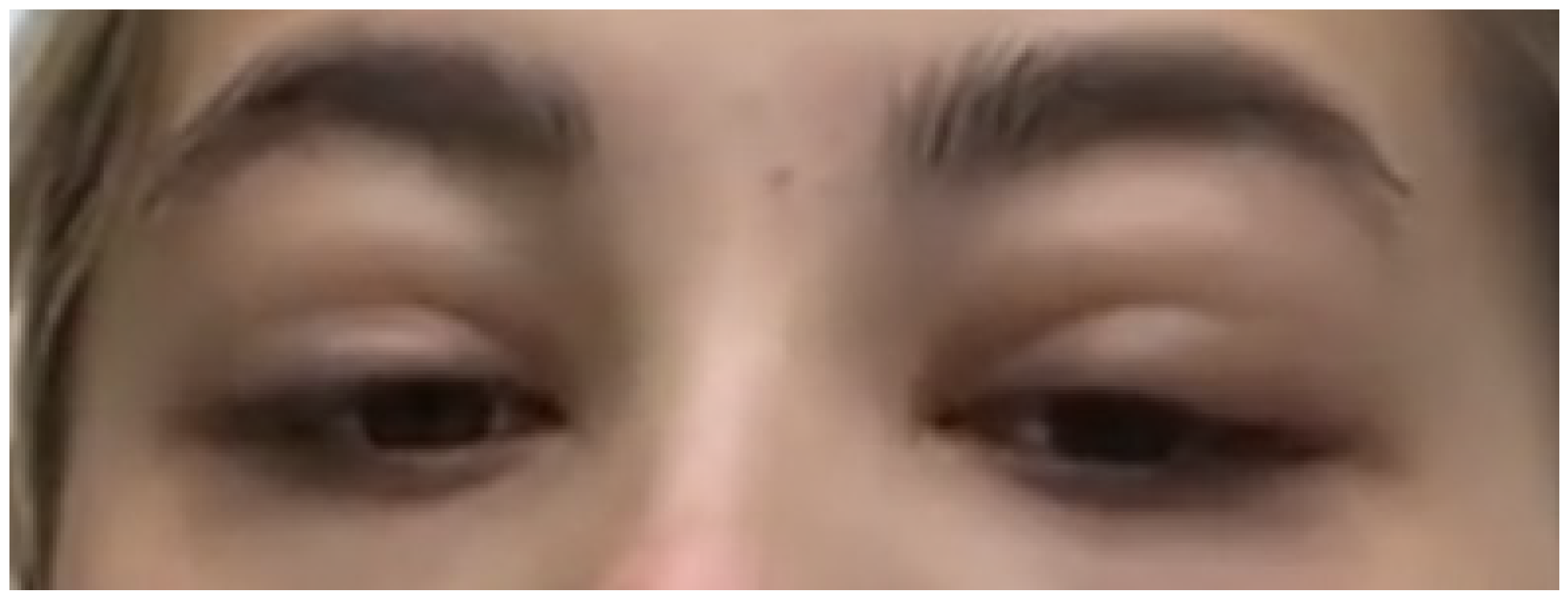
2. Case
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naughton, P.; Healy, M.; Enright, F.; Lucey, B. Infectious Mononucleosis: Diagnosis and clinical interpretation. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 78, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronz, G.; Zanetti, B.; Bianchetti, M. Bilateral upper eyelid swelling (Hoagland sign) in Epstein-Barr infectious mononucleosis: Prospective experience. Infection 2022, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louppides, S.; Kakoullis, L.; Parpas, G.; Panos, G. Upper eyelid oedema in a patient with pharyngitis/exudative tonsillitis and malaise: Hoagland sign in infectious mononucleosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e233719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, Y.; Kishida, M. Hoagland sign: Bilateral upper eyelid oedema. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e250857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Miyata, Y.; Maekawa, M. Infectious Mononucleosis with Eyelid Edema and Palatal Petechiae. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 36, 1027–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunmire, S.; Hogquist, K.; Balfour, H. Infectious Mononucleosis. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 390, 211–240. [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland, R. Infectious mononucleosis. Am. J. Med. 1952, 13, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bass, M. Periorbital edema as the initial sign of infectious mononucleosis. J. Pediatr. 1954, 45, 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süer, K.; Kaptanoglu, A. Association of Periorbital Edema and Fever in Acute Infectious Mononucleosis: A Case Report. Kafkas J. Med. Sci. 2013, 3, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Thurau, S.; Haritoglou, C. Beidseitige Oberlidschwellung bei Mononucleosis Infectiosa (Hoagland-Zeichen). Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 2005, 222, 1014–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburn, N.; Sullivan, T. Infectious Mononucleosis Presenting with Dacryoadenitis. Ophthalmology 1996, 103, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, S. Hoagland Sign: An early manifestation of acute infectious mononucleosis—A case report. Curr. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 21, 400–401. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hasselt, W.; Schreuder, R.; Houwerzijl, E. Periorbital oedema. Neth. J. Med. 2009, 67, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demonchy, E.; Pulcini, C. Three cases of primary EBV infection in young adults manifested by periorbital and eye-lid oedema. Infection 2008, 41, 1029–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.; Doerr, T.; Hengerer, A. Infectious Mononucleosis and Corticosteroids. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 131, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rafailidis, P.; Falagas, M. Fever and Periorbital Edema: A Review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2007, 52, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depetri, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Cugno, M. Angioedema and emergency medicine: From pathophysiology to diagnosis and treatment. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 59, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medović, R.; Igrutinović, Z.; Radojević-Marjanović, R.; Marković, S.; Rasković, Z.; Simović, A.; Tanasković-Nestorović, J.; Radovanović, M.; VuIetić, B. Clinical and laboratory differences between Epstein-Barr and cytomegalovirus infectious mononucleosis in children. Srpski Arhiv Celokupno Lekarstvo 2016, 144, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, R. Clinical presentation & management of glomerular diseases: Hematuria, nephritic & nephrotic syndrome. Mo Med. 2011, 108, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiala, M.; Heiner, D.; Turner, J.; Rosenbloom, B.; Guze, L. Infectious mononucleosis and mononucleosis syndromes. West J. Med. 1977, 126, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricardo, D. A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 942-945. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14060092
Ricardo D. A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus. Infectious Disease Reports. 2022; 14(6):942-945. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14060092
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicardo, Daryl. 2022. "A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus" Infectious Disease Reports 14, no. 6: 942-945. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14060092
APA StyleRicardo, D. (2022). A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus. Infectious Disease Reports, 14(6), 942-945. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14060092





