Performance and Emission Parameters of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engine: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Comparative Performance Analysis of HCCI Engine
2.1. Cylinder Pressure
2.2. Brake Specific Fuel Consumption and Brake Thermal Efficiency
3. Comparative Emission Analysis of HCCI Engine
3.1. CO Emission
3.2. HC Emission
3.3. NOx Emission
4. Effects of Fuel Types on HCCI Engine Combustion
5. Effects of Additives on HCCI Engine Combustion
6. Effects of Engine Parameters on HCCI Engines Combustion
6.1. Intake Temperature
6.2. Intake Pressure
6.3. Compression Ratio (CR)
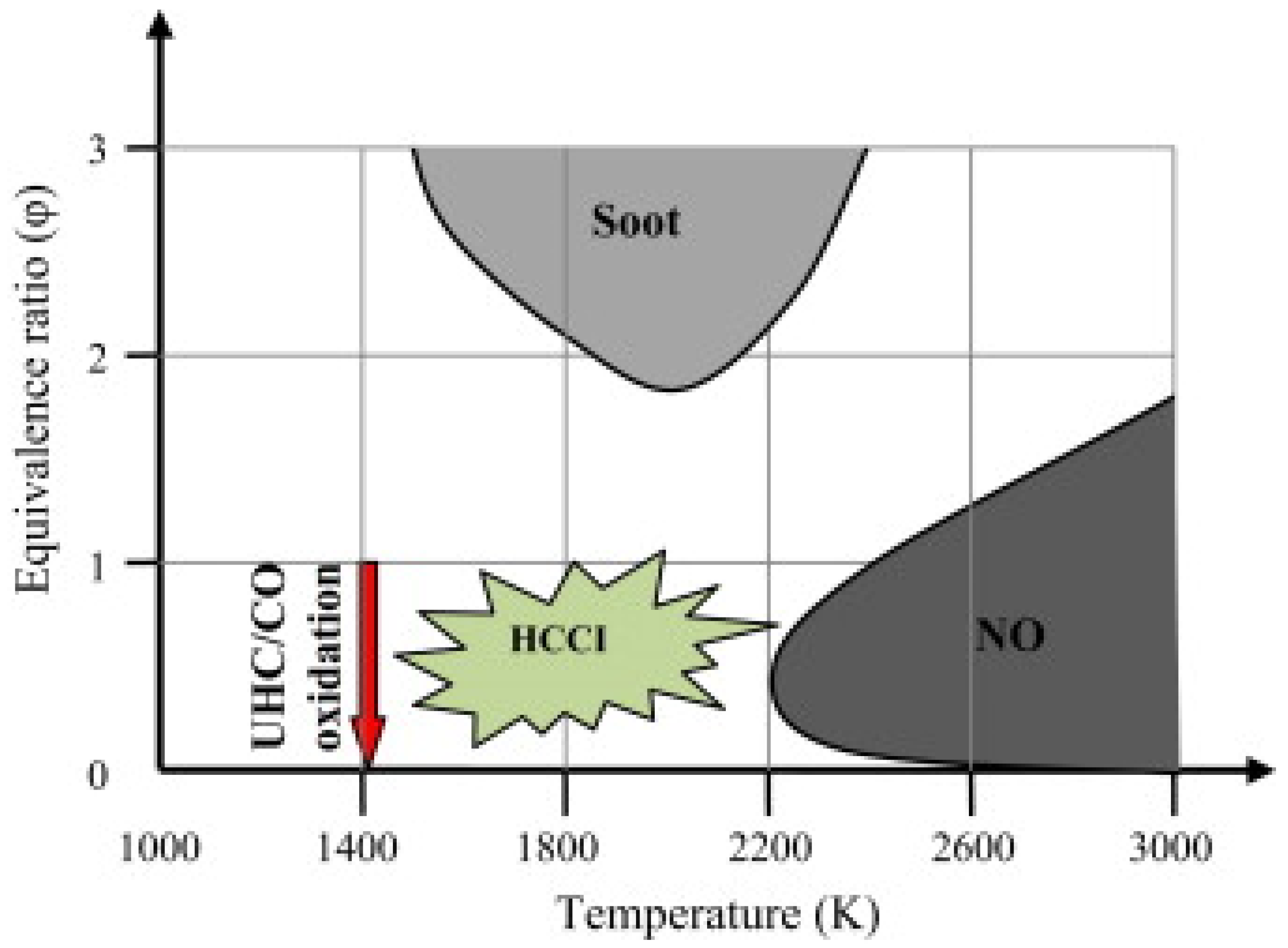
7. HCCI Challenges
8. Conclusions
- The chemical kinetics dominates HCCI combustion.
- HCCI combustion can achieve higher thermal efficiency.
- Compared to SI engine, HCCI engine emits much less NOx and PM emissions and higher HC and CO emissions.
- Various types of fuel can be used in HCCI combustion modes. The fuel choice has a significant impact on engine design and control strategies.
- Auto-ignition of HCCI may be controlled by changing the fuel properties. The addition of an ignition inhibitor in the fuel can make it more chemically reactive.
- Engine parameters have significant influences on HCCI combustion. Better performance from HCCI engine operation is solely dependent on the proper tuning of different engine parameters.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mofijur, M.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Silitonga, A.S.; Ong, H.C.; Silakhori, M.; Hasan, M.H.; Putra, N.; Rahman, S.M.A. Phase Change Materials (PCM) for Solar Energy Usages and Storage: An Overview. Energies 2019, 12, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.S.; Moghavvemi, M.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Techno-economic analysis of an optimized photovoltaic and diesel generator hybrid power system for remote houses in a tropical climate. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 69, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Techato, K.; Taweekun, J.; Rahman, M.M.; Rasul, M.G.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ashrafur, S.M. An Overview of Recent Developments in Biomass Pyrolysis Technologies. Energies 2018, 11, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Putra, N.; Kosasih, E.A.; Prawiro, E.; Luanto, R.A.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Thermal properties of beeswax/graphene phase change material as energy storage for building applications. Appl. Eng. 2017, 112, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrali, M.; Latibari, S.T.; Mehrali, M.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Metselaar, H.S.C.; Naghavi, S.M.; Sadeghinezhad, E.; Akhiani, A.R. Preparation and characterization of palmitic acid/graphene nanoplatelets composite with remarkable thermal conductivity as a novel shape-stabilized phase change material. Appl. Eng. 2013, 61, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofijur, M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Atabani, A.E.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Mobarak, H.M. Comparative evaluation of performance and emission characteristics of Moringa oleifera and Palm oil based biodiesel in a diesel engine. Industrial Crops and Products 2014, 53, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristovski, Z.D.; Miljevic, B.; Surawski, N.C.; Morawska, L.; Fong, K.M.; Goh, F.; Yang, I.A. Respiratory health effects of diesel particulate matter. Respirology 2012, 17, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raitanapaibule, K.; Aung, K. Performance predictions of a hydrogen-enhanced natural gas HCCI engine. ASME 2005 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2005, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Rahman, M.M. Homogeneous charge compression ignition combustion: Advantages over compression ignition combustion, challenges and solutions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epping, K.; Aceves, S.; Bechtold, R.; Dec, J. The Potential of HCCI Combustion for High Efficiency and Low Emissions; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2002-01-1923/ (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Kusumo, F.; Silitonga, A.S.; Masjuki, H.H.; Ong, H.C.; Siswantoro, J.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Optimization of transesterification process for Ceiba pentandra oil: A comparative study between kernel-based extreme learning machine and artificial neural networks. Energy 2017, 134, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.-C.; Reitz, R.D. Use of detailed chemical kinetics to study HCCI engine combustion with consideration of turbulent mixing effects. J. Eng. Gas. Turb. Power 2002, 124, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najt, P.M.; Foster, D.E. Compression-ignited homogeneous charge combustion. SAE Technical paper: 1983. SAE Trans. 1983, 92, 964–979. [Google Scholar]
- Killingsworth, N.J.; Aceves, S.M.; Flowers, D.L.; Krstić, M. A Simple HCCI Engine Model for control. Computer Aided Control System Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 4–6 October 2006; pp. 2424–2429. [Google Scholar]
- Mack, J.H.; Aceves, S.M.; Dibble, R.W. Demonstrating direct use of wet ethanol in a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engine. Energy 2009, 34, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, C.; Uyumaz, A.; Solmaz, H.; Topgul, T. Effects of valve lift on the combustion and emissions of a HCCI gasoline engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 94, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.; Johansson, B.; Amnéus, P.; Mauss, F. Supercharged homogeneous charge compression ignition. SAE Technical paper1998. SAE Trans. 1998, 107, 1129. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau, S.; Lemoult, B.; Tazerout, M. Combustion characterization of natural gas in a lean burn spark-ignition engine. J. Automob. Eng. 1999, 213, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Huang, Z.; Liu, B.; Liu, L.; Jiang, D.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J. Combustion characteristics of a direct-injection natural gas engine under various fuel injection timings. Appl. Eng. 2006, 26, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnatz, J.; Maas, U.; Dibble, R.W. Combustion: Physical and Chemical Fundamentals, Modeling and Simulation, Experiments, Pollutant Formation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, S.S.; Mallikarjuna, J.; Ramesh, A. An experimental study of the biogas–diesel HCCI mode of engine operation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, D.; Peucheret, S.; Megaritis, A.; Wyszynski, M.; Xu, H. Natural gas HCCI engine operation with exhaust gas fuel reforming. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2006, 31, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.-C.; Reitz, R.D. Numerical study of premixed HCCI engine combustion and its sensitivity to computational mesh and model uncertainties. Combust. Theory Model. 2003, 7, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuboyama, T.; Moriyoshi, Y.; Hatamura, K.; Takanashi, J.; Urata, Y.; Yamada, T. A Study of Newly Developed HCCI Engine With Wide Operating Range Equipped With Blowdown Supercharging System. SAE Int. J. Engines 2012, 5, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, D.; Karlovsky, J.; Megaritis, A.; Wyszynski, M.; Xu, H. An investigation into propane homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engine operation with residual gas trapping. Fuel 2005, 84, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polovina, D.; McKenna, D.; Wheeler, J.; Sterniak, J.; Miersch-Wiemers, O.; Mond, A.; Hakan, Y. Steady-state combustion development of a downsized multi-cylinder engine with range extended HCCI/SACI capability. SAE Int. J. Engines 2013, 6, 504–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, B.; Ortiz-Soto, E.; Gupta, R.; Peng, H.; Filipi, Z.S. Hybrid electric vehicle powertrain and control strategy optimization to maximize the synergy with a gasoline HCCI engine. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuboyama, T.; Moriyoshi, Y.; Hatamura, K.; Takanashi, J.; Urata, Y. Extension of operating range of a multi-cylinder gasoline HCCI engine using the blowdown supercharging system. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 1150–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. HCCI and CAI Engines for the Automotive Industry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, K.K. Principles of Combustion; John Wiley &Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.A.; Bowman, C.T. Mechanism and modeling of nitrogen chemistry in combustion. Progress Energy Combust. Sci. 1989, 15, 287–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Koike, N.; Suzuki, H.; Odaka, M. Exhaust Purification of Diesel Engines by Homogeneous Charge with Compression Ignition Part 2: Analysis of Combustion Phenomena and NOx Formation by Numerical Simulation with Experiment; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/970315/ (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Tree, D.R.; Svensson, K.I. Soot processes in compression ignition engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Rasul, M.G.; Ashwath, N.; Rahman, M.M. Optimisation of Second-Generation Biodiesel Production from Australian Native Stone Fruit Oil Using Response Surface Method. Energies 2018, 11, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payri, F.; Lujan, J.; Martin, J.; Abbad, A. Digital signal processing of in-cylinder pressure for combustion diagnosis of internal combustion engines. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2010, 24, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szybist, J.P.; Edwards, K.D.; Foster, M.; Confer, K.; Moore, W. Characterization of engine control authority on HCCI combustion as the high load limit is approached. SAE Int. J. Engines 2013, 6, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Wermuth, N.; Najt, P. Extending the high load operating limit of a naturally-aspirated gasoline HCCI combustion engine. SAE Int. J. Engines 2010, 3, 681–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Dec, J.E.; Dernotte, J.; Cannella, W. Effect of Ignition Improvers on the Combustion Performance of Regular-Grade E10 Gasoline in an HCCI Engine. SAE Int. J. Eng. 2014, 7, 790–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Sako, T.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Kanematsu, S.; Suzuki, K.; Nakazono, T.; Ohtsubo, H. Development of HCCI natural gas engines. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2011, 3, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, S.; Kuboyama, T.; Moriyoshi, Y.; Hatamura, K.; Yamada, T.; Takanashi, J.; Urata, Y. Evaluation of the Performance of a Boosted HCCI Gasoline Engine with Blowdown Supercharge System. SAE Int. J. Engines 2013, 6, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H. Investigation of combustion, performance and emission characteristics of 2-stroke and 4-stroke spark ignition and CAI/HCCI operations in a DI gasoline. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, N.; Blundell, D.; Pearson, R.; Turner, J.; Chen, R. Enlarging the operational range of a gasoline HCCI engine by controlling the coolant temperature. In Proceedings of the SAE World Congress, Detroit, MI, USA, 11–14 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aceves, S.M.; Flowers, D.L.; Westbrook, C.K.; Smith, J.R.; Pitz, W.; Dibble, R.; Christensen, M.; Johansson, B. A multi-zone model for prediction of HCCI combustion and emissions. SAE Trans. 2000, 109, 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Hyvönen, J.; Haraldsson, G.; Johansson, B. Operating Conditions Using Spark Assisted HCCI Combustion During Combustion Mode Transfer to SI in a Multi-Cylinder VCR-HCCI Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 11 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Weall, A.; Szybist, J.P.; Edwards, K.D.; Foster, M.; Confer, K.; Moore, W. HCCI load expansion opportunities using a fully variable HVA research engine to guide development of a production intent cam-based VVA engine: The low load limit. SAE Int. J. Engines 2012, 5, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemberger, I.; Floweday, G. 25cc HCCI Engine Fuelled with DEE. SAE Int. J. Engines 2009, 2, 1559–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khairi, N.N.; Naveenchandran, P.; Aziz, A.R.A. Comparison of HCCI and SI Characteristics on Low Load CNG-DI Combustion. Appl. Sci. 2011, 11, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofijur, M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Atabani, A.E. Evaluation of biodiesel blending, engine performance and emissions characteristics of Jatropha curcas methyl ester: Malaysian perspective. Energy 2013, 55, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Hong, G. Primary investigation to leveraging effect of using ethanol fuel on reducing gasoline fuel consumption. Fuel 2013, 105, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machrafi, H.; Cavadias, S.; Amouroux, J. A parametric study on the emissions from an HCCI alternative combustion engine resulting from the auto-ignition of primary reference fuels. Appl. Energy 2008, 85, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-Q.; Liu, M.-B.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, H. Combustion and emission characteristics of a HCCI engine fuelled with n-butanol–gasoline blends. Fuel 2013, 108, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-Q.; Yuan, J.; Liu, M.-B.; Zhao, H. Combustion and emission characteristics of a n-butanol HCCI engine. Fuel 2014, 115, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghawi, U.; Mayouf, A.; Tsolakis, A.; Wyszynski, M. Vapour-phase and particulate-bound PAHs profile generated by a (SI/HCCI) engine from a winter grade commercial gasoline fuel. Fuel 2010, 89, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A-Gasoline, R.E.P. Regulatory Impact Analysis—Control of Air Pollution from New Motor Vehicles: Tier 2 Motor Vehicle Emissions Standards and Gasoline Sulfur Control Requirements, US Environmental Protection Agency, Air and Radiation. USA Environ. Prot. Agency Air Radiat. EPA420 1999. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/P100F1UV.PDF?Dockey=P100F1UV.PDF (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Popp, D. International innovation and diffusion of air pollution control technologies: The effects of NOx and SO2 regulation in the US, Japan, and Germany. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2006, 51, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselink, L.; Buijsman, E.; Annema, J. The Impact of Euro 5: Facts and Figures; Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, H.C.; Masjuki, H.H.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Silitonga, A.S.; Chong, W.T.; Yusaf, T. Engine performance and emissions using Jatropha curcas, Ceiba pentandra and Calophyllum inophyllum biodiesel in a CI diesel engine. Energy 2014, 69, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharma, S.; Masjuki, H.; Ong, H.C.; Sebayang, A.; Silitonga, A.; Kusumo, F.; Mahlia, T. Optimization of biodiesel production process for mixed Jatropha curcas–Ceiba pentandra biodiesel using response surface methodology. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silitonga, A.S.; Masjuki, H.H.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ong, H.C.; Chong, W.T. Experimental study on performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine fuelled with Ceiba pentandra biodiesel blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 76, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.C.; Masjuki, H.; Mahlia, T.; Silitonga, A.; Chong, W.T.; Leong, K. Optimization of biodiesel production and engine performance from high free fatty acid Calophyllum inophyllum oil in CI diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 81, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silitonga, A.; Shamsuddin, A.; Mahlia, T.; Milano, J.; Kusumo, F.; Siswantoro, J.; Dharma, S.; Sebayang, A.; Masjuki, H.; Ong, H.C. Biodiesel synthesis from Ceiba pentandra oil by microwave irradiation-assisted transesterification: ELM modeling and optimization. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silitonga, A.; Masjuki, H.; Ong, H.C.; Sebayang, A.; Dharma, S.; Kusumo, F.; Siswantoro, J.; Milano, J.; Daud, K.; Mahlia, T.; et al. Evaluation of the engine performance and exhaust emissions of biodiesel-bioethanol-diesel blends using kernel-based extreme learning machine. Energy 2018, 159, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.-C.; Reitz, R.D.; Christensen, M.; Johansson, B. Modeling the effects of geometry generated turbulence on HCCI engine combustion. SAE Trans. 2003, 112, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, S.Q. Lubricant Chemistry, Technology, Selection, and Design; ASTM International: Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Neill, W.S.; Chippior, W.; Graham, L.; Connolly, T.; Taylor, J.D. An Experimental Investigation on the Emission Characteristics of HCCI Engine Operation Using n-Heptane; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2007-01-1854 (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Aceves, S.M.; Flowers, D.L.; Martinez-Frias, J.; Smith, J.R.; Dibble, R.; Au, M.; Girard, J. HCCI Combustion: Analysis and Experiments; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2001. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/771071 (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Dec, J.E. A Computational Study of the Effects of Low Fuel Loading and EGR on Heat Release Rates and Combustion Limits in HCCI Engines; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2002-01-1309 (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Silitonga, A.S.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Kusumo, F.; Dharma, S.; Sebayang, A.H.; Sembiring, R.W.; Shamsuddin, A.H. Intensification of Reutealis trisperma biodiesel production using infrared radiation: Simulation, optimisation and validation. Renew. Energy 2019, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bression, G.; Soleri, D.; Savy, S.; Dehoux, S.; Azoulay, D.; Hamouda, H.B.-H.; Doradoux, L.; Guerrassi, N.; Lawrence, N. A study of methods to lower HC and CO emissions in diesel HCCI. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2008, 1, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, D.; Nagarajan, G.; Ibrahim, M.M. Study of performance, combustion and emission characteristics of diesel homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) combustion with external mixture formation. Fuel 2008, 87, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.M.; He, B.-Q. Spark ignition natural gas engines—A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, J.H. Investigation of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines Fuelled with Ethanol Blends Using Experiments and Numerical Simulations. Ph.D Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Aceves, S.; Flowers, D. Engine Shows Diesel Efficiency Without the Emissions; Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 2004.
- Papagiannakis, R.G.; Hountalas, D.T. Combustion and exhaust emission characteristics of a dual fuel compression ignition engine operated with pilot Diesel fuel and natural gas. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silitonga, A.S.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ong, H.C.; Riayatsyah, T.M.I.; Kusumo, F.; Ibrahim, H.; Dharma, S.; Gumilang, D. A comparative study of biodiesel production methods for Reutealis trisperma biodiesel. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2017, 39, 2006–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, N.; Nagarajan, G. An experimental investigation on hydrogen fuel injection in intake port and manifold with different EGR rates. Energy Env. 2010, 1, 221. [Google Scholar]
- Fiveland, S.B.; Assanis, D.N. A four-stroke homogeneous charge compression ignition engine simulation for combustion and performance studies. SAE Trans. 2000, 109, 452–468. [Google Scholar]
- Kusumo, F.; Silitonga, A.S.; Ong, H.C.; Masjuki, H.H.; Mahlia, T.M.I. A comparative study of ultrasound and infrared transesterification of Sterculia foetida oil for biodiesel production. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2017, 39, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, T.W.; Callahan, T.J. Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition of Diesel Fuel; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/961160 (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Gray, A.W.B.; Ryan, T.W. Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) of Diesel Fuel; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Available online: https://doi.org/10.4271/971676 (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Mase, Y.; Kawashima, J.-I.; Sato, T.; Eguchi, M. Nissan’s new Multivalve DI Diesel Engine Series; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/981039 (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Kimura, S.; Aoki, O.; Ogawa, H.; Muranaka, S.; Enomoto, Y. New Combustion Concept for Ultra-Clean and high-Efficiency Small DI Diesel Engines.; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/1999-01-3681 (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Mercuri, R.; Bauen, A.; Hart, D. Options for refuelling hydrogen fuel cell vehicles in Italy. J. Power Sources 2002, 106, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.C.; Milano, J.; Silitonga, A.S.; Hassan, M.H.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Wang, C.T.; Indra Mahlia, T.M.; Siswantoro, J.; Kusumo, F.; Sutrisno, J. Biodiesel production from Calophyllum inophyllum-Ceiba pentandra oil mixture: Optimization and characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.G.; Mikalsen, R.; Roskilly, A. An investigation of hydrogen-fuelled HCCI engine performance and operation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 5823. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Z. The Effect of PRF Fuel Octane Number on HCCI Operation; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yao, M.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, Z. Influence of fuel and operating conditions on combustion characteristics of a homogeneous charge compression ignition engine. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalghatgi, G.; Risberg, P.; Ångstrom, H.-E. A Method of Defining Ignition Quality of Fuels in HCCI Engines; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2003-01-1816 (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Amann, M.; Ryan, T.W.; Kono, N. HCCI fuels Evaluations-Gasoline Boiling Range Fuels; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2005-01-3727 (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Szybist, J.P.; Bunting, B.G. Cetane Number and Engine Speed Effects on Diesel HCCI Performance and Emissions; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2005-01-3723 (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Goh, B.H.H.; Ong, H.C.; Cheah, M.Y.; Chen, W.-H.; Yu, K.L.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Sustainability of direct biodiesel synthesis from microalgae biomass: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 107, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Okabe, Y.; Izumi, H.; Shudo, T.; Ogawa, H. Dependence of Ultra-High EGR low Temperature Diesel Combustion on Fuel Properties; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2006-01-3387 (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Christensen, M.; Hultqvist, A.; Johansson, B. Demonstrating the multi fuel capability of a homogeneous charge compression ignition engine with variable compression ratio. SAE Trans. 1999, 2099–2113. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly-Zion, P.L.; Dec, J.E. A computational study of the effect of fuel type on ignition time in homogenous charge compression ignition engines. Combust. Inst. 2000, 28, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, N.; Ando, H.; Ogawa, H.; Miyamoto, N. Expansion of the Operating Range with in-Cylinder Water Injection in a Premixed Charge Compression Ignition Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2002-01-1743 (accessed on 13 March 2019).
- Suzuki, T.; Kakegawa, T.; Hikino, K.; Obata, A. Development of Diesel Combustion for Commercial Vehicles; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/972685 (accessed on 13 March 2019).
- Takeda, Y.; Keiichi, N.; Keiichi, N. Emission Characteristics of Premixed Lean Diesel Combustion with Extremely Early Staged Fuel Injection; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/961163 (accessed on 13 March 2019).
- Yokota, H.; Kudo, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Kakegawa, T.; Suzuki, T. A New Concept for Low Emission Diesel Combustion; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Available online: https://doi.org/10.4271/970891 (accessed on 13 March 2019).
- Walter, B.; Gatellier, B. Development of the High Power NADI™ Concept Using Dual Mode Diesel Combustion to Achieve Zero NOx and Particulate Emissions; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2002-01-1744 (accessed on 13 March 2019).
- Nakagome, K.; Shimazaki, N.; Niimura, K.; Kobayashi, S. Combustion and Emission Characteristics of Premixed Lean Diesel Combustion Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/970898 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Zhao, F. Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines: Key Research and Development Issues; Society of Automotive Engineers: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 421–450. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.-Q.; Yuan, J.; Liu, M.-B.; Zhao, H. Low-Temperature Combustion Characteristics of an-Butanol/Isooctane HCCI Engine. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, K.; Jang, J.; Bae, C. Homogeneous charge compression ignition of LPG and gasoline using variable valve timing in an engine. Fuel 2007, 86, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, N.; Igarashi, T. Auto-Ignition and Combustion of n-Butane and DME/air Mixtures in a Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2000-01-1832 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Campbell, M.; Wyszyński, Ł.P.; Stone, R. Combustion of LPG in a spark-Ignition Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2004-01-0974 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Cedrone, K.; Cheng, W.K.; Chahine, S.; Williams, J.; VanDerWege, B. Fuel Effects on HCCI Operation in a Spark Assisted Direct Injection Gasoline Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2011-01-1763 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Hiltner, J.; Agama, R.; Mauss, F.; Johansson, B.; Christensen, M. HCCI operation with natural gas: Fuel composition implications. ASME J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2003, 125, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, J.-O.; Tunestål, P.; Johansson, B.; Fiveland, S.; Agama, R.; Willi, M.; Assanis, D. Compression Ratio Influence on Maximum Load of a Natural Gas Fueled HCCI Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Flowers, D.; Aceves, S.; Westbrook, C.; Smith, J.; Dibble, R. Detailed chemical kinetic simulation of natural gas HCCI combustion: Gas composition effects and investigation of control strategies. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2001, 123, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanglmaier, R.H.; Ryan, T.W.; Souder, J.S. HCCI Operation of a Dual-Fuel Natural Gas Engine for Improved Fuel Efficiency and Ultra-Low NOx Emissions at Low to Moderate Engine Loads; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2001-01-1897 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Christensen, M.; Johansson, B.; Einewall, P. Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Using Isooctane, Ethanol and Natural Gas—A Comparison with Spark Ignition Operation; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/972874 (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Ricklin, P.; Kazakov, A.; Dryer, F.; Kong, S.; Reitz, R.D. The Effects of NOx Addition on the Auto Ignition Behavior of Natural Gas under HCCI Conditions; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2002-01-1746 (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Chen, Z.; Konno, M.; Oguma, M.; Yanai, T. Experimental Study of CI Natural-Gas/DME Homogeneous Charge Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2000-01-0329 (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Au, M.Y.; Girard, J.W.; Dibble, R.; Flowers, D.; Aceves, S.M.; Martínez-Frías, J.; Smith, R.; Seibel, C.; Maas, U. 1.9-Liter Four-Cylinder HCCI Engine Operation with Exhaust Gas Recirculation; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2001-01-1894 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Flowers, D.; Aceves, S.M.; Martínez-Frías, J.; Smith, J.R.; Au, M.; Girard, J.; Dibble, R. Operation of a Four-Cylinder 1.9L Propane Fueled Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition Engine: Basic Operating Characteristics and Cylinder-to-Cylinder Effects; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Iida, N. Combustion Analysis of Methanol-Fueled Active Thermo-Atmosphere Combustion (ATAC) Engine Using a Spectroscopic Observation; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Oakley, A.; Zhao, H.; Ladommatos, N.; Ma, T. Dilution Effects on the Controlled Auto-Ignition (CAI) Combustion of Hydrocarbon and Alcohol Fuels; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2001-01-3606 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Shudo, T.; Ono, Y. HCCI Combustion of Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide and Dimethyl Ether; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2002-01-0112 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Eng, J.A.; Leppard, W.R.; Sloane, T. The Effect of Di-Tertiary Butyl Peroxide (DTBP) Addition to Gasoline on HCCI Combustion; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2003-01-3170 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Aceves, S.M.; Flowers, D.; Martinez-Frias, J.; Espinosa-Loza, F.; Pitz, W.J.; Dibble, R. Fuel and Additive Characterization for HCCI Combustion; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2003-01-1814 (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Shibata, G.; Oyama, K.; Urushihara, T.; Nakano, T. Correlation of Low Temperature Heat Release with Fuel Composition and HCCI Engine Combustion; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2005-01-0138 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Farrell, J.T.; Bunting, B. Fuel Composition Effects at Constant RON and MON in an HCCI Engine Operated with Negative Valve Overlap; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2006-01-3275 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Iida, M.; Aroonsrisopon, T.; Hayashi, M.; Foster, D.E.; Martin, J. The Effect of Intake Air Temperature, Compression Ratio and Coolant Temperature on the Start of Heat Release in an HCCI (Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition) Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2001-01-1880 (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Yap, D.; Megaritis, A. Applying forced induction to bioethanol HCCI operation with residual gas trapping. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megaritis, A.; Yap, D.; Wyszynski, M. Effect of inlet valve timing and water blending on bioethanol HCCI combustion using forced induction and residual gas trapping. Fuel 2008, 87, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szybist, J.P.; McFarlane, J.; Bunting, B.G. Comparison of Simulated and Experimental Combustion of Biodiesel Blends in a Single Cylinder Diesel HCCI Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2007-01-4010 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Leppard, W.R. The Chemical Origin of fuel Octane Sensitivity; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook, C.K.; Pitz, W.J.; Leppard, W.R. The Autoignition Chemistry of Paraffinic Fuels and pro-Knock and anti-Knock Additives: A detailed Chemical Kinetic Study; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/912314 (accessed on 16 March 2019).
- Haraldsson, G.; Tunestål, P.; Johansson, B.; Hyvönen, J. HCCI Combustion Phasing in a Multi Cylinder Engine Using Variable Compression Ratio; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2002-01-2858 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Verhelst, S.; Wallner, T. Hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2009, 35, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolakis, A.; Megaritis, A. Partially premixed charge compression ignition engine with on-board production by exhaust gas fuel reforming of diesel and biodiesel. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2005, 30, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwaja, S.; Grab-Rogalinski, K. Hydrogen combustion in a compression ignition diesel engine. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-C.; Chen, W.; Huang, Z. A fundamental study on the control of the HCCI combustion and emissions by fuel design concept combined with controllable EGR. Part 2. Effect of operating conditions and EGR on HCCI combustion. Fuel 2005, 84, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machrafi, H.; Cavadias, S.; Amouroux, J. Influence of fuel type, dilution and equivalence ratio on the emission reduction from the auto-ignition in an Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition engine. Energy 2010, 35, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagawa, H.; Miyamoto, T.; Harada, A.; Sasaki, S.; Shimazaki, N.; Hashizume, T.; Tsujimura, K. Approaches to Solve Problems of the Premixed Lean Diesel Combustion; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.; Miles, P.C.; Yun, H.; Reitz, R.D. A parametric study of low-temperature, late-injection combustion in a HSDI diesel engine. Jsme Int. J. Ser. B Fluids Therm. Eng. 2005, 48, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.; Johansson, B.; Amnéus, P.; Mauss, F. Supercharged homogeneous charge compression ignition. SAE Trans. J. Engines 1998, 107, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, M.; Johansson, B. Supercharged Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) with Exhaust Gas Recirculation and Pilot Fuel; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hyvonen, J.; Haraldsson, G.; Johansson, B. Supercharging HCCI to Extend the Operating Range in a Multi-Cylinder VCR-HCCI Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2003; p. 3214. Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2003-01-3214 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Iwabuchi, Y.; Kawai, K.; Shoji, T.; Takeda, Y. Trial of New Concept Diesel Combustion System—Premixed Compression-Ignited Combustion; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/1999-01-0185 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Olsson, J.-O.; Tunestål, P.; Haraldsson, G.; Johansson, B. A Turbocharged Dual-Fuel HCCI Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2001-01-1896 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Gan, S.; Ng, H.K.; Pang, K.M. Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) combustion: Implementation and effects on pollutants in direct injection diesel engines. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheman, H.; Phadatare, A. Diesel engine emissions and performance from blends of karanja methyl ester and diesel. Biomass Bioenerg. 2004, 27, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, J.-O.; Tunestal, P.; Johansson, B.; Fiveland, S.; Agama, R.; Willi, M.; Assanis, D.N. Compression Ratio Influence on Maximum Load of a Natural Gas Fueled HCCI Engine. SAE Tech. Pap. Ser. 2002, 111, 442. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ma, T.; Ladommatos, N. Characteristics of homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) combustion and emissions of n-heptane. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2005, 177, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguitton, O.; Crua, C.; Cowell, T.; Heikal, M.; Gold, M. The effect of compression ratio on exhaust emissions from a PCCI diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbakhti, M. Modeling and Experimental Study of an HCCI Engine for Combustion Timing Control. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Najafabadi, M.I.; Aziz, N.A. Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition Combustion: Challenges and Proposed Solutions. J. Comb. 2013, 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najt, P.M.; Foster, D.E. Compression-Ignited Homogeneous Charge Combustion; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 964–979. Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/830264 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Christensen, M.; Johansson, B. Influence of Mixture Quality on Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 951–963. Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/982454 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Atkins, M.J.; Koch, C. The effect of Fuel Octane and Dilutent on Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition Combustion. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2005, 219, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, M.; Ohta, Y.; Kono, M.; Hasegawa, M. An Ultra-Lean Premixed Compression-Ignition Engine Concept and its Characteristics. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium COMODIA, Kyoto, Japan, 20–23 July 1998; pp. 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, V.; Checkel, M.D. Using Reformer Gas to Enhance HCCI Combustion of CNG in a CFR Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2006-01-3247 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Hosseini, V.; Checkel, M.D. Effect of Reformer Gas on HCCI Combustion—Part I:High Octane Fuels; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2007-01-0208 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Dec, J.E.; Sjöberg, M. Isolating the Effects of Fuel Chemistry on Combustion Phasing in an HCCI Engine and the Potential of Fuel Stratification for Ignition Control. SAE Tech. Paper Ser. 2004, 239–257. Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2004-01-0557 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Berntsson, A.W.; Denbratt, I. HCCI Combustion Using Charge Stratification for Combustion; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2007-01-0210 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Aoyama, T.; Hattori, Y.; Mizuta, J.i.; Sato, Y. An Experimental Study on Premixed-Charge Compression Ignition Gasoline Engine; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Thomas, R.; Gray, C.L. An HCCI Engine: Power Plant for a Hybrid Vehicle; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2004-01-0933 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Olsson, J.-O.; Tunestål, P.; Johansson, B. Boosting for high load HCCI. SAE Trans 2004, 579–588. Available online: https://saemobilus.sae.org/content/2004-01-0940 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Pandey, S.; Diwan, P.; Sahoo, P.K.; Thipse, S.S. A review of combustion control strategies in diesel HCCI engines. Biofuels 2018, 9, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.K.; No, S.-Y. Effect of bioethanol on combustion and emissions in advanced CI engines: HCCI, PPC and GCI mode—A review. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 782–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaberi, H.A.; Hairuddin, A.A.; Aziz, N.A. The use of different types of piston in an HCCI engine: A review. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2017, 14, 4348–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandal, S.V.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Gaitonde, V.N.; Hiremath, S.S. Paradigm shift from mechanical direct injection diesel engines to advanced injection strategies of diesel homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engines- A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goteti, G.S.; Selvan, P.T. HCCI combustion in a diesel engine using oxygenated fuels and various operating parameters - A review. Int. J Renew. Energy Res. 2017, 7, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, M.; Jahanian, O.; Shahbakhti, M. Modeling and controller design architecture for cycle-by-cycle combustion control of homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engines—A comprehensive review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 139, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.K.; Rao, G.A.P.; Murthy, K.M. Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines: A Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2016, 23, 623–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komninos, N.P.; Rakopoulos, C.D. Heat transfer in hcci phenomenological simulation models: A review. Appl. Energy 2016, 181, 179–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairuddin, A.A.; Yusaf, T.; Wandel, A.P. A review of hydrogen and natural gas addition in diesel HCCI engines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 739–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komninos, N.P.; Rakopoulos, C.D. Modeling HCCI combustion of biofuels: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1588–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaberi, H.A.; Hairuddin, A.A.; Abdul, N.A. Effect of fuel injection strategies on performance and emissions in HCCI engines: A review. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. 2018, 12, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | SI | HCCI | CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ignition method | Spark ignition | Auto-ignition | Compression ignition |
| Charge | Premixed homogeneous before ignition | Premixed homogeneous before ignition | In-cylinder heterogeneous |
| Ignition point | Single | Multiple | Multiple |
| Throttle loss | Yes | No | - |
| Compression ratio | Low | High | - |
| Speed | High | Low | - |
| Combustion flame | Flame propagation | Multi-point auto-ignition | Diffusive flame |
| Fuel economy | Good | Best | Better |
| Max. efficiency | 30% | >40% | 40% |
| Major emissions | HC, CO and NOx | HC and CO | NOx, PM and HC |
| Injection type | Gasoline direct injection | Port and direct injection | Direct injection |
| Equivalence ratio | 1 | <1 | - |
| Engine | Test Condition | Fuel | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↑: Cylinder pressure ↓: BSFC | [28] |
| 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 10.8:1, RS: 2000 rpm | VS and VL | Gasoline and ethanol | ↑: Cylinder pressure −: BSFC ↓: BTE | [26] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12.5:1 and 15:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VR | Propane | ↑: Cylinder pressure | [25] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 11.3:1, RS: 2500 rpm | VS and CL | Gasoline | −−−−− | [53] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, DI, CR: 11.85:1 | CS and VL | Gasoline–ethanol blend | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BSFC, BTE | [36] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12:1, RS: 2500 rpm | VS and VL | Gasoline | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BSFC | [37] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 14:1 | CS and VL | Gasoline–ethanol blend | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BTE | [38] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 14:1, RS: 2100 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline and CNG | ↑: BSFC, BTE | [47] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BSFC, BTE | [29] |
| 1and 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 17:1, 19:1 and 21:1 RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VR | Gasoline and CNG | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BSFC, BTE | [39] |
| 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BTE | [40] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 11.78:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BTE ↓: BSFC | [41] |
| 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 4-16:1, RS: 600 rpm | CS and VR | n-heptane and iso-octane | ↑: BTE | [50] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 10.66:1, RS: 1500 rpm | VS and CL | Gasoline and n-butanol | ↑: BTE | [51] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 10.66:1, RS: 1500 rpm | VS and CL | n-butanol | ↑: BTE | [52] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, WC, PFI, CR: 10.5:1, RS: 2000 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↓: Cylinder pressure | [42] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 12:1, RS: 1500 rpm | VS and CL | Gasoline | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BTE ↓: BSFC | [43] |
| 5-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 10-30:1 | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BTE ↓: BSFC | [44] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 11.85:1, RS: 2000 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline–ethanol blend | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BTE | [45] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 8;1:1, RS: 9000 rpm | VS and CL | Diethyl ether | ↑: Cylinder pressure, BTE ↓: BSFC | [46] |
| Engine | Test Condition | Fuel | Emission | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↓: CO, NOx −: HC | [28] |
| 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 10.8:1, RS: 2000 rpm | VS and VL | Gasoline and ethanol | ↓: NOx | [26] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12.5:1 and15:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VR | Propane | ↑: HC, CO ↓: NOx | [25] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 11.3:1, RS: 2500 rpm | VS and CL | Gasoline | ↑: HC, CO ↓: NOx, PM | [53] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, DI, CR: 11.85:1 | CS and VL | Gasoline–ethanol blend | ↓: NOx | [36] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12:1, RS: 2500 rpm | VS and VL | Gasoline | ↑: NOx | [37] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 14:1 | CS and VL | Gasoline–ethanol blend | ↑: NOx | [38] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 14:1, RS: 2100 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline and CNG | ↑: CO ↓: HC, NOx | [47] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↓: NOx | [29] |
| 1and 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 17:1, 19:1 and 21:1 RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VR | Gasoline and CNG | ↑: HC, CO ↓: NOx | [39] |
| 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 12:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | −−−−− | [40] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 11.78:1, RS: 1500 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↑: HC, CO ↓: NOx | [41] |
| 4-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 4-16:1, RS: 600 rpm | CS and VR | n-heptane and iso-octane | ↓: NOx, CO | [50] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 10.66:1, RS: 1500 rpm | VS and CR | Gasoline and n-butanol | ↓: NOx | [51] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 10.66:1, RS: 1500 rpm | VS and CL | n-butanol | ↓: NOx | [52] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, WC, PFI, CR: 10.5:1, RS: 2000 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↓: HC, CO, NOx | [42] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 12:1, RS: 1500 rpm | VS and CL | Gasoline | ↑: HC, CO ↓: NOx | [43] |
| 5-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 10-30:1 | CS and VL | Gasoline | ↑: HC, CO ↓: NOx | [44] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, GDI, CR: 11.85:1, RS: 2000 rpm | CS and VL | Gasoline–ethanol blend | ↑: NOx | [45] |
| 1-cylinder, 4S, AC, PFI, CR: 8;1:1, RS: 9000 rpm | VS and CL | Diethyl ether | ↑: HC, CO ↓: NOx | [46] |
| Ref. | Topic Discussed | HCCI Combustion Parameters | HCCI Performance Parameters | HCCI Emission Parameters | Effect of Fuel Choice on HCCI Combustion | Effect of Additive on HCCI Combustion | Effect of Engine Parameter on HCCI Combustion | Challenges of HCCI Combustion | Modelling of HCCI Combustion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Study | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | |
| [160] | A | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| [161] | B | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [162] | C | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [163] | D | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| [164] | E | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [165] | F | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| [166] | G | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [167] | H | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| [168] | I | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| [169] | J | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| [170] | K | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mofijur, M.; Hasan, M.M.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Silitonga, A.S.; Ong, H.C. Performance and Emission Parameters of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engine: A Review. Energies 2019, 12, 3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183557
Mofijur M, Hasan MM, Mahlia TMI, Rahman SMA, Silitonga AS, Ong HC. Performance and Emission Parameters of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engine: A Review. Energies. 2019; 12(18):3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183557
Chicago/Turabian StyleMofijur, M., M.M. Hasan, T.M.I. Mahlia, S.M. Ashrafur Rahman, A.S. Silitonga, and Hwai Chyuan Ong. 2019. "Performance and Emission Parameters of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engine: A Review" Energies 12, no. 18: 3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183557
APA StyleMofijur, M., Hasan, M. M., Mahlia, T. M. I., Rahman, S. M. A., Silitonga, A. S., & Ong, H. C. (2019). Performance and Emission Parameters of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engine: A Review. Energies, 12(18), 3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183557











