Abstract
This paper proposes a back electromotive force estimation error compensation method for accurate rotor position estimation of surface mounted permanent magnet synchronous motors. When estimating the rotor position of surface mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor sensorless drives, a direct current offset error component occurs in the voltage sensor. As a result, the rotor position is distorted and the sensorless control in surface mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor is degraded. In addition, the dq-axis voltages in the synchronous reference frame have the direct current offset error component, ripples compared with the motor frequency under the distorted rotor position. In this paper, the effects of the direct current offset errors are analyzed based on the synchronous reference frame phase locked loop. To remove this direct current offset error component, a d-axis voltage is converted into a synchronous reference frame again to compensate. In other words, it is a dual synchronous coordinate conversion compensation method. The compensator utilizes a proportional-integral controller that compensates by estimating the direct current offset error component. The proposed method is useful for the improvement of surface mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor sensorless control and operating performance. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified through PSIM simulation and experimental results.
1. Introduction
Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) have advantages such as high torque density and efficiency, robust structure, low inertia efficiency compared with output torque and excellent control performance. Recently, the decreasing cost of permanent magnets has made them attractive as alternatives to the existing direct current motors and induction motors in many industrial applications, and they are used in various industries. Generally, a PMSM performs vector control based on current control, and rotor position information is essential to perform vector control, however, the encoders and resolvers used to acquire the position information of the rotor are not used because they increase system cost, volume, mechanical attachment and impair system reliability. Among the various applications, sensorless control is preferred for fan and pump products [1,2,3], and for this reason, sensorless methods for driving PMSMs are an active research topic [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. The sensorless methods can be roughly divided into back electromotive force (back-EMF) estimation- based methods [3,4,5,6,7,8] and methods based on inductance changes according to the rotor position [9,10]. generally, the back-EMF based methods estimate the back-EMF using the stator voltages and motor currents without requiring any additional high frequency signal injection and the inductance-based methods estimate the inductance value through an external signal injection. However, sensorless control methods based on the inductance can be applied to the interior type PMSM (IPMSM) in which the inductance varies depending on the position, but they are not applicable to surface mounted type PMSMs (SPMSMs) in which the inductance value is constant depending on the position. However, the SPMSM is usable regardless of the polarity, has no noise and the advantage of not using additional external voltage injection. Therefore, this paper is focused on the back-EMF-based sensorless control method of SPMSM.
When using the sensorless control method based on the back-EMF estimation, the back-EMF information is measured by the voltage sensor of the system after passing the digital controller signal through a low pass filter (LPF) and analog to digital conversion (ADC). In this process, back-EMF measurement errors can occur due to the nonlinearity of the voltage sensor, the thermal variation of the analog electric device, and ADC quantization errors [11,12,13,14]. At this time, the main component of any occurring nonlinear errors is the direct current (DC) offset error, and when this DC offset error component occurs, it causes a pulsation in the synchronous coordinate system d axis voltage. Therefore, a distortion occurs in following the position of the rotor, and the sensorless control and operation performance of the SPMSM are degraded.
Recently, some compensation methods for reducing the pulsation of the synchronous coordinate system dq-axis caused by the DC offset error component have been studied [15,16,17]. However, the compensator method proposed in [15] requires precise mechanical parameters. Any inaccurate determination may cause an instability problem. The algorithm in [16] requires complex procedures to minimize the periodic torque ripple resulting from current measurement errors. It needs a memory to store the controller output data and Fourier series expansion to analyze the harmonics that are present in the stored data. The approach of [17] utilizes an integral output of the d-axis current controller to compensate for undesirable periodic speed oscillations. The performance heavily depends on the accuracy of feedforward back-EMF voltage in the current controller and the controller bandwidth. In addition, it has the disadvantage that the convergence rate is quite slow [18].
In this paper we propose a compensation algorithm to remove the DC offset error component generated by the voltage sensor during the rotor position estimation for precise rotor position estimation. The proposed compensation algorithm compensates by estimating the DC offset error component using a proportional-integral (PI) controller after analyzing the synchronous d-axis voltage, including the DC offset error component. To verify the proposed method, the compensation algorithm used to remove the DC offset error component was subjected to a theoretical analysis and the validity of the proposed method was verified by simulation using PSIM and experiments using a 20 W SPMSM.
2. System Modeling
2.1. Back-EMF-Based Sensorless Method [4,5]
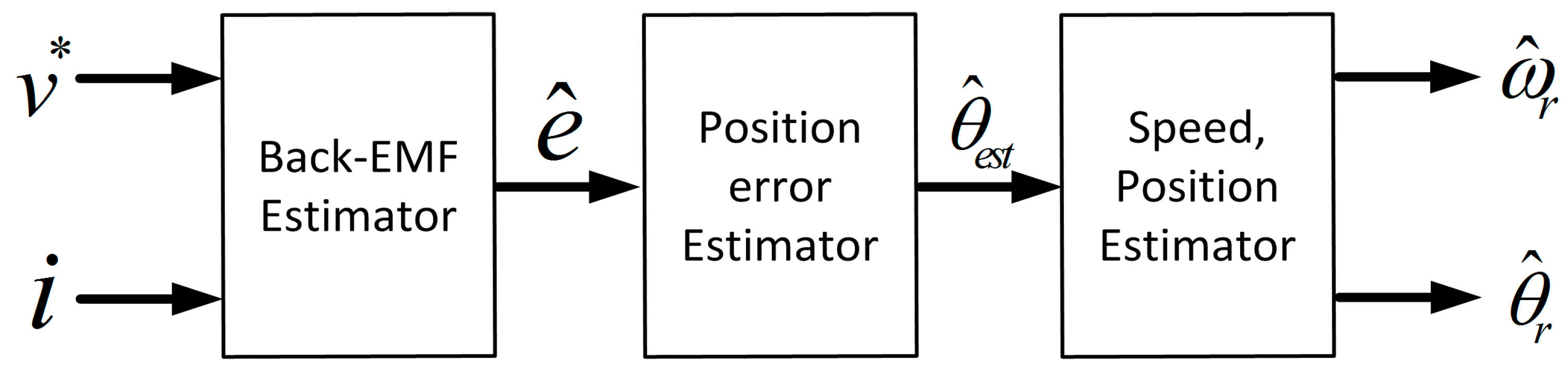
The functional elements of the back-EMF based sensorless methods include a back-EMF estimator, a position error estimator and speed estimator (Figure 1). As shown in Figure 1, the back-EMF estimator makes use of the stator command voltage (), stator currents (), and a mathematical model of the SPMSM to derive the back-EMF signals. In Figure 1 the position error estimator calculates the rotor position or position error using the estimated back-EMF information. In Figure 1 the speed estimator estimates the position and speed of the rotor to be used in the controller based on the position information calculated in position error estimator.
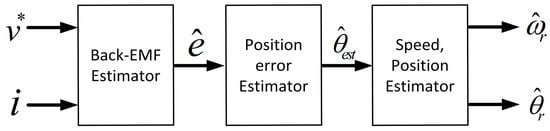
Figure 1.
Back-EMF based sensorless method system configuration.
The rotor speed and position are observed from the estimated back-EMF signals by means of another estimator such as a phase-locked-loop (PLL) type estimator or a Luenberger type state filter. Because the rotor speed and position are observed from the estimated back-EMF signals, the accuracy of the back-EMF estimator has a direct influence on the performance of the sensorless drive, therefore, accurate back-EMF estimation is very important for sensorless control of SPMSMs.
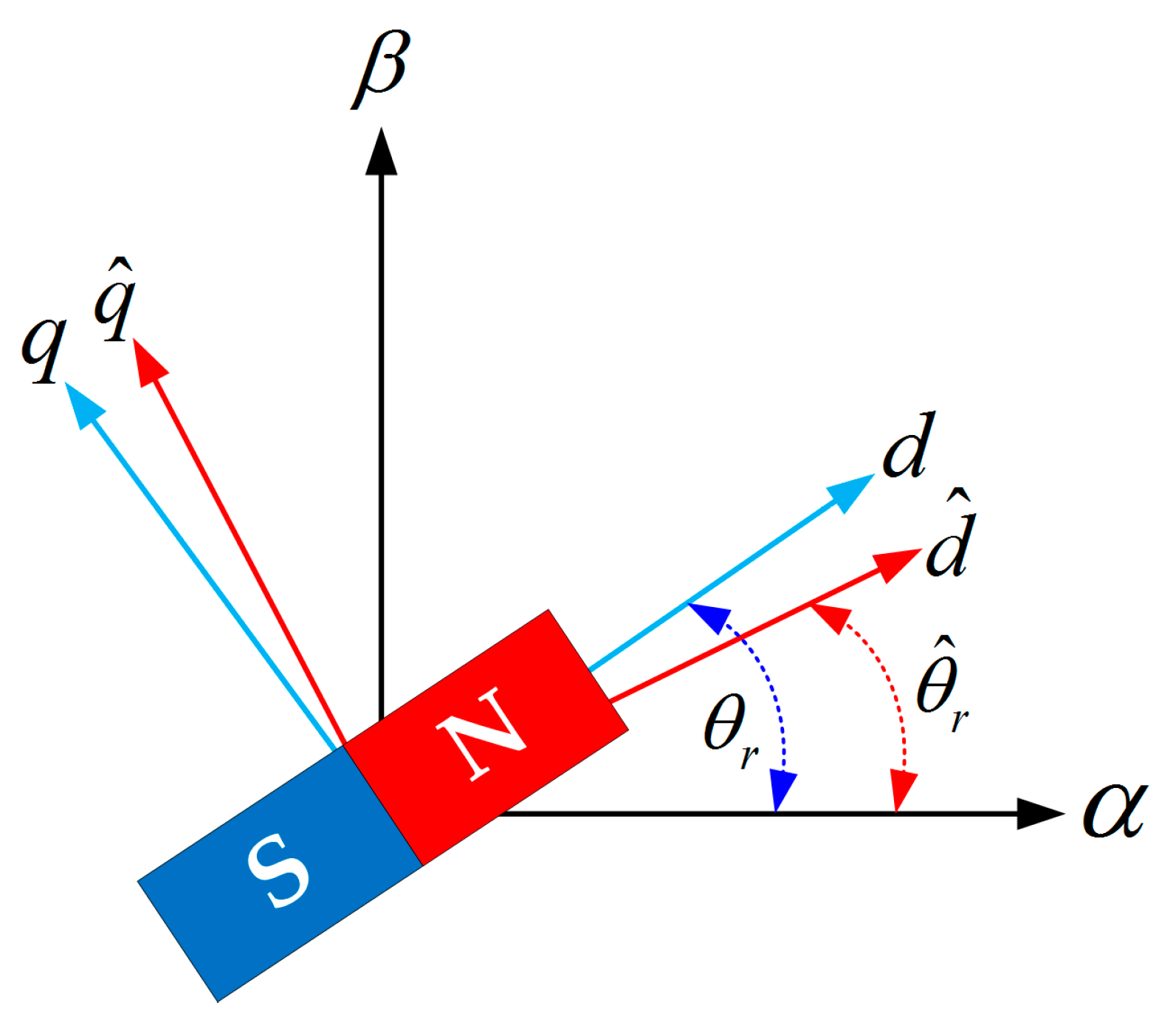
Figure 2 shows a space vector diagram for a SPMSM [4]. The and frames represent the stationary and the rotor reference frames, respectively. The axis corresponds to the magnetic axis of the phase and the d axis is aligned with the direction of the N pole of the rotor. The frame is an estimated frame used in sensorless vector control using the rotor reference frame. and are the actual and estimated rotor positions, respectively.
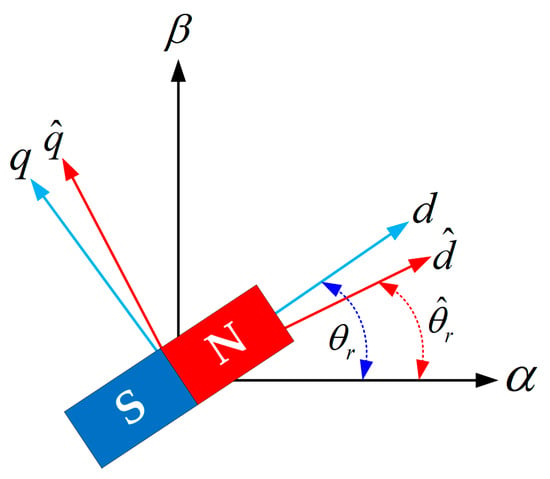
Figure 2.
Space vector diagram of SPMSM.
The phase-voltage equation of the three-phase SPMSM is expressed as Equation (1):
where are phase stator voltages, are stator winding resistance, are phase stator current, are phase stator inductance, and are phase back-EMF:
where is flux linkage, N is number of turns, is flux. The flux linkage has rotor position information of the SPMSM as a function of position.
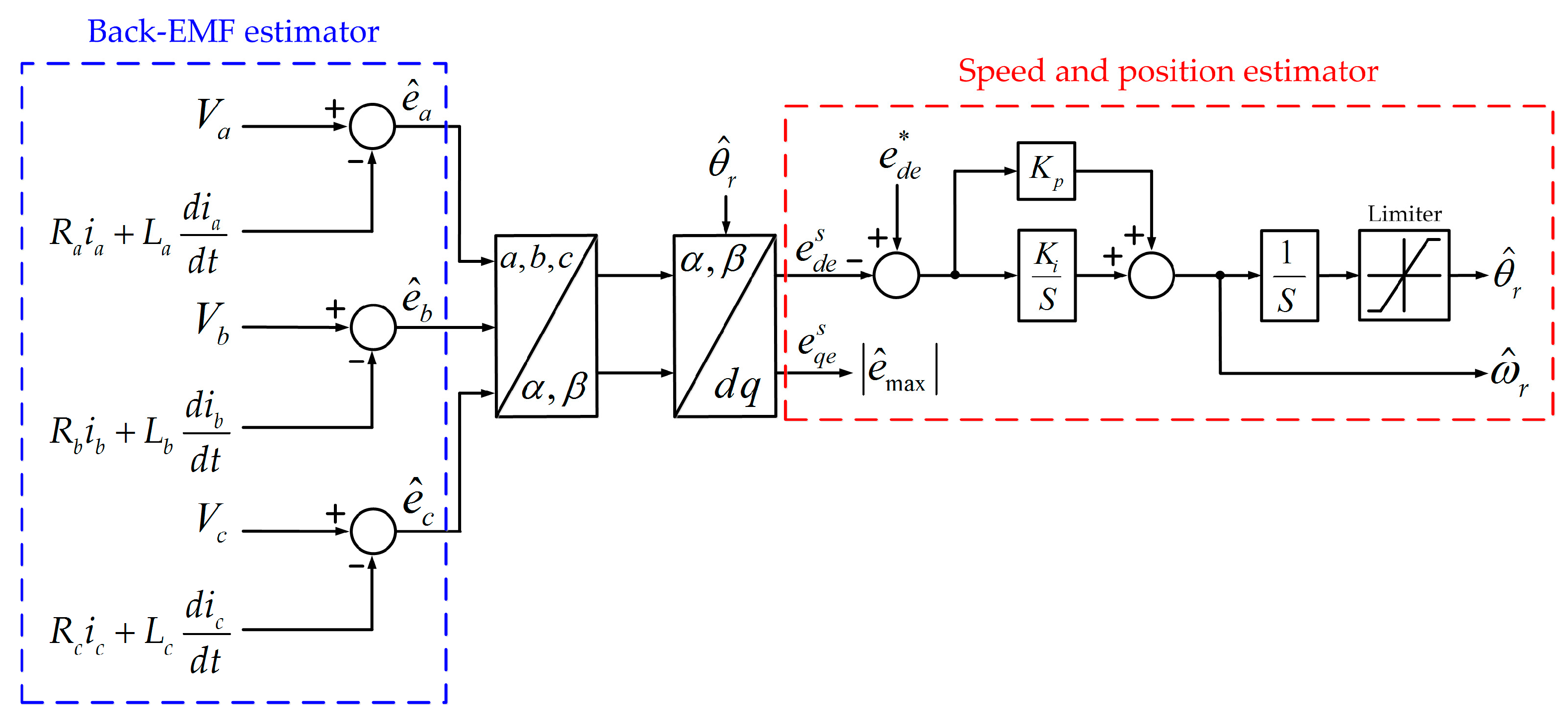
Since the back-EMF contains the SPMSM rotor position information, the accurate back-EMF estimation is an essential element for the sensorless control of the SPMSM. The back-EMF was estimated in Figure 1. It can be calculated as (2) by substituting Equation (1) into the equation for back-EMF. Figure 3 shows the back-EMF, speed, and position estimator block diagram.
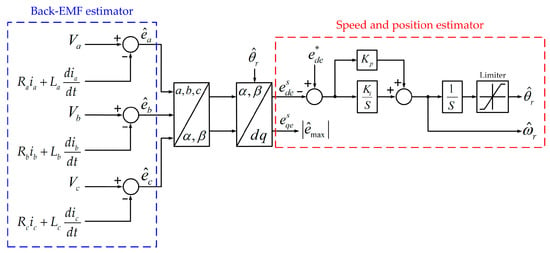
Figure 3.
Block diagram of back-EMF, speed and position estimator.
2.2. Effect of DC Offset Error
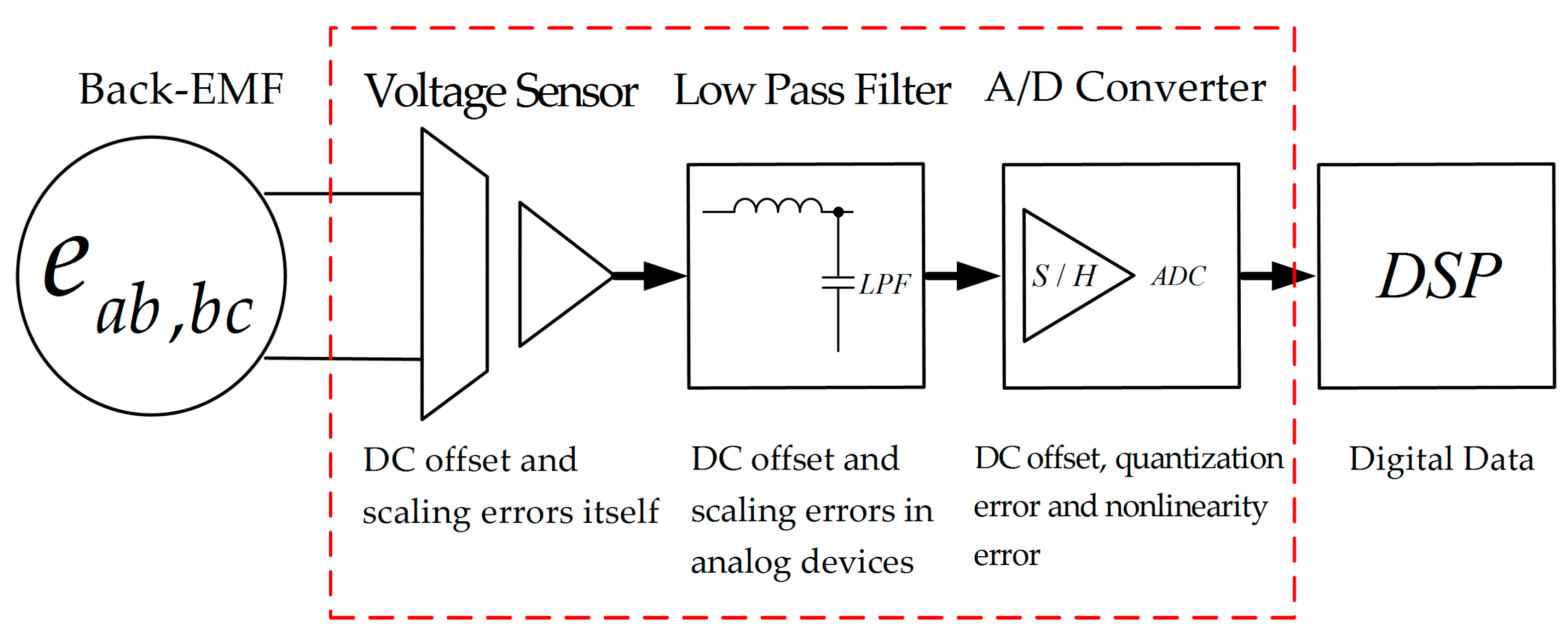
Figure 4 represents the error factors in the voltage measurement path. Typically, the measured back-EMF is digitalized through matching circuits including voltage sensor, low pass filter, and A/D converter. As a result, a DC offset error may be generated from the voltage sensor itself because of sensor errors, the thermal variation of the analog electric device and the quantization error of the A/D converter [11,12,13,14].
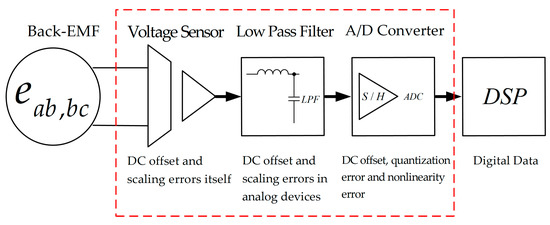
Figure 4.
The back-EMF measurement path.
The accurate detection of back-EMF in any sensorless method for SPMSMs is necessary. However, if the DC offset is contained in the measured back-EMF, the synchronous d-q axis voltage will be included in the AC component when the voltage of the stationary reference frame is converted to synchronous coordination in the PLL. The rotor position is estimated by controlling the synchronous d-axis voltage constantly. However, if the d-axis voltage is included DC offset, the rotor position estimation is distorted by the error.
In this paper, only two voltage sensors are used to measure the two-phase line-to-line back-EMF. Therefore, in order to obtain information on the three phases back-EMF, the two line to line back-EMFs are calculated by converting the three phases back-EMFs.
The line-to-line back-EMF including the DC offset error component generated in the measurement process can be expressed as Equation (4):
where, is the back-EMF peak value, is a rotor position, and is DC offset error component.
When the two-phase back-EMF including the DC offset error component is converted into the three-phase back-EMF, it can be expressed as Equation (5):
Considering the aforementioned DC offset error component, the α-axis and β-axis voltages of the stationary reference frame in the PLL can be given by Equation (6):
In order to obtain the estimated rotor position and frequency, the stationary dq-axis voltages are transformed by using the αβ to dq transformation matrix. The transformation matrix is given by Equation (7):
where is the estimated rotor position.
Therefore, using the Equations (6) and (7), the synchronous dq-axis voltage, can be expressed by Equation (8):
For getting the estimated rotor position and frequency, the synchronous d-axis voltage has to be converged to zero. However, it may not be possible to converge the synchronous d-axis voltage to zero due to the DC offset error .
From Equation (8), the synchronous dq-axis voltages including the DC offset error component can be calculated by Equation (9):
where is the real rotor position.
If the difference between the real rotor position and the estimated rotor position is too small, the synchronous dq-axis voltages can be rewritten using Equation (10):
where , .
Therefore, the error value of the converted synchronous dq-axis voltage can confirm that it has a component of the sine and cosine term. Also, the ripple frequency should have the same frequency of the motor rotation frequency.
In this paper, only the d-axis voltage of the dq-axis voltage is considered to reduce the distortion of the estimated rotor position and frequency because the d-axis voltage is related to the phase and period of the voltage, and the q-axis voltage is related to the magnitude of the voltage. In other words, the d-axis voltage is related to the estimation of the rotor position.
3. The Proposed DC Offset Error Compensation Method
The DC offset of synchronous d-axis voltage causes a distorted rotor position in the PLL system. The frequency component of the synchronous d-axis voltage is same as the motor rotation frequency, therefore, the proposed method compensates the DC offset error by reducing the ripple component of the synchronous d-axis voltage in a PLL.
From Equation (10), the synchronous d-axis voltage including the DC offset error is composed of the sine and cosine term. Therefore, the DC offset error value is estimated by using the , The is set by Equation (11):
where, is sinusoidal wave caused by the DC offset error.
The two axes of the , are required for the synchronous coordinated conversion. Thus, the virtual voltage is delayed by 90° from the and it can be determined by using the digital all pass filter (APF). The stationary , can be calculated by Equation (12):
Equation (12) is converted into the synchronous coordinate system using Equation (6), and it can be calculated as Equation (13). The d-axis voltage of Equation (12) has the value of and the q-axis voltage has the value of :
The values of the d-axis and the q-axis are subtracted to increase the scaling of estimated DC offset error component as shown in Equation (14), because it follows the estimated DC offset error value quickly through the PI controller.
The difference between and can be obtained as follows:
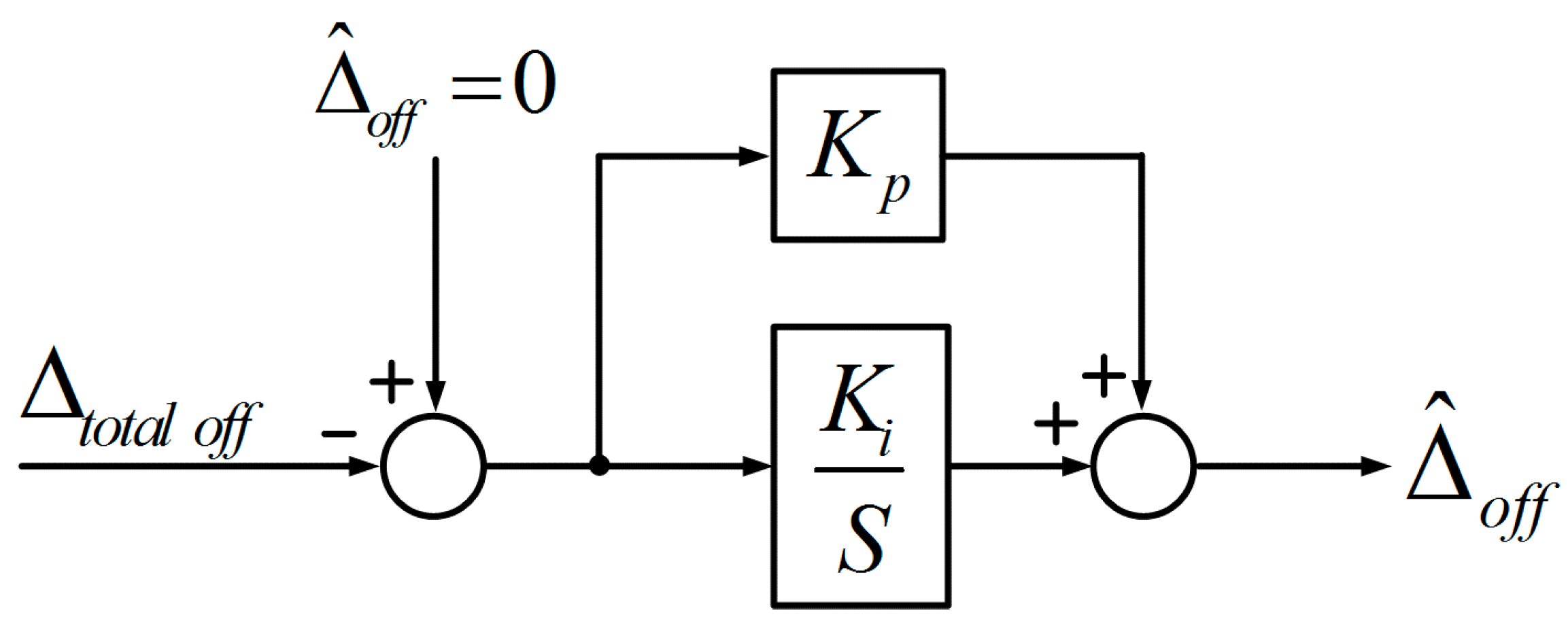
Figure 5 shows a block diagram of the PI controller to estimate . Generally, a PI controller is a widely used industrial controller which uses a linear combination of proportional and integral action on the error to form the output of the controller. However, it has drawbacks that compromise its performance in terms of system response speed and stability [19,20]. Even though it does not have a high dynamic capability, has a linear component in the proposed method, so it can be estimated with a simple PI controller. Also, the PI controller makes the steady state error zero. The relevant deduction is provided in Appendix A.
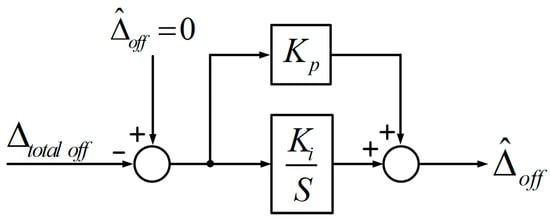
Figure 5.
Block diagram of the PI controller to estimate .
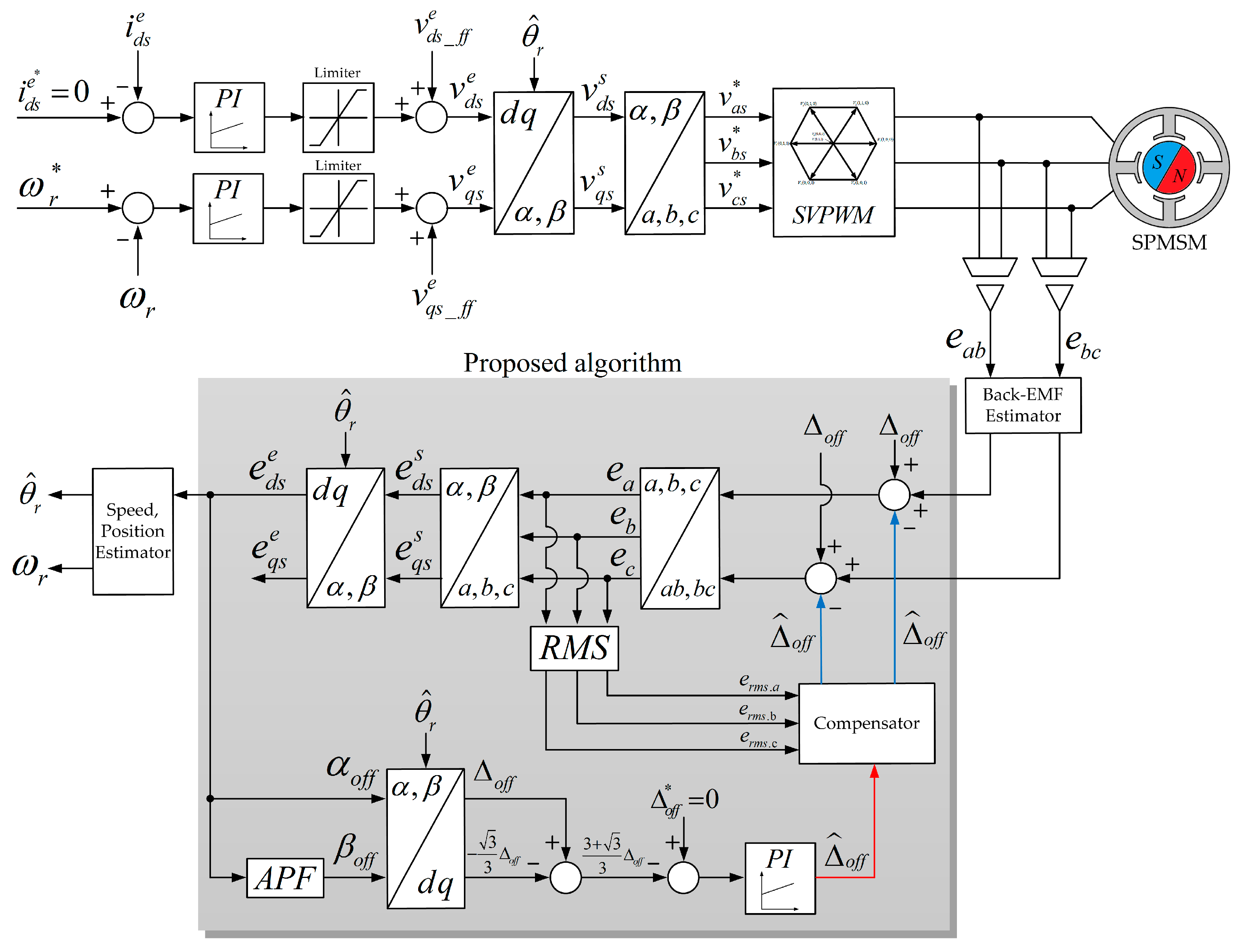
The algorithm of the proposed DC offset error compensator consists of two parts as shown in Figure 6. The first part is the dq-axis coordinated transformation system used for estimating the DC offset error. In the second part, the error between the estimated DC offset error component and the estimated value is removed by using the PI controller. In addition, the output of the proposed PI controller is updated to get the constant of the exact DC offset error value in real time.
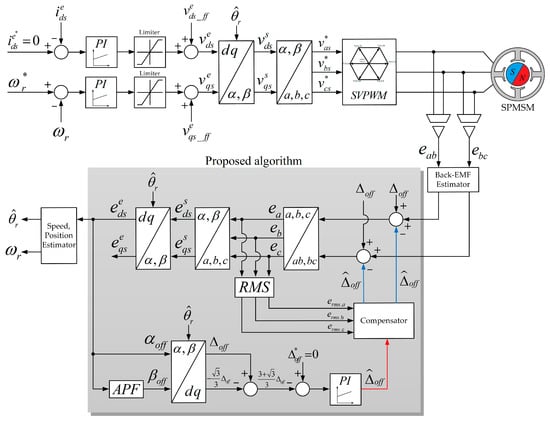
Figure 6.
Proposed rotor position estimation algorithm block diagram.
4. Simulation
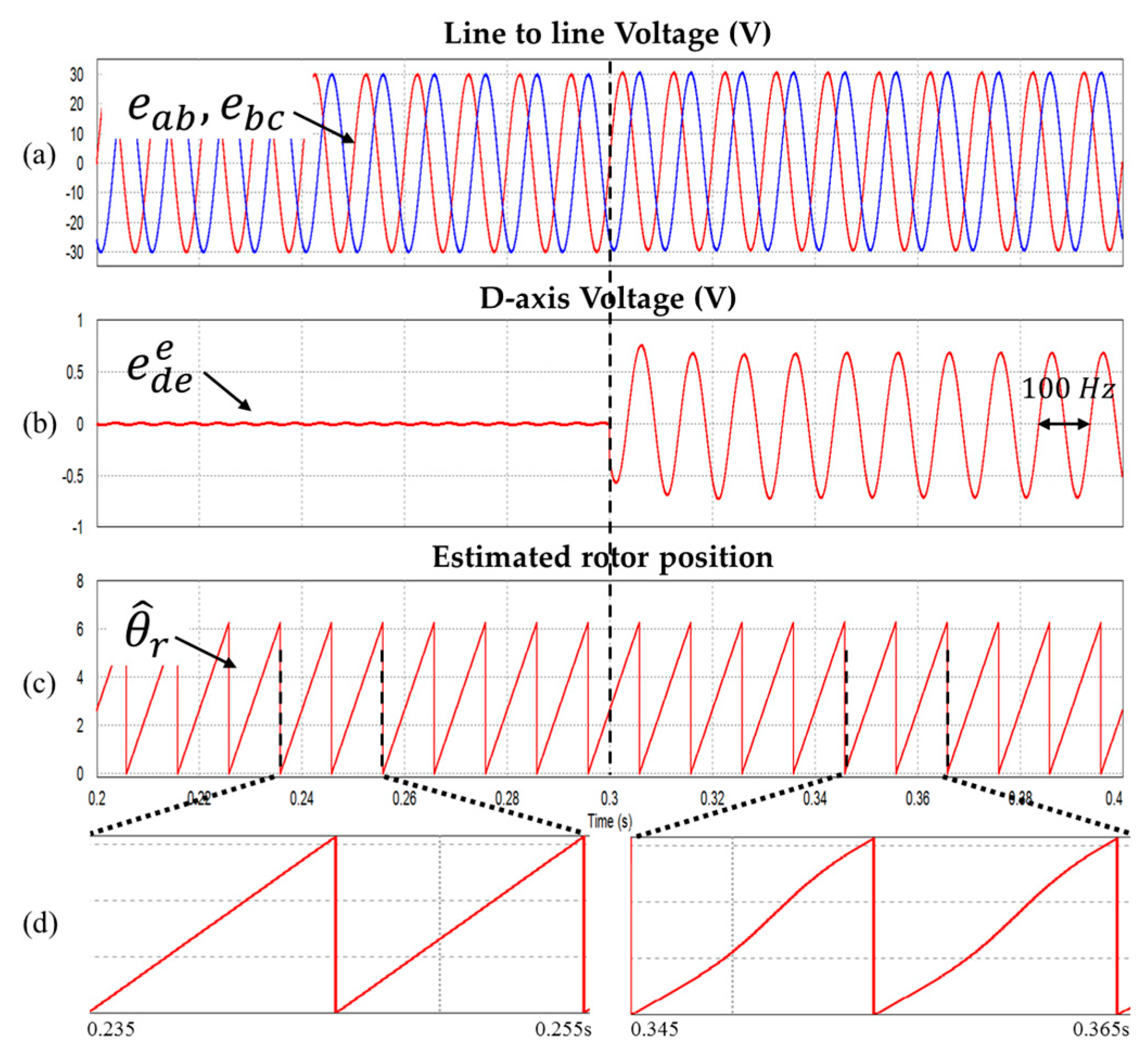
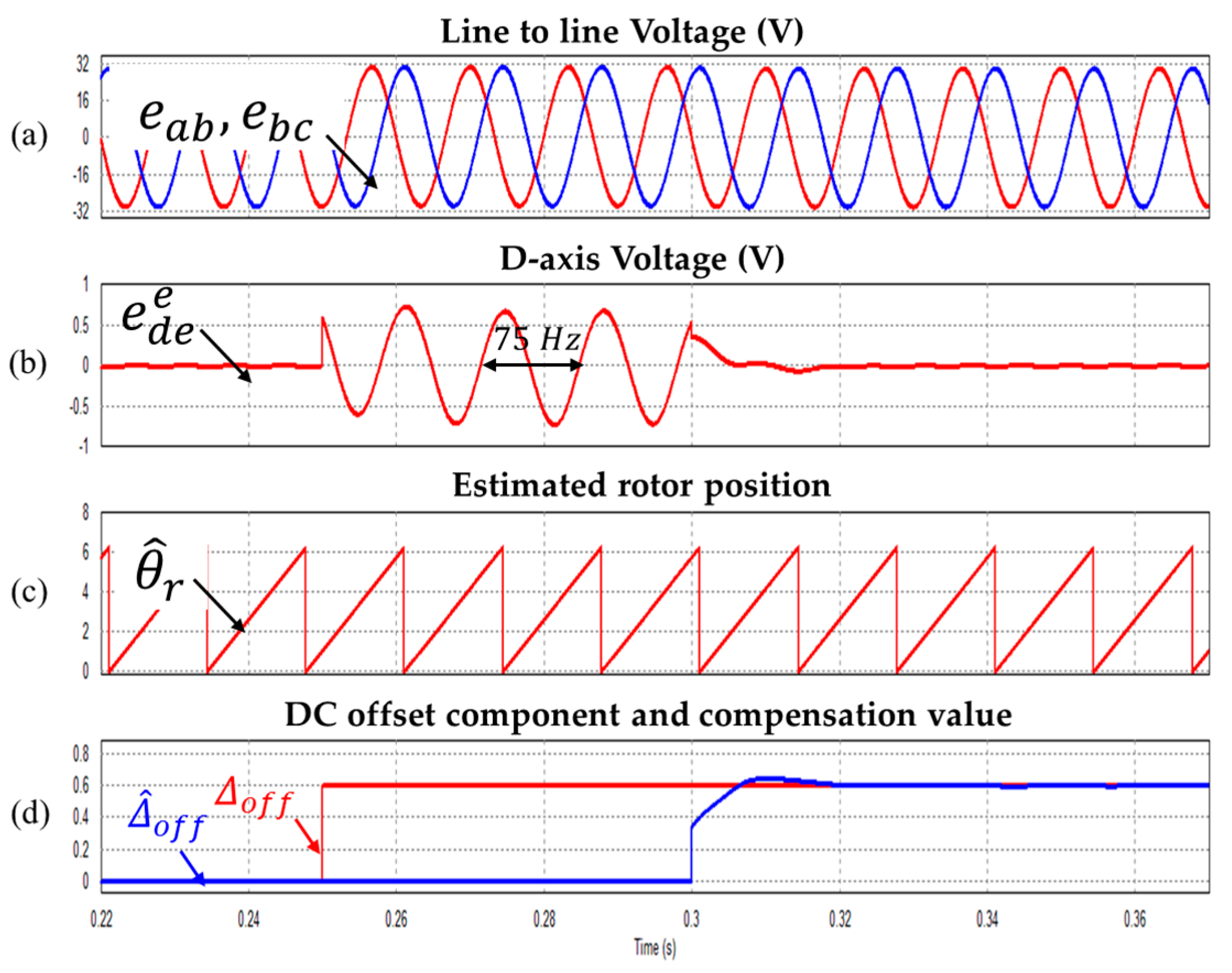
The simulation was performed using PSIM simulator, and the control circuit was constructed using a SPMSM model and C-block. The SPMSM model used 4-pole, 3000 r/min, and 20 W capacity model. Figure 7 shows the simulation waveform with the DC offset error component applied to the line to line voltage in rated speed ( = 3000 r/min).
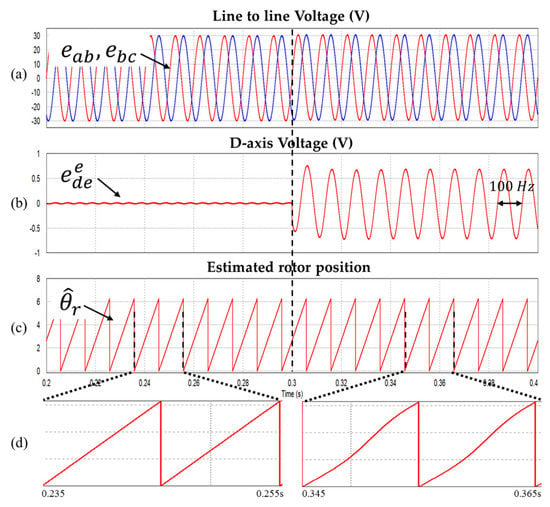
Figure 7.
Waveform during injecting the 0.6 V DC offset (a) Line to line voltages (b) Synchronous d-axis voltage (c) Estimated rotor position (d) Enlarged of the portion in (c) (Operating condition: = 3000 r/min).
A 0.6 V DC offset error (2% of rated voltage; the reason why this DC offset error value was used is explained in Section 5: Experimental Results) is applied to the line to line voltage at 0.3 s, and as a result, the estimated rotor position is distorted and pulsation of the same frequency as the motor rotation frequency of 100 Hz occurs in the d axis voltage of the synchronous coordinate system.
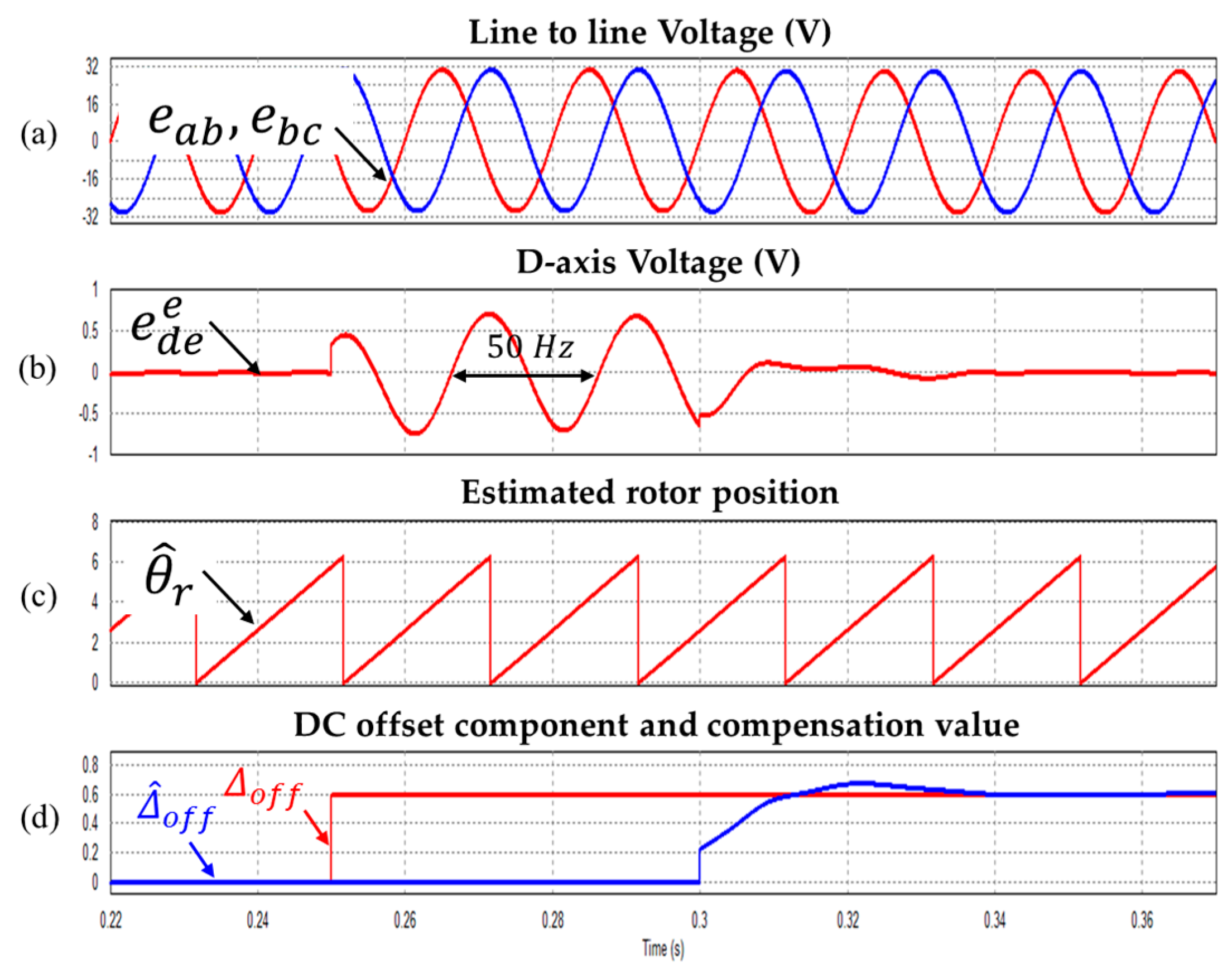
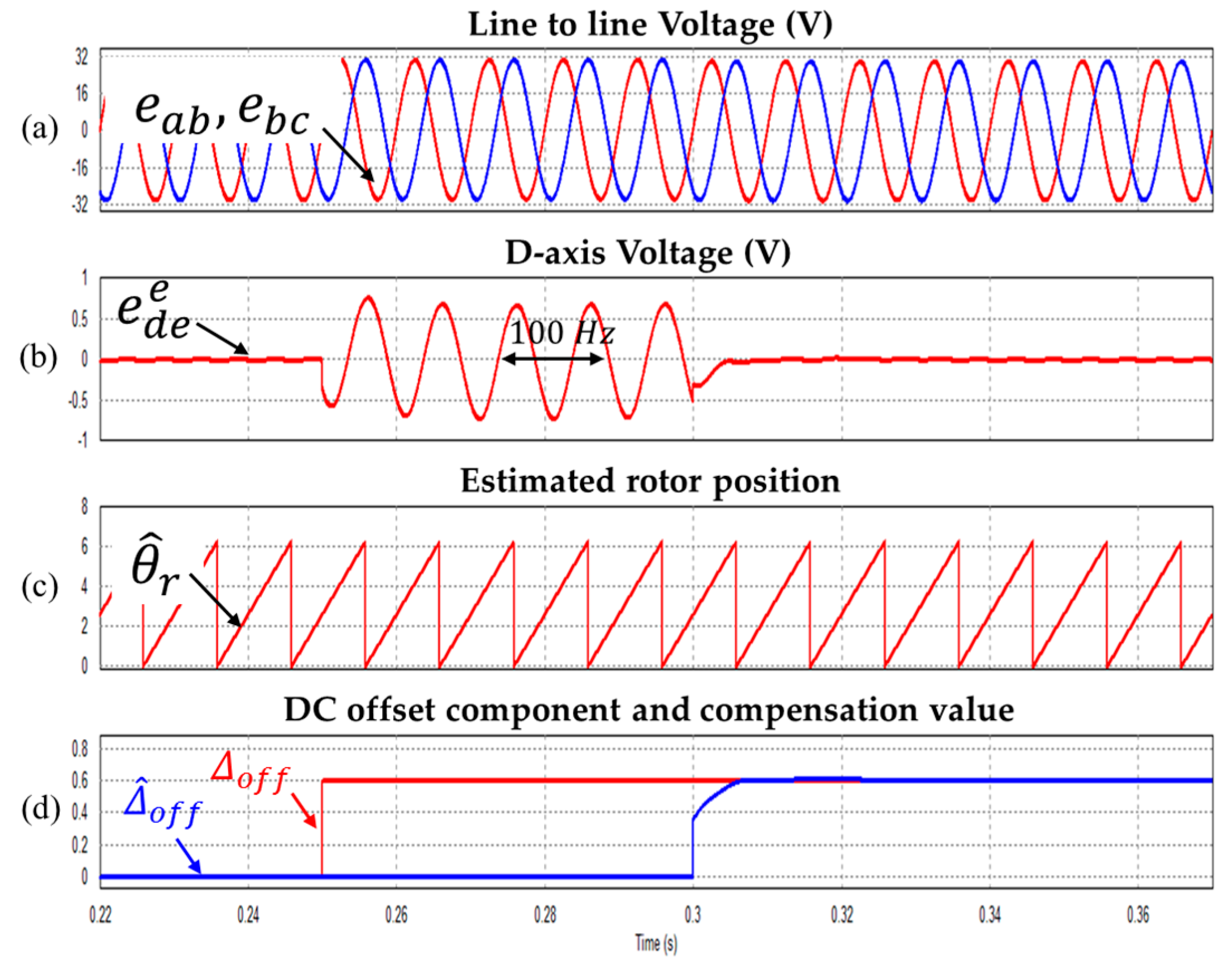
Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10 show DC offset error component compensation characteristic waveforms at 1500 r/min, 2250 r/min and 3000 r/min respectively. As mentioned above, The 0.6 V DC offset error is applied to the line to line voltage at 0.3 s. As a result, it is verified that the DC offset error component is well compensated.
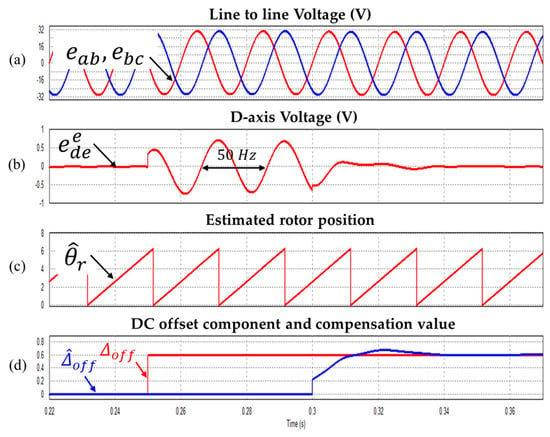
Figure 8.
Waveform during injecting the 0.6 V DC offset (a) Line to line voltages (b) Synchronous d-axis voltage (c) Estimated rotor position (d) DC offset component and compensation value (Operating condition: = 1500 r/min).
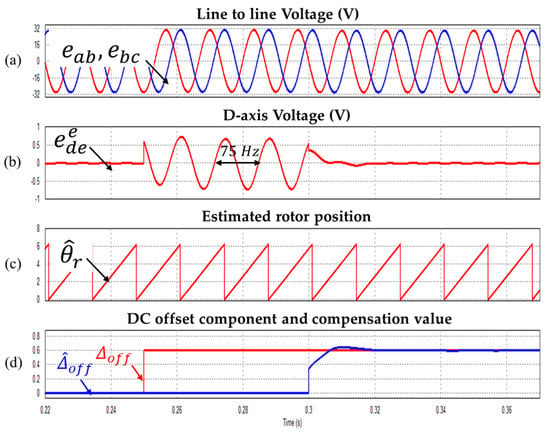
Figure 9.
Waveform during injecting the 0.6 V DC offset (a) Line to line voltages (b) Synchronous d-axis voltage (c) Estimated rotor position (d) DC offset component and compensation value (Operating condition: = 2250 r/min).
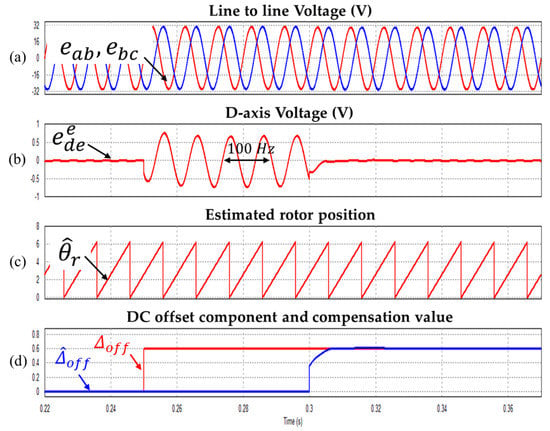
Figure 10.
Waveform during injecting the 0.6 V DC offset (a) Line to line voltages (b) Synchronous d-axis voltage (c) Estimated rotor position (d) DC offset component and compensation value (Operating condition: = 3000 r/min).
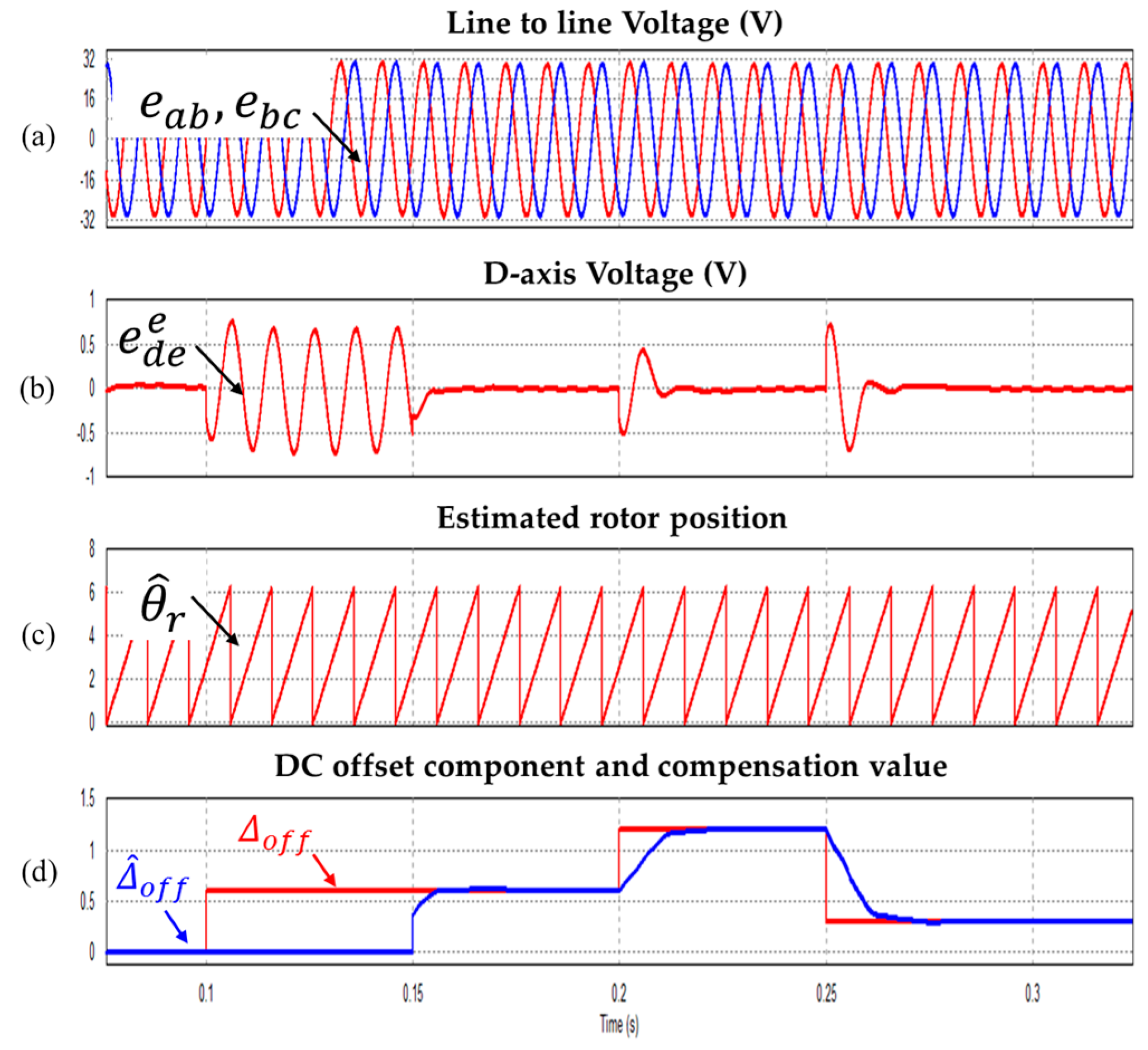
Figure 11 shows the dynamic characteristics of the proposed algorithm according to the variation of the DC offset error component. When a 0.6 V (2% of rated voltage) DC offset error in the line to line back-EMF is applied at 0.1 s, the serious pulsation generated in maintained in the constant synchronous d-axis voltage. The proposed algorithm immediately started the DC offset error compensation in real time at 0.15 s. The DC offset error value is changed to 1.2 V (4% of rated voltage) at 0.2 s. Finally, the DC offset error value is reduced to 0.3 V (1% of rated voltage) at 0.25 s. Since the compensation is performed even if the DC offset error component is applied, the pulsation of the d axis voltage of the synchronous coordinate system is immediately eliminated and a stable value is maintained. It can also be confirmed that the real-time compensation characteristics are excellent, even if the magnitude of the DC offset error component varies.
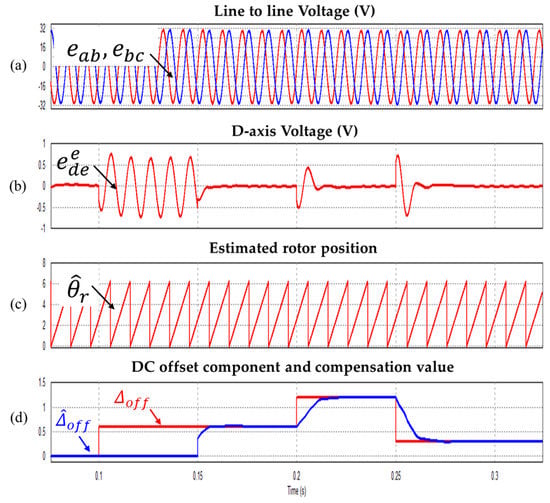
Figure 11.
Waveform according to changing the DC offset (a) Line to line voltages (b) Synchronous frame d-axis voltage (c) Estimated rotor position (d) DC offset component and compensation value.
5. Experimental Results
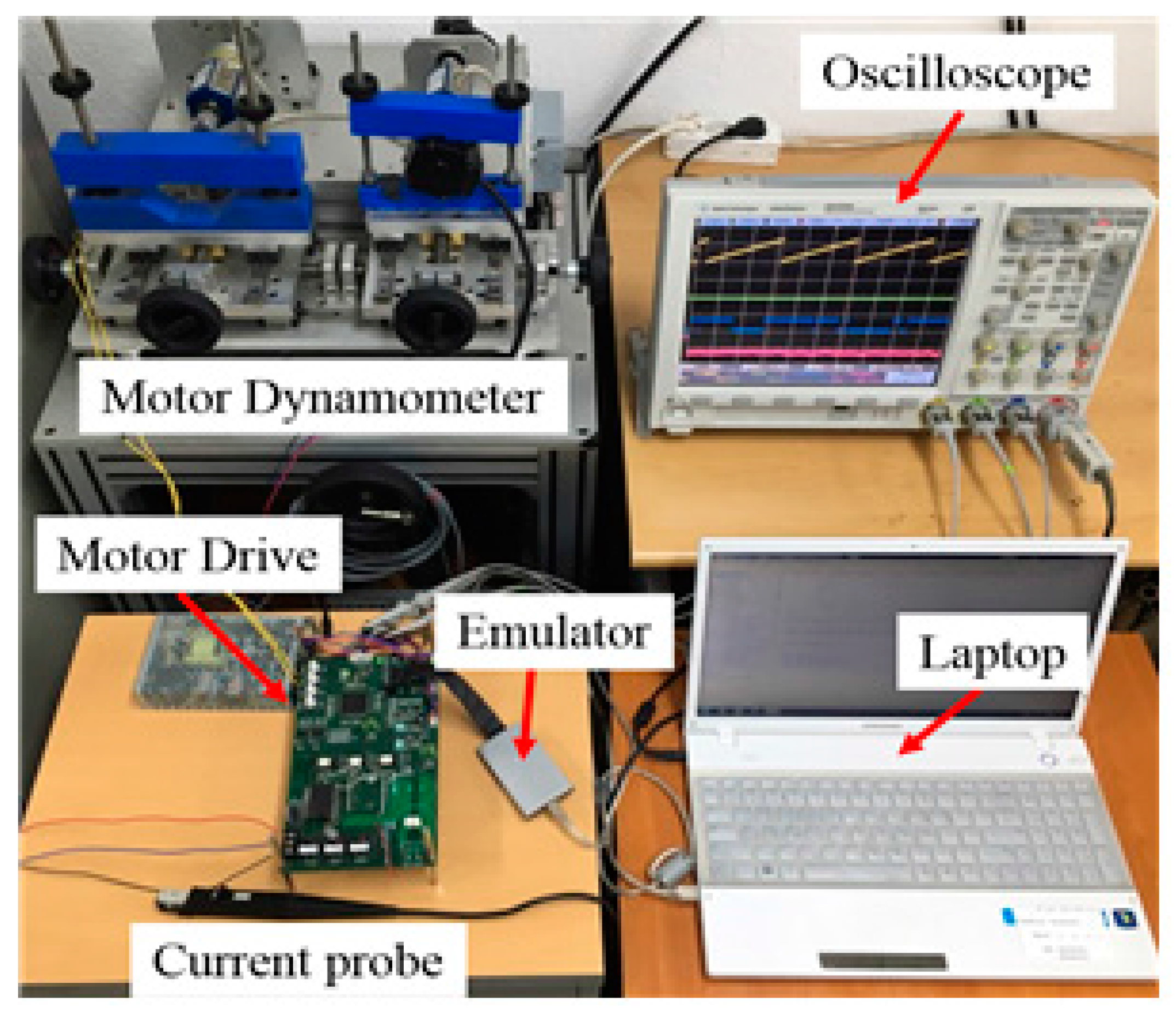
The proposed DC offset error compensation method was verified on a 50 W class sensorless drive and a 20 W SPMSM with dynamo set. This sensorless motor drive is designed based on the 32-bit TMS320F28335 digital signal processor (DSP) control system operating at 10 kHz. Analog signals are converted to digital values by 12-bit A/D converters and all internal data of the DSP can be displayed on an oscilloscope through a 12-bit D/A converter. SPMSM parameters are shown in Table 1 as described above. Figure 12 shows the motor performance experiment using the dynamo set.

Table 1.
The properties of a SPMSM parameters.
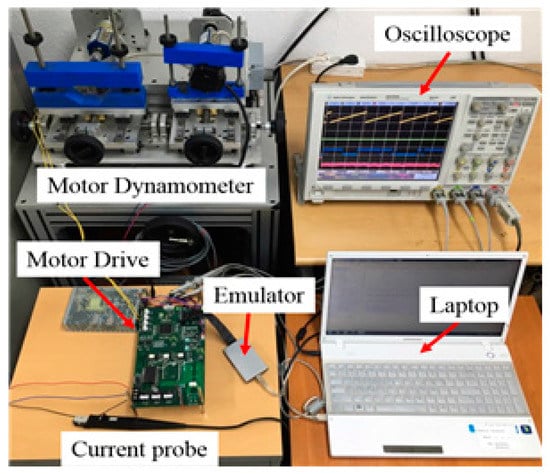
Figure 12.
Experimental of SPMSM drive set up.
Since the range of voltage input is −30–30 V, the voltage value per on least significant bit (LSB) of the A/D converter is 14.6 mV. The range of offset errors on the DSP datasheet is −15–15 LSB, which corresponds to 0.73% of 30 V. However, the effect of the thermal drift of analog devices and the offset errors of op-amp and voltage sensor are considered. Therefore, in this experiment, the offset error was injected 0.6 V, 2% of the rated voltage.
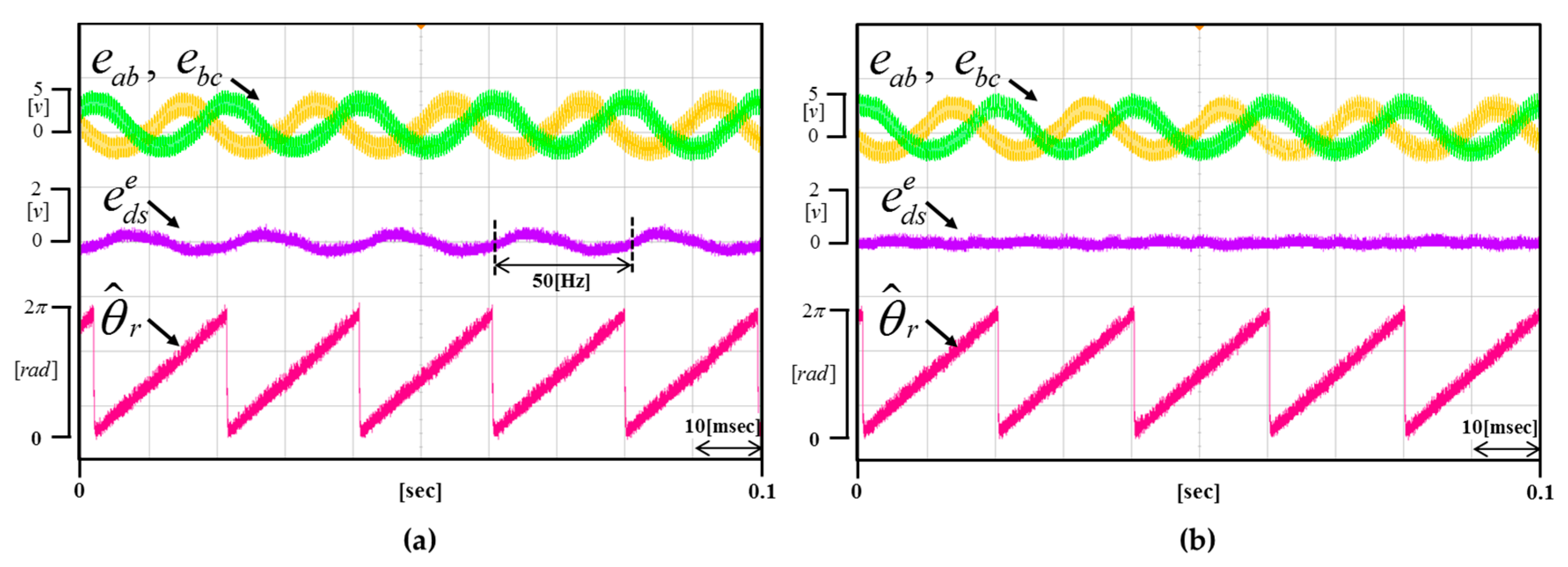
Figure 13a,b shows he waveforms obtained when the motor rotates at 1500 r/min. Figure 13a shows the waveform when the proposed method is not applied. Figure 13b shows the waveform of real-time compensation applying the proposed method (neither artificially injected DC offset error component). As a result of the comparison, it can be inferred that the DC offset error component generated in the sensor and the ADC converter process is about 0.6 V. Also, it can be seen that the d-axis voltage converges to zero exactly due to the proposed method.
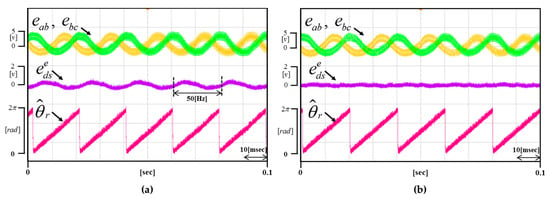
Figure 13.
(a) Waveform of the not applied proposed method (b) Waveform of the applied proposed method (Operating condition: = 1500 r/min).
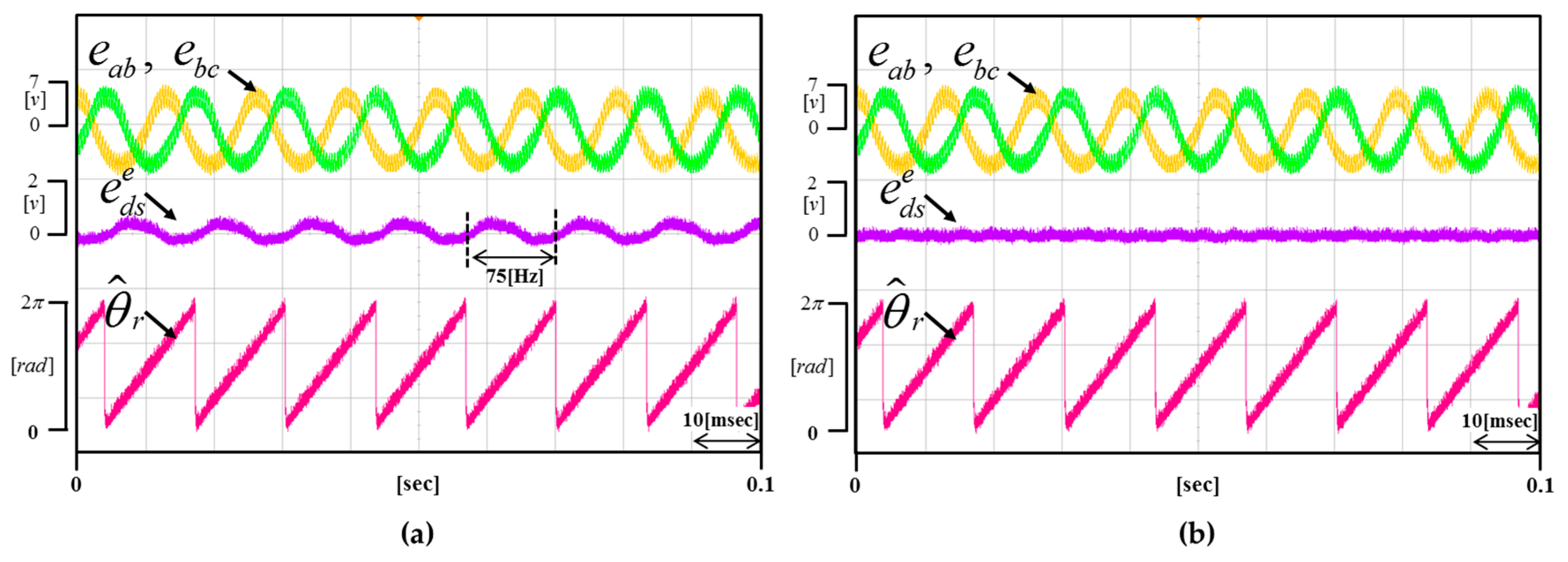
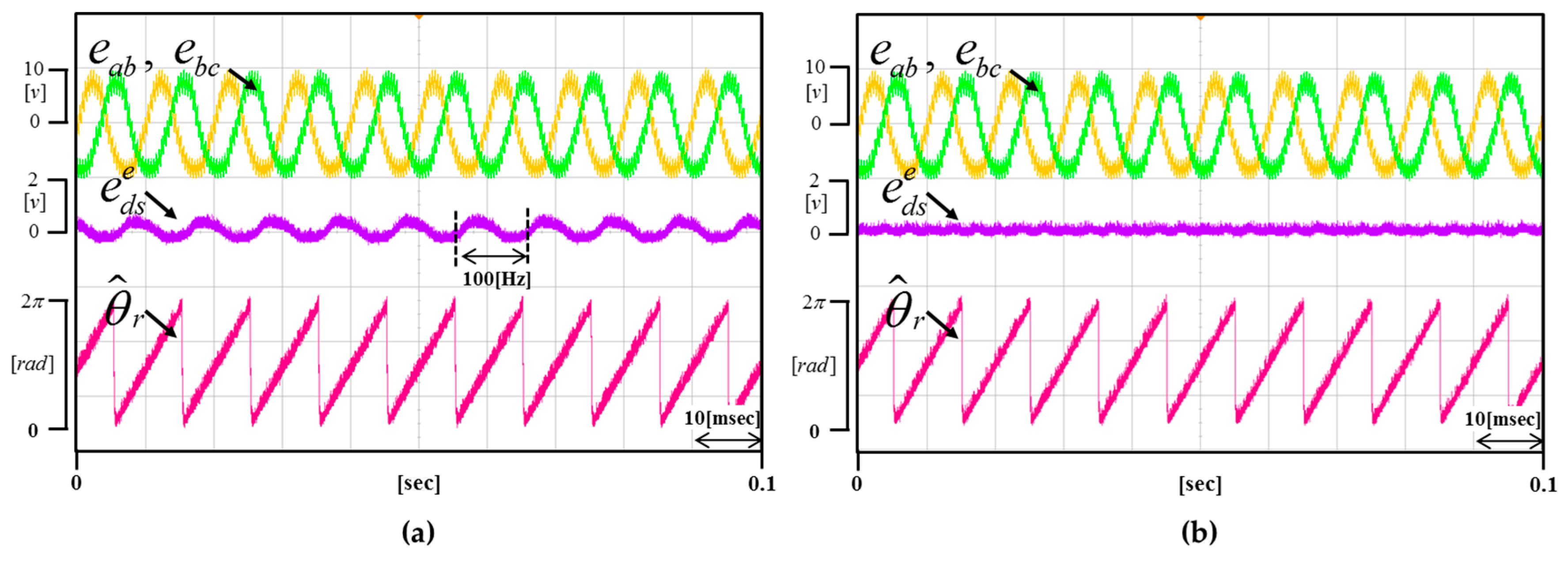
Figure 14 and Figure 15 show the result waveforms when the motor rotates at 2250 r/min and 3000 r/min, respectively. Even if the speed changes, it is verified that the proposed method is equally well compensated.
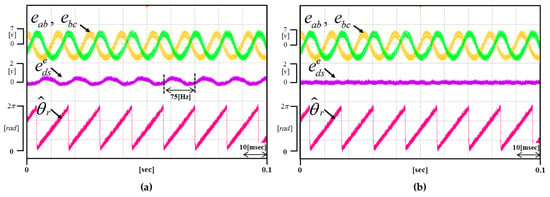
Figure 14.
(a) Waveform of the not applied proposed method (b) Waveform of the applied proposed method (Operating condition: = 2250 r/min).
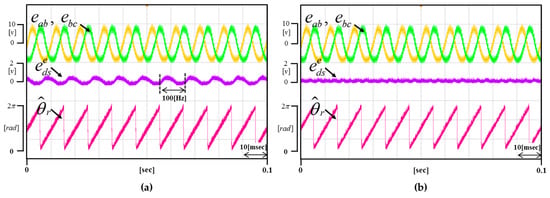
Figure 15.
(a) Waveform of the not applied proposed method (b) Waveform of the applied proposed method (Operating condition: = 3000 r/min).
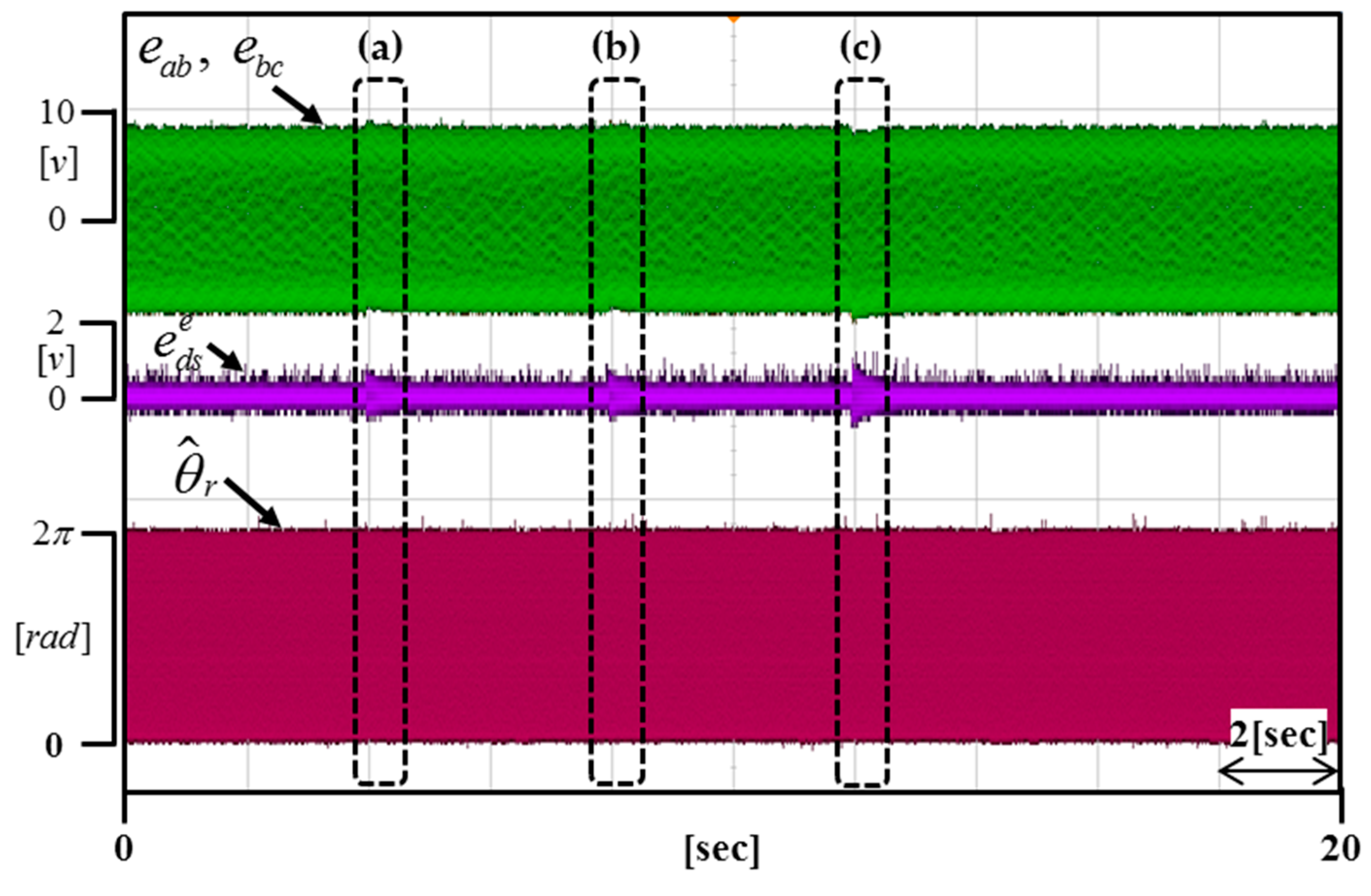
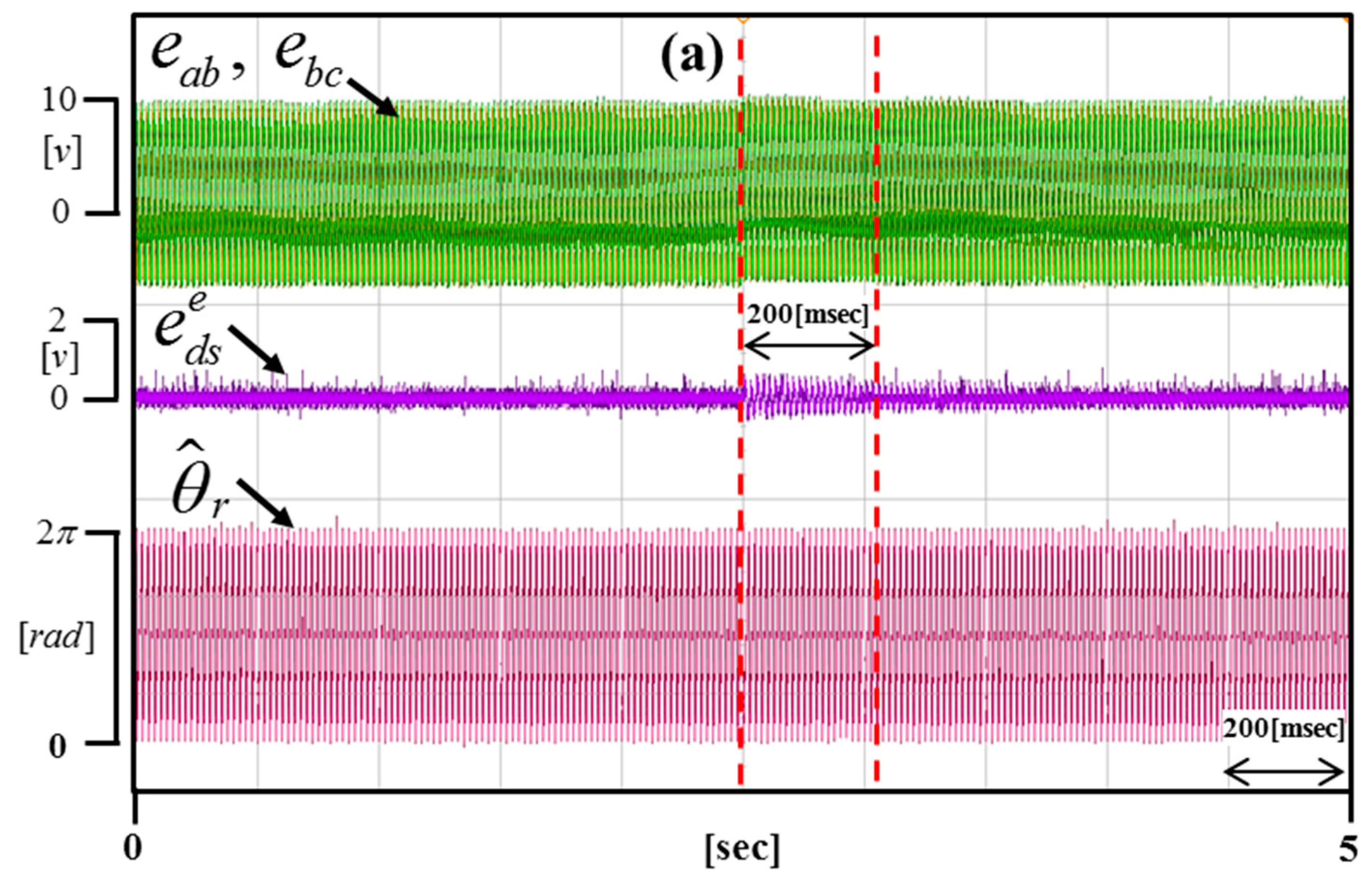
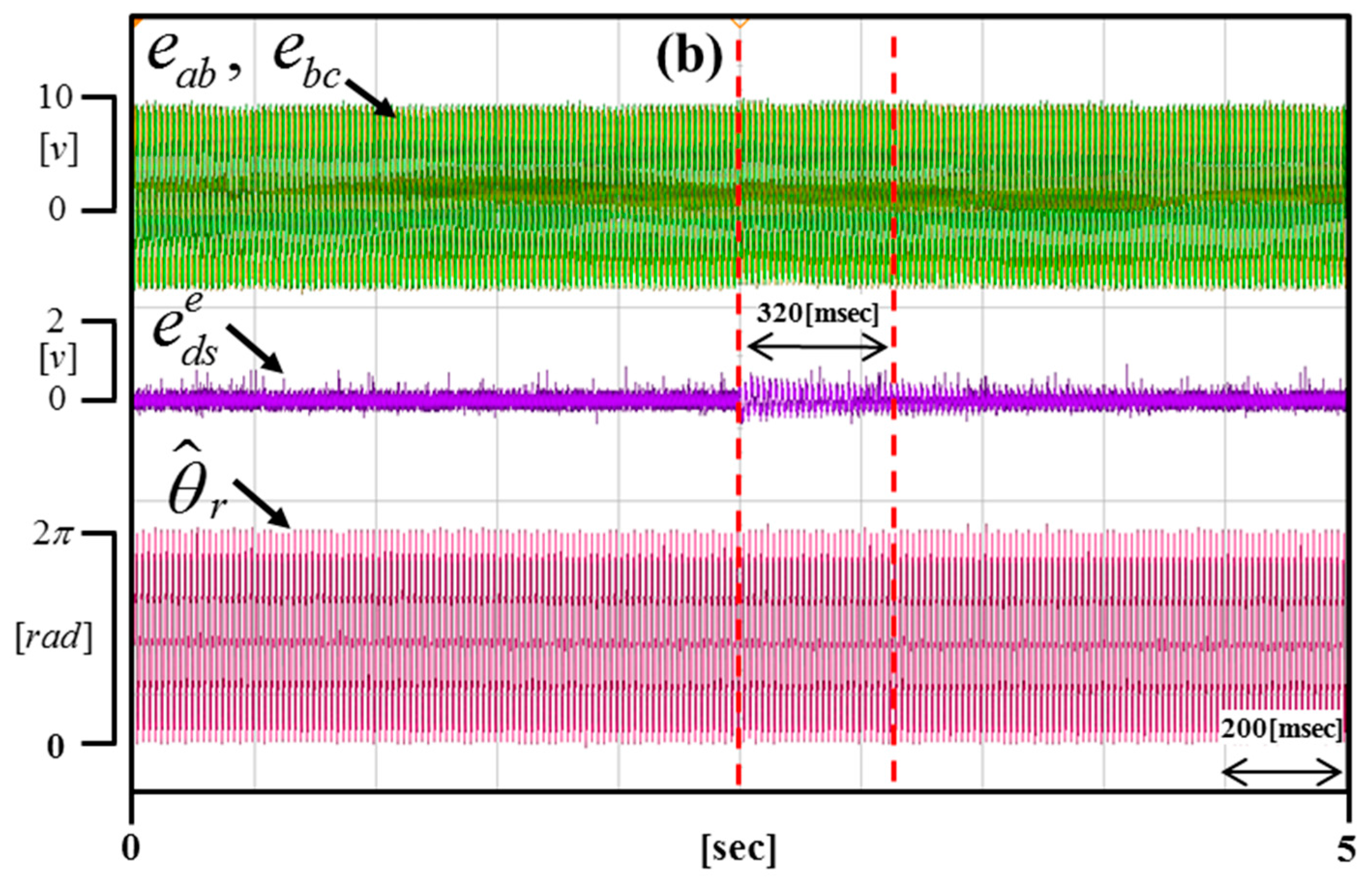
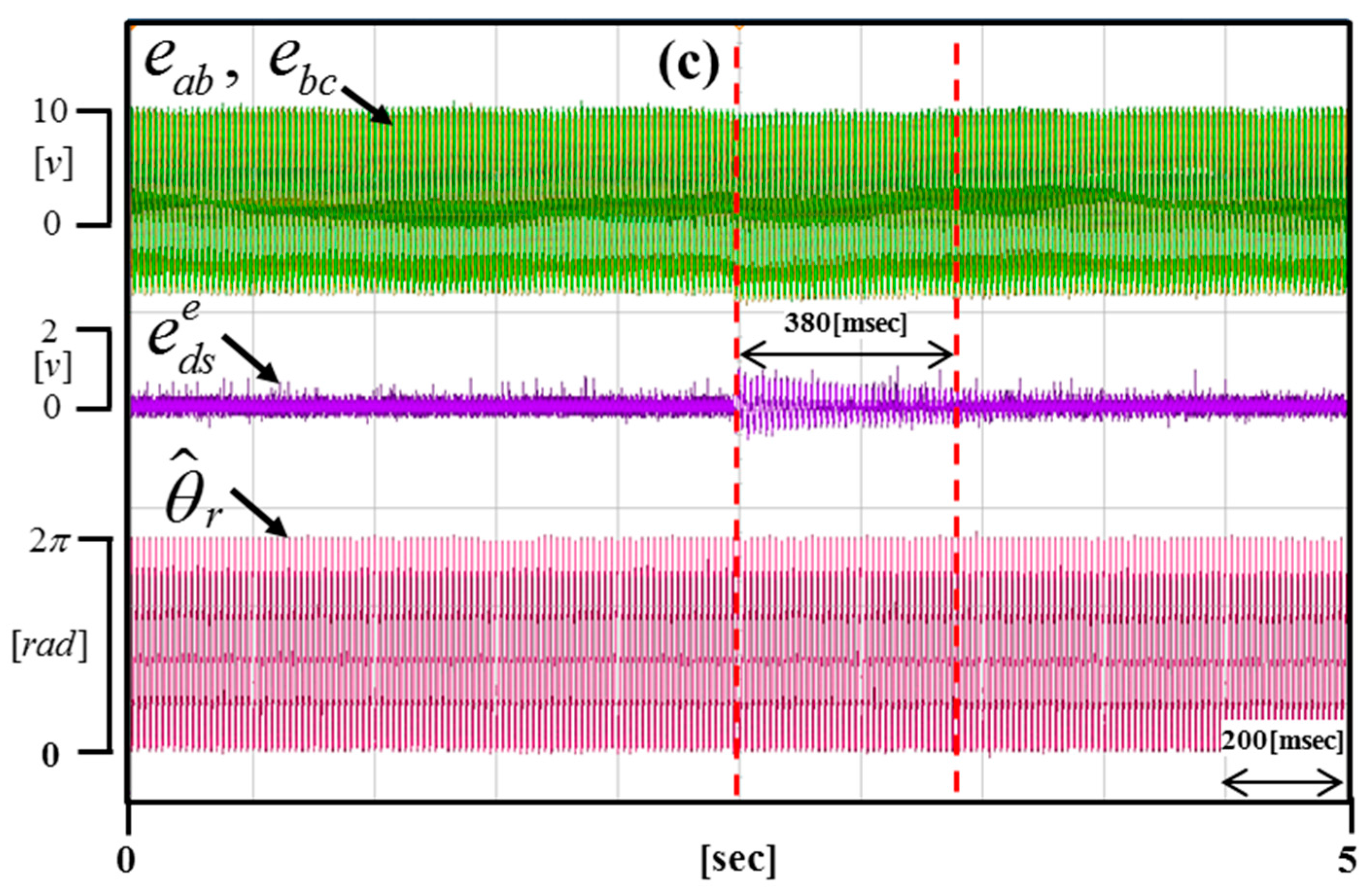
Figure 16 shows the real-time dynamic characteristics of the DC offset error component by applying 0.6 V to the portion (a), 1.2 V to the portion (b), and 0.3 V to the portion (c).
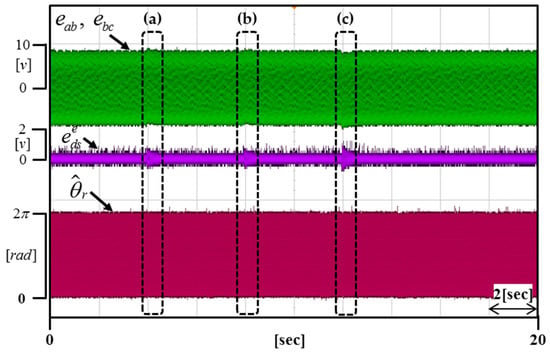
Figure 16.
Experimental results according to changing the DC offset error (Operating condition: = 3000 r/min).
Figure 17, Figure 18 and Figure 19 are enlargements of each portion in Figure 16 (a–c). Figure 17 shows that the time of compensation is 200 ms. Figure 18 shows that the time of compensation is 320 ms. Figure 19 shows that the time of compensation is 380 ms.
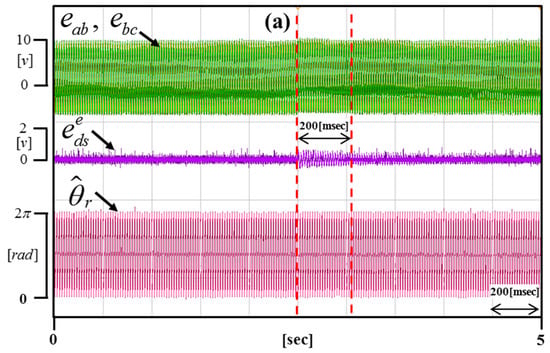
Figure 17.
Enlargement of the portion in Figure 16a.
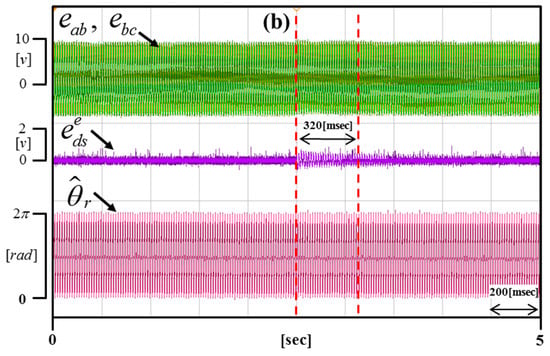
Figure 18.
Enlargement of the portion in Figure 16b.
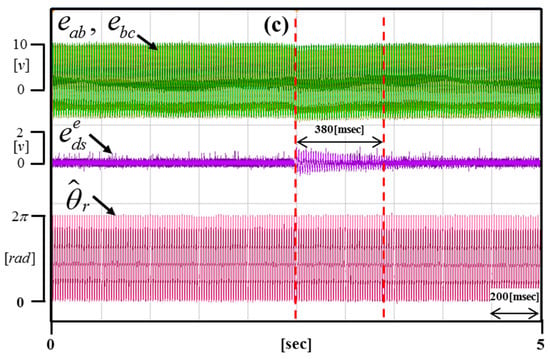
Figure 19.
Enlargement of the portion in Figure 16c.
Although The DC offset error value is changed, the pulsation of the synchronous d-axis voltage is quickly eliminated because the DC offset error value is immediately estimated. In other words, the proposed method verified that the real-time compensation characteristic is excellent even when there is a change in the DC offset error value.
Finally, the conventional method in [17,18,19] was compared with the proposed method. Fundamentally, the purpose of control is different. However, the performance comparison seemed to be equivalent in that it compensates for the error component. In addition, it is difficult to comment whether either the conventional method or proposed method showed better performance under injected error conditions. However, the proposed simple control method showed a better dynamic performance without the use of high mathematical knowledge, and did not cause any steady-state error; this is shown previous plots (Figure 11).
6. Conclusions
In this paper we propose a method to estimate the exact rotor position by compensating the DC offset error component generated by the A/D converter, op-amp and voltage sensor when estimating the rotor position of a SPMSM sensorless drive. The effect of the DC offset error component on sensorless control of SPMSM was theoretically analyzed and the DC offset error component was compensated by using the proposed algorithm. Through the PSIM simulation, the accurate rotor position estimation of the SPMSM after DC offset compensation was confirmed, and the proposed method was verified through a motor performance test using a 50 W class sensorless motor drive and 20 W SPMSM. In addition, the proposed method has the advantage of being configurable without any additional hardware, and the simplicity of the control method which can be tuned in a short time without the use of high mathematical knowledge. Moreover, it was experimentally demonstrated that the proposed method can improve SPMSM operation performance and sensorless control.
This paper is an analysis of the sensorless drive of SPMSM using the back-EMF. Therefore, the results of this paper cannot be applied to the IPMSMs that follow the rotor position by using inductance variation.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Kyungnam University Foundation Grant, 2017.
Author Contributions
Tae-Uk Jung supervised all process. Jung-Hoon Jang implemented simulation and experiment. Chang-Seok Park proposed the algorithm.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
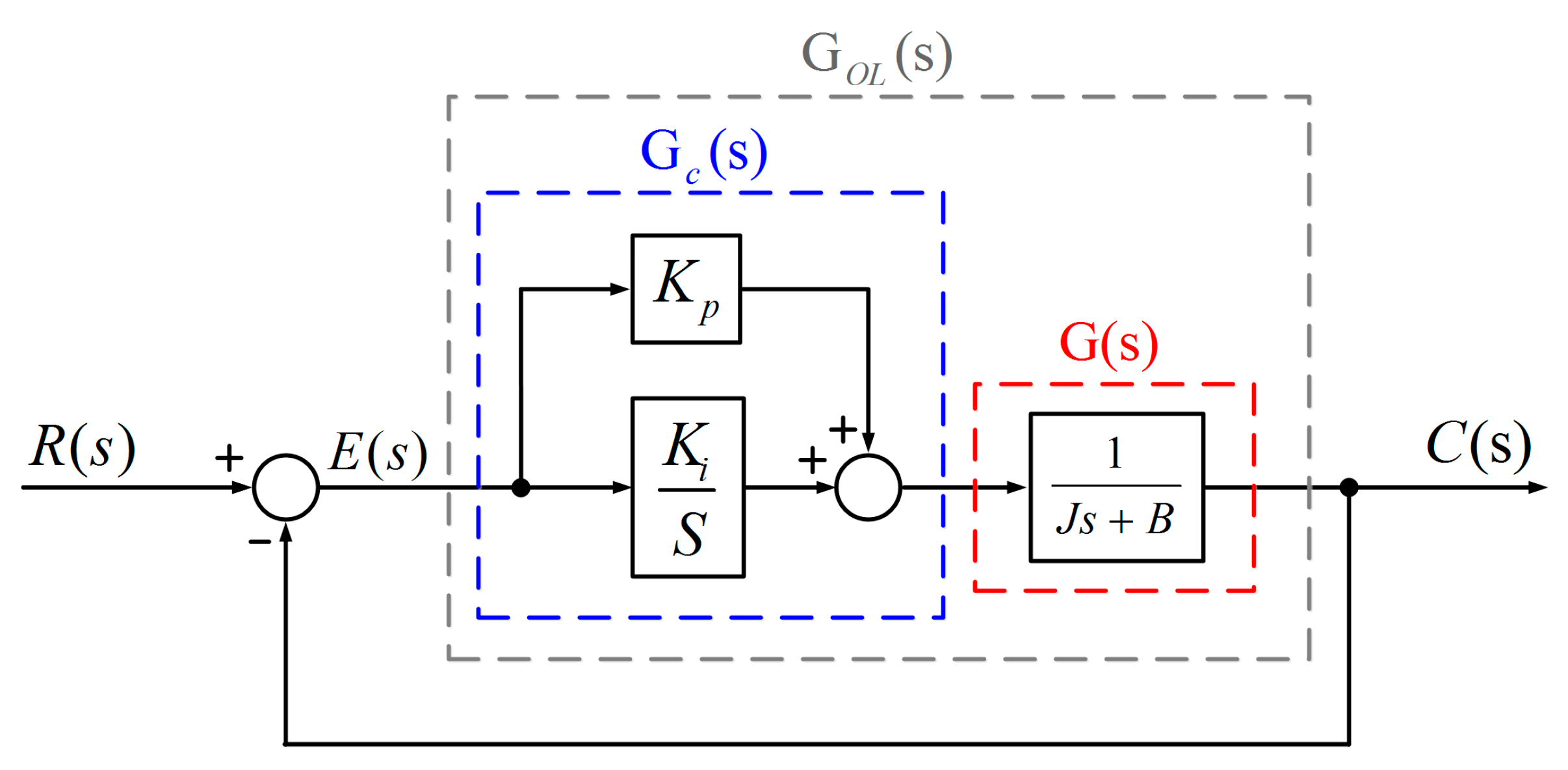
Figure A1 shows the block diagram of the overall control system of the motor. In this figure, is the input, is the output, is the PI controller, is the motor transfer function, , are the proportional gain and integral gain of the PI controller, is the friction coefficient and is the inertia coefficient.
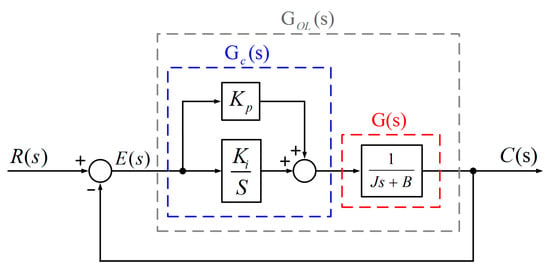
Figure A1.
Block diagram of the overall control system of the motor.
Figure A1.
Block diagram of the overall control system of the motor.
The (PI controller) is expressed as Equation (A1). It is a controller with a pole , zero as L
where .
The is expressed as Equation (A2):
The error constant () of steady state response is expressed as Equation (A3):
Therefore, the steady state error can be set to zero as shown in Equation (A4):
References
- Baik, I.C. Improved nonlinear speed control of PM synchronous motor using time delay control. J. Power Electron. 2003, 3, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, H.; Honda, Y.; Kiriyama, H.; Morimoto, S.; Takeda, Y. The performance comparison of SPMSM, IPMSM, and SynRM in use as air-conditioning compressor. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1999 IEEE Industry Applications Conference: Thirty-Fourth IAS Annual Meeting, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 3–7 October 1999; Volume 2, pp. 840–845. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, B.H.; Sul, S.K.; Kwon, J.H.; Byeon, J.S. Implementation of sensorless vector control for super-high-speed PMSM of turbo-compressor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Ha, J.I. Evaluation of back-EMF estimators for sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motors. J. Power Electron. 2012, 12, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kwon, Y.; Sul, S. Comparison of rotor position estimation performance in fundamental-model-based sensorless control of PMSM. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 September 2015; Volume 7, pp. 5624–5633. [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani, R.; Takeshita, T.; Matsui, N. Current model-based sensorless drives of salient-pole PMSM at low speed and standstill. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, N. Sensorless PM Brushless DC motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tomita, M.; Ichikawa, S.; Okuma, S. Sensorless control of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor by estimation of an extended electromotive force. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2000 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Rome, Italy, 8–12 October 2000; Volume 3, pp. 1814–1819. [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara, S.; Akagi, H. Implementation and position control performance of a position-sensorless IPM motor drive system based on magnetic saliency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Ha, J.I.; Sul, S.K. PWM switching frequency signal injection sensorless method in IPMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobotaru, M.; Teodorescu, R.; Agelidis, V.G. Offset rejection for PLL based synchronization in grid-connected converters. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Third Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Austin, TX, USA, 24–28 February 2008; pp. 1611–1617. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi-Ghartemani, M.; Khajehoddin, S.A.; Jain, P.K.; Bakhshai, A.; Mojiri, M. Addressing DC component in PLL and notch filter algorithms. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Jung, T.U. Improved DC offset error compensation algorithm in phase locked loop system. JEET 2016, 11, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Liu, L.; Kim, J.M. DC offset error compensation for synchronous reference frame PLL in single-phase grid-connected converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3467–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.W.; Sul, S.K. Analysis and compensation of current measurement error in vector-controlled AC motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Panda, S.K.; Xu, J.X. Torque ripple minimization in PM synchronous motors using iterative learning control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, C.U.; Choi, C. Diminution of current measurement error for vector-controlled AC motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.R.; Seok, J.K. Correction on current measurement errors for accurate flux estimation of AC drives at low stator frequency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Jiang, M.; Guo, X.; Chen, Q. Sensorless position control of SPMLSM based on high-gain observer. J. Comput. 2013, 3, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.X.; Zheng, C.H.; Duan, B.H. Automatic disturbances rejection controller for precise motion-control of permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 3, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).