Exploring the Energy Flexibility of Electric Water Heaters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Developed System (EFsyst)
3. Results and Analysis
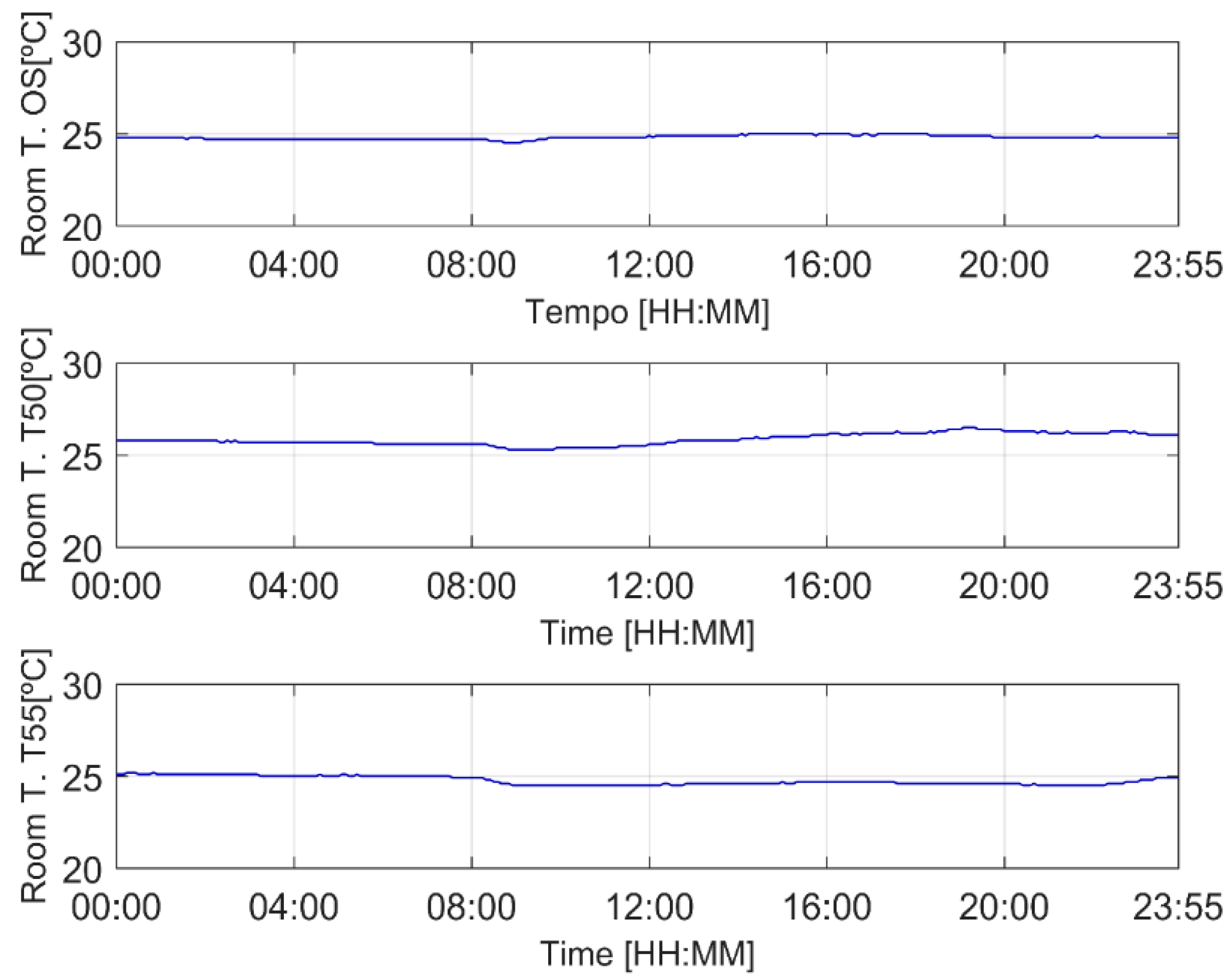
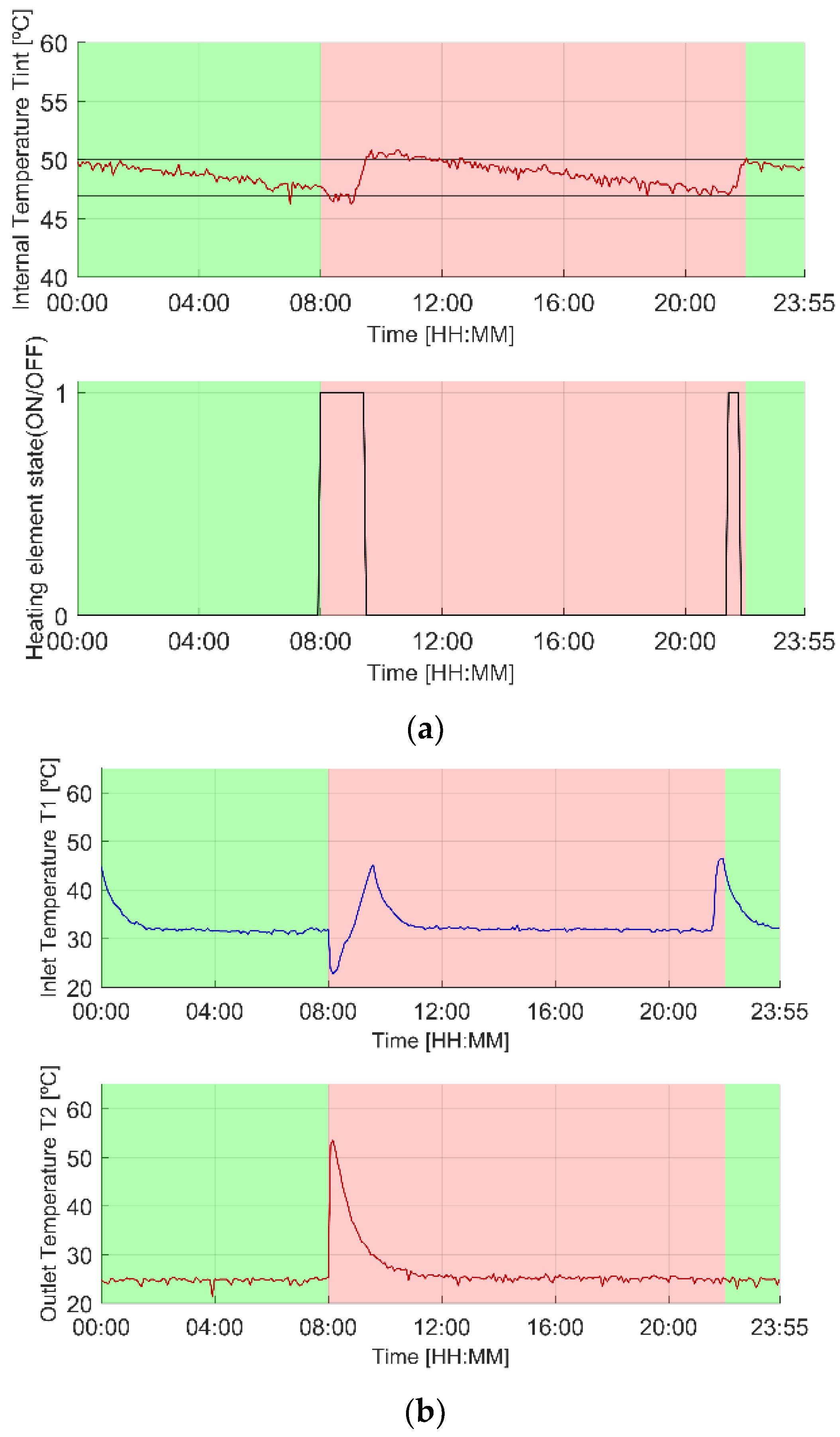
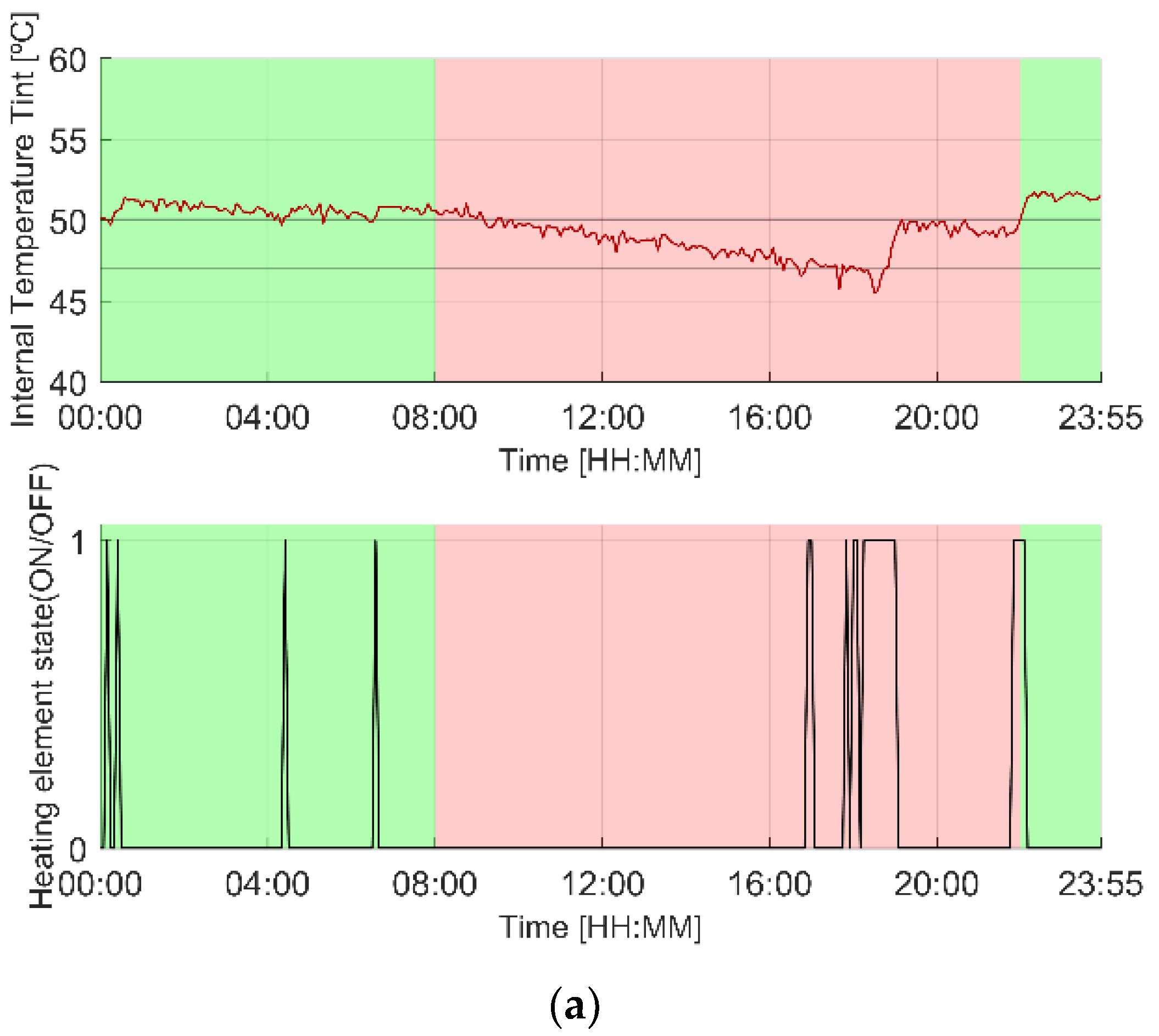
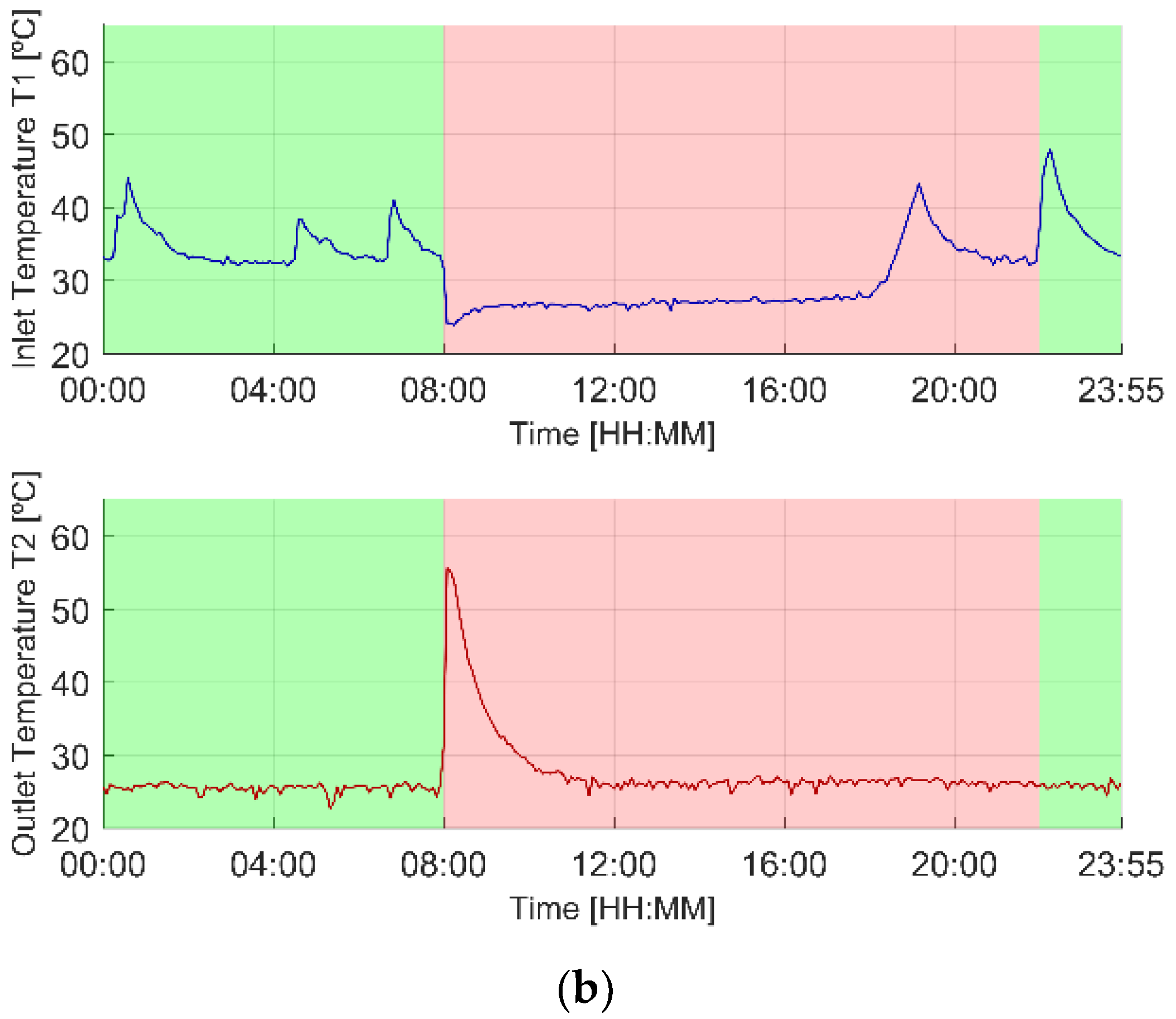
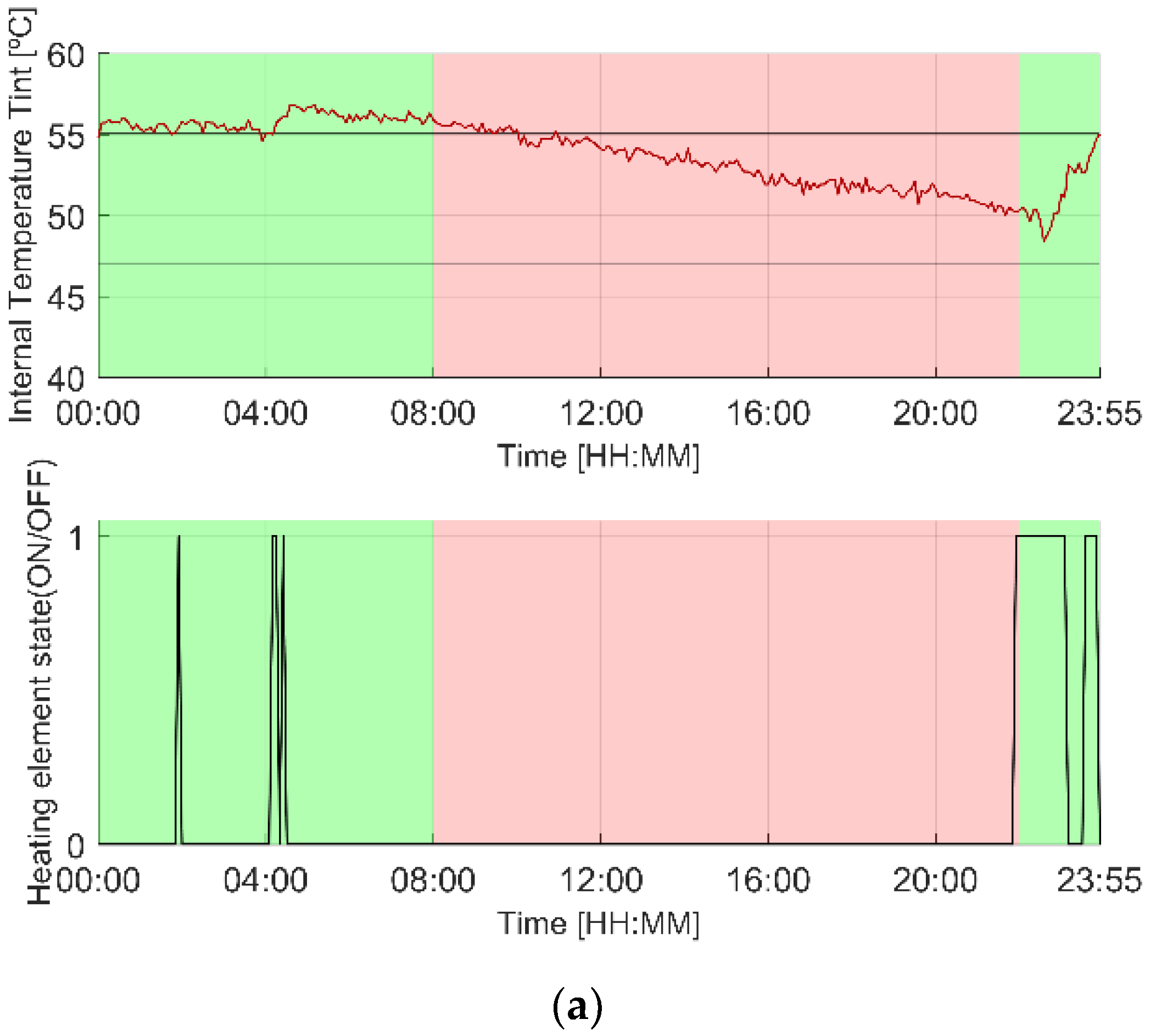
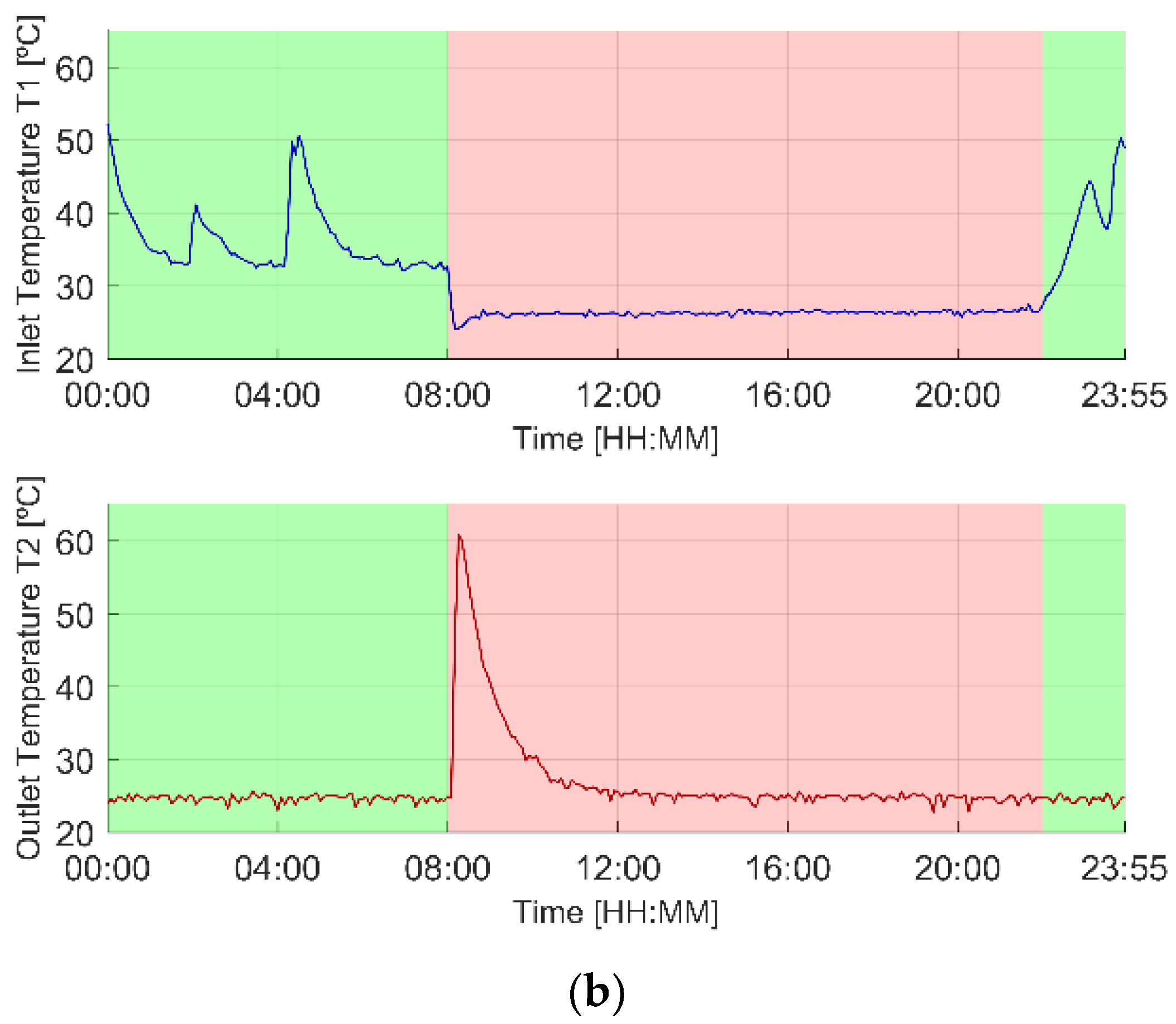
3.1. Illustrative Operation
3.1.1. Original Scenario
3.1.2. T50 Scenario
3.1.3. T55 Scenario
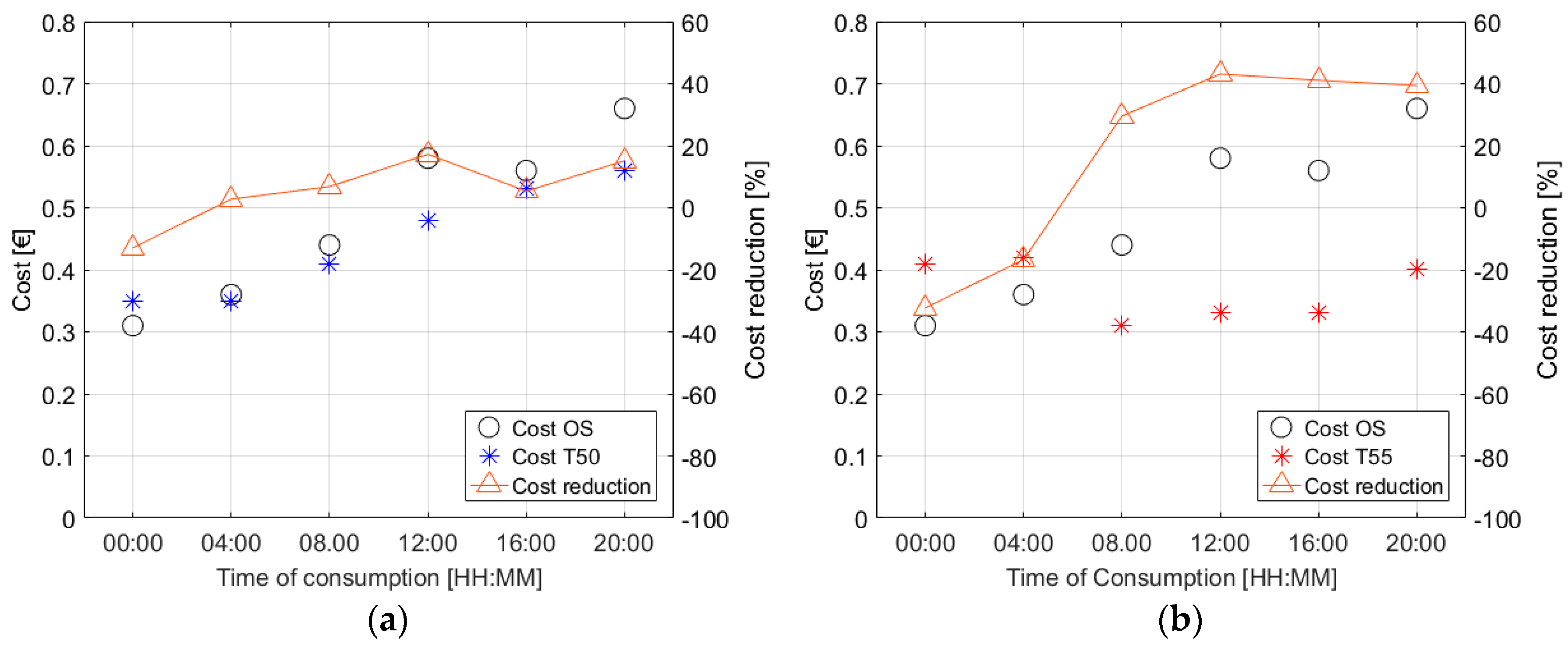
3.2. Assessing the Benefits of Using Energy Flexibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Comission. Energy Performance of Building Directive (EPBD). 2014. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/energy/en/topics/energy-efficiency/energy-performance-of buildings/overview#content-heading-0 (accessed on 17 October 2019).
- Jensen, S.Ø.; Madsen, H.; Lopes, R. Energy Flexibility as a Key Asset in a Smart Building Future—Contribution of Annex 67 to the European Smart Building Initiatives. Position Paper of the IEA-EBC Annex 67 Energy Flexible Buildings. Available online: http://www.annex67.org/publications/position-paper/ (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Pérez-Lombard, L.; Ortiz, J.; Pout, C. A review on buildings and energy consumption information. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaleiro, Â.; Figueiredo, R.; Neves, D.; Brito, M.C.; Silva, C.A. Optimization of Photovoltaic Self-consumption using Domestic Hot Water Systems. JSDEWES 2018, 6, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heleno, M.; Rua, D.; Gouveia, C.; Madureira, A.; Matos, M.A.; Lopes, J.P.; Silva, N.; Salustio, S. Optimizing PV self-consumption through electric water heater modeling and scheduling. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Eindhoven PowerTech (PowerTech 2015), Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 29 June–2 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, N.; Foley, A.M.; McKeogh, E. Integrating wind power using intelligent electric water heating. Energy 2012, 48, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmousavi, S.A.; Patrick, S.N.; Nehrir, M.H. Real-Time Demand Response through Aggregate Electric Water Heaters for Load Shifting and Balancing Wind Generation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Lu, N. Appliance Commitment for Household Load Scheduling. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2011, 2, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jabery, K.; Xu, Z.; Yu, W.; Wunsch, D.C.; Xiong, J.; Shi, Y. Demand-Side Management of Domestic Electric Water Heaters Using Approximate Dynamic Programming. IEEE Trans. Comput. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2017, 36, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepplinger, P.; Huber, G.; Petrasch, J. Autonomous optimal control for demand side management with resistive domestic hot water heaters using linear optimization. Energy Build. 2015, 100, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsalis, V.; Safouri, G.; Hadellis, L. Cost/comfort-oriented optimization algorithm for operation scheduling of electric water heaters under dynamic pricing. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Li, S.; Xiao, Y. Optimal and learning-based demand response mechanism for electric water heater system. Energies 2017, 10, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, B. An optimized demand response strategy for electric water heaters and the associated impact on power system operational reliability. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Wuxi, China, 14–17 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruelens, F.; Claessens, B.J.; Quaiyum, S.; de Schutter, B.; Babuška, R.; Belmans, R. Reinforcement Learning Applied to an Electric Water Heater: From Theory to Practice. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 3792–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.J.; Nielsen, M.C.; Shaffer, T.S.; Fittro, R.L. Cost-Optimal Consumption-Aware Electric Water Heating Via Thermal Storage under Time-of-Use Pricing. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFsyst Data. Available online: https://github.com/taapereira/EFsystdata (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Kalogirou, S.A. Solar Water-Heating Systems. In Solar Energy Engineering Processes and Systems, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 257–321. ISBN 978-0-12-397270-5. [Google Scholar]
- ThingSpeak. Available online: https://thingspeak.com/ (accessed on 11 August 2019).
- Arduino Uno Rev 3. Available online: https://store.arduino.cc/arduino-uno-rev3 (accessed on 11 August 2019).
- ESP8266. Available online: https://www.espressif.com/en/products/hardware/esp8266ex/overview (accessed on 11 August 2019).
- Electric Water Heater Delta V 100L. Available online: https://www.leroymerlin.pt/Produtos/Canalizacao/Termoacumuladores/WPR_REF_14429254 (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- EDP Comercial. Available online: https://www.edp.pt/particulares/energia/tarifarios/ (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Departamento de Engenharia Eletrotécnica e de Computadores da Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologias. Universidade Nova de Lisboa. Available online: https://www.dee.fct.unl.pt/ (accessed on 11 September 2019).
- MATLAB. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html (accessed on 11 September 2019).


| Tariff | Periods | Price (€/kWh) |
|---|---|---|
| TOU-2 | Off-peak [00:00; 8:00] and [22:00; 00:00] | 0.110 |
| Half-peak [08:00; 20:00] | 0.187 | |
| TOU-3 | Off-peak [0:00; 8:00] and [22:00; 00:00] | 0.104 |
| Hal-peak [08:00; 10:30], [13:00; 19:30] and [21:00; 22:00] | 0.157 | |
| Peak [10:30; 13:00] and [19:30; 21:00] | 0.274 |
| Consumption Event | Scenario | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | T50 | T55 | |||||||
| Energy [kWh] | Cost [€] | Energy [kWh] | Cost [€] | Energy [kWh] | Cost [€] | ||||
| TOU-2 | TOU-3 | TOU-2 | TOU-3 | TOU-2 | TOU-3 | ||||
| 00:00 | 2.75 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 2.88 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 3.88 | 0.44 | 0.41 |
| 04:00 | 3.25 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 3.25 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 4.00 | 0.45 | 0.42 |
| 08:00 | 2.88 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 2.88 | 0.48 | 0.41 | 2.88 | 0.33 | 0.31 |
| 12:00 | 2.63 | 0.48 | 0.58 | 3.00 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 3.13 | 0.35 | 0.33 |
| 16:00 | 3.25 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 2.50 | 0.42 | 0.53 | 3.13 | 0.35 | 0.33 |
| 20:00 | 3.38 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 3.00 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 3.75 | 0.42 | 0.40 |
| Average | 3.02 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 2.92 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 3.46 | 0.39 | 0.37 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, T.C.; Amaral Lopes, R.; Martins, J. Exploring the Energy Flexibility of Electric Water Heaters. Energies 2020, 13, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13010046
Pereira TC, Amaral Lopes R, Martins J. Exploring the Energy Flexibility of Electric Water Heaters. Energies. 2020; 13(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13010046
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Tiago Cardoso, Rui Amaral Lopes, and João Martins. 2020. "Exploring the Energy Flexibility of Electric Water Heaters" Energies 13, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13010046
APA StylePereira, T. C., Amaral Lopes, R., & Martins, J. (2020). Exploring the Energy Flexibility of Electric Water Heaters. Energies, 13(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13010046






