Analysis and Design of a Maglev Permanent Magnet Synchronous Linear Motor to Reduce Additional Torque in dq Current Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Maglev Permanent Magnet Linear Motor Electromagnetic Model
2.1. Coordinate Definition
2.2. Magnetic Field Analysis
2.3. Electromagnetic Force and Torque Analysis
3. Additional Torque Analysis and Offset
3.1. dq Coordinate Transformation
3.2. Torque Analysis
3.3. Finite Element Analysis of AdditionalTorque
4. Optimal and Design of Motor Structure
4.1. Structure Design
4.2. Optimization of Halbach Permanent Magnet Array
4.3. Optimization of Coil Thickness
5. Simulation Result and Analysis
5.1. Finite Element Simulation
5.2. Position Closed Loop Verification
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tutelea, L.N.; Kim, M.C.; Topor, M.; Lee, J.; Boldea, I. Linear Permanent Magnet Oscillatory Machine: Comprehensive Modeling for Transients with Validation by Experiments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi1, S.E.; Mirzayee, M.; Mirsalim, M. Design and Analysis of a Double-Sided Linear Induction Motor for Transportation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8106307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldea, I.; Tutelea, L.N.; Parsa, L.; Dorrell, D. Automotive Electric Propulsion Systems with Reduced or No Permanent Magnets: An Overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5696–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chen, Z.; Yao, B.; Wang, Q.F. A Two-Loop Performance-Oriented Tip-Tracking Control of a Linear-Motor-Driven Flexible Beam System with Experiments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profumo, F.; Tenconi, A.; Gianolio, G. Design and Realization of a PM Linear Synchronous Motor with a Very High Thrust/Normal Force Ratio. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Industry Applications Conference (36th IAS Annual Meeting), Chicago, IL, USA, 30 September–4 October 2001; pp. 1984–1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, B. Speed Control of Complementary and Modular Linear Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 4056–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.F.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Ye, Y.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Modeling and Investigation of Thermal Characteristics of a Water-Cooled Permanent-Magnet Linear Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Q. Electromagnetic Analysis on Two Structures of Bilateral Switched Reluctance Linear Motor. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 5205109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.J.; Yee, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kwak, S.B. Development of High Precision X-Y Stage Using for Production and Inspection Equipment of Organic Electro Luminescence Display. In Proceedings of the SICE Annual Conference 2007, Takamatsu, Japan, 17–20 September 2007; pp. 1649–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, S.; Hoshino, T.; Obinata, G.; Ouchi, K. Air-Bearing Linear Actuator for Highly Precise Tracking. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2003, 39, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenhöfer, G.; Slocum, A. Reducing Pitch Error of a Linear Motion System Actuated by a Permanent Magnet Open Face Linear Motor. J. Precis. Eng. 2009, 33, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khong, P.C.; Leidhold, R.; Mutschler, P. Magnetic Guidance of the Mover in a Long-Primary Linear Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Kim, W.J. Two-Phase Lorentz Coils and Linear Halbach Array for Multiaxis Precision-Positioning Stages with Magnetic Levitation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2017, 22, 2662–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.G.; Jin, J.X.; Zhu, J.G.; Lu, H.Y. Design and Analysis of a Prototype Linear Motor Driving System for HTS Maglev Transportation. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2007, 17, 2087–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Boldea, I. Linear Electric Machines, Drives and MAGLEVs Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, C.H.; Ha, C.W.; Park, D.Y. Analysis and Experimental Evaluation of Normal Force of Linear Induction Motor for Maglev Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 8300504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overboom, T.T.; Smeets, J.P.C.; Jansen, J.W.; Lomonova, E.A. Semianalytical Calculation of the Torque in a Linear Permanent-Magnet Motor with Finite Yoke Length. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3575–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.F.; Li, Y.X.; Ye, Y.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Investigation of Forces in Linear Induction Motor Under Different Slip Frequency for Low-Speed Maglev Application. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overboom, T.T.; Smeets, J.P.C.; Jansen, J.W.; Lomonova, E. Topology Comparison for a Magnetically Suspended Ceiling Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC11), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–18 May 2011; pp. 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Van Lierop, C.M.M.; Jansen, J.W.; Damen, A.A.H.; Lomonova, E.A.; van den Bosch, P.P.J.; Vandenput, A.J.A. Model-Based Commutation of a Long-Stroke Magnetically Levitated Linear Actuator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overboom, T.T.; Smeets, J.P.C.; Jansen, J.W.; Lomonova, E. Torque Decomposition and Control in an Iron Core Linear Permanent Magnet Motor. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Raleigh, NC, USA, 15–20 September 2012; pp. 2662–2669. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, B.Q.; Xing, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.N.; Zhou, Y.H. A Real-Time Computation Model of the Electromagnetic Force and Torque for a Maglev Planar Motor with the Concentric Winding. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.W.; van Lierop, C.M.M.; Lomonova, E.A.; Vandenput, A.J.A. Modeling of Magnetically Levitated Planar Actuators with Moving Magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumper, D.L.; Kim, W.J.; Williams, M.E. Design and Analysis Framework for Linear Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1996, 32, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Huang, S.D.; Lu, K.Y. Magnetic Field and Thrust Analysis of the U-Channel Air-Core Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 8201504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, T.J.; Zhu, H.Y.; Pang, C.K. Modeling of a Two Degrees-of-Freedom Moving Magnet Linear Motor for Magnetically Levitated Positioners. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 8300512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamers, H.R. Actuation Principles of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Planar Motors: A Literature Survey; Working Paper; Eindhoven University of Technology: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, F.; Kou, B.Q.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.R.; Zhou, Y.H. Design of a Control System for a Maglev Planar Motor Based on Two-Dimension Linear Interpolation. Energies 2017, 10, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.W. Magnetically Levitated Planar Actuator with Moving Magnets: Electromechanical Analysis and Design. Ph.D. Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, November 2007. [Google Scholar]





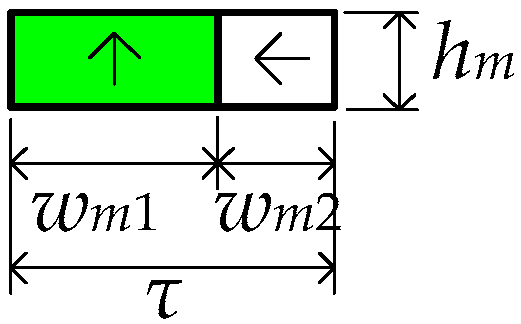




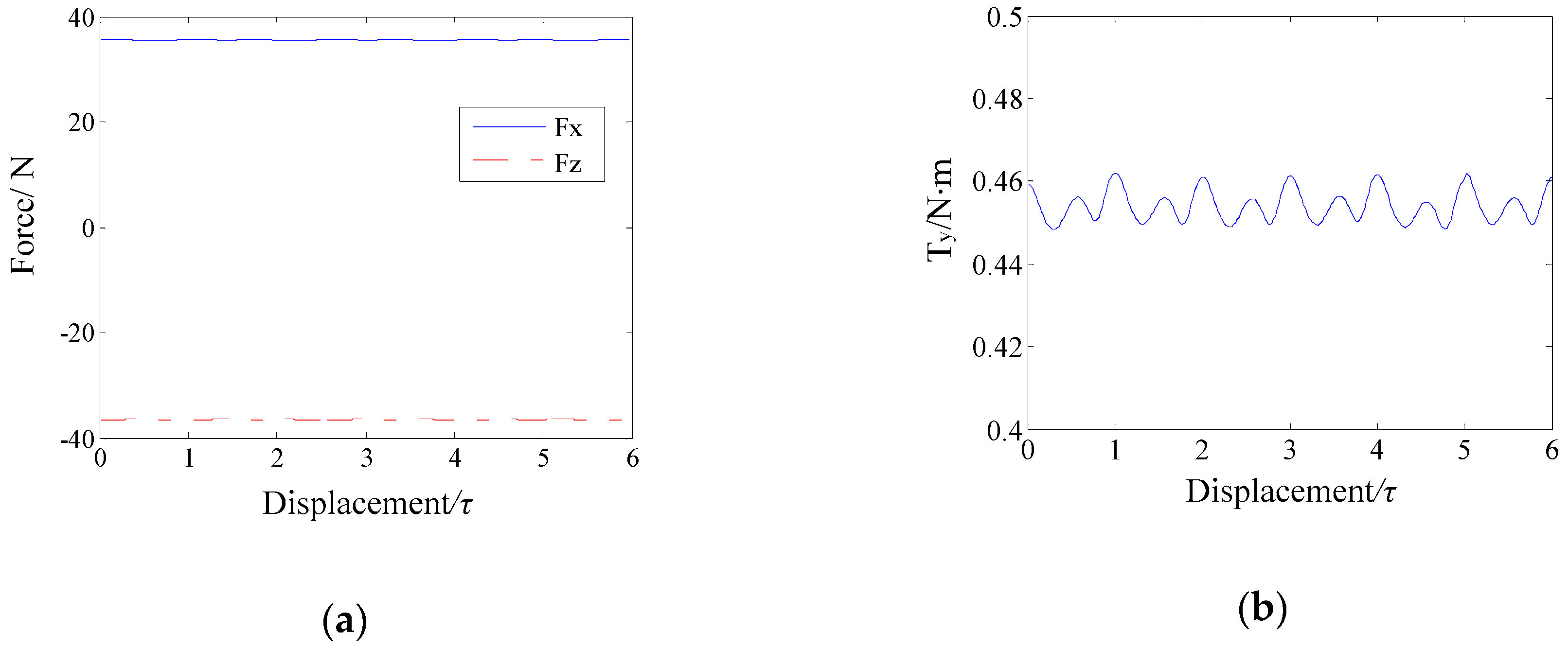


| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pole pitch τ | 15 | mm |
| Winding size (lc × wc × hc) | 100 × 5 × 10 | mm |
| Major permanent magnet size (lm1 × wm1 × hm) | 100 × 10 × 8 | mm |
| Auxiliary permanent magnet size (lm2 ×wm2 × hm) | 100 × 5 × 8 | mm |
| Air gap δ | 1 | mm |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pole pitch τ | 15 | mm |
| Air gap δ | 1 | mm |
| Winding size (lc × wc × hc) | 100 × 5 × 12 | mm |
| Major permanent magnet size (lm1 × wm1 × hm) | 100 × 8.7 × 20 | mm |
| Auxiliary permanent magnet size (lm2 × wm2 × hm) | 100 × 6.3 × 20 | mm |
| Mover size (l × w × h) | 150 × 120 × 20 | mm |
| Mover mass | 2.1 | kg |
| Number of turns N | 100 | - |
| Parameter | Controller I | Controller II | Controller III |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kp | 98 | 98 | 223 |
| Ki | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.07 |
| Kd | 1.5 | 1.5 | 3.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, F.; Kou, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C. Analysis and Design of a Maglev Permanent Magnet Synchronous Linear Motor to Reduce Additional Torque in dq Current Control. Energies 2018, 11, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030556
Xing F, Kou B, Zhang L, Wang T, Zhang C. Analysis and Design of a Maglev Permanent Magnet Synchronous Linear Motor to Reduce Additional Torque in dq Current Control. Energies. 2018; 11(3):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030556
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Feng, Baoquan Kou, Lu Zhang, Tiecheng Wang, and Chaoning Zhang. 2018. "Analysis and Design of a Maglev Permanent Magnet Synchronous Linear Motor to Reduce Additional Torque in dq Current Control" Energies 11, no. 3: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030556
APA StyleXing, F., Kou, B., Zhang, L., Wang, T., & Zhang, C. (2018). Analysis and Design of a Maglev Permanent Magnet Synchronous Linear Motor to Reduce Additional Torque in dq Current Control. Energies, 11(3), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030556






