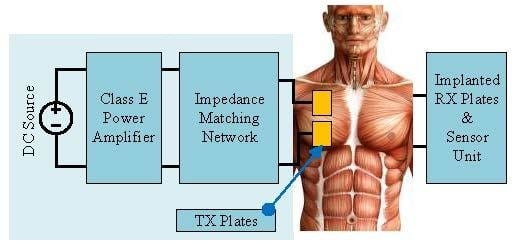
Class E Power Amplifier Design and Optimization for the Capacitive Coupled Wireless Power Transfer System in Biomedical Implants
Abstract
Share and Cite
R., N.; A., V.J.; Chokkalingam, B.; Padmanaban, S.; Leonowicz, Z.M. Class E Power Amplifier Design and Optimization for the Capacitive Coupled Wireless Power Transfer System in Biomedical Implants. Energies 2017, 10, 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091409
R. N, A. VJ, Chokkalingam B, Padmanaban S, Leonowicz ZM. Class E Power Amplifier Design and Optimization for the Capacitive Coupled Wireless Power Transfer System in Biomedical Implants. Energies. 2017; 10(9):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091409
Chicago/Turabian StyleR., Narayanamoorthi, Vimala Juliet A., Bharatiraja Chokkalingam, Sanjeevikumar Padmanaban, and Zbigniew M. Leonowicz. 2017. "Class E Power Amplifier Design and Optimization for the Capacitive Coupled Wireless Power Transfer System in Biomedical Implants" Energies 10, no. 9: 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091409
APA StyleR., N., A., V. J., Chokkalingam, B., Padmanaban, S., & Leonowicz, Z. M. (2017). Class E Power Amplifier Design and Optimization for the Capacitive Coupled Wireless Power Transfer System in Biomedical Implants. Energies, 10(9), 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091409