Assessment, Mitigation, and Control of Potential Gas Leakage in Existing Buildings Not Designed for Gas Installation in Indonesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
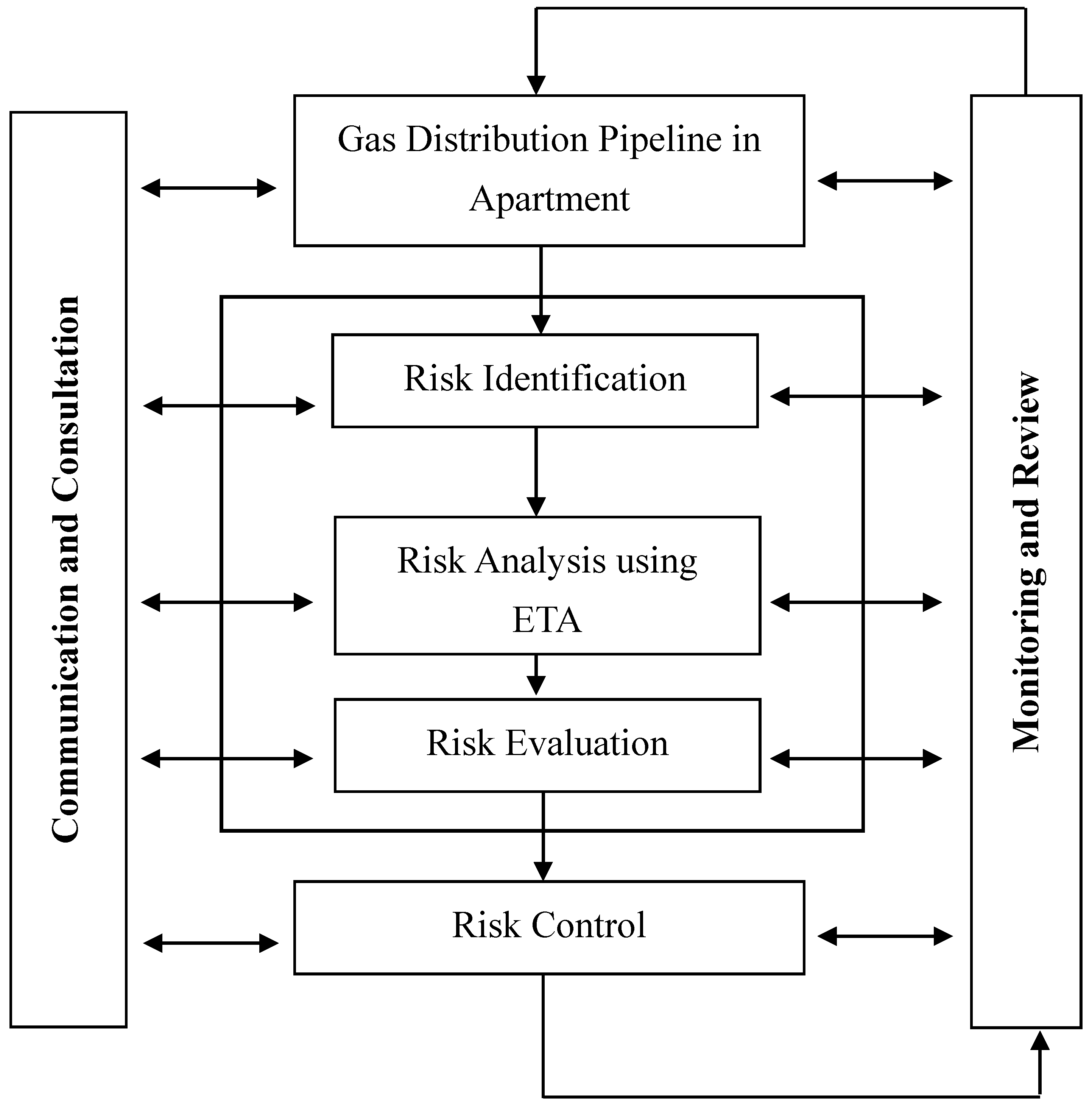
2. Methods
Event Tree Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gas Leakage Analysis of Small-Scale Leak Scenario
3.2. Gas Leakage Analysis of Large-Scale Gas Release Scenario
3.3. Gas Leakage Analysis of Gas Pipeline Rupture Scenario
3.4. Gas Leakage Risk Evaluation
3.5. Gas Leakage Risk Control
3.6. Risk Control in Small-Scale Leak Scenario
3.7. Risk Control in Large-Scale Gas Release Scenario
3.8. Risk Control in Gas Pipeline Rupture Scenario
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dirjen Migas ESDM. Pembangunan Jaringan Gas Bumi untuk Rumah Tangga. Jakarta. Indonesia. 2010. Available online: http://edoc.site/buku-jargas-jaringan-gas-city-gas-indonesia-pdf-free.html (accessed on 15 May 2018).
- Demirbas, A. Methane Gas Hydrate. X. 186, p. 47. Illus. 2010. Available online: http://www.springer.com/us/book/9781848828711 (accessed on 15 May 2018).[Green Version]
- ASME B31.8. ASME Managing System Integrity of Gas Pipelines. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2004. Available online: http://law.resource.org/pub/us/cfr/ibr/002/asme.b31.8s.2004.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2018).
- Muhlbauer, W.K. Pipeline Risk Management Manual: Ideas Technique and Resources; Gulf Publishing Company: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bariha, N.; Mishra, I.M.; Srivastava, V.C. Hazard Analysis of Failure of Natural Gas and Petroleum Gas Pipeline. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 40, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.D.; Crowl, D.A. Individual Risk Analysis of High-Pressure Natural gas pipelines. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2008, 21, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.B. A Review of Quantitative Risk Assessment of Onshore Pipelines. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 44, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beizma, M.V.; Agudo, D.; Barron, G. A Fuzzy Logic Method: Predicting Pipeline External Corrosion Rate. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2018, 163, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Jo, Y.D. An Approach to Risk Management of City Gas Pipeline. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2004, 82, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S.; Liu, K.; Sun, P.L. Risk Analysis on Leakage Failure of Natural Gas Pipelines by Fuzzy Bayesian Network with a Bow-Tie Model. Sci. Program. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.J.; You, Q.J.; Yue, Z. Risk analysis of urban gas pipeline network based on improved bow-tie model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 93, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuhua, D.; Datao, Y. Estimation of failure probability of oil and gas transmission pipelines by fuzzy fault tree analysis. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2005, 18, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheliyan, A.S.; Bhattacharyya, S.K. Fuzzy event tree analysis for quantified risk assessment due to oil and gas leakage in offshore installations. Ocean Syst. Eng. 2018, 8, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, J.D.; Dunnett, S.J. Event Tree Analysis Using Binary Decision Diagrams. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2000, 49, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Duncan, I.J. Likelihood, causes, and consequences of focused leakage and rupture of US natural gas transmission pipelines. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2014, 30, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standards Australia/Standards New Zealand. Risk Management Guidelines Companion to AS/NZS 4360:2004. Standards Australia International Ltd.: Sydney, Australia, 2004. Available online: https://www.saiglobal.com/PDFTemp/Previews/OSH/as/misc/handbook/HB436-2004(+A1).pdf (accessed on 12 May 2018).
- Kishawy, H.; Gabbar, A. Review of pipeline integrity management practices. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2010, 87, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čepin, M. Assessment of Power System Reliability: Methods and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ashe, B.S.W.; Rew, P.J. Effects of Flashfire on Building Occupants. WS Atkins Consultants Ltd.: Surrey, 2003. Available online: http://www.hse.gov.uk/research/rrhtm/rr084.htm (accessed on 17 May 2018).
- Schmidt, M. Tolerable Risk, Chemical Engineering. The YGS Group, ER-00054. 2007. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/72e0/82bcb61cc2f6433976b25c40a384f59396cb.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2018).
- Oreda. Det Norske Veritas. Norway. 2009. Available online: http://www.putrastandards.net/shop/product.php?id_product=779 (accessed on 21 March 2018).
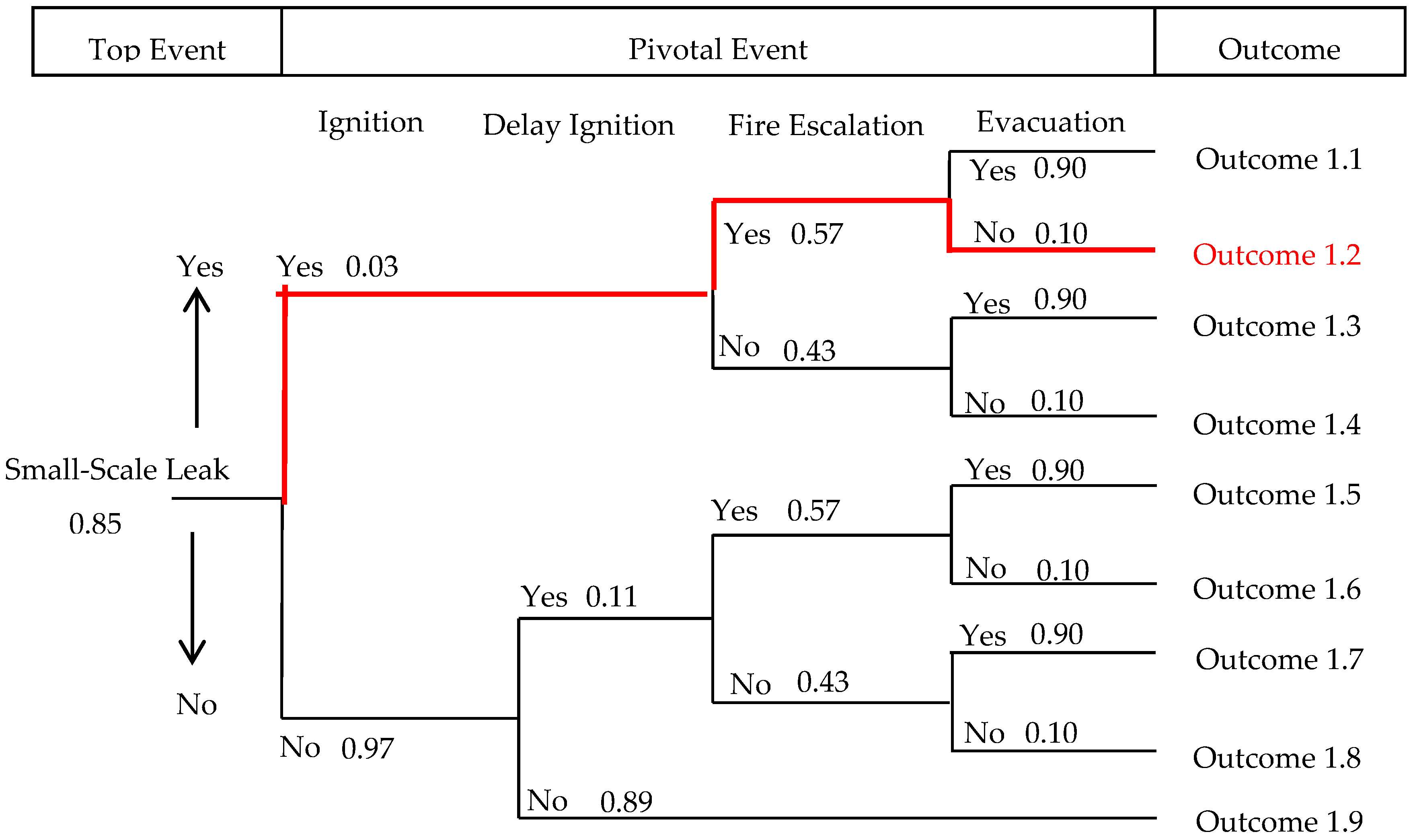
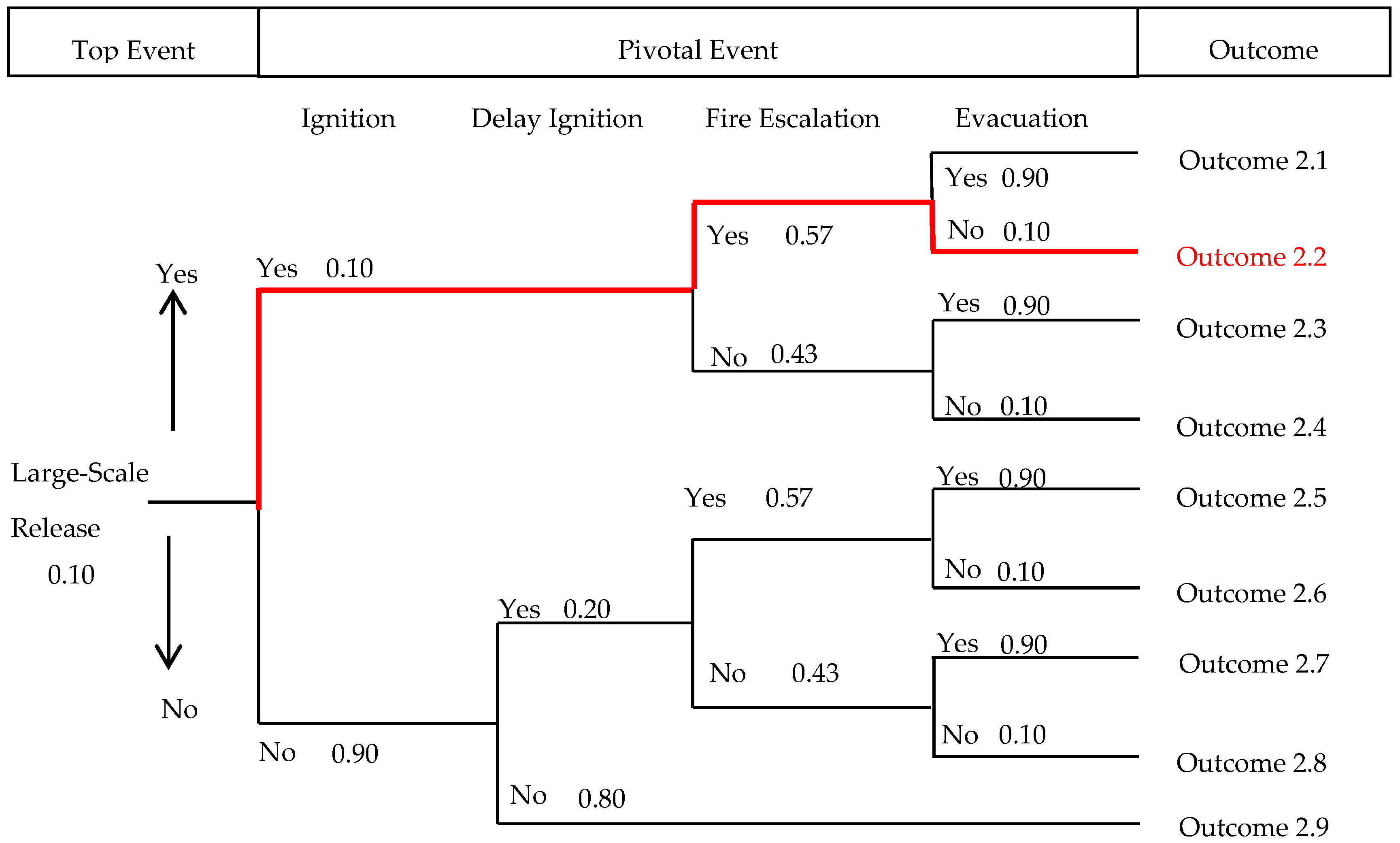
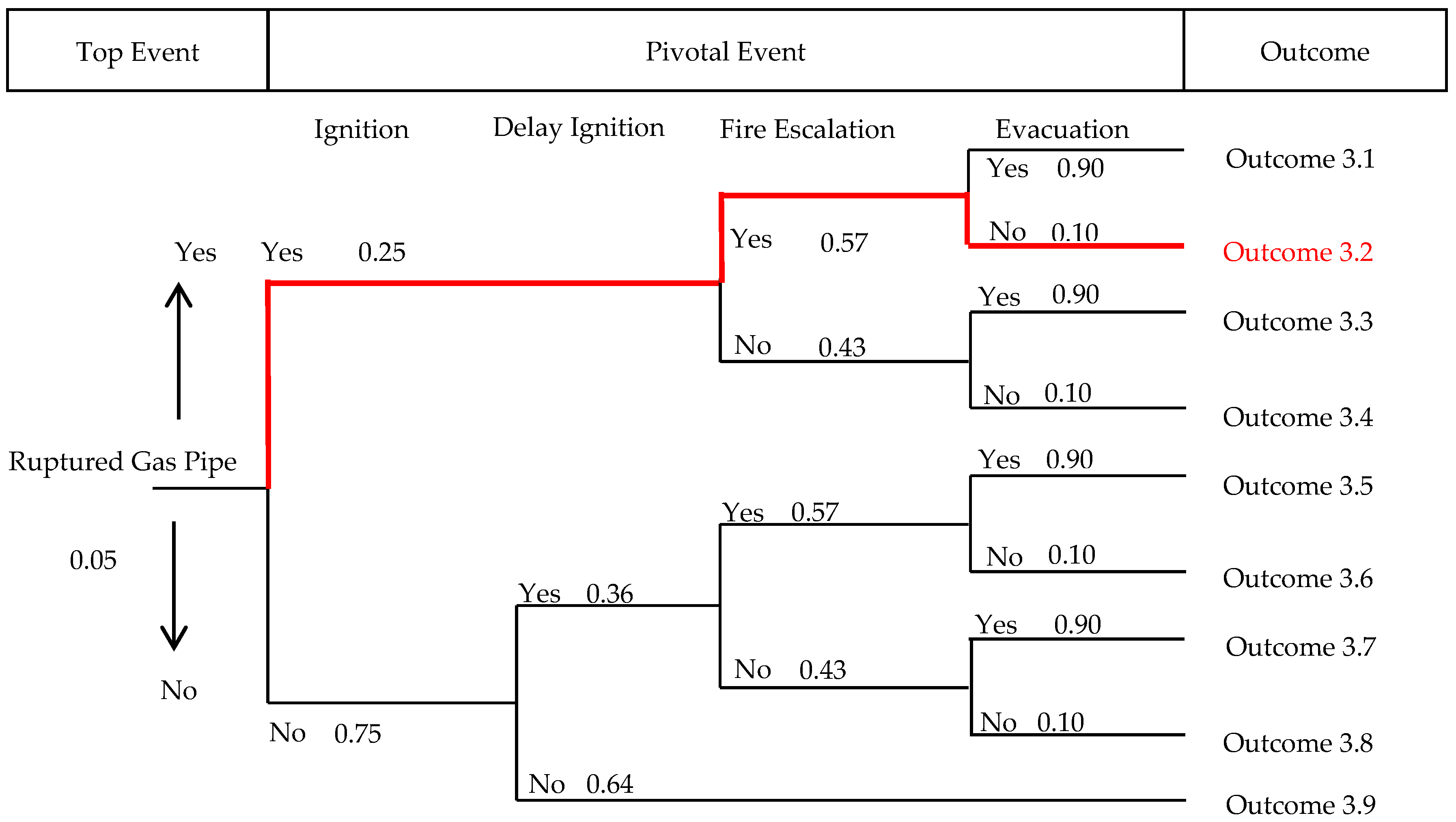
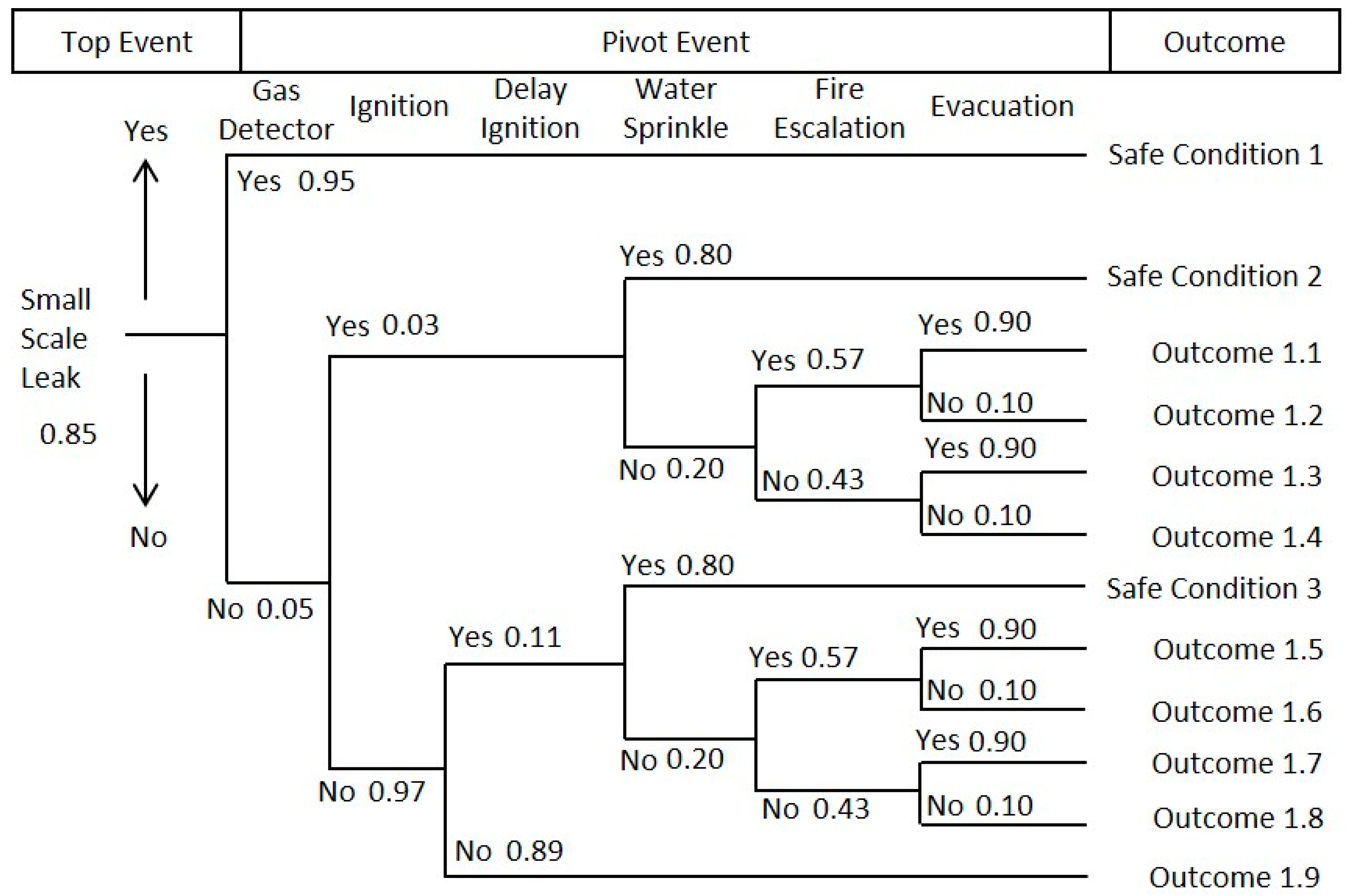
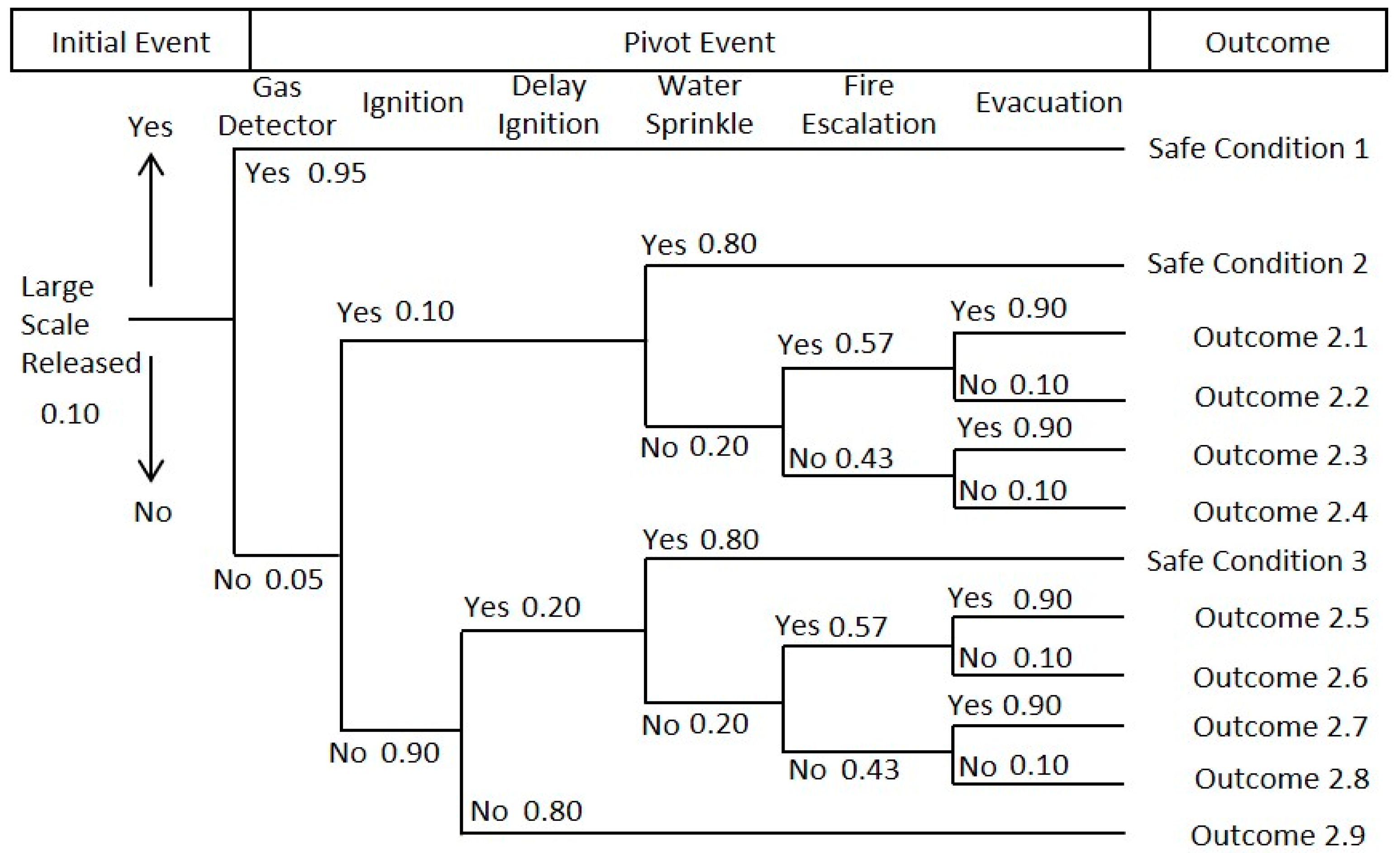
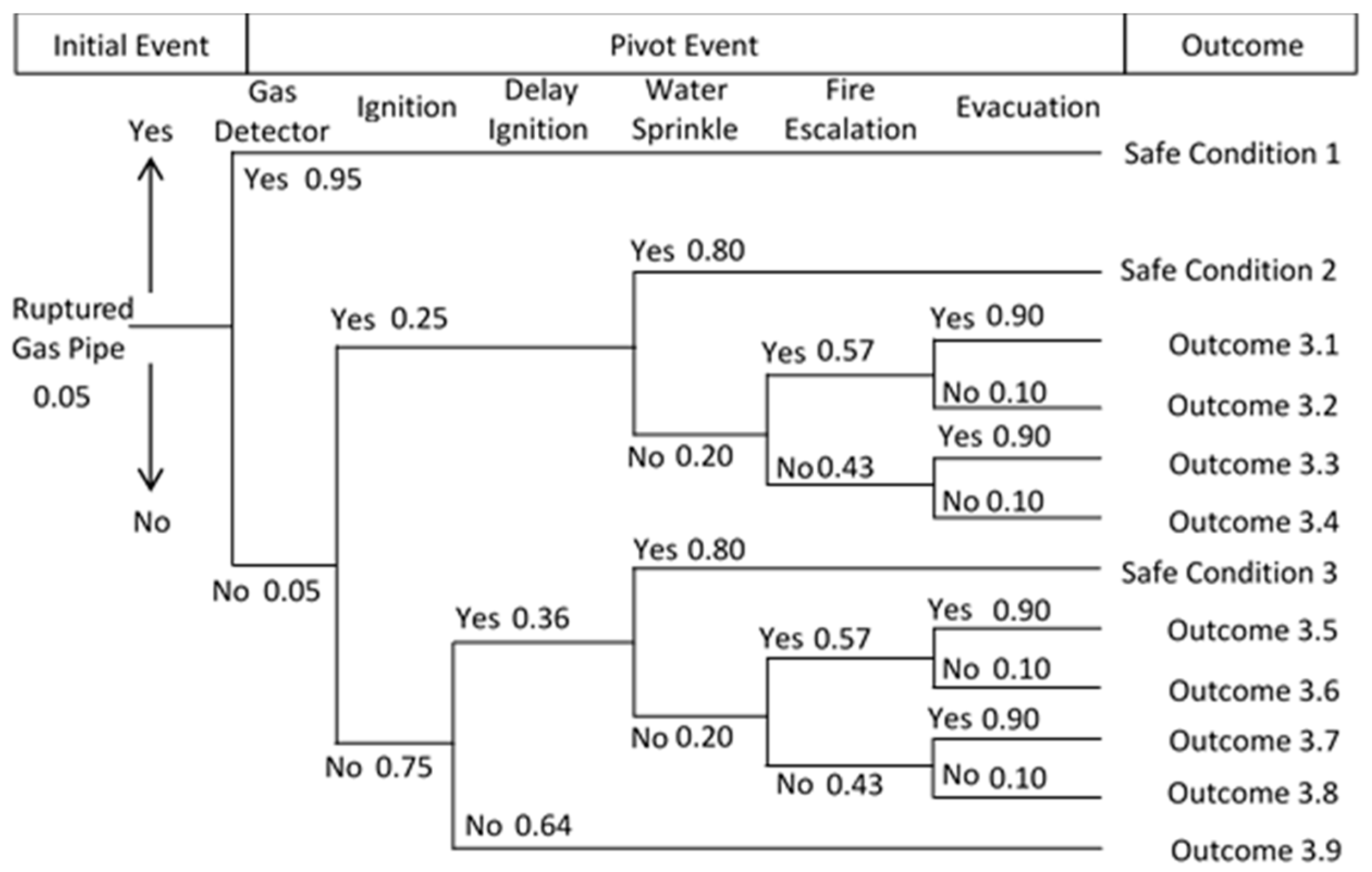
| Outcome | Risk | Probability |
|---|---|---|
| Outcome 1.1 | Fireball, light poisoning | 1.3 × 10−2 |
| Outcome 1.2 | Fireball, severe casualties, light poisoning | 1.5 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 1.3 | Fireball, light poisoning | 9.9 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 1.4 | Fireball, severe casualties, light poisoning | 1.0 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 1.5 | Flash fire, light poisoning | 4.6 × 10−2 |
| Outcome 1.6 | Flash fire, severe casualties, light poisoning | 5.1 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 1.7 | Flash fire, light poisoning | 3.5 × 10−2 |
| Outcome 1.8 | Flash fire, light casualties, light poisoning | 3.9 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 1.9 | Severe poisoning | 7.3 × 10−1 |
| Total | 8.5 × 10−1 |
| Outcome | Risk | Probability |
|---|---|---|
| Outcome 2.1 | Fireball, light poisoning | 5.1 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 2.2 | Fireball, severe casualties, light poisoning | 6.0 × 10−4 |
| Outcome 2.3 | Fireball, light poisoning | 3.9 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 2.4 | Fireball, severe casualties, light poisoning | 4.0 × 10−4 |
| Outcome 2.5 | Flash fire, light poisoning | 9.2 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 2.6 | Flash fire, severe casualties, light poisoning | 1.0 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 2.7 | Flash fire, light poisoning | 7.0 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 2.8 | Flash fire, light casualties, light poisoning | 8.0 × 10−4 |
| Outcome 2.9 | Severe poisoning | 7.2 × 10−2 |
| Total | 1.0 × 10−1 |
| Outcome | Risk | Probability |
|---|---|---|
| Outcome 3.1 | Fireball, light poisoning | 6.4 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 3.2 | Fireball, severe casualties, light poisoning | 7.0 × 10−4 |
| Outcome 3.3 | Fireball, light poisoning | 4.8 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 3.4 | Fireball, severe casualties, light poisoning | 5.0 × 10−4 |
| Outcome 3.5 | Flash fire, light poisoning | 6.9 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 3.6 | Flash fire, severe casualties, light poisoning | 8.0 × 10−4 |
| Outcome 3.7 | Flash fire, light poisoning | 5.2 × 10−3 |
| Outcome 3.8 | Flash fire, light casualties, light poisoning | 6.0 × 10−4 |
| Outcome 3.9 | Severe poisoning | 2.4 × 10−2 |
| Total | 5.0 × 10−2 |
| Outcome | Probability | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Outcome 1.2 | >10−4 | Intolerable |
| Outcome 2.2 | >10−4 | Intolerable |
| Outcome 3.2 | >10−4 | Intolerable |
| Outcome | Probability | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Outcome 1.2 | 1.5 × 10−5 | Tolerable |
| Outcome 2.2 | 5.7 × 10−6 | Tolerable |
| Outcome 3.2 | 7.1 × 10−6 | Tolerable |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hermansyah, H.; Nur Hidayat, M.E.; Kumaraningrum, A.R.; Yohda, M.; Shariff, A.B.M. Assessment, Mitigation, and Control of Potential Gas Leakage in Existing Buildings Not Designed for Gas Installation in Indonesia. Energies 2018, 11, 2970. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112970
Hermansyah H, Nur Hidayat ME, Kumaraningrum AR, Yohda M, Shariff ABM. Assessment, Mitigation, and Control of Potential Gas Leakage in Existing Buildings Not Designed for Gas Installation in Indonesia. Energies. 2018; 11(11):2970. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112970
Chicago/Turabian StyleHermansyah, Heri, Mohamad Evi Nur Hidayat, Anggraini Ratih Kumaraningrum, Masafumi Yohda, and Azmi B. Mohd Shariff. 2018. "Assessment, Mitigation, and Control of Potential Gas Leakage in Existing Buildings Not Designed for Gas Installation in Indonesia" Energies 11, no. 11: 2970. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112970
APA StyleHermansyah, H., Nur Hidayat, M. E., Kumaraningrum, A. R., Yohda, M., & Shariff, A. B. M. (2018). Assessment, Mitigation, and Control of Potential Gas Leakage in Existing Buildings Not Designed for Gas Installation in Indonesia. Energies, 11(11), 2970. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112970






