Replacement and Maintenance Decision Analysis for Hydraulic Machinery Facilities at Reservoirs under Imperfect Maintenance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Replacement Analysis and Decision
4. The Process of Imperfect Maintenance
5. Economic Evaluation of Replacement
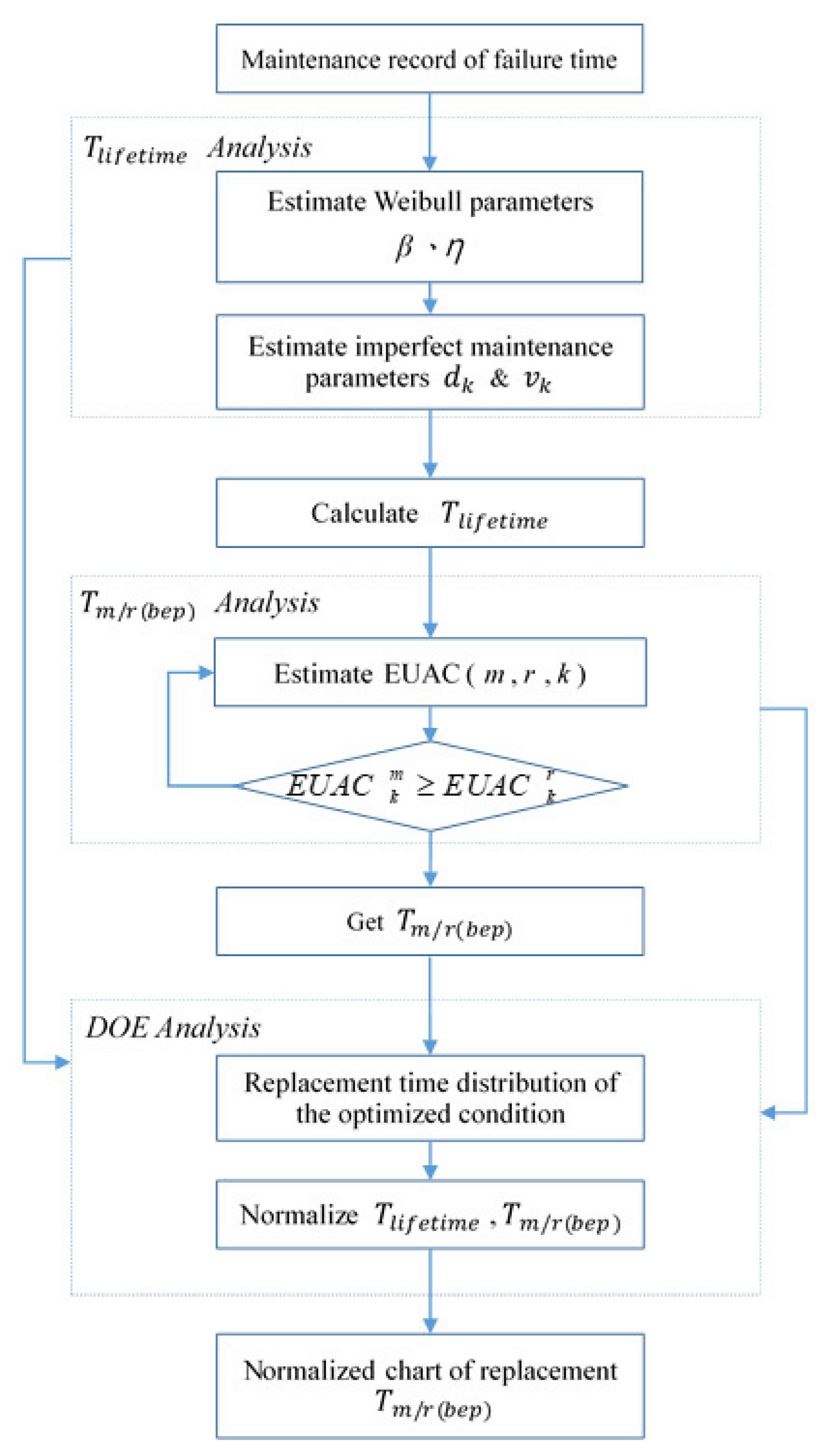
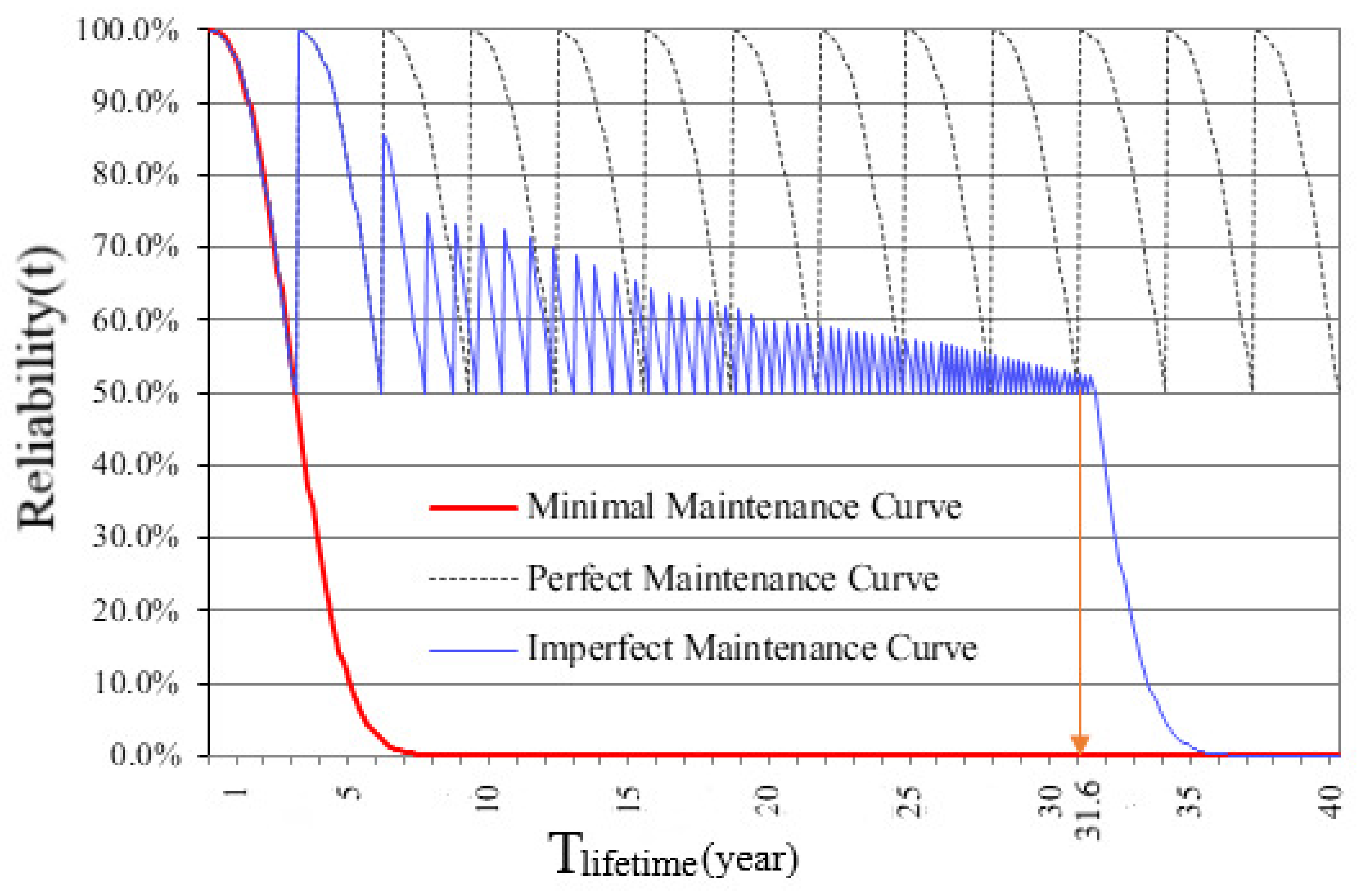
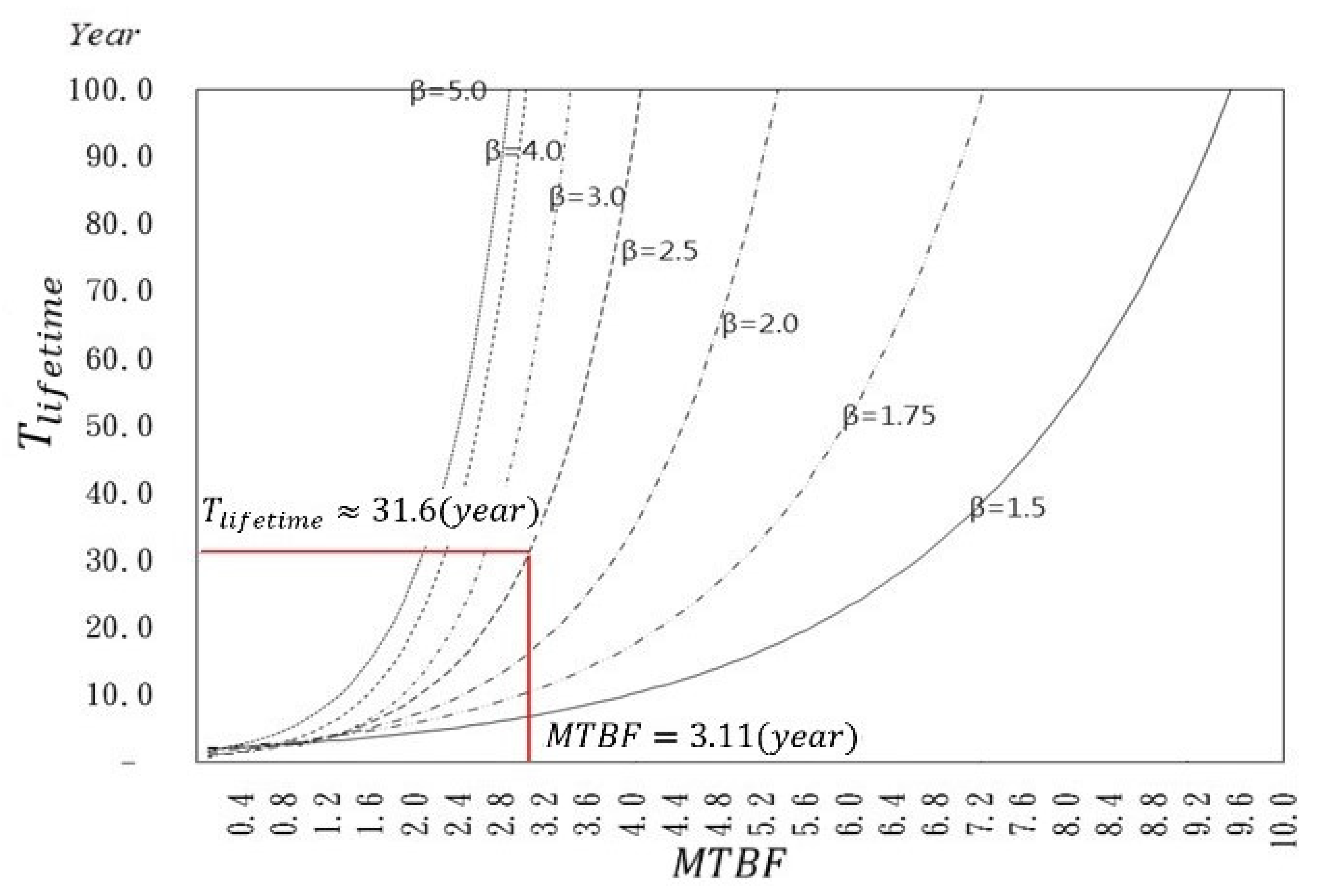
6. Replacement Time Assessment Under Imperfect Maintenance
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lotka, A.J. A Contribution to the Theory of Self-Renewing Aggregates with Special Reference to Industrial Replacement. Ann. Math. Stat. 1939, 10, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.H. On the theory of replacement of machinery with a random failure time. Naval Res. Logist. 1956, 3, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, I.R. Cycling. Naval Res. Logist. 1956, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, S.; Nakagawa, T. A note on age replacement. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1975, 24, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beichelt, F. A Replacement Policy Based on Limits for the Repair Cost Rate. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1982, 31, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabalan, V.; Chaudhuri, D. Optimal maintenance and replacement policy for a deteriorating system with increased mean downtime. Naval Res. Logist. 1992, 39, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aven, T.; Dekker, R. Useful framework for optimal replacement models. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 1997, 58, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheu, S.H. Extended block replacement policy of system subject to shocks. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1997, 46, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, O.; Labeau, P.E.; Mercier, S. Monte Carlo optimization of the replacement strategy of components subject to technological obsolescence. Probab. Saf. Assess. Manag. 2004, 6, 3098–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, S. Optimal replacement policy for obsolete components with general failure rates submitted to obsolescence. Appl. Stoch. Models Bus. Ind. 2008, 24, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Thi, P.K.; Castanier, B.; Yeung, T. Optimal Maintenance and Replacement Decisions under Technological Change. European Safety and Reliability; Greece, 2010; pp. 1430–1437. Available online: http://hal.univ-nantes.fr/hal-00538529v1 (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Berrade, M.D.; Scarf, P.A.; Cavalcante, C.A.V.; Dwight, R.A. Imperfect inspection and replacement of a system with a defective state: A cost and reliability analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 120, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Mizutani, S. A summary of maintenance policies for a finite interval. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2009, 94, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badía, F.G.; Berrade, M.D. Optimum Maintenance Policy of a Periodically Inspected System under Imperfect Repair. Adv. Oper. Res. 2009, 2009, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gage, M.W. Equipment Maintenance and Replacement Decision Making Processes; California Polytechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vorster, M. Equipment Replacement Decisions; C.E.M.P.Central Inc.: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, M.A.K. Reliable Preventive Maintenance Scheduling. AIIE Trans. 1979, 11, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijima, M.; Morimura, H.; Suzuki, Y. Periodic replacement problem without assuming minimal repair. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1988, 37, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipi, T.F.; Lim, J.-H.; Zuo, M.J. A condition- and age-based replacement model using delay time modelling. J. Risk Reliab. 2011, 14, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Z. Fault sample generation for virtual testability demonstration test subject to minimal maintenance and scheduled replacement. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beranek, D.A. Engineering and Design: Reliability Analysis of Navigation Lock and Dam Mechanical and Electrical Equipment (No. ETL-1110-2-560); Corps of Engineers Washington DC: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Kalantarnia, M. Reliability Analysis of Spillway Gate Systems; Department of Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics, McGill University: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]

| Item | Dam | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| No. of samples | 60 | 64 | 33 |
| Critical region (1 − ) | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| Test statistic | 0.908 | 0.726 | 0.931 |
| Null hypothesis | accept | accept | accept |
| : Weibull distribution | |||
| Regression function | 1.637x − 14.24 | 2.373x − 20.535 | 4.885x − 41.716 |
| Shape parameter () | 1.637 | 2.373 | 4.885 |
| Scale parameter () | 5986 h | 5727 h | 5115 h |
| Correlation coefficient () | 0.937 | 0.946 | 0.943 |
| Maintenance/Replacement Cost Ratio | Interest Rate | Mean Time between Failures | Lifetime of Facility | Maintenance Time Point | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 100 | 1.15% | 3.11 | 31.6 | 12.6 |
| 3.11 | 6.22 | 9.33 | 12.44 | 15.55 | 17.80 | 18.66 | 21.77 | 24.88 | 27.99 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.98 | 4.57 | 8.03 | 12.80 | 19.69 | 25.32 | 30.29 | 48.30 | 84.87 | 195.73 | |
| 13.19 | 14.59 | 16.40 | 18.81 | 22.20 | 25.32 | 27.27 | 35.75 | 52.70 | 103.58 | |
| 11.21 | 10.03 | 8.37 | 6.01 | 2.50 | 0.00 | −3.01 | −12.55 | −32.17 | −92.16 | |
| Break-even point * | * |
| Total Lifetime of the Facility | Economic Replacement Time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Parameter | ||||
| (%) | |||||
| 1 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 0.45 | 2 |
| 2 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 6 |
| 3 | 5.0 | 10 | 5.0 | 0.7 | 10 |
| Taguchi Array | Taguchi Array | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Parameters = 2, No. of Levels = 3 | No. of Parameters = 3, No. of Levels = 3 | |||||
| Run # | Para.1 | Para.2 | Run # | Para.1 | Para.2 | Para.3 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leu, S.-S.; Ying, T.-M. Replacement and Maintenance Decision Analysis for Hydraulic Machinery Facilities at Reservoirs under Imperfect Maintenance. Energies 2020, 13, 2507. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102507
Leu S-S, Ying T-M. Replacement and Maintenance Decision Analysis for Hydraulic Machinery Facilities at Reservoirs under Imperfect Maintenance. Energies. 2020; 13(10):2507. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102507
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeu, Sou-Sen, and Tao-Ming Ying. 2020. "Replacement and Maintenance Decision Analysis for Hydraulic Machinery Facilities at Reservoirs under Imperfect Maintenance" Energies 13, no. 10: 2507. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102507
APA StyleLeu, S.-S., & Ying, T.-M. (2020). Replacement and Maintenance Decision Analysis for Hydraulic Machinery Facilities at Reservoirs under Imperfect Maintenance. Energies, 13(10), 2507. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102507





