Fault Location Method for DC Distribution Systems Based on Parameter Identification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model of Line Faults in DC Distribution Systems
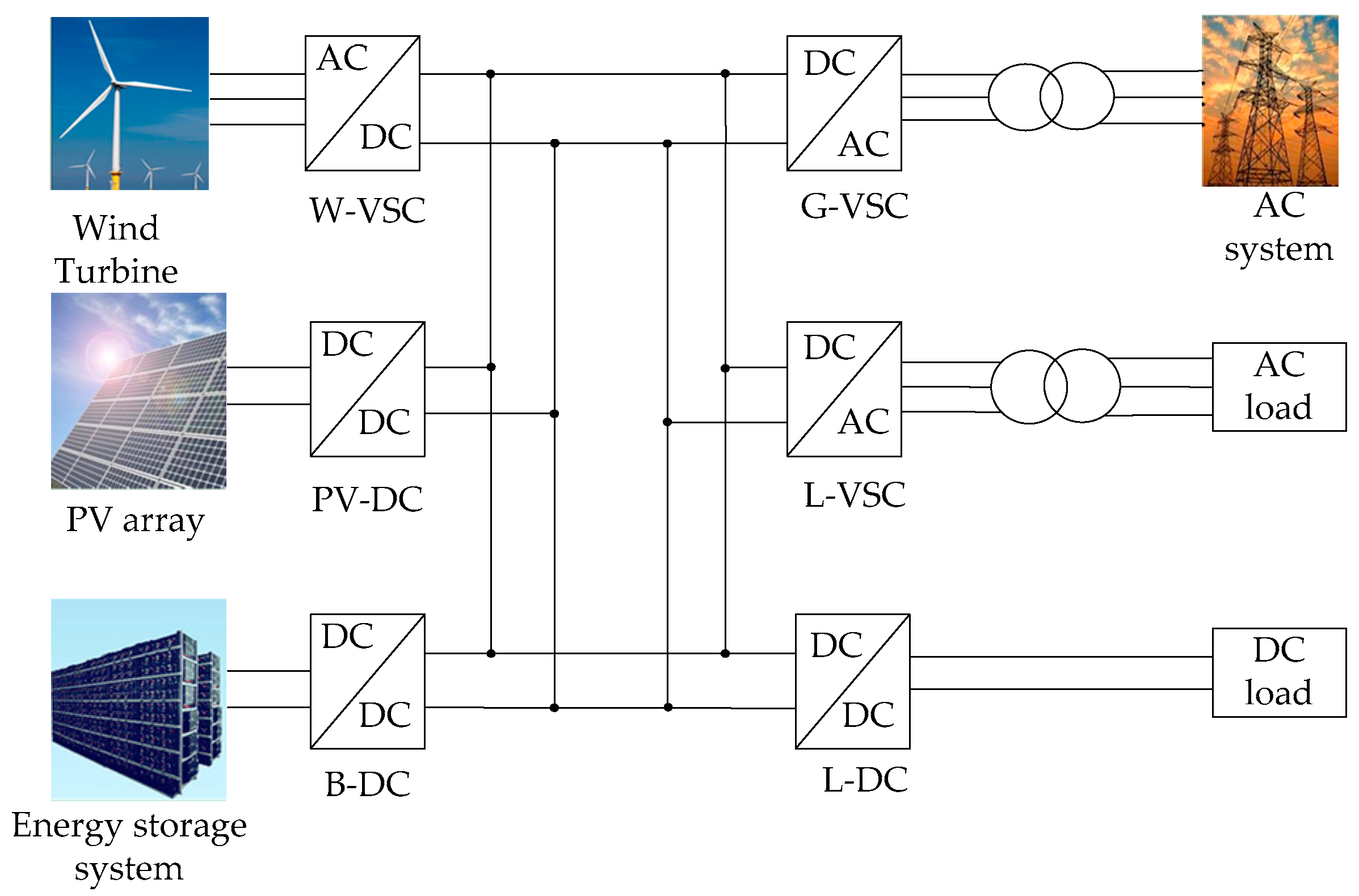
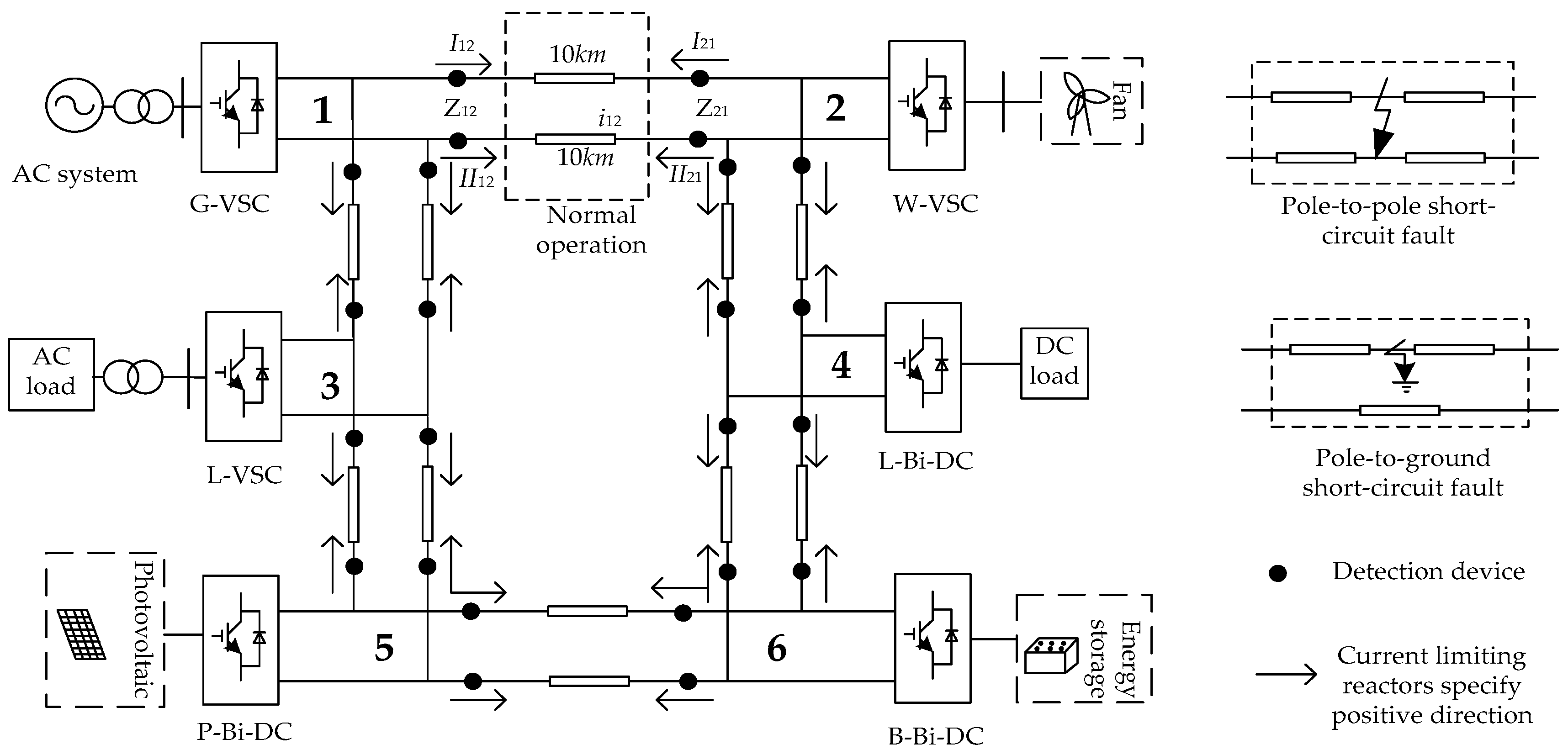
2.1. System Structure
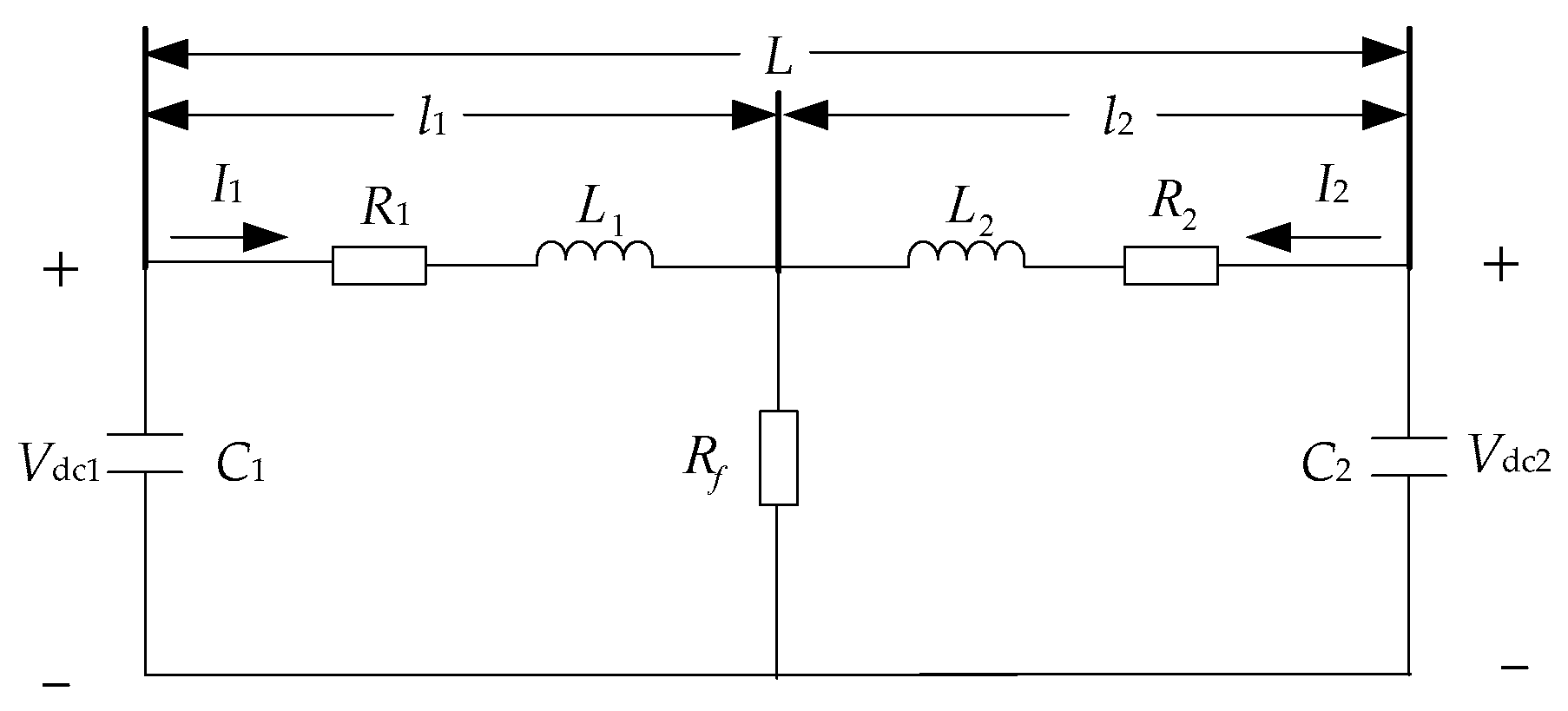
2.2. Mathematical Model of Pole-to-Pole Short-Circuit Fault
2.3. Mathematical Model of Pole-to-Ground Short-Circuit Fault
3. Fault Type Identification Algorithm Based on Graph Theory
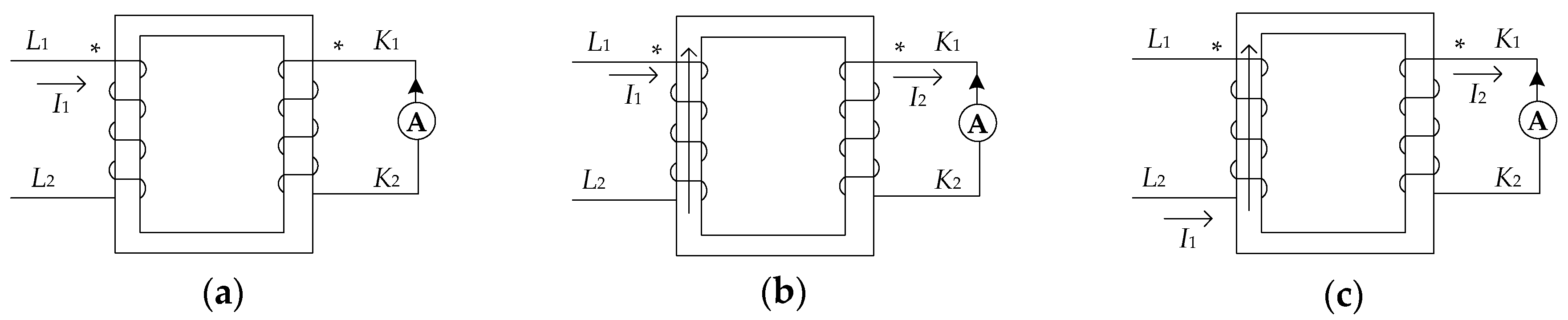
3.1. The Basic Knowledge of Graph Theory
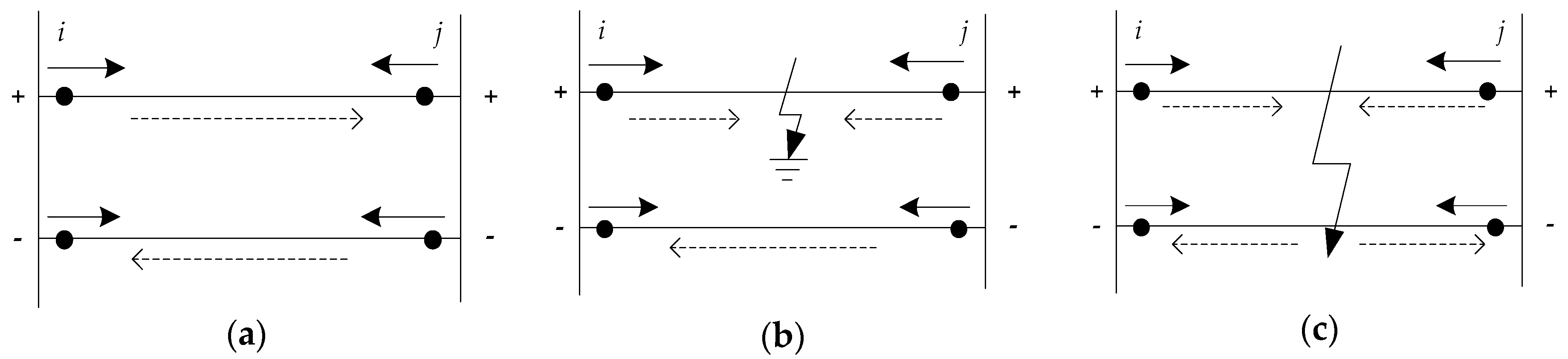
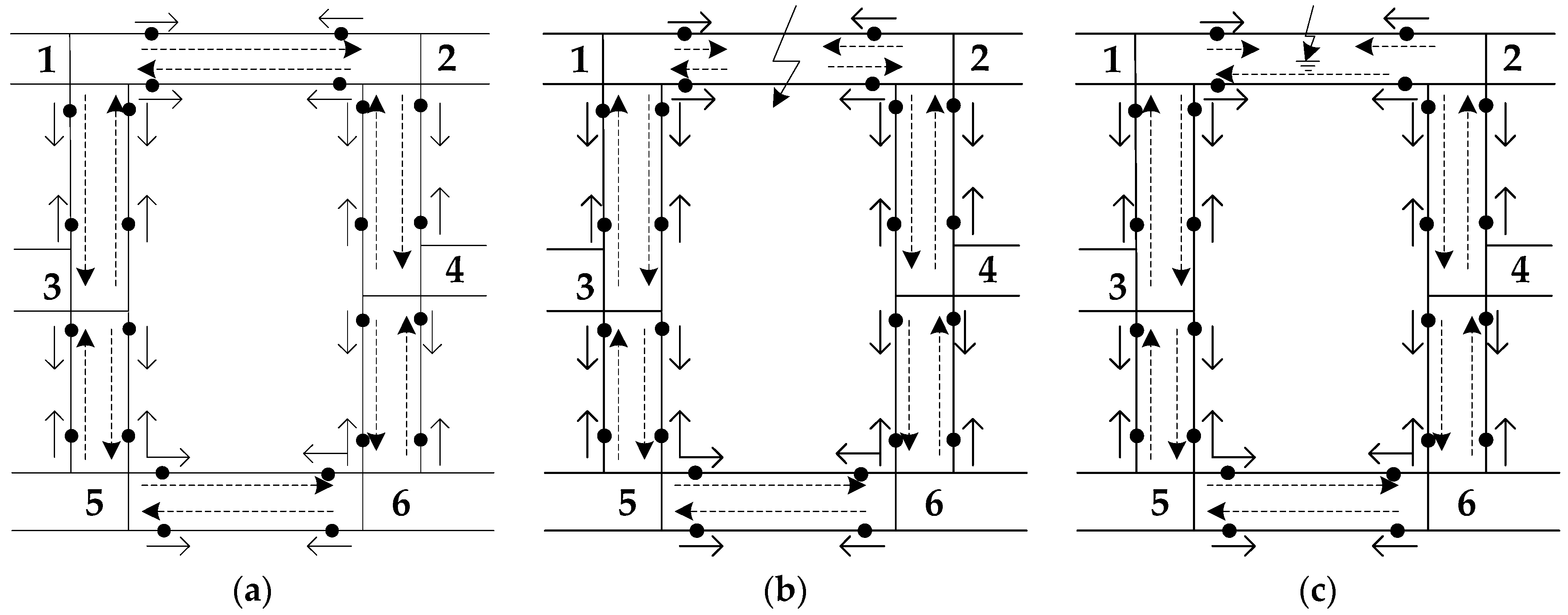
3.2. Directed Topology Description of a Distribution System
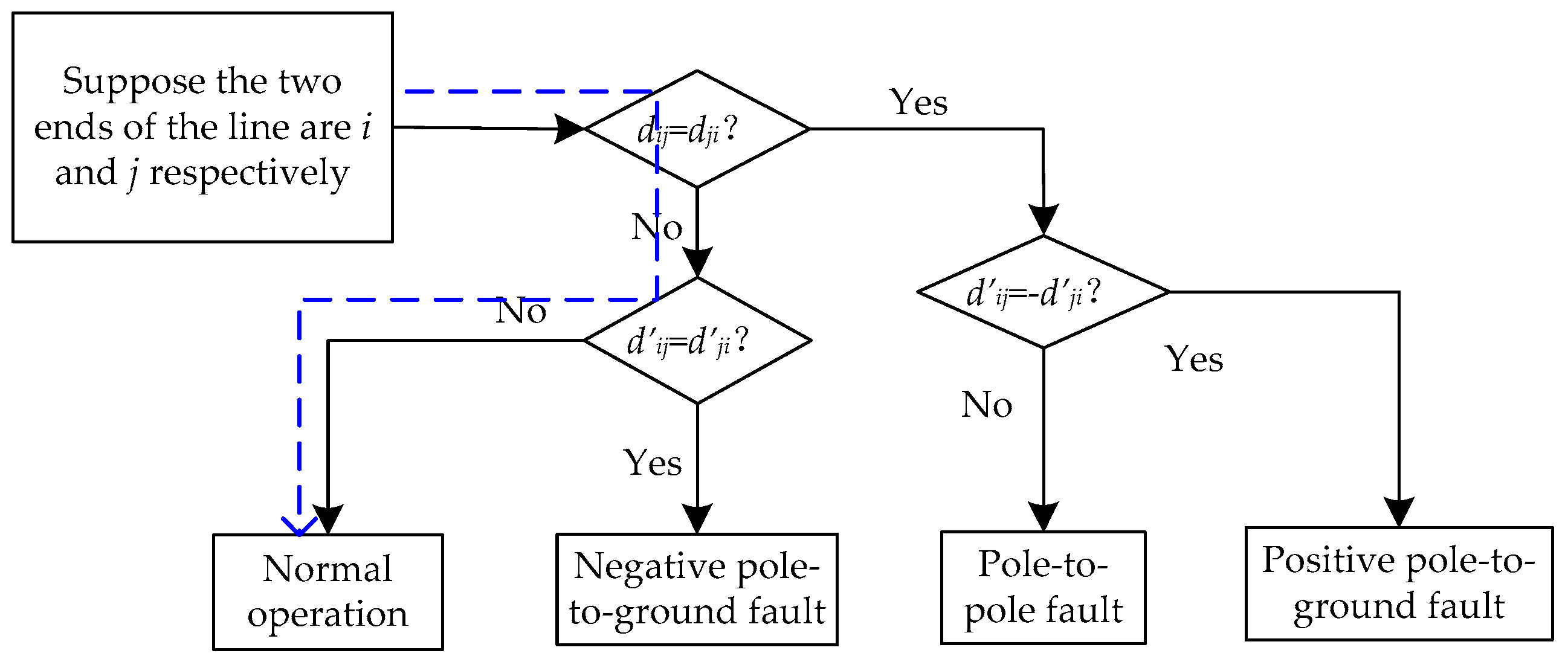
3.3. Fault Type Identification Algorithm
4. Fault Identification Method Based on Parameter Identification
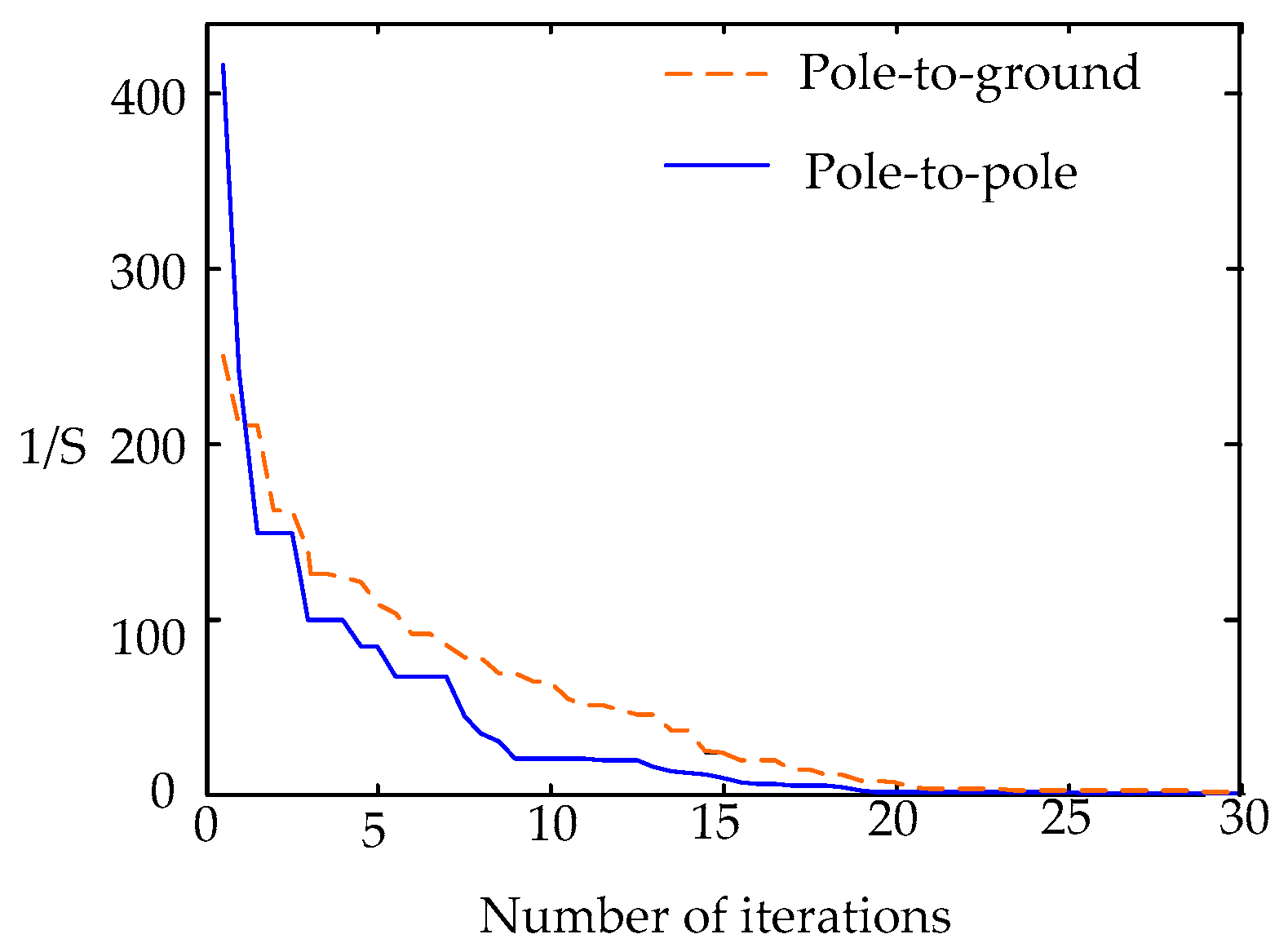
4.1. Application of GA in Parameter Identification
- Population initialization operation. This step needs to determine the evolutionary generation, population size, crossover probability, mutation probability, and so on.
- Determination of fitness function. In the natural world, there is greater chance of survival for individuals with greater fitness, so it is necessary to transform the parameter identification problem into a fitness function. Individuals with a high degree of fitness are retained for the next generation of operations.
- Perform crossover and mutation operations on the remaining individuals.
- Diagnose whether the fitness value obtained and the last iteration meets the accuracy requirements. If it is satisfied, stop the iteration. Otherwise, continue to iterate until it reaches the optimal value. Then stop the iteration and output the result.
4.2. Differential Variable Extraction
4.3. Fault Location Principle
5. Simulation Verification
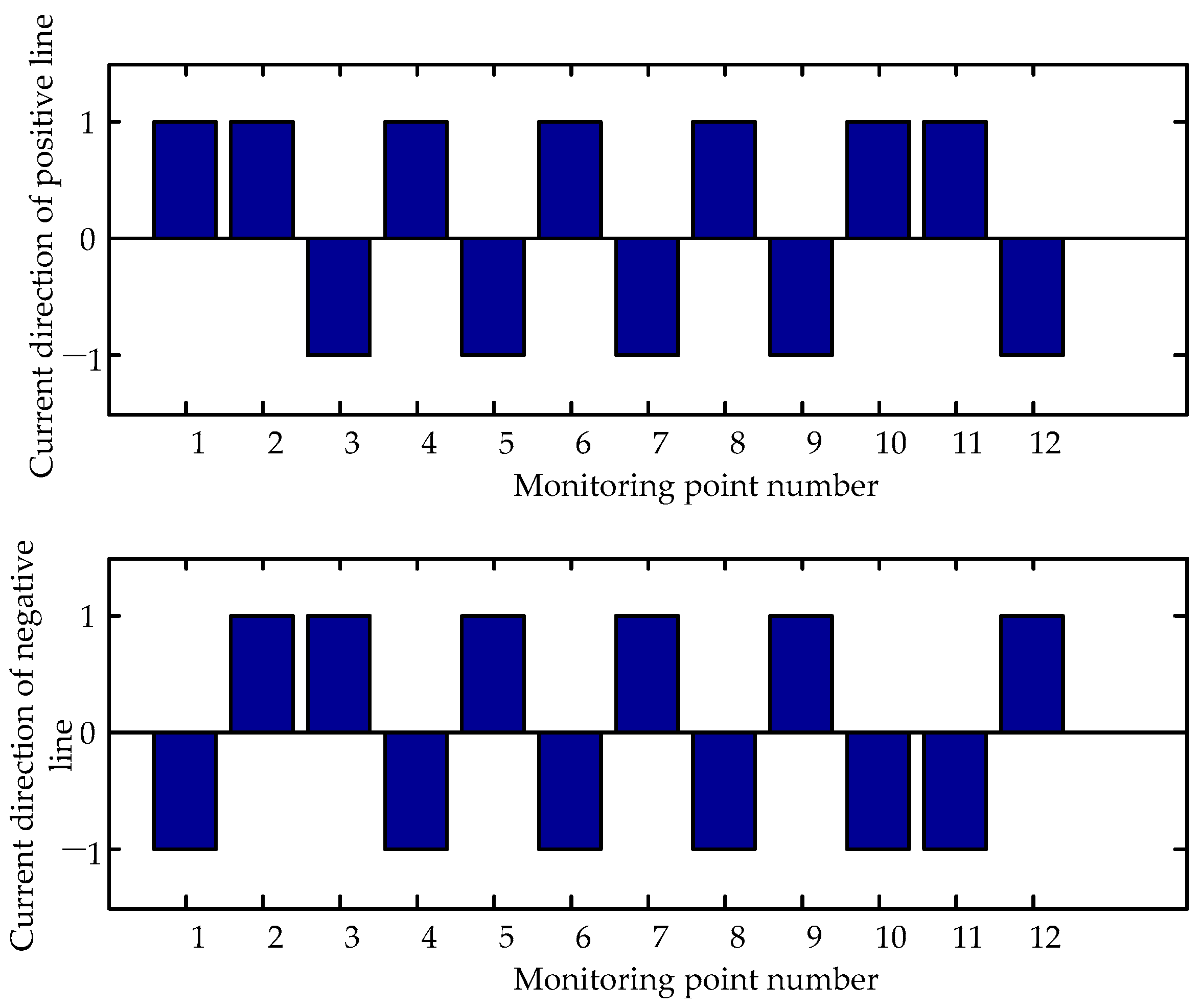
5.1. Simulation Results for Fault Type Identification
5.1.1. Parameter Settings
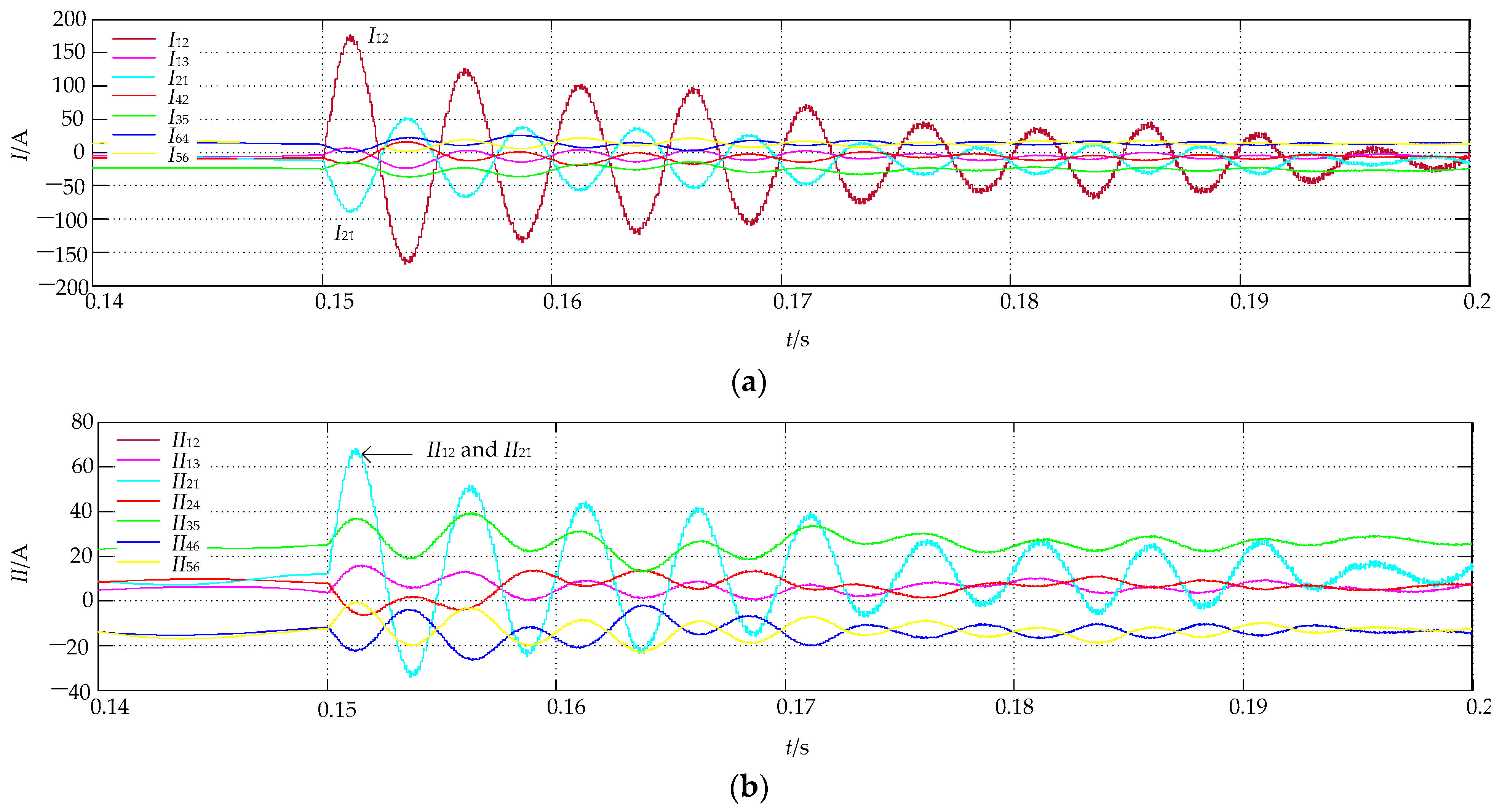
5.1.2. Results Analysis
Normal Operation
Pole-to-Pole Short-Circuit Fault
Positive Pole-to-Ground Short-Circuit Fault
5.2. Fault Location Results
5.2.1. Parameter Settings
5.2.2. Results Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vahedi, H.; Al-Haddad, K. Real-Time implementation of a packed U-Cell seven-Level inverter with low switching frequency voltage regulator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5967–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Cho, B.H. Master–Slave based hierarchical control for a small power DC-distributed microgrid system with a storage device. Energies 2016, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tai, N.; Fan, C.; Chen, S. A hybrid current-limiting circuit for DC line fault in multi-terminal VSC-HVDC system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 64, 5595–5607. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; He, J. DC fault analysis and current limiting technique for VSC-based DC distribution system. Proc. CSEE 2015, 35, 3026–3036. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.M.; Liu, C.; Sciubba, E. Line-to-Line fault analysis and location in a VSC-based Low-Voltage DC distribution network. Energies 2018, 11, 536. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Boon-Teck, O. Locating and isolating DC faults in multi-terminal DC systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2007, 22, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.D.; Candelaria, J.; Ma, L.; Dunn, K. DC ring-bus microgrid fault protection and identification of fault location. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.E.; Mahajan, N.R. Overcurrent protection on voltage-source-converter-based multi-terminal DC distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2007, 22, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Guan, M.; Tang, L.; Huang, H.; Chen, X.; Xie, J. Paralleled multi-terminal DC transmission line fault locating method based on travelling wave. Let Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2014, 8, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liao, K.; Li, X.; Lin, S.; Yang, J.; Mai, R. Natural frequency-based Line fault location in HVDC Lines. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2014, 29, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zou, G.; Huang, Q.; Gao, H. A traveling-wave-based fault location scheme for MMC-based multi-terminal DC grids. Energies 2018, 11, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tai, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. EMTR-based fault location for DC line in VSC-MTDC system using high-frequency currents. Let Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 2499–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jia, K.; Bi, T.; Yang, Q. Sixth harmonic-based fault location for VSC-DC distribution systems. LET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 3485–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Sun, J.; Song, G.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, Z. Fault location method for HVDC transmission lines on the basis of the distributed parameter model. Proc. CSEE 2010, 30, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Song, G.; Gao, S.; Suonan, J.; Li, G. A novel fault-location method for VSC-HVDC transmission lines based on natural frequency of current. Proc. CSEE 2011, 31, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Fletcher, J.F.; O’Reilly, J. Short-circuit and ground fault analyses and location in VSC-based DC network cables. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 59, 3827–3837. [Google Scholar]
- Steven, D.A.F.; Patrick, J.N.; Stuart, J.G.; Paul, C.; Graeme, M.B. Optimizing the roles of unit and non-unit protection methods within DC microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, K.H.; Mota, I. Maximum photovoltaic power tracking: An algorithm for rapidly changing atmospheric conditions. IEE Proc. Gener. Transm. Distrib. 1995, 142, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Xu, Z. DC side grounding methodology for a Two-level VSC HVDC system. Automat. Electr. Power Syst. 2009, 33, 55–60. [Google Scholar]











| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| DC bus voltage | 500 V |
| Converter DC side capacitance | 2 mF |
| Wind power unit | 20 kW/220 V Permanent Magnet Wind Turbine Rated wind speed is 12 m/s Rated speed is 75 r/min |
| Rated power of G-VSC | 20 kW |
| Battery rated power | 20 kW |
| Load unit rated power | 20 kW |
| Line resistance | 0.0139 Ω/km |
| Line inductance | 0.159 mH/km |
| Line length | 10 km |
| Sampling frequency | 25 μs |
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monitoring point-positive line | Z12 | Z21 | Z13 | Z31 | Z24 | Z42 | Z35 | Z53 | Z46 | Z64 | Z56 | Z65 |
| Monitoring point-negative line | Z’12 | Z’21 | Z’13 | Z’31 | Z’24 | Z’42 | Z’35 | Z’53 | Z’46 | Z’64 | Z’56 | Z’65 |
| The range of R1 | 0~r × D |
| Range of R2 | 0~r × D |
| Range of L1 | 0~l × D |
| Range of L2 | 0~l × D |
| Search dimension | 4 |
| Population size | 20 |
| Crossover probability | 0.7 |
| Mutation probability | 0.01 |
| Generation gap | 0.95 |
| Largest genetic generation | 30 |
| Fault Type | Transition Resistance | Code | Actual Value | Targeting Value | The Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pole-to-pole short-circuit fault | 0 Ω | 1 | 1 km | 1.0231 km | 0.3100% |
| 2 | 5 km | 4.9938 km | 0.1240% | ||
| 3 | 7 km | 7.0297 km | 0.4243% | ||
| 10 Ω | 4 | 1 km | 0.9810 km | 0.1900% | |
| 5 | 5 km | 5.0102 km | 0.2040% | ||
| 6 | 7 km | 6.9984 km | 0.0229% | ||
| 50 Ω | 7 | 1 km | 1.0333 km | 0.3300% | |
| 8 | 5 km | 5.0014 km | 0.0280% | ||
| 9 | 7 km | 6.9969 km | 0.0443% | ||
| Pole-to-ground short-circuit fault | 0 Ω | 10 | 1 km | 1.0072 km | 0.7200% |
| 11 | 5 km | 5.0100 km | 0.2000% | ||
| 12 | 7 km | 7.0003 km | 0.0043% | ||
| 10 Ω | 13 | 1 km | 0.9922 km | 0.7800% | |
| 14 | 5 km | 4.8991 km | 0.2180% | ||
| 15 | 7 km | 6.9893 km | 0.1529% | ||
| 50 Ω | 16 | 1 km | 0.9918 km | 0.8200% | |
| 17 | 5 km | 5.0027 km | 0.0540% | ||
| 18 | 7 km | 6.9931 km | 0.0986% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Jin, W.; Fu, Y.; Yang, H. Fault Location Method for DC Distribution Systems Based on Parameter Identification. Energies 2018, 11, 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081983
Xu Y, Liu J, Jin W, Fu Y, Yang H. Fault Location Method for DC Distribution Systems Based on Parameter Identification. Energies. 2018; 11(8):1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081983
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yan, Jingyan Liu, Weijia Jin, Yuan Fu, and Hui Yang. 2018. "Fault Location Method for DC Distribution Systems Based on Parameter Identification" Energies 11, no. 8: 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081983
APA StyleXu, Y., Liu, J., Jin, W., Fu, Y., & Yang, H. (2018). Fault Location Method for DC Distribution Systems Based on Parameter Identification. Energies, 11(8), 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081983




