Advanced Control Strategies of Induction Machine: Field Oriented Control, Direct Torque Control and Model Predictive Control †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model of an Induction Machine
3. Control Strategies in Theory
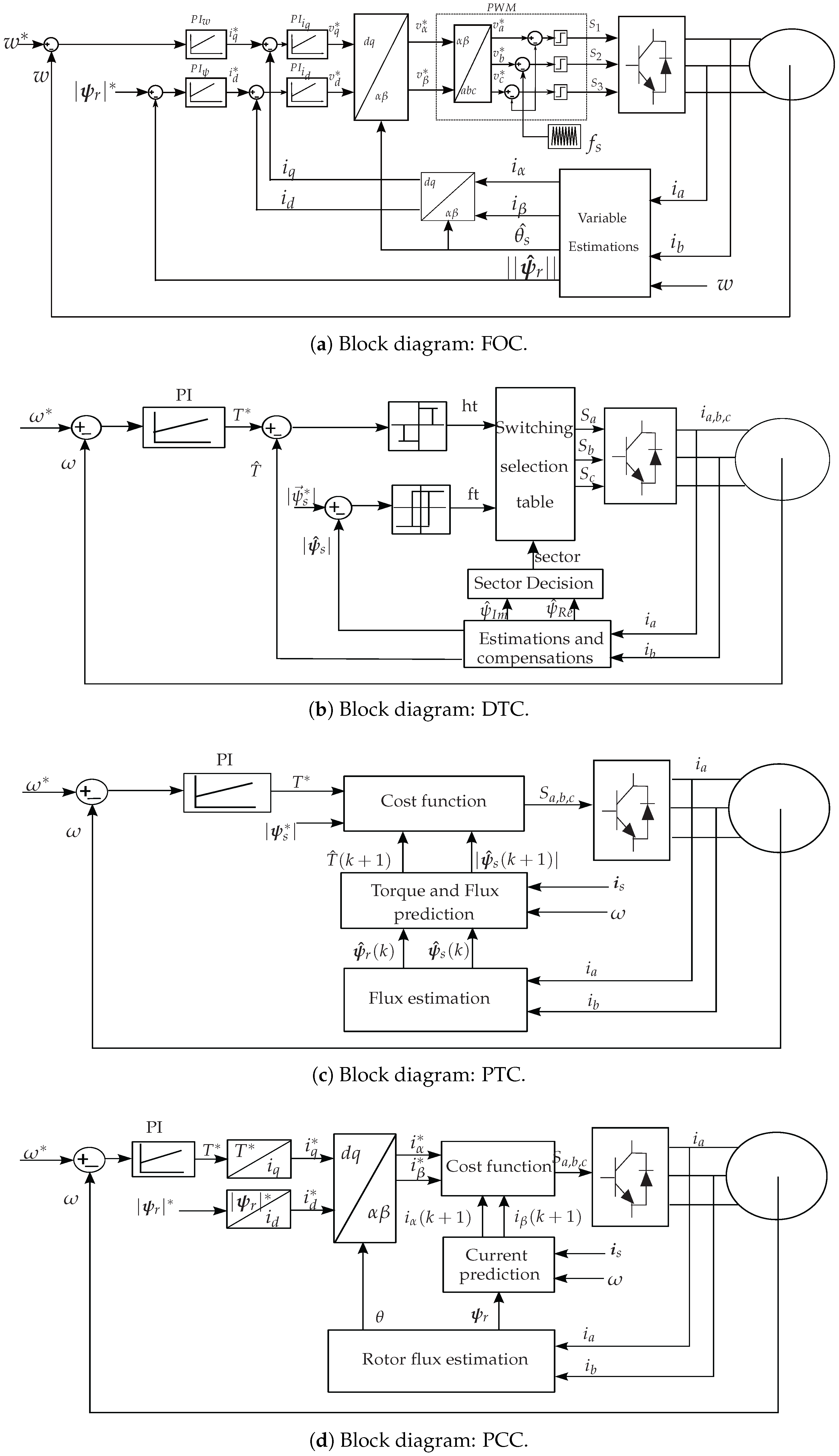
3.1. FOC Strategy
3.2. DTC Strategy
3.3. MPC Strategy
3.3.1. PTC Strategy
3.3.2. PCC Strategy
3.3.3. Discussions of Different Control Strategies
4. Implementation and Experimental Comparisons
4.1. Test Bench Description
4.2. Experimental Comparisons
4.3. Analysis of Experimental Comparisons
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holtz, J. Pulsewidth modulation for electronic power conversion. Proc. IEEE 1994, 82, 1194–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, I.; Ohmori, Y. High-performance direct torque control of an induction motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1989, 25, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschler, P.; Flach, E. Digital implementation of predictive direct control algorithms for induction motors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Thirty-Third IAS Annual Meeting Industry Applications Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 12–15 October 1998; pp. 444–451. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrozic, V.; Buja, G.S.; Menis, R. Band-constrained technique for direct torque control of induction motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stando, D.; Kazmierkowski, M.P. Novel speed sensorless DTC-SVM scheme for induction motor drives. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Compatibility and Power Electronics (CPE), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 5–7 June 2013; pp. 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Franquelo, L.G.; Rodriguez, J.; Perez, M.A.; Leon, J.I. High-Performance Motor Drives. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2011, 5, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Sun, T.; Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R. FPGA-Based Experimental Investigation of a Quasi-Centralized Model Predictive Control for Back-to-Back Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Pontt, J.; Silva, C.A.; Correa, P.; Lezana, P.; Cortes, P.; Ammann, U. Predictive Current Control of a Voltage Source Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 54, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, P.; Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Kennel, R.; Quevedo, D.E.; Rodriguez, J. Predictive Control in Power Electronics and Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 4312–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, J.; Stadtfeldt, S. A predictive controller for the stator current vector of AC machines fed from a switched voltage source. In Proceedings of the International Power Electronics Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 27–31 March 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Kennel, R.; Schöder, D. A predictive control strategy for converters. In Proceedings of the Control in Power Electronics and Electrical Drives, Lausanne, Switzerland, 12–14 September 1983; Volume 12, pp. 415–422. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.; Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Espinoza, J.R.; Zanchetta, P.; Abu-Rub, H.; Young, H.A.; Rojas, C.A. State of the Art of Finite Control Set Model Predictive Control in Power Electronics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, R.; Ammann, U.; Rodriguez, J. Predictive Approach to Increase Efficiency and Reduce Switching Losses on Matrix Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Qu, C. Relationship Between Two Direct Power Control Methods for PWM Rectifiers Under Unbalanced Network. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 12, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, T.; Papafotiou, G.; Morari, M. Model Predictive Direct Torque Control—Part I: Concept, Algorithm, and Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preindl, M.; Bolognani, S. Model Predictive Direct Torque Control With Finite Control Set for PMSM Drive Systems, Part 1: Maximum Torque Per Ampere Operation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 56, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, F.; Prieto, J.; Levi, E.; Gregor, R.; Toral, S.; Duran, M.J.; Jones, M. An Enhanced Predictive Current Control Method for Asymmetrical Six-Phase Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 3242–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Davari, S.A.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Khaburi, D.A.; Rodriguez, J.; Kennel, R. Finite Control Set Model Predictive Torque Control of Induction Machine with a Robust Adaptive Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 58, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Davari, S.A.; Fotouhi, R.; Khaburi, D.A.; Rodriguez, J.; Kennel, R. An Encoderless Predictive Torque Control for an Induction Machine With a Revised Prediction Model and EFOSMO. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6635–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Stolze, P.; Stumper, J.F.; Rodriguez, J.; Kennel, R. Encoderless Finite-State Predictive Torque Control for Induction Machine With a Compensated MRAS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfling, M.; Mouton, H.; Karamanakos, P.; Geyer, T. Experimental evaluation of sphere decoding for long-horizon direct model predictive control. In Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’17 ECCE Europe), Warsaw, Poland, 11–14 September 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kakosimos, P.; Abu-Rub, H. Predictive Speed Control with Short Prediction Horizon for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 99, 2740–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidya, R.; Aguilera, R.P.; Acuña, P.; Vazquez, S.; Mouton, H.D.T. Multistep Model Predictive Control for Cascaded H-Bridge Inverters: Formulation and Analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Kennel, R.; Espinoza, J.R.; Trincado, M.; Silva, C.A.; Rojas, C.A. High-Performance Control Strategies for Electrical Drives: An Experimental Assessment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, S.; Mei, X.; Xie, W.; Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R.M. Model-Based Predictive Direct Control Strategies for Electrical Drives: An Experimental Evaluation of PTC and PCC Methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennel, R.; Rodriguez, J.; Espinoza, J.; Trincado, M. High performance speed control methods for electrical machines: An assessment. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Vina del Mar, Chile, 14–17 March 2010; pp. 1793–1799. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, F. The principle of field-orientation as applied to the new transvector closed-loop system for rotating-field machines. Siemens Rev. 1972, 34, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Vas, P. Vector Control of AC Machines; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, D. Elektrische Antriebe 2: Regelung von Antrieben; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Buja, G.S.; Kazmierkowski, M.P. Direct torque control of PWM inverter-fed AC motors—A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, M.; Nedeljkovic, D.; Ambrozic, V. Predictive torque control of induction machines using immediate flux control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, P.; Pacas, M.; Rodriguez, J. Predictive torque control for inverter-fed induction machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papafotiou, G.; Kley, J.; Papadopoulos, K.; Bohren, P.; Morari, M. Model predictive direct torque control—Part II: Implementation and experimental evaluation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Pontt, J.; Silva, C.A.; Correa, P.; Lezana, P.; Cortes, P.; Ammann, U. Direct torque control of PWM inverter-fed AC motors—A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczynski, T.; Mertens, A. Predictive stator current control for medium voltage drives with LC filters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolze, P.; Tomlinson, M.; Kennel, R.; Mouton, T. Heuristic finite-set model predictive current control for induction machines. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE ECCE Asia Downunder (ECCE Asia), Melbourne, Australia, 3–6 June 2013; pp. 1221–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Holtz, J. Heuristic finite-set model predictive current control for induction machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Istanbul, Turkey, 1–4 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Holtz, J. The induction motor-a dynamic system. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Control and Instrumentation, Bologna, Italy, 5–9 September 1994; Volume 1, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Yang, H. Performance Improvement of Two-Vectors-Based Model Predictive Control of PWM Rectifier. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 6016–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| FOC | DTC | PTC | PCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuned Parameters Number | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| External Controller | PI | PI | PI | PI |
| Inner Controller | 2 PI | 2 hysteresis | 1 cost function | 1 cost function |
| Flux Angle | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Coordinate Transformation | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| PWM (pulse width modulation) | Yes | No | No | No |
| System Constraints’ Inclusion | Difficult | Difficult | Easy | Easy |
| Conceptual Complexity | High | Medium | Low | Low |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| DC (direct current) link voltage | 582 V |
| 2.68 Ω | |
| 2.13 Ω | |
| 275.1 mH | |
| 283.4 mH | |
| 283.4 mH | |
| p | 1.0 |
| 2772.0 RPM | |
| 7.5 Nm | |
| J | 0.005 kg/m2 |
| FOC | DTC | PTC | PCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculation Time | 8 μs | 8 μs | 24 μs | 17.8 μs |
| Current THD (total harmonic distortion) | Better | Worse | Good | Good |
| Torque Ripple | Less | More | Some | Some |
| Dynamics | Slower | Faster | Faster | Faster |
| Switching Frequency | Constant | Variable | Variable | Variable |
| Lm Sensitivity | Small | Small | Small | Big |
| Rs Sensitivity | Small | Big | Big | Small |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Mei, X.; Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R. Advanced Control Strategies of Induction Machine: Field Oriented Control, Direct Torque Control and Model Predictive Control. Energies 2018, 11, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010120
Wang F, Zhang Z, Mei X, Rodríguez J, Kennel R. Advanced Control Strategies of Induction Machine: Field Oriented Control, Direct Torque Control and Model Predictive Control. Energies. 2018; 11(1):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010120
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fengxiang, Zhenbin Zhang, Xuezhu Mei, José Rodríguez, and Ralph Kennel. 2018. "Advanced Control Strategies of Induction Machine: Field Oriented Control, Direct Torque Control and Model Predictive Control" Energies 11, no. 1: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010120
APA StyleWang, F., Zhang, Z., Mei, X., Rodríguez, J., & Kennel, R. (2018). Advanced Control Strategies of Induction Machine: Field Oriented Control, Direct Torque Control and Model Predictive Control. Energies, 11(1), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010120






