Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution and Heat Losses of a Molten Salt Heat Storage Tank
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molten Salt Tank and Insulation System
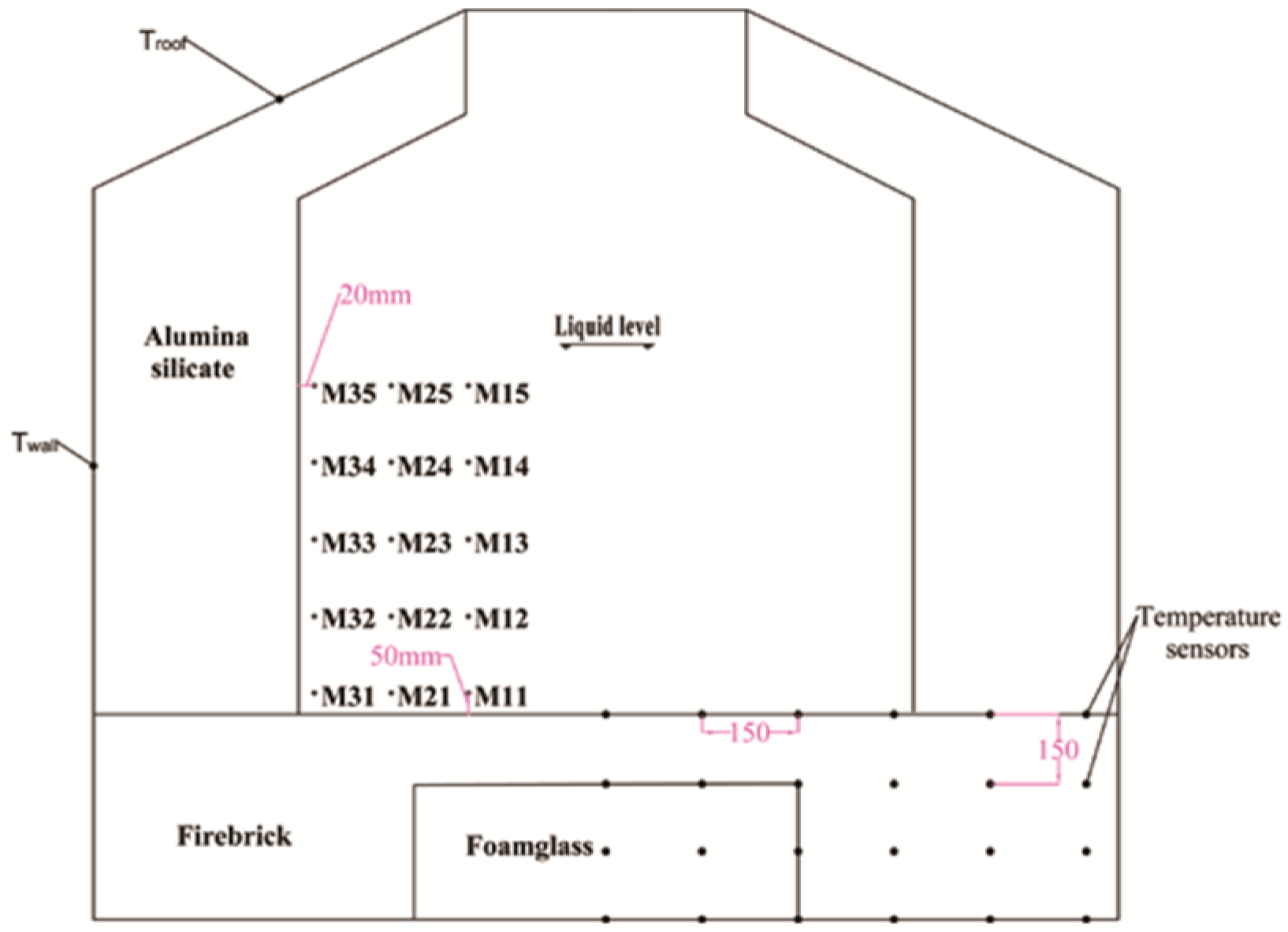
2.2. Temperature Sensors
2.3. Molten Salt Material
2.4. Methodology
2.4.1. Temperature Distribution Tests
2.4.2. Heat Losses
- (1)
- The insulated roof surface is geometrically an inclined plane;
- (2)
- The effect of the pump on the heat losses is approximately equal to the convection heat transfer calculated in an equivalent area;
- (3)
- The temperature sensors Twall and Troof are representative for all of the areas that they represent.
3. Results and Discussion
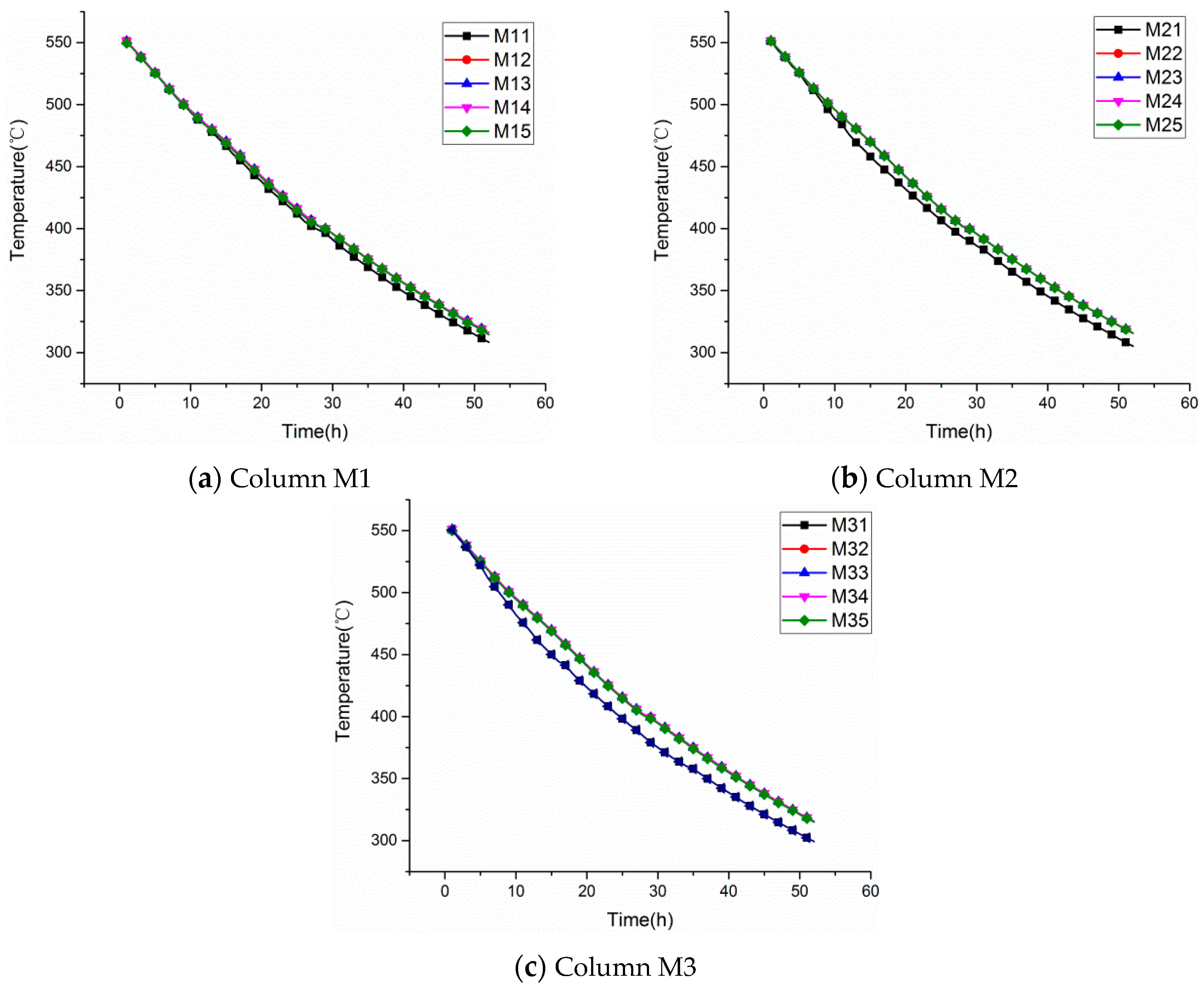
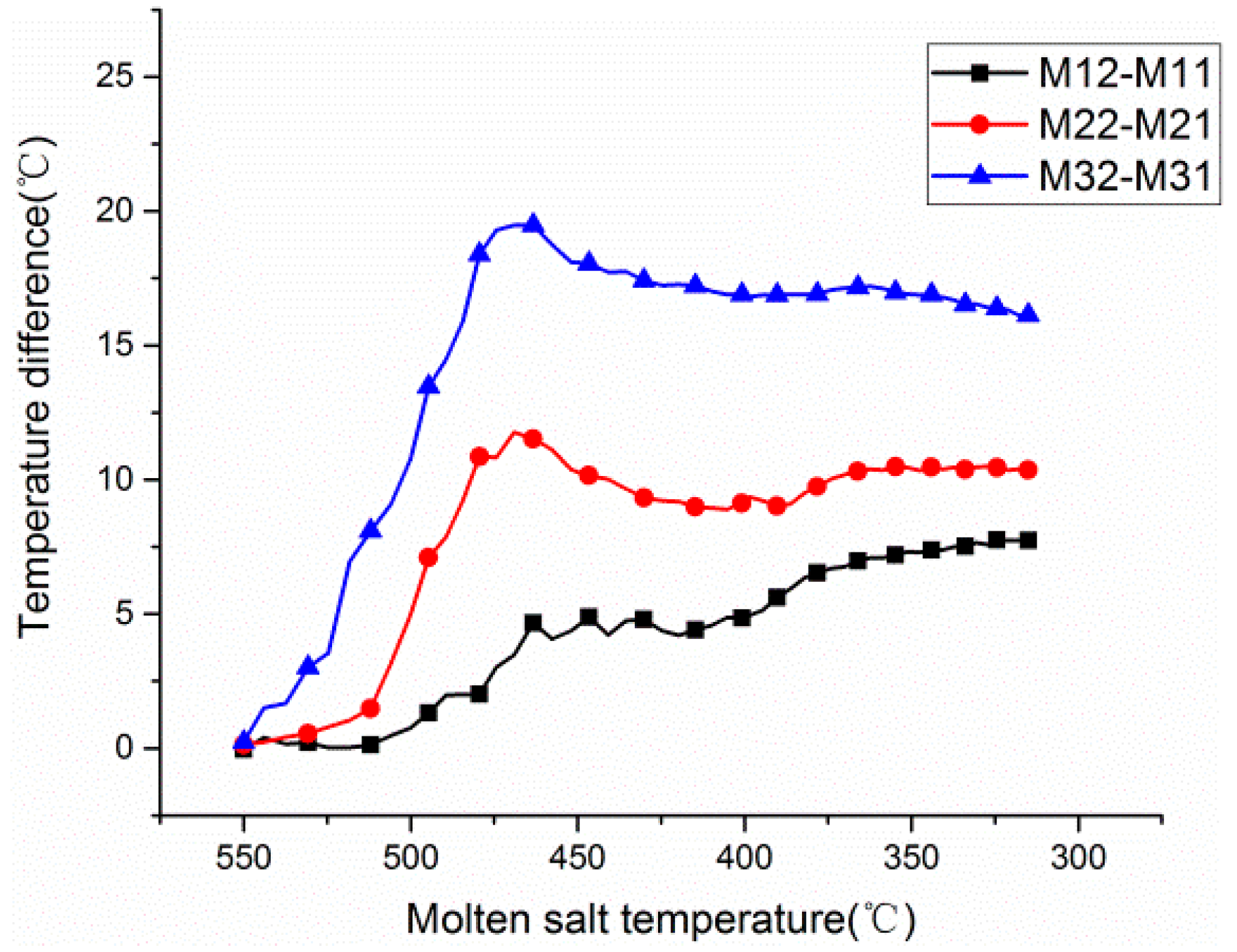
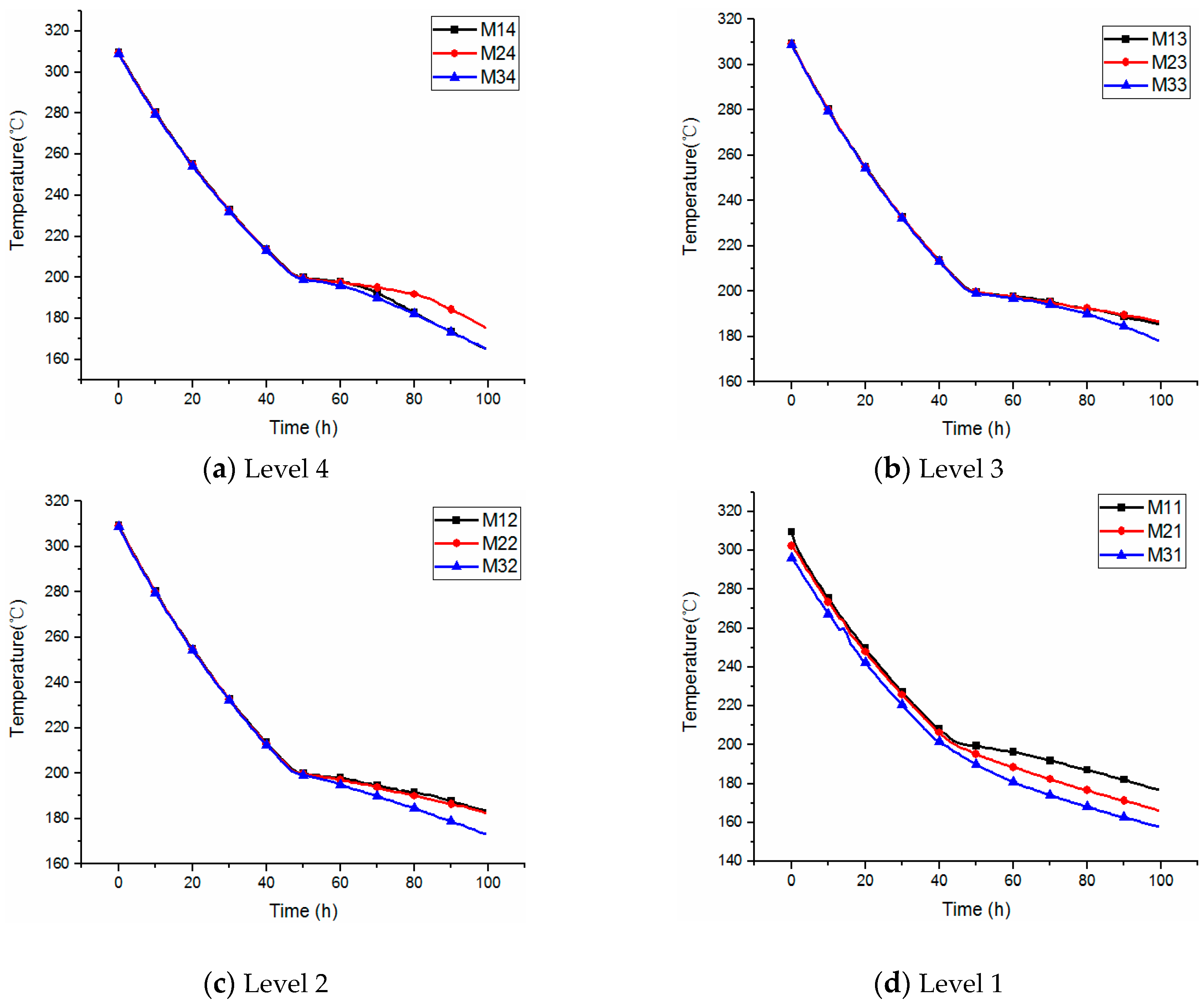
3.1. Temperature Distribution from 550 to 310 °C
3.2. Temperature Distribution from 300 to 180 °C
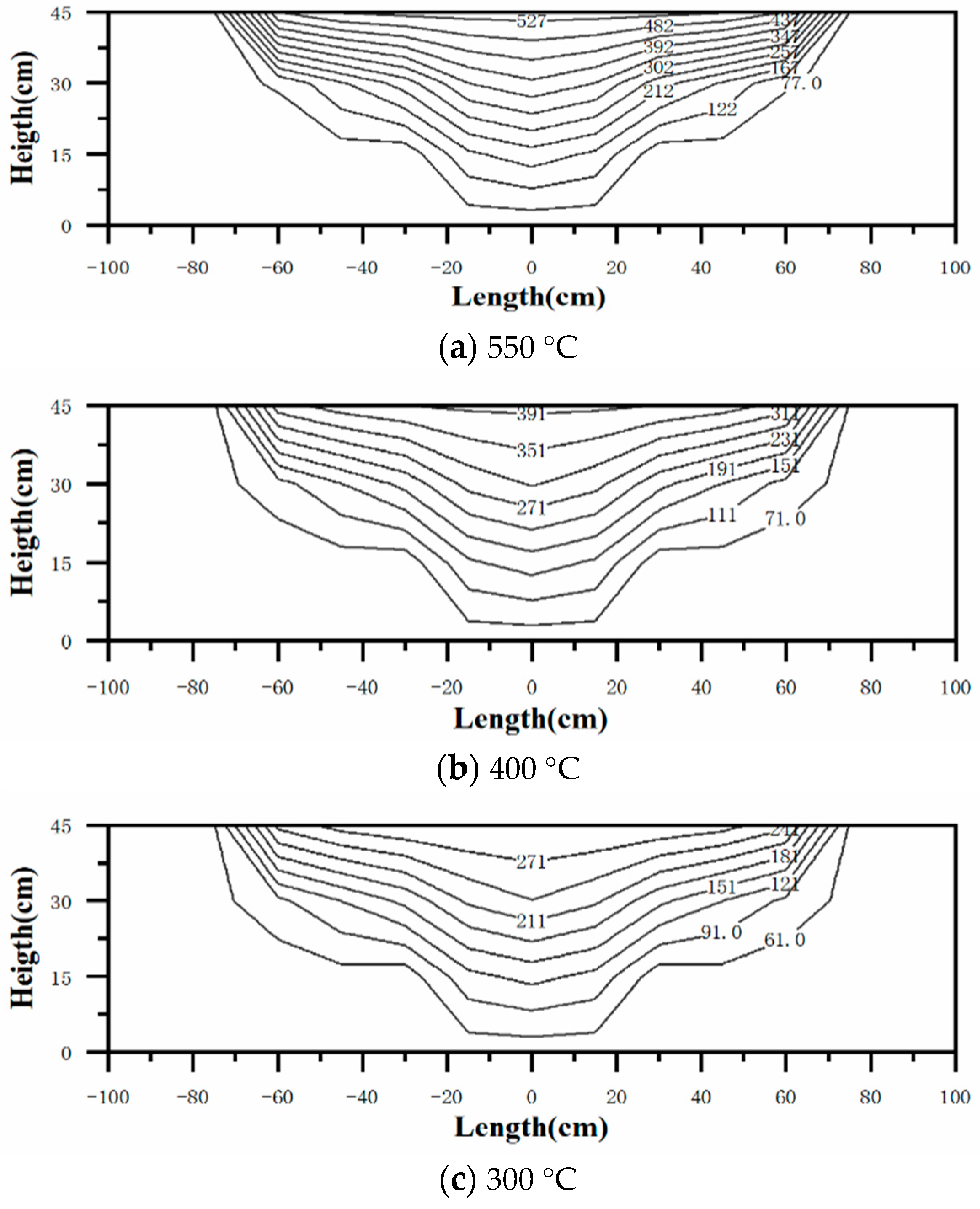
3.3. Temperature Distribution of the Insulation Foundation
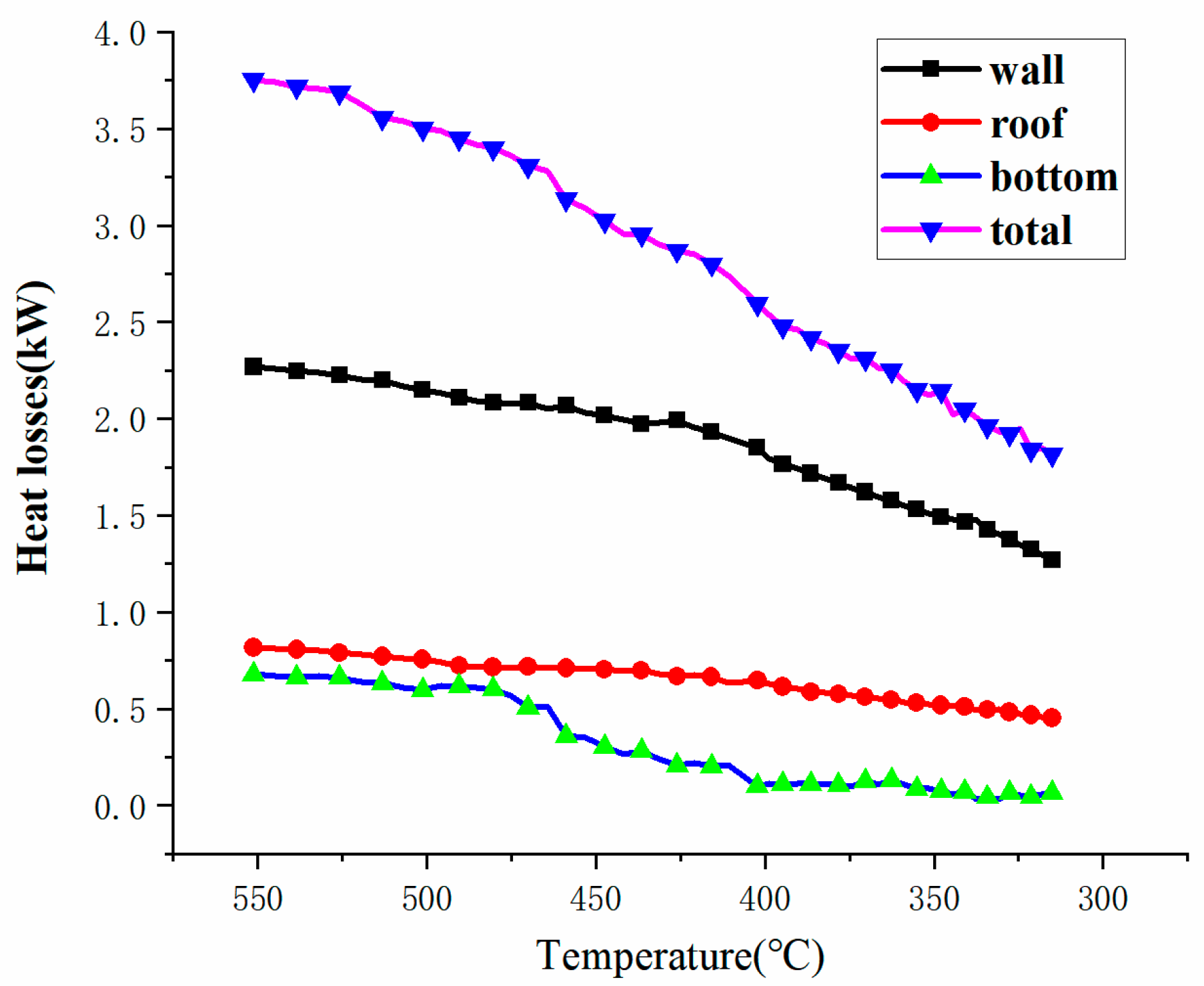
3.4. Heat Losses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Qheatloss | Heat losses of the tank (kW) |
| Caverage | Mean temperature of the specific heat of molten salt () |
| m | The weight of molten salt in the tank (kg) |
| Tt,Tt+Δt | The mean temperature of molten salt at time t and t+Δt (K) |
| Qwall, Qroof, Qbottom | Heat losses of the tank’s wall, roof, and bottom (kW) |
| Twall, Troof, Tbottom | Temperature of the insulation wall, roof, and bottom (°C) |
| Tatm | Temperature of the environment (°C) |
| Awall, Aroof | Area of the insulation wall and insulation roof (m2) |
| awall, aroof | Heat transfer coefficients of the insulation wall and roof (W/(m2·K)) |
| ac | Convection heat transfer coefficient (W/(m2·K) |
| ar | Radiation heat transfer coefficient (W/(m2·K) |
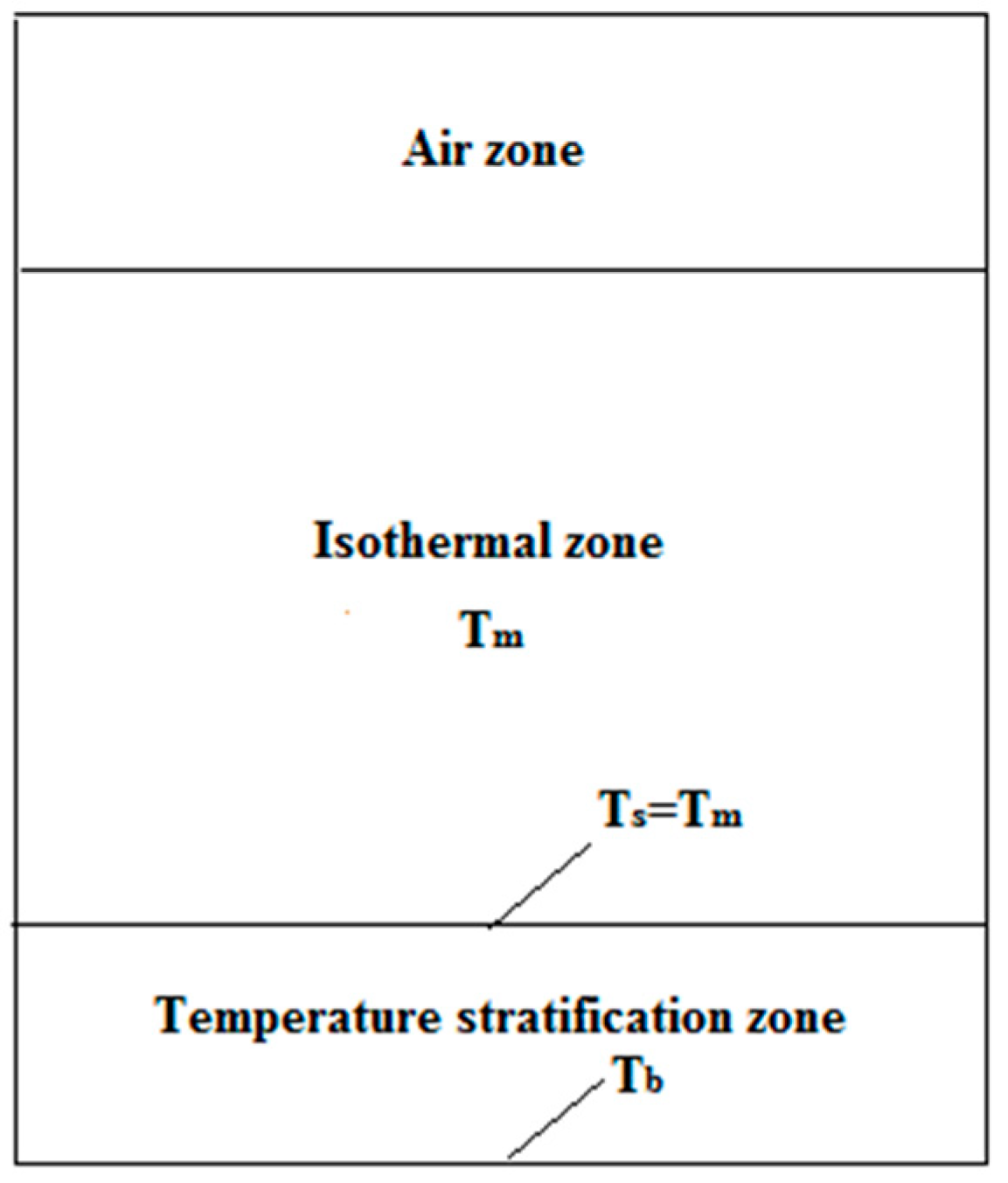
| Tm | Temperature of molten salt of the isothermal zone (°C) |
| Ts | Boundary temperature of the molten salt of the isothermal zone and the stratification zone (°C) |
| Tb | Temperature of the molten salt of the tank’s bottom (°C) |
| Tf | Temperature of the insulation foundation’s bottom (°C) |
| R | Thermal resistance of the insulation foundation (K/W) |
| γ | Rate of decline of heat losses caused by the thermal stratification zone |
References
- Xu, X.; Vignarooban, K.; Xu, B.; Hsu, K.; Kannan, A.M. Prospects and problems of concentrating solar power technologies for power generation in the desert regions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1106–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaversky, F.; García-Barberena, J.; Sánchez, M.; Astrain, D. Transient molten salt two-tank thermal storage modeling for CSP performance simulations. Sol. Energy 2013, 93, 294–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Baeyens, J.; Cáceres, G.; Degrève, J.; Lv, Y. Thermal energy storage: Recent developments and practical aspects. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2016, 53, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, E.; Song, S.; Wang, X.; Yuan, G. Dynamic simulation of two-tank indirect thermal energy storage system with molten salt. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Osuna, R.; Fernández, A.I.; Cabeza, L.F. Thermal storage in a MW scale. Molten salt solar thermal pilot facility: Plant description and commissioning experiences. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 852–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, M.R.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, A.; Marugan-Cruz, C.; Santana, D. Saving assessment using the PERS in solar power towers. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 87, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, I.L.; Álvarez, J.L.; Blanco, D. Performance model for parabolic trough solar thermal power plants with thermal storage: Comparison to operating plant data. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 2443–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relloso, S.; Delgado, E. Experience with molten salt thermal storage in a commercial parabolic trough plant; Andasol 1 commissioning and operation. In Proceedings of the 15th International Solar PACES Symposium, Berlin, Germany, 15–18 September 2009; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Fischedick, J.; Tamme, R.; Herrmann, U. CFD Analysis of the Cool down Behaviour of Molten Salt Thermal Storage Systems; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 515–524. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez, C.; Iranzo, A.; Pino, F.J.; Guerra, J. Transient analysis of the cooling process of molten salt thermal storage tanks due to standby heat loss. Appl. Energy 2015, 142, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, I.; Pérez-Segarra, C.D.; Lehmkuhl, O.; Oliva, A. Modular object-oriented methodology for the resolution of molten salt storage tanks for CSP plants. Appl. Energy 2013, 109, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, R.; Dawson, D.B.; Daniel, B.; Rosa, D.L.; Gilbert, R. Final Test and Evaluation Results from the Solar Two Project; SAND2002-0120; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, C.; Laia, M.; Gerard, P.; Oró, G.; Gil, A.; Cabeza, L.F. Temperature distribution and heat losses in molten salts tanks for CSP plants. Sol. Energy 2016, 135, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalifa, A.J.N.; Mustafa, A.T.; Khammas, F.A. Experiment study of temperature stratification in a thermal storage tank in the static mode for different aspect. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2011, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Azharul, K.; Ashley, B.; Sabrina, F. Investigation of Stratified Thermal Storage Tank Performance for Heating and Cooling Applications. Energies 2018, 11, 1049. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, B.; Kearney, D. Thermal Storage Commercial Plant Design Study for a 2-Tank Indirect Molten Salt System: Final Report, 13 May 2002–31 December 2004; NERL: Lakewood, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.L.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.T.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.F. Experimental study of thermo physical properties and thermal stability of quaternary nitrate molten salts for thermal energy storage. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 190, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Committee. C680-2003 Standard Practice for Estimate of the Heat Gain or Loss and the Surface Temperatures of Insulated Flat, Cylindrical, and Spherical Systems by Use of Computer Programs; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
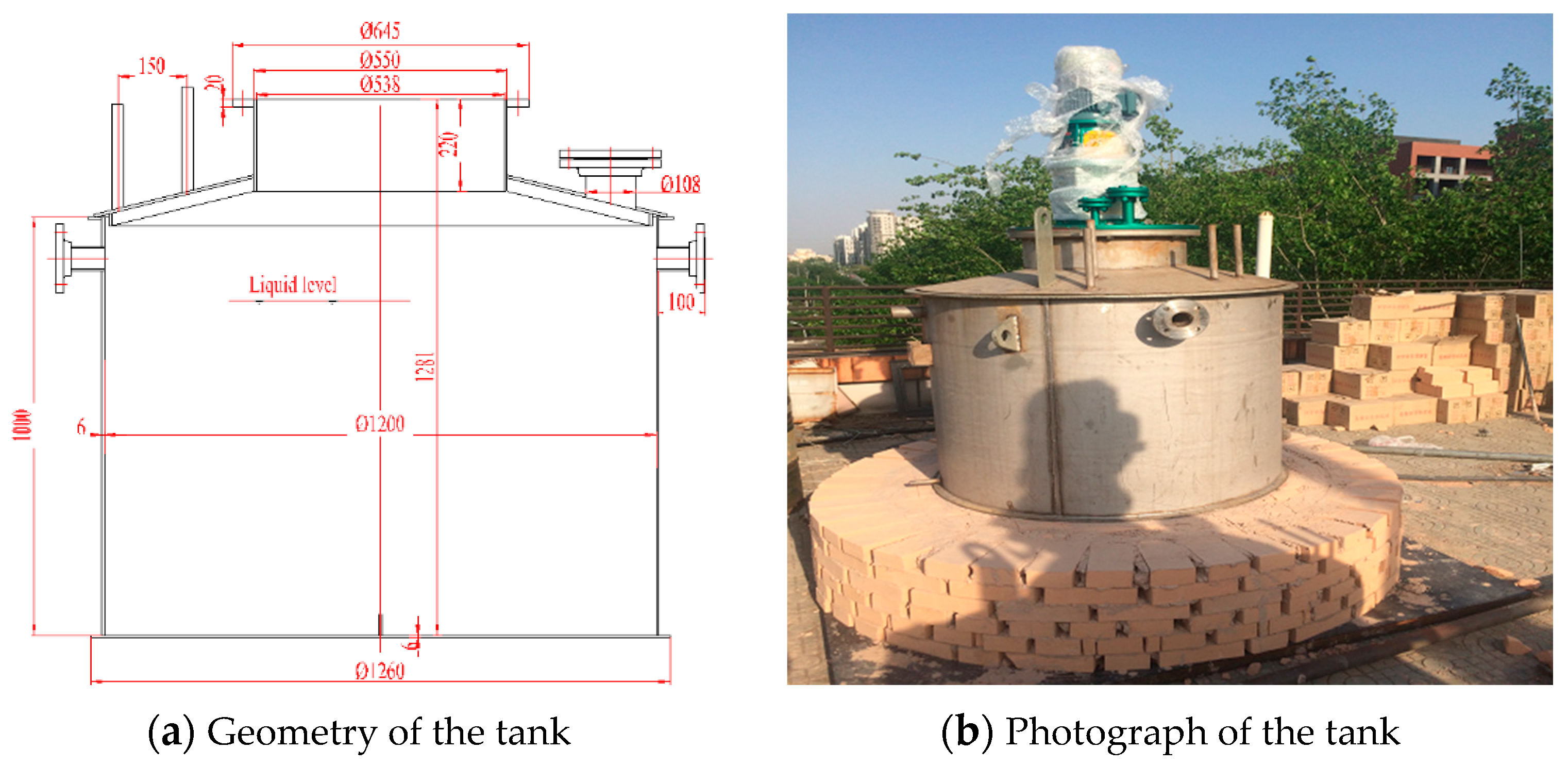




| Parameter | Units | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Internal diameter | mm | 1200 |
| Cylinder height | mm | 1000 |
| Pump mounting bracket height | mm | 220 |
| Total height | mm | 1281 |
| Thickness of the walls | mm | 6 |
| Position | Insulation Material | Conductivity (W/m·K) | Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roof of the tank | Alumina silicate fiber | 200 | |
| Side wall of the tank | Alumina silicate fiber | 350 | |
| Insulation foundation | Foam glass | 300 | |
| Insulation foundation | Firebrick | 450 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Melting point, °C | 94 |
| Density, kg/m3 | |
| Heat capacity, J/kg·K | |
| Thermal conductivity, W/m·K | |
| Dynamic viscosity, kg/m·s |
| Data Sources | Heat Losses Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roof | Wall | Bottom | Average Value | |
| Experiment result (550 °C) | 231.4 | 219.1 | 216.6 | 220.2 |
| Solar Two data (565 °C) | — | — | — | 176.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Ma, C.; Meng, Q.; Hu, X.; Yang, C. Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution and Heat Losses of a Molten Salt Heat Storage Tank. Energies 2019, 12, 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101943
Zhang X, Wu Y, Ma C, Meng Q, Hu X, Yang C. Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution and Heat Losses of a Molten Salt Heat Storage Tank. Energies. 2019; 12(10):1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101943
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoming, Yuting Wu, Chongfang Ma, Qiang Meng, Xiao Hu, and Cenyu Yang. 2019. "Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution and Heat Losses of a Molten Salt Heat Storage Tank" Energies 12, no. 10: 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101943
APA StyleZhang, X., Wu, Y., Ma, C., Meng, Q., Hu, X., & Yang, C. (2019). Experimental Study on Temperature Distribution and Heat Losses of a Molten Salt Heat Storage Tank. Energies, 12(10), 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101943





