Hybrid Forecasting Model for Short-Term Wind Power Prediction Using Modified Long Short-Term Memory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
2.2. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Existing LSTM Problems and Solution
3.2. Proposed Long Short-Term Memory
3.2.1. Input Gate Layer
3.2.2. Forget Gate Layer
3.2.3. Cell State Update
3.2.4. Output Gate Layer
3.2.5. Learning Options and Simulation Result
3.3. Data Set
3.4. Multivariate Models
4. Test and Discussion
4.1. Test Environments
4.2. Performance Metrics for Evaluation
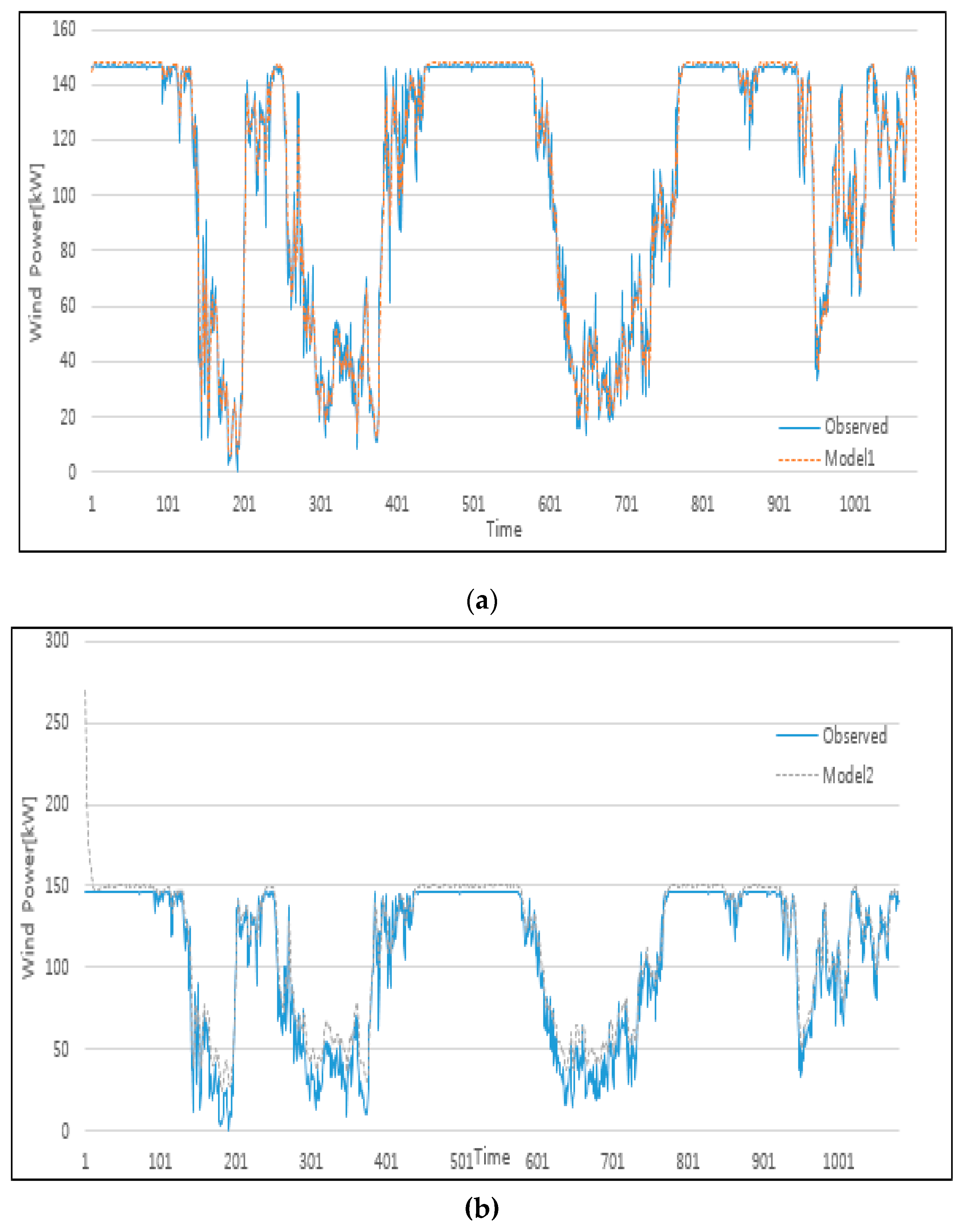
4.3. Comparison and Analysis of Multivariate Models
4.4. Comparison and Analysis of Hybrid Forecasting Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woori Finance Research Institute. Recent Trends in Renewable Energy Industry; Woori Finance Research Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, I.Y.; Ha, B.N.; Kim, S.O.; Koong, W.N.; Seo, D.W.; Kim, S.J. Short term wind power prediction using wavelet transform and ARIMA. J. Energy Power Eng. 2012, 6, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.Y.; Yu, T.H.; Liu, C.Y. Hour-Ahead wind speed and power forecasting using empirical mode decomposition. Energies 2013, 6, 6137–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, C.H.; Jang, W.H.; Kim, C.H. Recent Trends in Renewable energy Resources for Power Generation in the Republic of Korea. Resources 2015, 4, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumus, I.; Dinler, A. Current status of wind energy forecasting and a hybrid method for hourly predictions. Energy Convers. Manage. 2016, 123, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwat, A.; Amini, M.; Domijan, A.; Damnjanovic, A.; Kaleem, F. Weather-based interruption prediction in the smart grid utilizing chronological data. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2016, 4, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Qian, Z.; Nabney, I.T.; Meng, X. Wind power forecasts using Gaussian processes and numerical weather prediction. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 29, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, K.; Liao, Y. Short-term wind power forecasting using hybrid method based on enhanced boosting algorithm. J. M. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2015, 5, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fathall, A.; Timothy, M.; Siddharth, S.; Edwin, K.P. Employing ARIMA models to improve wind power forecasts: A case study in ERCOT. In Proceedings of the 2016 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Denver, CO, USA, 18–20 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nury, A.H.; Hasan, K.; Alam, M.J.B. Comparative Study of Wavelet-ARIMA and Wavelet-ANN Models for Temperature Time Series Data in Northeastern Bangladesh. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2017, 29, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayar, M.; Wang, J.; Manthouri, M. Interval Deep Generative Neural Network for Wind Speed Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 3974–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Zheng, D.H.; Wei, D. Short term wind power prediction using ANFIS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy (ICPRE), Shanghai, China, 21–23 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Fang, K.; Pang, W.; Sun, J. Wind power interval prediction based on improved PSO and BO neural network. J. Electr. Eng. Tech. 2017, 12, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhan, Z. Wind Power Prediction Based on Genetic Neural Network, AIP Conference Proceedings 1834; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mariya, S.; Ilya, K.; Thorsten, S. Supervised Classification with Interdependent Variable to Support Targeted Energy Efficiency Measures in the Residential Sector. Decis. Analytics 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Renani, E.; Elias, M.; Rahim, N.A. Using Data-driven Approach for Wind Power Prediction: A Comparative Study. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 118, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. An Empirical Study for 2.5GW Offshore Wind Power in the Southwest Sea; Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy: Sejong City, Korea, 2014.
- Kim, H.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Jang, M.S. Cluster Analysis and Meteor-Statistical Model Test to Develop a Daily Forecasting Model for Jejudo Wind Power Generation. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2010, 19, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botterud, A.; Miranda, V.; Wang, J.; Monteiro, C. Wind Power Forecasting and Electricity Market Operations. In Proceedings of the CPES Annual Conference, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 5–7 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zack, J.W. Overviw of the Current Status and Future Prospects of Wind Power Production Forecasting for the ERCOT System. In Proceedings of the Wind Workshop III ERCOT Workshop, Austin, TX, USA, 26 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cellura, M.; Cirrincione, G.; Marvuglia, A.; Miraoui, A. Wind Speed Spatial Estimation for Energy Planning in Sicily: Introduction and Statistical Analysis. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, L.D.; Wang, Z.Y. The Status and Development of the Combination Forecast Method. Forecast 1997, 6, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, M.; Shiyan, L.; Chuanwen, J.; Hongling, L.; Yan, Z. A Review on the Forecasting of Wind Speed and Generated Power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, H.; Inalli, M.; Sengur, A.; Esen, M. Modeling a Ground-coupled Heat Pump System by a Support Vector Machine. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1814–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. The Validity of the Theory and its Application of Combination Forecast Methods; Beijing Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Lu, H. Combining Forecasts of Electricity Consumption in China with Time-varying Weights Updated by a High-order Markov Chain. Omega 2014, 45, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tascikaraoglu, A.; Uzunoglu, M. A Review of Combined Approaches for Prediction of Short-term Wind Speed and Power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzgou, H.; Benoudjit, N. Multiple Architecture System for Wind Speed Prediction. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Ran, L. Short-term Wind Speed Forecasting Model for Wind Farm based on Wavelet Decomposition. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT), Nanjing, China, 6–9 April 2008; pp. 2525–2529. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, W.; Lu, H.; Wang, J. Multi-step Forecasting for Wind Speed using a Modified EMD-based Artificial Neural Network Model. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, J.; Huang, M. Short-term Wind Power Prediction based on Statistical Clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Detroit, MI, USA, 24–28 July 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kani, S.P.; Ardehali, M.M. Very Short-term Wind Speed Prediction: A New Artificial Neural Network-Markov Chain Model. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Xin, W. Wind Speed Prediction based on Genetic Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Xi’an, China, 25–27 May 2009; pp. 2448–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Zhao, G. A New Hybrid Model Optimized by an Intelligent Optimization Algorithm for Wind Speed Forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 85, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.; Niu, D. Combining Simulate Anneal Algorithm with Support Vector Regression to Forecast Wind Speed. In Proceedings of the Second IITA International Conference on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (IITA-GRS), Qingdao, China, 28–31 August 2010; pp. 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.; Kang, X.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, S.; Ma, X. Short-term Prediction of Wind Power based on Deep Long Short-term Memory. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific IEEE, Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Xi’an, China, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 1148–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Louka, P.; Galanis, G.; Siebert, N.; Kariniotakis, G.; Katsafados, P.; Pytharoulis, I. Improvements in Wind Speed Forecasts for Wind Power Prediction Purposes using Kalman Filtering. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 2348–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. LSTM can Solve Hard Long Time Lag Problems. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 2–5 December 1996; pp. 473–479. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, J.; Gibson, A. Deep Learning. A Practitioner’s Approach; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Colah.github.io. Understanding LSTM Networks—Colah’s Blog. Available online: http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs (accessed on 12 October 2019).
- Negnevitsky, M.; Potter, C.W. Innovative short-term wind generation prediction techniques. IEEE Power Syst. Conf. Expo. 2006, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, A.M.; Leahy, P.G.; Marvuglia, A.; McKeogh, E.J. Current methods and advances in forecasting of wind power generation. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Jang, M.S.; Kim, H.G. A study on comparing short-term wind power prediction models in Gunsan wind farm. J. Korean Data Inf. Sci. Soc. 2013, 24, 585–592. [Google Scholar]
- Computation Time. Available online: http://mathworld.wolfram.com/ComputationTime.html (accessed on 12 October 2019).













| Region | Collection Period | Collection Time | Learning Data | Test Data | Total Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2014.01.11–25 | 10 min | 1080 | 1080 | 2160 |
| B | 2014.01.11–20 | 10 min | 1008 | 432 | 1440 |
| C | 2014.01.11–25 | 10 min | 1440 | 720 | 2160 |
| Area | A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specifications | ||||
| Model | U88 | U50 | ||
| Output | 2000 kW | 750 kW | ||
| Wind speed | 12 m/s | 12.5 m/s | ||
| Rotor speed range | 6–17.5 rpm | 9–28 rpm | ||
| Voltage and frequency | 690V/60 Hz | 690V/60 Hz | ||
| Rotor diameter | 88 m | 50 m | ||
| Hub height | 80 m | 50 m | ||
| Power control | Pitch | Pitch | ||
| Model | Variables |
|---|---|
| Model 1 (M1) | wind power |
| Model 2 (M2) | wind power, wind direction |
| Model 3 (M3) | wind power, wind speed |
| Model 4 (M4) | wind power, wind direction, wind speed |
| Region | RMSE | MAPE (%) | Complex Time (s) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | |
| A | 6.3 | 13.2 | 8.1 | 12.7 | 7.9 | 28.0 | 10.5 | 14.0 | 36.6 | 65.8 | 65.2 | 94.5 |
| B | 6.7 | 35.8 | 6.9 | 11.5 | 5.1 | 41.9 | 3.1 | 30.2 | 32.1 | 57.0 | 55.1 | 78.2 |
| C | 10.6 | 11.8 | 11.4 | 11.6 | 32.6 | 39.5 | 34.8 | 34.7 | 26.3 | 47.0 | 45.3 | 64.4 |
| Region | RMSE | MAPE (%) | Complex Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 3.67 | 5.04 | 45.18 |
| B | 3.39 | 3.36 | 39.20 |
| C | 5.64 | 17.09 | 32.11 |
| Region | RMSE | MAPE (%) | Complex Time (s) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| △M1 | △M2 | △M3 | △M4 | △M1 | △M2 | △M3 | △M4 | △M1 | △M2 | △M3 | △M4 | |
| A | −2.6 | −9.5 | −4.4 | −9.0 | −2.8 | −22.9 | −5.4 | −8.9 | 8.5 | −20.6 | −20.0 | −49.3 |
| B | −3.3 | −32.4 | −3.5 | −8.1 | −1.7 | −38.5 | 0.2 | −26.8 | 7.1 | −17.8 | −15.9 | −39.0 |
| C | −4.9 | −6.1 | −5.7 | −5.9 | −15.5 | −22.4 | −17.7 | −17.6 | 5.8 | −14.8 | −13.1 | −32.2 |
| Avg. | −3.6 | −16.0 | −4.6 | −7.7 | −6.7 | −28.0 | −7.6 | −17.8 | 7.2 | −17.8 | −16.4 | −40.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, N.; Yang, S.; Na, J. Hybrid Forecasting Model for Short-Term Wind Power Prediction Using Modified Long Short-Term Memory. Energies 2019, 12, 3901. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12203901
Son N, Yang S, Na J. Hybrid Forecasting Model for Short-Term Wind Power Prediction Using Modified Long Short-Term Memory. Energies. 2019; 12(20):3901. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12203901
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Namrye, Seunghak Yang, and Jeongseung Na. 2019. "Hybrid Forecasting Model for Short-Term Wind Power Prediction Using Modified Long Short-Term Memory" Energies 12, no. 20: 3901. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12203901
APA StyleSon, N., Yang, S., & Na, J. (2019). Hybrid Forecasting Model for Short-Term Wind Power Prediction Using Modified Long Short-Term Memory. Energies, 12(20), 3901. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12203901





