A Novel Approach for an MPPT Controller Based on the ADALINE Network Trained with the RTRL Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling of the PV System
2.1. FV Module
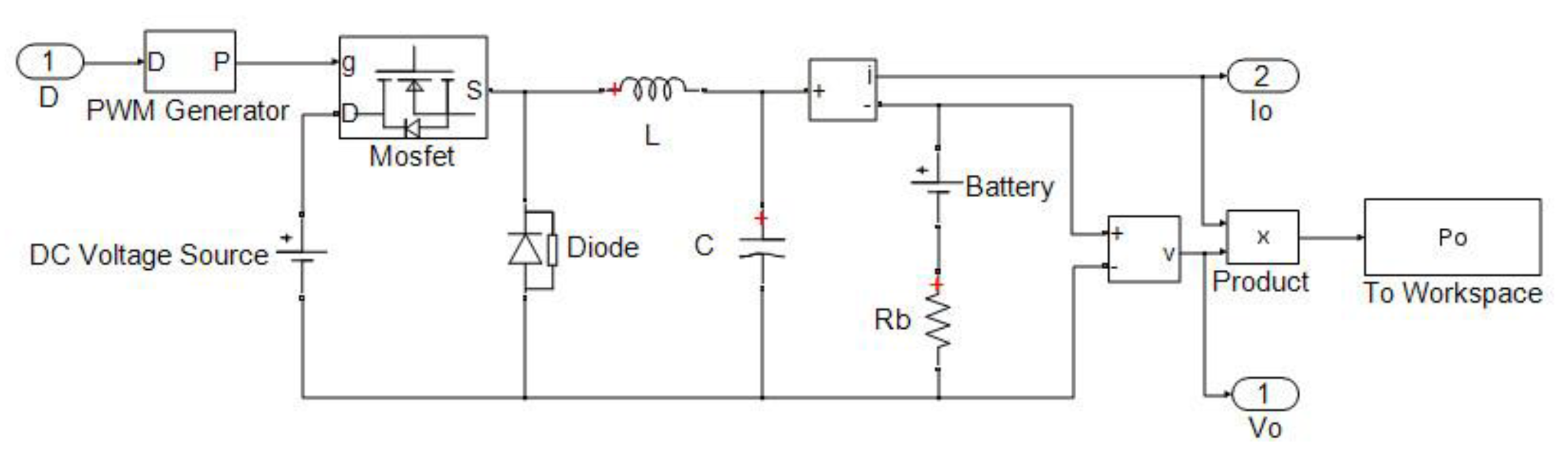
2.2. DC-DC Buck Converter
2.3. MPPT Controller
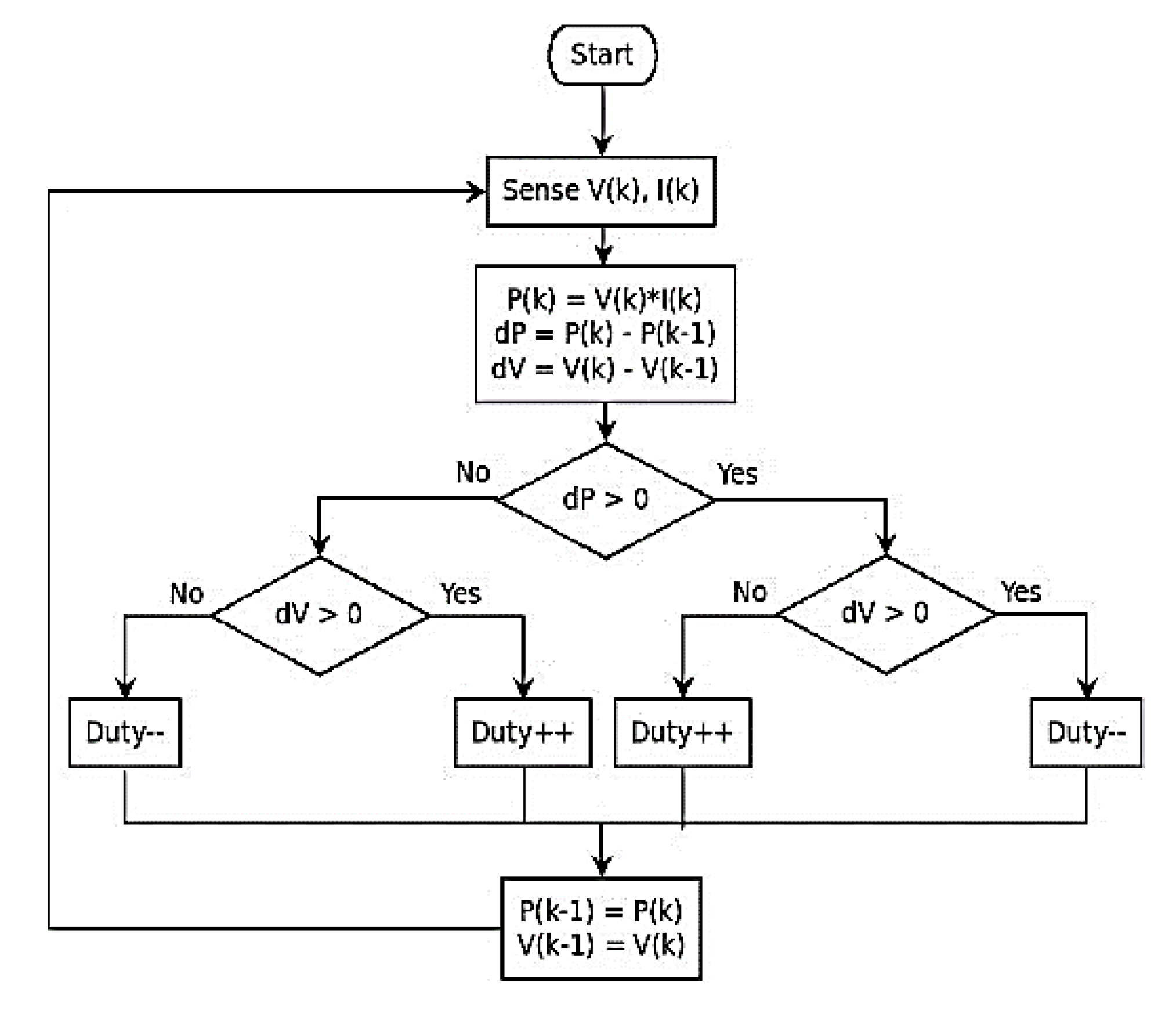
2.3.1. P&O Algorithm
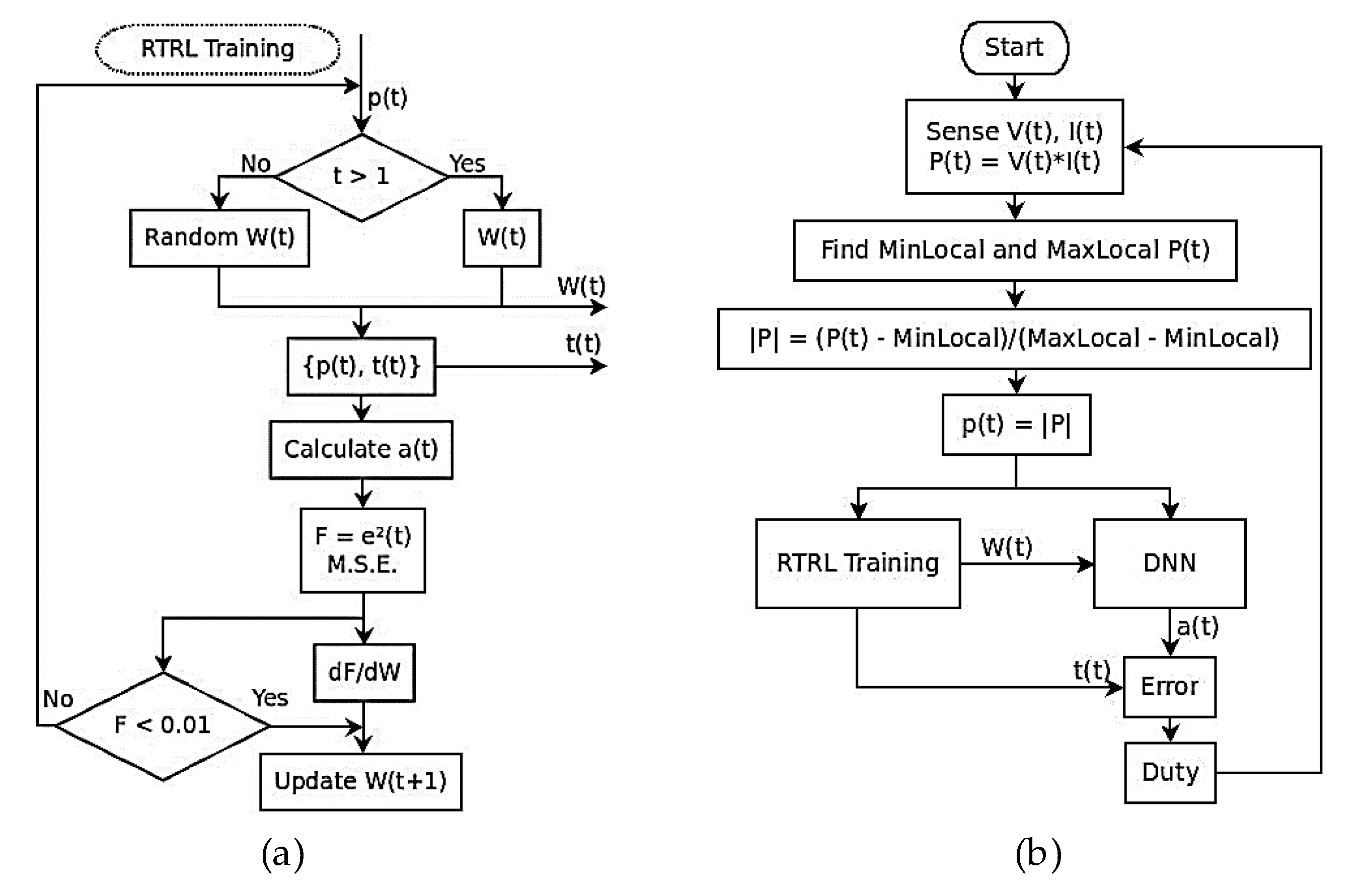
2.3.2. RTRL Algorithm
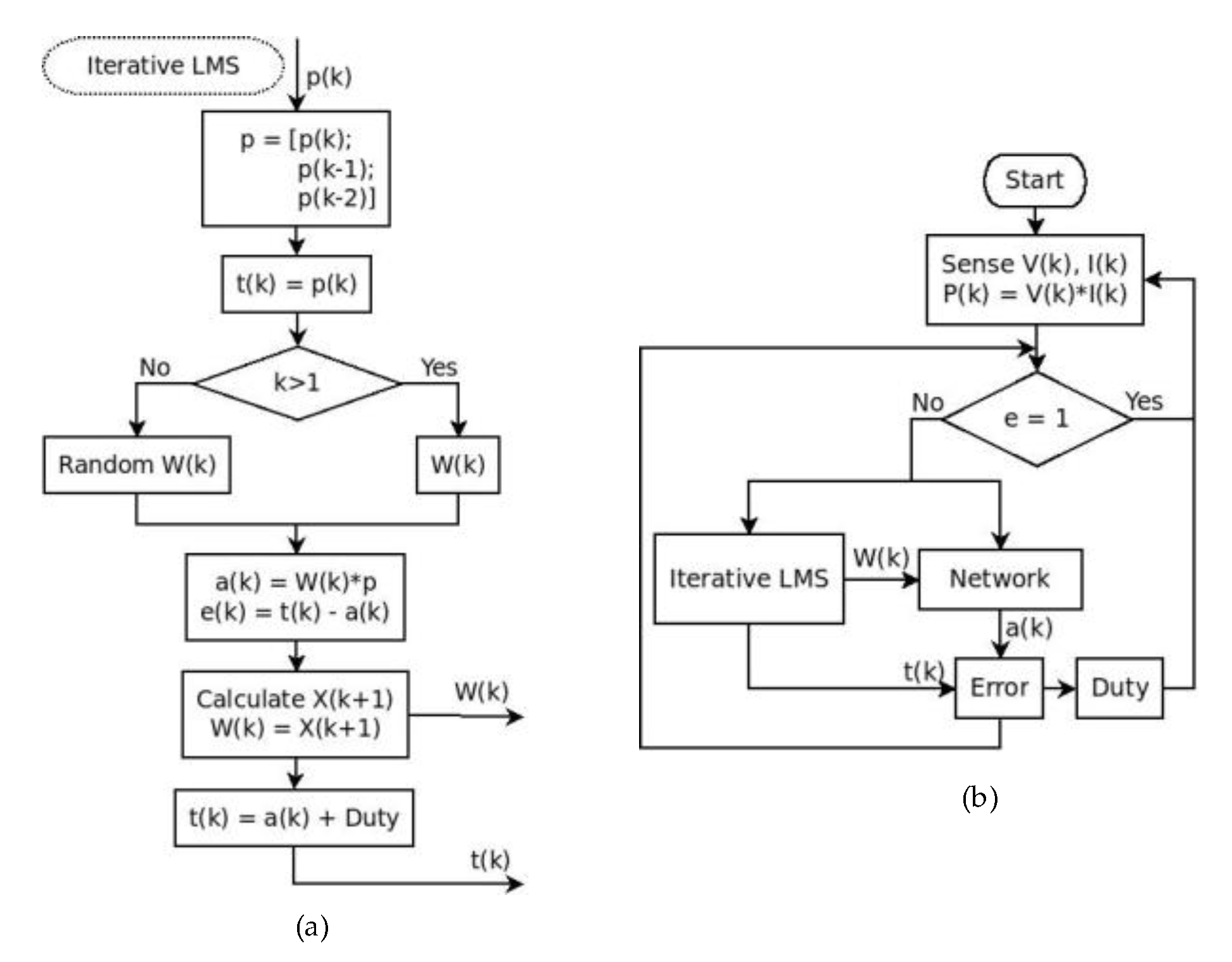
2.3.3. LMS Algorithm
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of the RTRL Neurocontroller
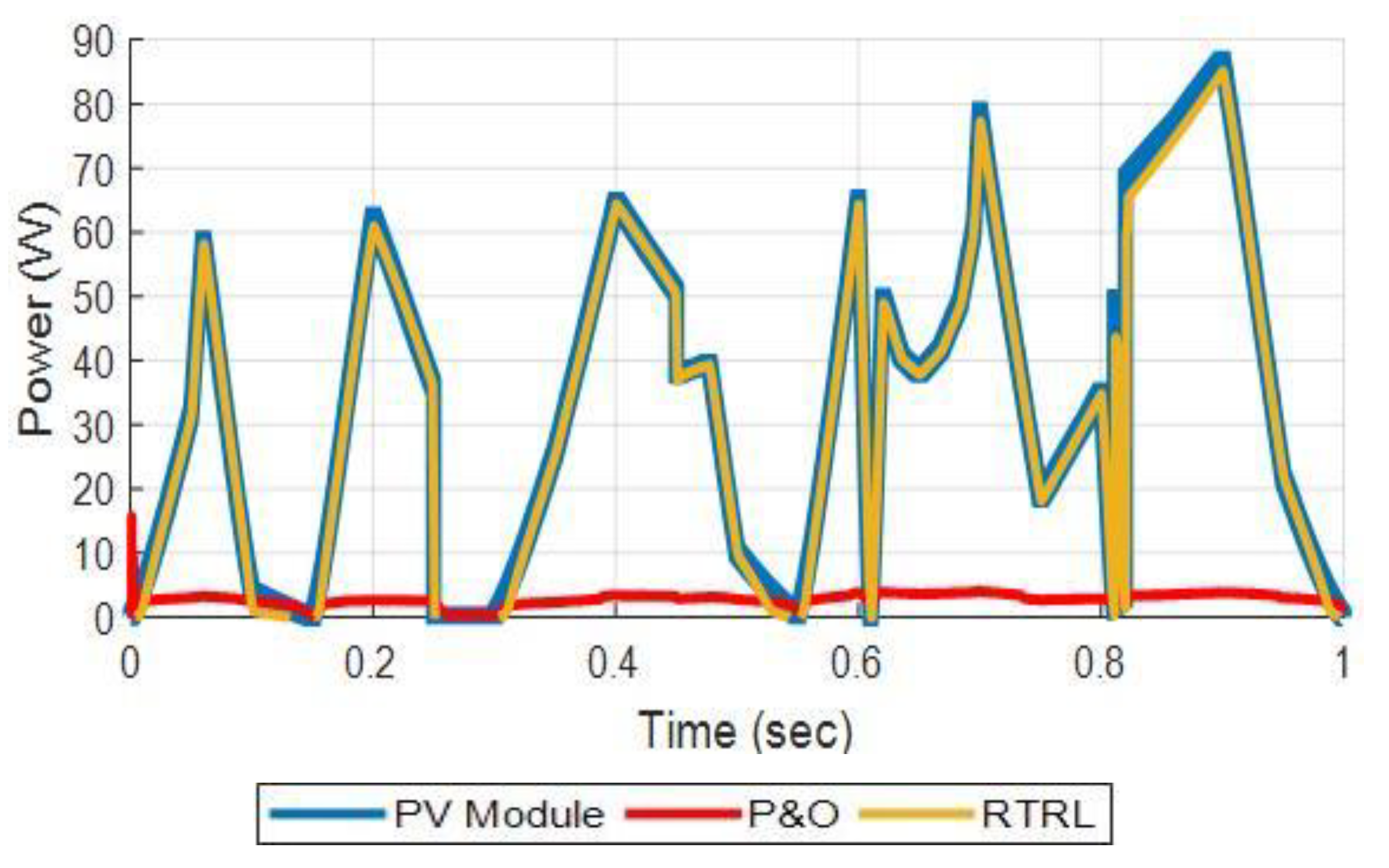
3.2. Comparison of the RTRL Neurocontroller with the P&O Controller
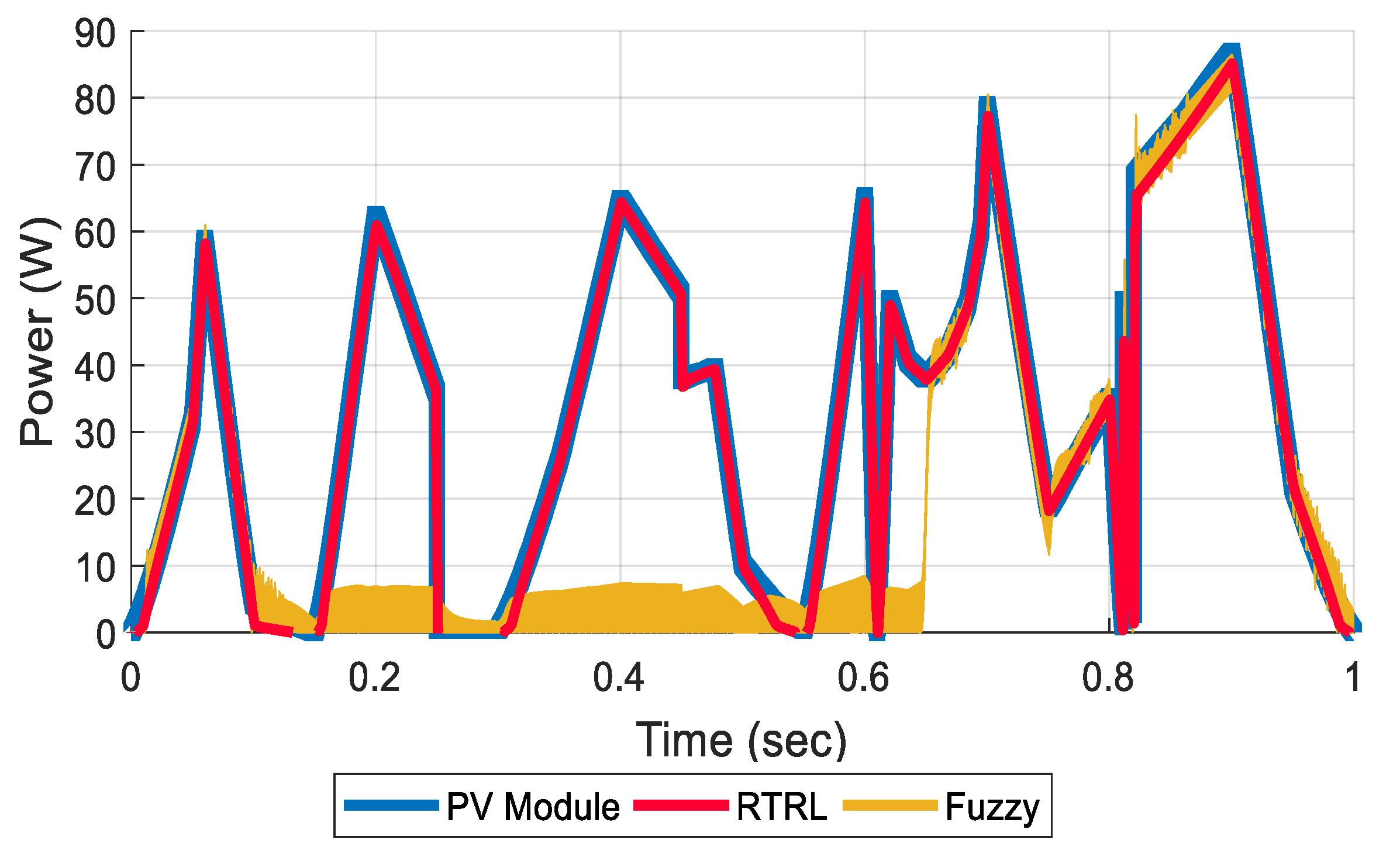
3.3. Comparison of the RTRL Neurocontroller with the Fuzzy Controller
3.4. Comparison of the RTRL Neurocontroller with the NARX Neurocontroller
3.5. Performance of the Control Algorithms for the MPPT
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Available online: https://goo.gl/8EDxDv (accessed on 11 October 2018).
- REN21-IRENA. Available online: https://goo.gl/Pc2WuA (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Stamatescu, I.; Fagarasan, I.; Stamatescu, G.; Arghira, N.; Iliescu, S.S. Design and Implementation of a Solar Tracking Algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2014, 69, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.G.; Guerra, F.K.O.M.V.; Vale, M.R.B.G.; Araújo, M.M. Comparative performance analysis between static solar panels and single-axis tracking system on a hot climate region near to the equator. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kadmiri, Z.; El Kadmiri, O.; Masmoudi, L.; Najib, M. A Novel Solar Tracker Based on Omnidirectional Computer Vision. J. Sol. Energy 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.F.; Rahim, N.A.; Al-Turki, Y.A. Performance of Dual-Axis Solar Tracker versus Static Solar System by Segmented Clearness Index in Malaysia. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarín, C.R.; Castro, A.O.; Naranjo, J.C. Dual-axis solar tracker for using in photovoltaic systems. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2017, 7, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, S.; Abdi, S. Application of the Hybrid Big Bang–Big Crunch algorithm for optimal sizing of a stand-alone hybrid PV/wind/battery system. Sol. Energy 2016, 134, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumila, Z.; Rekioua, D.; Rekioua, T. Energy management based fuzzy logic controller of hybrid system wind/photovoltaic/diesel with storage battery. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19525–19535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee Jordehi, A. Maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic (PV) systems: A review of different approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borni, A.; Abdelkrim, T.; Bouarroudj, N.; Bouchakour, A.; Zaghba, L.; Lakhdari, A.; Zarour, L. Optimized MPPT Controllers Using GA Heating for Grid Connected Photovoltaic Systems, Comparative study. Energy Procedia 2017, 119, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles Algarín, C.; Taborda Giraldo, J.; Rodríguez Álvarez, O. Fuzzy Logic Based MPPT Controller for a PV System. Energies 2017, 10, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarín, C.R.; Fuentes, R.L.; Castro, A.O. Implementation of a cost-effective fuzzy MPPT controller on the Arduino board. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2018, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Jhang, Y.-C.; Liang, R.-H. A fuzzy-logic based auto-scaling variable step-size MPPT method for PV systems. Sol. Energy 2016, 126, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, T.H.; Wu, X. Maximum power point tracking using a variable antecedent fuzzy logic controller. Sol. Energy 2016, 137, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipour, M.; Razaz, M.; Seifossadat, S.G.; Mortazavi, S.S. A new MPPT scheme based on a novel fuzzy approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1147–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.Z.; Li, H.; Kamal, T.; Arifo˘glu, U.; Mumtaz, S.; Khan, L. Neuro-Fuzzy Wavelet Based Adaptive MPPT Algorithm for Photovoltaic Systems. Energies 2017, 10, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheldoun, A.; Bradai, R.; Boukenoui, R.; Mellit, A. A new Golden Section method-based maximum power point tracking algorithm for photovoltaic systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 111, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, R.; Ezhilarasi, G.A. Golden section search based maximum power point tracking strategy for a dual output DC-DC converter. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, E.N.; Reis, J.H.; Coelho, E.A.A.; Freitas, L.C.G.; Júnior, J.B.V.; Freitas, L.C. Simulated Annealing-MPPT in Partially Shaded PV Systems. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyoucef, A.S.; Chouder, A.; Kara, K.; Silvestre, S.; Sahed, O.A. Artificial bee colony based algorithm for maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for PV systems operating under partial shaded conditions. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 32, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pradhan, R.; Subudhi, B. Design and real-time implementation of a new auto-tuned adaptive MPPT control for a photovoltaic system. Int. J. Electr. Power 2015, 64, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Jin, J.; Zhu, C.; Li, G. A Novel Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithm Based on Glowworm Swarm Optimization for Photovoltaic Systems. Int. J. Photoenergy 2016, 2016, 4910862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titri, S.; Larbes, C.; Toumi, K.Y.; Benatchba, K. A new MPPT controller based on the Ant colony optimization algorithm for Photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 58, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles Algarín, C.; Sevilla Hernández, D.; Restrepo Leal, D. A Low-Cost Maximum Power Point Tracking System Based on Neural Network Inverse Model Controller. Electronics 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouselham, L.; Hajji, M.; Hajji, B.; Bouali, H. A New MPPT-based ANN for Photovoltaic System under Partial Shading Conditions. Energy Procedia 2017, 111, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoun, M.A.; Ugalde, H.M.R.; Carmona, J.-C.; Gomand, J. Maximum power point tracking using P&O control optimized by a neural network approach: A good compromise between accuracy and complexity. Energy Procedia 2013, 42, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub Essefi, R.; Souissi, M.; Abdallah, H. Maximum Power Point Tracking Control Using Neural Networks for Stand-Alone Photovoltaic Systems. Int. J. Mod. Nonlinear Theory Appl. 2014, 3, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofinas, P.; Dounis, A.I.; Papadakis, G.; Assimakopoulos, M.N. An Intelligent MPPT controller based on direct neural control for partially shaded PV system. Energy Build. 2015, 90, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messalti, S.; Harrag, A.; Loukriz, A. A new variable step size neural networks MPPT controller: Review, simulation and hardware implementation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Amir, A.; Selvaraj, J.; Rahim, N.A. Study of the MPP tracking algorithms: Focusing the numerical method techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, M.T.; Demuth, H.B.; Beale, M.H.; De Jesús, O. Neural Network Design, 2nd ed.; Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 2014; pp. 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hen Hu, Y.; Hwang, J.-N. Handbook of Neural Network Signal Processing; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Robles Algarín, C.; Rodríguez Álvarez, O.; Ospino Castro, A. Data from a photovoltaic system using fuzzy logic and the P&O algorithm under sudden changes in solar irradiance and operating temperature. Data Brief 2018, 21, 1618–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, E. Modeling and Analysis of Solar Distributed Generation. Ph.D. Thesis, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, O. Modelado y Simulación de Dispositivos Fotovoltaicos. Master’s Thesis, Universidad de Puerto Rico, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.L.; Ye, H.; Rashid, M. Digital Power Electronics and Applications; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 7. ISBN 0-1208-8757-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.; Hamada, M. Performance Comparison of Feed-Forward Neural Networks Trained with Different Learning Algorithms for Recommender Systems. Computation 2017, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







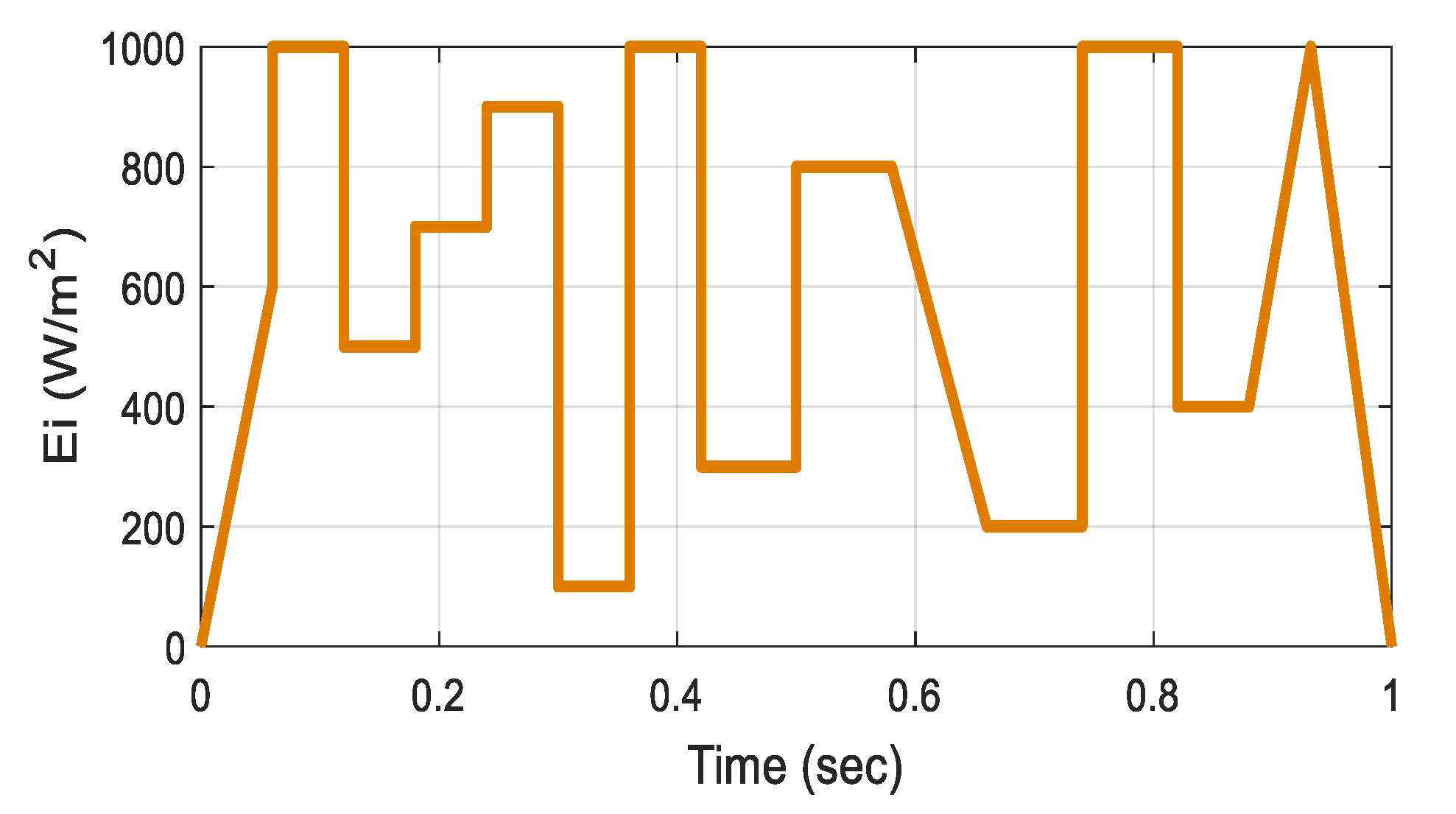

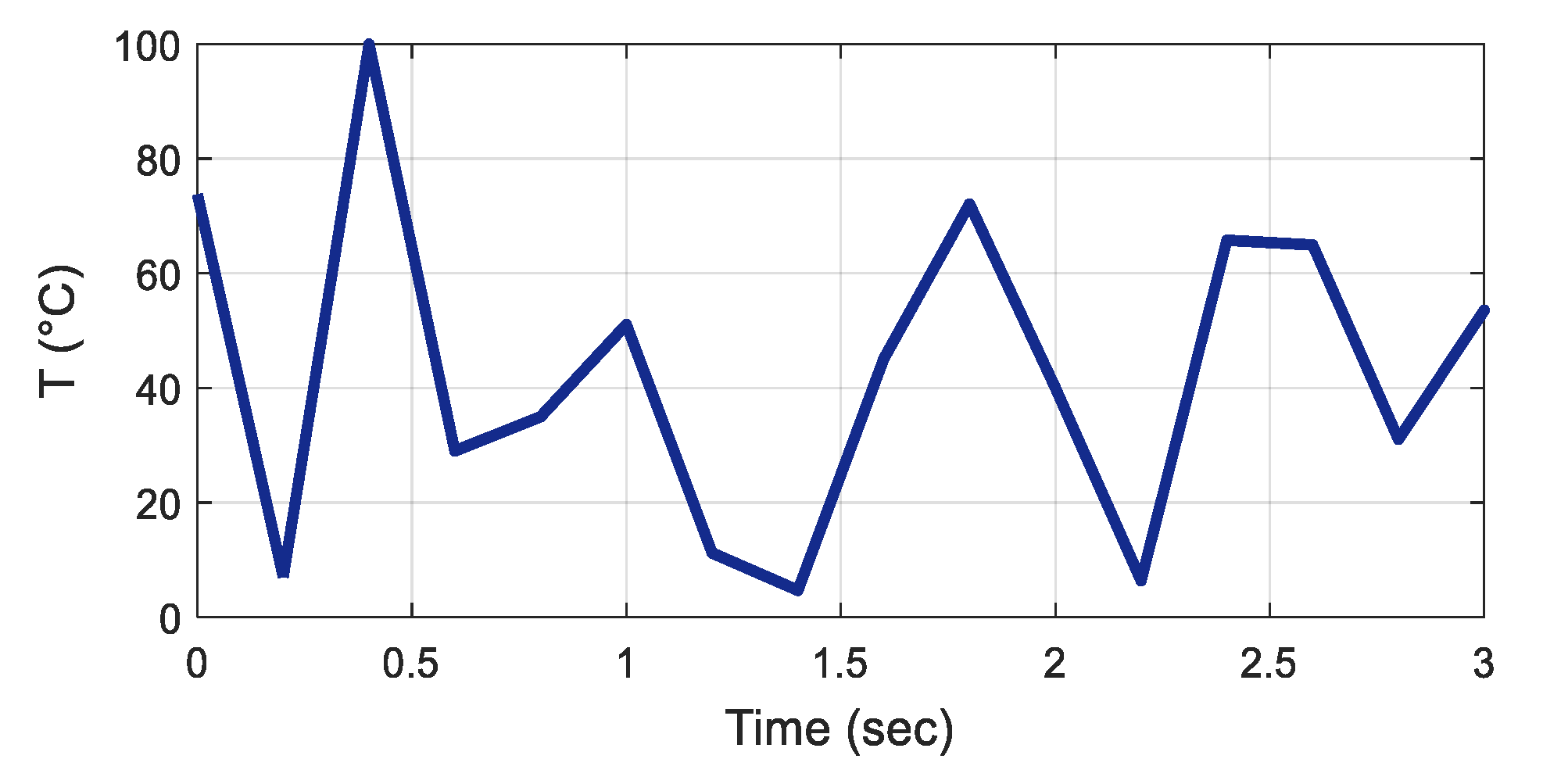







| Case | Test Signals | |
|---|---|---|
| Ei (W/m2) | T (°C) | |
| 1 | 1000 | 25 |
| 2 | 588.38 | 25 |
| 3 | 1000 | 41.79 |
| 4 | 545.12 | 28.85 |
| 5 | 631.65 | 28.95 |
| Case | Pref (W) | P&O (W) | LMS (W) | Iterative LMS (W) | RTRL (W) | Fuzzy (W) | NARX (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 64.87 | 56.05 | 60.16 | 61.14 | 61.33 | 57.28 | 58.88 |
| 2 | 36.13 | 22.37 | 20.5 | 35.37 | 35.47 | 33.03 | 34.57 |
| 3 | 61.4 | 56.3 | 39.61 | 55.33 | 57.09 | 57.47 | |
| 4 | 33.25 | 2.79 | 28.86 | 31.96 | 32.36 | 16.87 | 31.61 |
| 5 | 38.86 | 12.84 | 36.29 | 36.43 | 37.19 | 32.54 |
| Case | η (P&O) | η (LMS) | η (Iterative LMS) | η (RTRL) | η (Fuzzy) | η (NARX) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 86.4% | 92.74% | 94.25% | 94.54% | 88.3% | 90.77% |
| 2 | 61.92% | 56.74% | 97.9% | 98.17% | 91.42% | 95.68% |
| 3 | 91.69% | 64.51% | 90.11% | 92.98% | 93.6% | |
| 4 | 8.39% | 86.8% | 96.12% | 97.32% | 50.74% | 95.07% |
| 5 | 33.04% | 93.39% | 93.75% | 95.7% | 83.74% |
| Case | Simulation Time (Seconds) | MPPT Controller | Computation Time (hh:mm:ss) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.025 | P&O | 00:00:02 |
| LMS | 00:00:01 | ||
| Iterative LMS | 00:00:02 | ||
| RTRL | 00:00:01 | ||
| Fuzzy | 00:00:27 | ||
| NARX | 00:02:18 | ||
| 2 | 1 | P&O | 00:00:18 |
| LMS | 00:00:19 | ||
| Iterative LMS | 00:00:19 | ||
| RTRL | 00:00:21 | ||
| Fuzzy | 00:15:16 | ||
| NARX | 06:07:46 | ||
| 3 | 3 | P&O | 00:00:35 |
| LMS | 00:00:56 | ||
| Iterative LMS | 00:00:41 | ||
| RTRL | 00:00:45 | ||
| Fuzzy | 00:36:48 | ||
| NARX | |||
| 4 | 1 | P&O | 00:00:19 |
| LMS | 00:00:18 | ||
| Iterative LMS | 00:00:20 | ||
| RTRL | 00:00:22 | ||
| Fuzzy | 00:12:02 | ||
| NARX | 07:29:00 | ||
| 5 | 25 | P&O | 00:08:00 |
| LMS | 00:07:03 | ||
| Iterative LMS | 00:06:32 | ||
| RTRL | 00:07:33 | ||
| Fuzzy | 05:41:14 | ||
| NARX |
| MPPT Controller | Rise Time (ms) | Settling Time (ms) | Peak (W) | Peak Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P&O | 0.42 | 16.36 | 64.67 | 2.55 |
| LMS | 0.46 | 3.16 | 65.15 | 2.45 |
| Iterative LMS | 0.58 | 3.32 | 64.71 | 2.55 |
| RTRL | 0.59 | 3.34 | 65.17 | 2.50 |
| Fuzzy | 0.81 | 8.65 | 64.98 | 2.70 |
| NARX | 0.34 | 4.37 | 64.70 | 1.35 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viloria-Porto, J.; Robles-Algarín, C.; Restrepo-Leal, D. A Novel Approach for an MPPT Controller Based on the ADALINE Network Trained with the RTRL Algorithm. Energies 2018, 11, 3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123407
Viloria-Porto J, Robles-Algarín C, Restrepo-Leal D. A Novel Approach for an MPPT Controller Based on the ADALINE Network Trained with the RTRL Algorithm. Energies. 2018; 11(12):3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123407
Chicago/Turabian StyleViloria-Porto, Julie, Carlos Robles-Algarín, and Diego Restrepo-Leal. 2018. "A Novel Approach for an MPPT Controller Based on the ADALINE Network Trained with the RTRL Algorithm" Energies 11, no. 12: 3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123407
APA StyleViloria-Porto, J., Robles-Algarín, C., & Restrepo-Leal, D. (2018). A Novel Approach for an MPPT Controller Based on the ADALINE Network Trained with the RTRL Algorithm. Energies, 11(12), 3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123407





