Aging Cost Optimization for Planning and Management of Energy Storage Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Inputs and Constraints of the Model
2.2. Optimization Procedure and Outputs
2.3. Battery Cost Model
3. Case Study
3.1. The Test Grid
3.2. Cost Functions
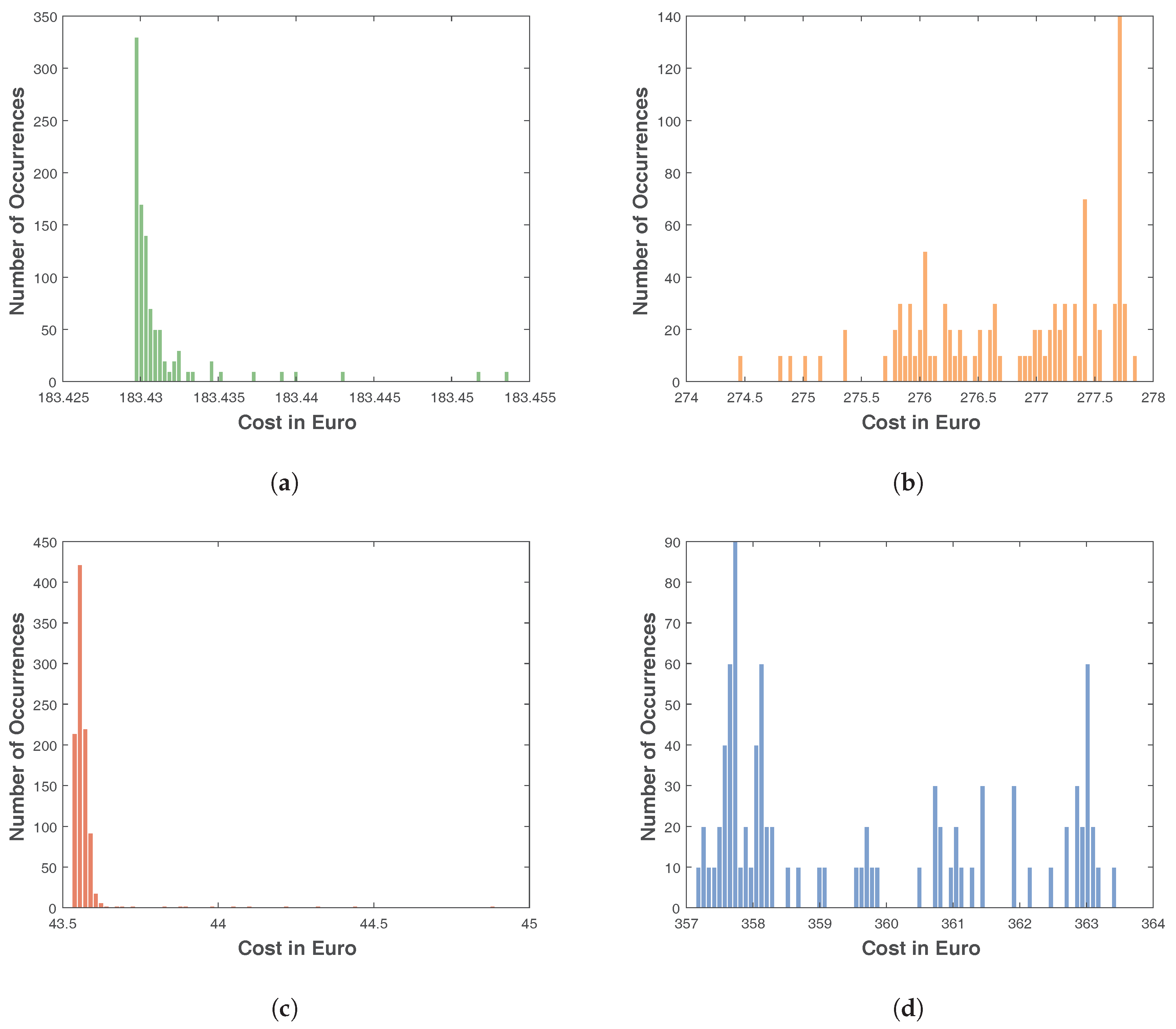
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESS | Energy Storage System |
| BESS | Battery Energy Storage System |
| RES | Renewable Energy Sources |
| MPOPF | Multi-Period Optimal Power Flow |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GA-MPOPF | Genetic Algorithm-based Multi Period Optimal Power Flow |
| SOC | State Of Charge |
| VPP | Virtual Power Plant |
| BDM | Battery Degradation Model |
| BDCM | Battery Degradation Costs Model |
| CG | Controllable Generator |
| MV | Medium Voltage |
| PCC | Point of Common Coupling |
References
- Facchini, A. Distributed energy resources: Planning for the future. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marongiu, A.; Damiano, A.; Heuer, M. Experimental analysis of lithium iron phosphate battery performances. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Bari, Italy, 4–7 July 2010; pp. 3420–3424. [Google Scholar]
- Beltran, H.; Bilbao, E.; Belenguer, E.; Etxeberria-Otadui, I.; Rodriguez, P. Evaluation of Storage Energy Requirements for Constant Production in PV Power Plants. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadian, G.; Khalili, N.; Khodayar, M.; Shahidehpour, M. Optimal scheduling of distributed battery storage for enhancing the security and the economics of electric power systems with emission constraints. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 124, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, M.; Arabali, A.; Etezadi-Amoli, M.; Fadali, M.S. A Framework for Optimal Placement of Energy Storage Units within a Power System with High Wind Penetration. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, R.; Baumann, L.; Damiano, A.; Boggasch, E. A Vanadium-Redox-Flow-Battery Model for Evaluation of Distributed Storage Implementation in Residential Energy Systems. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Mureddu, M.; Damiano, A. A statistical approach for resilience analysis of ESS deployment in RES-based power systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 26th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Edinburgh, UK, 19–21 June 2017; pp. 2069–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Gayme, D.; Topcu, U. Optimal power flow with distributed energy storage dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2011 American Control Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1536–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Warrington, J.; Goulart, P.; Mariethoz, S.; Morari, M. Policy-Based Reserves for Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 4427–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, A.; Raghunathan, A.U.; Nikovski, D.; Biegler, L.T. Global optimization of multi-period optimal power flow. In Proceedings of the 2013 American Control Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 17–19 June 2013; pp. 1157–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Jabr, R.A.; Karaki, S.; Korbane, J.A. Robust Multi-Period OPF With Storage and Renewables. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 2790–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, A.; Parniani, M. Voltage security constrained multi-period optimal reactive power flow using benders and optimality condition decompositions. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.; Thiébaux, S. Distributed Multi-Period Optimal Power Flow for Demand Response in Microgrids. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM Sixth International Conference on Future Energy Systems (e-Energy’15), Bangalore, India, 14–17 July 2015; pp. 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Oudalov, A.; Ulbig, A.; Andersson, G.; Kirschen, D. Modeling of Lithium-Ion Battery Degradation for Cell Life Assessment. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 28, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, L. The Practical Handbook of Genetic Algorithms: Applications, 2nd ed.; Chapman&Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, R.D.; Murillo Sanchez, C.; Thomas, R. MATPOWER: Steady-State Operations, Planning, and Analysis Tools for Power Systems Research and Education. IEEE Trans Power Syst. 2011, 26, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.W.; Chu, S.Y.; Wang, H.L. An Improved Backward/Forward Sweep Load Flow Algorithm for Radial Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 882–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, C.G. Atificial Life: An Overview; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Georgilakis, P.; Hatziargyriou, N. Optimal distributed generation placement in power distribution networks: Models, methods, and future research. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 3420–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, J.C.; Kagan, N. Reconfiguration of distribution networks to minimize loss and disruption costs using genetic algorithms. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2010, 80, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Wang, Z.; Ai, Q.; Lee, W.J. Interactive Model for Energy Management of Clustered Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 9994, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.E.; Wu, F.F. Optimal capacitor placement on radial distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1989, 4, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefifar, S.A.; Mohamed, Y.A.R.I.; El-Fouly, T.H.M. Supply-adequacy-based optimal construction of microgrids in smart distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefifar, S.A.; Mohamed, Y.A.R.I.; El-Fouly, T.H.M. Optimum microgrid design for enhancing reliability and supply-security. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekpour, A.R.; Pahwa, A. Radial Test Feeder including primary and secondary distribution network. In Proceedings of the 2015 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Charlotte, NC, USA, 4–6 October 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- IESO. 2017. Available online: http://ieso.ca/ (accessed on 15 May 2017).










| Monthly Considered Costs | Costs (Euro) | Cumulative Costs (Euro) |
|---|---|---|
| Fines with a BESS | 5200 | 5200 |
| Calendar aging | 1800 | 7000 |
| Cycling aging | 1700 | 8700 |
| Fines w/o a BESS | 10,500 | 10,500 |
| Type | Energy (MWh) |
|---|---|
| With a BESS | 49.7 |
| Without a BESS | 70.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korjani, S.; Mureddu, M.; Facchini, A.; Damiano, A. Aging Cost Optimization for Planning and Management of Energy Storage Systems. Energies 2017, 10, 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111916
Korjani S, Mureddu M, Facchini A, Damiano A. Aging Cost Optimization for Planning and Management of Energy Storage Systems. Energies. 2017; 10(11):1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111916
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorjani, Saman, Mario Mureddu, Angelo Facchini, and Alfonso Damiano. 2017. "Aging Cost Optimization for Planning and Management of Energy Storage Systems" Energies 10, no. 11: 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111916
APA StyleKorjani, S., Mureddu, M., Facchini, A., & Damiano, A. (2017). Aging Cost Optimization for Planning and Management of Energy Storage Systems. Energies, 10(11), 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111916







