Experimental Investigation of Diesel Engine Performance, Combustion and Emissions Using a Novel Series of Dioctyl Phthalate (DOP) Biofuels Derived from Microalgae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
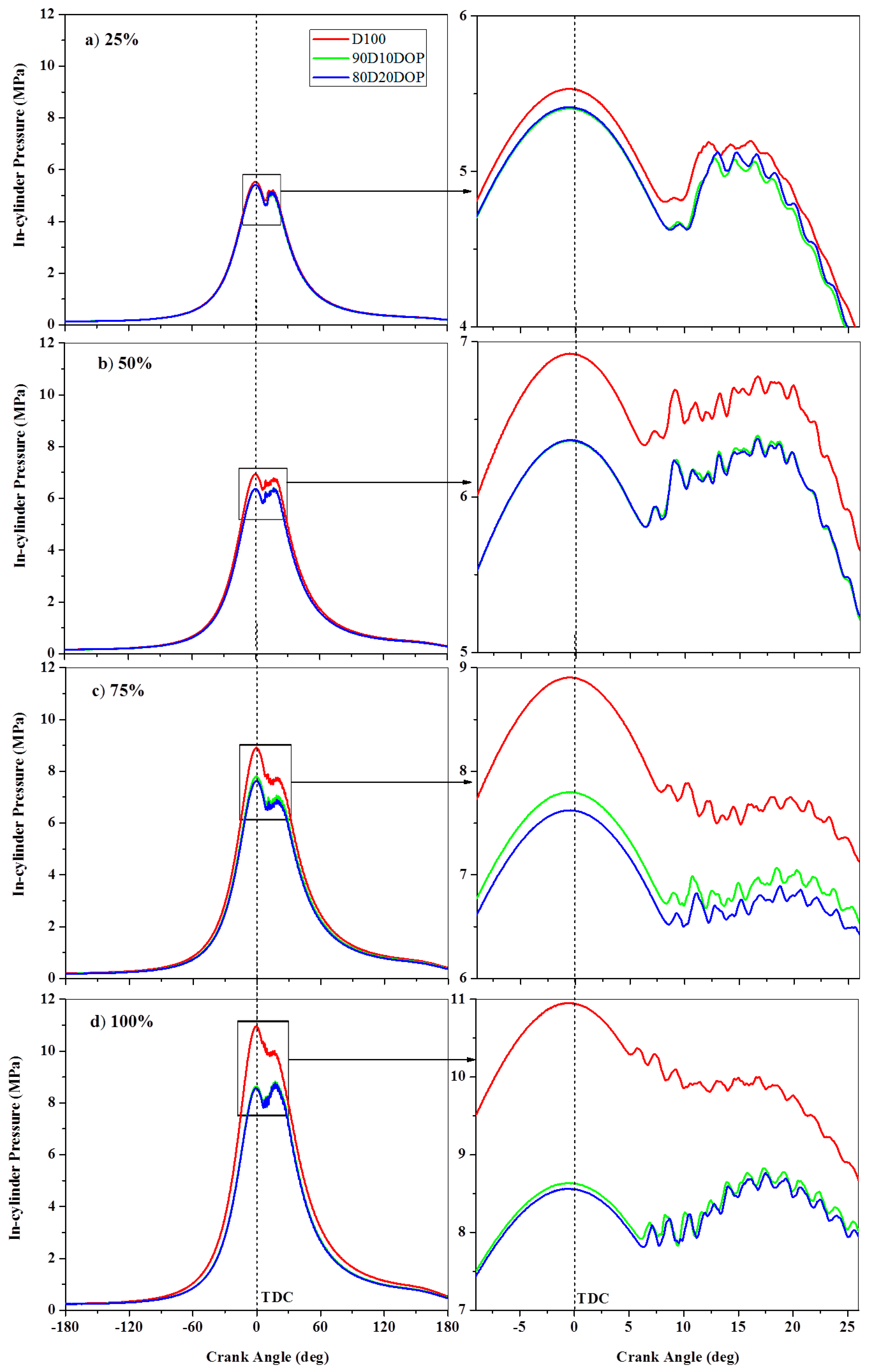
3.1. Engine Performance and Combustion Parameters
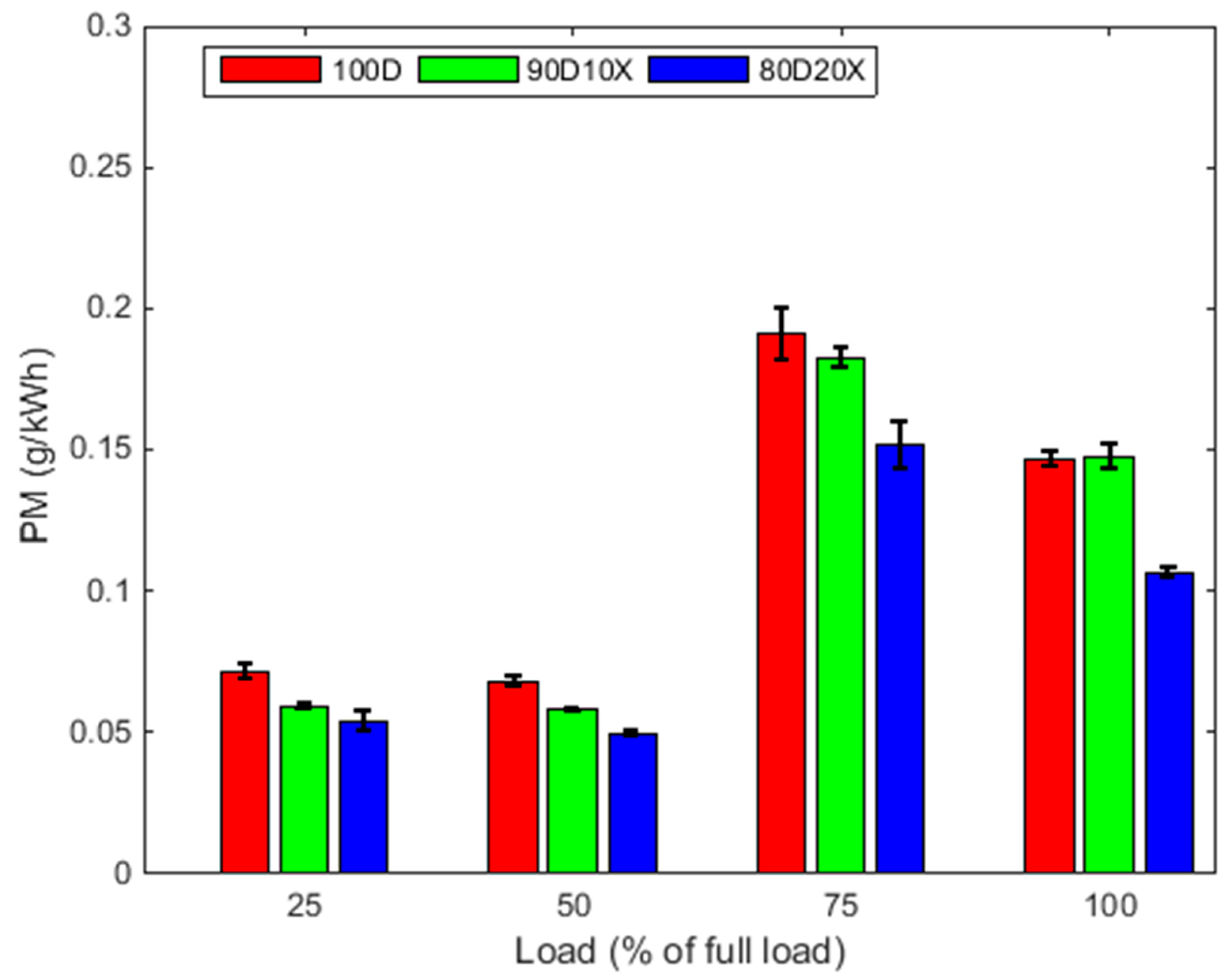
3.2. Exhaust Emissions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| 100D | 100% Diesel |
| 90D10DOP | 90D% Diesel + 10%DOP |
| 80D20DOP | 80D% Diesel + 20%DOP |
| BERF | Biofuel Engine Research Facility |
| BMEP | Brake Mean Effective Pressure |
| BP | Brake Power |
| BTE | Brake Thermal Efficiency |
| CA | Crank Angle |
| CAI | California Analytical Instruments |
| CN | Cetane Number |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide |
| DI | Direct Injection |
| DOP | Dioctyl Phthalate |
| EGR | Exhaust Gas Recirculation |
| kJ | Kilojoule |
| kW | Kilowatt |
| kWh | Kilo Watt Hour |
| IMEP | Indicated Mean Effective Pressure |
| HHV | Higher Heating Value |
| LHV | Lower Heating Value |
| MPa | Megapascal |
| MJ | Megajoule |
| NDIR | Non-Dispersive Infrared |
| NOx | Nitrogen Oxides |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| PVC | Polyvinyl Chloride |
| PN | Particle Number |
References
- Huo, S.; Dong, R.; Wang, Z.; Pang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Zhu, S.; Chen, L. Available Resources for Algal Biofuel Development in China. Energies 2011, 4, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Kosinkova, J.; Brown, R.; Ristovski, Z.; Hankamer, B.; Stephens, E.; Rainey, T. Experimental Investigations of Physical and Chemical Properties for Microalgae HTL Bio-Crude Using a Large Batch Reactor. Energies 2017, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIA. Transportation Sector Energy Consumption. 2019; Chapter 8. Available online: www.eia.gov/outlooks/ieo/pdf/transportation.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2019).
- Kalghatgi, G.T. The outlook for fuels for internal combustion engines. Int. J. Engine Res. 2014, 15, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodisco, T.A.; Rahman, S.A.; Hossain, F.M.; Brown, R.J. On-road NOx emissions of a modern commercial light-duty diesel vehicle using a blend of tyre oil and diesel. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamrozik, A.; Tutak, W.; Gnatowska, R.; Nowak, Ł. Comparative Analysis of the Combustion Stability of Diesel-Methanol and Diesel-Ethanol in a Dual Fuel Engine. Energies 2019, 12, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkmann, H.; Brannigan, C. Transport. and Climate Change: Module 5e; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ): Eschborn, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, D.T.; Samanic, C.M.; Lubin, J.H.; Blair, A.E.; Stewart, P.A.; Vermeulen, R.; Coble, J.B.; Rothman, N.; Schleiff, P.L.; Travis, W.D.; et al. The diesel exhaust in miners study: A nested case-control study of lung cancer and diesel exhaust. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.C.; Yoon, S.K.; Choi, N.J. Using Canola Oil Biodiesel as an Alternative Fuel in Diesel Engines: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Armas, O.; Rodríguez-Fernández, J. Effect of biodiesel fuels on diesel engine emissions. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 198–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Grift, T.E.; Hansen, A.C. Effect of biodiesel on engine performances and emissions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golimowski, W.; Krzaczek, P.; Marcinkowski, D.; Gracz, W.; Wałowski, G. Impact of Biogas and Waste Fats Methyl Esters on NO, NO2, CO, and PM Emission by Dual Fuel Diesel Engine. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, M.N.; Zare, A.; Hossain, F.M.; Ristovski, Z.D.; Brown, R.J. Reductions in diesel emissions including PM and PN emissions with diesel-biodiesel blends. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Pourkhesalian, A.M.; Jahirul, M.I.; Stevanovic, S.; Pham, P.X.; Wang, H.; Masri, A.R.; Brown, R.J.; Ristovski, Z.D. Particle emissions from biodiesels with different physical properties and chemical composition. Fuel 2014, 134, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Brown, R.J.; O’Hara, I.; Kent, M.; Heimann, K. Effect of temperature and moisture on high pressure lipid/oil extraction from microalgae. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, D.L.; Prins, W.; Ronsse, F.; Brilman, W. Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) of microalgae for biofuel production: State of the art review and future prospects. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 53, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.M.; Nabi, M.N.; Brown, R.J. Investigation of diesel engine performance and exhaust emissions of microalgae fuel components in a turbocharged diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 186, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.M.; Rainey, T.J.; Ristovski, Z.; Brown, R.J. Performance and exhaust emissions of diesel engines using microalgae FAME and the prospects for microalgae HTL biocrude. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 4269–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.M.; Nabi, M.N.; Rainey, T.J.; Bodisco, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Suara, K.; Rahman, S.M.; Van, T.C.; Ristovski, Z.; Brown, R.J. Investigation of microalgae HTL fuel effects on diesel engine performance and exhaust emissions using surrogate fuels. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 152, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamriska, M.; Morawska, L.; Thomas, S.; He, C. Diesel bus emissions measured in a tunnel study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6701–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Stevanovic, S.; Brown, R.J.; Ristovski, Z. Influence of Different Alternative Fuels on Particle Emission from a Turbocharged Common-Rail Diesel Engine. Procedia Eng. 2013, 56, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NREL. Biodiesel Handling and Use Guide. 2009. Fourth Edition. Available online: http://www.biodiesel.org/docs/using-hotline/nrel-handling-and-use.pdf?sfvrsn=4 (accessed on 4 May 2019).
- Saad, I.; Bari, S. Optimize vane length to improve in-cylinder air characteristic of CI engine using higher viscous fuel. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 393, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharin, M.S.; Abdullah, N.R.; Najafi, G.; Sharudin, H.; Yusaf, T. Effects of physicochemical properties of biodiesel fuel blends with alcohol on diesel engine performance and exhaust emissions: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, S.; Saad, I. Performance and emissions of a compression ignition (CI) engine run with biodiesel using guide vanes at varied vane angles. Fuel 2015, 143, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chybowski, L.; Laskowski, R.; Gawdzińska, K. An overview of systems supplying water into the combustion chamber of diesel engines to decrease the amount of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gas. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2015, 20, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekman, S.K.; Robbins, C. Review of the effects of biodiesel on NOx emissions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 96, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.; Williams, J.; Rogerson, J. Effect of the Molecular Structure of Individual Fatty Acid Alcohol Esters (Biodiesel) on the Formation of Nox and Particulate Matter in the Diesel Combustion Process. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2008, 1, 849–872. [Google Scholar]
- Nabi, M.N.; Zare, A.; Hossain, F.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Bodisco, T.A.; Ristovski, Z.D.; Brown, R.J. Influence of fuel-borne oxygen on European Stationary Cycle: Diesel engine performance and emissions with a special emphasis on particulate and NO emissions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 127, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Lee, C.-F.F. Particulate matter emission characteristics of diesel engines with biodiesel or biodiesel blending: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Stevanovic, S.; Islam, M.A.; Heimann, K.; Nabi, M.N.; Thomas, G.; Feng, B.; Brown, R.J.; Ristovski, Z.D. Particle emissions from microalgae biodiesel combustion and their relative oxidative potential. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, J.P.; Reavell, K.S.; Olfert, J.S.; Campbell, B.W.; Swift, S.J. Diesel soot mass calculation in real-time with a differential mobility spectrometer. J. Aerosol Sci. 2007, 38, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M. Monitoring Motor Vehicle PM Emissions: An Evaluation of Three Portable Low-Cost Aerosol Instruments. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, D.C.; Yoon, S.; Dwyer, H.A.; Collins, J.F.; Zhu, Y.; Huai, T. Measuring particulate matter emissions during parked active diesel particulate filter regeneration of heavy-duty diesel trucks. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 73, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Model | Cummins ISBe220 31 |
|---|---|
| Cylinders | 6 in-line |
| Capacity (dm3) | 5.9 |
| Bore × Stroke (mm) | 102 × 120 |
| Maximum power (kW/rpm) | 162/2500 |
| Maximum torque (Nm/rpm) | 820/1500 |
| Compression ratio | 17.3 |
| Aspiration | Turbocharged and after cooled |
| Fuel Injection | Common rail |
| Emissions certification | Euro III |
| Properties | Methods | Diesel | DOP | 90D10DOP | 80D20DOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Density, at 20 °C, kg/m3 | ASTM D4052 | 840 | 960 | 850 | 860 |
| 1 Kinematic Viscosity, m2/s at 40 °C | ASTM D445 | 2.66 | 27.40 | 5.13 | 7.60 |
| 1 HHV, MJ/kg | ASTM D240 | 45.64 | 35.70 | 44.65 | 43.65 |
| 2 LHV, MJ/kg | - | 43.95 | 33.71 | 41.92 | 41.01 |
| 3,4 Flash point (Close cup), °C | ASTM D93 | 67.5 | 207 | 81.45 | 95.4 |
| 1 Surface Tension, mN/m | - | 26.77 | 30.55 | 27.15 | 27.53 |
| 2 Carbon, (m/m %) | - | 91.66 | 73.79 | 89.87 | 88.09 |
| 2 Hydrogen, (m/m %) | - | 8.34 | 9.81 | 8.49 | 8.63 |
| 2 Oxygen, (m/m %) | - | 0 | 16.4 | 1.64 | 3.28 |
| 4,5 Cetane index | ASTM D4737A | 51.74 | 48 | 51.37 | 50.99 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hossain, F.M.; Nabi, M.N.; Rahman, M.M.; Bari, S.; Van, T.C.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Rainey, T.J.; Bodisco, T.A.; Suara, K.; Ristovski, Z.; et al. Experimental Investigation of Diesel Engine Performance, Combustion and Emissions Using a Novel Series of Dioctyl Phthalate (DOP) Biofuels Derived from Microalgae. Energies 2019, 12, 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101964
Hossain FM, Nabi MN, Rahman MM, Bari S, Van TC, Rahman SMA, Rainey TJ, Bodisco TA, Suara K, Ristovski Z, et al. Experimental Investigation of Diesel Engine Performance, Combustion and Emissions Using a Novel Series of Dioctyl Phthalate (DOP) Biofuels Derived from Microalgae. Energies. 2019; 12(10):1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101964
Chicago/Turabian StyleHossain, Farhad M., Md. Nurun Nabi, Md. Mostafizur Rahman, Saiful Bari, Thuy Chu Van, S. M. Ashrafur Rahman, Thomas J. Rainey, Timothy A. Bodisco, Kabir Suara, Zoran Ristovski, and et al. 2019. "Experimental Investigation of Diesel Engine Performance, Combustion and Emissions Using a Novel Series of Dioctyl Phthalate (DOP) Biofuels Derived from Microalgae" Energies 12, no. 10: 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101964
APA StyleHossain, F. M., Nabi, M. N., Rahman, M. M., Bari, S., Van, T. C., Rahman, S. M. A., Rainey, T. J., Bodisco, T. A., Suara, K., Ristovski, Z., & Brown, R. J. (2019). Experimental Investigation of Diesel Engine Performance, Combustion and Emissions Using a Novel Series of Dioctyl Phthalate (DOP) Biofuels Derived from Microalgae. Energies, 12(10), 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101964








