Arrangement of Indocyanine Green in a 1.5-Nanometer Channel to Achieve High-Efficiency Imaging of the Intestinal Lymphatic System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
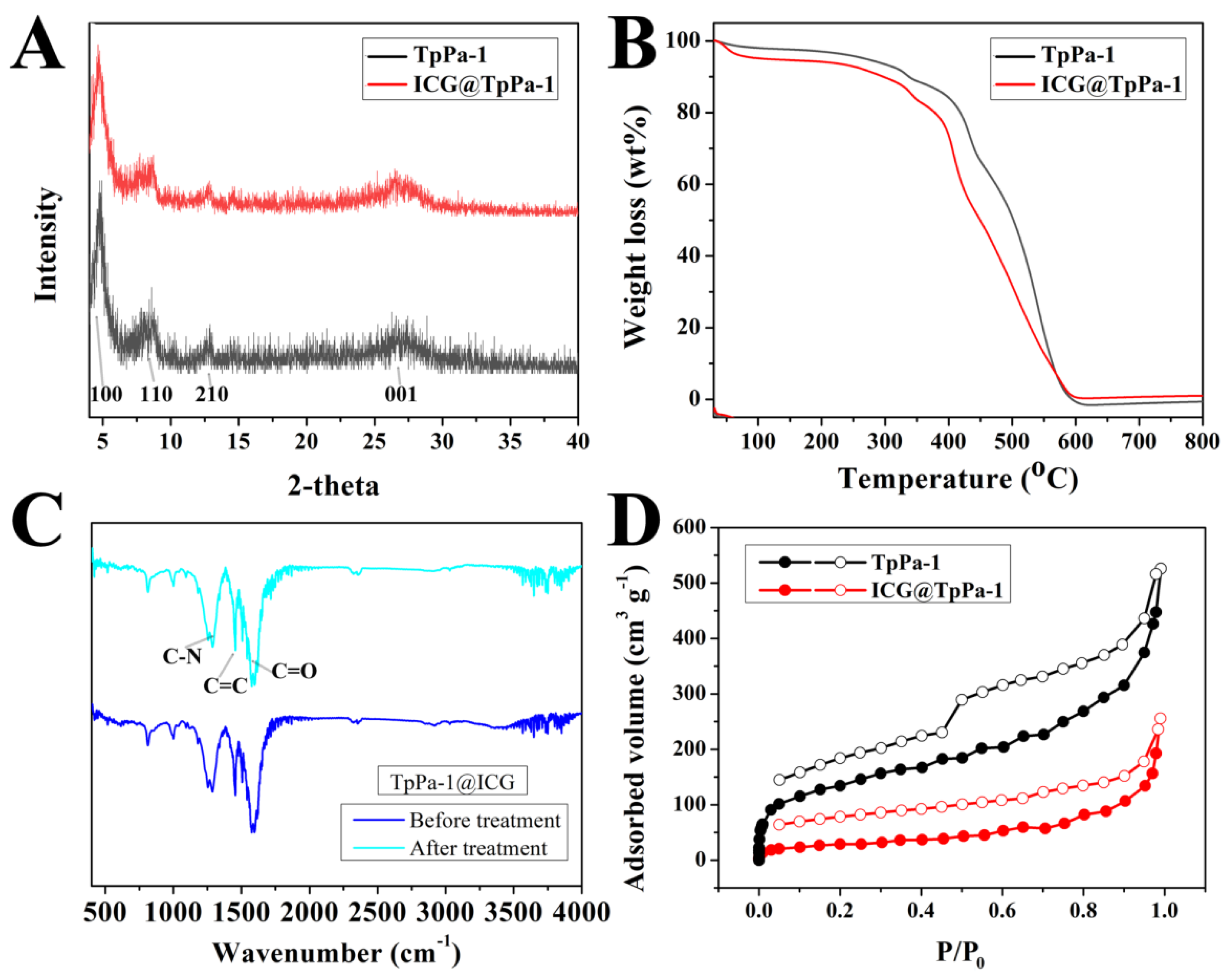
2.1. Characterization of TpPa-1@ICG
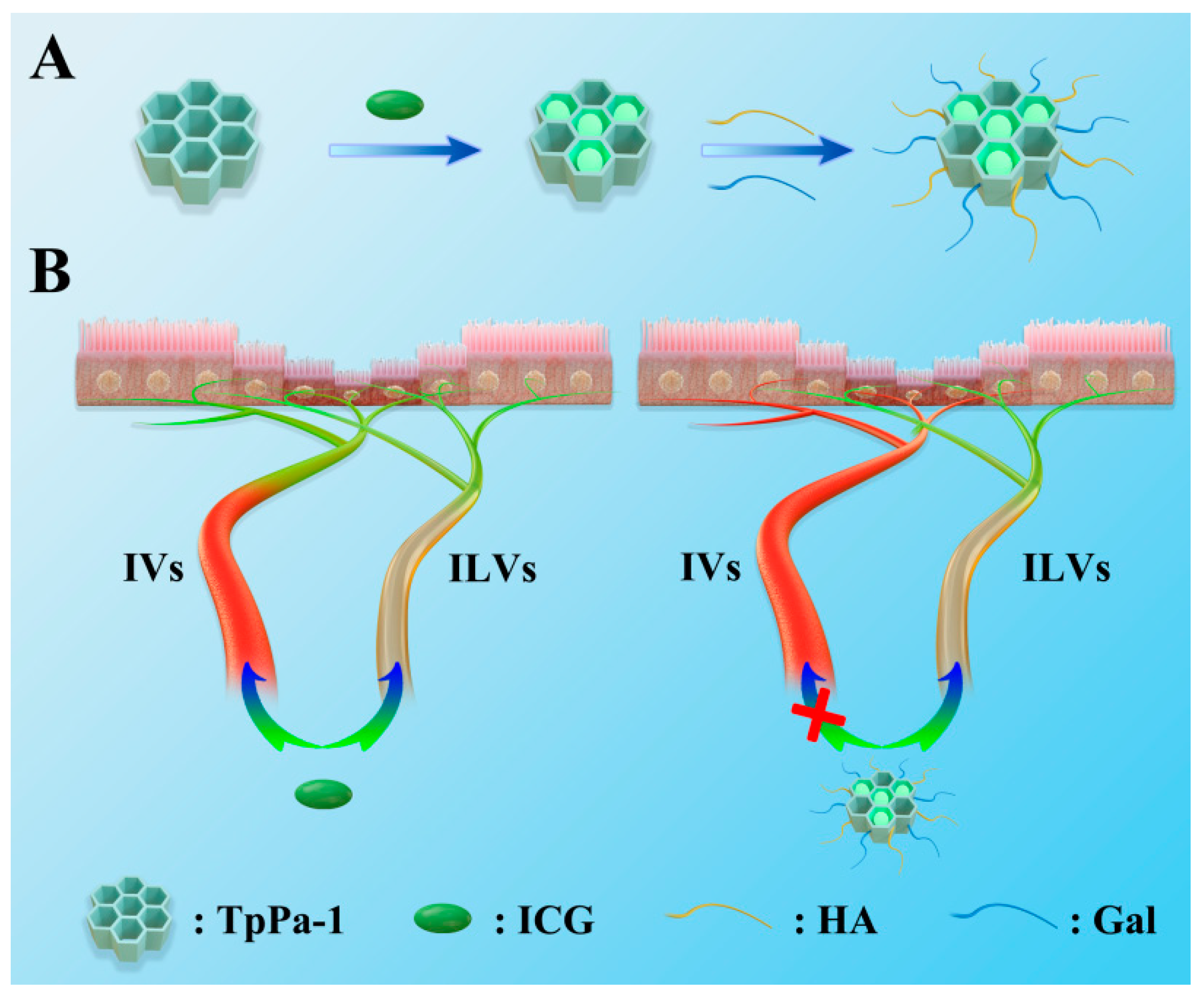
2.2. Build LVs-Targeted TpPa-1@ICG
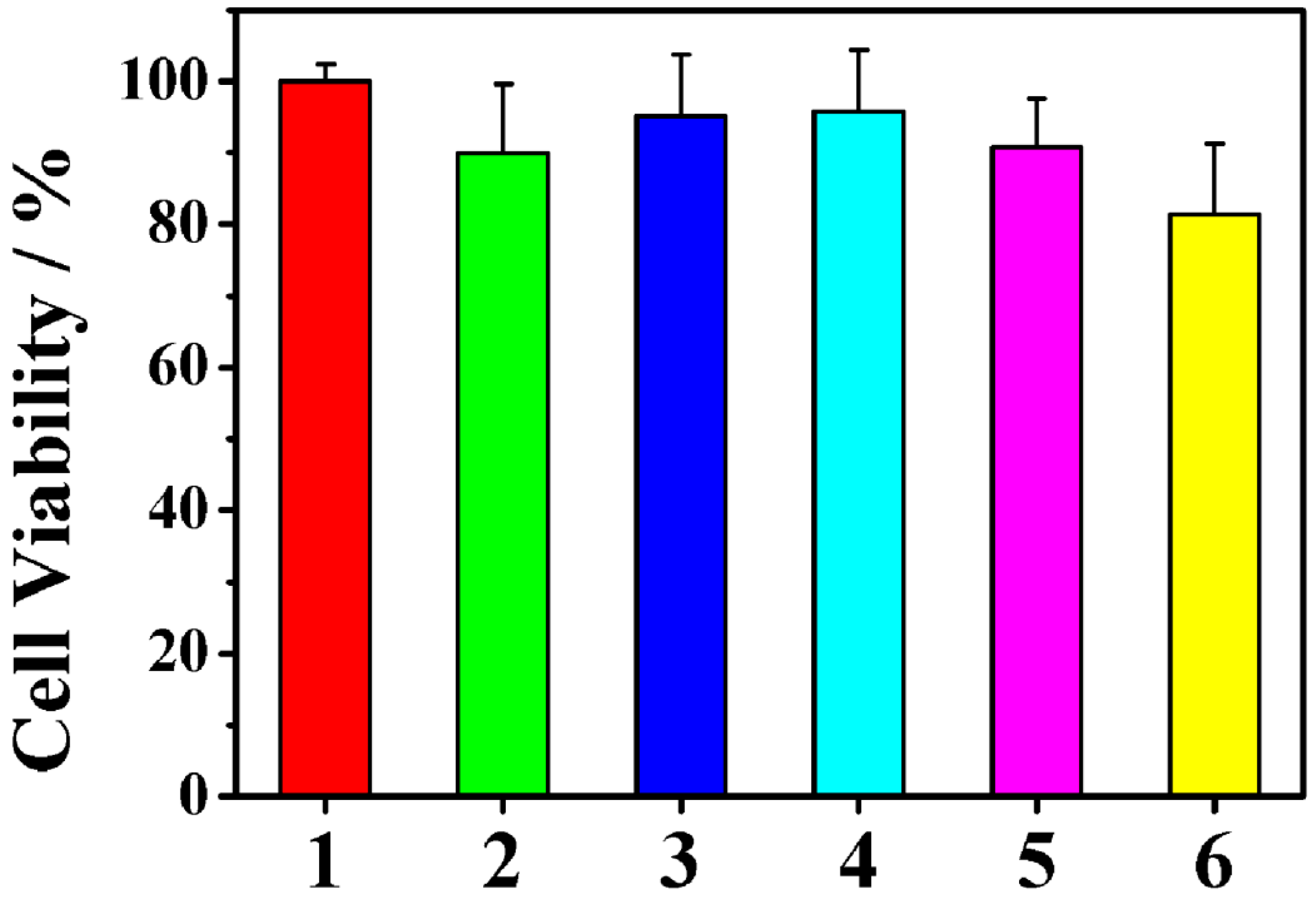
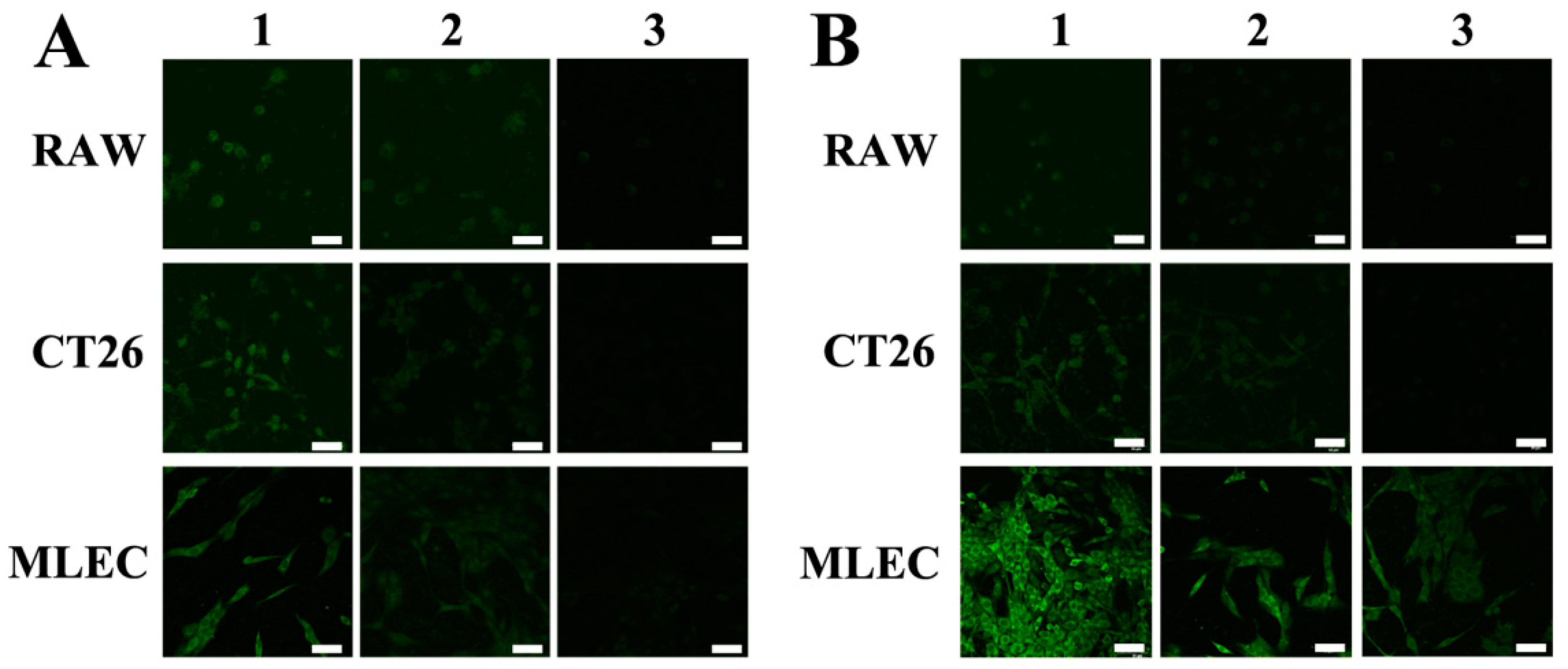
2.3. Targeting LVs by TpPa-1@ICG-HA Proving by Cell Assays
2.4. Construction of Rat IBD Models
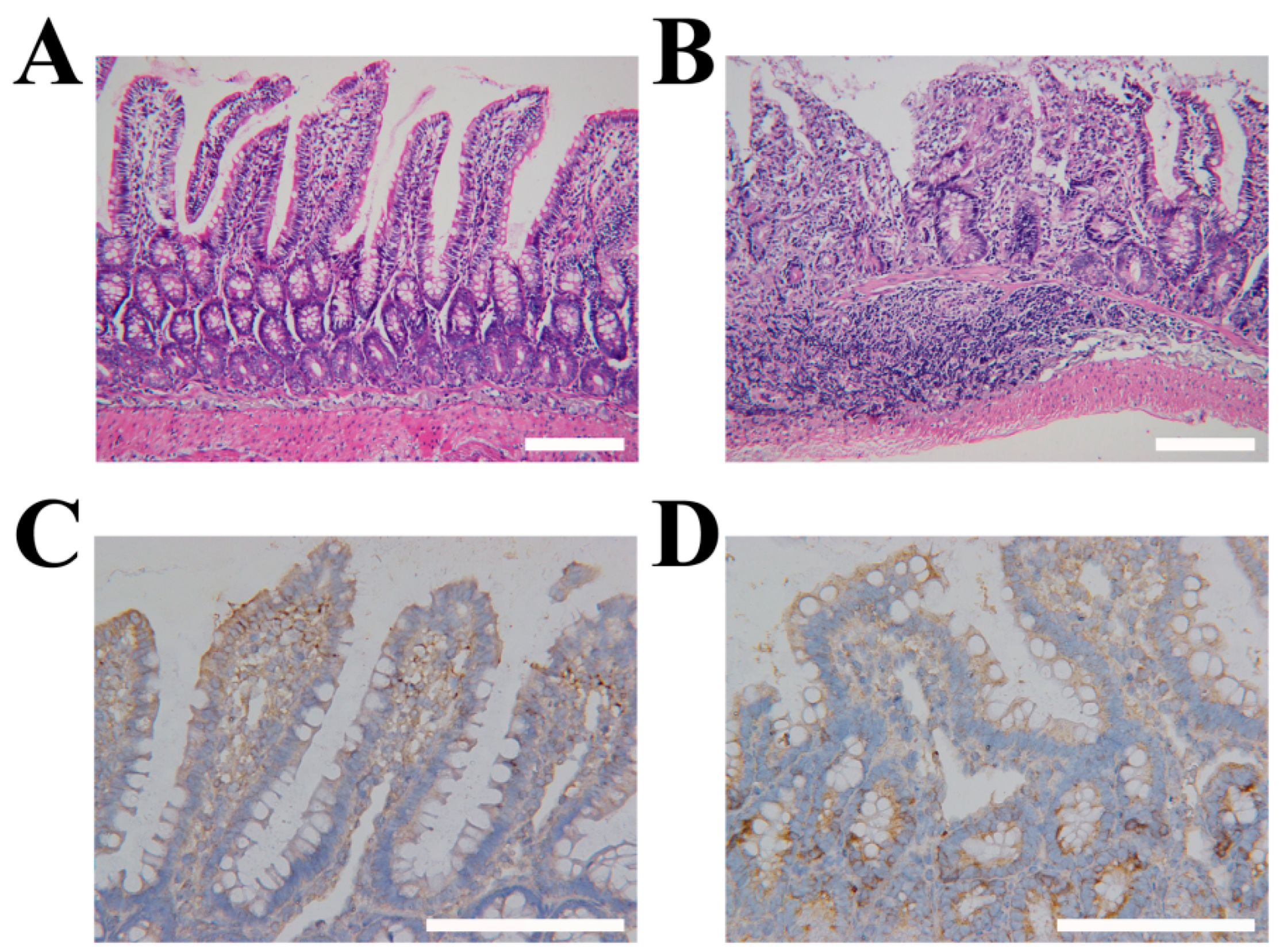
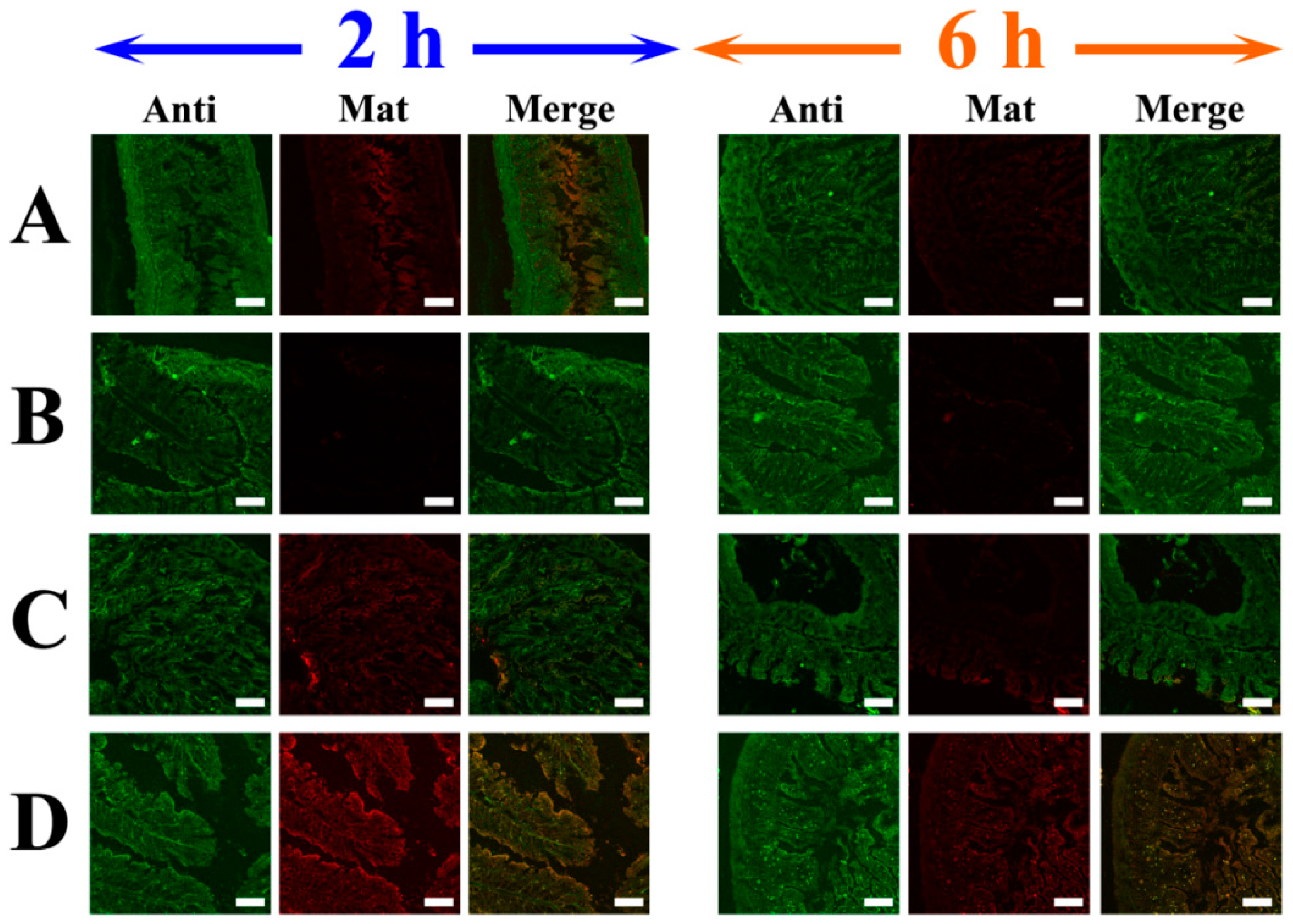
2.5. Targeting LVs by TpPa-1@ICG-HA Proving by Rat IBD Models
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Synthesis of POF Sample with 1.5-Nanometer Pore Channels (TpPa-1)
4.3. Synthesis of ICG Molecules Incorporated POF (TpPa-1@ICG)
4.4. Characterization
4.5. Cellular Accumulation and Quantification of the Fluorescence Intensity
4.6. Rat IBD Model Construction
4.7. Rat Intestinal Slices Assays
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Rahier, J.-F.; Dubuquoy, L.; Colombel, J.-F.; Jouret-Mourin, A.; Delos, M.; Ferrante, M.; Sokol, H.; De Hertogh, G.; Salleron, J.; Geboes, K.; et al. Decreased lymphatic vessel density is associated with postoperative endoscopic recurrence in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2013, 19, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.W.; Liu, B.; Zhao, H.; Yu, Y.Q. The Effect of Window Setting Technique on Measuring Colon Disease in CT Virtual Colonoscopy. Chin. J. Radiol. 2007, 41, 316–318. [Google Scholar]
- Zondervan, R.L.; Hahn, P.F.; Sadow, C.A.; Liu, B.; Lee, S.I. Body CT Scanning in Young Adults: Examination Indications, Patient Outcomes, and Risk of Radiation-Induced Cancer. Radiology 2013, 267, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, M.S.; Salotti, J.A.; Little, M.P.; McHugh, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, K.P.; Howe, N.L.; Ronckers, C.M.; Rajaraman, P.; Craft, A.W.; et al. Radiation Exposure from CT Scans in Childhood and Subsequent Risk of Leukaemia and Brain Tumours: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2012, 380, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, M.A.; Guerrini, S.; Cioffi Squitieri, N.; Imbriaco, G.; Chieca, R.; Civitelli, S.; Savelli, V.; Mazzei, F.G.; Volterrani, L. Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Is There a Role in Clinical Management for Acute Ischemic Colitis? World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobellis, F.; Berritto, D.; Somma, F.; Cavaliere, C.; Corona, M.; Cozzolino, S.; Fulciniti, F.; Cappabianca, S.; Rotondo, A.; Grassi, R. Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A New Tool for Diagnosis of Acute Ischemic Colitis? World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.J.; Semelka, R.C.; Martin, D.R.; Marcos, H.B. Colon Diseases: MR Evaluation using Combined T2-Weighted Single-Shot Echo Train Spin-Echo and Gadolinium-Enhanced Spoiled Gradient-Echo Sequences. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 12, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsman, M.L.; Kwant, G.; Mook, G.A.; Zijlstra, W.G. Light-Absorbing Properties, Stability, and Spectral Stabilization of Indocyanine Green. J. Appl. Physiol. 1976, 40, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, A.G.; Saha, S.; Monson, K.M.; Wiese, D.; Schochet, E.; Barber, K.R.; Ganatra, B.; Desai, D.; Kaushal, S. 1% Lymphazurin Vs 10% Fluorescein for Sentinel Node Mapping in Colorectal Tumors. Arch. Surg. 2004, 139, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maegawa, J.; Yabuki, Y.; Tomoeda, H.; Hosono, M.; Yasumura, K. Outcomes of Lymphaticovenous Side-to-End Anastomosis in Peripheral Lymphedema. J. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 55, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Tsuboi, S.; Komatsuzaki, A.; Imamura, Y.; Muranaka, Y.; Sakata, T.; Yasuda, H. Enhancement of Aqueous Stability and Fluorescence Brightness of Indocyanine Green using Small Calix[4]arene Micelles for Near-infrared Fluorescence Imaging. Med. Chem. Commun. 2016, 7, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosco, E.D.; Lim, I.; Sletten, E.M. Photophysical Properties of Indocyanine Green in the Shortwave Infrared Region. ChemPhotoChem 2021, 5, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza, R.; Skoracki, R.; Hock, K.; Povoski, S.P. A Comprehensive Overview on the Surgical Management of Secondary Lymphedema of the Upper and Lower Extremities Related to Prior Oncologic Therapies. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridner, S.H.; Dietrich, M.S.; Kidd, N. Breast Cancer Treatment-Related Lymphedema Self-Care: Education, Practices, Symptoms, and Quality of Life. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 19, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, G. Molecularly Imprinted Porous Aromatic Frameworks for Molecular Recognition. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1082–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.I. Conjugated Microporous Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jin, S.; Xu, H.; Nagai, A.; Jiang, D. Conjugated Microporous Polymers: Design, Synthesis and Application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8012–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, D.; Zhang, S.; Meng, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sha, H.; Faller, R.; Bian, Z.; Zou, X.; et al. Porous Organic Frameworks Featured by Distinct Confining Fields for the Selective Hydrogenation of Biomass-Derived Ketones. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1908243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Meng, Q.; Faheem, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Deng, D.; Sun, F.; He, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. A Molecular Coordination Template Strategy for Designing Selective Porous Aromatic Framework Materials for Uranyl Capture. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Meng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ma, X.; Ruan, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, G. Constructing Uranyl-Specific Nanofluidic Channels for Unipolar Ionic Transport to Realize Ultrafast Uranium Extraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14523–14529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté Adrien, P.; Benin Annabelle, I.; Ockwig Nathan, W.; O’Keeffe, M.; Matzger Adam, J.; Yaghi Omar, M. Porous, Crystalline, Covalent Organic Frameworks. Science 2005, 310, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhu, G. Porous Aromatic Frameworks as a Platform for Multifunctional Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElroy, M.; Hayashi, K.; Garmy-Susini, B.; Kaushal, S.; Varner, J.A.; Moossa, A.; Hoffman, R.M.; Bouvet, M. Fluorescent Lyve-1 Antibody to Image Dynamically Lymphatic Trafficking of Cancer Cells in Vivo. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 151, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, G.; Song, J.; Teng, G.-J.; Niu, G.; Chen, X. Mapping Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis by Dual-Probe Optical Imaging. Theranostics 2017, 7, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubokura, K.; Vong, K.K.H.; Pradipta, A.R.; Ogura, A.; Urano, S.; Tahara, T.; Nozaki, S.; Onoe, H.; Nakao, Y.; Sibgatullina, R.; et al. In Vivo Gold Complex Catalysis within Live Mice. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3579–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, H.; Cheng, K.F.; Al-Abed, Y.; Rothstein, T.L. A novel mechanism of B cell-mediated immune suppression through CD73 expression and adenosine production. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5904–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Guo, H.Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, A.P.; Wang, X.X.; Ren, F.Z. Oral administration of Lactobacillus paracasei alleviates clinical symptoms of colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium salt in BALB/c mice. Benef. Microbes. 2014, 5, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Briley-Saebo, K.; Xie, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; He, C.; Tang, C.Y.; Tao, X. Inflammatory bowel disease: MR- and SPECT/CT-based macrophage imaging for monitoring and evaluating disease activity in experimental mouse model–pilot study. Radiology 2014, 271, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandambeth, S.; Mallick, A.; Lukose, B.; Mane, M.V.; Heine, T.; Banerjee, R. Construction of Crystalline 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks with Remarkable Chemical (Acid/Base) Stability via a Combined Reversible and Irreversible Route. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19524–19527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, S.; Tong, Y.; Wei, S.; Chen, G.; Huang, S.; Ouyang, G. In-situ Layer-by-Layer Synthesized TpPa-1 COF Solid-Phase Microextraction Fiber for Detecting Sex Hormones in Serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1137, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Faheem, M.; Wang, L.; Meng, Q.; Sha, H.; Yang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, G. Surface Pore Engineering of Covalent Organic Frameworks for Ammonia Capture through Synergistic Multivariate and Open Metal Site Approaches. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, G. Lymphatic Vasculature Development. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, G.; Alitalo, K. The Lymphatic Vasculature: Recent Progress and Paradigms. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 457–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, T.V.; Koh, G.Y. Organ-Specific Lymphatic Vasculature: From Development to Pathophysiology. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 215, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammela, T.; Alitalo, K. Lymphangiogenesis: Molecular Mechanisms and Future Promise. Cell 2010, 140, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Subasic, C.; Minchin, R.F.; Kaminskas, L.M. Drug Formulation and Nanomedicine Approaches to Targeting Lymphatic Cancer Metastases. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouta, E.M.; Bell, R.D.; Rahimi, H.; Xing, L.; Wood, R.W.; Bingham, C.O.; Ritchlin, C.T.; Schwarz, E.M. Targeting Lymphatic Function as a Novel Therapeutic Intervention for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Wang, X.; Chang, K.; Shen, W.; Yu, G.; Du, J. The Bright Future of Nanotechnology in Lymphatic System Imaging and Imaging-Guided Surgery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, X.; Gao, N.; Du, J.; Zhao, Q. Arrangement of Indocyanine Green in a 1.5-Nanometer Channel to Achieve High-Efficiency Imaging of the Intestinal Lymphatic System. Molecules 2022, 27, 8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248704
Kong X, Gao N, Du J, Zhao Q. Arrangement of Indocyanine Green in a 1.5-Nanometer Channel to Achieve High-Efficiency Imaging of the Intestinal Lymphatic System. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248704
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Xiangyi, Nan Gao, Jianshi Du, and Qing Zhao. 2022. "Arrangement of Indocyanine Green in a 1.5-Nanometer Channel to Achieve High-Efficiency Imaging of the Intestinal Lymphatic System" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248704
APA StyleKong, X., Gao, N., Du, J., & Zhao, Q. (2022). Arrangement of Indocyanine Green in a 1.5-Nanometer Channel to Achieve High-Efficiency Imaging of the Intestinal Lymphatic System. Molecules, 27(24), 8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248704








