3D-Basin Modelling of the Lishui Sag: Research of Hydrocarbon Potential, Petroleum Generation and Migration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Settings
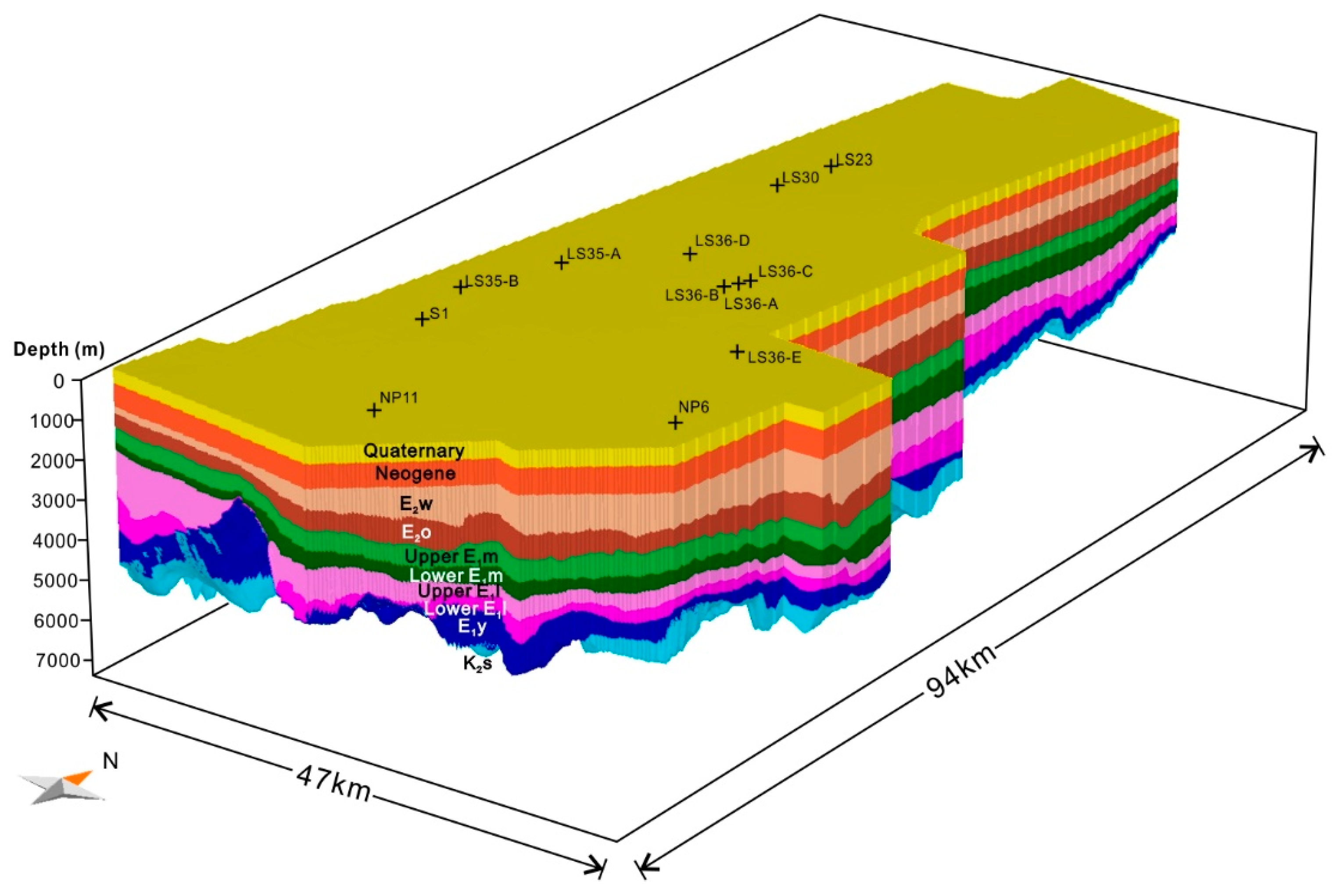
3. Construction of the Model
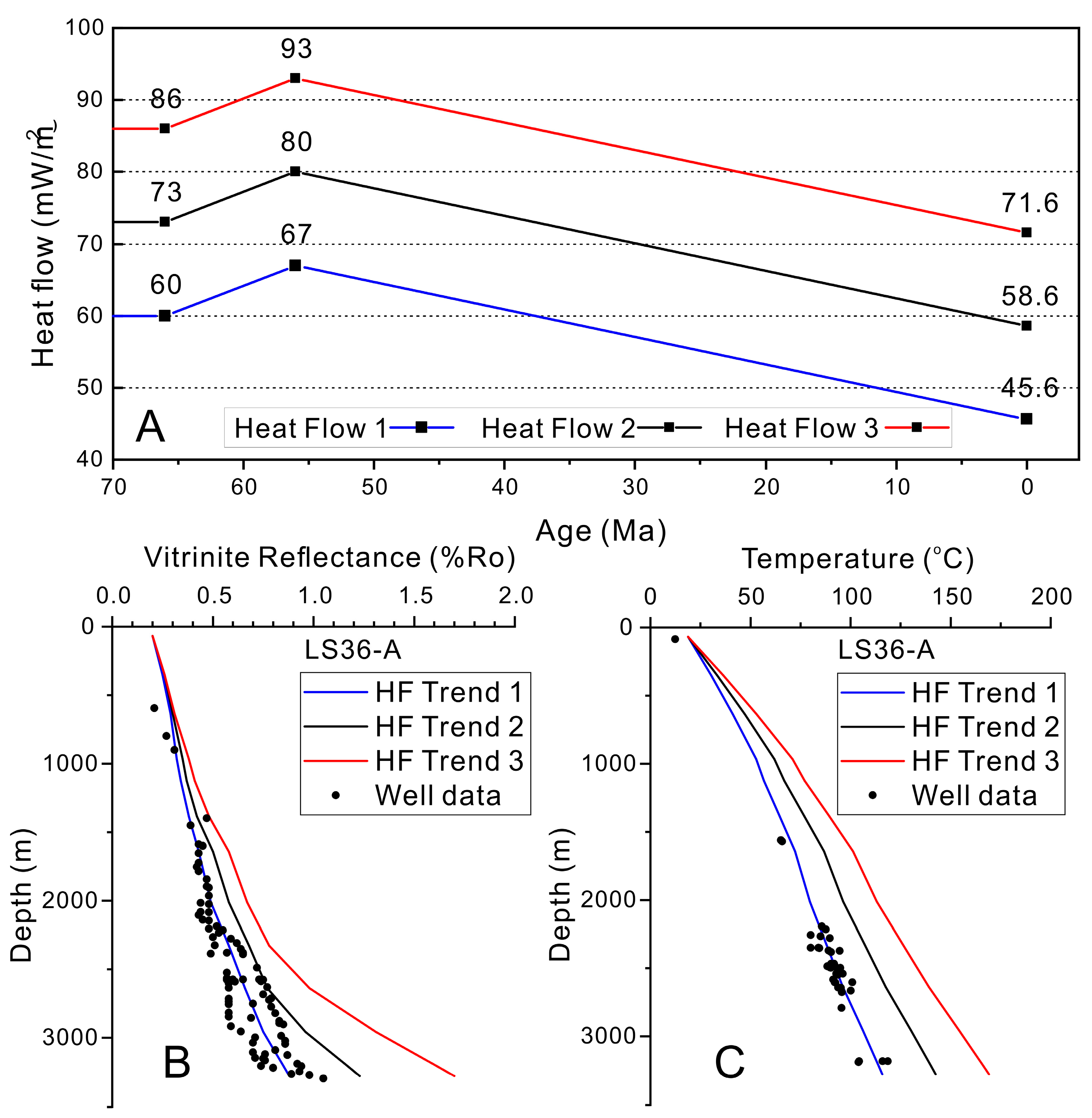
3.1. Erosion Thickness
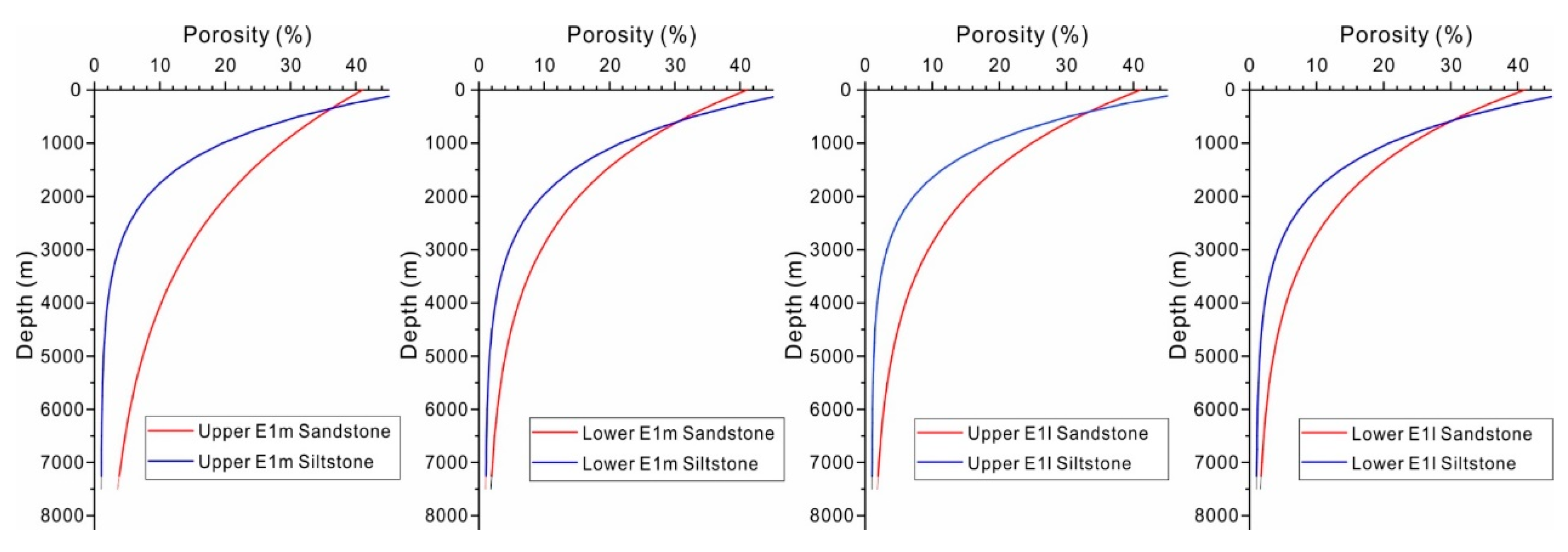
3.2. Lithology and Petroleum System Elements
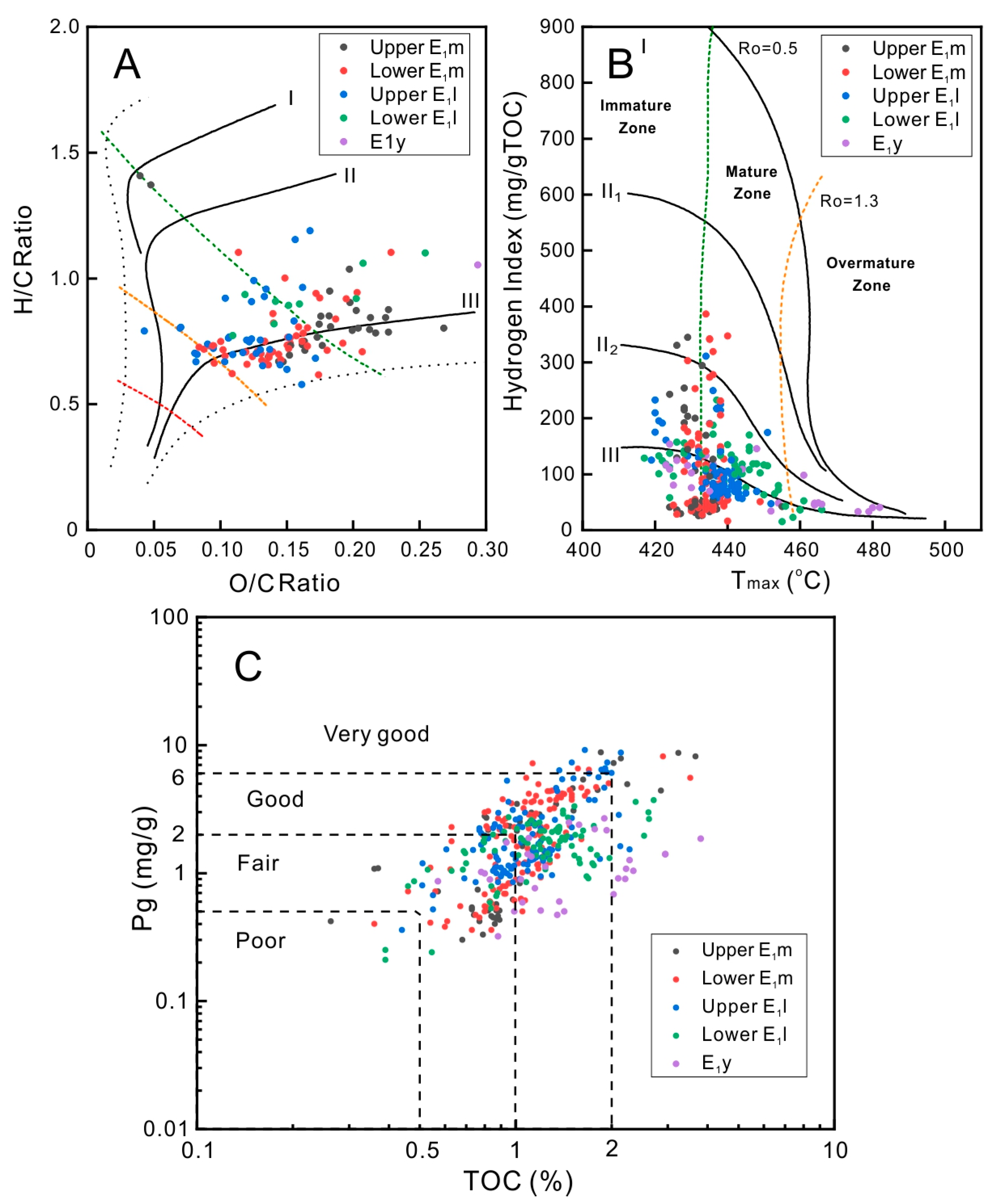
3.3. Source Rock Properties and Kinetics Model
3.4. Boundary Conditions
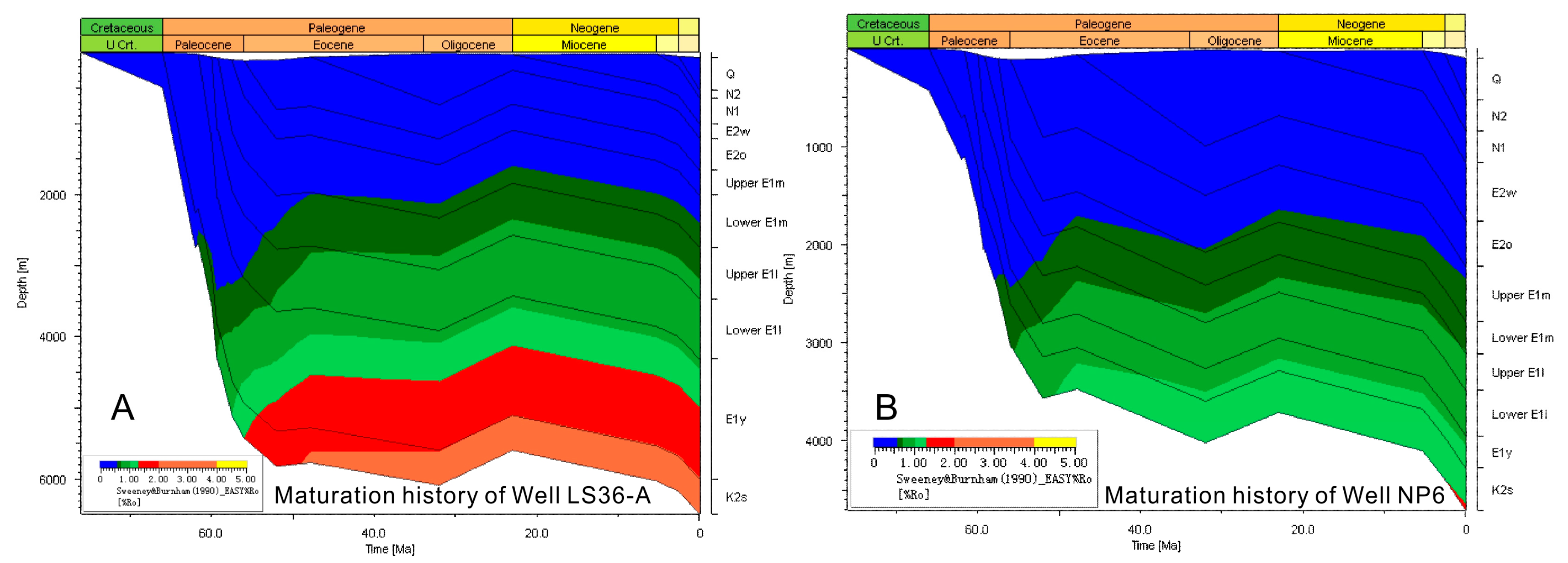
4. Study Results
5. Discussion
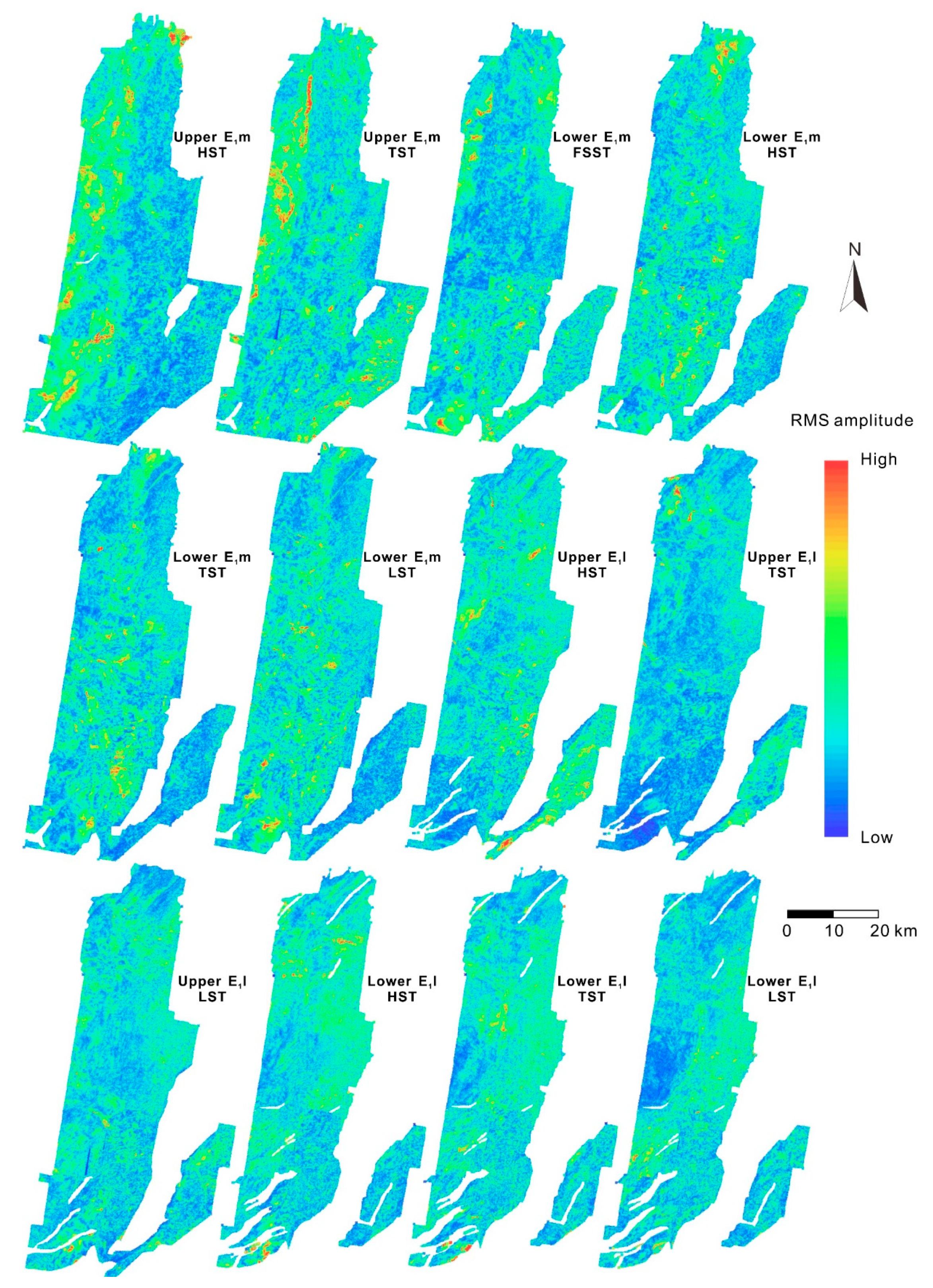
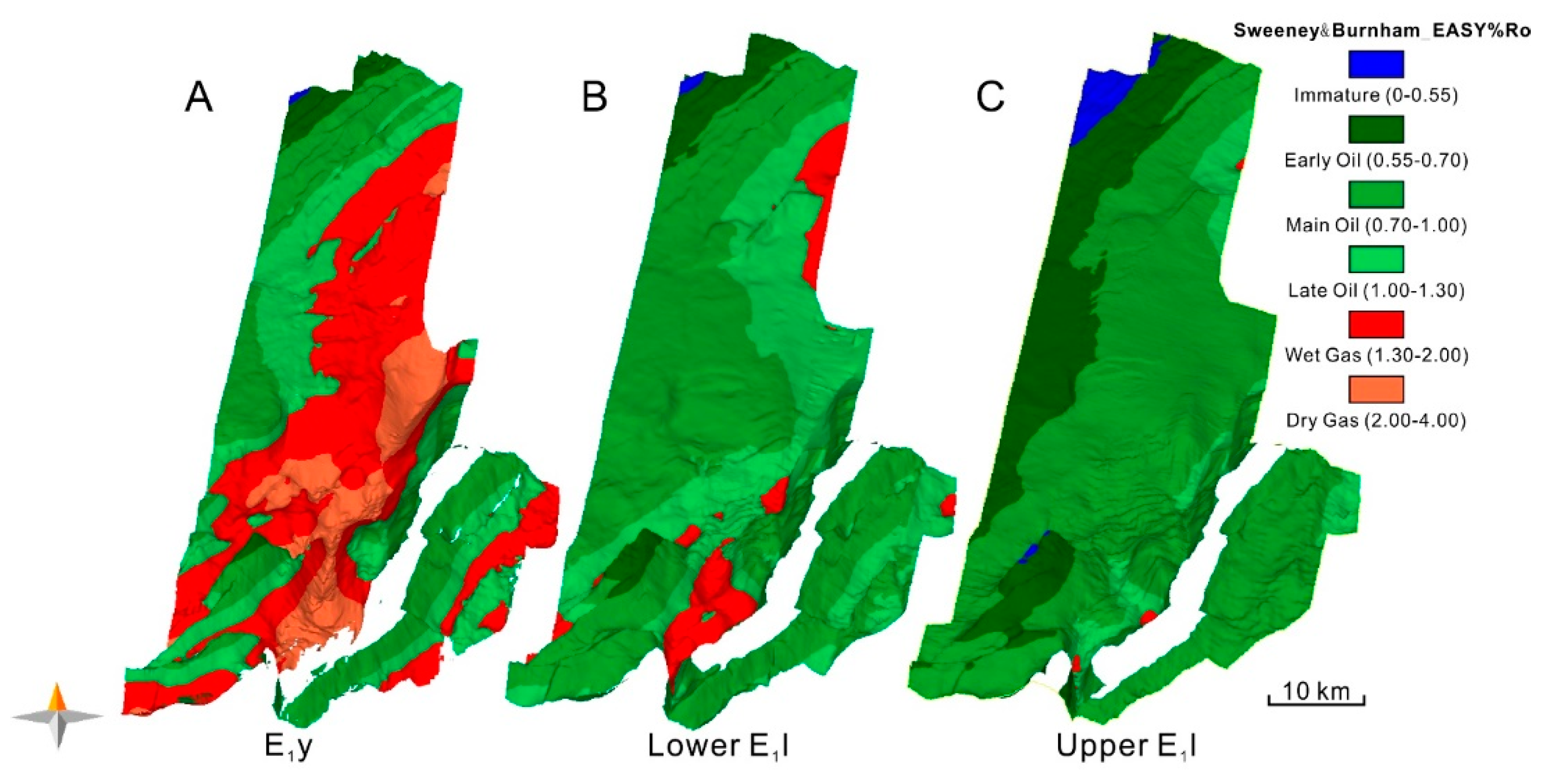
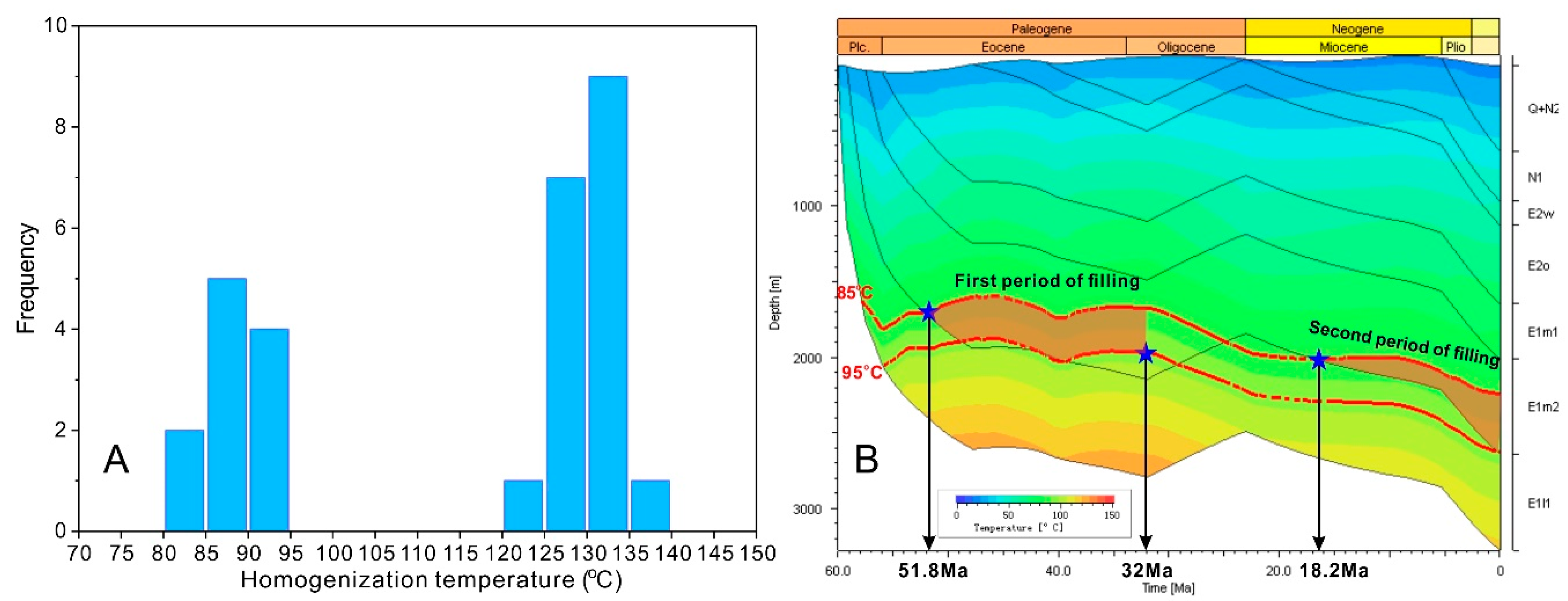
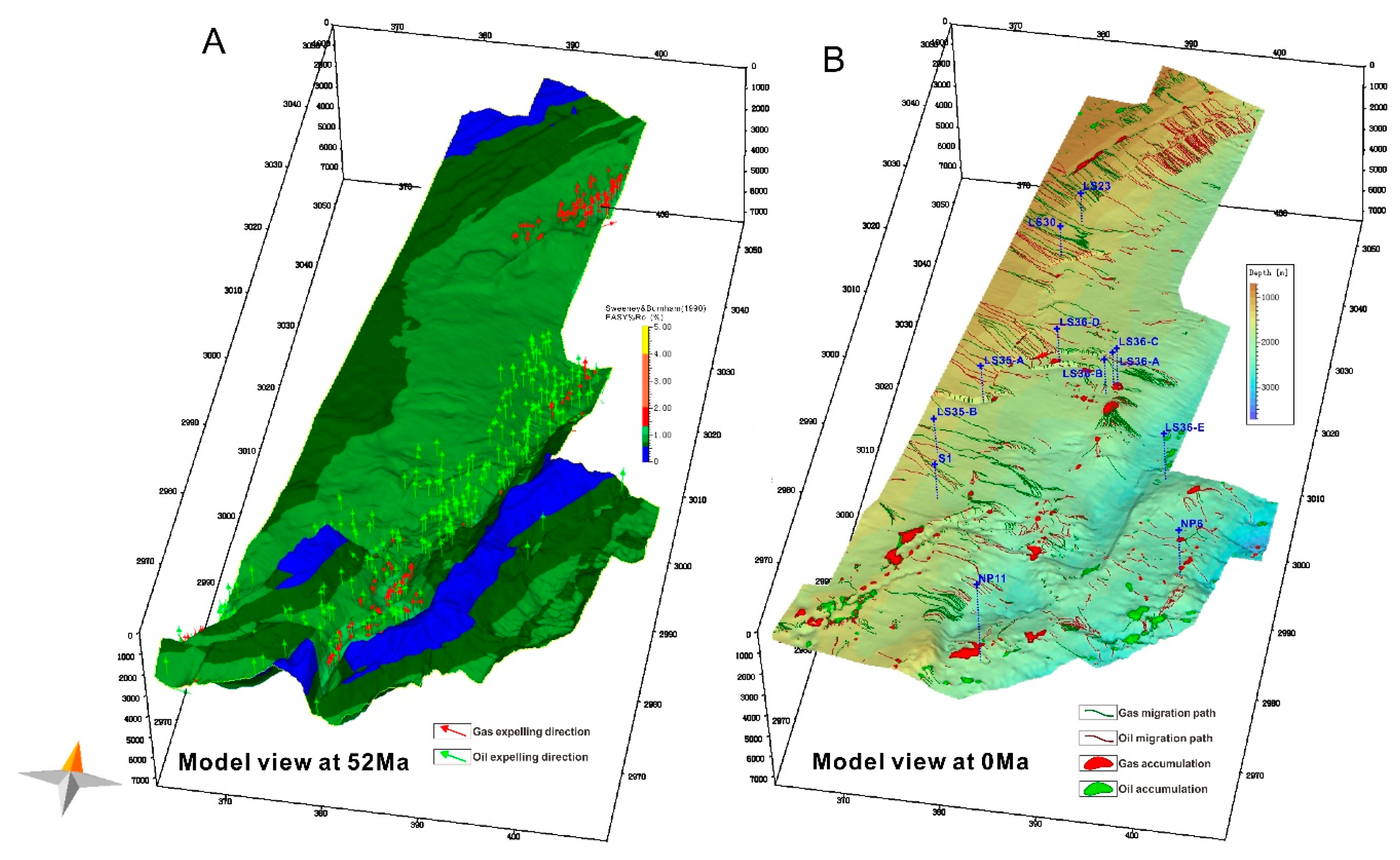
5.1. Hydrocarbon Generation and Expulsion
5.2. Hydrocarbon Migration and Accumulation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.P.; Ge, H.P.; Chen, X.D.; Deng, C.P.; Liang, D.G. Classification and origin of natural gases from Lishui Sag, the East China Sea Basin. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Wu, P.K.; Wu, Z.X. Petroleum geology and exploration potential of Lishui Sag. China Offshore Oil Gas (Geol.) 2000, 14, 384–391. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Y.; Jiang, X.D.; Xu, F.; Liu, J.S.; Hou, G.W. Geochemistry of the Paleocene in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin: Implications for Tectonic Background and Provenance. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2016, 90, 166–181. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, G.X. Three-dimensinal Structure Modeling of Lishui Depression, East China Sea Basin. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 853, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, P.H. Tectonic evolution and sequence filling of Paleocene in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 807–809, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, C.L. 3D Visualization for Detailed Sedimentary-Facies Modeling of Lishui Depression, East China Sea Basin. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 442, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.H.; Cao, L.S.; Lei, M.Z.; Wang, C.W.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, P.J. Genesis, source and charging of oil and gas in Lishui sag, East China Sea Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2014, 41, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.L.; Li, Y.J.; Du, H.L.; Zhang, Y.F. The Cenozoic structural evolution and its influences on gas accumulation in the Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 22, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S. Fine description of structure research of Lishui sag, East China Sea Basin. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 4433–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.P.; Chen, Z.Y.; Fang, L.F.; Shen, W.F. A discussion on hydrocarbon accumulation periods in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin. China offshore Oil Gas (Geol.) 2003, 17, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y. Study on hydrocarbon accumulation rule in the Lishui Sag, East China Sea Continental Shelf Basin. Master dissertation, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Welte, D.H.; Yukler, M.A. Petroleum Origin and Accumulation in Basin Evolution—A Quantitative Model. AAPG Bull. 1981, 65, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Welte, D.H.; Yalcin, M.N. Basin Modeling—A New Comprehensive Method in Petroleum Geology. Org. Geochem. 1988, 13, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, B.; Primio, R.D.; Berner, U.; Littke, R.J.G. Petroleum system evolution in the inverted Lower Saxony Basin, northwest Germany: A 3D basin modeling study. Geofluids 2013, 13, 246–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, B.; Littke, R.; Gasparik, M.; van Wees, J.D.; Nelskamp, S. Thermal evolution and shale gas potential estimation of the Wealden and Posidonia Shale in NW-Germany and the Netherlands: A 3D basin modelling study. Basin Res. 2016, 28, 2–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, C.; Astorga, A.; Littke, R.; Winsemann, J. Basin modelling of the Limon Back-arc Basin (Costa Rica): Burial history and temperature evolution of an island arc-related basin-system. Basin Res. 2008, 20, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, V.F.; Anka, Z.; Littke, R.; Rodriguez, J.F.; Horsfield, B.; di Primio, R. Burial Temperature and Maturation History of the Austral and Western Malvinas Basins, Southern Argentina, Based on 3d Basin Modelling. J. Pet. Geol. 2016, 39, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Wolf, S.; Faille, I.; Pot, D. A 3D basin model for hydrocarbon potential evaluation: Application to Congo offshore. Oil Gas Sci. Technol.-Rev. D Ifp Energies Nouv. 2000, 55, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.L.; Xu, F.; Li, J.Z.; Liu, J.S.; Hou, G.W.; Zhang, P.H. Paleocene sequence stratigraphy and depositional systems in the Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 59, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.H.; Wang, C.W.; Li, P.J.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, W.L.; Lei, M.Z. Genesis and maturity identification of oil and gas in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, H. Basin Modeling Perspectives Preface. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H.; Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H.; Zhang, J.P. Cenozoic positive inversion tectonics and its migration in the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Geol. J. 2016, 51, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Zhang, T.; Tang, X.J. Basin type and dynamic environment in the East China Sea Shelf Basin. ACTA Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, B.; Zhang, M.Q.; Wan, Z.F.; Sun, X.Y.; Lv, B.F. Structural styles and hydrocarbon prospects in the Lishui-Jiaojiang Sag, the East China Sea. S. China J. Selsmology 2007, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.L.; Xia, B. Characters of tectonic evolution of the Lishui-Jiaojiang Sag and oil accumulation. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2005, 16, 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Cukur, D.; Horozal, S.; Kim, D.C.; Han, H.C. Seismic stratigraphy and structural analysis of the northern East China Sea Shelf Basin interpreted from multi-channel seismic reflection data and cross-section restoration. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1003–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantschel, T.; Kauerauf, A.I. Fundamentals of Basin and Petroleum Systems Modeling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Baniasad, A.; Rabbani, A.; Sachse, V.F.; Littke, R.; Moallemi, S.A.; Soleimany, B. 2D basin modeling study of the Binak Trough, northwestern Persian Gulf, Iran. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenian, E.; Fathi-Mobarakabad, A.; Sachsenhofer, R.F.; Asadi-Eskandar, A. 3D Basin Modelling in the Central Persian Gulf, Offshore Iran. J. Pet. Geol. 2014, 37, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Duran, E.; di Primio, R.; Anka, Z.; Stoddart, D.; Horsfield, B. 3D-basin modelling of the Hammerfest Basin (southwestern Barents Sea): A quantitative assessment of petroleum generation, migration and leakage. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 45, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, W.G. Kerogen Studies and Geological Interpretations. J Geochem. Explor. 1977, 7, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magara, K. Thickness of Removed Sedimentary-Rocks, Paleopore Pressure, and Paleotemperature, Southwestern Part of Western Canada Basin. AAPG Bull. 1976, 60, 554–565. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Y.; Guo, T.Y.; Jiang, X.D.; Zhao, H.Q.; Wang, H.P. Erosion thickness recovery and tectonic evolution characterization of southern East China Sea Shelf Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2015, 36, 913–923. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, K.M.; Finney, S.C.; Gibbard, P.L.; Fan, J.X. The ICS International Chronostratigraphic Chart. Available online: https://dspace.library.uu.nl/handle/1874/289106 (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- Athy, L.F. Density, porosity, and compaction of sedimentary rocks. Bull. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. 1930, 14, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, A.C.; Yang, X.-S. Fast and Slow Compaction in Sedimentary Basins. SIAM J. App. Math. 1998, 59, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Xia, Q.L.; Zhou, X.H. Geologic-seismic models, prediction of shallow-water lacustrine delta sandbody and hydrocarbon potential in the Late Miocene, Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, northern China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2018, 7, 66–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyab, M.N.; Asim, S. Application of spectral decomposition for the detection of fluvial sand reservoirs, Indus Basin, SW Pakistan. Geosci. J. 2017, 21, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penguang, A.S.A.; Lubis, L.A.; Hermana, M.; Ghosh, D.P. Study of Rock Physics and Seismic Attributes of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Sabah Basin. Available online: http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/88/1/012009/meta (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- Burnham, A.K. A Simple Kinetic Model of Petroleum Formation and Cracking; Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 1989.
- Tissot, B.P.; Welte, D.H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Espitalie, J. Use of Tmax as a maturation index for different types of organic matter: Comparison with vitrinite reflectance. Thermal Model. Sediment. Basins 1986, 44, 475–496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Ge, H.P.; Yang, Y.Q.; Liang, J. Division and controlling factors of Paleocene sequence strata in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2012, 17, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.D.; Li, S.T.; Lu, Y.C.; Li, P.L.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, J.H. The tertiary sea-level changes in the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Sci. Geol. Sin. 1998, 33, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Yalçin, M.N.; Littke, R.; Sachsenhofer, R.F. Thermal History of Sedimentary Basins. In Petroleum and Basin Evolution; Welte, D.H., Horsfield, B., Baker, D.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wygrala, B.P. Integrated Study of an Oil Field in the Southern Po Basin, Northern Italy. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.B.; Liu, B.H.; Li, N.S. A probe heat flow value of the East China Sea shelf. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2006, 24, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.C.; Hu, S.B.; Cai, D.S.; Feng, X.J.; Chen, L.L.; Le, G. Present-day heat flow, thermal history and tectonic subsidence of the East China Sea Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2004, 21, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larter, S. Chemical-Models of Vitrinite Reflectance Evolution. Geol. Rundsch. 1989, 78, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerche, I.; Yarzab, R.F.; Kendall, C.G.S.C. Determination of Paleoheat Flux from Vitrinite Reflectance Data. AAPG Bull. 1984, 68, 1704–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, J.J.; Burnham, A.K. Evaluation of a Simple-Model of Vitrinite Reflectance Based on Chemical-Kinetics. AAPG Bull. 1990, 74, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.L.; Chang, X.C.; Liu, B.J.; Mao, F.M. Fluid history analysis and formation mechanism of the Yancheng petroleum reservoir. ACTA Geol. Sin. 2002, 76, 252–260. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.H.; Tarantola, A.; Wang, W.J.; Caumon, M.C.; Pironon, J.; Lu, W.J.; Yan, D.T.; Zhuang, X.G. Charge history of CO2 in Lishui sag, East China Sea basin: Evidence from quantitative Raman analysis of CO2-bearing fluid inclusions. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, N. Petrographic and stable isotopic evidences of CO2-induced alterations in sandstones in the Lishui sag, East China Sea Basin, China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 90, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Age (Ma) | Top Surface | Formation | Petroleum System Elements | Symbol | Lithology | Porosity (%) Functionvs. Depth (km) | Permeability [log(mD)] Function vs. Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.6–0 | Sea bed | Donghai Gp. | Overburden rock | Q | Siltstone (organic lean) | 54*EXP(−0.51*z) | 1.7142*ln(por)−6.3191 |
| 5.3–2.6 | T0 | Santan Fm. | Overburden rock | N2 | Siltstone (organic lean) | 54*EXP(−0.51*z) | 1.7142*ln(por)−6.3191 |
| 23–5.3 | T10 | Liulang−Longjing fms. | Overburden rock | N1 | Siltstone (organic lean) | 54*EXP(−0.51*z) | 1.7142*ln(por)−6.3191 |
| 32–23 | Erosion event | Erosion d | |||||
| 47.8–32 | T20 | Wenzhou Fm. | Overburden rock | E2w | Sandstone (typical) | 40*EXP(−0.31*z) | 1.5934*ln(x)−1.8387 |
| 52–47.8 | Erosion event | Erosion c | |||||
| 56–52 | T50 | Oujiang Fm. | Seal rock | E2o | Shale (organic lean, typical) | 69*EXP(−0.83*z) | 1.7569*ln(por)−8.5464 |
| 57.5–56 | T80 | Upper Mingyuefeng Fm. | Reservoir rock | Upper E1m | Sandstone (arkose, quartz poor) | 40*EXP(−0.37*z) | 0.2184*por−3.4052 |
| Seal rock | Siltstone (organic lean) | 49*EXP(−0.97*z) | 1.9754*ln(por)−4.0093 | ||||
| 59.2–57.5 | T83 | Lower Mingyuefeng Fm. | Reservoir rock | Lower E1m | Sandstone (arkose, quartz poor) | 40*EXP(−0.51*z) | 0.1757*por−2.4609 |
| Source rock | Siltstone (organic rich, 2–3% TOC) | 49*EXP(−0.86*z) | 1.9272*ln(por)−3.9322 | ||||
| 59.3–59.2 | Erosion event | Erosion b | |||||
| 60–59.3 | T85 | Upper Lingfeng Fm. | Source rock | Upper E1l | Siltstone (organic rich, 2–3% TOC) | 49*EXP(−1.03*z) | 1.7305*ln(por)−4.8916 |
| Reservoir rock | Sandstone (clay rich) | 40*EXP(−0.52*z) | 0.1641*por−2.9967 | ||||
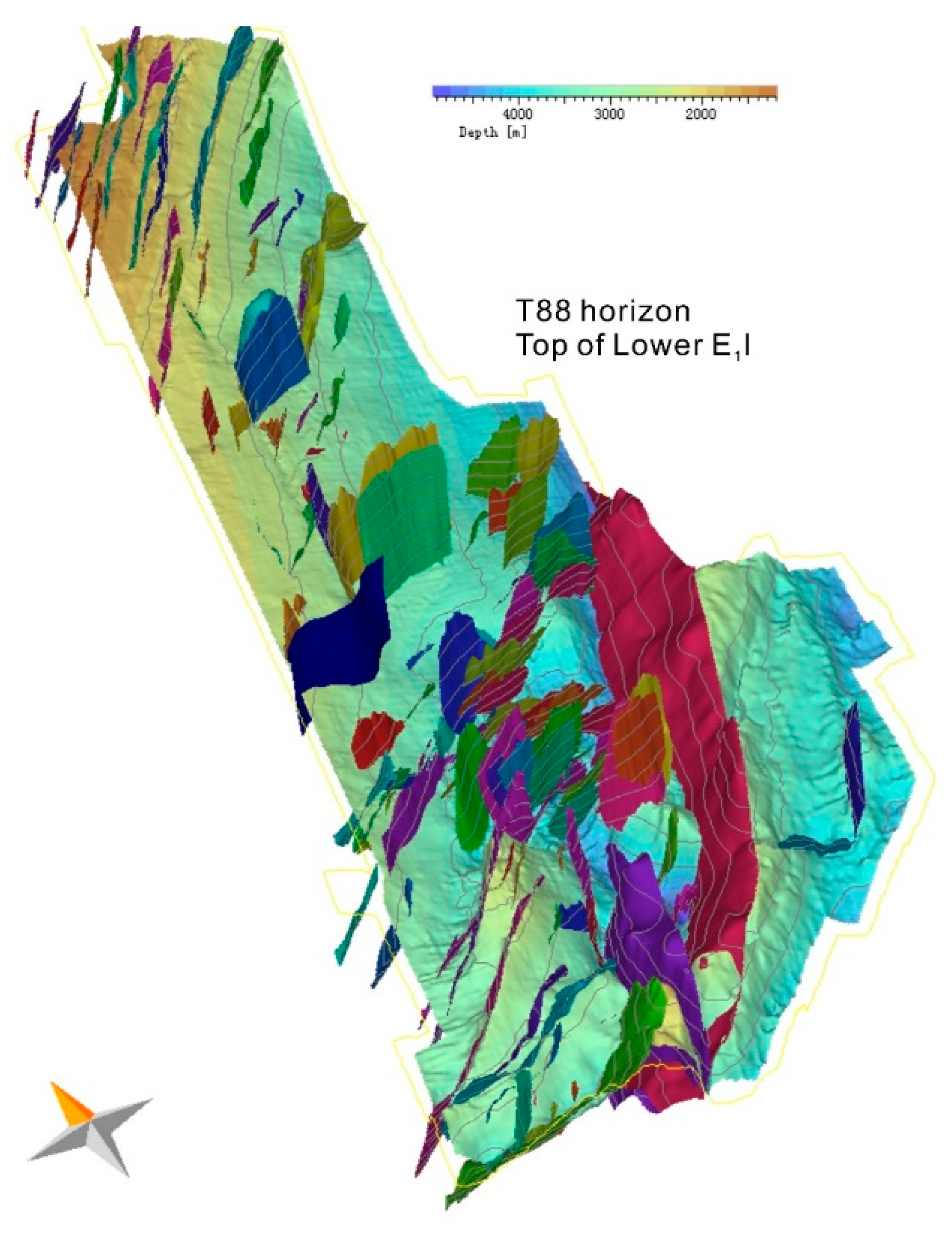
| 61.6–60 | T88 | Lower Lingfeng Fm. | Source rock | Lower E1l | Siltstone (organic rich, 2–3% TOC) | 49*EXP(−0.91*z) | 2.1441*ln(por)−4.9172 |
| Reservoir rock | Sandstone (clay rich) | 40*EXP(−0.55*z) | 0.0813*por−1.7413 | ||||
| 62–61.6 | Erosion event | Erosion a | |||||
| 66–62 | T90 | Yueguifeng Fm. | Source rock | E1y | Shale (organic rich, typical) | 69*EXP(−0.83*z) | 1.7569*ln(por)−8.5464 |
| Underburden rock | Sandstone (clay rich) | 40*EXP(−0.5*z) | 1.6492*ln(x)−2.8575 | ||||
| 76–66 | T100 | Shimengtan Fm. | Underburden rock | K2s | Granite | - | - |
| Formation | Porosity (%) | Permeability (mD) | Sample Amount | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Average | Maximum | Minimum | Average | ||
| Upper E1m | 25.10 | 1.30 | 16.88 | 236.91 | 0.01 | 34.35 | 131 |
| Lower E1m | 23.00 | 2.14 | 13.74 | 155.88 | 0.01 | 7.56 | 332 |
| Upper E1l | 14.00 | 2.60 | 11.01 | 1.53 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 137 |
| Lower E1l | 18.20 | 2.80 | 6.91 | 5.07 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 222 |
| Formation | TOC (%) | S1 + S2 (mg/g) | HI (mg/g) | Tmax (°C) | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper E1m | 1.31 | 2.41 | 148 | 397 | 51 |
| Lower E1m | 1.16 | 2.28 | 162 | 402 | 123 |
| Upper E1l | 1.15 | 2.34 | 152 | 414 | 109 |
| Lower E1l | 1.25 | 1.71 | 119 | 421 | 86 |
| E1y | 1.68 | 1.99 | 89 | 452 | 32 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Shen, W.; Li, N.; Xu, G. 3D-Basin Modelling of the Lishui Sag: Research of Hydrocarbon Potential, Petroleum Generation and Migration. Energies 2019, 12, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040650
Zhang J, Guo J, Liu J, Shen W, Li N, Xu G. 3D-Basin Modelling of the Lishui Sag: Research of Hydrocarbon Potential, Petroleum Generation and Migration. Energies. 2019; 12(4):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040650
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinliang, Jiaqi Guo, Jinshui Liu, Wenlong Shen, Na Li, and Guangchen Xu. 2019. "3D-Basin Modelling of the Lishui Sag: Research of Hydrocarbon Potential, Petroleum Generation and Migration" Energies 12, no. 4: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040650
APA StyleZhang, J., Guo, J., Liu, J., Shen, W., Li, N., & Xu, G. (2019). 3D-Basin Modelling of the Lishui Sag: Research of Hydrocarbon Potential, Petroleum Generation and Migration. Energies, 12(4), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040650





