Data-Driven Distributionally Robust Stochastic Control of Energy Storage for Wind Power Ramp Management Using the Wasserstein Metric
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
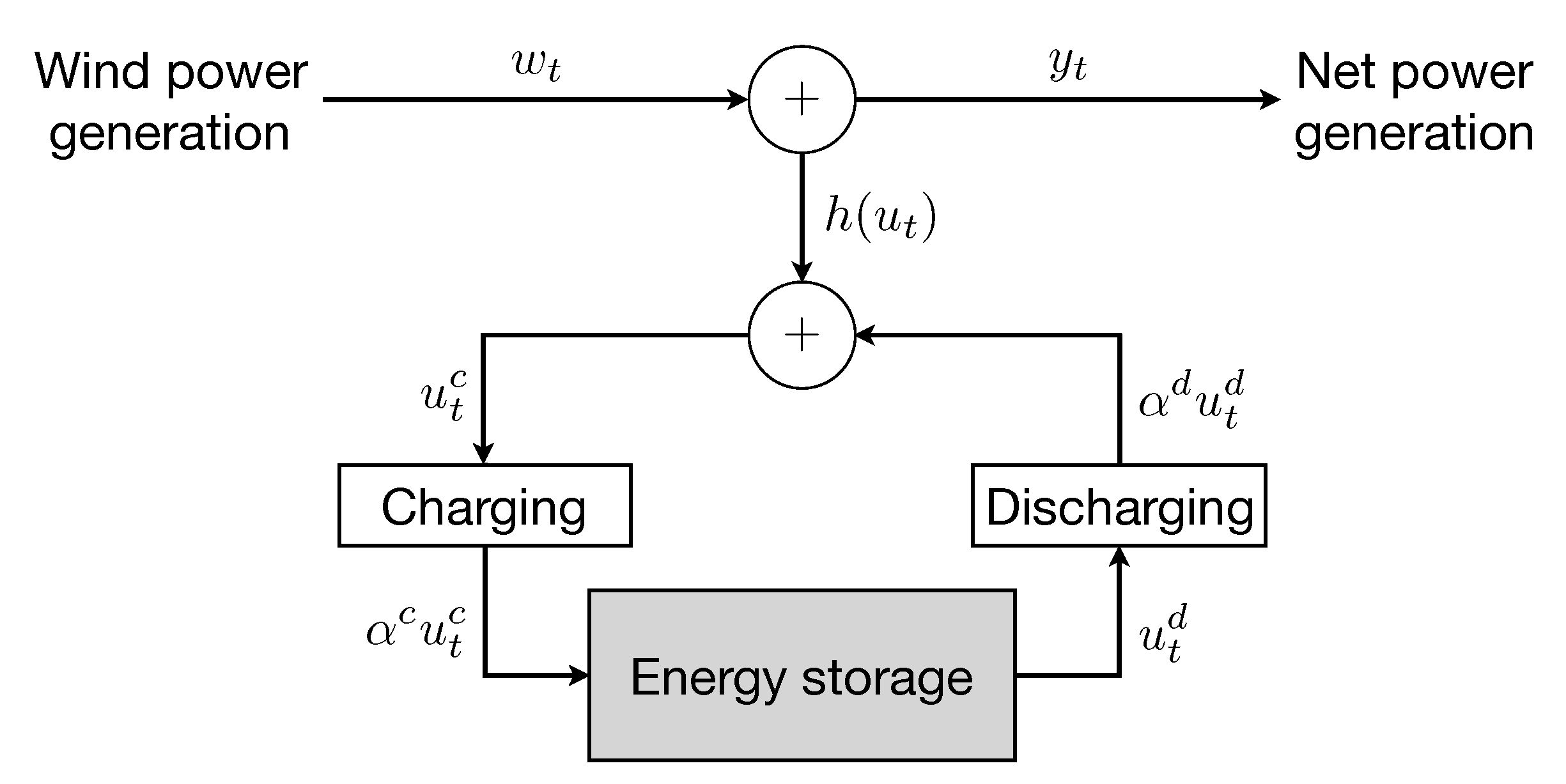
2.1. Energy Storage Model
2.2. Wind Power Ramp Management
- If , then the ramp penalty, denoted by , is linear in , i.e.,
- If , then the ramp penalty is given bywhere . In other words, for the amount exceeding the ramp-up limit, we are penalized with price greater than p.
- If , then the ramp penalty is given by
- If , then the amount below the ramp-down limit is penalized with price , i.e.,
2.3. Ambiguity of Wind Ramp Distribution
2.4. Wasserstein Distributionally Robust Stochastic Control
3. Solution via Dynamic Programming
3.1. Bellman Equation
3.2. Tractable Reformulation
3.3. Controller Design Algorithm Using Linear Programming
| Algorithm 1: Distributionally Robust Storage Controller Design via Linear Program (LP). |
 |
4. Case Studies
4.1. Comparison with Stochastic Optimal Control
4.2. Effect of Ambiguity Set Size
4.3. Effect of Storage Size
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPA | Bonneville Power Administration |
| DP | dynamic programming |
| DRO | distributionally robust optimization |
| LP | linear program (or linear programming) |
| SOC | state of charge |
References
- Wan, Y.H. Analysis of Wind Power Ramping Behavior in ERCOT; Technical Report NREL/TP-5500-49218; National Renewable Energy Lab: Golden, CO, USA, 2011.
- Huang, B.; Krishnan, V.; Hodge, B.M. Analyzing the impacts of variable renewable resources on California net-load ramp events. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto, K.; Nanahara, T.; Koshimizu, G.; Uchida, Y. New control method for regulating state-of-charge of a battery in hybrid wind power/battery energy storage system. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2006; pp. 1244–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Tewari, S.; Mohan, N. Value of NAS energy storage toward integrating wind: Results from the wind to battery project. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 28, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleke, S.; Baran, M.E.; Bhattacharya, S.; Huang, A.Q. Optimal control of battery energy storage for wind farm dispatching. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Ng, D.W.K.; Lee, W.; Schober, R. Optimal storage-aided wind generation integration considering ramping requirements. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–24 October 2013; pp. 648–653. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Kim, J.; Baldick, R. Stochastic optimal control of the storage system to limit ramp rates of wind power output. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 2256–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Baldick, R. Ramp event forecast based wind power ramp control with energy storage system. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Powell, W.B. Optimal energy commitments with storage and intermittent supply. Oper. Res. 2011, 59, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.I.; El Gamal, A. Modeling and analysis of the role of energy storage for renewable integration: Power balancing. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 4109–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha, P.; Dahleh, M. Optimal management and sizing of energy storage under dynamic pricing for the efficient integration of renewable energy. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 1164–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, D.F.; Powell, W.B. Benchmarking a scalable approximate dynamic programming algorithm for stochastic control of grid-level energy storage. INFORMS J. Comput. 2017, 30, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, I.R.; James, M.R.; Dupuis, P. Minimax optimal control of stochastic uncertain systems with relative entropy constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2000, 45, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Mannor, S. Distributionally robust Markov decision processes. Math. Oper. Res. 2012, 37, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Parys, B.P.G.; Kuhn, D.; Goulart, P.J.; Morari, M. Distributionally robust control of constrained stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2016, 61, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzortzis, I.; Charalambous, C.D.; Charalambous, T. Infinite horizon average cost dynamic programming subject to total variation distance ambiguity. SIAM J. Control Optim. 2019, 57, 2843–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I. A convex optimization approach to distributionally robust Markov decision processes with Wasserstein distance. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2017, 1, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I. A dynamic game approach to distributionally robust safety specifications for stochastic systems. Automatica 2018, 94, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I. Wasserstein distributionally robust stochastic control: A data-driven approach. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.09808. [Google Scholar]
- Mohajerin Esfahani, P.; Kuhn, D. Data-driven distributionally robust optimization using the Wasserstein metric: Performance guarantees and tractable reformulations. Math. Program. 2018, 171, 115–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Guan, Y. Data-driven risk-averse stochastic optimization with Wasserstein metric. Oper. Res. Lett. 2018, 46, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Kleywegt, A.J. Distributionally robust stochastic optimization with Wasserstein distance. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1604.02199. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Walrand, J.; Ramchandran, K. Optimal demand response with energy storage management. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications, Tainan, Taiwan, 5–8 November 2012; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Chow, Y.; Yang, J.; Rajagopal, R. Online modified greedy algorithm for storage control under uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, S.; Yang, I. Data-driven distributionally robust control of energy storage to manage wind power fluctuations. In Proceedings of the 1st IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications, Mauna Lani, HI, USA, 27–30 August 2017; pp. 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Lerma, O.; Lasserre, J.B. Discrete-Time Markov Control Processes: Basic Optimality Criteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Reemtsen, R. Discretization methods for the solution of semi-infinite programming problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1991, 71, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettich, R.; Kortanek, K.O. Semi-infinite programming: Theory, methods, and applications. SIAM Rev. 1993, 35, 380–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Still, G. Semi-infinite programming. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 180, 491–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I. A convex optimization approach to dynamic programming in continuous state and action spaces. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.03847. [Google Scholar]
- Bertsimas, D.; Tsitsiklis, J.N. Introduction to Linear Optimization; Athena Scientific: Belmont, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig, G.B. Linear Programming and Extensions; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderbei, R.J. Linear Programming; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, D.; Esfahani, P.M.; Nguyen, V.A.; Shafieezadeh-Abadeh, S. Wasserstein distributionally robust optimization: Theory and applications in machine learning. In Operations Research & Management Science in the Age of Analytics; INFORMS TutORials in Operations Research; INFORMS: Catonsville, MD, USA, 2019; pp. 130–166. [Google Scholar]
- BPA. Balancing Authority Load and Total Wind Generation. 2019. Available online: https://transmission.bpa.gov/business/operations/wind/ (accessed on 1 November 2019).





| Sample Size | 5 | 10 | 15 | Avg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stochastic optimal control | 0.9939 | 0.9902 | 0.9970 | 0.9937 |
| Distributionally robust control | 0.9612 | 0.9399 | 0.9363 | 0.9458 |
| Cost saving | 3.29% | 5.08% | 6.09% | 4.82% |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, I. Data-Driven Distributionally Robust Stochastic Control of Energy Storage for Wind Power Ramp Management Using the Wasserstein Metric. Energies 2019, 12, 4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234577
Yang I. Data-Driven Distributionally Robust Stochastic Control of Energy Storage for Wind Power Ramp Management Using the Wasserstein Metric. Energies. 2019; 12(23):4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234577
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Insoon. 2019. "Data-Driven Distributionally Robust Stochastic Control of Energy Storage for Wind Power Ramp Management Using the Wasserstein Metric" Energies 12, no. 23: 4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234577
APA StyleYang, I. (2019). Data-Driven Distributionally Robust Stochastic Control of Energy Storage for Wind Power Ramp Management Using the Wasserstein Metric. Energies, 12(23), 4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234577





