New Fast MPPT Method Based on a Power Slope Detector for Single Phase PV Inverters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
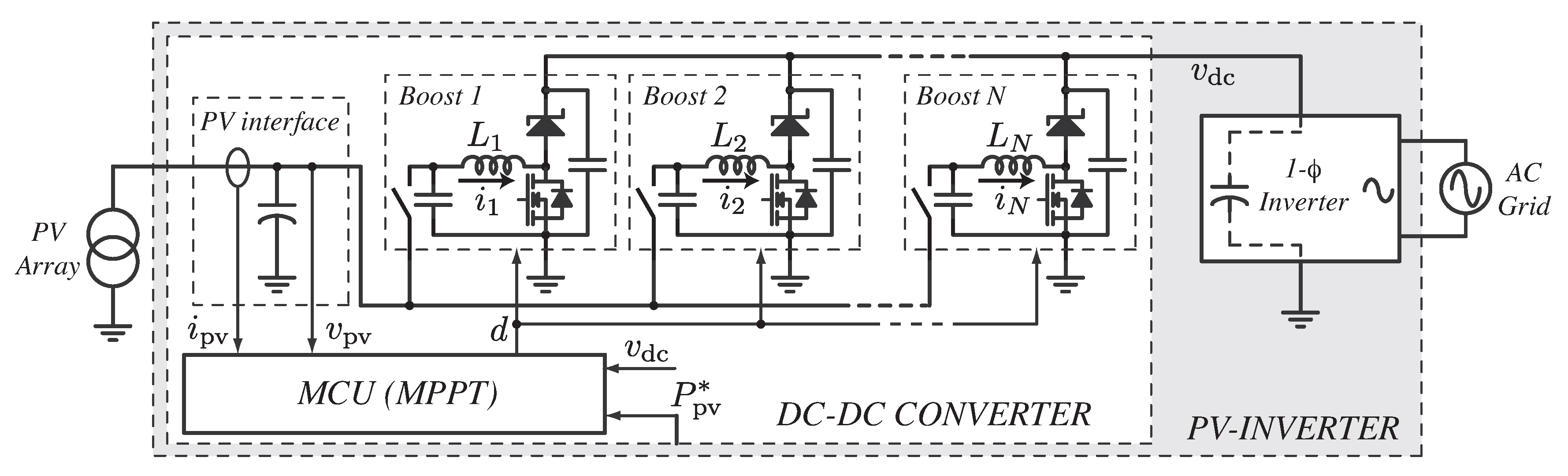
2. Converter Modeling
3. DC-Bus Voltage Modulation and PV Efficiency
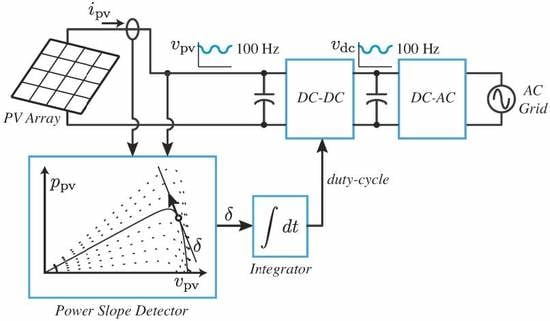
4. Proposed P-V Slope Detector
5. Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on the P-V Slope Detector
6. Modification for Power Reference Tracking
7. Experimental Results
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sajadian, S.; Ahmadi, R.; Zargarzadeh, H. Extremum Seeking-Based Model Predictive MPPT for Grid-Tied Z-Source Inverter for Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 7, 1904–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahari, O.P.; Subudhi, B. Integral sliding mode-improved adaptive MPPT control scheme for suppressing grid current harmonics for PV system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 12, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Hussain, I.; Singh, B.; Panigrahi, B.K. Normal Harmonic Search Algorithm-Based MPPT for Solar PV System and Integrated With Grid Using Reduced Sensor Approach and PNKLMS Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. App. 2018, 54, 6343–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwongwanich, A.; Blaabjerg, F. Mitigation of Interharmonics in PV Systems With Maximum Power Point Tracking Modification. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 8279–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, H.; Aly, M.; Al-Dhaifallah, M.; Shoyama, M. Design and Hardware Implementation of New Adaptive Fuzzy Logic-Based MPPT Control Method for Photovoltaic Applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 106427–106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Medina, R.; Liberos, M.; Marzal, S.; Figueres, E.; Garcera, G. A Control Scheme without Sensors at the PV Source for Cost and Size Reduction in Two-Stage Grid Connected Inverters. Energies 2019, 12, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Mouli, G.R.; Schijffelen, J.H.; Bauer, P.; Zeman, M. Design and Comparison of a 10-kW Interleaved boost Converter for PV Application Using Si and SiC Devices. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.N.; Breuninger, H.; Pettersson, S.; Escobar, G.; Serpa, L.A.; Coccia, A. Practical Design and Implementation Procedure of an Interleaved boost Converter Using SiC Diodes for PV Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 2835–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Salam, Z. An Enhanced Adaptive P&O MPPT for Fast and Efficient Tracking Under Varying Environmental Conditions. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, J.; Salam, Z. A Modified P&O Maximum Power Point Tracking Method With Reduced Steady-State Oscillation and Improved Tracking Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 4, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Macaulay, J.; Zhou, Z. A Fuzzy Logical-Based Variable Step Size P&O MPPT Algorithm for Photovoltaic System. Energies 2018, 11, 1340. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, D.; Liu, J.; Zeng, J. A High-Performance Adaptive Incremental Conductance MPPT Algorithm for Photovoltaic Systems. Energies 2016, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espi, J.M.; Castello, J. A Novel Fast MPPT Strategy for High Efficiency PV Battery Chargers. Energies 2019, 12, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano, I.; Ordonez, M. PV Energy Harvesting Under Extremely Fast Changing Irradiance: State-Plane Direct MPPT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 1852–1861. [Google Scholar]
- Paz, F.; Ordonez, M. High-Performance Solar MPPT Using Switching Ripple Identification Based on a Lock-In Amplifier. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3595–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwongwanich, A.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F.; Wang, H. Benchmarking of Constant Power Generation Strategies for Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. App. 2018, 54, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
























| Description | Variable | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Number of PV modules in series | 3 | |
| Number cells/module | 36 | |
| Open-circuit voltage @ 1kW/m | 65 V | |
| Short-circuit current @ 1kW/m | 8.5 A | |
| Maximum power point voltage @ 1kW/m | 55.5 V | |
| Maximum power point current @ 1kW/m | 7.6 V | |
| Efficiency @ = 2% peak-peak | 99.94% | |
| Efficiency @ = 4% peak-peak | 99.78% | |
| Efficiency @ = 6% peak-peak | 99.44% | |
| Efficiency @ = 8% peak-peak | 99.09% | |
| Efficiency @ = 10% peak-peak | 98.50% |
| Description | Variable | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Number of boost converters | N | 3 |
| Nominal power | P | 450 W |
| Switching frequency | 10 kHz | |
| DC-bus voltage | 150 V | |
| DC-bus capacitance | 1470 F | |
| Input filter inductances | 1200 H | |
| Inductor series resistances | 25 m | |
| Input capacitance | C | 470 F |
| Description | Variable | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sampling frequency | 20/11 kHz | |
| Slope detector’s gain | 2500 | |
| Bandpass filters, center-frequency | 100 Hz | |
| Bandpass filters, bandwidth | 100 Hz | |
| Integrator’s gain | 2 rad/s | |
| Power gain (power control) | 0.01 | |
| Minimum PV current for start-up | 50 mA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espi, J.M.; Castello, J. New Fast MPPT Method Based on a Power Slope Detector for Single Phase PV Inverters. Energies 2019, 12, 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224379
Espi JM, Castello J. New Fast MPPT Method Based on a Power Slope Detector for Single Phase PV Inverters. Energies. 2019; 12(22):4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224379
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspi, Jose Miguel, and Jaime Castello. 2019. "New Fast MPPT Method Based on a Power Slope Detector for Single Phase PV Inverters" Energies 12, no. 22: 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224379
APA StyleEspi, J. M., & Castello, J. (2019). New Fast MPPT Method Based on a Power Slope Detector for Single Phase PV Inverters. Energies, 12(22), 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224379