Abstract
The rise of multidrug resistance (MDR) bacteria in nosocomial and health-care institutions is widespread and is currently recognized as a major medical challenge. Mechanisms of bacterial resistance, namely, quorum sensing (QS), biofilm formation, and efflux pumps, have been identified as critical biological processes in MDR bacteria. Following previous reports on the activity of phenothiazines against mechanisms of bacterial resistance, in this work we focus on the synthesis of xanthene derivatives aiming to discover phenothiazine bioisosteres with improved activity. Four compounds were obtained from the conjugation of xanthydrol with sulfonamides and aniline and were fully characterized. Their antibacterial activity was assessed considering their minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains, efflux pump inhibition, influence on biofilm formation and quorum-sensing (QS) inhibition. It was observed that the MIC of all the tested compounds was above 64 µg/mL The four 9-xanthenyl derivatives obtained, particularly the xanthene sulfonamide derivatives 3b and 3c, showed promising results on QS inhibition with a reduction of pigment production of 48 and 41 mm, and on biofilm formation with a reduction of 78 and 79%, respectively.
1. Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance has become a major threat to global health, enhanced by the decreasing effectiveness of antibacterial agents due to their wide use in both human and veterinary medicine. Currently, multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria are widespread in nosocomial and health-care-acquired infections, and are responsible for more than 700,000 deaths each year, which are predicted to grow to 10 million by 2050 [1,2,3].
Regarding the mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria, the formation of biofilm plays a central role, allowing their survival even in the presence of antibiotics and other adverse environmental conditions. For instance, in the field of biomedical implants, a clinical procedure that is increasing worldwide, biofilms are responsible for the persistence of implant infections and are a source of bacterial dissemination to other body sites and eventually lead to systemic and fatal infections [4,5]. One of the processes that regulate the formation of biofilms is quorum-sensing (QS), a bacterial cell-cell communication process that involves the production, detection, and response to extracellular signaling molecules called autoinducers. The contribution of QS to biofilm formation, as well as bacteriocin production and virulence, reveals its importance to bacterial pathogenesis [6,7,8].
These phenomena are intrinsically connected to efflux pumps [9], whose overexpression contributes not only to the potentiation of these mechanisms, but also to increase transport of antibiotics and antiseptics outside the bacterial cell. In fact, efflux pumps can increase the efflux of QS molecules, such as acyl-homoserine lactones (AHL), as well as extracellular polymeric substances for biofilm formation, and regulate biofilm genes and promote bacterial aggregation [10]. Hence, the identification of new agents capable of overtaking these mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance would represent a novel and important strategy to fight multidrug resistance strains.
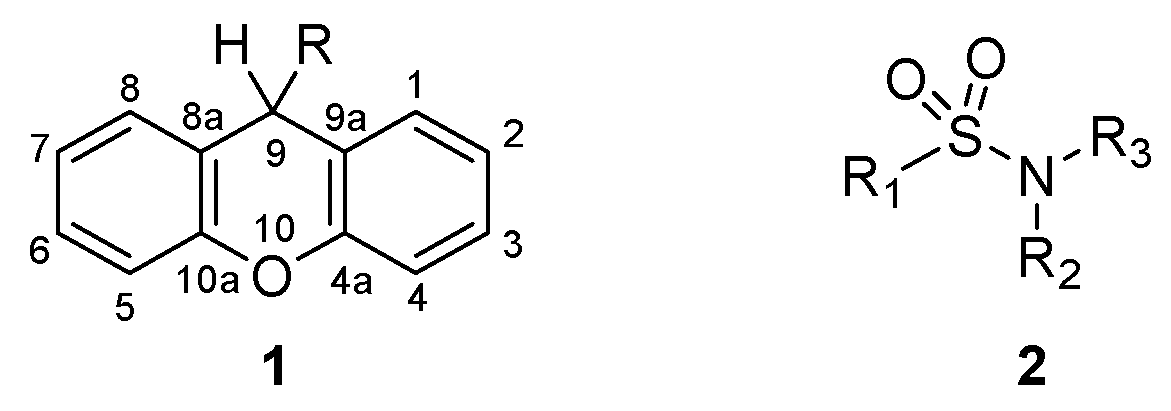
Xanthenes (1, Figure 1) are a class of oxygen-incorporating tricyclic compounds, explored for different biological applications, where the presence of different substituents in position 9 impacts their chemical properties and bioactivity [11]. The synthesis of xanthenes through the modification of the carbonyl in position 9 of xanthones represents the most straightforward procedure to easily obtain a variety of xanthenes [11] Several studies have shown their potential as antibacterial agents, where xanthenes revealed moderate to good inhibition in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria [12,13,14,15,16,17]. Additionally, the tricyclic nucleus of xanthenes possesses electronic and geometrical similarities to phenothiazines, thioxanthones and thioxanthenes, classes of compounds known for their activity in inhibiting biological processes responsible for antimicrobial resistance, namely QS [18,19] and efflux pump activity [19,20,21,22,23]. Sulfonamides (2, Figure 1) represent another important class of therapeutic agents in medicine. After their discovery as potent antimicrobial agents for systemic infections in humans [24,25], sulfonamides were further derivatized to yield compounds with different biological applications. This strategy led to the development of sulfonamides with diuretic [26], hypoglycemic [27], anticonvulsant [28], anticancer [29] and antiviral activity [30].
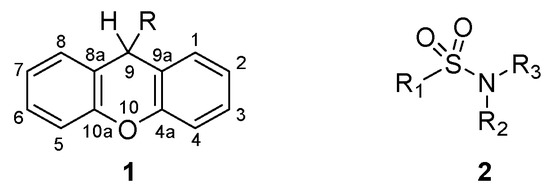
Figure 1.
Structure of xanthene (1) and sulfonamide (2) derivatives.
Therefore, in this work we focus on the synthesis of xanthene sulfonamide derivatives, aiming to explore their activity against bacterial resistance mechanisms. The compounds obtained were fully characterized and evaluated regarding their minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) on Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains, efflux pump inhibition (EPI) activity, influence on biofilm formation, and QS inhibition.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
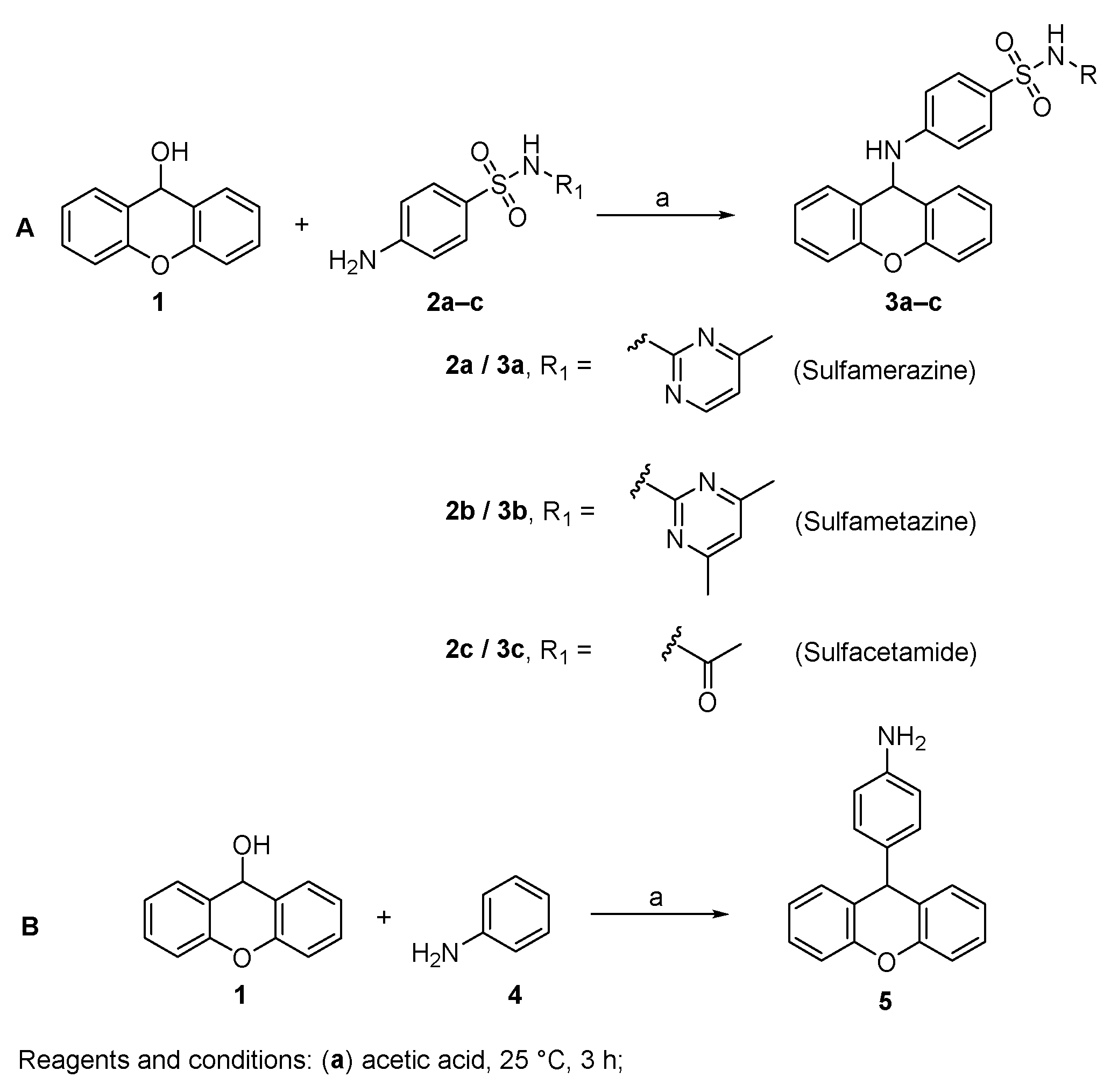
The desired 9-xanthenyl derivatives were obtained following a previously reported procedure describing the condensation of benzenoid sulfonamides with xanthydrol [31]. The solubilization of xanthydrol in glacial acetic acid allows the formation of the xanthylium ion. Then, the nucleophilic attack by an electron pair from a molecule of relatively high electron density leads to the substitution product (Figure 2A) [32].
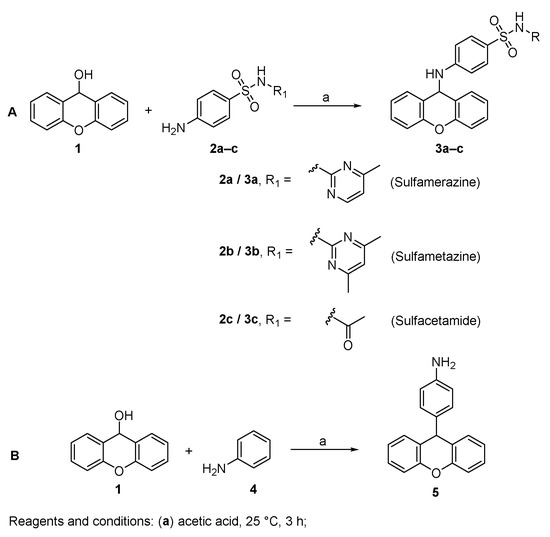
Figure 2.
Synthesis of 9-xanthenyl derivatives 3a–c (A) and 5 (B).
The synthesis of a xanthene derivative possessing an aniline in position 9 (5) was also performed for structure-activity relationship purposes. When using an aniline nucleophile, due to the activating influence of the amine, the electrophilic aromatic substitution at the para position of the aromatic ring with the xanthenyl group was observed (Figure 2B) [33].
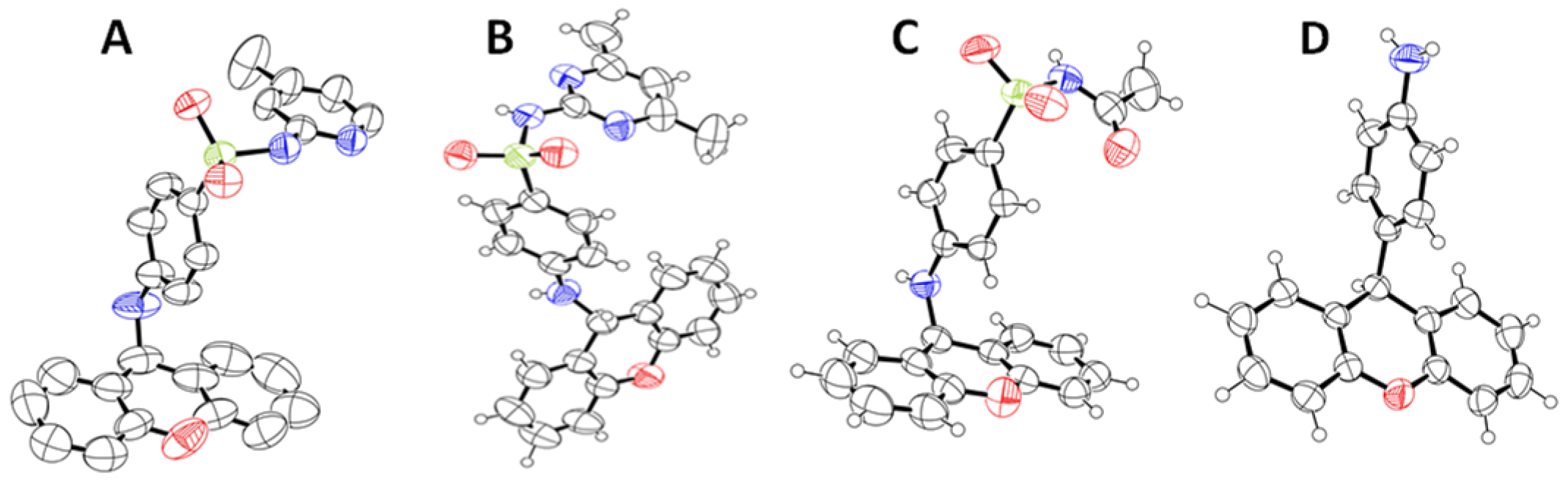
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that these compounds have been fully characterized and explored against mechanisms of bacterial resistance. Figure 3 depicts the structure of compounds 3a–c and 5 obtained by single-crystal X-ray crystallography. Further details regarding the characterization data are provided in Supplementary Materials (Figures S1–S8).
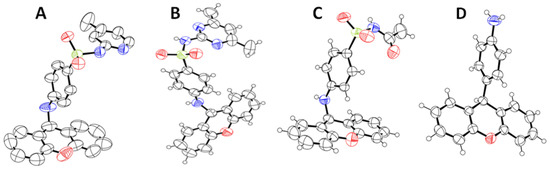
Figure 3.
ORTEP view of the crystal structure of xanthenyl sulfonamides (3a (A), 3b (B), and 3c (C)) and compound 5 (D).
2.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
Sulfonamide drugs are important antimicrobial drugs with a broad spectrum of actions, effective against Gram-positive and certain Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella sp., Salmonella sp., Shigella sp. and Enterobacter sp. strains. They act as bacteriostatic agents through the competitive inhibition of para-aminobenzoic acid, an essential component in the synthesis of folic acid synthesis, which prevents the growth and reproduction of bacteria [34,35]. Structure-activity relationship studies of sulfonamides have shown that, in addition to the sulfonamide group attached directly to the benzene ring, the presence of the free aromatic NH2 group in the para position is essential for the activity of sulfonamides [36].
Firstly, compounds 3a–c and 5 were evaluated for their antibacterial activity by assessing their minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) on eight different strains of bacteria: the reference strains E. coli American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) 25922, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853, and Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212; the clinical strains S. aureus 272123 (oxacillin- and methicillin-resistant), the extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing E. coli SA/2, and the vancomycin-resistant E. faecalis B3/101; and the acrA gene-deleted strain Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium SL1344. The broth microdilution method was used, in a 96-well plate, and the concentrations tested ranged from 64 µg/mL to 4 µg/mL. It was observed that the MIC of all the tested compounds was above 64 µg/mL, which means they do not present antibacterial activity for the strains used, in the concentrations tested.
Therefore, despite possessing a sulfonamide moiety, the presence of the xanthenyl group in the free amine of the sulfonamide drug 2a–c should be responsible for the absence of bacteriostatic activity of compound 3a–c. Compound 5, not structurally related to sulfonamides, also presents unsatisfactory antibacterial activity.
2.3. Quorum-Sensing Inhibition
The QS inhibitory effect of compounds 3a–c and 5 was examined against three Gram-negative strains: Sphingomonas paucimobilis Ezf 10–17 (EZF) and the sensor C. violaceum CV026 (CV026) strains, Chromobacterium violaceum wild type 85 (wt85) and Serratia marcescens AS-1 [37]. The results are depicted in Table 1.

Table 1.
Results of the quorum sensing inhibition assay.
It was observed that compounds 3b and 3c inhibited QS in EZF and sensor CV026 strain, showing a reduction of pigment production of 48 and 41 mm, respectively. Compounds 3a and 5a showed no activity as QS inhibitors.
Previous works reported the QS inhibition activity of phenothiazines and related compounds, namely, promethazine, amitriptyline and acridine orange [38]. These compounds possess a tricyclic nucleus and a heterogenic substituent at the central ring. Varga et al. [18] suggest that their tricyclic nucleus, quasi-planar structure, and electron donor capacity of the conjugated electron system appear to be critical for the inhibition of QS. Nevertheless, the substituents at position 9 should also play an important role, justifying the different activities found for the compounds explored. Particularly, more hydrophobic substituents (comparing 3b with 3a sulfonamides) favor this activity.
2.4. Biofilm Formation Inhibition
Biofilm formation inhibition was performed with the strains S. aureus ATCC 25923 and the oxacillin- and methicillin-resistant S. aureus 272123, a strain with a strong impact in nosocomial infections [4,5]. The biofilm inhibition, presented in percentages, is depicted in Table 2. It was observed that compounds 3b and 3c were effective in inhibiting the formation of biofilm in S. aureus 272123 strain, showing a reduction of 78 and 79%, respectively. Compounds 3a and 5 showed a slight inhibition of biofilm formation in this strain. Regarding S. aureus ATCC 25923, none of the tested compounds showed significant activity.

Table 2.
Percentage of biofilm inhibition of compounds 3a–c and 5.
Similarly to what was observed in QS inhibition, the introduction of hydrophobic substituents at C-9 led to a more pronounced inhibition of biofilm formation, suggesting this property increases compound penetration on biofilm matrices.
2.5. Efflux Pump Inhibition
Lastly, the compounds were evaluated for their ability to inhibit efflux pumps. The assay was performed on the strain Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium SL1344, with the acrA gene deleted, and on S. aureus 272123, by monitoring the intracellular accumulation of the efflux pump substrate ethidium bromide (EB) through the real-time fluorimetry. Reserpine and carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) were used as positive controls.
As depicted in Table 3, compounds 3a–c and 5 increase the fluorescence in comparison to the positive control, which can be attributed to the inhibition of the efflux of EB in the tested strains. Nonetheless, for compounds 3a–c, a high fluorescence value at t = 0 in relation to the positive control was observed, which indicates a potential intrinsic fluorescence of these compounds (Supplementary Materials, Figures S9 and S10). To clarify this matter, the compounds were tested alone in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) against a solution of EB and a solution of EB and the compound together (Supplementary Materials, Figures S11–S13). If the compound presents an irregular fluorescence pattern, or if the fluorescence of the compound with EB is higher than the fluorescence of the compound alone, no conclusions can be drawn, as this is a limitation of the assay.

Table 3.
Efflux pump inhibition assay for compounds 3a–c and 5.
The analysis of the curves of the variation of fluorescence over the course of the assay showed that compounds 3a–c displayed an erratic curve in combination with EB, their effect being considered inconclusive. On the other hand, compound 5 showed a regular fluorescence pattern (Figures S9 and S10), confirming that the relative fluorescence index (RFI) result obtained with this compound is related to the inhibition of the efflux pump of the bacterial strains tested, which warranted no further fluorescence studies. This compound showed a 5-fold higher RFI value compared with the respective reference standard on strain S. typhimurium SL1344. These results are in line with previous studies regarding the inhibition of some efflux pumps by phenothiazines and thioxanthenes [20,21,22,23].
Additionally, xanthones and thioxanthones—two classes of tricyclic compounds also structurally related to xanthenes—were recently explored as potential efflux pump inhibitors [19,39,40]. Once again, the tricyclic nucleus appears to be an important structural characteristic for the activity as efflux pump inhibitors.
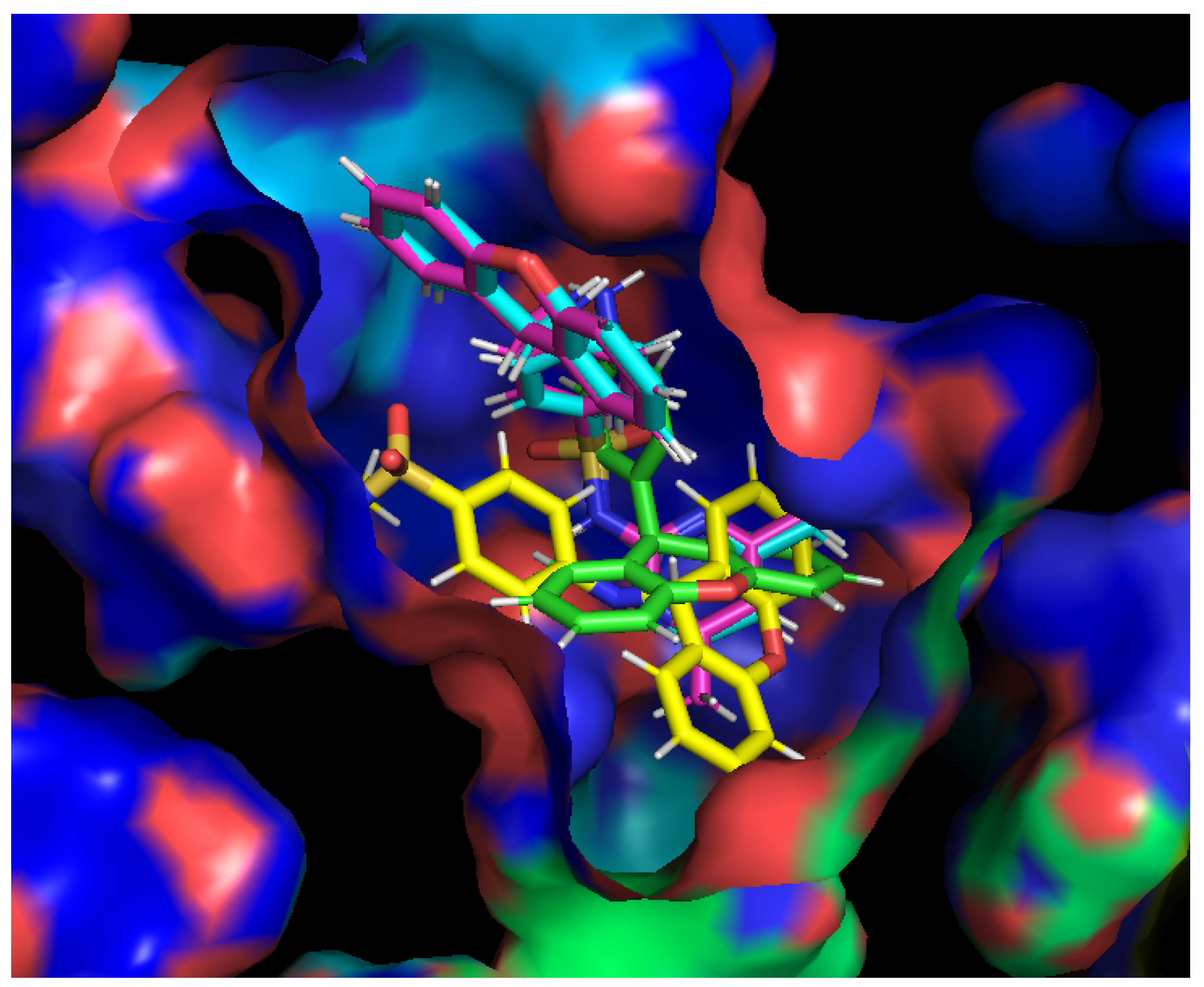
Docking studies were performed for compounds 3a–c and 5 with the crystal structure of AcrB (PDB: 4DX5 [41]), the efflux pump portion of the AcrAB-TolC efflux system, as it presented the most favorable docking scores (Supplementary Materials, Table S1). The sites studied in this scope were the substrate binding site and the hydrophobic trap, which have been described in [42]. Furthermore, intermolecular interactions were observed between these compounds and the substrate binding site of AcrB, as the best docking scores were obtained in this portion. The compounds were predicted to fit into the substrate binding site, and bind in the same sites, with slight variations in the residues they interact with (Figure 4).
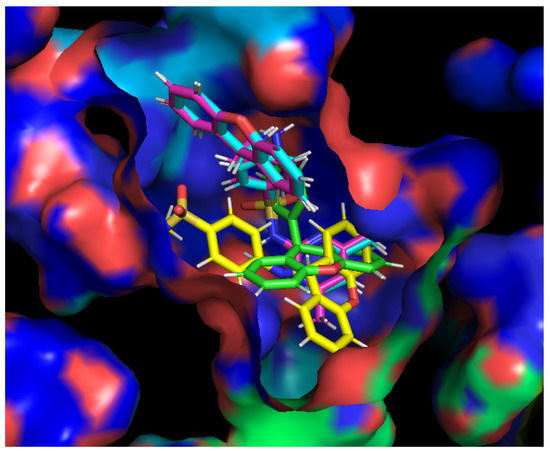
Figure 4.
Compounds 3a (blue), 3b (pink), 3c (yellow), and 5 (green) in the substrate binding site of the AcrB portion. Crystal structure of the AcrB portion obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB: 4DX5 [41]).
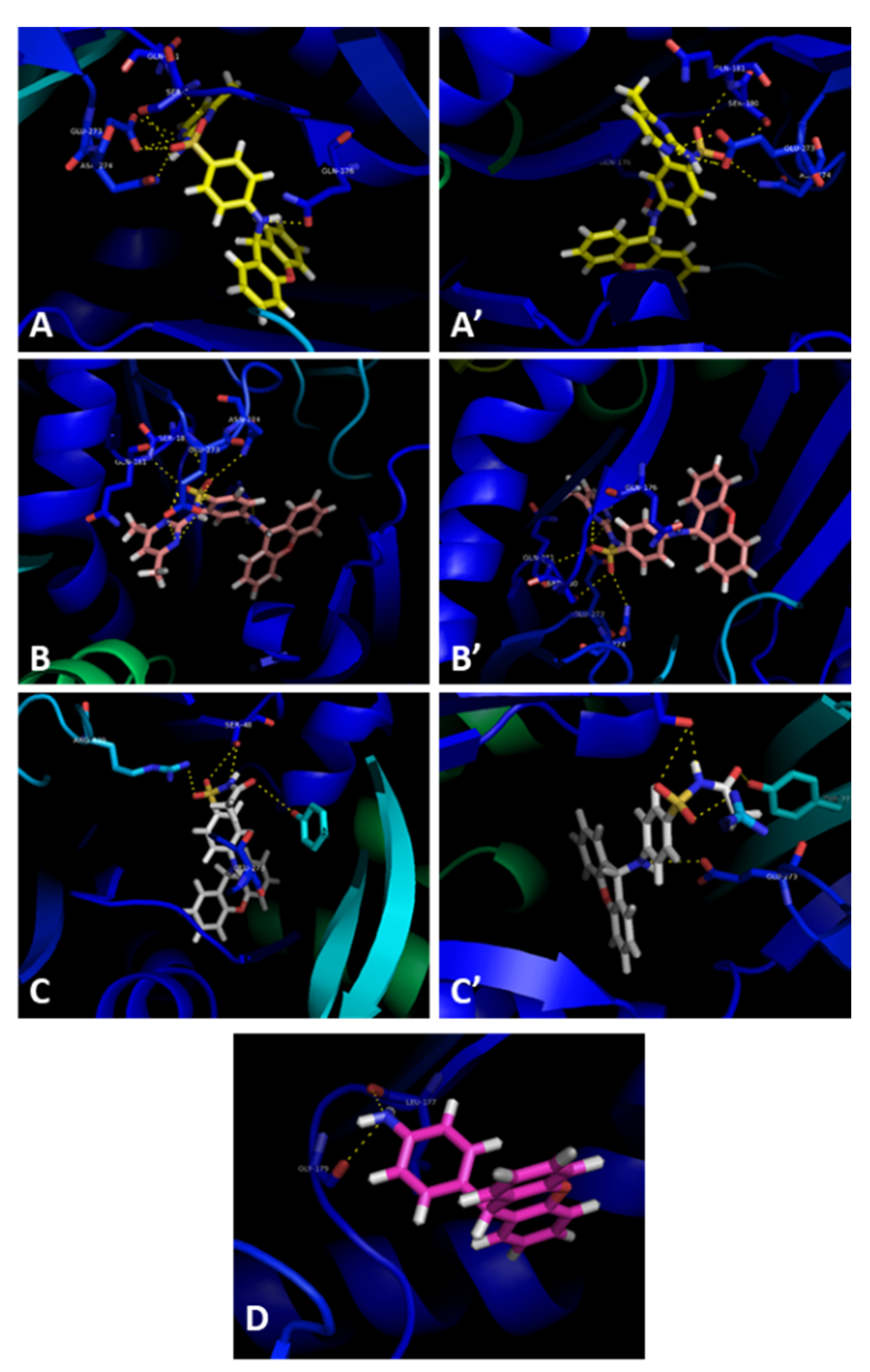
Compounds 3a (Figure 5A,A’) and 3b (Figure 5B,B’) have similar interactions, being able to establish hydrogen interactions between Gln-176, Ser-180, Gln-181, Glu-273, and Asn-274. Compound 3c interacts with the residues Ser-48 and Glu-273 (Figure 5C,C’). Interestingly, this compound also interacts with Arg-620 and Tyr-772, present in a different subunit of the efflux pump portion. It is noteworthy that Arg-620 and Gln-176 were previously reported as interaction points with xanthone derivatives in a previous work of our group [39]. Finally, compound 5 appears to interact with Leu-177 and Gly-179 (Figure 5D). For compounds 3a–c, their capacity to inhibit efflux pumps should be repeated with a different bioassay in which their fluorescent properties have no influence on the results.
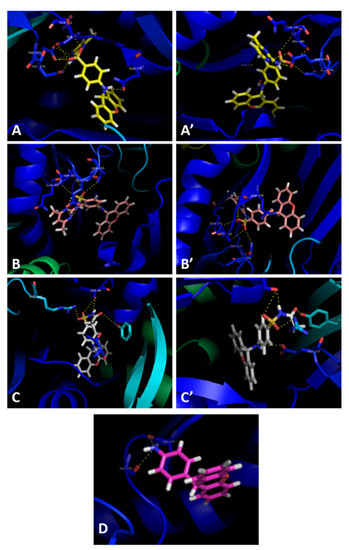
Figure 5.
Molecular visualization of compounds 3a (A,A’), 3b (B,B’), 3c (C,C’), and 5 (D) A in the AcrB portion of the AcrAB-TolC efflux system. Crystal structure of the AcrB portion obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB: 4DX5 [41]).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
All reagents and solvents were purchased from TCI (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co. Ltd., Chuo-ku, Tokyo, Japan), Acros Organics (Geel, Belgium), Sigma-Aldrich (Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd., Dorset, UK), or Alfa Aesar (Thermo Fisher GmbH, Kandel, Germany) and were used directly without any further purification. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) was used to monitor the reactions, and Merck silica gel 60 (GF254) precoated plates were used for this end, accompanied by the appropriate mobile phases. The synthesized compounds were purified by flash column chromatography using Merck silica gel 60 (0.040–0.063 mm), and their melting points (mp) were measured by using a Köfler microscope (Wagner and Munz, Munich, Germany) equipped with a Crison TM 65 (Crison Instruments, Barcelona, Spain) and were uncorrected. 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were taken in deuterated chloroform or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), purchased from Deutero GmbH (Kastellaun, Germany), on a Bruker Avance 300 instrument (300.13 or 500.16 MHz for 1H and 75.47 or 125.77 MHz for 13C, Bruker Biosciences Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) or Bruker AVANCE III (400.14 MHz for 1H and 100.62 MHz for 13C), all at room temperature. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) was used as an internal reference, in relation to which all the chemical shifts are expressed. In order to assign the carbons, 2D heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) and heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) experiments were performed. HPLC Analysis (Purity & Peak Purity determination) were performed with a system consisting of a Shimadzu LC-20AD pump, equipped with a Shimadzu DGV-20A5 degasser, a Rheodyne 7725i injector fitted with a 20 µL loop, and an SPD-M20A DAD detector (Kyoto, Japan). The data was acquired using a Shimadzu LCMS Lab Solutions software, version 3.50 SP2. An ACE-C18 column (150 × 4.6 mm I.D., particle size 5 µm; Advanced Chromatography Technologies Ltd., Aberdeen, UK) was used. The mobile phase used was composed of water, methanol, and acetic acid (85:15:0.1 v/v/v), and the solvents were HPLC grade, purchased from Merck Life Science S.L.U. (Darmstadt, Germany). The flow rate was 1.0 mL/minute and the ultraviolet (UV) detection wavelength was 254 nm. Analyses were performed at 27 °C in a 30-min run, isocratically. Peak purity index was determined by total peak UV-Visible spectra between 210–800 nm with a step of 4 nm.
3.2. Chemistry
Compounds 3a–c and 5 were synthetized as described in previous works [32,43] with the following modifications.
Synthesis of 4-((9H-xanthen-9-yl)amino)-N-(4-methylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide (3a):
To 1.2 mmol of xanthydrol in 5 mL of glacial acetic acid was added 1 mmol of sulfamerazine dissolved in 2 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). Stirring was continued at room temperature and the derivative began to precipitate in minutes. After 3 h, the product was collected through filtration with a vacuum filtration unit possessing a nylon membrane filter with Ø of 47 mm and pore size of 0.45 µm. After washing with 100 mL of water, the product was dried in a vacuum desiccator over P2O5. The crude derivative was dissolved in a minimum volume of THF at room temperature, and the resulting solution was filtered. Water was slowly added until the visualization, which was a sign of cloudiness. Then the solution was placed in a refrigerator at 8–10 °C for crystallization. After crystallization was complete, the product was collected by filtration with a nail glass funnel. Compound 3a was obtained as white crystals (298.3 mg, 66.7%).
Compound 3a: mp 207–208 °C (literature [32]: 206–207 °C); Purity (HPLC): 99.2%; 1H NMR (300.13 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 11.21 (s, 1H), 8.32 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 7.43–7.27 (m, 4H), 7.19 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.3 Hz, 2H), 7.09 (td, J = 7.3, 1.1 Hz, 2H), 6.84–6.90 (m, 3H), 6.12 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 2.30 (s, 3H), 2.30 (s, 3H) ppm; 13C NMR (75.47 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 168.1, 157.8, 156.9, 151.3, 150.7, 130.0, 129.0, 128.4, 125.9, 123.5, 122.5, 116.3, 114.9, 110.9, 46.10, 23.4 ppm.
Synthesis of 4-((9H-xanthen-9-yl)amino)-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide (3b):
The same procedure described for the synthesis of compound 3a was applied to the synthesis of compound 3b, with exception of the sulfonamide compound added to the solution, where in this case sulfametazine was added to the reaction media. Compound 3b was obtained as off-white needles (210.6 mg, 45.8%).
Compound 3b: mp 171–173 °C (literature [32]: 174–175 °C); Purity (HPLC): 99.9%; 1H NMR (300.13 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 11.07 (s, 1H), δ = 7.68 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.46 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 7.42–7.26 (m, 4H), 7.18 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.2 Hz, 2H), 7.08 (td, J = 7.4, 1.3 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), δ = (s, 1H), 6.12 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 2.24 (s, 6H) ppm; 13C NMR (75.47 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 167.9, 157.1, 151.6, 151.1, 130.7, 129.4, 128.8, 123.9, 123.0, 116.7, 114.2, 111.2, 46.5, 23.6 ppm.
Synthesis of N-((4-((9H-xanthen-9-yl)amino)phenyl)sulfonyl)acetamide (3c):
The same procedure described for the synthesis of compound 3a was applied to the synthesis of compound 3c, with exception of the sulfonamide used, where in this case sulfacetamide was added to the reaction media. Compound 3c was obtained as white needles (254.9 mg, 64.7%).
Compound 3c: mp 215 °C (literature [32] 208–208.5 °C); Purity (HPLC): 99.9%; 1H NMR (300.13 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 11.70 (s, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.45–7.28 (m, 4H), 7.20 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.2 Hz, 2H), 7.12 (td, J = 7.4, 1.3 Hz, 2H), 6.87 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.16 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 1.88 (s, 3H) ppm; 13C NMR (75.47 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 168.9, 152.2, 151.3, 130.2, 129.5, 128.8, 125.1, 124.0, 122.8, 116.8, 111.6, 46.5, 23.7 ppm.
Synthesis of 4-(9H-xanthen-9-yl)aniline (5):
The same procedure described for the synthesis of compound 3a–3c was applied to the synthesis of compound 5, where instead of a sulfonamide compound, aniline was added to the reaction media. Compound 5 was obtained as yellowish needles (162.9 mg, 59.1%)
Compound 5: mp 183 °C (literature [44]: 175–180 °C); Purity (HPLC): 99.5%; 1H NMR (300.13 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.19 (ddd, J = 8.5, 6.7, 1.8 Hz, 2H), 7.11 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.4 Hz, 2H), 7.06 (dd, J = 7.9, 1.9 Hz, 2H), 6.97 (td, J = 7.0, 1.2 Hz, 4H), 6.64–6.55 (m, 2H), 5.15 (s, 1H), 3.57 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (75.47 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 151.1, 145.0, 136.8, 129.7, 129.4, 127.7, 125.0, 123.1, 116.4, 115.4, 43.5 ppm.
3.3. X-ray Crystallography
X-ray diffraction data were collected with a Gemini PX Ultra (Rigaku/Oxford, Neu-Isenburg, Germany) equipped with CuKα radiation (λ = 1.54184 Å), at 290 K. The structures were solved by direct methods using SHELXS-97 and refined with SHELXL-97 [45]. Non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically. Hydrogen atoms were either placed at their idealized positions using appropriate HFIX instructions in SHELXL and included in subsequent refinement cycles or were directly found from difference Fourier maps and were refined freely with isotropic displacement parameters.
3a: Crystal was triclinic, space group P1, unit cell dimensions a = 9.6353 (4) Å, b = 10.7815 (7) Å and c = 12.0410 (7) Å, and angles α = 75.152 (5)°, β = 88.427 (4)° and γ = 78.045 (5)° (uncertainties in parentheses). The refinement converged to R (all data) = 8.02% and wR2 (all data) = 13.51%.
3b: Crystal was monoclinic, space group P21/n, unit cell dimensions a = 8.3568 (4) Å, b = 10.1765 (4) Å and c = 32.294 (1) Å, and β = 94.539 (4)°. The refinement converged to R (all data) = 8.98% and wR2 (all data) = 14.31%.
3c: Crystal was monoclinic, space group C2/c, unit cell dimensions a = 13.8772 (3) Å, b = 10.0064 (3) Å and c = 30.2805 (9) Å, and β = 95.769 (3)°. The refinement converged to R (all data) = 8.01% and wR2 (all data) = 13.99%.
5: Crystal was monoclinic, space group P21/n, unit cell dimensions a = 9.0383 (3) Å, b = 10.7961 (4) Å and c = 14.5840 (5) Å, and β = 101.539 (4)°. The refinement converged to R (all data) = 5.88% and wR2 (all data) = 12.65%.
3.4. Microorganisms
The bacterial strains used were S. aureus ATCC 25923, E. faecalis ATCC 29212, and methicillin and ofloxacin-resistant S. aureus 272123 clinical isolate, as Gram-positive microorganisms, and E. coli ATCC 25922, P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853, the acrA gene inactivated mutant S. enterica serovar Typhimurium SL1344, and clinical isolates of the extended-spectrum β-lactamase producer (ESBL) E. coli SA/2, as Gram-negative microorganisms.
To assay QS inhibition, Gram-negative strains were used: C. violaceum wild type 85 (wt85), which produces the purple pigment violacein, mediated by endogenously produced AHL (signal molecules); C. violaceum CV026 (CV026), a Tn5 transposase-mutant incapable of producing AHL, but still able to produce violacein in the present of an external stimuli, provided in this case by S. paucimobilis Ezf 10–17 (EZF); and S. marcescens AS-1, which produces the prodigiosin, an orange-red pigment, in response to the self-production of the QS signal molecule N-hexanoyl-l-homoserine lactone [37].
3.5. Antibacterial Assay
The method used for the assessment of the MIC of the compounds towards the bacterial strains used (S. aureus ATCC 25923, E. faecalis ATCC 29212, S. aureus 272123, E. coli ATCC 25922, P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853, S. typhimurium SL1344, and E. coli SA/2) was the broth microdilution method, according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) guidelines [46]. This was performed in 96-well microplates, using cation adjusted Müller-Hinton broth (Sigma-Aldrich, St- Louis, MO, USA and Biokar Diagnostics, Allone, Beauvais, France) as culture medium, using concentrations ranging from 64 µg/mL to 4 µg/mL, which were later converted to µM. The compound solutions were prepared from a stock solution of 10 mg/mL in DMSO, kept at −20 °C, assuring that the concentration of this solvent did not exceed the recommended 1% v/v. The MICs of the compounds were determined visually, as the first well was devoid of bacterial growth. As negative control, DMSO 1% v/v was used, and as positive control, the quinolone ciprofloxacin was used (MIC S. aureus ATCC 25923 and P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 = 1.50 µM; MIC E. faecalis ATCC 29212 = 3.00 µM; MIC E. coli ATCC 25922 = 0.048 µM; MIC S. aureus 272123 = 12.5 µM; MIC S. typhimurium SL1344 = 6.25 µM).
3.6. Quorum-Sensing Inhibition
The QS inhibitory effect of the compounds was examined on the previously described bacterial strains. Using a modified Luria-Bertani Agar medium [1.0 g yeast extract (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), 10.0 g tryptone (Biolab, Budapest, Hungary), 10.0 g NaCl (Molar Chemicals, Halásztelek, Hungary), 1.0 g K2HPO4 (Biolab, Budapest, Hungary), 0.3 g MgSO4 × 7H2O (Reanal, Budapest, Hungary), 5 mL Fe-EDTA stock solution and 20.0 g of bacteriological agar (Molar Chemicals, Halásztelek, Hungary) per 1 L of media], the bacteria were directly inoculated as single lines, with EZF and CV026 being paralleled inoculated at an approximate distance of 5 mm. The volume of compound solution applied was 8 µL of a stock solution of 10 mM, through the impregnation of filter paper disks (7 mm diameter), which were placed on the center of the inoculated line(s). As a positive control, the antipsychotic PMZ was used.
After a 24–48 h period of incubation at room temperature (20 °C), the results were determined by visual inspection and measurement of the discolored, but intact, bacterial colonies with a ruler [37,47].
3.7. Inhibition of Biofilm Formation
The ability of the compounds to inhibit the formation of biofilm was assessed by the crystal violet (CV) method. For this assay, the Gram-positive S. aureus ATCC 25923 and S. aureus 272123 were used. The dye CV, used in ethanol at 0.1% v/v, made the visualization of the biofilm formation possible.
The initial inoculum was incubated in Tryptic-Soy broth (TSB, Biokar Diagnostics, Allone, Beauvais, France), overnight, followed by the dilution to 0.1 (OD600). Afterwards, the bacterial suspension was added to 96-well microtiter plates and the compounds were added at a concentration of half their MIC, or 100 µM if their MIC was above this concentration, to a final volume of 200 µL per well.
The assay lasted for 48 h, with the plates being gently stirred (100 rpm) at 30 °C. After this incubation period, the TSB medium was discarded, and the plates were washed three times with tap water to remove unattached cells. Then, 200 µL of the CV solution were added to the wells, followed by a 15-min incubation at room temperature. The CV solution was then discarded, followed by two times of tap water washing. Finally, 200 µL of 70% ethanol solution were added to the wells, followed by a gentle shake to form a homogenous mixture.
The determination of biofilm formation was performed using a Multiscan EX ELISA plate reader (Thermo Labsystems, Cheshire, WA, USA) to measure the OD600. The effect of the compounds against the formation of biofilm was expressed as the percentage (%) of decrease in biomass. The alkaloid reserpine, which has been described to be a biofilm formation inhibitor in S. aureus strains, was used as positive control [48].
3.8. Efflux Pump Inhibition Assay
The ability of the compounds to inhibit efflux pumps was evaluated through the real-time ethidium bromide accumulation assay, based on measuring the fluorescence emmited by a complex formed between ethidium bromide, an efflux pump substrate, and the bacterial nucleic acids, using a CLARIOstar Plus plate reader (BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany). The strains used were S. typhimurium SL1344 and S. aureus 272123, which were cultured in Luria-Bertani broth (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and TSB, respectively, at 37 °C until they reached an OD600 between 0.4 and 0.6. When this OD was achieved, the culture was centrifuged at 13,000× g for 3 min, and the pellet was washed and resuspended with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), followed by another centrifugation and PBS washing. A solution of EB was prepared at a nontoxic concentration in PBS (1 µg/mL), which was used for making the solution of the compounds at 50 µM. Then, to a 96-well black microtiter plate (Greiner Bio-One Hungary Kft, Mosonmagyaróvár, Fertősor, Hungary), 50 µL of the compound solution and 50 µL of bacterial suspension were added to each well.
The fluorescence was monitored at excitation and emission wavelengths of 530 nm and 600 nm every minute for one hour, on a real-time basis. The activity of the compounds was calculated considering the RFI at the last time point (minute 60) of the assay, using the following formula:
In this scope, RFtreated corresponds to the relative fluorescence (RF) at minute 60 of the EB accumulation assay in the presence of the compound. Oppositely, RFuntreated is the same time point of the negative control, consisting only of the solvent used, which was DMSO 1% v/v. As positive controls, reserpine (S. aureus 272123) and CCCP (S. typhimurium SL1344) were used, at the concentration of 25 µM.
The accumulation curves containing the RFI for each time point were designed using Microsoft Excel® (Redmond, WA, USA).
3.9. Docking Studies
The docking studies were performed on the crystal structures of the three portions of the AcrAB-TolC efflux system, which were all deposited in the Protein Data Bank [49] (AcrB (PDB: 4DX5) [41]; AcrA (PDB: 2F1M) [50]; TolC (PDB: 1EK9) [51]). The docking scores obtained are in Table S1 (Supplementary Materials). The sites chosen were the ones described as relevant in the literature: for the efflux pump AcrB, the substrate-binding site (SBS) and the hydrophobic trap (HT) [42]; the helical hairpin (HH) and the lipoyl domain (LD) for the periplasmic adaptor AcrA [52]; and for the transmembrane channel TolC, the region containing the lysine residues that interact with the 3,3′-dithiobis(sulfosuccinimidyl propionate) bifunctional crosslinker [52].
The structures of compound 3a–c and 5 were drawn with ChemDraw (PerkinElmer Informatics, Waltham, MA, USA), as were the known AcrAB-TolC inhibitors phenyl-arginyl-β-naphthylamide (PAβN), minocycline, D13-9001, MBX-3132, and doxorubicin. In order to obtain the most favorable energetical conformation, ArgusLab was used. For the docking studies, the software applied was AutoDock Vina (Scripps, San Diego, CA, USA) [53], and the top nine poses were collected for each molecule. The most favorable binding conformation, associated with the lowest docking score value, was visualized using PyMol (Schrödinger, New York, NY, USA) [54].
4. Conclusions
In summary, we have synthetized four 9-xanthenyl derivatives and assessed their antibacterial activity and influence on bacterial mechanisms of resistance, namely, efflux pump inhibition, QS inhibition, and influence on biofilm formation. The compounds herein studied, particularly the xanthene sulfonamide derivatives 3b and 3c, showed interesting preliminary results regarding their impact on different mechanisms of bacterial resistance. In the future, a comprehensive series of related compounds will be synthesized to allow their assessment against a larger set of bacterial strains and the establishment of a structure-activity relationship of the 9-xanthenyl derivatives, as well as to study their safety, stability, and pharmacokinetic properties. Furthermore, studies on the specific pump being inhibited are warranted, which can be achieved by genetic assays.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ddc1010004/s1, Figure S1: 1H and 13C NMR of compound 3a; Figure S2. 1H and 13C NMR of compound 3b; Figure S3. 1H and 13C NMR of compound 3c; Figure S4. 1H and 13C NMR of compound 5; Figure S5. Chromatogram (HPLC) of compound 3a. Purity (% a/a): 99.2%; Figure S6. Chromatogram (HPLC) of compound 3b. Purity (% a/a): 99.9%; Figure S7. Chromatogram (HPLC) of compound 3c. Purity (% a/a): 99.9%; Figure S8. Chromatogram (HPLC) of compound 5. Purity (% a/a): 99.5%; Figure S9. RFI curves of the tested compounds against S. aureus 272123; Figure S10. RFI curves of the tested compounds against S. typhimurium SL1344; Figure S11. Fluorescence studies of compound 3a; Figure S12. Fluorescence studies of compound 3b; Figure S13. Fluorescence studies of compound 3c; Table S1. Docking scores (kcal/mol) for the xanthenes and reference compounds against bacterial efflux pumps.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S. and E.S.; Investigation, M.M., F.D., L.G. and P.M.-d.-C.; Methodology, D.I.S.P.R. and N.S.; Writing—original draft, M.M. and F.D.; Writing—review & editing, M.P., P.M.-d.-C., G.S. and E.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by national funds through FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology within the scope of UIDB/04423/2020, UIDP/04423/2020, and under the project PTDC/SAU-PUB/28736/2017 (reference POCI-01-0145-FEDER-028736), PTDC/CTA-AMB/0853/2021, and EXPL/CTA-AMB/0810/2021, co-financed by COMPETE 2020, Portugal 2020 and the European Union through the ERDF and by FCT through national funds, and CESPU by the Project CHIRALSINTESE_APSFCT_IINFACTS_2021.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of the article is available within the article.
Acknowledgments
F.D. and M.M. acknowledge FCT for their PhD grants (SFRH/BD/144681/2019 and SFRH/BD/146211/2019, respectively). The authors thank Sara Cravo, Gisela Adriano and Gabor Tóth for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
No conflict of interest was declared.
References
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations/the Review on Antimicrobial Resistance Chaired by Jim O’Neill. Available online: https://wellcomecollection.org/works/rdpck35v (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Kong, Q.; Yang, Y. Recent advances in antibacterial agents. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 35, 127799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi Bezmin Abadi, A.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Haertlé, T.; Blatt, N.L. World Health Organization Report: Current Crisis of Antibiotic Resistance. BioNanoScience 2019, 9, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, J.L. Biofilm-related disease. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2018, 16, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhas, A.M.; Lawton, R.; Reidy, M.; Nathwani, D.; Clift, B.A. Causative organisms in revision total hip & knee arthroplasty for infection: Increasing multi-antibiotic resistance in coagulase-negative Staphylococcus and the implications for antibiotic prophylaxis. Surgeon 2015, 13, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial Quorum Sensing: Its Role in Virulence and Possibilities for Its Control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Givskov, M. Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqua, C.; Greenberg, E.P. Listening in on bacteria: Acyl-homoserine lactone signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang-Kan, X.; Neuberger, A.; van Veen, H.W.; Pos, K.M.; Piddock, L.J.V.; Luisi, B.F. Multidrug efflux pumps: Structure, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alav, I.; Sutton, J.M.; Rahman, K.M. Role of bacterial efflux pumps in biofilm formation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2003–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, M.; Resende, D.I.S.P.; Durães, F.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Sousa, E. Xanthenes in Medicinal Chemistry—Synthetic strategies and biological activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 113085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmak, A.; Niknam, K.; Mohebbi, G.; Pournabi, H. Antibacterial studies of hydroxyspiro[indoline-3,9-xanthene]trione against spiro[indoline 3,9-xanthene]trione and their use as acetyl and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, V.S.; Padalkar, V.S.; Phatangare, K.R.; Umape, P.G.; Borase, B.N.; Sekar, N. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of Novel (1H-Benzo[d]imidazole-2-yl)-6-(diethylamino)-3H-one-xanthene, Phenoxazine, and Oxazine. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2015, 52, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Demir, E.; Bekci, H. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of novel xanthene sulfonamide and carboxamide derivatives. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2013, 28, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaki, D.; Amininasab, S.M.; Namazi, H. Novel poly(imide-ether)s based on xanthene and a corresponding composite reinforced with a GO grafted hyperbranched polymer: Fabrication, characterization, and thermal, photophysical, antibacterial and chromium adsorption properties. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 17346–17359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorokhov, V.Y.; Makhova, T.V. Synthesis and Antibactericidal Activities of Amines and Imines Containing (Aza, Thio) Xanthene Rings. Pharm. Chem. J. 2016, 50, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amininasab, S.M.; Esmaili, S.; Shami, Z. Synthesis of polyamides contains pyridine and xanthene pendant group: Study of optical, thermal, antibacterial activity and hexavalent chromium ion adsorption. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2020, 57, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabor Varga, Z.; Agnes Szabo, M.; Schelz, Z.; Szegedi, E.; Amaral, L.; Molnar, J. Quorum Sensing Inhibition by Phenothiazines and Related Compounds. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2011, 8, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durães, F.; Palmeira, A.; Cruz, B.; Freitas-Silva, J.; Szemerédi, N.; Gales, L.; da Costa, P.M.; Remião, F.; Silva, R.; Pinto, M.; et al. Antimicrobial Activity of a Library of Thioxanthones and Their Potential as Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, M.M.; Leandro, C.; Ordway, D.; Martins, M.; Viveiros, M.; Pacheco, T.; Kristiansen, J.E.; Amaral, L. Phenothiazines alter resistance of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to oxacillin in vitro. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2003, 22, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, M.M.; Leandro, C.; Ordway, D.; Martins, M.; Viveiros, M.; Pacheco, T.; Molnar, J.; Kristiansen, J.E.; Amaral, L. Thioridazine reduces resistance of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus by inhibiting a reserpine-sensitive efflux pump. Vivo 2006, 20, 361. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, L.; Martins, A.; Spengler, G.; Molnar, J. Efflux pumps of Gram-negative bacteria: What they do, how they do it, with what and how to deal with them. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaatz, G.W.; Moudgal, V.V.; Seo, S.M.; Kristiansen, J.E. Phenothiazines and thioxanthenes inhibit multidrug efflux pump activity in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.L. Sulphonamides: Updates on use in veterinary medicine. Vet. Dermatol. 1999, 10, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, M.; Kristiansen, J.E. On the 75th anniversary of Prontosil. Dye. Pigment. 2011, 88, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- al-Rashida, M.; Hussain, S.; Hamayoun, M.; Altaf, A.; Iqbal, J. Sulfa Drugs as Inhibitors of Carbonic Anhydrase: New Targets for the Old Drugs. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 162928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubatières-Mariani, M.-M. La découverte des sulfamides hypoglycémiants. J. Soc. Biol. 2007, 201, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, N.; Pandeya, S.N.; Khan, S.A.; Stables, J.; Rana, A.; Alam, M.; Arshad, M.F.; Bhat, M.A. Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of sulfonamide derivatives-hydrophobic domain. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolotowicz, K.J.; Dwyer, M.; Ryan, D.; Cheng, J.; Cashman, E.A.; Moore, S.; Mercola, M.; Cashman, J.R. Novel tertiary sulfonamides as potent anti-cancer agents. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4441–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, S.; Takashi, O.; Antonio, M.; Claudiu, T.S. Anticancer and Antiviral Sulfonamides. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 925–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.F.; Frank, V.S. Xanthydrol as a reagent for the identification of sulfonamides. J. Org. Chem. 1944, 9, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalyk, R.E.; Chatten, L.G. Alkylation by secondary alcohols. I. The reaction of xanthydrol with some N1-monosubstituted sulfanilamides and related compounds. Can. J. Chem. 1967, 45, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westcott, W.L. Reactions of Xanthydrol with the Amino Acids and Cytochrome C; University of Utah: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Tacic, A.; Nikolic, V.; Nikolic, L.; Savic, I. Antimicrobial sulfonamide drugs. Adv. Technol. 2017, 6, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, E.E. Sulfonamide antibiotics. Prim. Care Update OB/GYNS 1998, 5, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydel, J.K. Sulfonamides, Structure-Activity Relationship, and Mode of Action: Structural Problems of the Antibacterial Action of 4-Aminobenzoic Acid (PABA) Antagonists. J. Pharm. Sci. 1968, 57, 1455–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdács, M.; Spengler, G. Standard operating procedure (SOP) for disk diffusion-based quorum sensing inhibition assays. Acta Pharm. Hung. 2020, 89, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gajdács, M.; Spengler, G. The Role of Drug Repurposing in the Development of Novel Antimicrobial Drugs: Non-Antibiotic Pharmacological Agents as Quorum Sensing-Inhibitors. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durães, F.; Resende, D.I.S.P.; Palmeira, A.; Szemerédi, N.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Spengler, G.; Sousa, E. Xanthones Active against Multidrug Resistance and Virulence Mechanisms of Bacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durães, F.; Cravo, S.; Freitas-Silva, J.; Szemerédi, N.; Martins-da-Costa, P.; Pinto, E.; Tiritan, M.E.; Spengler, G.; Fernandes, C.; Sousa, E.; et al. Enantioselectivity of Chiral Derivatives of Xanthones in Virulence Effects of Resistant Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, T.; Cha, H.; Seeger, M.A.; Brandstaetter, L.; El-Delik, J.; Bohnert, J.A.; Kern, W.V.; Verrey, F.; Gruetter, M.G.; Diederichs, K.; et al. 4DX5. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4DX5 (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Aron, Z.; Opperman, T.J. The hydrophobic trap-the Achilles heel of RND efflux pumps. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Espenson, J.H. Organic Reactions Catalyzed by Methylrhenium Trioxide: Dehydration, Amination, and Disproportionation of Alcohols. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xia, W.; Yang, M.; Zhang, T. Palladium–copper catalyzed C(sp3)–C(sp2) bond C–H activation cross-coupling reaction: Selective arylation to synthesize 9-aryl-9H-xanthene and 9,9-diaryl-xanthene derivatives. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 84748–84751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 11th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nové, M.; Kincses, A.; Szalontai, B.; Rácz, B.; Blair, J.M.A.; González-Prádena, A.; Benito-Lama, M.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Spengler, G. Biofilm Eradication by Symmetrical Selenoesters for Food-Borne Pathogens. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parai, D.; Banerjee, M.; Dey, P.; Mukherjee, S.K. Reserpine attenuates biofilm formation and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, J.L.; Lin, D.; Jiang, J.; Manning, N.O.; Prilusky, J.; Ritter, O.; Abola, E.E. Protein Data Bank (PDB): Database of three-dimensional structural information of biological macromolecules. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 1998, 54, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolosko, J.; Bobyk, K.; Zgurskaya, H.I.; Ghosh, P. Conformational Flexibility in the Multidrug Efflux System Protein AcrA. Structure 2006, 14, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronakis, V.; Sharff, A.; Koronakis, E.; Luisi, B.; Hughes, C. Crystal structure of the bacterial membrane protein TolC central to multidrug efflux and protein export. Nature 2000, 405, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, M.; Yu, Z.; Bell, J.M.; Wang, H.; Forrester, I.; Villarreal, H.; Jakana, J.; Du, D.; Luisi, B.F.; et al. In situ structure and assembly of the multidrug efflux pump AcrAB-TolC. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, D.; de Groot, B.L. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).