A Study of Electrical Aging of the Turn-to-Turn Oil-Paper Insulation in Transformers with a Step-Stress Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Electric Aging Theory of Oil-Immersed Insulation under Step Stress
3. Electrical Aging Test for Coil Model
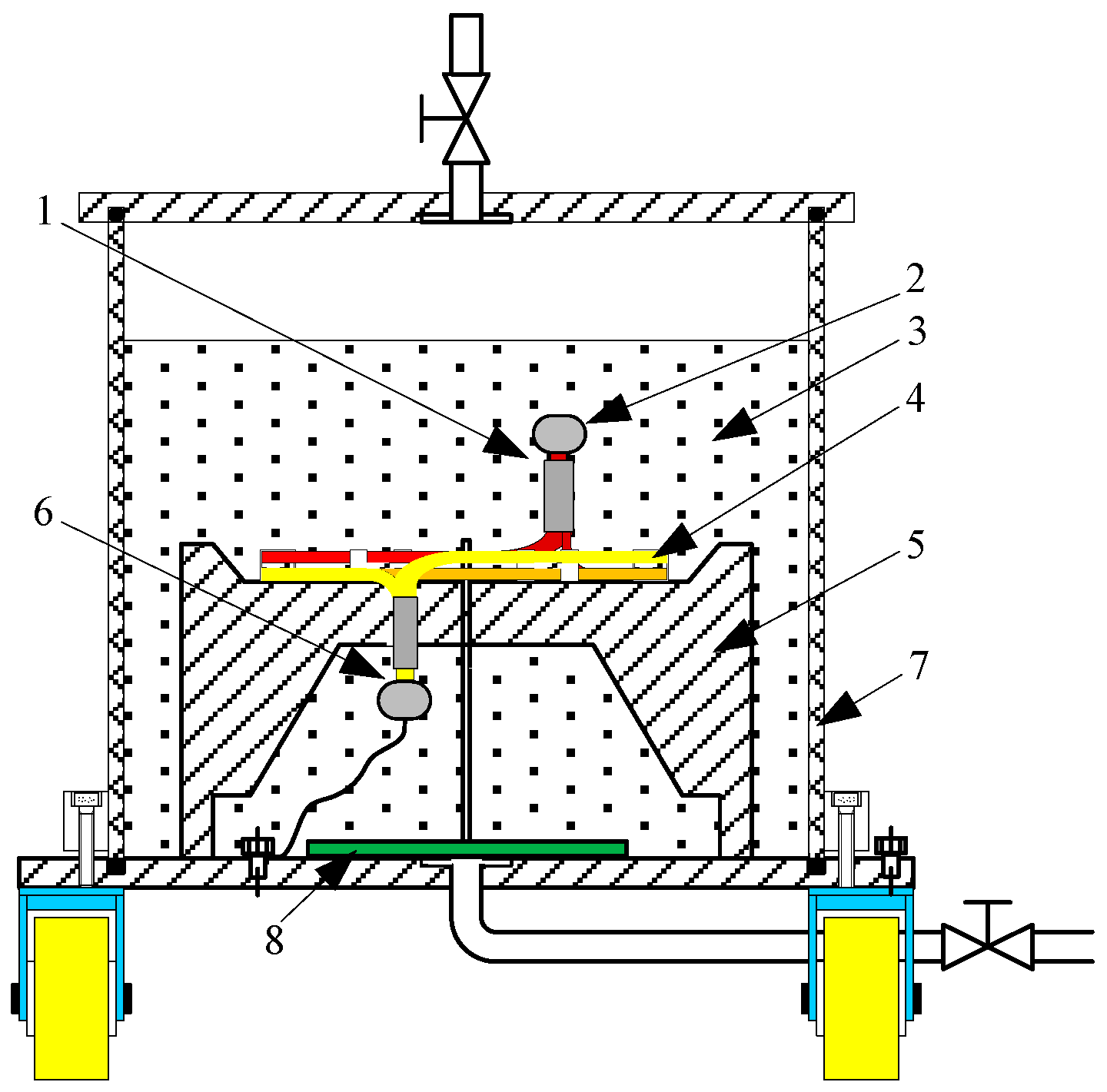
3.1. Test Circuit
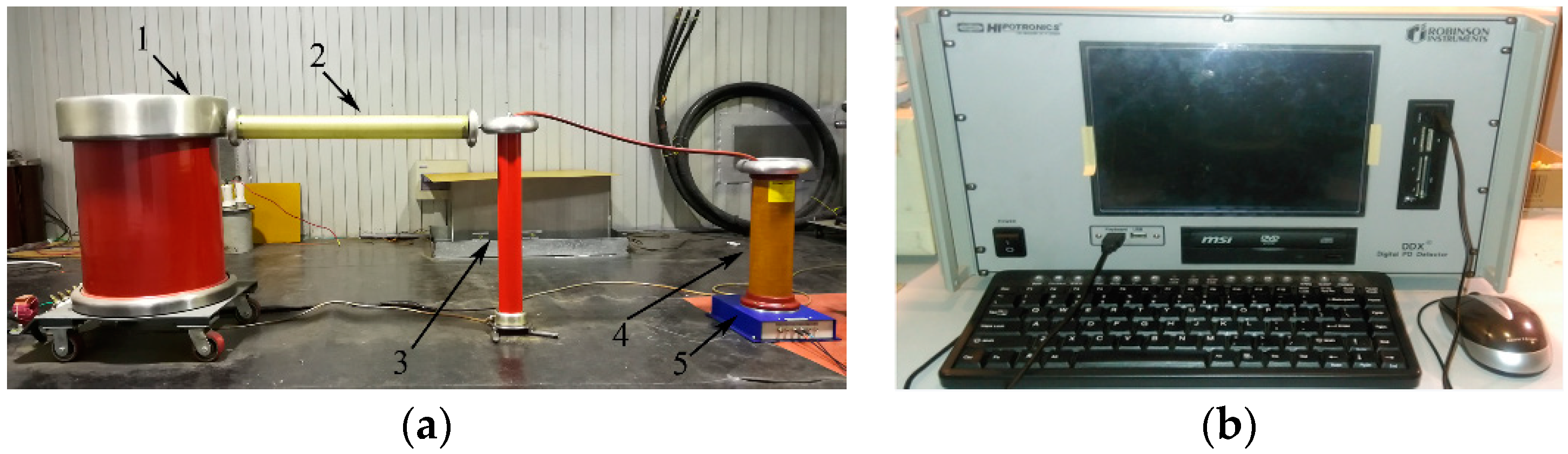
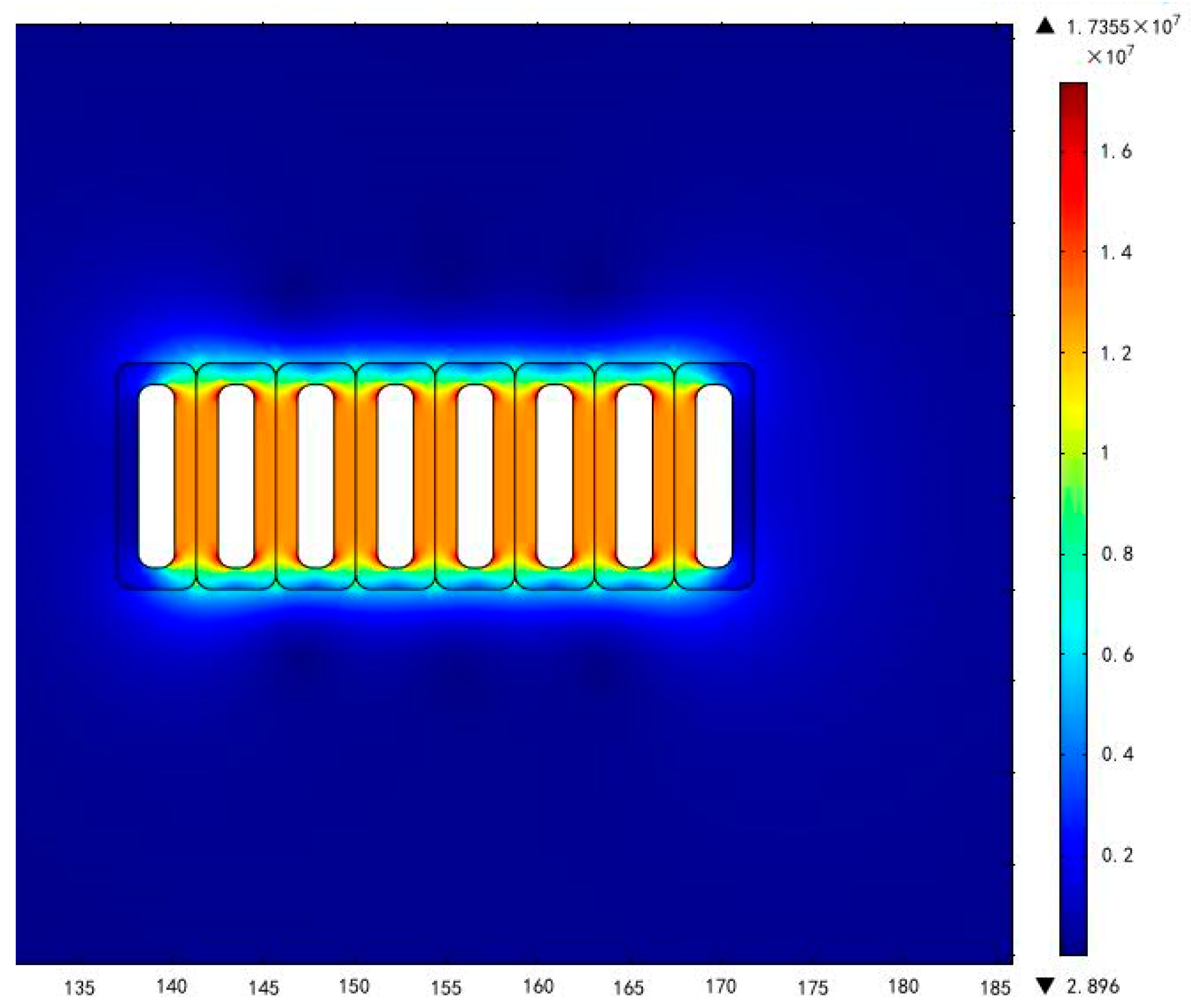
3.2. Coil Model and Test System
3.3. The Pretreatment of the Sample
3.4. Preliminary Experiments
- (1)
- The average of PD inception voltage and breakdown voltage is:
- (2)
- The standard deviation of PD inception voltage and breakdown voltage is:
- (3)
- The minimum PD inception voltage and breakdown voltage estimate values are:
3.5. Determination of Test Program
4. Data Processing
4.1. Explanation of the New Parameter Estimation Method
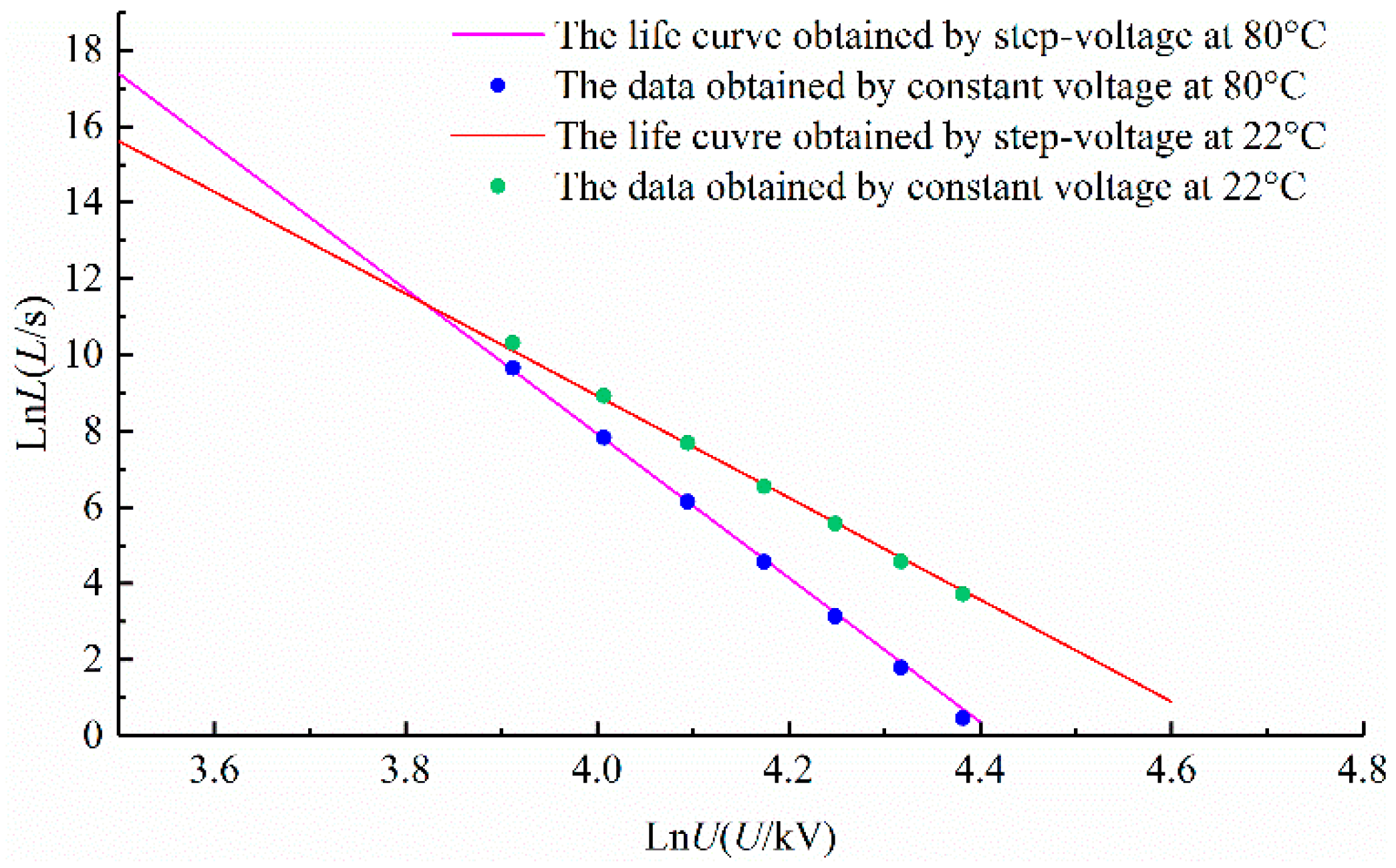
4.2. Solve and Verify the Life Equation
5. Discussion
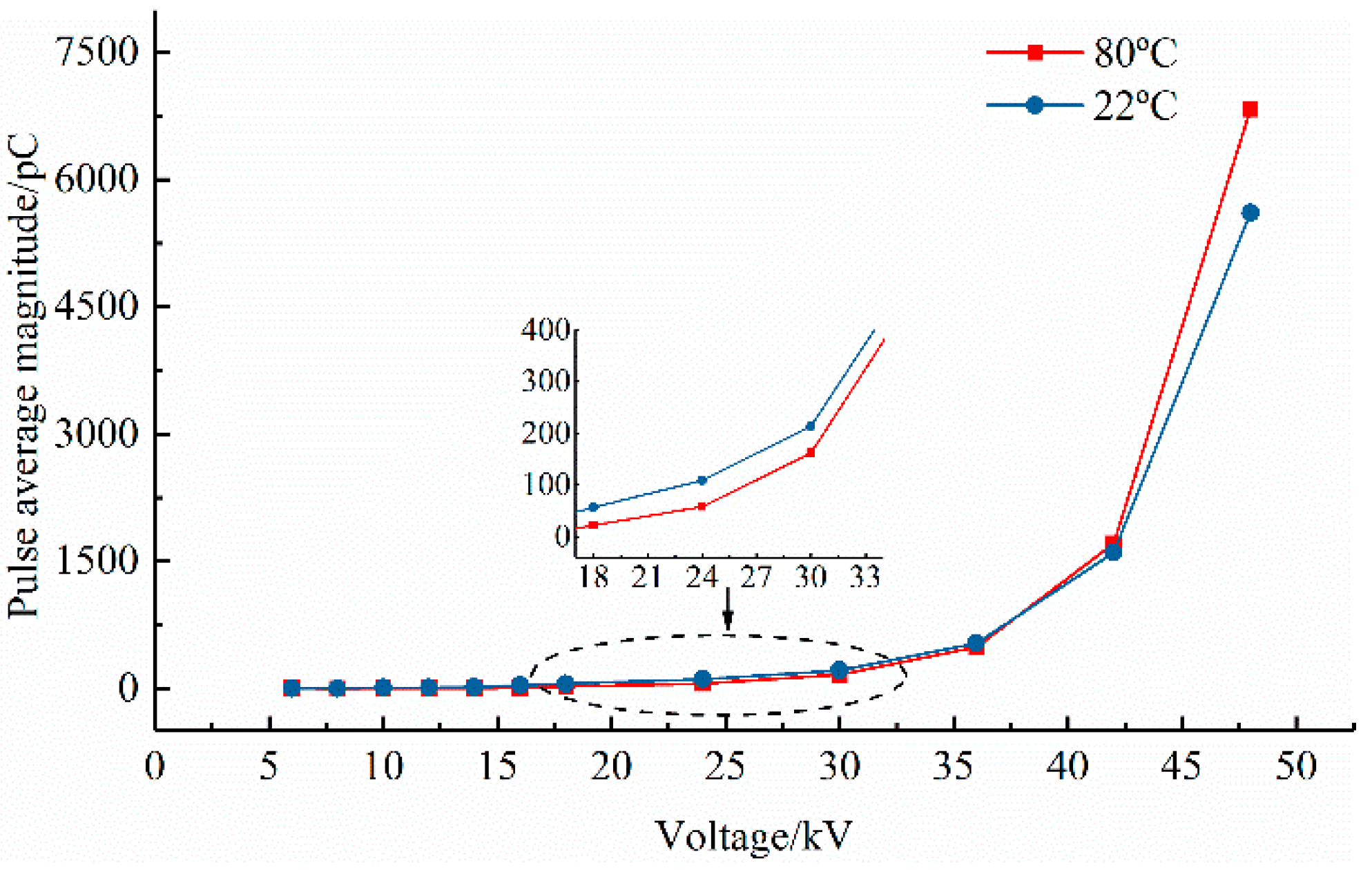
5.1. Analysis of Test Results
5.2. Discussion of Application
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- It is considered that a modest increase of the turn-to-turn oil-paper insulation design field is viable in the design of turn-to-turn insulation for a large power transformer.
- (2)
- Step-stress aging can be used for the accelerated electrical aging test of transformer turn-to-turn oiled paper insulation. The proposed method can be used to solve the unknown parameters of solid insulation against the power model under step-stress aging, it has a clear physical meaning, and its operation is simple.
- (3)
- Compared with that at room temperature, when the stressed voltage is below a certain threshold value, the life of the transformer coil turn-to-turn insulation grease paper model is longer at operating temperatures. When the voltage is higher than the threshold, it presents the opposite tendency.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boudraa, S.; Mokhnache, L.; Fofana, I. A comparative study of impact of electrical stress and thermal aging on transformer oil. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices, Barcelona, Spain, 11–14 February 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Y. Condition diagnosis of oil-paper insulation during the accelerated electrical aging test based on polarization and depolarization current. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 11th International Conference on the Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials (ICPADM), Sydney, Australia, 19–22 July 2015; pp. 448–451. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Ren, M.; Wen, F.X.; Zhang, C.X.; Liu, J.L.; Sumereder, C.; Muhr, M. Explanation and analysis of oil-paper insulation based on frequency-domain dielectric spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 2684–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.J.; Yang, L.J.; Li, J.A.; Grzybowski, S. Aging condition assessment of transformer oil-paper insulation model based on partial discharge analysis. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niasar, M.G.; Taylor, N.; Edin, H.; Kiiza, R.C. Impact of thermal and electrical aging on breakdown strength of oil-impregnated paper. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Eindhoven PowerTech Conference, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 29 June–2 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kiiza, R.C.; Niasar, M.G.; Nikjoo, R.; Wang, X.; Edin, H. The effect of partial discharge by-products on the dielectric frequency response of oil-paper insulation comprising of a small cavity. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Yan, J. Electrical and mechanical properties of the oil-paper insulation under stress of the hot spot temperature. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalik, A.A. Analysis of thermally aged insulation paper in a natural ester-based dielectric fluid. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 2408–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, W.; Walczak, K.; Przybylek, P. Moisture migration in an oil-paper insulation system in relation to online partial discharge monitoring of power transformers. Energies 2016, 9, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, G.; Montanari, G.C. Electrical aging and life models: The role of space charge. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2005, 12, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Mu, H.; Wang, D.; Lei, M.; Suwarno, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Takada, T. Effects of paper-aged state on space charge characteristics in oil-impregnated paper insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2012, 19, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W. Study on TSC characteristics of aged insulation cardboard in oil-immersed transformer. In Proceedings of the 2013 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Shenzhen, China, 20–23 October 2013; pp. 194–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.J.; Liao, R.J.; Sun, C.X.; Zhu, M.Z. Influence of vegetable oil on the thermal aging of transformer paper and its mechanism. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Jiang, T.M. Step stress accelerated life testing data analysis for repairable system using proportional intensity model. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 26–29 January 2009; pp. 360–364. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, W. Accelerated life testing—Step-stress models and data analyses. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1980, R-29, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Wu, J.W.; Lei, C.L. Assessing the lifetime performance index of exponential products with step-stress accelerated life-testing data. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2013, 62, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, S.; Grzybowski, S. Reliability Evaluation Method for Oil–Paper Insulation in Power Transformers. Energies 2011, 4, 1362–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.J.; Milliken, G.A. Step-stress life-testing with random stress-change times for exponential data. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1999, 48, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.C.; Sun, Y.S.; Goh, T.N.; Ong, H.L. Analysis of step-stress accelerated-life-test data: A new approach. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1996, 45, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lv, Z.P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, K.; Dissado, L.A.; Peng, Z.X.; Li, R.H. A new method of estimating the inverse power law ageing parameter of XLPE based on step-stress tests. In Proceedings of the 2013 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Shenzhen, China, 20–23 October 2013; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Laghari, J.R.; Cygan, P.; Khechen, W. A short method of estimating lifetime of polypropylene film using step-stress tests. IEEE Trans. Elect. Insul. 1990, 25, 1180–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLinn, J.A. Ways to improve the analysis of step-stress testing. In Proceedings of the 1998 International Symposium on Product Quality and Integrity, Anaheim, CA, USA, 19–22 January 1998; pp. 358–364. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, S.L.; Yeo, K.P. A least-squares approach to analyzing life-stress relationship in step-stress accelerated life tests. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2002, 51, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klersztyn, S.E. Formal theoretical foundation of electrical aging of dielectrics. IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst. 1981, PAS-100, 4333–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallini, A.; Montanari, G.C.; Tozzi, M.; Chen, X.L. Diagnostic of hvdc systems using partial discharges. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fofana, I.; Hadjadj, Y. Electrical-based diagnostic techniques for assessing insulation condition in aged transformers. Energies 2016, 9, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarracin, R.; Robles, G.; Ardila-Rey, J.A.; Cavallini, A.; Passaglia, R. Partial discharges: Keys for condition monitoring and diagnosis of power transformers. In Power Transformer Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis; Abu-Siada, A., Ed.; Institution of Engineering and Technology: Stevenage, UK, 2018; pp. 39–85. [Google Scholar]
- Montanari, G.C. Aging and life models for insulation systems based on PD detection. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1995, 2, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Casale, M.D.L. On multistress aging of epoxy resins: PD and temperature. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2001, 8, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cavallini, A.; Montanari, G.C.; Testa, L. Evolution of PD patterns in polyethylene insulation cavities under ac voltage. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2012, 19, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Xie, B.; Lu, Y. Study on the insulation life models of power transformer. In Proceedings of the 2008 World Automation Congress, Hawaii, HI, USA, 28 September–2 October 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Niasar, M.G.; Taylor, N.; Janus, P.; Wang, X.; Edin, H.; Kiiza, R.C. Partial discharges in a cavity embedded in oil-impregnated paper: Effect of electrical and thermal aging. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
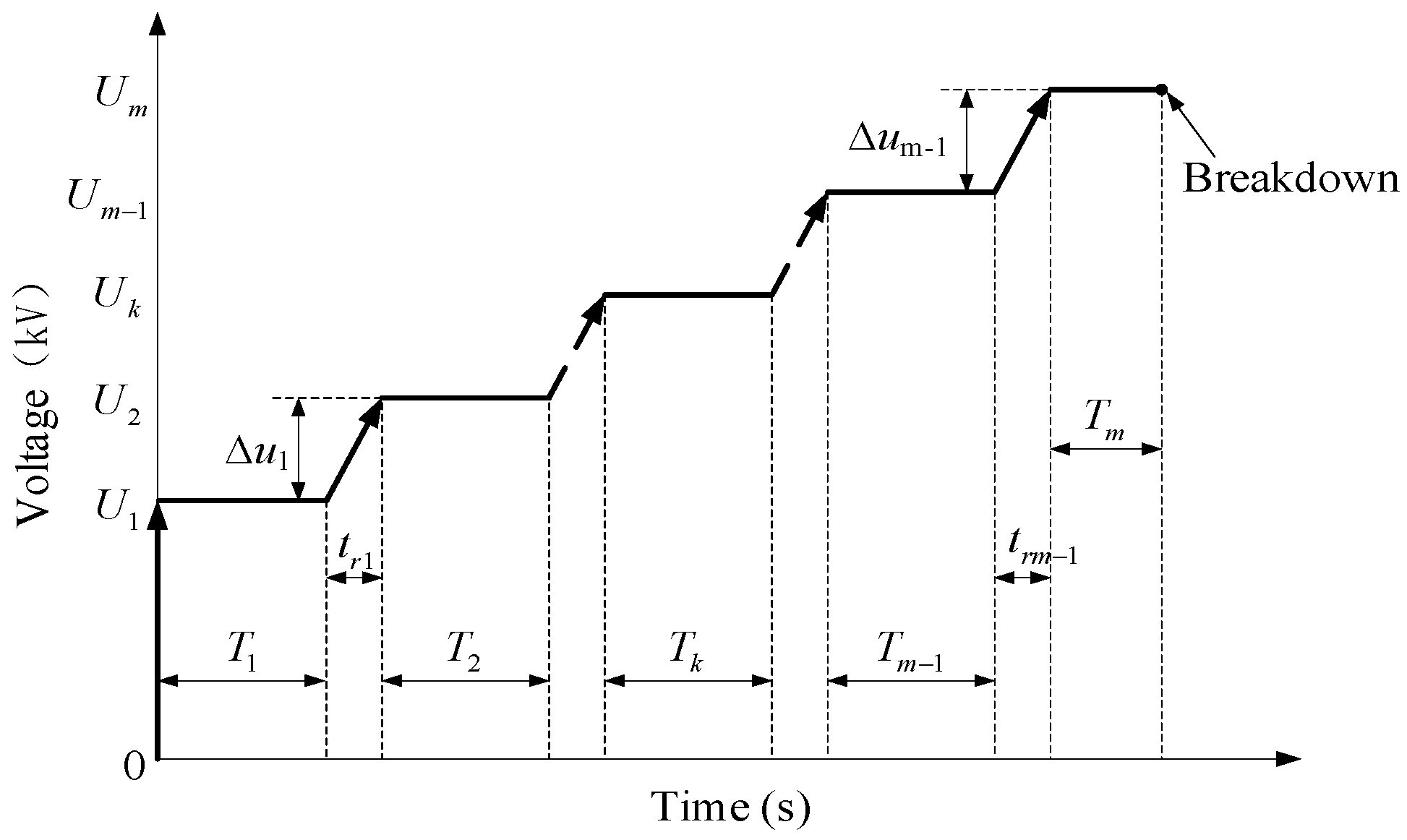
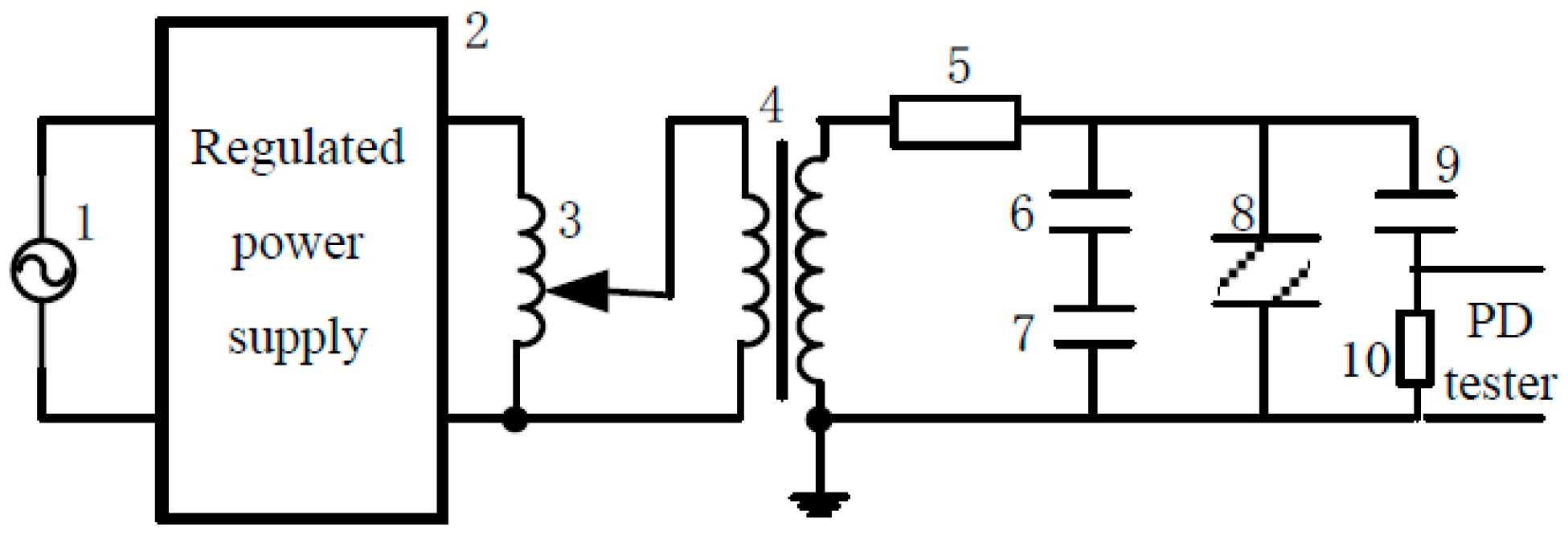
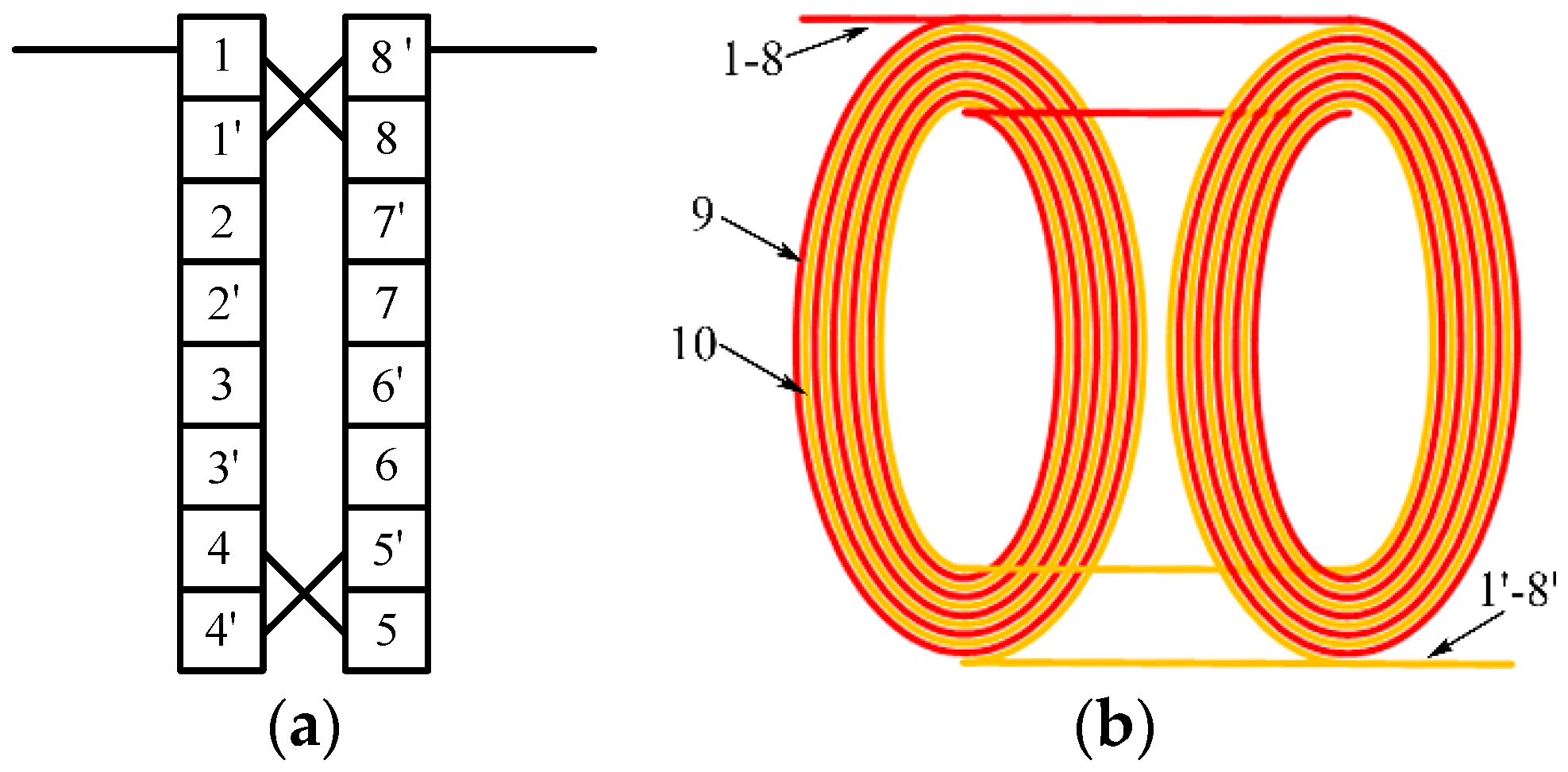
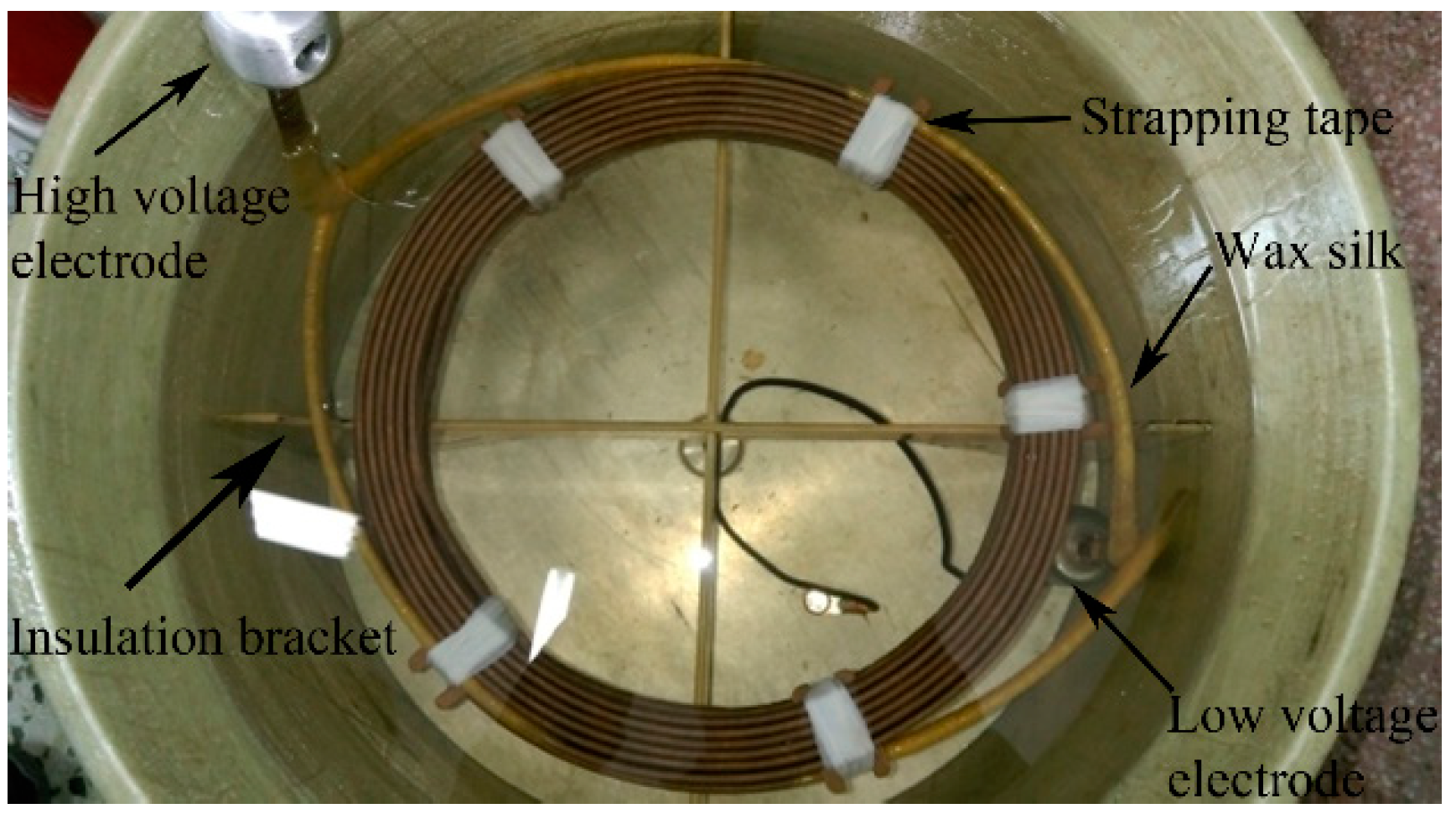


| PD inception voltage (kV) | 12 | 11.1 | 9.2 | 12.6 | 10.1 | 10.5 | 10.7 |
| 11.2 | 10.5 | 10.3 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 11.3 | 11.6 | |
| Breakdown voltage (kV) | 88.5 | 92.5 | 82.1 | 93.8 | 90.1 | 88.7 | 89.7 |
| 88.6 | 86.6 | 81.3 | 87.8 | 84.3 | 92.1 | 86.9 |
| Dwell Time (s) | Title of Data | Room Temperature (22 ℃) | Operating Temperature (80 ℃) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 360 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 72 | 72 | 72 | 72 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 |
| Steps | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 190 | 209 | 231 | 297 | 331 | 26 | 19 | 66 | 80 | 99 | 127 | 207 | 209 | 257 | 295 | 41 | 56 | 56 | 72 | 76 | |
| 720 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 72 | 72 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 |
| Steps | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 585 | 641 | 642 | 681 | 10 | 93 | 278 | 453 | 85 | 137 | 251 | 39 | 145 | 191 | 236 | 236 | 270 | 312 | 389 | 100 | |
| 1080 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 72 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 |
| Steps | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 487 | 496 | 519 | 584 | 913 | 97 | 121 | 306 | 398 | 209 | 643 | 20 | 66 | 78 | 147 | 199 | 205 | 210 | 350 | 42 | |
| 1440 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 72 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 |
| Steps | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 182 | 255 | 1360 | 230 | 315 | 580 | 1217 | 145 | 459 | 559 | 172 | 540 | 82 | 148 | 199 | 248 | 253 | 253 | 333 | 6 | |
| 1800 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Steps | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 534 | 943 | 1465 | 284 | 306 | 573 | 228 | 496 | 499 | 535 | 28 | 1613 | 1694 | 57 | 144 | 157 | 159 | 218 | 220 | 308 | |
| 2160 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 72 | 48 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Steps | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 1542 | 2246 | 175 | 443 | 589 | 1155 | 151 | 347 | 454 | 125 | 1380 | 444 | 1776 | 165 | 167 | 206 | 216 | 316 | 332 | 337 | |
| 2520 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 48 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Steps | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 12 | 611 | 1742 | 2520 | 120 | 245 | 1075 | 401 | 516 | 1547 | 2425 | 109 | 417 | 1425 | 69 | 92 | 261 | 264 | 271 | 295 | |
| 2880 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 48 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Steps | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 545 | 710 | 1430 | 1668 | 2217 | 716 | 1268 | 2109 | 436 | 542 | 985 | 1083 | 1206 | 2533 | 118 | 150 | 165 | 247 | 302 | 536 | |
| 3240 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 66 | 48 | 48 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Steps | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 534 | 890 | 943 | 1465 | 2120 | 297 | 305 | 583 | 1200 | 2783 | 1692 | 3214 | 90 | 953 | 82 | 143 | 215 | 267 | 622 | 633 | |
| 3600 | Breakdown voltage (kV) | 48 | 48 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 66 | 42 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Steps | 12 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | |
| Hold time on last step (s) | 1058 | 3506 | 315 | 1428 | 3184 | 3300 | 590 | 710 | 2336 | 972 | 36 | 727 | 938 | 2635 | 148 | 178 | 185 | 201 | 218 | 1068 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nie, H.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q. A Study of Electrical Aging of the Turn-to-Turn Oil-Paper Insulation in Transformers with a Step-Stress Method. Energies 2018, 11, 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123338
Nie H, Wei X, Wang Y, Chen Q. A Study of Electrical Aging of the Turn-to-Turn Oil-Paper Insulation in Transformers with a Step-Stress Method. Energies. 2018; 11(12):3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123338
Chicago/Turabian StyleNie, Hongyan, Xinlao Wei, Yonghong Wang, and Qingguo Chen. 2018. "A Study of Electrical Aging of the Turn-to-Turn Oil-Paper Insulation in Transformers with a Step-Stress Method" Energies 11, no. 12: 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123338
APA StyleNie, H., Wei, X., Wang, Y., & Chen, Q. (2018). A Study of Electrical Aging of the Turn-to-Turn Oil-Paper Insulation in Transformers with a Step-Stress Method. Energies, 11(12), 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123338




