Performance Analysis of Direct Injection Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel-Tomato Seed Oil Biodiesel Blending by ANOVA and ANN
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
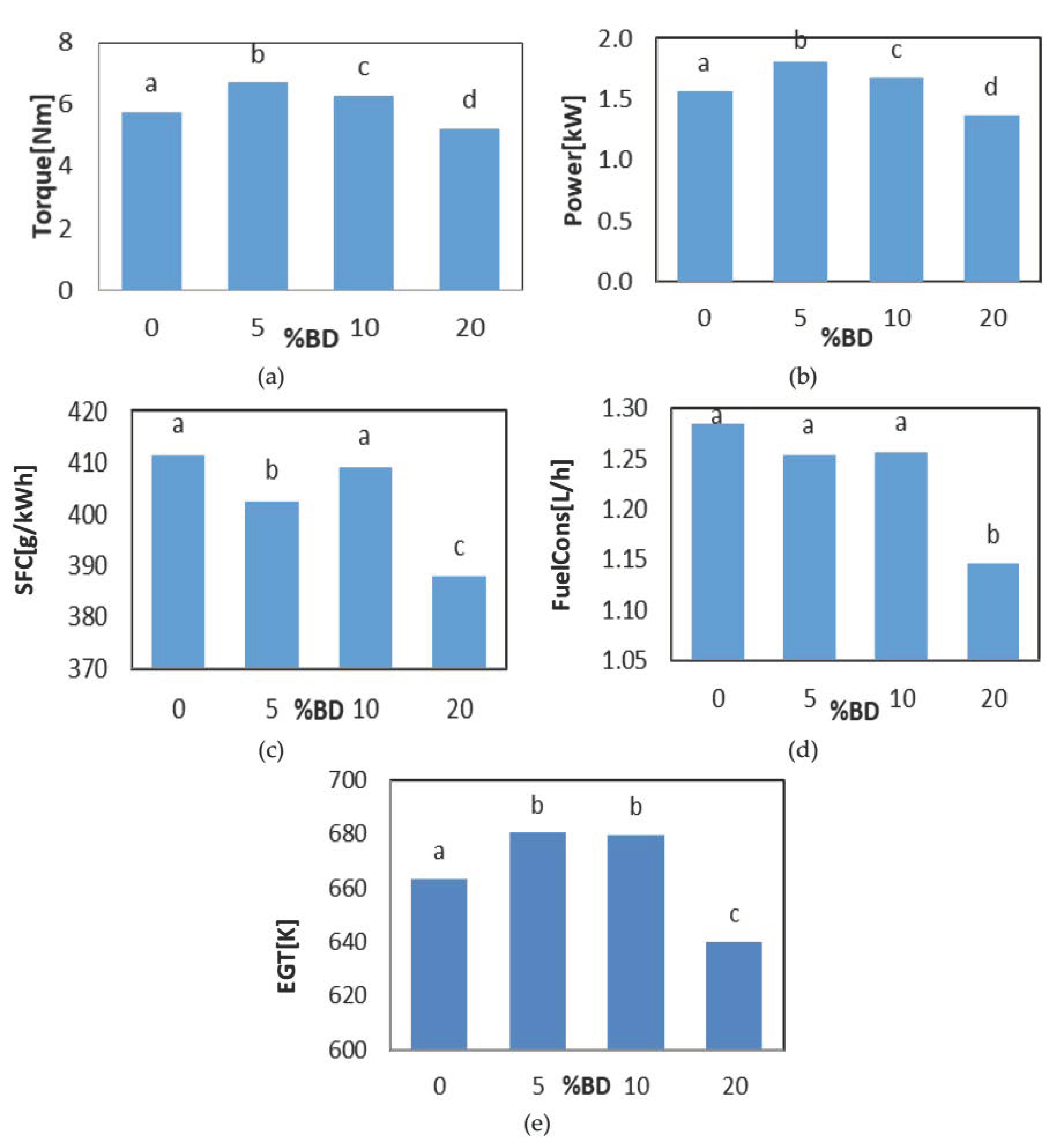
3.1. ANOVA Using Post Hoc Duncan Multi-Domain Test
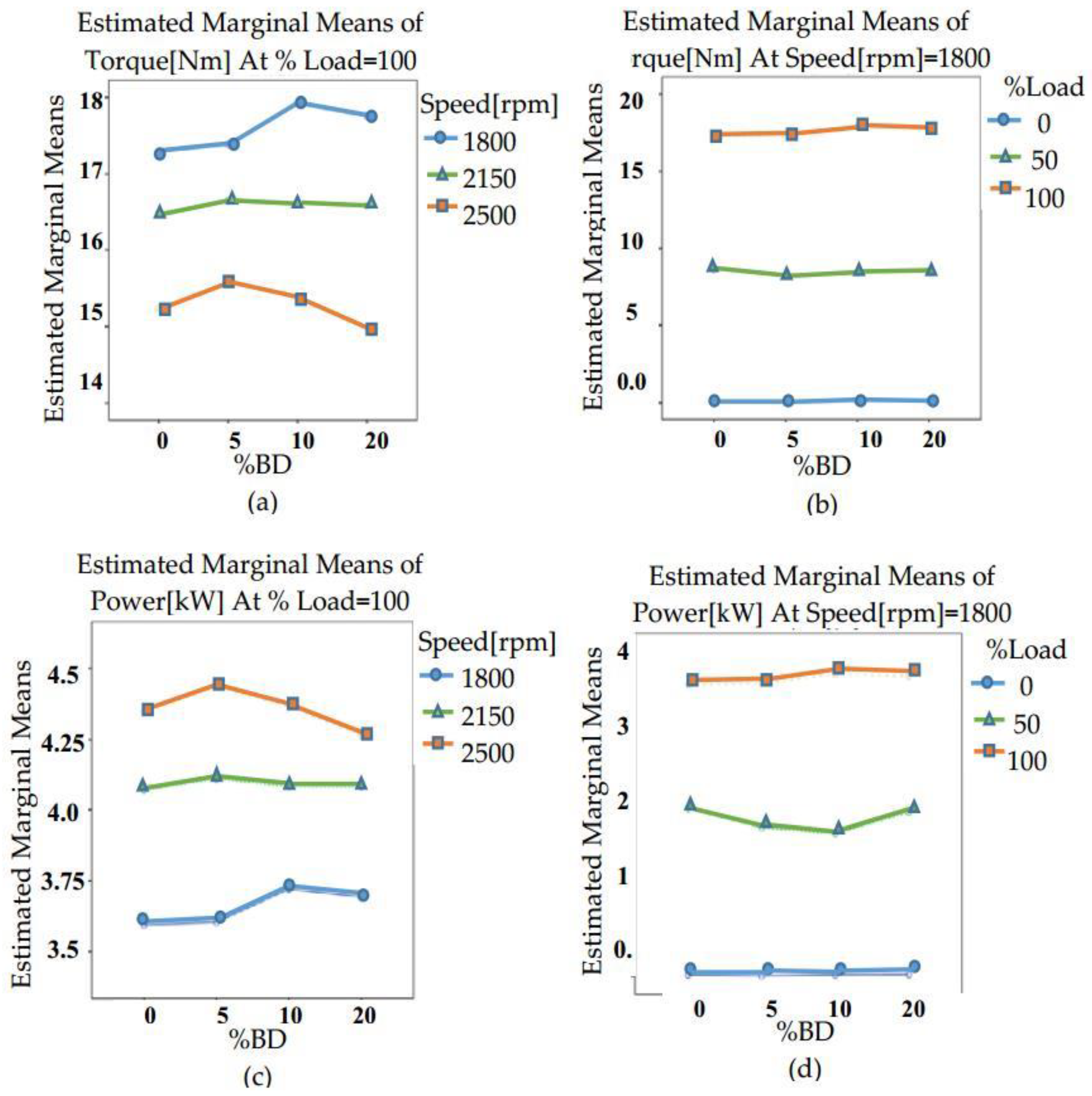
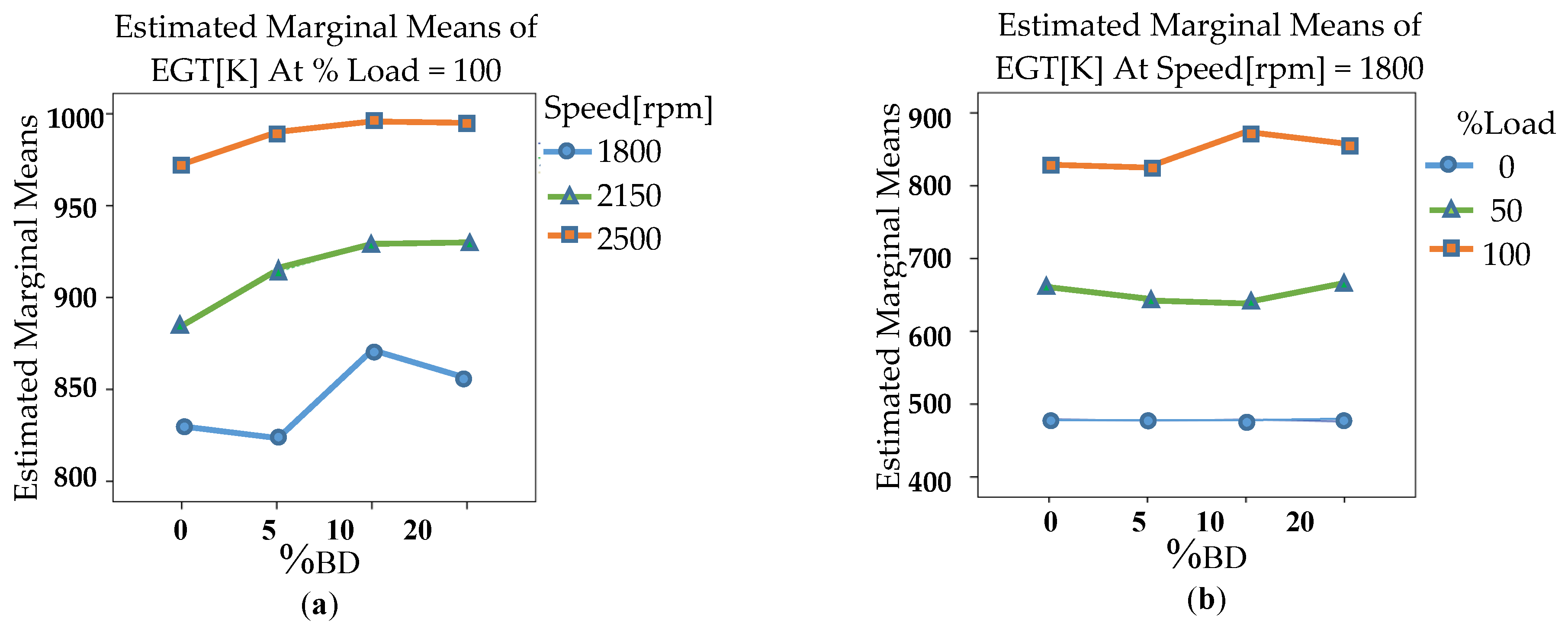
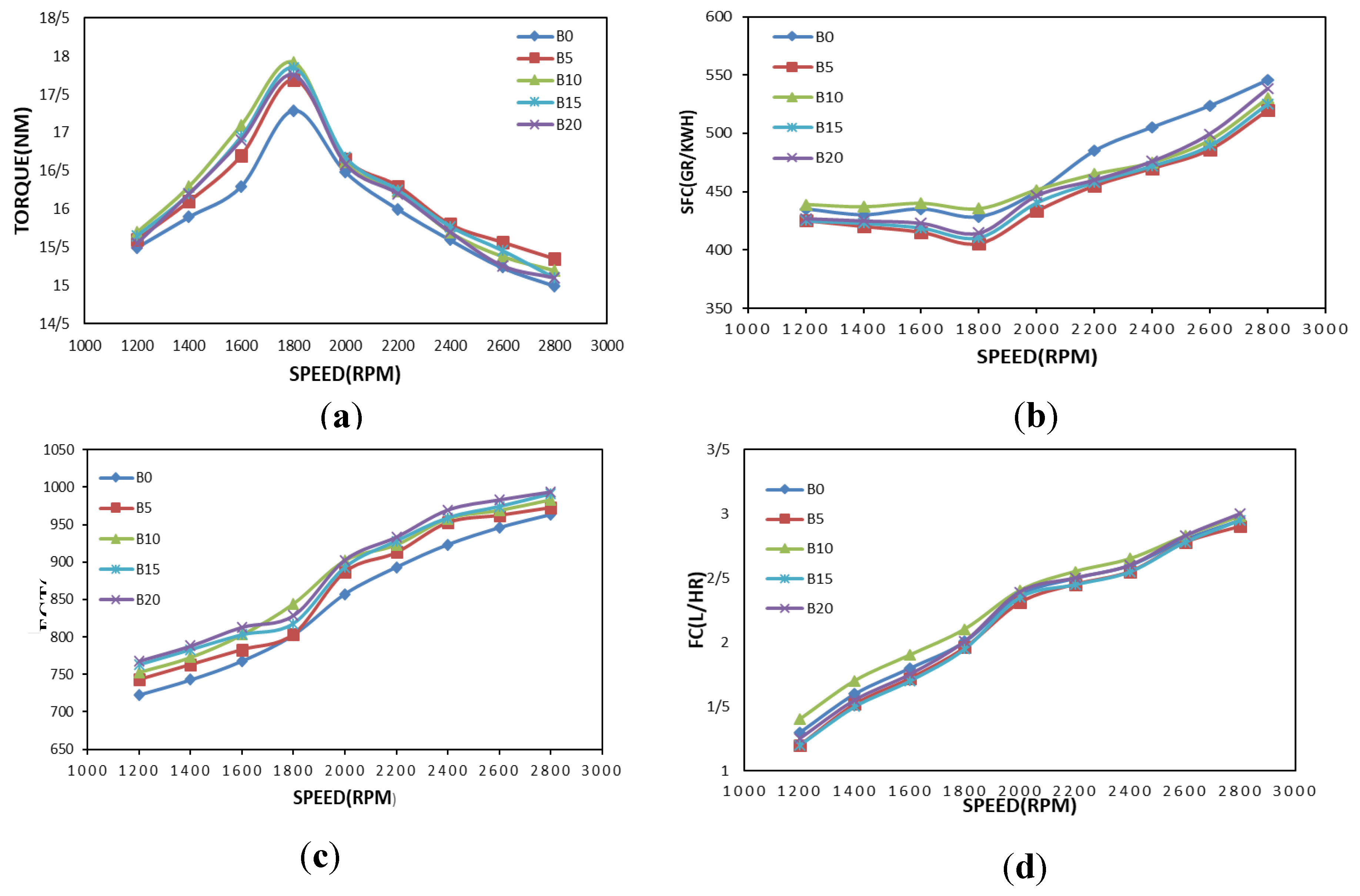
3.2. Effect of Speed, Load and %BD Variations on Engine Performance
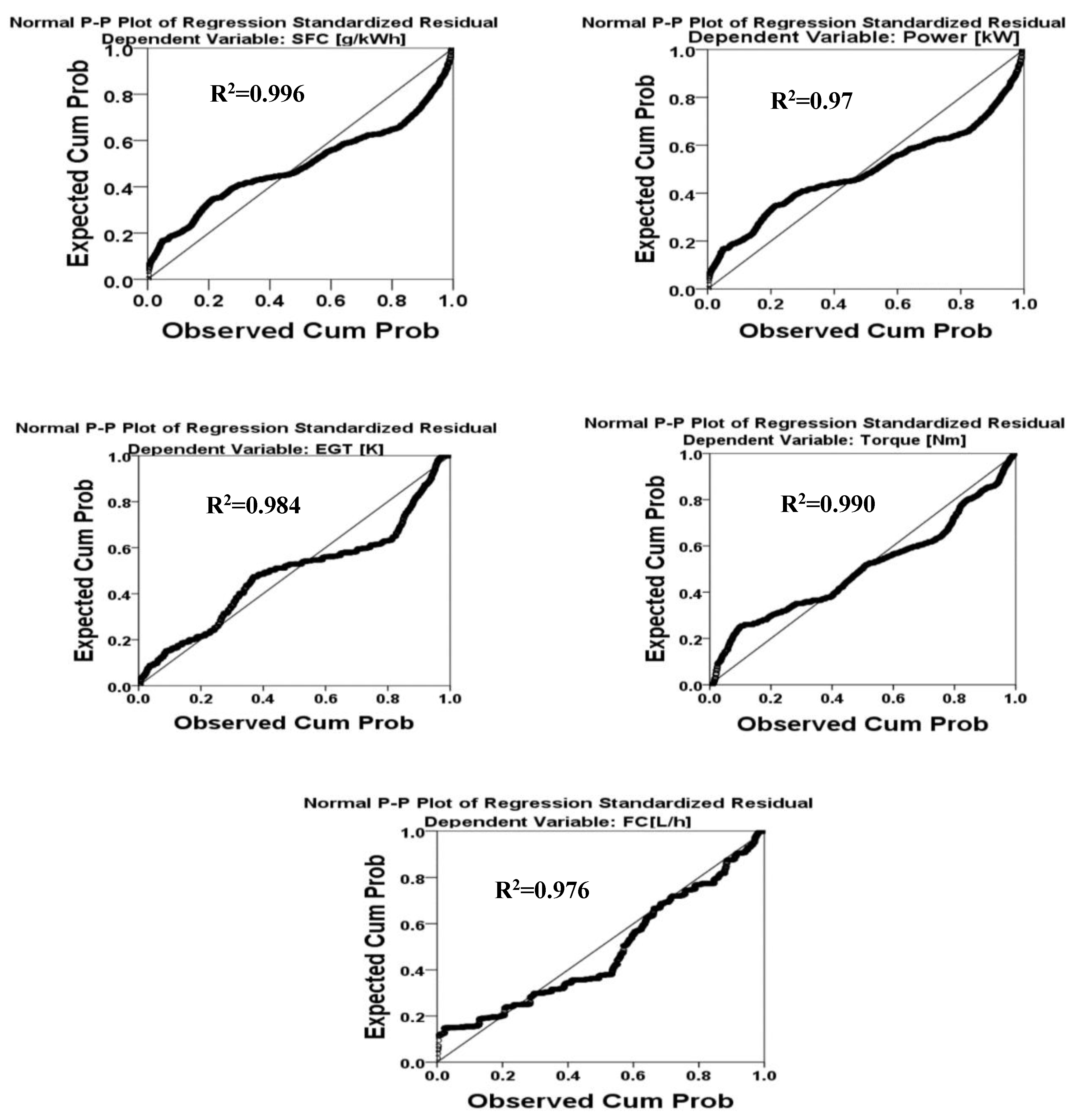
3.3. Regression Analysis of Parameters
3.3.1. Performance Evaluation Model
3.3.2. Engine Performance Prediction Equations Based on the Independent Variables
Torque
Power
SFC
FC
EGT
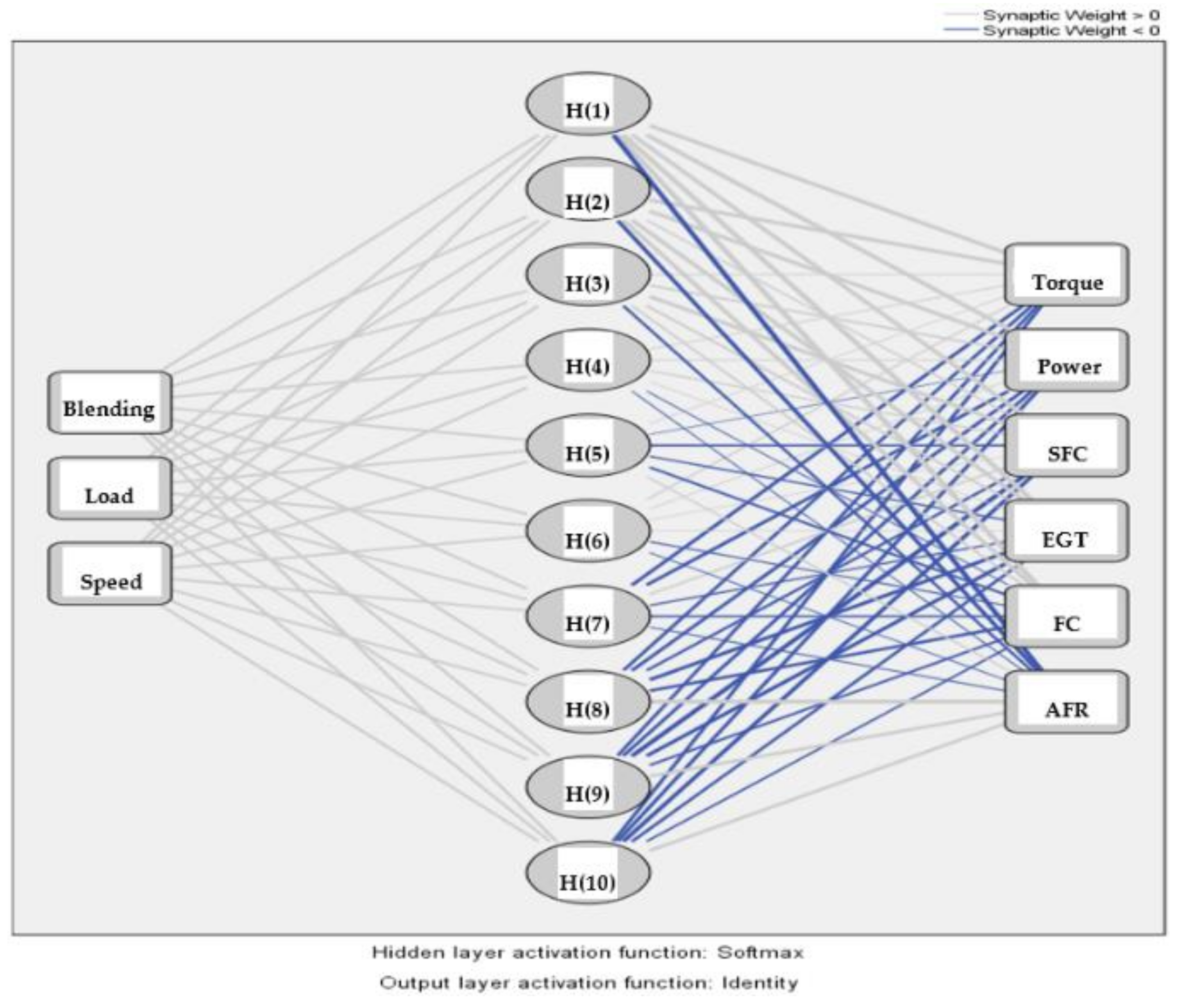
3.4. Neural Network Modeling
4. Results and Discussion of Neural Network Modeling
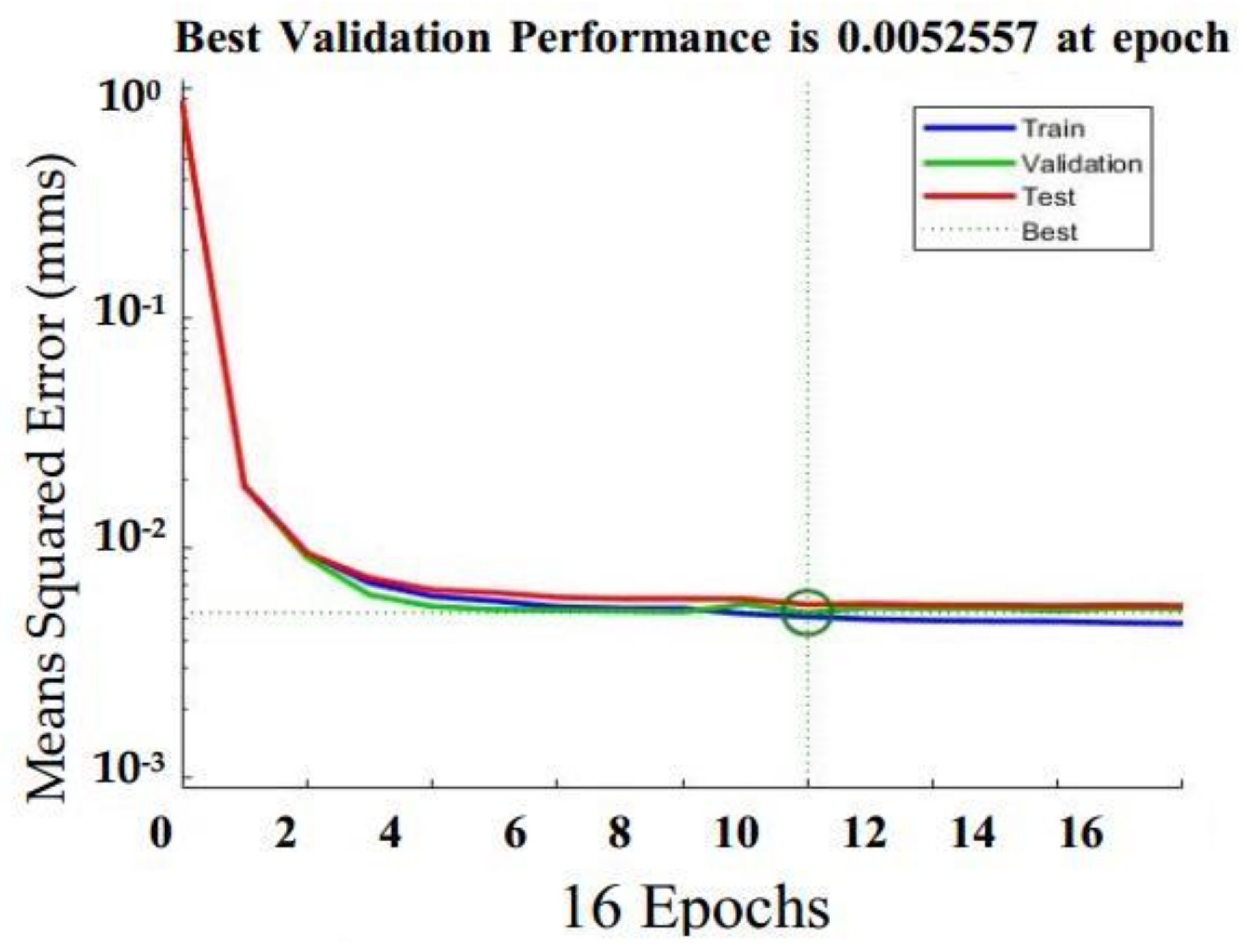
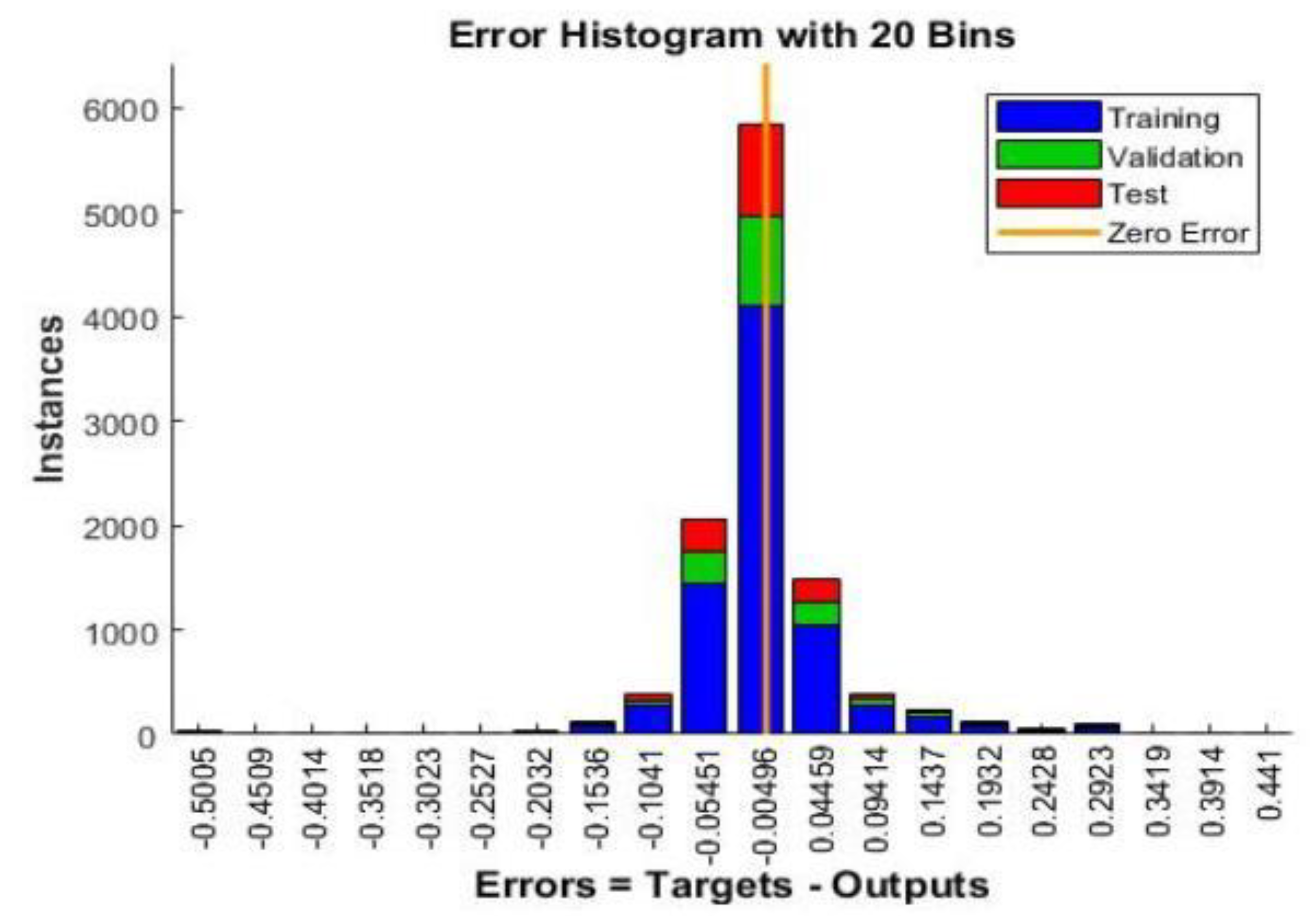
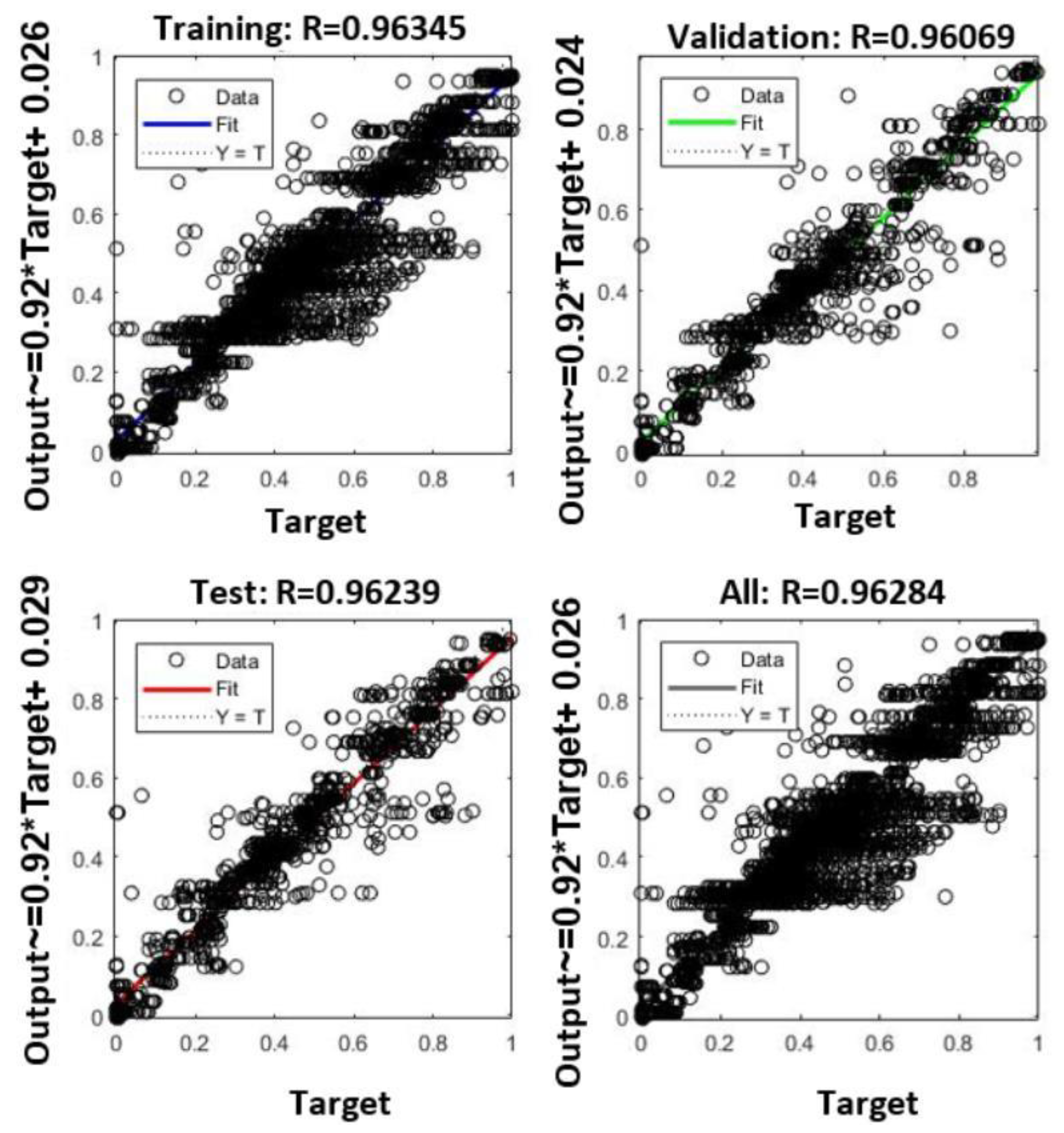
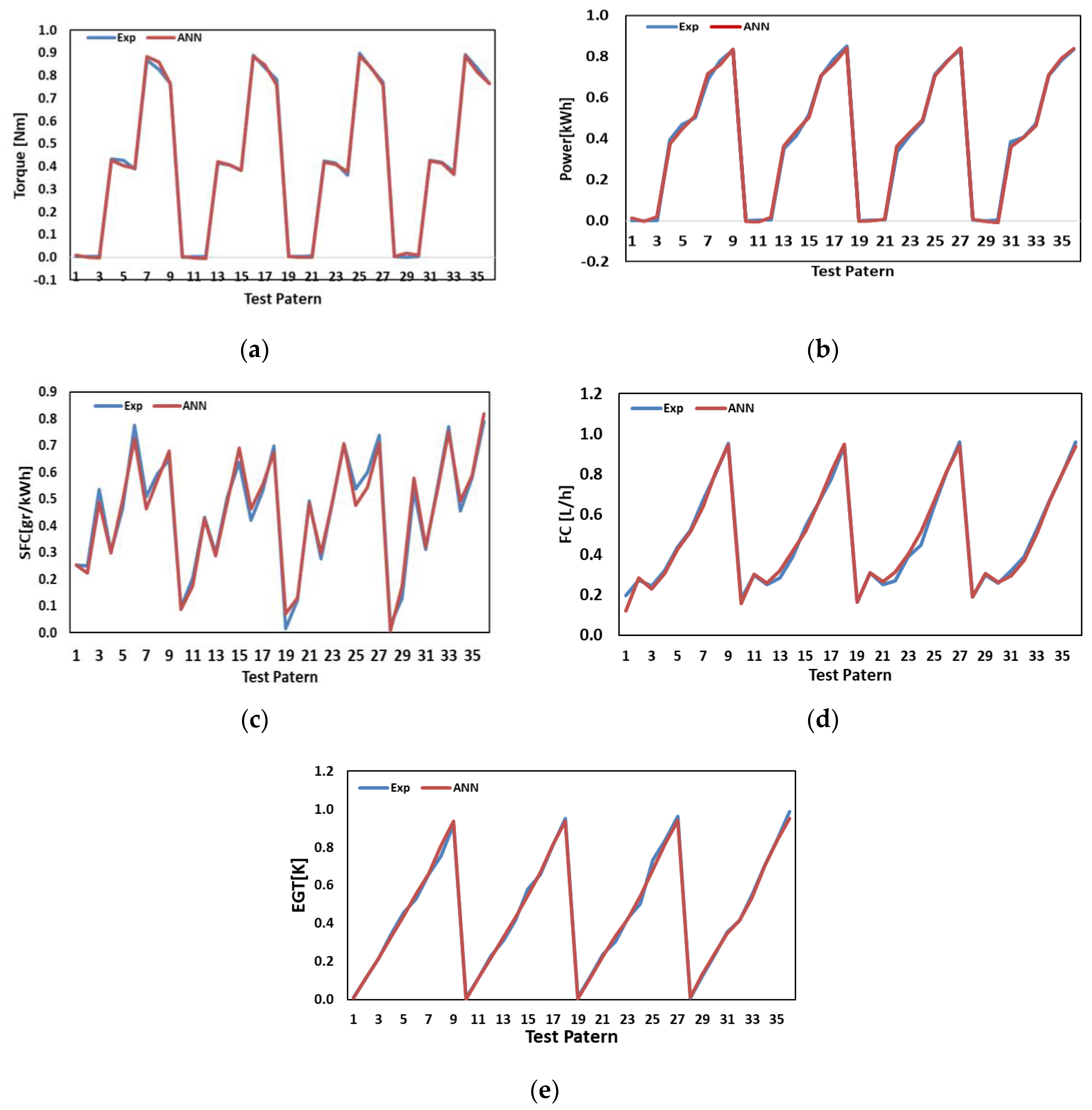
4.1. Neural Network Assessment
4.2. Use of Simulation with ANN
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| TSOB | Tomato Seed Oil Biodiesel |
| B0 | 0% Biodiesel + 100% Diesel |
| B5 | 5% Biodiesel + 95% Diesel |
| B10 | 10% Biodiesel + 90% Diesel |
| B20 | 20% Biodiesel + 80% Diesel |
| DI | Direct Injection |
| L | Load |
| T | Torque |
| P | Power |
| S | speed |
| BD | Biodiesel |
| D | Diesel |
| ASTM | American Society for Testing and Materials |
| CRD | Completely Randomized Design |
| AFR | Air–fuel ratio |
| SFC | Specific Fuel Consumption |
| BSFC | Break Specific Fuel Consumption |
| FC | Fuel Consumption |
| Nm | Newton meter |
| EGT | Exhaust Gas Temperature |
| RMSE | root-mean-square error |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Networks |
| Exp | experience |
| DF | Degrees of Freedom |
| K | Kelvin |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| LHV | Lower Heating Value |
References
- Knoblich, M.; Anderson, B.; Latshaw, D. Analyses of tomato peel and seed by products and their use as a source of carotenoids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogi, D.S.; Sidhu, J.S.; Arora, M.S.; Garg, S.K.; Bawa, A.S. Effect of Tomato Seed Meal Supplementation On the Dough and Bread Characteristics of Wheat (Pbw 343) Flour. Int. J. Food Prop. 2007, 5, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persia, M.E.; Parsons, C.M.; Schang, M.; Azcona, J. Nutritional Evaluation of Dried Tomato Seeds. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Betawi, N.A. Preliminary study on tomato pomace as unusual feedstuff in broiler diets. Pak. J. Nutr 2005, 1, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Karami, R.; Kamgar, S.; Karparvarfard, S.H.; Rasul, M.G.; Khan, M.M.K. Biodiesel production from tomato seed and its engine emission test and simulation using Artificial Neural Networ. J. Oil Gas Petrochem. Technol. 2019, 1, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrè, A.M.; Sicari, V.; Capocasale, M.; Zappia, C.; Pellicanò, T.M.; Poiana, M. Physico-chemical properties of tomato seed oil (Solanum lycopersicum L) for biodiesel production. Acta Hortic. 2015, 1081, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrè, A.M.; Capocasale, M.; Zappia, C.; Sicari, V.; Pellicanò, T.M.; Poiana, M.; Panzera, G. Tomato seed oil for biodiesel production. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B. Experimental Investigation and Mathematical Modelling of Combustion Using Biodiesel from Restaurant Waste Cooking Oil. JER 2010, 17, 60–70. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, M.; Rasul, M.G.; Ashwath, N.; Nabi, M.D.N. The potential of utilising papaya seed oil and stone fruit kernel oil as non-edible feedstock for biodiesel production in Australia—A review. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, R.L.; Graboski, M.S.; Alleman, T.L.; Herring, A.M.; Tyson, K.S. Impact of Biodiesel Source Material and Chemical Structure on Emission of Criteria Pollutants from a Heavy-duty Engine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A.; Kaul, H.P.; Senn, T.; Aufhammer, W. Costs of Ethanol Production from Winter Cereals. The Effect of Growing Conditions and Crop Production Intensity Levels. Mech. Eng. 2002, 15, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Rasul, M.G.; Ashwath, N. Production optimization and quality assessment of papaya (Carica papaya) biodiesel with response surface methodology. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 156, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B. The effect of ethyl esters of fatty acids in biodiesel fuel on diesel engine performance. Available online: https://www.civilica.com/Paper-CCI04-CCI04_064.html (accessed on 8 August 2019).
- Anwar, M.; Rasul, M.G.; Ashwath, N. The synergistic effects of oxygenated additives on papaya biodiesel binary and ternary blends. Fuel 2019, 256, 115980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, S.; Vivek, S.; Shri, K.R.; Sudharsan, R.S.; Saravana, K.N. Investigation of biodiesel obtained from tomato seed as a potential fuel alternative in a CI engine. Biofuels 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Armas, O.; Rodrı´guez-Fernandez, J. Effect of Biodiesel Fuels on Diesel Engine Emissions. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 3, 198–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, S.; Mıguez, J.L.; Porteiro, J.; Granada, E.; Moran, J.C. Performance and Exhaust Emissions in the use of Biodiesel in Outboard Diesel Engines. Fuel 2007, 86, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Grift, T.; Hansen, A. Effect of Biodiesel on Engine Performances and Emissions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi Neicharan, M.; Ghobadian, B.; Najafi, G. Experimental Investigation of a Diesel Engine Performance Parameters Using Biodiesel Fuel. J. Engine Res. 2009, 16, 29–35. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Sundarapandian, S.; Devaradjane, G. Performance and Emission Analysis of Bio Diesel Operated CI Engine. J. Eng. Comput. Archit. 2007, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Cheung, C.S.; Zhang, W.G.; Huang, Z. Combustion, performance and emission characteristics of a di diesel engine fueled with ethanol-biodiesel blends. Fuel 2011, 90, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, M.N.; Rahman, M.M.; Akhter, M.S. Biodiesel from cotton seed oil and its effect on engine performance and exhaust emissions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2009, 29, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, M.; Atmaca, M. Use of Hazelunt Kernel Oil Methyl Ester and Its Blends as Alternative Fuels in Diesel Engines. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2008, 32, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.H.; Taghizadeh-Alisaraei, A.; Ghobadian, B.; Abbaszadeh-Mayvan, A. Effect of added alumina as Nano-catalyst to diesel-biodiesel blends on performance and emission characteristics of CI engine. Energy 2017, 124, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaafi, T.; Velraj, R. Influence of alumina nanoparticles, ethanol and isopropanol blend as additive with diesel soybean biodiesel blend fuel: Combustion, engine performance and emissions. Renew. Energy 2015, 80, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari-maleney, K.; Taghizadeh-alisaraei, A.; Ghobadian, B.; Abbaszadehmayvan, A. Analyzing and evaluation of carbon nanotubes additives to diesohol-B2 fuels on performance and emission of diesel engines. Fuel 2017, 196, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Das, L.M. Biodiesel development and characterization for use as a fuel in compression ignition engines. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2001, 123, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeckas, G.; Slavinskas, S. The Effect of Rapeseed Oil Methyl Ester on Direct Injection Diesel Engine Performance and Exhaust Emissions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 1954–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan, J.; Bermudez, V.; Tormos, B.; Pla, B. Comparative Analysis of a DI Diesel Engine Fuelled with biodiesel Blends during the European MVEG-A Cycle. Performance and Emissions. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 33, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Hanna, M.A. Biodiesel production a review. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 70, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalgundwar, A.; Paul, B.; Sharma, S.K. Comparison of performance and emissions characteristics of DI CI engine fuelled with dual biodiesel blends of palm and jatropha. Fuel 2016, 173, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavafa, M.; Eshghi, H.; Ghobadian, B.; Farzad, A.; Tabasizadeh, M. Biodiesel extraction from poultry fatty oil containing high free fatty acid. In Proceedings of the Fifth Iranian Fuel and Combustion Conference, Tehran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran, 5–6 February 2014. (In Persian). [Google Scholar]
- Mbarawa, M.; Milton, B.E.; Casey, R.T.; Miao, H. Fuel injection characteristics of diesel stimulated natural gas combustion. Ind. Energy Res. 1999, 23, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B.; Torkian, M.; Hejazi, M.A.; Zamzamian, A.A. Effect of Microalgae Biodiesel on Performance Parameters and Exhaust Emissions from IDI Diesel Engine. Fuel Combust. 2012, 4, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sabet Sarvestani, N.; Rohani, A.; Farzad, A.; Aghkhani, M.H. Modeling of specific fuel consumption and emission parameters of compression ignition engine using Nano fluid combustion experimental data. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 154, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B. Artificial neural networks used for the prediction of the diesel engine performance and pollution of waste cooking oil biodiesel. Modares Mech. Eng. 2011, 11, 11–20. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, R.; Savadkouhi, L.; Ghobadian, B.; Mirmohammadi, A.; Rostami, S. Numerical study of Injection Pressure and Timing Effects on a Diesel Engine Performance using Biodiesel Fuel. Biomed. Eng. J. 2013, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaeefard, M.H.; Tahani, M.; Etghani, M.M.; Akbari, M. Investigation of performance and exhaust emissions in direct injection engine using coconut oil biodiesel. J. Sel. Top. Energy 2014, 1, 1–7. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Gumus, M.; Kasifoglu, S. Performance and emission evaluation of a compression ignition engine using a biodiesel (apricot seed kernel oil methyl ester) and its blends with diesel fuel. Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakci, M.; Ozsezen, A.; Arcaklioglu, E.; Erdil, A. Prediction of performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine fuelled with biodiesel produced from waste frying palm oil. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 9268–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, S.; Ghobadian, B.; Savadkouhi, L.; Ebrahimi, R. Experimental Investigation of Effect of Injection Pressure on Performance of a Diesel Engine Using Blends of Biodiesel and Diesel. J. Engine Res. 2010, 21, 73–82. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Adaileh, W.A.; AlQdah, K.S. Performance of Diesel Engine Fuelled by a Biodiesel Extracted from A Waste Cocking Oil. Energy Procedia 2012, 18, 1317–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Lin, H.A. Diesel engine performance and emission characteristics of biodiesel produced by the peroxidation process. Fuel 2006, 85, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, G.H.; Ghobadian, B. Investigation of diesel engine performance and emission variables using diesel fuel and biodiesel oil palm blending. In Proceedings of the First Iranian Thermal Science Conference, Mashhad, Iran, 8 February 2008. (In Persian). [Google Scholar]


| Test Name | Unit | TSOB Result | Limit Range | Test Method STM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kin. Viscosity @40 °C | cSt | 5 | 1.9–6 | D445 |
| Density-@15 °C | kg/m3 | 883 | max 900 | D4052 |
| Cloud Point | °C | 12 | min −7 | D2500 |
| Flash Point (Closed Cup) | °C | 190 | min 130 | D93 |
| TAN | mg KOH/g | 0.74 | max 0.8 | D974 |
| Water & Sediment | vol.% | 0.05 | max 0.05 | D96–D2273 |
| Copper Corrosion @ | 100 °C | 1a | D130 | |
| Sulfated Ash | wt% | 0.02 | max 0.02 | D874 |
| Sulfur | ppm | 172 ppm | D4294 | |
| Cetane Index | 0 | 47.7 | min 47 | D976 |
| Rams bottom Carbon Residue | wt% | 0.05 | D524 |
| Property | Specifications, Model | Property | Specifications, Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | LD510 | Power (N DIN 70020) | 8.2 kW |
| Number of cylinders | 1 | Power (NB DIN 6270) | 7.46 kW |
| Number of valve | 2 | Power (NA DIN 6270) | 9 |
| Max rpm | 3000 | Maximum torque@ rpm | 33 Nm |
| Cylinder stroke | 90 mm | Injection pressure | 200 bar |
| Cylinder diameter | 85 mm | Oil consumption | 0.008 kg/h |
| Total cylinder volume | 510 cc | Combustion air volume at 3000 rpm | 630 L/1 |
| Compression ratio | 17.5:1 | Max. axial load permissible for | 250 kg |
| Type of combustion chamber | B type | drive shaft in two directions |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karami, R.; Rasul, M.G.; Khan, M.M.K.; Anwar, M. Performance Analysis of Direct Injection Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel-Tomato Seed Oil Biodiesel Blending by ANOVA and ANN. Energies 2019, 12, 4421. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234421
Karami R, Rasul MG, Khan MMK, Anwar M. Performance Analysis of Direct Injection Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel-Tomato Seed Oil Biodiesel Blending by ANOVA and ANN. Energies. 2019; 12(23):4421. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234421
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarami, Rahim, Mohammad G. Rasul, Mohammad M. K. Khan, and Mohammad Anwar. 2019. "Performance Analysis of Direct Injection Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel-Tomato Seed Oil Biodiesel Blending by ANOVA and ANN" Energies 12, no. 23: 4421. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234421
APA StyleKarami, R., Rasul, M. G., Khan, M. M. K., & Anwar, M. (2019). Performance Analysis of Direct Injection Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel-Tomato Seed Oil Biodiesel Blending by ANOVA and ANN. Energies, 12(23), 4421. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234421






