Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Construction Machinery: Evolution, Classification, Comparison and Future Trends
Abstract
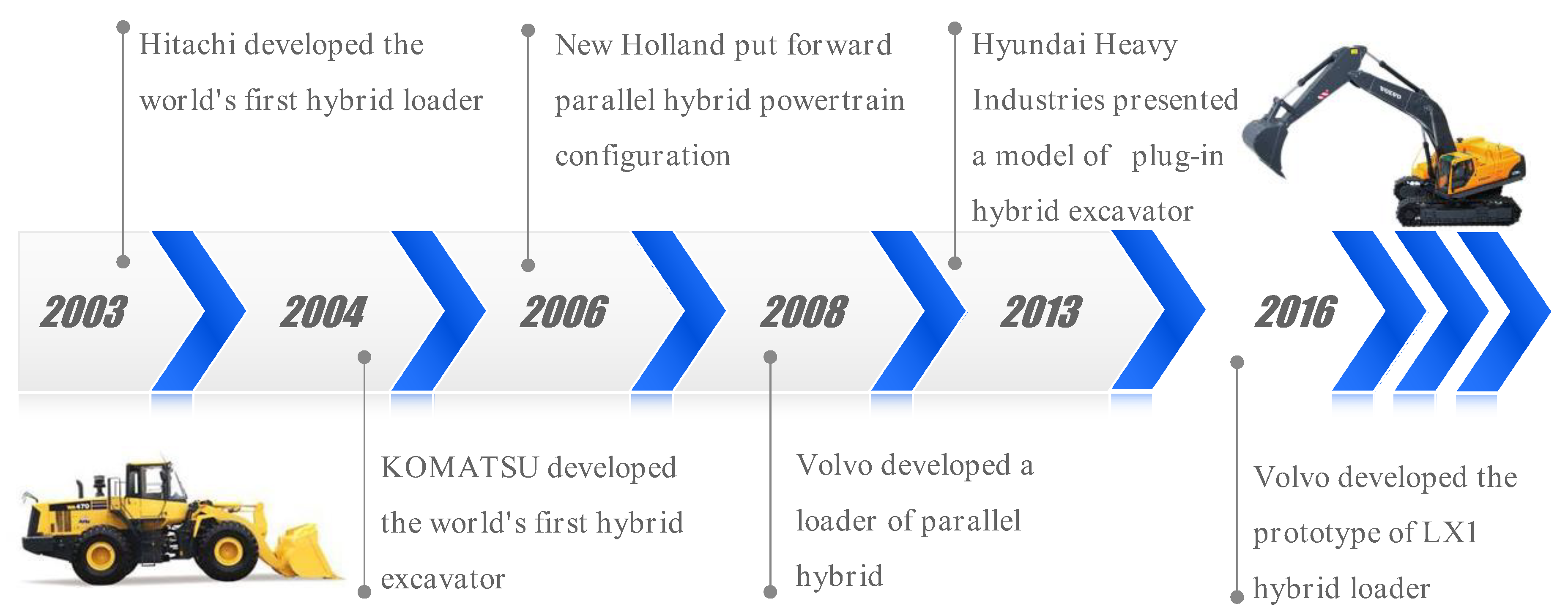
1. Introduction
2. Configuration of HCM
2.1. Diesel-Electric Hybrid
2.2. Diesel-Hydraulic Hybrid
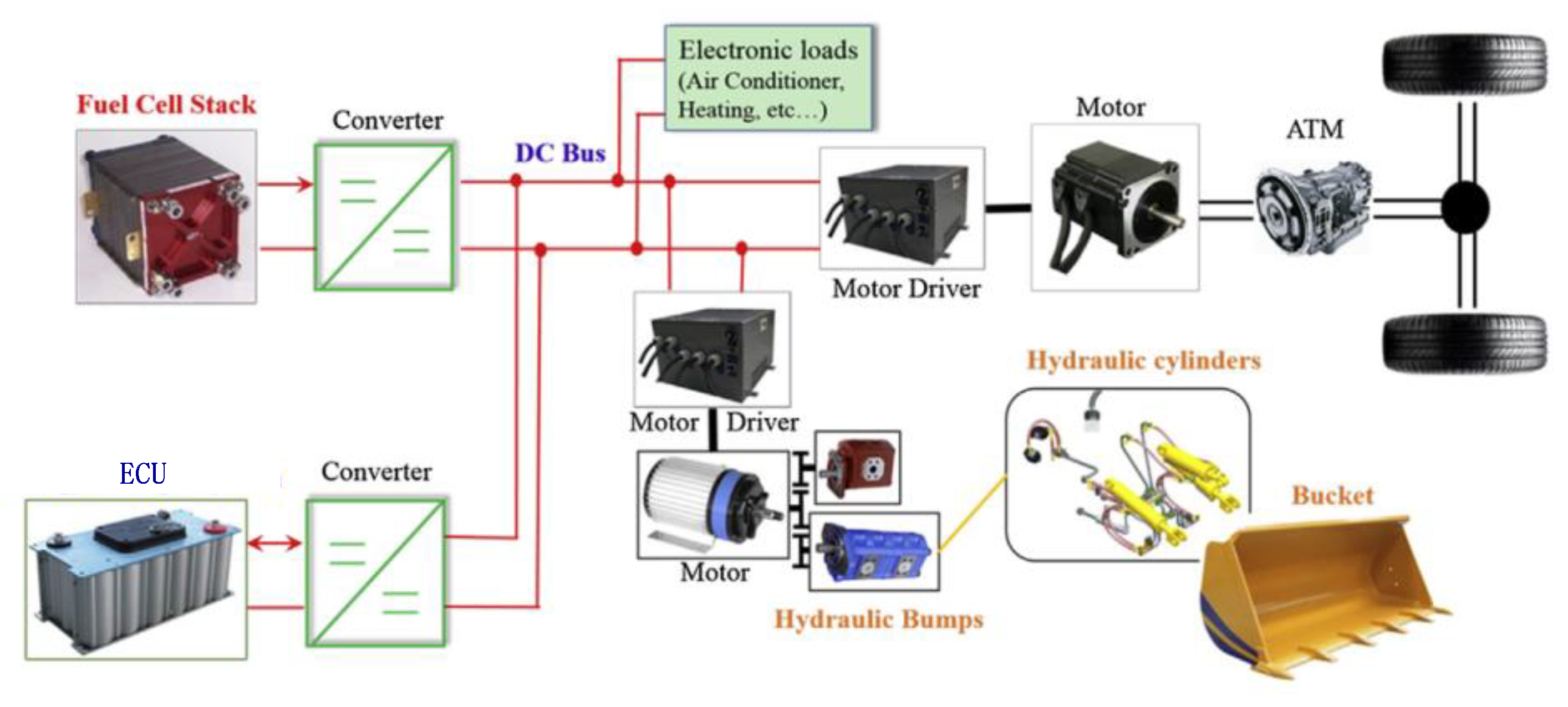
2.3. Fuel Cell Hybrid
2.4. Comparative Analysis
3. Energy Management Strategy of HCM
3.1. Rule-based strategies
3.1.1. Deterministic rule strategies
3.1.2. Fuzzy rule strategies
3.2. Optimization Based Strategies
3.2.1. Global Optimization strategies
3.2.2. Real-time optimization strategies
4. Discussion and Analysis
4.1. Theoretical Level
4.2. Manufacturer and Market Level
- >Increasing the energy output performance (specific energy and specific density) of ESS;
- >Increasing energy recovery rate.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Abbreviations | |
| HCM | hybrid construction machinery |
| ICE | internal-combustion engine |
| HEV | hybrid electric vehicle |
| DHH | diesel-hydraulic hybrid |
| DEH | diesel-electric hybrid |
| FCH | fuel cell hybrid |
| ESS | energy storage system |
| EG | electric generator |
| EM | electric motor |
| M/G | motor/generator |
| FC | fuel cell |
| HP | hydraulic pump |
| HM | hydraulic motor |
| INV | inverter |
| CON | converter |
| UC | ultracapacitor |
| ACC | accumulator |
| BAT | battery |
| HYDS | hydraulic system |
| TCS | torque coupling structure |
| FCS | flow coupling structure |
| HP | high-pressure |
| LP | low-pressure |
| MP | medium pressure |
| SOC | state of charge |
| PEMFC | proton exchange membrane fuel cell |
| ISG | integrated starter and generator |
| RBSs | rule-based strategies |
| OBSs | optimization-based strategies |
| DRSs | deterministic rule strategies |
| FRSs | fuzzy rule strategies |
| TSs | thermostatic strategies |
| PFSs | power follower strategies |
| BCSs | baseline control strategies |
| CSs | combinatorial strategies |
| OBSs | optimization based strategies |
| GOSs | global optimization strategies |
| DP | dynamic programming |
| GA | genetic algorithm |
| PSO | particle swarm optimization |
| SDP | stochastic dynamic programming |
| EMD | empirical mode decomposition |
| RTOSs | real-time optimization strategies |
| ECMS | equivalent consumption minimization strategy |
| MPC | model predictive control |
| RL | reinforcement learning |
| TPM | transition probability matrix |
| PMP | pontryagin’s minimum principle |
| HDLM | heavy duty lifting machinery |
| CF | configuration |
| ER | emission reduction |
| CR | consumption reduction |
| OW | operating weight |
| IP | ICE power |
| Variables and parameters | |
| SOC value of ESS at time | |
| / | lower and upper bounds of SOC |
| Power provided by ESS | |
| required power | |
| total instantaneous equivalent fuel consumption of the system | |
| ICE fuel consumption at time t | |
| equivalent fuel consumption of ESS at time | |
| equivalent factor | |
| ICE fuel consumption corresponding to maximum power at time | |
| / | lower and upper bounds of |
| discounted reward | |
| discount factor | |
| strategy function | |
References
- Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y. A Comprehensive overview of hybrid construction machinery. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Wang, Q.; Hu, B.; Gong, W. Development of hybrid powered hydraulic construction machinery. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Chen, Q.; Ren, H.; Huang, W.; Chen, Q.; Fu, S. Review of boom potential energy regeneration technology for hydraulic construction machinery. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jiang, Y. Review of hybrid electric systems for construction machinery. Autom. Constr. 2018, 92, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filla, R. Hybrid Power Systems for Construction Machinery: Aspects of System Design and Operability of Wheel Loaders. In Proceedings of the ASME 2009 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 13–19 November 2009; pp. 611–620. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, B. Using Optimal Control in Concept Evaluation and System Optimization of Diesel-Electric Hybrid Construction Machines. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles & International Transportation Electrification Conference, Toulouse, France, 2–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, L.A.; de Almeida D’Agosto, M.; Fernandes, V.A.; de Oliveira, C.M. A financial and environmental evaluation for the introduction of diesel-hydraulic hybrid-drive system in urban waste collection. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, C.; Qiu, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, D. Braking energy regeneration control of a fuel cell hybrid electric bus. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 76, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.S.; Tan, C.; Yatim, A.H.M. Fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles: A review on power conditioning units and topologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 268–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.T.; Wong, Y. Overview of power management in hybrid electric vehicles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 1953–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, T.; Froberg, A.; Aslund, J. Predictive control of a diesel electric wheel loader powertrain. Control Eng. Pract. 2015, 41, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Masami, O.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Hu, B.; Gong, W. Research on parallel hybrid hydraulic excavator with energy regeneration system. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Fluid Power Trasmission and Control, Hangzhou, China, 7–10 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, L.T.; Louey, R. Development of ultra-battery for hybrid-electric vehicle applications. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjo, T.; Imanishi, E.; Kagoshima, M. Power simulation on the actual operation in hybrid excavator. Trans. -Soc. Automot. Eng. Jpn. 2004, 35, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Guan, C.; Pan, S.; Zhang, M.; Lin, X. Performance analysis of hydraulic excavator powertrain hybridization. Autom. Constr. 2009, 18, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Guan, C. Optimal Control for a Parallel Hybrid Hydraulic Excavator Using Particle Swarm Optimization. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 831564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Pan, S.-X.; Wang, D.-Y. Dynamic simulation and optimal control strategy for a parallel hybrid hydraulic excavator. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 2008, 9, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.C.; Bueno, P.G.; Sanchez-Sutil, F. Enhanced utility-scale photovoltaic units with frequency support functions and dynamic grid support for transmission systems. IET Renew. Power Gen. 2017, 11, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.C.; Sanchez-Sutil, F.; Vidal, P.G.; Rus-Casas, C. Primary frequency control and dynamic grid support for vehicle-to-grid in transmission systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 100, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, H. A comparative study on the applicability of ultracapacitor models for electric vehicles under different temperatures. Appl. Energy 2017, 196, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, W.B.; Sun, Y.B. The preparation and application of mesoporous materials for energy storage. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 83, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Khajepour, A.; He, H.; Cao, D. A novel energy management for hybrid off-road vehicles without future driving cycles as a priori. Energy 2017, 133, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yoo, S.; Cho, S.; Yi, K. Hybrid control algorithm for fuel consumption of a compound hybrid excavator. Autom. Constr. 2016, 68, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, B.N.; Truong, D.Q.; Young, L.S.; Young, L.S.; Kwan, A.K.; Thanh, T.Q. Study on Energy Regeneration System for Hybrid Hydraulic Excavator. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Fluid Power and Mechatronics, Harbin, China, 5–7 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.I.; Dinh Quang, T.; Ahn, K.K. A generation step for an electric excavator with a control strategy and verifications of energy consumption. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hredzak, B.; Agelidis, V.G.; Jang, M. A Model Predictive Control System for a Hybrid Battery-Ultracapacitor Power Source. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Energy Efficiency Comparison between Hydraulic Hybrid and Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Energies 2015, 8, 4697–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, D. The gravitational potential energy regeneration system with closed-circuit of boom of hydraulic excavator. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 82, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Guan, C.; Li, P.Y.; Wang, F. Optimal Design of a Compound Hybrid System consisting of Torque Coupling and Energy Regeneration for Hydraulic Hybrid Excavator. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Susan, Korea, 7–11 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Guan, C.; Lai, X. Research on the design and control strategy for a flow-coupling-based hydraulic hybrid excavator. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2014, 228, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippalgaonkar, R.; Ivantysynova, M. A Series-Parallel Hydraulic Hybrid Mini-Excavator with Displacement Controlled Actuators. In Proceedings of the 13th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power, Linköping, Sweden, 3–5 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, J.; Hippalgaonkar, R.; Ivantysynova, M. Optimal control for the series-parallel deplacemant controlled hydraulic hybrid excavator. In Proceedings of the ASME Dynamic Systems and Control Conference and Bath/Asme Symposium on Fluid Power and Motion Control, Arlington, VA, USA, 31 October–2 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Leifeld, R.; Vukovic, M.; Murrenhoff, H. Hydraulic Hybrid Architecture for Excavators. ATZoffhighway Worldw. 2016, 9, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.L.; Wang, Q.F.; Hu, B.Z.; Gong, W. Research on the energy regeneration systems for hybrid hydraulic excavators. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, L.; Jing, J. Hydraulic/electric synergy system (HESS) design for heavy hybrid vehicles. Energy 2010, 35, 5328–5335. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, W.; Guo, Q.; Gao, L.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X. Comparative life cycle assessment of manufactured and remanufactured loading machines in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 131, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Eom, T.; Park, Y.; Won, C. Design and Control of Fuel Cell-Battery Hybrid System for Forklift. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Busan, Korea, 1–4 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Liu, H.; Zhao, D.; Wang, L. Design and analysis of a fuel cell supercapacitor hybrid construction vehicle. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 12307–12319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Jeong, J.; Cha, S.; Zheng, C. Optimal Component Sizing of Fuel Cell-Battery Excavator Based on Workload. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2018, 5, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Chang, Q.; Tang, T. A quick evaluating method for automotive fuel cell lifetime. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 3829–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Mortensen, H.H.; Jensen, J.V.; Andersen, M.A.E. Fuel Cell and Battery Powered Forklifts. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Beijing, China, 15–18 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, G.; Hong, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, K. Reduction Design of Vibration and Noise in IPMSM Type Integrated Starter and Generator for HEV. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2454–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Lin, C.C.; Filipi, Z.; Peng, H.; Assanis, D. Optimal power management for a hydraulic hybrid delivery truck. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2004, 42, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, N.; Kheir, N.A.; Salman, M. Rule-based energy management strategy for a series hybrid vehicle. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 4–6 June 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, X.; Guan, C.; Lin, X. Fuzzy Logical Control Algorithm Based on Engine on/off State Switch for Hybrid Hydraulic Excavator. Advvanced Materials Research 2011, 228–229, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cao, S.; Li, J.; Gao, Y. Present Study Situation and Develping Trend of Control Strategies of Hybrid Electric Vehicle. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2006, 42, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Filipi, Z. Series Hydraulic Hybrid Propulsion for a Light Truck—Optimizing the Thermostatic Power Management. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Engines for Automobiles, Capri/Naples, Italy, 14–19 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y. Comparison Research of Different Control Strategies on Parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicle. J. Syst. Simul. 2006, 18, 401–404. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Du, M.; Chen, H. Energy management strategy development of a forklift with electric lifting device. Energy 2017, 128, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, S. Fuzzy PID Control for Boom Energy Recovery on Hybrid Hydraulic Excavator. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Automation Engineering, Beijing, China, 10–12 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Lin, X.; Qin, D.; Deng, T. Power-balancing instantaneous optimization energy management for a novel series-parallel hybrid electric bus. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2012, 25, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Peng, H.; Grizzle, J.; Kang, J. Power management strategy for a parallel hybrid electric truck. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2003, 11, 839–849. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, X.; Guan, C. A Parameter Matching Method of the Parallel Hydraulic Hybrid Excavator Optimized with Genetic Algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, J.; Yi, K. Development of supervisory control strategy for optimized fuel consumption of the compound hybrid excavator. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2012, 226, 1652–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, P.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H. Prediction-based stochastic dynamic programming control for excavator. Autom. Constr. 2017, 83, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalin Stefan, T.; Vandenplas, S.; Depraetere, B.; Shariatmadar, K.; Vyncke, T.; Dutlou, J.; Nowe, A. An ECMS-based powertrain control of a parallel hybrid electric forklift. In Proceedings of the 2017 21st International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing, Sinaia, Romania, 19–21 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, Q. Real-time energy management controller design for a hybrid excavator using reinforcement learning. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2017, 18, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, H.; Ding, D. Predictive energy management of fuel cell supercapacitor hybrid construction equipment. Energy 2018, 149, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S.; Monika, I. Investigation and energetic analysis of a novel hydraulic hybrid architecture for on-road vehicles. In Proceedings of the 13th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power, Linköping, Sweden, 3–5 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, I.; Murtagh, M.; Kee, R.; McCulloug, G.; Douglas, R. Sustainable non-automotive vehicles: The simulation challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H. Introduction of PC200-8 Hybrid Hydraulic Excavators. Available online: https://www.research-gate.net/publication/285714112_Introduction_of_PC200-8_hybrid_hydraulic_excavators (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- HB205LC-1M0 Hybrid Excavators Brochure. Available online: https://www.komatsu.com.au/getattach-ment/1ee83813-5784-4971-83aa-906b7256df90/HB215LC-1M0 (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- HB215LC-1 Hybrid Excavator Brochure. Available online: https://www.forconstructionpros.com/equip-ment/earthmoving/product/10243535/komatsu-america-corp-hb215lc1-hybrid-excavator (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Komatsu, Generation 2 Wheel Loader Product Overview. Available online: http://info.cm.hc360.com/2015/12/081716607440.shtml (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Hybrid Hydraulic Excavator. Available online: https://www.jase-w.eccj.or.jp/technologies/pdf/construc-tion_transport/C-04.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- New Generation ZH210 Hybrid Excavator. Available online: https://www.hellopro.fr/documentation/pdf_prod/2/4/5/202354action=integrer_produits_354f6ef2fbc40b6fb1d53387631802e8_5785542.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Ishida, K.; Higurashi, M. Hybrid Wheel Loaders Incorporating Power Electronics. Hitachi Rev. 2015, 64, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Kagoshima, M. Development of an 8 Tonne Class Hybrid Hydraulic Excavator SK80H. Kobel Technol. Rev. 2013, 31, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- SK200H/SK210H Hybrid Excavator. Available online: https://www.kobelco-kenki.co.jp/pickup/SK200_9/SK200_9.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- SH200HB/SH220HBL-7 Hybrid Excavator. Available online: https://www.sumitomokenki.co.jp/special/pdf/metal_recycle_sh200hb.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Doosan Intgrated Report. Available online: http://www.doosaninfracore.com/en/media/publication/ (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- K-Series Loaders 644K/724K. Available online: https://www.deere.com/assets/publications/index.html?id=d861a139#1 (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- K-Series 944K Wheel Loader—A Hybrid of Epic Innovations. Available online: http://docplayer.net/77232251-K-series-944k-wheel-loader-a-hybrid-of-epic-innovations.html (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Sokolsky, S. Joint Military Evaluation of the Benefits of an Electric-Drive Bulldozer. Available online: https://westcoastcollaborative.org/files/meetings/2012-12-12/sokolskyHybridBulldozerWCCwebcast-12-2012.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Specalog for 336E H Hydraulic Excavator. Available online: http://s7d2.scene7.com/is/content/Caterpillar/C811713 (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Large Specalog for 336D2 XE/D2 L XE Hydraulic Excavator. Available online: https://www.cehome.com/news/20150227/202585.shtml (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- RX 70 Technical Data—Diesel and LPG Forklift Trucks. Available online: http://pdf.directindustry.com/pdf/still/rx-70-30-hybrid/14182-529257.html (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- 862H Wheel Loader. Available online: https://www.liugong.com/en/Product/Machines/Wheel-Loaders/862H (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- SWE 385ES Product Manual. Available online: http://www.sunward.com.cn/product/product-detail-7604.htm (accessed on 17 March 2019).










| Characteristic | Construction Machinery | Automobile |
| Travel speed | Low | High |
| Periodicity | √ | × |
| Load | Changes sharply and frequently | Changes smoothly |
| Weight | There may be huge differences between products or models | The difference is relatively small. |
| System | Mechanical system; Hydraulic system; Electrical system; Control system. | Mechanical system; Electrical system; Control system. |
| Structure | Complex (Existence of different actuators) | Simple (No actuator) |
| Start-stop | Very frequent (Including travel device and actuator) | Not so frequent |
| Fuel consumption and emission | High | Low |
| - | DEH | DHH | FCH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Series hybrid |  |  |  |
| Parallel hybrid |  |  | _ |
| Series-parallel hybrid |  |  | _ |
 mechanical connection;
mechanical connection;  electrical connection;
electrical connection;  hydraulic connection.
hydraulic connection.| TSs | PFSs |
|---|---|
| (1) If , ICE start; (2) If , ICE stop; (3), ICE remains in its current state; (4) ICE maintains at its most efficient operating point. | (1) and , ICE stop; (2) and , ICE start; (3) , ICE start; (4) ICE should ensure while following the power requirement, and during which ICE maintains at its most efficient operation point. |
| Manufacturer | Product Mode | Year | Type | Cf | ER | CR | OW | IP | ESS | Remark | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KOMATSU | PC200-8 hybrid | 2004 | Exc | DEH | 20% | 20 t | 104 kw | Capacitor | First Hybrid Excavator. Parallel system | [61] | |
| HB205-1 | 2011 | 40% | 22% | 20 t | 110 kw | UC | 6 working modes | [62] | |||
| HB215LC -1 hybrid | 2011 | 20% | 25% | 21 t | 110 kw | UC | Improved version of PC200-8 H | [63] | |||
| L-1150 | 2017 | - | 40% | 140 t | 899 kw | UC/BAT | Switch reluctance hybrid drive with KESS | [64] | |||
| HITACHI | ZH200 HYBRID | 2011 | Exc | DEH | 15% | 15% | 20 t | 113 kw | UC | - | [65] |
| ZH210LC-5 | 2014 | - | 31% | 21 t | 122 kw | UC | - | [66] | |||
| ZW220HYB | 2014 | Lod | 26% | 26% | 18 t | - | UC | Series system; CVT | [67] | ||
| KOBELCO | SK70H | 2006 | Exc | DEH | - | 40% | - | - | UC/BAT | Series system; Prototype | - |
| SK80H | 2010 | - | 40% | 8 t | 27 kw | NI-MH battery | [68] | ||||
| SK200H-9 | 2012 | - | 17% | 20 t | Capacitor | [69] | |||||
| SK210H | 2016 | - | 12% | 22 t | 124 kw | Lithium battery | |||||
| SUMITOMO | SH200HB-6 | 2013 | Exc | DEH | - | 15% | 20 t | 119 kw | UC | Swing: electic driven; Excavation and travel: Hydraulic driven. | [70] |
| MITSUBISHI | GRENDIA EX HYBRID | 2009 | Fkl | DEH | 33% | 6 t | - | BAT | Lithium battery; Prototype | - | |
| TOYOTA | 88-7 FD | 2015 | Fkl | DEH | 45% | 50% | 5 t | - | BAT | Prototype | - |
| DOOSAN | DH215-HYBRID | 2012 | Exc | DEH | 30% | 25% | 21 t | 110 kw | UC | - | [71] |
| JOHN DEERE | Deere 644K | 2012 | Lod | DEH | - | 25% | 18 t | 170 kw | N/A | No ESS strategy | [72] |
| Deere 944K | 2013 | - | 30% | 54 t | 400 kw | BAT | - | [73] | |||
| CAT | D7E | 2009 | Bdz | DEH | - | 25% | 27 t | 175 kw | N/A | Series system | [74] |
| CAT336E H | 2013 | Exc | DHH | - | 25% | 35 t | 220 kw | ACC | - | [75] | |
| CAT336D2-XE | 2014 | - | 25% | 35 t | 208 kw | ACC | Optimized ICE and emission system. | [76] | |||
| CASE | CX210B Hybrid | 2009 | Exc | DEH | - | 20% | 202 kw | UC | Prototype | - | |
| STILL | RX70 Hybrid | 2010 | Fkl | DEH | - | 20% | 6 t | 30 kw | UC | - | [77] |
| VOLVO | L220F HYBRID | 2008 | Lod | DEH | - | 10% | 22 t | 261 kw | BAT | Parallel system; Prototype | - |
| LX1 | 2016 | 35% | 35% | 8 t | - | Series system; Distribute driving; Prototype | - | ||||
| LIUGONG | CLG862-HYBRID | 2010 | Lod | DEH | - | 10.5% | 6 t | UC | Brake energy recovery rate: 75% | [78] | |
| CLG922 HYBRID | 2010 | - | 20% | 20 t | 112 kw | UC | Prototype | - | |||
| SUNWARD | SWE385ES | 2016 | Exc | DHH | - | 18% | 38 t | 227 kw | ACC | Potential energy recovery system | [79] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Du, S.; Ma, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, H. Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Construction Machinery: Evolution, Classification, Comparison and Future Trends. Energies 2019, 12, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12102024
Zhang W, Wang J, Du S, Ma H, Zhao W, Li H. Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Construction Machinery: Evolution, Classification, Comparison and Future Trends. Energies. 2019; 12(10):2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12102024
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wei, Jixin Wang, Shaofeng Du, Hongfeng Ma, Wenjun Zhao, and Haojie Li. 2019. "Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Construction Machinery: Evolution, Classification, Comparison and Future Trends" Energies 12, no. 10: 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12102024
APA StyleZhang, W., Wang, J., Du, S., Ma, H., Zhao, W., & Li, H. (2019). Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Construction Machinery: Evolution, Classification, Comparison and Future Trends. Energies, 12(10), 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12102024




