Control Strategy for Power Conversion Systems in Plasma Generators with High Power Quality and Efficiency Considering Entire Load Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
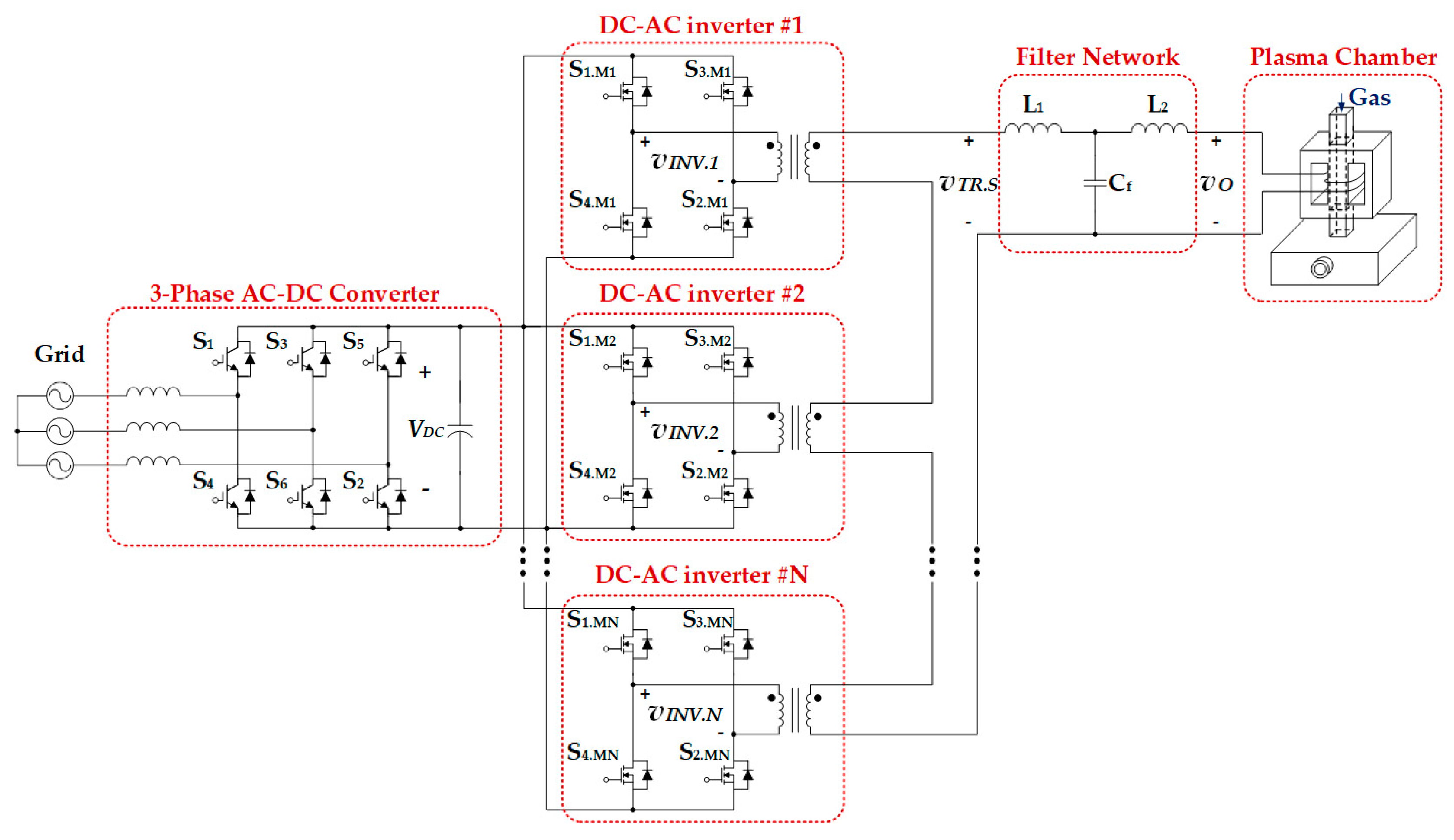
2. Conventional Control Algorithm of DC-AC Inverters for Plasma Generators
3. Proposed Control Algorithm of DC-AC Inverters for Plasma Generators
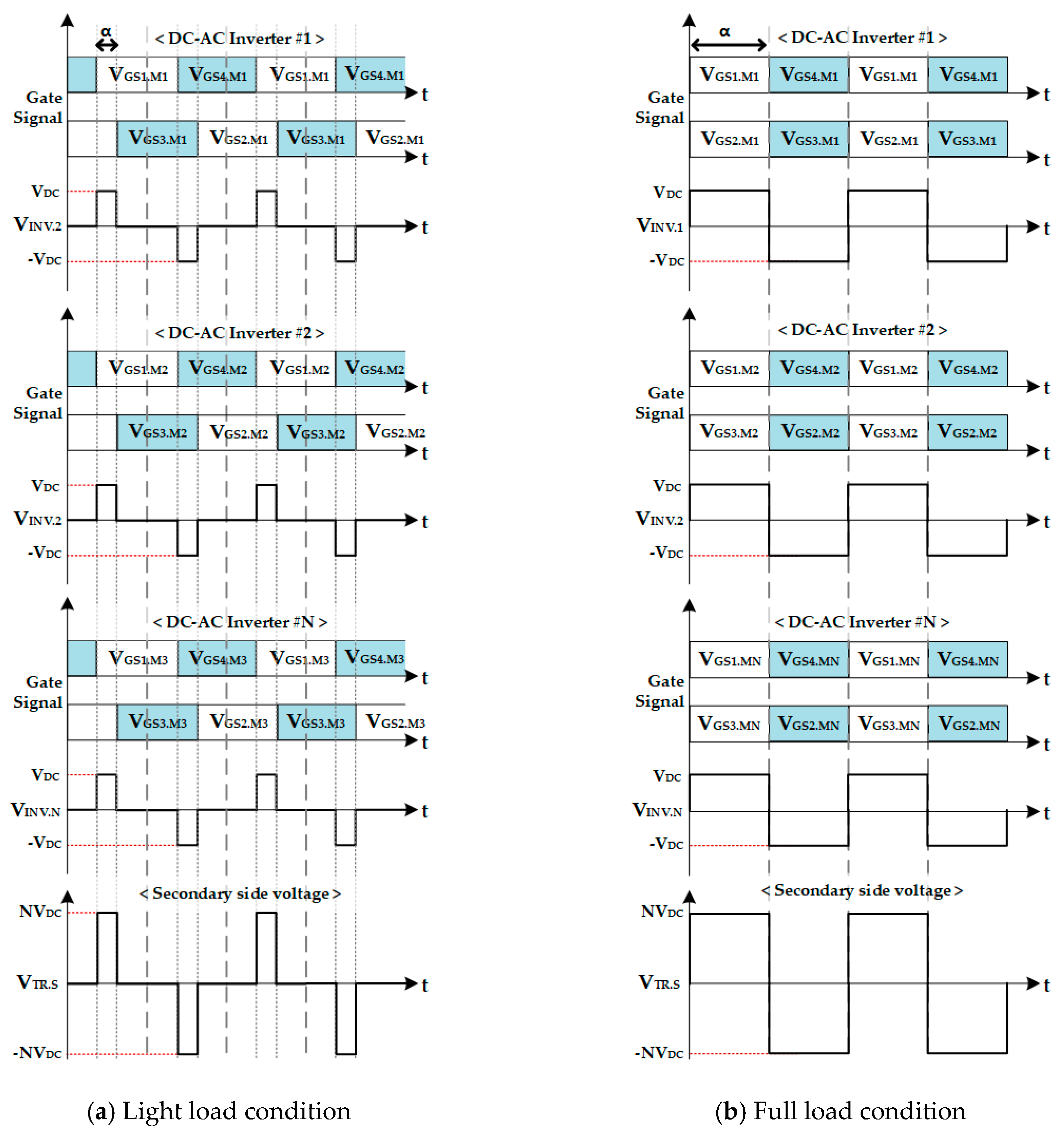
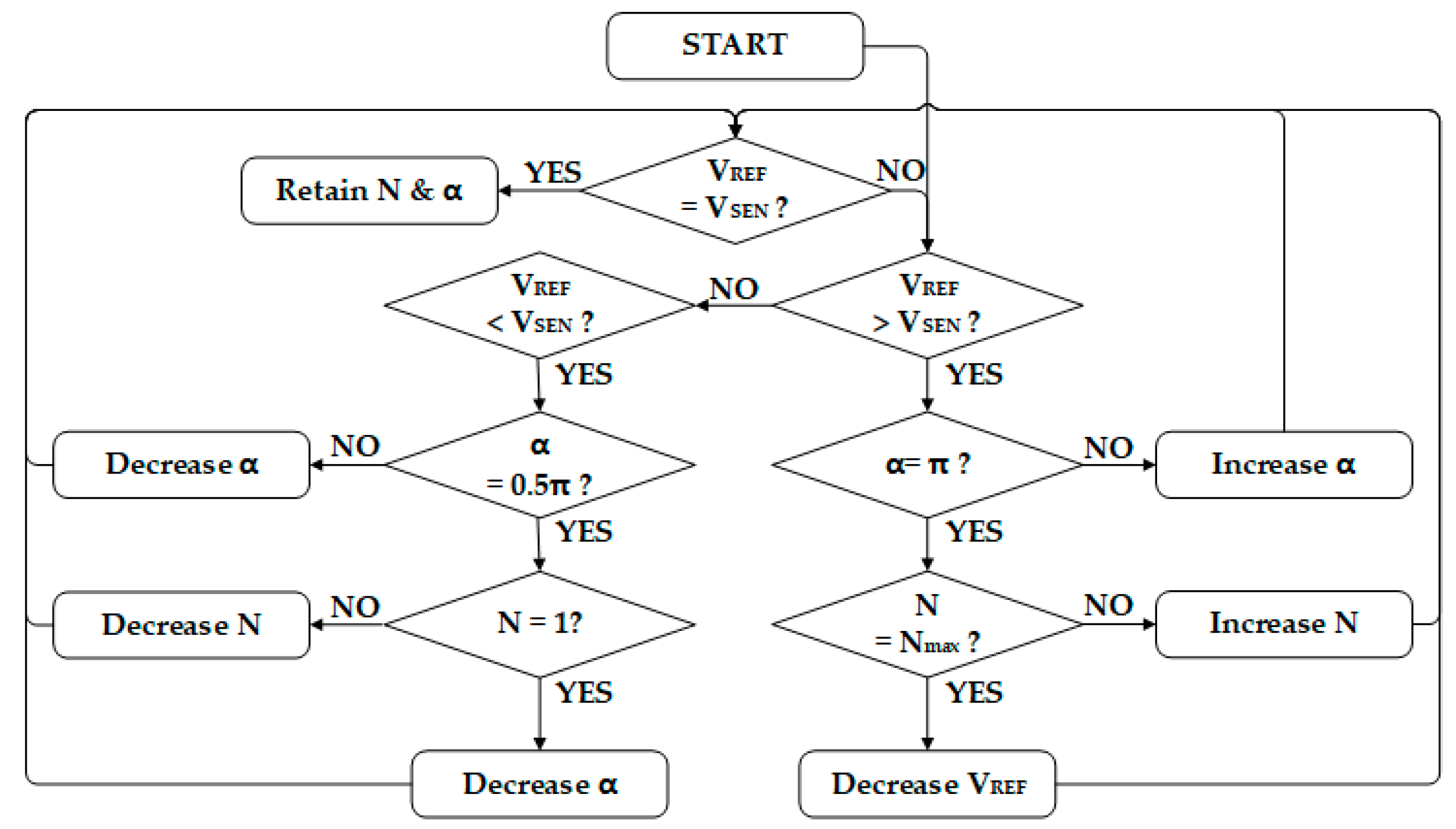
3.1. Principle and Characteristics of the Proposed Control Algorithm
3.2. Mathematical Model of the Proposed Control Algorithm.
4. Simulation and Experimental Results
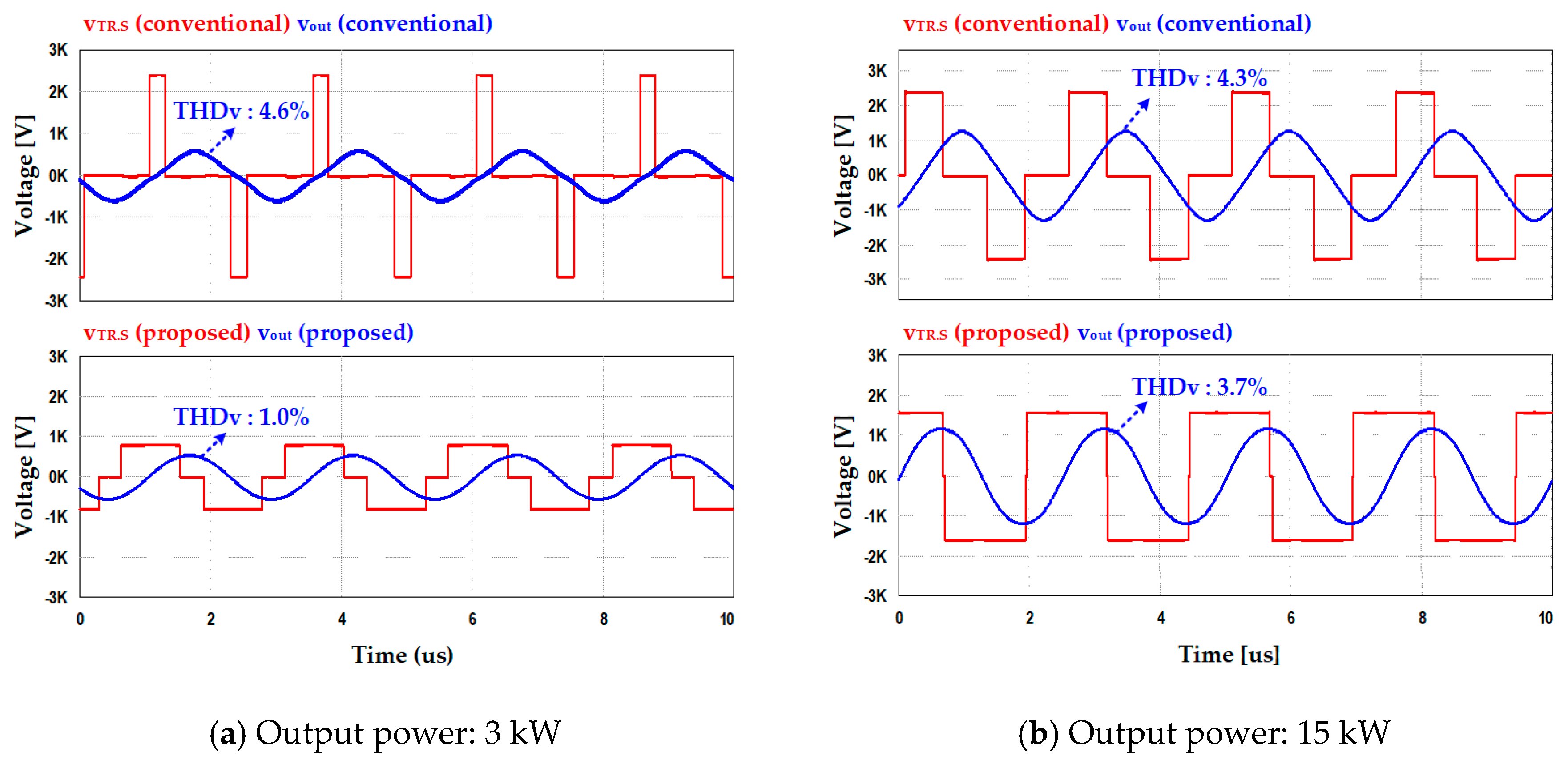
4.1. Simulation Results
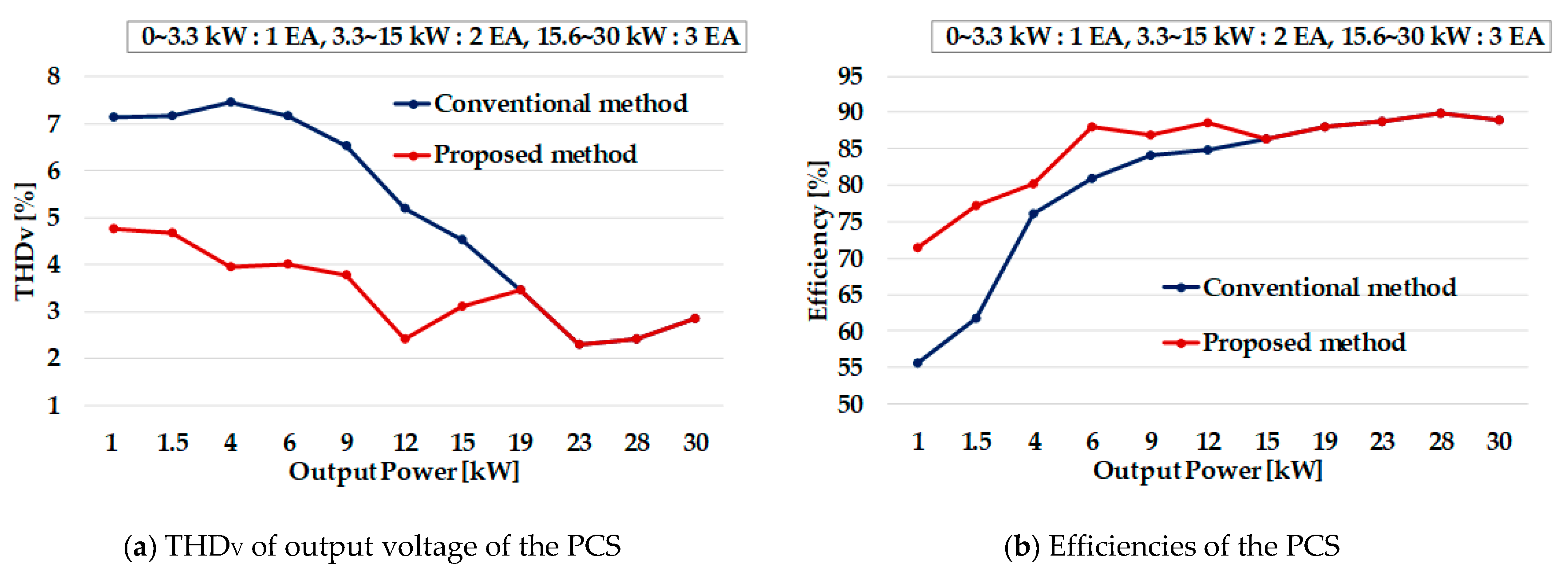
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamieniecki, E.; Foggiato, G. Analysis and control of electrically active contaminants by surface charge analysis. In Handbook of Semiconductor Wafer Cleaning Technology, 3rd ed.; Noyes Publications: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 497–536. ISBN 978-032-351-084-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Holber, W.; Loomis, P.; Sevillano, E.; Shao, S.Q. Advances in Remote Plasma Sources for Cleaning 300 mm and Flat Panel CVD Systems. Semiconductor® Magazine, 20 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Ren, C.S.; Fan, Q.Q.; Yan, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. Surface Cleaning Using an Atomospheric-Pressure Plasma Jet in O2/Ar Mixtures. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2003, 40, 2706–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balish, K.E.; Nowak, T.; Tanaka, T.; Beals, M. Dilute Remote Plasma Clean. U.S. Patent 6329297B1, 11 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yong-Nong, C.; Chih-Ming, K. Design of Plasma Generator Driven by High-frequency High-Voltage Power Supply. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2013, 11, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.; Millner, A. A New Power Supply to Ignite and Sustain Plasma in a Reactive Gas Generator. In Proceedings of the 2008 Twenty-Third Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (2008 APEC), Austin, TX, USA, 24–28 February 2008; pp. 1885–1892. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Mun, S.P.; Lee, H.W.; Kwon, S.K.; Suh, K.Y. The design of inverter power system for plasma generator. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Nanjing, China, 27–29 September 2005; pp. 1309–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, H.M.; Sung, W.Y.; Lee, B.K. Analysis and Design of Resonant Inverter for Reactive Gas Generator Considering Characteristics of Plasma Load. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2018, 13, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhuang, K.; Ruan, X. A Input-Series- and Output-Parallel-Connected Inverter System for High-Input-Voltage Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, I.; Elgenedy, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Williams, B.W. Full-bridge Modular Multilevel Submodule-based High-voltage Bipolar Pulse Generator with Low-voltage DC, Input for Pulsed Electric Field Applications. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2017, 45, 2857–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luc-André, G.; Bélanger, J. A Modular Multilevel Converter Pulse Generation and Capacitor Voltage Balance Method Optimized for FPGA Implementation. IEEE. Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2859–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgenedy, A.M.; Darwish, A.; Ahmed, S.; Williams, B.W. A Modular Multilevel-Based High-Voltage Pulse Generator for Water Disinfection Applications. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elserougi, A.A.; Massoud, A.M.; Ahmed, S. A Modular High-Voltage Pulse-Generator with Sequential Charging for Water Treatment Applications. IEEE. Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7898–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Darwish, A.; Williams, B.W. A Transition Arm Modular Multilevel Universal Pulse-Waveform Generator for Electroporation Applications. IEEE. Trans. Power. Electron. 2017, 32, 8979–8981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.L.; Silva, J.F.; Redondo, L.M. Multilevel High-Voltage Pulse Generation Based on a New Modular Solid-State Switch. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2014, 42, 2956–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Ruan, X.; Tse, C.K. Control Strategy to Achieve Input and Output Voltage Sharing for Input-Series-Output-Series-Connected Inverter Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Sha, D.; Liao, X.; Luo, J. Input-Series-Output-Parallel Phase-Shift Full-Bridge Derived DC–DC Converters with Auxiliary LC Networks to Achieve Wide Zero-Voltage Switching Range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 5081–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.M.; Sung, W.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Ryu, S.H.; Lim, C.S.; Lee, B.K. Control Method of Input-Parallel and Output-Series Connected Inverters for Plasma Generator. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 4–8 March 2018; pp. 3563–3568. [Google Scholar]
- Alou, P.; Oliver, J.; Cobos, J.A.; Garcia, O.; Uceda, J. Buck+half Bridge (d=50%) Topology Applied to very Low Voltage Power Converters. In Proceedings of the 2001 Sixteenth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (2001 APEC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 4–8 March 2001; pp. 715–721. [Google Scholar]
- Borage, M.; Tiwari, S.; Kotaiah, S. Analysis and Design of an LCL-T Resonant Converter as a Constant-Current Power Supply. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, A.K.S. A Fixed Frequency LCL-Type Series Resonant Converter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1995, 31, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| AC-DC Converter | |
| Parameter | Value |
| Rated Power | 30 kW |
| Grid voltage | 3Φ 440VLL.RMS |
| Grid frequency | 60 Hz |
| Switching frequency | 10 kHz |
| DC-link voltage | 800 Vdc |
| DC-AC Inverter | |
| Parameter | Value |
| Rated Power | 10 kW (1 EA) |
| Number of connected inverters | 3 EA |
| Switching frequency (operating inverter) | 400 kHz |
| Switching frequency (freewheeling inverter) | 10 kHz |
| Turn ratio of transformer | 1 |
| Equivalent resistor of chamber (Ro) | 50 Ω |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| L1 | 26 uH |
| L2 | 20 uH |
| Cf | 4.7 nF |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, H.M.; Jang, E.; Ryu, S.-H.; Lim, C.S.; Lee, B.K. Control Strategy for Power Conversion Systems in Plasma Generators with High Power Quality and Efficiency Considering Entire Load Conditions. Energies 2019, 12, 1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091723
Ahn HM, Jang E, Ryu S-H, Lim CS, Lee BK. Control Strategy for Power Conversion Systems in Plasma Generators with High Power Quality and Efficiency Considering Entire Load Conditions. Energies. 2019; 12(9):1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091723
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Hyo Min, Eunsu Jang, Seung-Hee Ryu, Chang Seob Lim, and Byoung Kuk Lee. 2019. "Control Strategy for Power Conversion Systems in Plasma Generators with High Power Quality and Efficiency Considering Entire Load Conditions" Energies 12, no. 9: 1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091723
APA StyleAhn, H. M., Jang, E., Ryu, S.-H., Lim, C. S., & Lee, B. K. (2019). Control Strategy for Power Conversion Systems in Plasma Generators with High Power Quality and Efficiency Considering Entire Load Conditions. Energies, 12(9), 1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091723





