Structural Parameters of the Interaction between Ciprofloxacin and Human Topoisomerase-II β Enzyme: Toward New 19F NMR Chemical Shift Probes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
2.2. 19F NMR Chemical Shift (δ) Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
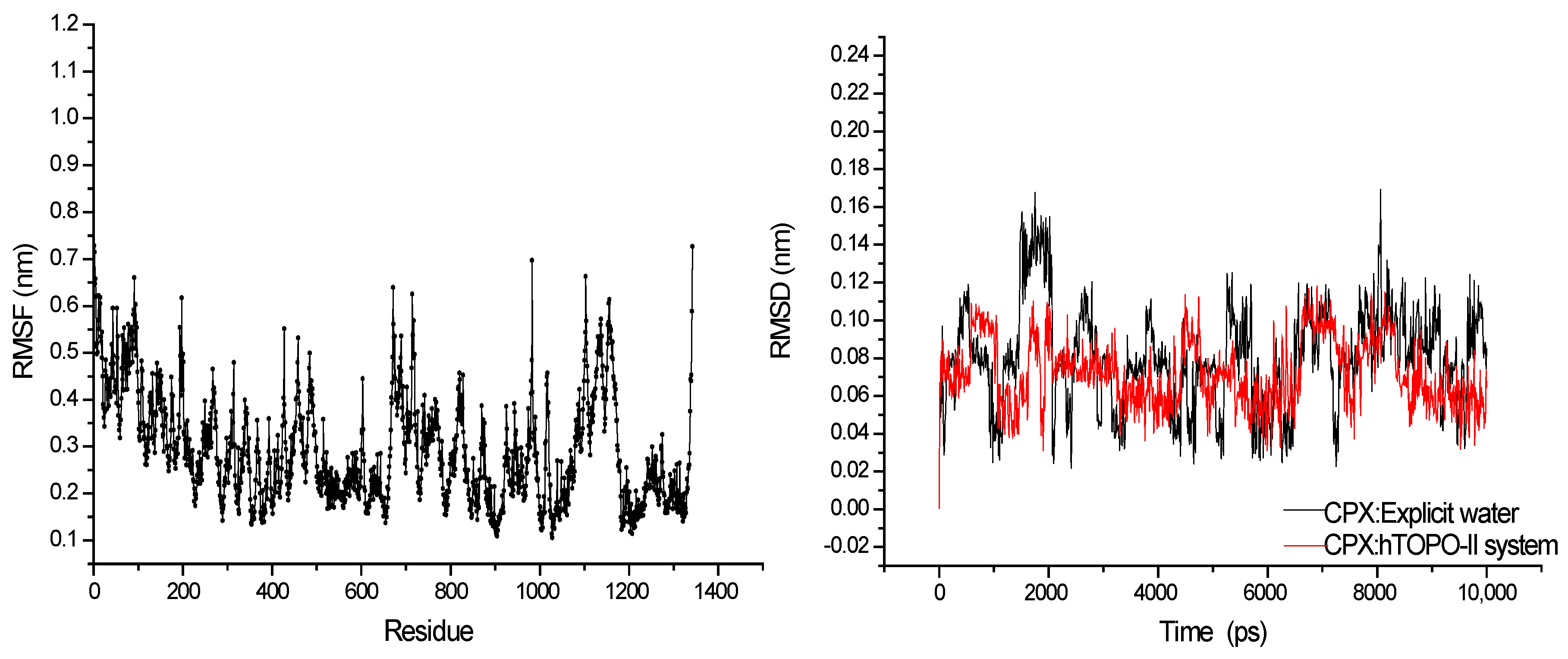
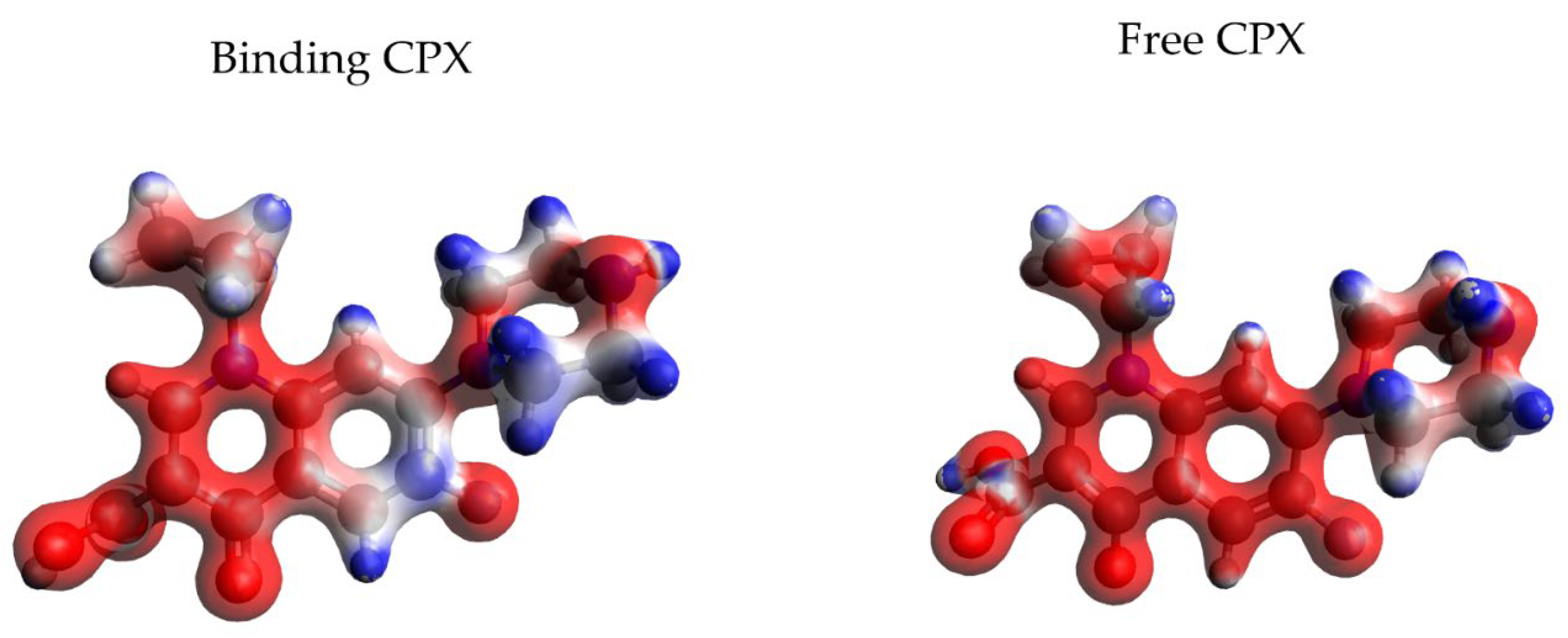
3.1. MD Simulations
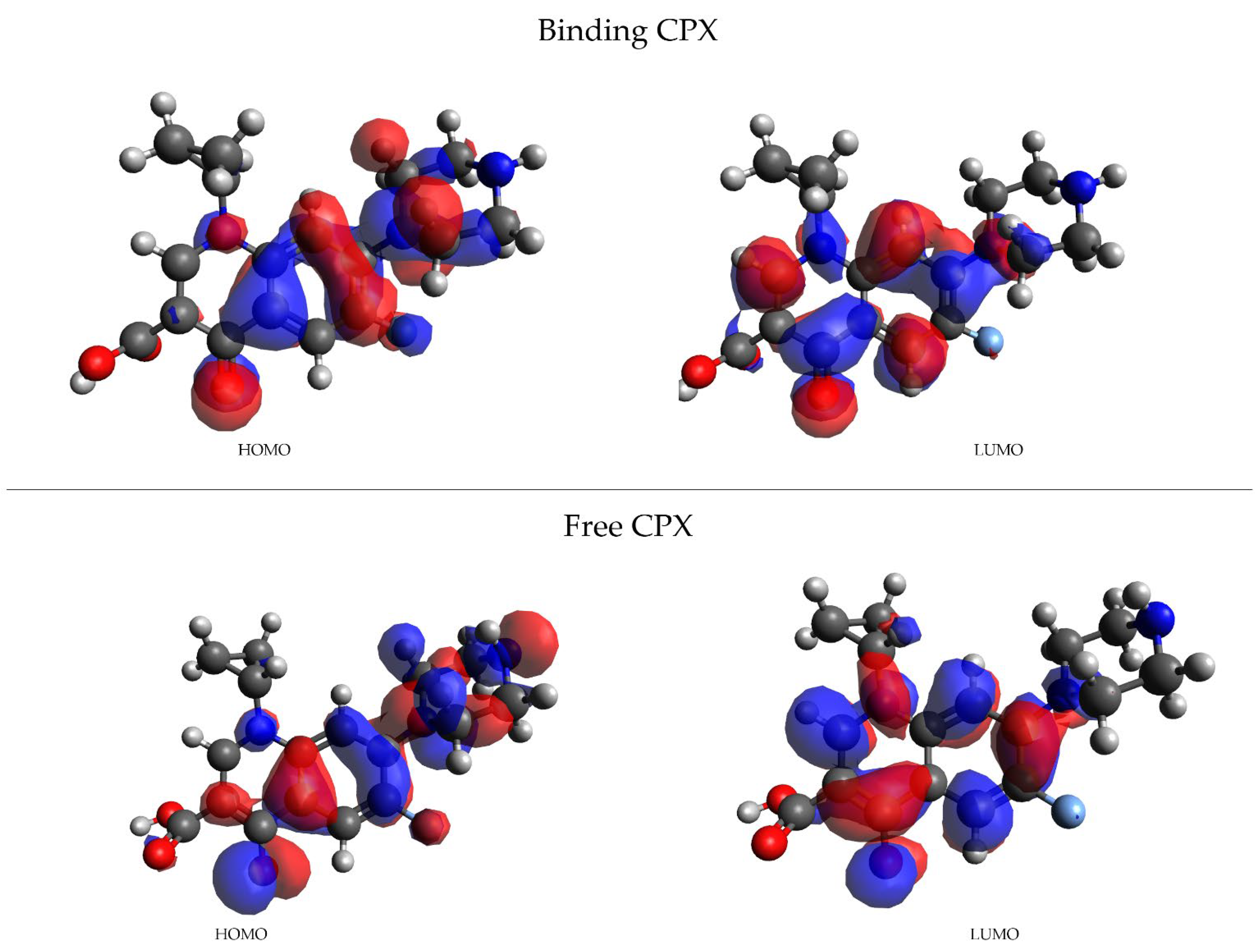
3.2. Spectroscopic Parameters: 19F- Chemical Shifts (δ)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pitman, S.K.; Hoang, U.T.P.; Wi, C.H.; Alsheikh, M.; Hiner, D.A.; Percival, K.M. Revisiting oral fluoroquinolone and multivalent cation drug-drug interactions: Are they still relevant? Antibiotics 2019, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, P.; Su, B.; Liu, R. Probing the binding of two fluoroquinolones to lysozyme: A combined spectroscopic and docking study. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suaifan, G.A.R.Y.; Mohammed, A.A.M. Fluoroquinolones structural and medicinal developments (2013–2018): Where are we now? Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3005–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.; Alminderej, F.M.; Messaoudi, S.; Saleh, S.M. Ratiometric ultrasensitive optical chemisensor film based antibiotic drug for Al(III) and Cu(II) detection. Talanta 2021, 221, 121412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.; Park, S.E.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.D.A.A.; Sayed, M.A.; Kwon, Y. Novel N-4-piperazinyl-ciprofloxacin-chalcone hybrids: Synthesis, physicochemical properties, anticancer and topoisomerase I and II inhibitory activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majalekar, P.P.; Shirote, P.J. Fluoroquinolones: Blessings or Curses. Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 1354–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.A.; Mercer, S.L.; Osheroff, N.; Deweese, J.E. Etoposide Quinone Is a Redox-Dependent Topoisomerase II Poison. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5660–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idowu, T.; Schweizer, F. Ubiquitous nature of fluoroquinolones: The oscillation between antibacterial and anticancer activities. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisacchi, G.; Hale, M. A “Double-Edged” Scaffold: Antitumor Power within the Antibacterial Quinolone. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 520–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heestand, G.M.; Schwaederle, M.; Gatalica, Z.; Arguello, D.; Kurzrock, R. Topoisomerase expression and amplification in solid tumours: Analysis of 24,262 patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 83, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, N.; Suresh, A.; Yerramsetty, S.; Bhadra, M.P.; Alvala, M.; Sekhar, K.V.G.C. Anti-proliferative activity, molecular modeling studies and interaction with calf thymus DNA of novel ciprofloxacin analogues. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 130, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beberok, A.; Wrześniok, D.; Rok, J.; Rzepka, Z.; Respondek, M.; Buszman, E. Ciprofloxacin triggers the apoptosis of human triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells via the p53/Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chekerov, R.; Klaman, I.; Zafrakas, M.; Könsgen, D.; Mustea, A.; Petschke, B.; Lichtenegger, W.; Sehouli, J.; Dahl, E. Altered Expression Pattern of Topoisomerase IIα in Ovarian Tumor Epithelial and Stromal Cells after Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faggad, A.; Darb-Esfahani, S.; Wirtz, R.; Sinn, B.; Sehouli, J.; Könsgen, D.; Lage, H.; Weichert, W.; Noske, A.; Budczies, J.; et al. Topoisomerase IIα mRNA and protein expression in ovarian carcinoma: Correlation with clinicopathological factors and prognosis. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Li, L.D.; Li, J.; Lu, X. Targeting of topoisomerases for prognosis and drug resistance in ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Kan, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.; Ma, H. A red lysosome-targeted fluorescent probe for carboxylesterase detection and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, E.; Hevenern, T.A.; Verstak, K.E.L.; Daniel, L.; Riggsbee, J.W.M. Recent developments in topoisomerase-targeted cancer chemotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 844–861. [Google Scholar]
- Cinelli, M.A. Topoisomerase 1B poisons: Over a half-century of drug leads, clinical candidates, and serendipitous discoveries. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1294–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A. Prions, prion-like prionoids, and neurodegenerative disorders. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2016, 19, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilleron, S.; Soto-Perez-de-Celis, E.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F.; Sarfati, D. Estimated global cancer incidence in the oldest adults in 2018 and projections to 2050. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, N.; Setua, S.; Kashyap, V.; Khan, S.; Jaggi, M.; Yallapu, M.; Chauhan, S.; Dan, N.; Setua, S.; Kashyap, V.K.; et al. Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Cancer Therapy: Chemistry to Clinical Implications. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassab, A.E.; Gedawy, E.M. Novel ciprofloxacin hybrids using biology oriented drug synthesis (BIODS) approach: Anticancer activity, effects on cell cycle profile, caspase-3 mediated apoptosis, topoisomerase II inhibition, and antibacterial activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashayan, N.; Pharoah, P.D.P. The challenge of early detection in cancer. Science 2020, 368, 589–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtedahl, K. Challenges in early diagnosis of cancer: The fast track. Scand. J. Prim. Health Care 2020, 38, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Module 3: Early Detection. Cancer Control: Knowledge into Action: WHO Guide for Effective Programmes 2007, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Unger-Saldaña, K. Challenges to the early diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer in developing countries. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lue, N.; Kang, J.W.; Yu, C.-C.; Barman, I.; Dingari, N.C.; Feld, M.S.; Dasari, R.R.; Fitzmaurice, M. Portable Optical Fiber Probe-Based Spectroscopic Scanner for Rapid Cancer Diagnosis: A New Tool for Intraoperative Margin Assessment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, B.T.L.L.; Gonçalves, M.A.; Mancini, D.T.; Kuca, K.; Ramalho, T.C. First attempts of the use of 195Pt NMR of phenylbenzothiazole complexes as spectroscopic technique for the cancer diagnosis. Molecules 2019, 24, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Rocha, E.P.; Rodrigues, H.A.; da Cunha, E.F.F.; Ramalho, T.C. Probing kinetic and thermodynamic parameters as well as solvent and substituent effects on spectroscopic probes of 2-amino-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2016, 1096, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, B.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, X. An enzyme activated fluorescent probe for LTA4H activity sensing and its application in cancer screening. Talanta 2023, 253, 123887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Bai, D.; Yu, H.; Fu, Y.; Song, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Detection of rare CTCs by electrochemical biosensor built on quaternary PdPtCuRu nanospheres with mesoporous architectures. Talanta 2023, 253, 123955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gab, M.; Allah, A.; Sarhan, M.A.; Elshennawy, M.N. Edge U-Net: Brain tumor segmentation using MRI based on deep U-Net model with boundary information. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 118833. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; An, Y.J.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, J.E.; Park, S.; Choi, S.H. Ex vivo NMR metabolomics approach using cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of primary CNS lymphoma: Correlation with MR imaging characteristics. Cancer Med. 2022, 00, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, H.; Maryam, A.; Bokhari, S.A.; Ashiq, A.; Rauf, S.A.; Khalid, R.R.; Qureshi, F.A.; Siddiqi, A.R. Design, synthesis, characterization and computational docking studies of novel sulfonamide derivatives. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, J.R.; Anthony, S.; Johanssen, V.A.; Yeo, T.; Sealey, M.; Yates, A.G.; Smith, C.F.; Claridge, T.D.W.; Nicholson, B.D.; Moreland, J.A.; et al. Metabolomic Biomarkers in Blood Samples Identify Cancers in a Mixed Population of Patients with Nonspecific Symptoms. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derveauex, E.; Thomeer, M.; Mesotten, L.; Reekmans, G.; Adriaensens, P. Detection of Lung Cancer via Blood Plasma and 1H-NMR Metabolomics: Validation by a Semi-Targeted and Quantitative Approach Using a Protein-Binding Competitor. Metabolites 2021, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.N.; Lee, H.; Park, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, S.; Kim, J.J. Screening for Early Gastric Cancer Using a Noninvasive Urine Metabolomics Approach. Cancers 2020, 12, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michálková, L.; Horník, Š.; Sýkora, J.; Habartová, L.; Setnička, V. Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer via1H NMR metabolomics of human plasma. Analyst 2018, 143, 5974–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkonen, J.J.W.; Singh, S.P.; Akhi, R.; Salo, T.; Lappalainen, R.; González-Arriagada, W.A.; Lopes, M.A.; Kullaa, A.M.; Myllymaa, S. Potential role of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to identify salivary metabolite alterations in patients with head and neck cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6795–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erben, V.; Bhardwaj, M.; Schrotz-King, P.; Brenner, H. Metabolomics Biomarkers for Detection of Colorectal Neoplasms: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2018, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Liao, G.; Wen, X.; Chen, W.; Cheng, S.; Stolzenburg, J.U.; Ganzer, R.; Neuhaus, J. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy as a new approach for improvement of early diagnosis and risk stratification of prostate cancer. J. Zhejiang Univ. B 2017, 18, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Yu, Q.; An, L.-K. The first small fluorescent probe as Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1) substrate. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 169, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, H. Design principles of spectroscopic probes for biological applications. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6309–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanley, P.D. Principles and Topical Applications of 19F NMR Spectrometry. In Organofluorines. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Neilson, A.H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 3N, pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- .Marsh, E.N.G.; Suzuki, Y. Using 19F NMR to Probe Biological Interactions of Proteins and Peptides. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, D.; Phelan, A.; Murphy, C.D.; Cobb, S.L. 19F NMR as a tool in chemical biology. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 293–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawaria, R.; Hussain, M.; Khalid, M.; Khan, M.U.; Tahir, M.N.; Naseer, M.M.; Braga, A.A.C.; Shafiq, Z. Synthesis, crystal structure analysis, spectral characterization and nonlinear optical exploration of potent thiosemicarbazones based compounds: A DFT refine experimental study. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 486, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.; Stamboliyska, B.; Mikhova, B.; Breznica-Selmani, P.; Mladenovska, K.; Popovski, E. Calculations of 13C NMR chemical shifts and F–C coupling constants of ciprofloxacin. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019, 57, S75–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Rhodes, S.; Winder, D.; Atkinson, A.; Gibson, J.; Ming, W.; Padgett, C.; Landge, S.; Aiken, K. Spectroscopic investigation of bis-appended 1,2,3-triazole probe for the detection of Cu(II) ion. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1134, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramalho, T.C.; Taft, C.A. Thermal and solvent effects on the NMR and UV parameters of some bioreductive drugs. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 054319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudipeddi, A.; Vasudevan, S.; Shanmugam, K.; Mohan, S.S.; Vairaprakash, P.; Neelakantan, P.; Balraj, A.S.; Solomon, A.P. Design, dynamic docking, synthesis, and in vitro validation of a novel DNA gyrase B inhibitor. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.; Sankhe, K.; Suvarna, V.; Sherje, A.; Patel, K.; Dravyakar, B. DNA gyrase inhibitors: Progress and synthesis of potent compounds as antibacterial agents. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malde, A.K.; Zuo, L.; Breeze, M.; Stroet, M.; Poger, D.; Nair, P.C.; Oostenbrink, C.; Mark, A.E. An Automated force field Topology Builder (ATB) and repository: Version 1.0. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 4026–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindah, E. Gromacs: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christen, M.; Hünenberger, P.H.; Bakowies, D.; Baron, R.; Bürgi, R.; Geerke, D.P.; Heinz, T.N.; Kastenholz, M.A.; Kräutler, V.; Oostenbrink, C.; et al. The GROMOS software for biomolecular simulation: GROMOS05. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1719–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.A.; Santos, L.S.; Prata, D.M.; Peixoto, F.C.; da Cunha, E.F.F.; Ramalho, T.C. Optimal wavelet signal compression as an efficient alternative to investigate molecular dynamics simulations: Application to thermal and solvent effects of MRI probes. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2017, 136, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dunning, T.H., Jr. Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. I. The atoms boron through neon and hydrogen. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 90, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.A.; Dunning, T.H., Jr.; Harrison, R.J. Electron affinities of the first-row atoms revisited. Systematic basis sets and wave functions. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 96, 6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woon, D.E., Jr. Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. III. The atoms aluminum through argon. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 98, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolinski, K.; Hinton, J.F.; Pulay, P. Efficient implementation of the gauge-independent atomic orbital method for NMR chemical shift calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 112, 8251–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Urueta, R.; Mestre-Quintero, K.; Vivas-Reyes, R. DFT-GIAO Calculation of Properties of 19 F NMR and Stability Study of Environmentally Relevant Perfluoroalkylsulfonamides (PFASAmide). Artic. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar]
- Dapprich, S.; Komáromi, I.; Byun, K.S.; Morokuma, K.; Frisch, M.J. A new ONIOM implementation in Gaussian98. Part I. The calculation of energies, gradients, vibrational frequencies and electric field derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem. 1999, 461–462, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal Solvation Model Based on Solute Electron Density and on a Continuum Model of the Solvent Defined by the Bulk Dielectric Constant and Atomic Surface Tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trefi, S.; Gilard, V.; Malet-Martino, M.; Martino, R. Generic ciprofloxacin tablets contain the stated amount of drug and different impurity profiles: A 19F, 1H and DOSY NMR analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 44, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-F.; Jiang, M.-H.; Sun, L.-L.; Zheng, F.; Dong, L.; Shah, V.; Shen, W.-B.; Ding, Y. Quantitative analysis of sitagliptin using the 19F-NMR method: A universal technique for fluorinated compound detection. Analyst 2015, 140, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezelarab, H.A.A.; Abbas, S.H.; Hassan, H.A.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.D.A. Recent updates of fluoroquinolones as antibacterial agents. Arch. Pharm. 2018, 351, 1800141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fief, C.A.; Hoang, K.G.; Phipps, S.D.; Wallace, J.L.; Deweese, J.E. Examining the Impact of Antimicrobial Fluoroquinolones on Human DNA Topoisomerase IIα and IIβ. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 4049–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beberok, A.; Wrześniok, D.; Minecka, A.; Rok, J.; Delijewski, M.; Rzepka, Z.; Respondek, M.; Buszman, E. Ciprofloxacin-mediated induction of S-phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in COLO829 melanoma cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, C.E.; Takahashi, K.C.; Williams, G.M. Inhibition of human topoisomerase IIα by fluoroquinolones and ultraviolet A irradiation. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 69, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swedan, H.K.; Kassab, A.E.; Gedawy, E.M.; Elmeligie, S.E. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel ciprofloxacin derivatives as potential anticancer agents targeting topoisomerase II enzyme. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazandaran, K.E.; Mirshokraee, S.A.; Didehban, K.; Houshdar Tehrani, M.H. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Ciprofloxacin- Peptide Conjugates as Anticancer Agents. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2019, 18, 1823. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, H.H.H.; Abd El-Hafeez, A.A.; Ebeid, K.; Mekkawy, A.I.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Wafa, E.I.; Alhaj-Suliman, S.O.; Salem, A.K.; Ghosh, P.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.D.A.; et al. New 1,2,3-triazole linked ciprofloxacin-chalcones induce DNA damage by inhibiting human topoisomerase I& II and tubulin polymerization. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 1346–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, H.H.H.; Abbas, S.H.; Hayallah, A.M.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.D.A.; Mostafa, Y.A. Novel urea linked ciprofloxacin-chalcone hybrids having antiproliferative topoisomerases I/II inhibitory activities and caspases-mediated apoptosis. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 106, 104422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, T.A.; Ramalho, T.C. Ciprofloxacin/Topoisomerase-II complex as a promising dual UV–Vis/fluorescent probe: Accomplishments and opportunities for the cancer diagnosis. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2022, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, T.; Karim, K.; Piletsky, S. No Title. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.K.; Karuppayil, S.M. Molecular docking studies on thirteen fluoroquinolines with human topoisomerase II a and b. Silico Pharmacol. 2017, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, J.R.; Joshi, H.V.; Shah, U.A.; Patel, J.K. A Review on Computational Software Tools for Drug Design and Discovery. Indo. Glob. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 53–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajeva, I.; Tsakovska, I.; Pencheva, T.; Alov, P.; Al Sharif, M.; Lessigiarska, I.; Jereva, D.; Diukendjieva, A. In silico Studies of Biologically Active Molecules. Stud. Comput. Intell. 2021, 934, 421–451. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero, J. The latest automated docking technologies for novel drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 16, 625–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, L.; Bhat, S.; Akinsanya, K.; Abel, R. From computer-aided drug discovery to computer-driven drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2021, 39, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.; Tripathi, T. Molecular Dynamics Simulation in Drug Discovery: Opportunities and Challenges. In Innovations and Implementations of Computer Aided Drug Discovery Strategies in Rational Drug Design; Singh, S.K.., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 295–316. [Google Scholar]
- McClendon, A.K.; Osheroff, N. DNA Topoisomerase II, Genotoxicity, and Cancer. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2007, 623, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sales, T.A.; Marcussi, S.; da Cunha, E.F.F.; Kuca, K.; Ramalho, T.C. Can inhibitors of snake venom phospholipases A2 lead to new insights into anti-inflammatory therapy in humans? A theoretical study. Toxins 2017, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreiner, W.; Karch, R.; Knapp, B.; Ilieva, N. Relaxation estimation of RMSD in molecular dynamics immunosimulations. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2012, 2012, 173521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Biswas, G.P.; Mahata, N.; Ghanta, S.; Bhunia, B. Exploration of binding mechanism of triclosan towards cancer markers using molecular docking and molecular dynamics. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekmenev, E.Y.; Chow, S.K.; Tofan, D.; Weitekamp, D.P.; Ross, B.D.; Bhattacharya, P. Fluorine-19 NMR chemical shift probes molecular binding to lipid membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 6285–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maxwell, R.J.; Workman, P.; Griffiths, J.R. Demonstration of tumor-selective retention of fluorinated nitroimidazole probes by 19F magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1989, 16, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, K.L.; Srivastava, K.; Pierre, V.C. Fluorinated paramagnetic complexes: Sensitive and responsive probes for magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojugo, A.S.E.; Mcsheehy, P.M.J.; Mcintyre, D.J.O.; Mccoy, C.; Stubbs, M.; Leach, M.O.; Judson, I.R.; Grifths, J.R. Measurement of the extracellular pH of solid tumours in mice by magnetic resonance spectroscopy: A comparison of exogenous 19 F and 31 P probes. NMR Biomed. Int. J. Devoted Dev. Appl. Magn. Reson. Vivo 1999, 12, 495–504. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Pielak, G.J.; Li, C. 19FNMR Spectroscopy as a Probe of Cytoplasmic Viscosity and Weak Protein Interactions in Living Cells. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 12705–12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, A.S. Solid state 19F NMR methods for studying biomembranes. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2005, 46, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outpatient Antibiotic Prescriptions—United States; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017.
- Crump, B.; Wise, R.; Dent, J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1983, 24, 784–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brunner, M.; Staß, H.; Möller, J.G.; Schrolnberger, C.; Erovic, B.; Hollenstein, U.; Zeitlinger, M.; Georg Eichler, H.; Müller, M. Target Site Concentrations of Ciprofloxacin after Single Intravenous and Oral Doses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, F.; Hu, C.; Hu, X.; Wei, D.; Chen, Y.; Qu, J. Photodegradation and toxicity changes of antibiotics in UV and UV/H2O2 process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburn, T.T.; Thor, K.B. Drug repositioning: Identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucke, H.A. The case of galantamine: Repurposing and late blooming of a cholinergic drug. Futur. Sci. OA 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. Drug repurposing programmes get lift off. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durães, F.; Pinto, M.; Sousa, E.; Durães, F.; Pinto, M.; Sousa, E. Old Drugs as New Treatments for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmond, L.Y.; Gerig, J.T. Origins of Fluorine NMR Chemical Shifts in Fluorine-Containing Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4408–4417. [Google Scholar]
- Modo, M. 19F Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy in Neuroscience. Neuroscience 2021, 474, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanics, F.; Kitevski, J.L.; Bezsonova, I.; Forman-Kay, J.; Prosser, R.S. 19F NMR studies of solvent exposure and peptide binding to an SH3 domain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2007, 1770, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, M.A.; Gonçalves, A.S.; Franca, T.C.C.; Santana, M.S.; da Cunha, E.F.F.; Ramalho, T.C. Improved Protocol for the Selection of Structures from Molecular Dynamics of Organic Systems in Solution: The Value of Investigating Different Wavelet Families. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2022, 18, 5810–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayene, K.; Imane, D.; Abdelaziz, B.; Leila, N.; Fatiha, M.; Abdelkrim, G.; Bouzid, G.; Ismahan, L.; Brahim, H.; Rabah, O. Molecular modeling study of structures, Hirschfield surface, NBO, AIM, RDG, IGM and 1HNMR of thymoquinone/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex from QM calculations. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1249, 131565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, D.F.; Jallad, M.A.N.; Abdelnoor, A.M. The effect of ciprofloxacin on the growth of B16F10 melanoma cells. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2017, 13, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

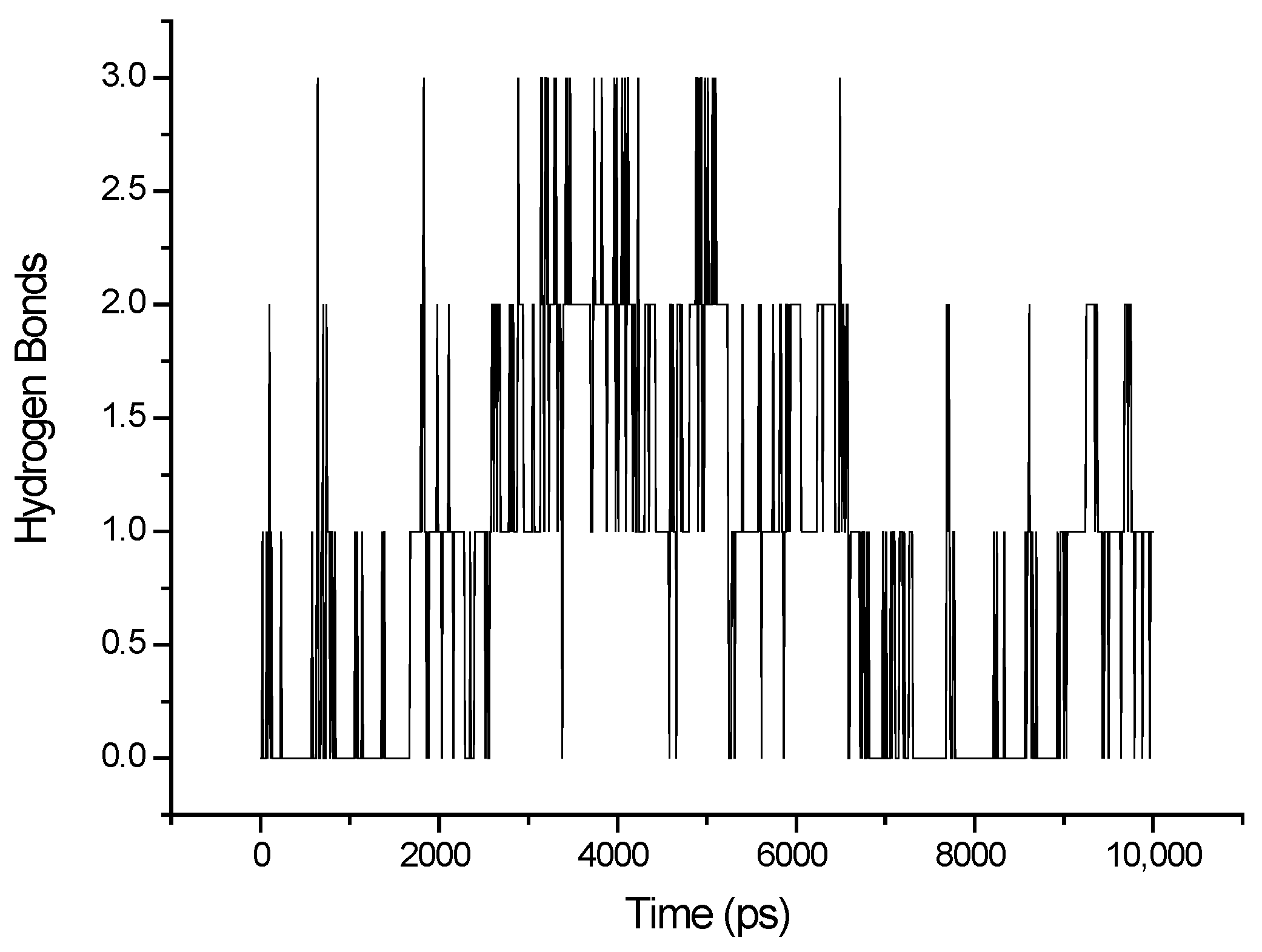
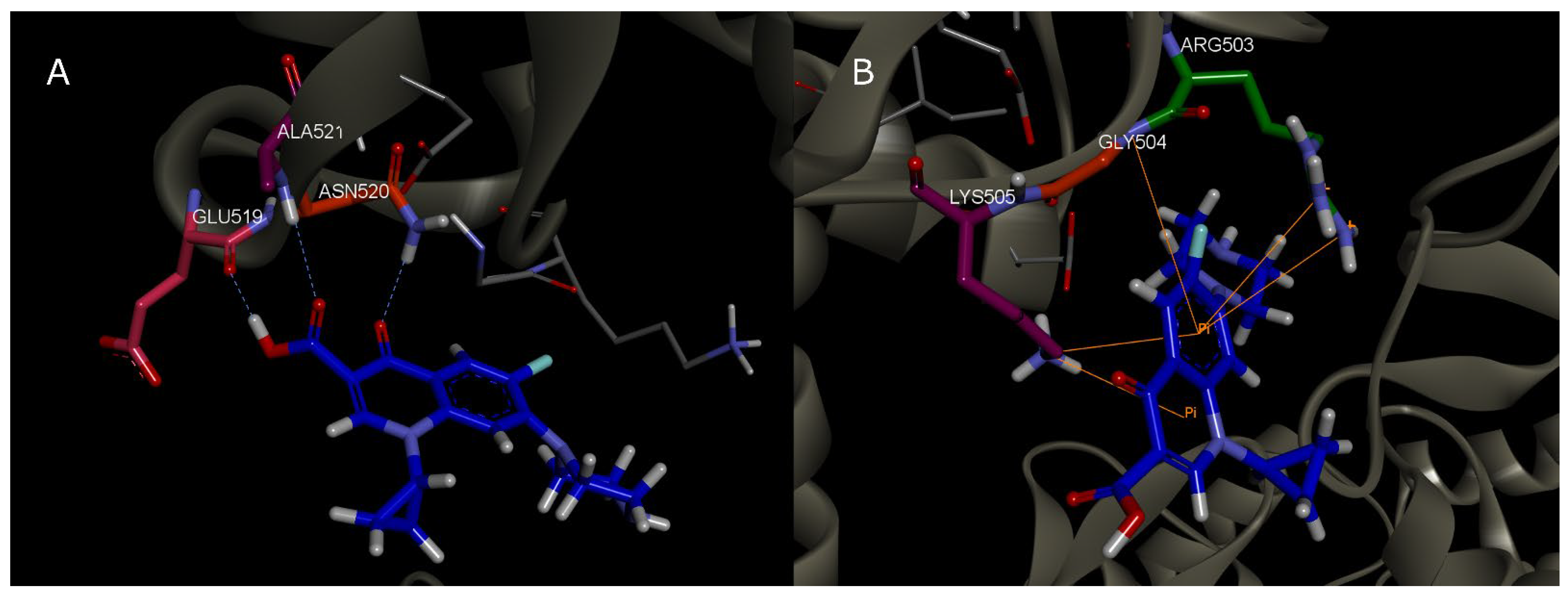

| Frame | Time (ps) | Residue | Interaction Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2000 | Asn 520 | HBond |
| 2 | 2200 | Asn 520 | HBond |
| 3 | 2300 | Leu 507 | HBond |
| 4 | 2400 | Asn 520 | HBond |
| 5 | 2600 | Asn 520; Gln 516 | HBond |
| 6 | 3000 | Asn 520 | HBond |
| 7 | 3100 | Asn 520 | HBond |
| 8 | 3200 | Glu 519; Asn 520; Ala 521 | HBond |
| 9 | 3700 | Asn 520; Ala 521 | HBond |
| 10 | 3900 | Asn 520; Ala 521 | HBond |
| 11 | 4200 | Asn 520 | HBond |
| 12 | 4400 | Asn 520; Ala 521 | HBond |
| 13 | 4700 | Asn 520; Ala 521 | HBond |
| 14 | 5100 | Asn 520; Ala 521 | HBond |
| 15 | 5500 | Ala 521 | HBond |
| 16 | 7000 | - | - |
| 17 | 7300 | Lys 505 | π-π; Electrostatic HBond |
| 18 | 7500 | - | - |
| 19 | 7700 | Arg 503 | HBond |
| 20 | 7900 | Arg 503; Lis 505; Gly 504 | π-π |
| 21 | 8000 | - | - |
| 22 | 8250 | Lys 505 | HBond; π-π |
| 23 | 8800 | - | - |
| 24 | 9000 | Ile 506 | HBond |
| 25 | 9200 | Ile 506 | HBond |
| 26 | 9400 | Ile 506 | HBond |
| 27 | 9500 | - | |
| 28 | 9800 | Ile 506 | HBond |
| 29 | 10,000 | Ile 506 | HBond |
| System | 19F δppm | Δδppm |
|---|---|---|
| CPX:aqueous solution (experimental) | −43.70 | 0.00 |
| CPX:explicit water | −43.54 | −0.16 |
| CPX:hTOPO-II | −49.73 | 6.03 |
| CPX:vacuum | −55.11 | 11.41 |
| CPX:implicit water | −56.20 | 12.50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sales, T.A.; Gonçalves, M.A.; Ramalho, T.C. Structural Parameters of the Interaction between Ciprofloxacin and Human Topoisomerase-II β Enzyme: Toward New 19F NMR Chemical Shift Probes. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120181
Sales TA, Gonçalves MA, Ramalho TC. Structural Parameters of the Interaction between Ciprofloxacin and Human Topoisomerase-II β Enzyme: Toward New 19F NMR Chemical Shift Probes. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(12):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120181
Chicago/Turabian StyleSales, Thais Aparecida, Mateus Aquino Gonçalves, and Teodorico Castro Ramalho. 2022. "Structural Parameters of the Interaction between Ciprofloxacin and Human Topoisomerase-II β Enzyme: Toward New 19F NMR Chemical Shift Probes" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 12: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120181
APA StyleSales, T. A., Gonçalves, M. A., & Ramalho, T. C. (2022). Structural Parameters of the Interaction between Ciprofloxacin and Human Topoisomerase-II β Enzyme: Toward New 19F NMR Chemical Shift Probes. Magnetochemistry, 8(12), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120181







