Study on the Mechanism of Ionic Stabilizers on Shale Gas Reservoir Mechanics in Northwestern Hunan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
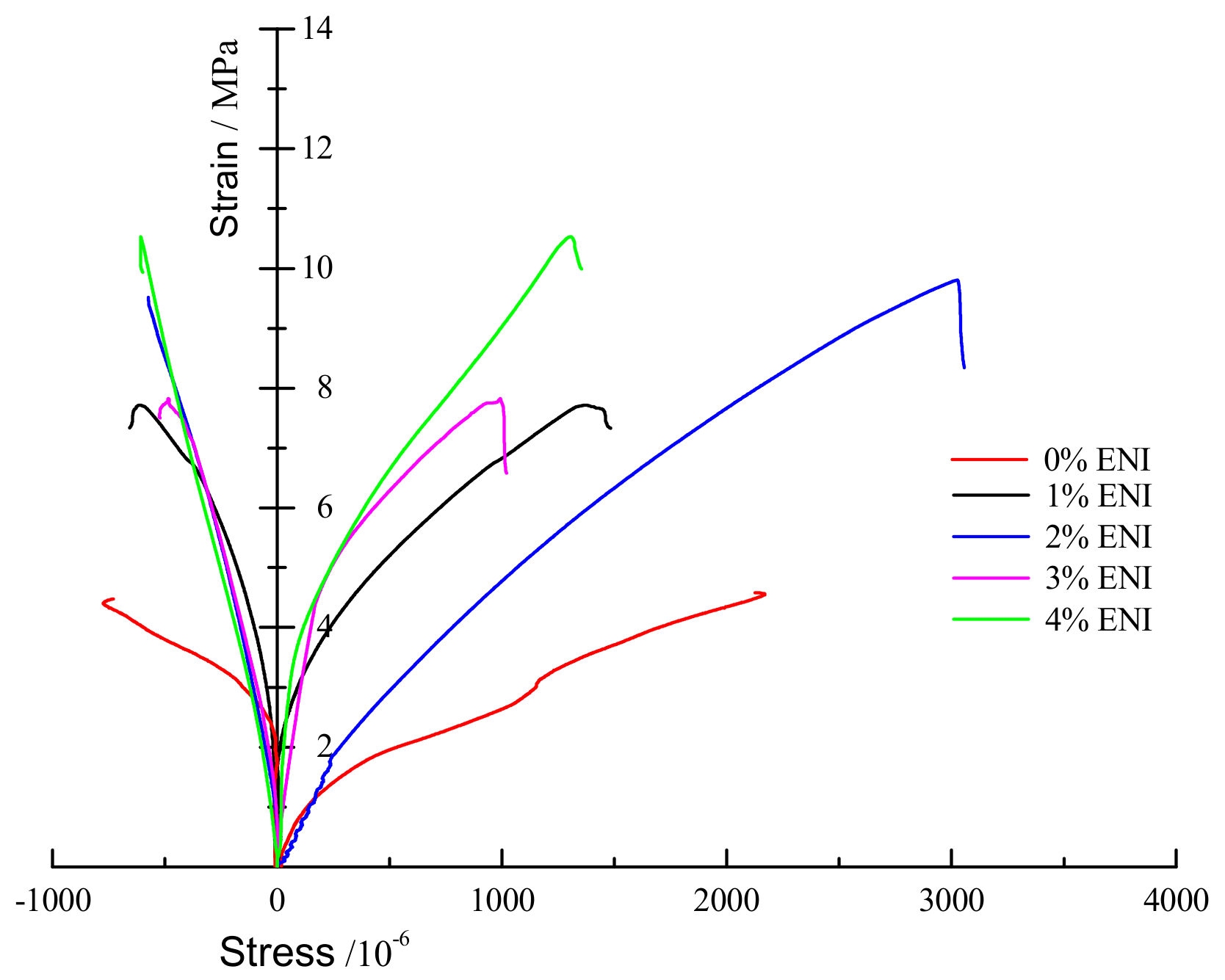
2.2. Uniaxial Compression Test
2.3. Microscopic Pore Test
2.3.1. Fractal Dimension
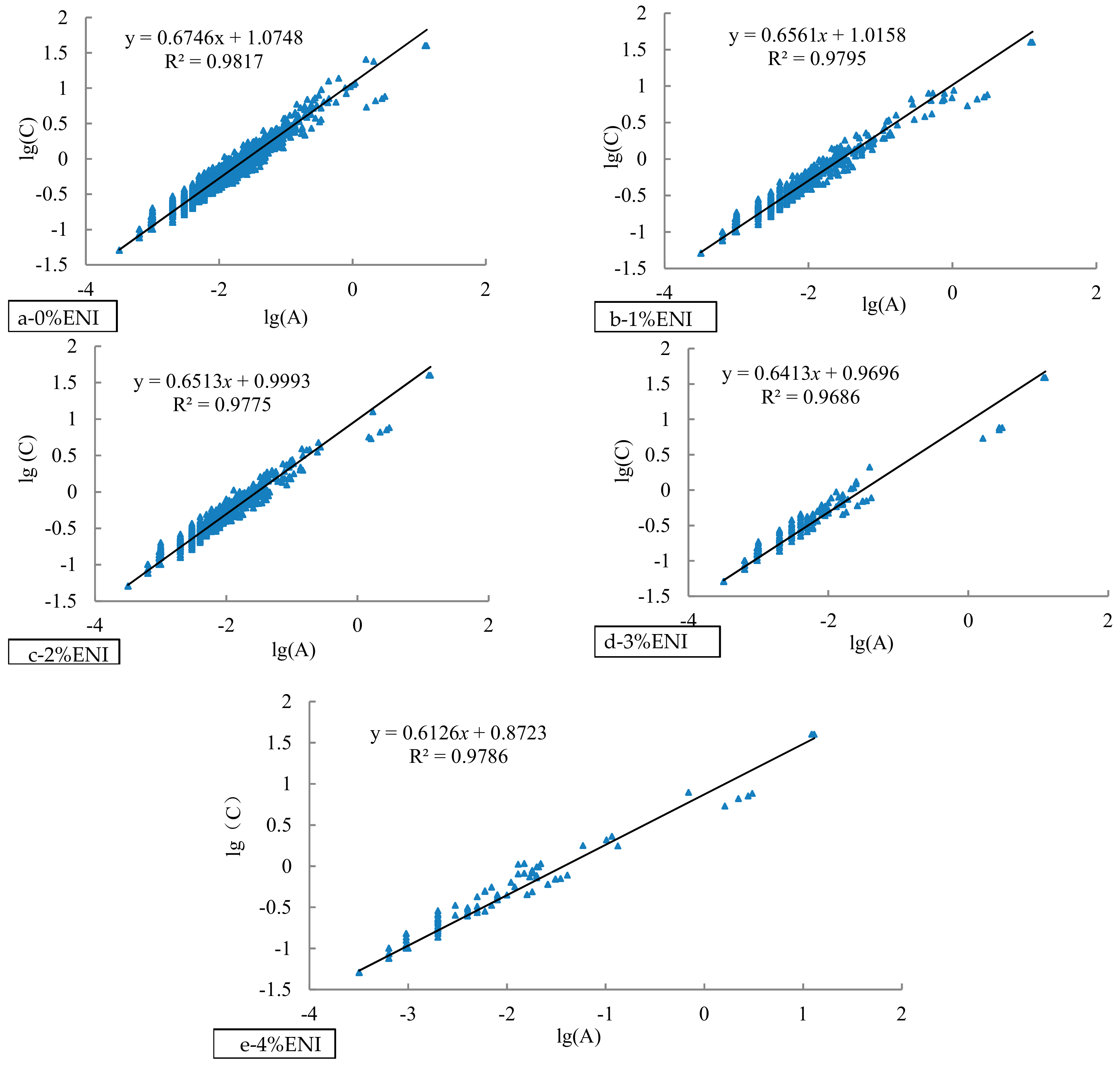
2.3.2. Ratio of Stability Coefficients
3. Results and Discussions
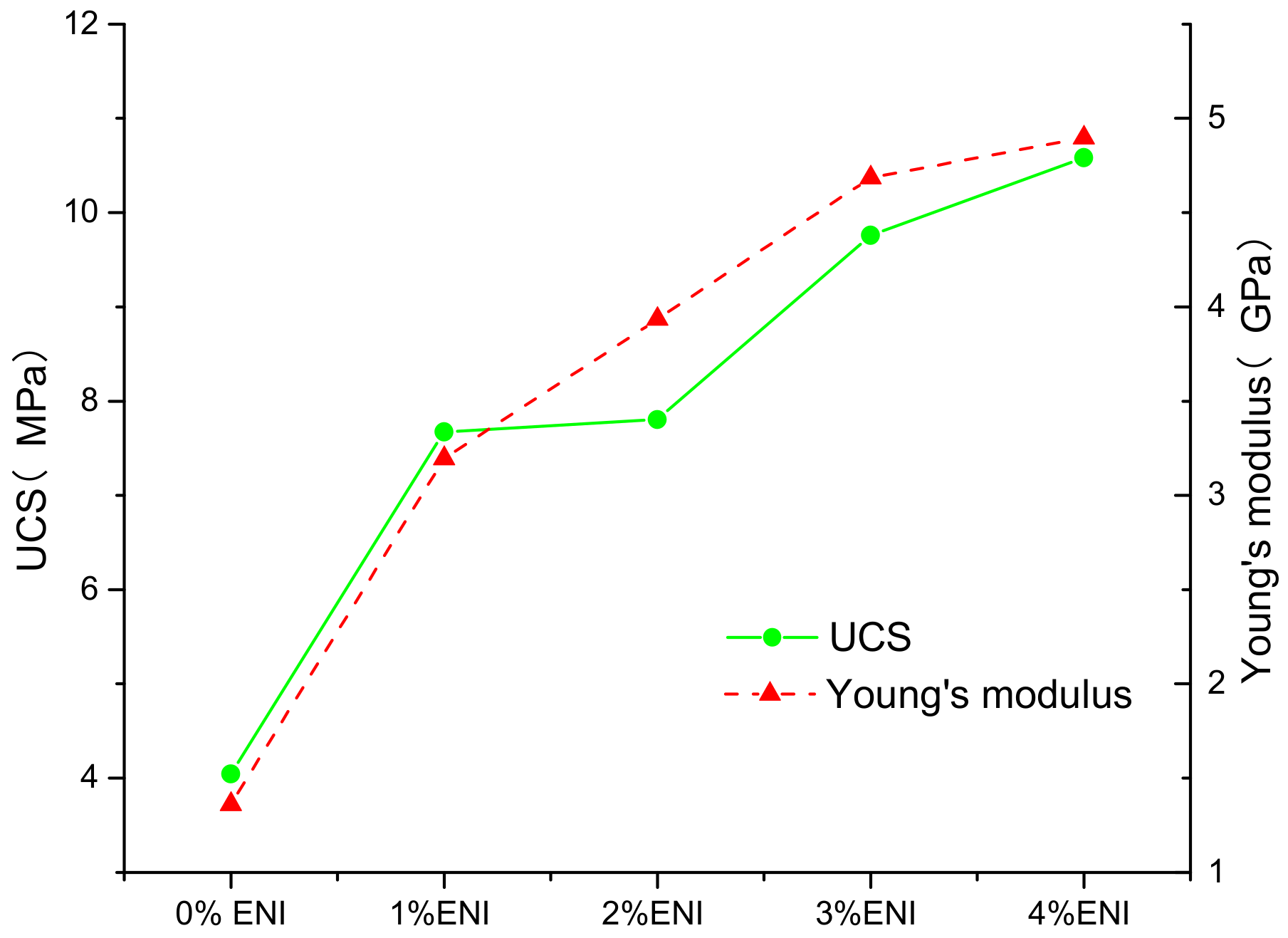
3.1. Uniaxial Compression Test
3.2. Pore Characteristics
3.2.1. Fractal Dimension
3.2.2. Ratio of Stability Coefficients
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tonglou, G. Key geological issues and main controls on accumulation and enrichment of Chinese shale gas. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 349–359. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Tang, S.; Pan, Z. Evaluation of the shale gas potential of the lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in northwest Hunan Province, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 79, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.-K.; Yang, L.; Shen, Y.-H.; Ren, K.; Meng, F.-B.; Ji, W.-M.; Wu, S. Experimental investigation of shale imbibition capacity and the factors influencing loss of hydraulic fracturing fluids. Pet. Sci. 2015, 12, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Wang, T.; Bao, T.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J. Effective exploitation potential of shale gas from lower cambrian niutitang formation, Northwestern Hunan, China. Energies 2018, 11, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cao, H.; Sun, P. Fracability evaluation of shale in Niutitang formation in northwestern Hunan. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 390–398. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Jain, R.; Chaudhary, P.; Mahto, V. Development of inhibitive water based drilling fluid system with synthesized graft copolymer for reactive Indian shale formation. In SPE Oil & Gas India Conf.Exhibit; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Dubai, UAE, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, W.; Liang, L.; Lei, M. Wellbore stability analysis for horizontal wells in shale formations. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.K.; Flori, R.E.; Al-Anssari, A.; Alsaba, M. Laboratory analysis to assess shale stability for the Zubair Formation, Southern Iraq. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 56, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Chenevert, M.E.; Sharma, M.M. Chemical–mechanical wellbore instability model for shales: Accounting for solute diffusion. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2003, 38, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahto, V.; Sharma, V.P. Rheological study of a water based oil well drilling fluid. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2004, 45, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Jiang, G.; Li, Y.; Geng, H.; Wang, J. A biomimetic drilling fluid for wellbore strengthening. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.C.; Teixeira, G.T.; Lachter, E.R.; Nascimento, R.S.V. Partially hydrophobized hyperbranched polyglycerols as non–ionic reactive shale inhibitors for water–based drilling fluids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-G.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Huang, W. Hydrophobic modified polymer based silica nanocomposite for improving shale stability in water–based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 153, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Koteeswaran, S.; Pashin, J.C.; Ramsey, J.D.; Clark, P.E. Quantitative characterization of polyacrylamide-shale interaction under various saline conditions. Pet. Sci. 2017, 14, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z. Novel micro and nano particle-based drilling fluids: Pioneering approach to overcome the borehole instability problem in shale formations. In SPE Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Dubai, UAE, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zulfiqar, S.; Sarwar, M.I.; Rasheed, N.; Yavuz, C.T. Influence of interlayer functionalization of kaolinite on property profile of copolymer nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 112, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryzas, Z.; Kelessidis, V.C. Nano-based drilling fluids: A review. Energies 2017, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, W.; Sun, D.; Zhang, D.; Cao, J. Synergistic stabilization of shale by a mixture of polyamidoamine dendrimers modified bentonite with various generations in water-based drilling fluid. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemizadeh, A.; Aghdam, S.K.-Y.; Shahbazi, K.; Zendehboudi, S. A triterpenoid saponin as an environmental friendly and biodegradable clay swelling inhibitor. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 247, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Mahto, V. Formulation of a water based drilling fluid system with synthesized graft copolymer for troublesome shale formations. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 38, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, L.E.; Rauch, A.F.; Liljestrand, H.M.; Harmon, J.S.; Shaw, K.S.; Albers, H. Mechanisms of soil stabilization with liquid ionic stabilizer. Transp. Res. Record 2001, 1757, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.L.; Boles, J.L.; Brannon, H.D.; Beall, B.B. Performance evaluation of ionic liquids as a clay stabilizer and shale inhibitor. In SPE International Symposium and Exhibition on Formation Damage Control; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Dubai, UAE, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Petry, T.M.; Das, B. Evaluation of chemical modifiers and stabilizers for chemically active soils—Clays. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2001, 1757, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanck, G.; Cuisinier, O.; Masrouri, F. Soil treatment with organic non–traditional additives for the improvement of earthworks. Acta Geotech. 2014, 9, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, N.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Siddiqua, S.; Horpibulsuk, S. Micro-structural analysis of strength development in low- and high swelling clays stabilized with magnesium chloride solution—A green soil stabilizer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 118, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, W.; Corely, T.; Yeh, T.-C.J.; Yuan, Y. The influences of freeze-thaw cycles on the shear strength of expansives treated with ionic soil stabilizer. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 2018, 55, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, G.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X. Application of ionic liquid and polymeric ionic liquid as shale hydration inhibitors. Energ. Fuels 2017, 31, 4308–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameni, A.; Pourafshary, P.; Ghanbarzadeh, M.; Ayatollahi, S. Effect of nanoparticles on clay swelling and migration. Egypt. J. Pet. 2015, 24, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, L.; Yu, P.; Chen, Z. Experimental study on the application of an ionic liquid as a shale inhibitor and inhibitive mechanism. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 150, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Tariq, A.; Elhajj, H.; Walter, S.; Ibrahim, A. Unconventional Clay Control Alternative to Inorganic Compounds that Can Prevent Swelling and Reduce Friction in Underbalanced Drilling. In SPE Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Dubai, UAE, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chenevert, M.E. Shale alteration by water adsorption. J. Pet. Tech. 1970, 22, 1–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandanand, S. Moisture adsorption rate and strength degradation of Illinois shales. In The 26th US Symposium on Rock Mechanics (USRMS); American Rock Mechanics Association: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Li, H.A. Pore structure characterization, permeability evaluation and enhanced gas recovery techniques of tight gas sandstones. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 28, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhao, B.; Cao, H.; Wang, J.; Mo, D.; Zhang, S. Lab study on the effect of cation exchange capacity on slurry performance in slurry shields. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Tian, M.; Cao, H.; Niu, L.; Zhang, S. Study on the mechanism of ENI action on preventing drilling fluid overflowing in HDD. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Tech. 2018, 77, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, T.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kyoya, T. Deformation and fracturing behaviour of discontinuous rock mass and damage mechanics theory. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Géoméch. 1988, 12, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Chan, A. Damage constitutive model of single flaw sandstone under freeze-thaw and load. Cold Reg. Sci. Tech. 2019, 159, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Lee, K.-S.; Cho, W.-J.; Choi, H.-J.; Cho, G.-C. A comparative evaluation of stress–strain and acoustic emission methods for quantitative damage assessments of brittle rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Were, P. Differences in the acoustic emission characteristics of rock salt compared with granite and marble during the damage evolution process. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6987–6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.B.; Wu, Q.H. The application of nonordinary, state-based peridynamic theory on the damage process of the rock-like materials. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; Zamanian, H.; Sahamieh, R.Z. The effect of density and porosity on the correlation between uniaxial compressive strength and P-wave velocity. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018, 51, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, M.A.; Moosavinasab, Z.; Rakhshandehroo, G. Effects of rock classes and porosity on the relation between uniaxial compressive strength and some rock properties for carbonate rocks. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2012, 45, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Rock | Mass Percentage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Mica | Feldspar | Smectite | Anatase | Amorphous Substance | |
| Carbonaceous shale | 16.57 | 13.64 | 10.82 | 25.58 | 5.26 | 28.13 |
| Pore Area/μm2 | Pore Perimeter/μm | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% ENI | 1% ENI | 2% ENI | 3% ENI | 4% ENI | 0% ENI | 1% ENI | 2% ENI | 3% ENI | 4% ENI | |
| Summary | 84.716 | 50.656 | 47.454 | 38.875 | 36.278 | 1955.551 | 589.734 | 656.714 | 204.437 | 166.272 |
| Average | 0.589 | 0.418 | 0.418 | 0.368 | 0.359 | 5.477 | 2.657 | 2.433 | 1.573 | 1.543 |
| Concentration | Fractal Dimension |
|---|---|
| 0% ENI | 1.35 |
| 1% ENI | 1.31 |
| 2% ENI | 1.30 |
| 3% ENI | 1.28 |
| 4% ENI | 1.23 |
| Number | K1 | K2 | K3 | K4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio of Shale Stability | 0.598 | 0.560 | 0.459 | 0.428 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, P.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.; Cao, H.; Tian, M.; Han, M.; Liu, W. Study on the Mechanism of Ionic Stabilizers on Shale Gas Reservoir Mechanics in Northwestern Hunan. Energies 2019, 12, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12122453
Sun P, Zhu J, Zhao B, Zhang X, Cao H, Tian M, Han M, Liu W. Study on the Mechanism of Ionic Stabilizers on Shale Gas Reservoir Mechanics in Northwestern Hunan. Energies. 2019; 12(12):2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12122453
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Pinghe, Junyi Zhu, Binkui Zhao, Xinxin Zhang, Han Cao, Mingjin Tian, Meng Han, and Weisheng Liu. 2019. "Study on the Mechanism of Ionic Stabilizers on Shale Gas Reservoir Mechanics in Northwestern Hunan" Energies 12, no. 12: 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12122453
APA StyleSun, P., Zhu, J., Zhao, B., Zhang, X., Cao, H., Tian, M., Han, M., & Liu, W. (2019). Study on the Mechanism of Ionic Stabilizers on Shale Gas Reservoir Mechanics in Northwestern Hunan. Energies, 12(12), 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12122453





