Electric Powertrain Topology Analysis and Design for Heavy-Duty Trucks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. System-Level Design
1.2. Contribution and Outline of the Work
2. Problem Description
2.1. System-Level Objective Function
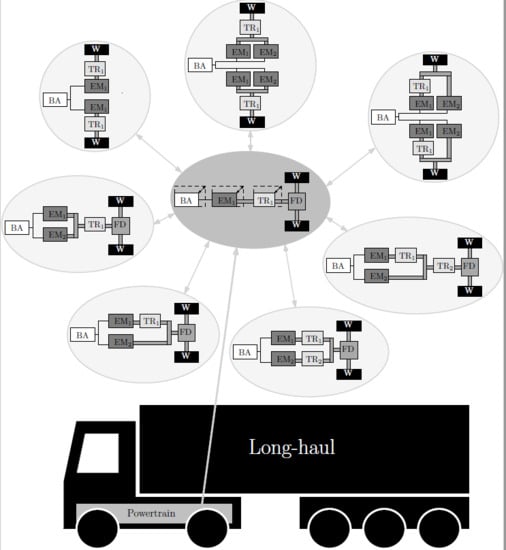
2.2. Topology Design Space
2.3. System Design Problem
2.4. Outer Loop-Component Sizing Problem
Component Constraints
2.5. Inner Loop Control Optimization
Constraints
2.6. Optimization Framework
3. System Modeling
3.1. Vehicle Road-Load Model
3.2. Final Drive Model
3.3. Transmission Model
3.4. Electric Machine Model
3.5. Battery Model
3.6. Auxiliary Units
3.7. Vehicle Mass Model
3.8. Cost Model Parameters
3.9. Drive Cycle
4. Design Results and Analysis
4.1. Total-Cost-of-Ownership
4.2. Optimal Component Sizing
4.3. Central Drive Versus Distributed Drive Topology
4.4. Gearbox Type and Location
4.4.1. Two-Speed Gearboxes
4.4.2. Three-Speed Gearboxes
4.4.3. Four-Speed Gearboxes
4.4.4. Gearbox Location
4.5. Single Versus Multiple Electric Machines
4.6. Comparison of the Influence of Design Choices
4.7. Results Discussion
4.7.1. Optimal Gear Use
4.7.2. Torque Split
4.8. Alternative Optimization Objective: Energy Consumption
5. Conclusions
List of Sub-Scripts
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BA | Battery |
| EAC | Electric air compressor |
| ECU | Electronic control unit |
| EHPS | Electric hydraulic power steering |
| EM | Electric machine |
| FD | Final drive |
| HVAC | air conditioning unit |
| PSO | Particle swarm optimization |
| TCO | Total-cost-of-ownership |
| TR | Transmission |
| VECTO | Vehicle Energy Consumption Calculation Tool |
| W | Driven wheel |
| A | frontal area | m2 | Q0 | battery capacity | Ah |
| ce | electricity cost | euro/kWh | rf | final drive ratio | - |
| C | cost parameters | euro | rl | vector with gear ratios of gearbox l | - |
| cd | air drag coefficient | - | rw | wheel radius | m |
| cr | rolling resistance coefficient | - | R | internal battery resistance | Ω |
| D | distance | km | R | Matrix with all gear ratios in the powertrain | - |
| Eb | battery energy content | kWh | Smk | electric machine scaling parameter | - |
| Ev | energy consumption, energy | kWh/100 km | t | time | s |
| Fr | road-load force | N | tacc | acceleration time | s |
| f | function indication | - | T | topology | - |
| g | inequality constraints | - | T | set of topologies | - |
| g | gravitational acceleration | m2/s | uts | torque split control variable | - |
| h | equality constraints | - | Uoc | open circuit voltage | V |
| i | topology name | - | v | vehicle speed | m/s |
| I | current | A | x | vector with design variables | - |
| jl | number of gears in gearbox uni l | - | xl | gear position of gearbox l | - |
| k | index of the electric machine | - | xg | vector with gear positions of all gearboxes | - |
| l | index of the gearbox unit | - | y | year | year |
| m | mass | kg | α | road slope | rad |
| n | total number of instances | - | η | efficiency | - |
| P | power | W | Λ | drive cycle | - |
| Pmk | mechanical peak power for electric machine k | W | ξ | battery state-of-charge | - |
| Pmk,e | electric power for electric machine k | W | ρ | air density | kg/m3 |
| Pm | vector with all electric machine peak powers | W | τ | torque | Nm |
| sum of electric machine peak powers | W | ω | angular speed | rad/s |
| 0 | begin time, nominal, base vehicle cost | l | gearbox index |
| 85 | related to 85 km/h constraint | m | electric machine |
| acc | acceleration | oc | open-circuit |
| b | battery | p | plant |
| c | drive cycle | pa | parallel |
| c | control | pt | powertrain |
| C | central | r | total number of gear ratios |
| ca | cargo | s | internal battery power |
| ch | charging | se | series |
| cl | single battery cell | st | related to standstill constraint |
| d | drag coefficient | t | number of transmission units |
| D | distributed | ta | tractor |
| di | discharge | TCO | total-cost-of-ownership |
| e | electricity cost, electric power | ti | transmission inlet |
| el | economical life time | to | transmission output |
| end | end time | top | top speed |
| f | final drive | tr | trailer |
| g | gearbox | ts | torque split |
| gp | gear pair | v | vehicle |
| i | inverter | w | wheel |
| i | topology name | y | yearly |
| k | electric machine index |
Appendix A. Design Parameters Per Topology
| Topology | Component Sizing Parameters | Control Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| D1. | ||
| D2. | ||
| D3. | ||
| C1. | ||
| C2. | ||
| C3. | ||
| C4. | ||
| C5. |
Appendix B. Optimization Results Data
| Topology | Performance Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top Speed | Gradeability | Acceleration 0–80 km/h | Range | ||
| (kWh/100 km) | (km/h) | (%) | (s) | (km) | |
| D1.1 | 173.2 | 143 | 11 | 37 | 98 |
| D1.2 | 171.7 | 131 | 11 | 46 | 98 |
| D1.3 | 172.0 | 126 | 12 | 51 | 98 |
| D1.4 | 171.4 | 128 | 11 | 47 | 98 |
| D2.1 | 171.6 | 148 | 11 | 35 | 98 |
| D2.2 | 170.9 | 150 | 11 | 34 | 98 |
| D2.3 | 170.6 | 135 | 32 | 40 | 99 |
| D2.4 | 170.7 | 156 | 38 | 25 | 98 |
| D3.1 | 173.2 | 111 | 11 | 36 | 98 |
| D3.2 | 173.2 | 101 | 25 | 43 | 98 |
| D3.3 | 172.0 | 104 | 37 | 37 | 98 |
| D3.4 | 172.7 | 120 | 50 | 32 | 100 |
| C1.1 | 175.7 | 145 | 11 | 35 | 98 |
| C1.2 | 175.7 | 127 | 12 | 48 | 98 |
| C1.3 | 175.6 | 125 | 18 | 49 | 98 |
| C1.4 | 174.7 | 132 | 15 | 42 | 98 |
| C2.1 | 174.0 | 155 | 12 | 30 | 99 |
| C2.2 | 172.6 | 141 | 12 | 37 | 100 |
| C2.3 | 173.7 | 129 | 30 | 44 | 98 |
| C2.4 | 174.4 | 131 | 45 | 41 | 98 |
| C3.1 | 176.0 | 147 | 11 | 36 | 98 |
| C3.2 | 174.3 | 149 | 17 | 35 | 98 |
| C3.3 | 173.5 | 150 | 38 | 29 | 98 |
| C3.4 | 175.6 | 130 | 21 | 44 | 101 |
| C4.11 | 173.9 | 153 | 11 | 32 | 98 |
| C4.21 | 175.6 | 94 | 11 | 43 | 99 |
| C4.22 | 174.6 | 147 | 40 | 30 | 98 |
| C4.24 | 173.4 | 136 | 17 | 39 | 98 |
| C4.31 | 173.4 | 142 | 17 | 36 | 99 |
| C4.32 | 174.4 | 136 | 40 | 38 | 99 |
| C4.33 | 173.8 | 142 | 43 | 33 | 98 |
| C4.34 | 176.0 | 129 | 33 | 44 | 99 |
| C4.41 | 173.6 | 148 | 37 | 31 | 98 |
| C4.44 | 175.2 | 135 | 39 | 38 | 99 |
| C5.11 | 177.2 | 126 | 11 | 62 | 98 |
| C5.12 | 175.1 | 151 | 37 | 41 | 98 |
| C5.13 | 173.8 | 164 | 48 | 29 | 100 |
| C5.14 | 173.7 | 146 | 90 | 33 | 98 |
| C5.21 | 175.5 | 134 | 11 | 50 | 98 |
| C5.22 | 175.8 | 135 | 57 | 57 | 106 |
| C5.23 | 176.8 | 184 | 90 | 20 | 98 |
| C5.31 | 177.6 | 141 | 20 | 36 | 98 |
| C5.32 | 177.8 | 132 | 90 | 41 | 101 |
| C5.33 | 175.8 | 148 | 90 | 29 | 98 |
| C5.41 | 175.2 | 17 | 84 | 34 | 98 |
| Topology | Sizing | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kWh) | (kW) | (kW) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | |
| D1.1 | 213 | 182 | 7.6 | |||||||||
| D1.2 | 211 | 149 | 9.3 | 5.3 | ||||||||
| D1.3 | 211 | 134 | 11.3 | 5.1 | 0.9 | |||||||
| D1.4 | 210 | 145 | 10.1 | 9.8 | 8.3 | 5.1 | ||||||
| D2.1 | 211 | 111 | 87 | 7.0 | ||||||||
| D2.2 | 210 | 122 | 85 | 6.7 | 6.0 | |||||||
| D2.3 | 211 | 111 | 47 | 24.2 | 6.8 | 5.1 | ||||||
| D2.4 | 210 | 122 | 112 | 19.8 | 15.9 | 6.8 | 6.2 | |||||
| D3.1 | 213 | 188 | 11 | 7.6 | ||||||||
| D3.2 | 212 | 147 | 14 | 21.3 | 6.5 | |||||||
| D3.3 | 211 | 164 | 10 | 27.0 | 18.3 | 5.4 | ||||||
| D3.4 | 215 | 175 | 71 | 33.7 | 29.4 | 20.4 | 5.4 | |||||
| C1.1 | 216 | 391 | 7.5 | 1 | ||||||||
| C1.2 | 216 | 285 | 10.5 | 6.7 | 1 | |||||||
| C1.3 | 215 | 272 | 16.8 | 12.8 | 6.1 | 1 | ||||||
| C1.4 | 214 | 313 | 12.9 | 9.4 | 9.3 | 6.5 | 1 | |||||
| C2.1 | 215 | 278 | 188 | 6.7 | 1 | |||||||
| C2.2 | 215 | 249 | 114 | 8.7 | 5.1 | 1 | ||||||
| C2.3 | 214 | 164 | 130 | 25.5 | 14.8 | 5.1 | 1 | |||||
| C2.4 | 214 | 297 | 13 | 35.6 | 29.1 | 7.0 | 5.2 | 1 | ||||
| C3.1 | 216 | 368 | 62 | 7.6 | 1 | |||||||
| C3.2 | 214 | 348 | 73 | 12.5 | 6.2 | 1 | ||||||
| C3.3 | 213 | 415 | 10 | 22.7 | 8.5 | 5.2 | 1 | |||||
| C3.4 | 221 | 295 | 10 | 18.8 | 14.7 | 14.5 | 6.7 | 1 | ||||
| C4.11 | 214 | 246 | 203 | 7.3 | 1 | 5.4 | ||||||
| C4.21 | 218 | 65 | 268 | 22.9 | 11.8 | 1 | 5.6 | |||||
| C4.22 | 215 | 393 | 16 | 24.9 | 6.1 | 1 | 18.4 | 3.9 | ||||
| C4.24 | 213 | 273 | 61 | 10.6 | 5.2 | 1 | 24.2 | 22.2 | 12.6 | 7.6 | ||
| C4.31 | 216 | 356 | 17 | 12.5 | 10.8 | 5.1 | 1 | 0.3 | ||||
| C4.32 | 215 | 185 | 149 | 26.7 | 19.7 | 5.1 | 1 | 32.2 | 7.8 | |||
| C4.33 | 213 | 210 | 161 | 34.2 | 22.9 | 6.8 | 1 | 20.6 | 17.5 | 5.1 | ||
| C4.34 | 218 | 144 | 151 | 23.6 | 14.3 | 9.4 | 1 | 33.3 | 10.6 | 8.5 | 5.1 | |
| C4.41 | 213 | 225 | 184 | 36.1 | 15.1 | 7.4 | 4.5 | 1 | 5.2 | |||
| C4.44 | 217 | 273 | 59 | 29.4 | 16.9 | 15.7 | 7.2 | 1 | 30.2 | 29.9 | 19.6 | 7.0 |
| C5.11 | 218 | 174 | 210 | 0.7 | 1 | 8.8 | ||||||
| C5.12 | 215 | 123 | 314 | 0.1 | 1 | 27.8 | 5.2 | |||||
| C5.13 | 217 | 126 | 407 | 0.6 | 1 | 23.5 | 12.4 | 5.1 | ||||
| C5.14 | 213 | 223 | 179 | 1 | 1 | 20.1 | 18.9 | 10.6 | 5.3 | |||
| C5.21 | 215 | 65 | 257 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 1 | 6.0 | |||||
| C5.22 | 233 | 118 | 213 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1 | 38.8 | 6.3 | ||||
| C5.23 | 217 | 293 | 550 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 1 | 39.3 | 6.8 | 6.1 | |||
| C5.31 | 218 | 337 | 31 | 28.7 | 17.3 | 10.3 | 1 | 0.5 | ||||
| C5.32 | 224 | 289 | 25 | 23.6 | 10.5 | 1.2 | 1 | 4.4 | 0.6 | |||
| C5.33 | 216 | 208 | 216 | 17.6 | 5.5 | 1.3 | 1 | 18.8 | 10.9 | 5.6 | ||
| C5.41 | 215 | 104 | 299 | 28.8 | 16.4 | 12.9 | 1.3 | 1 | 5.2 | |||
References
- Verbruggen, F.J.R.; Hoekstra, A.E.; Hofman, T. Evaluation of the state-of-the-art of full-electric medium and heavy-duty trucks. In Proceedings of the 2018 31th International Electric Vehicle Symposium & Exhibition (EVS), Kobe, Japan, 30 September–3 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Silvas, E. Integrated Optimal Design for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Ph.D. Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fathy, H.K.; Reyer, J.A.; Papalambros, P.Y.; Ulsov, A. On the coupling between the plant and controller optimization problems. In Proceedings of the 2001 American Control Conference (ACC), Arlington, VA, USA, 25–27 June 2001; Volume 3, pp. 1864–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, B.; Ercan, T.; Tatari, O. Does a battery-electric truck make a difference?—Life cycle emissions, costs, and externality analysis of alternative fuel-powered Class 8 heavy-duty trucks in the United States. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripad, S.; Viswanathan, V. Performance metrics required of next-generation batteries to make a practical electric semi truck. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çabukoglu, E.; Georges, G.; Küng, L.; Pareschi, G.; Boulouchos, K. Battery electric propulsion: An option for heavy-duty vehicles? Results from a Swiss case-study. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 88, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huismans, H. Electric Trucks: Wishful Thinking or the Real Deal? Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Roorda, M.J.; MacLean, H.L.; Luk, J. Life cycle GHG emissions and lifetime costs of medium-duty diesel and battery electric trucks in Toronto, Canada. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 55, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, A.; Domingues-Olavarría, G.; Alaküla, M. Alternative EV powertrain topologies designed for operation in a conductive electric road system. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles & International Transportation Electrification Conference (ESARS-ITEC), Nottingham, UK, 7–9 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Morozov, A.; Humphries, K.; Zou, T.; Rahman, T.; Angeles, J. Design, Analysis, and Optimization of a Multi-Speed Powertrain for Class-7 Electric Trucks. SAE Int. J. Altern. Powertrains 2018, 7, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, M.; Wolff, S.; Horlbeck, L.; Kerler, M.; Lienkamp, M.; Burke, A.; Fulton, L. Optimization of hybrid electric drive system components in long-haul vehicles for the evaluation of customer requirements. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 December 2017; pp. 1–141. [Google Scholar]
- Mareev, I.; Becker, J.; Sauer, D. Battery dimensioning and life cycle costs analysis for a heavy-duty truck considering the requirements of long-haul transportation. Energies 2017, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kollmeyer, P.; McFarland, J.; Jahns, T. Comparison of class 2a truck electric vehicle drivetrain losses for single-and two-speed gearbox systems with IPM traction machines. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), San Diego, CA, USA, 11–15 May 2015; pp. 1501–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Morozov, A.; Humphries, K.; Zou, T.; Martins, S.; Angeles, J. Design and optimization of a drivetrain with two-speed transmission for electric delivery step van. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference (IEVC), Florence, Italy, 17–19 December 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Hai, T.; Zhang, W. Gear Ratio Optimization of a Multi-Speed Transmission for Electric Dump Truck Operating on the Structure Route. Energies 2018, 11, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verbruggen, F.J.R.; Rangarajan, V.; Hofman, T. Powertrain design optimization for a battery electric heavy-duty truck. In Proceedings of the 2019 American Control Conference (ACC), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–12 July 2019; pp. 1488–1493. [Google Scholar]
- Katrašnik, T. Analytical framework for analyzing the energy conversion efficiency of different hybrid electric vehicle topologies. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, F.; Moreno-Eguilaz, M.; Alvarez, J.; Riera, J. Topological analysis of powertrains for refuse-collecting vehicles based on real routes–Part II: Hybrid electric powertrain. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2016, 17, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Guo, K.; Yang, F. A Comparative study of Different Hybrid Electric Powertrain Architectures for Heavy-Duty Truck. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagci, O.H.; Peng, H.; Grizzle, J.W. Hybrid electric powertrain design methodology with planetary gear sets for performance and fuel economy. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 9585–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Hofmann, H.; Li, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, M. A comparison study of different semi-active hybrid energy storage system topologies for electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2015, 274, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.L.; Polinder, H.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Energy consumption of electric powertrain architectures: A comparative study. In Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’17 ECCE Europe), Warsaw, Poland, 11–14 September 2017; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Bouscayrol, A.; Han, S.; Cui, S. Comparisons of electric vehicles using modular cascade machines system and classical single drive electric machine. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hung, D.L.S.; Zhong, J.; Teh, K.Y. Energy Consumption Analysis of Different Bev Powertrain Topologies by Design Optimization. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2018, 19, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues-Olavarría, G.; Márquez-Fernández, F.J.; Fyhr, P.; Reinap, A.; Andersson, M.; Alaküla, M. Optimization of Electric Powertrains Based on Scalable Cost and Performance Models. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvas, E.; Hofman, T.; Serebrenik, A.; Steinbuch, M. Functional and cost-based automatic generator for hybrid vehicles topologies. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebbesen, S.; Kiwitz, P.; Guzzella, L. A generic particle swarm optimization Matlab function. In Proceedings of the 2012 American Control Conference (ACC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–29 June 2012; pp. 1519–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzella, L.; Sciaretta, A. Vehicle Propulsion Systems, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhilper, W.; Sauer, B. Structural Elements of Mechanical Engineering 2: Fundamentals of Machine Elements for Powertrains, 7th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Naunheimer, H.; Bertsche, B.; Ryborz, J.; Novak, W. Automotive Transmissions: Fundamentals, Selection, Design and Application, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Staunton, R.H.; Ayers, C.W.; Marlino, L.; Chiasson, J.; Burress, B. Evaluation of 2004 Toyota Prius Hybrid Electric Drive System; Technical Report ONRL/TM-2006/423; Oak Ridge National Lab: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Argonne National Laboratory. Autonomie Vehicle System Simulation Tool. Available online: https://www.anl.gov/es/autonomie-vehicle-system-simulation-tool (accessed on 20 July 2018).
- Thielmann, A.; Sauer, A.; Wietschel. Gesamt-Roadmap fur die Elektromobilitat 2030; Technical Report; Fraunhofer ISI: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Den Boer, E.; Aarnink, S.; Kleiner, F.; Pagenkopf, J. Zero Emissions Trucks: An Overview of State-of-the-Art Technologies and Their Potential; Technical Report 13.4841.21; CE Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Summerton, P.; Harrison, P. An Economic Assessment of Low Carbon Vehicles; Technical Report; Cambridge Econometrics and Ricardo-AEA: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pourabdollah, M.; Egardt, B.; Murgovski, N.; Grauers, A. Effect of driving, charging, and pricing scenarios on optimal component sizing of a PHEV. Control Eng. Pract. 2017, 61, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvas, E.; Bergshoeff, E.; Hofman, T.; Steinbuch, M. Comparison of bi-level optimization frameworks for sizing and control of a hybrid electric vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Coimbra, Portugal, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Eurostat. Electricity Price Statistics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Electricity_price_statistics (accessed on 13 August 2018).
- Fontaras, G.; Rexeis, M.; Dilara, P.; Hausberger, S.; Anagnostopoulos, K. The Development of a Simulation Tool for Monitoring Heavy-Duty Vehicle CO2 Emissions and Fuel Consumption in Europe; Technical Report No. 2013-24-0150; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]














| Component Type | No. Instances | Degree | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1: | EMk | 4 | 1 |
| 2: | TR1 | 2 | 2 |
| 3: | FD | 1 | 3 |
| 4: | BA | 1 | 1 |
| Name | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheel radius | 0.492 | m | |
| Gravitational acceleration | 9.81 | m/s2 | |
| Rolling friction coefficient | 0.006 | - | |
| Aerodynamic drag coefficient | 0.73 | - | |
| Frontal area | A | 9.75 | m2 |
| Air density | 1.225 | kg/m3 |
| Name | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell capacity | 41 | Ah | |
| Nominal cell voltage | 3.62 | V | |
| Max. cell charge current | 150 | A | |
| Max. cell discharge current | 150 | A | |
| Battery nominal voltage | 520 | V | |
| Max. battery state of charge | 1.0 | - | |
| Min. battery state of charge | 0.2 | - | |
| Initial battery state of charge | 1.0 | - |
| Component | Mass Equation (kg) |
|---|---|
| Tractor mass | = 5400 |
| Trailer mass | = 7500 |
| Cargo mass | = 25,000 |
| Battery | = 6.7 |
| Inverter | |
| Electric machine | = 0.8 |
| Transmission [30] | = |
| Component | Cost Model | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electric machine cost model | euro | |
| Inverter cost model | euro | |
| Battery cost model | euro | |
| Transmission cost model [30] | euro | |
| Base vehicle cost | euro | |
| Years of ownership | 4 | year |
| Years of economical lifetime | 8 | year |
| Yearly mileage | km | |
| Electricity cost [38] | euro/kWh |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verbruggen, F.J.R.; Silvas, E.; Hofman, T. Electric Powertrain Topology Analysis and Design for Heavy-Duty Trucks. Energies 2020, 13, 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102434
Verbruggen FJR, Silvas E, Hofman T. Electric Powertrain Topology Analysis and Design for Heavy-Duty Trucks. Energies. 2020; 13(10):2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102434
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerbruggen, Frans J. R., Emilia Silvas, and Theo Hofman. 2020. "Electric Powertrain Topology Analysis and Design for Heavy-Duty Trucks" Energies 13, no. 10: 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102434
APA StyleVerbruggen, F. J. R., Silvas, E., & Hofman, T. (2020). Electric Powertrain Topology Analysis and Design for Heavy-Duty Trucks. Energies, 13(10), 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102434