Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cheese Whey and Industrial Hemp Residues Opens New Perspectives for the Valorization of Agri-Food Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources of Cheese Whey and Raw Hemp
2.2. Processing of Raw Hemp
2.3. Biochemical Methane Potential Assays
2.4. Assessment of the Effect of Anaerobic Co-Digestion
2.5. Analytical Procedures
2.6. Techno-Economic Assessment
2.7. Assumptions for the Estimation of the Biomethane Potential from Cheese Whey and Hemp Hurds in Italy
3. Results and Discussion
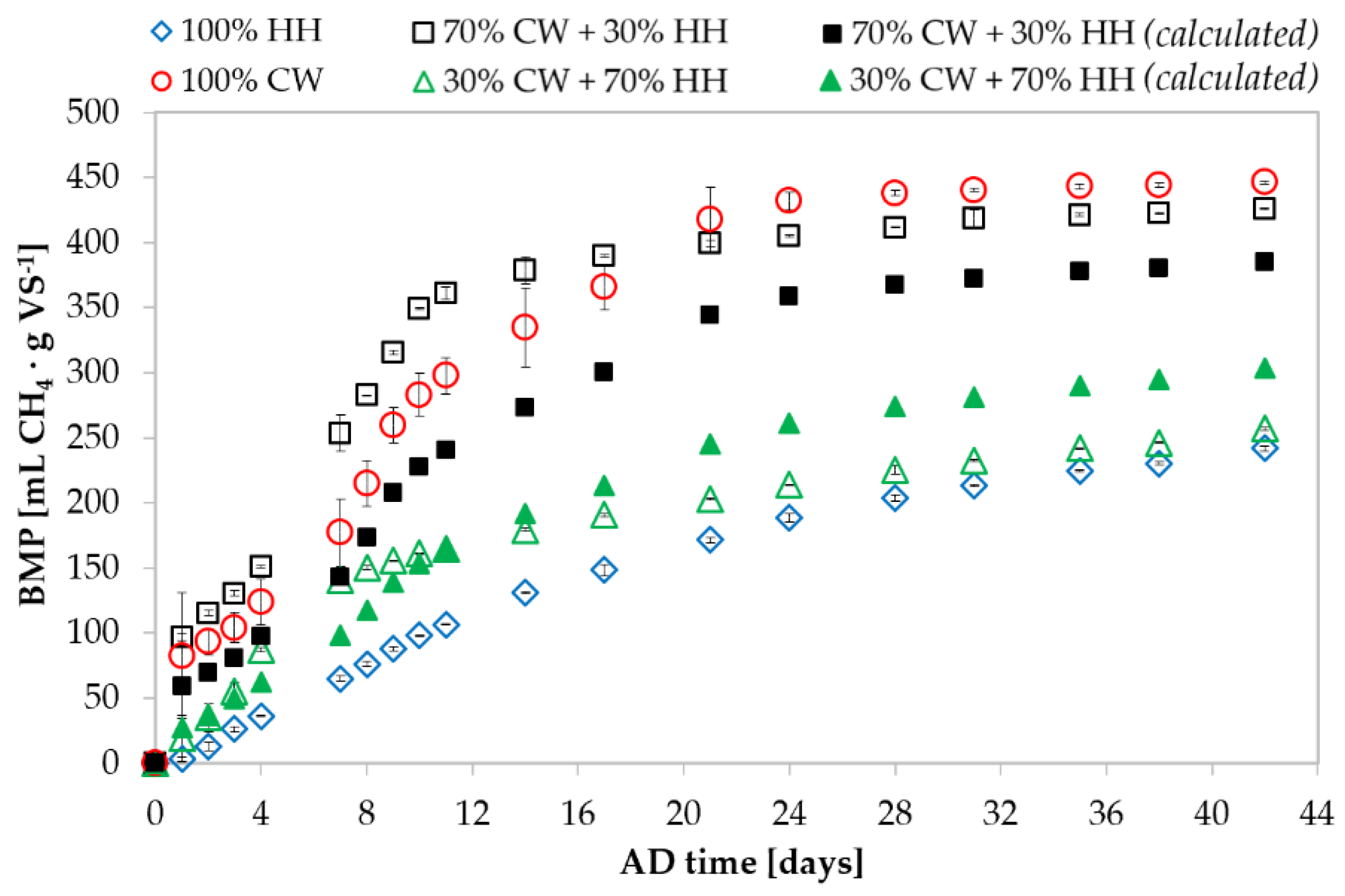
3.1. Anaerobic Digestion of Individual Cheese Whey and Hemp Hurds
3.2. Effect of Co-Digestion on the Biomethane Production of Cheese Whey and Hemp Hurds
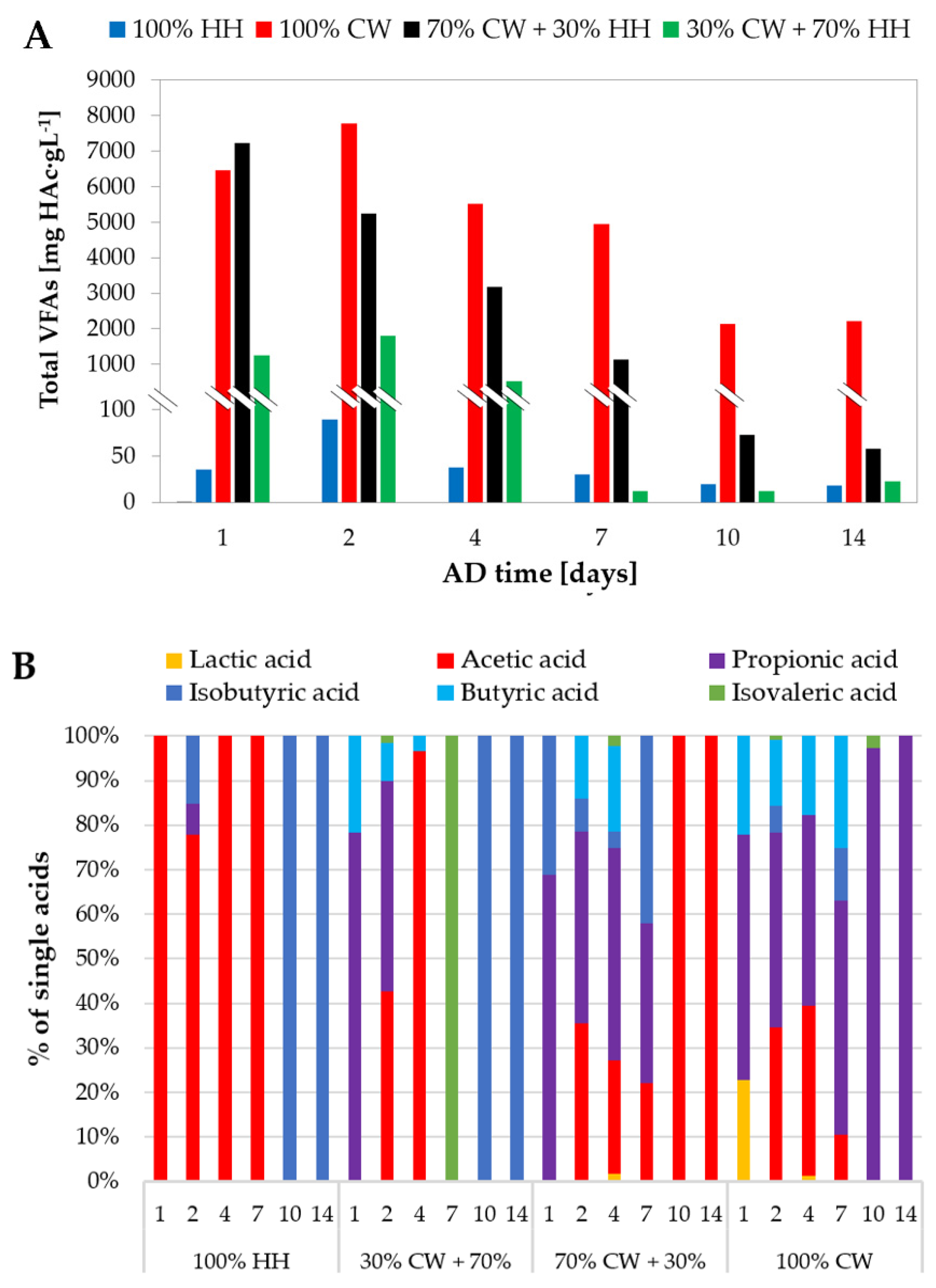
3.3. Evolution and Speciation of Volatile Fatty Acids
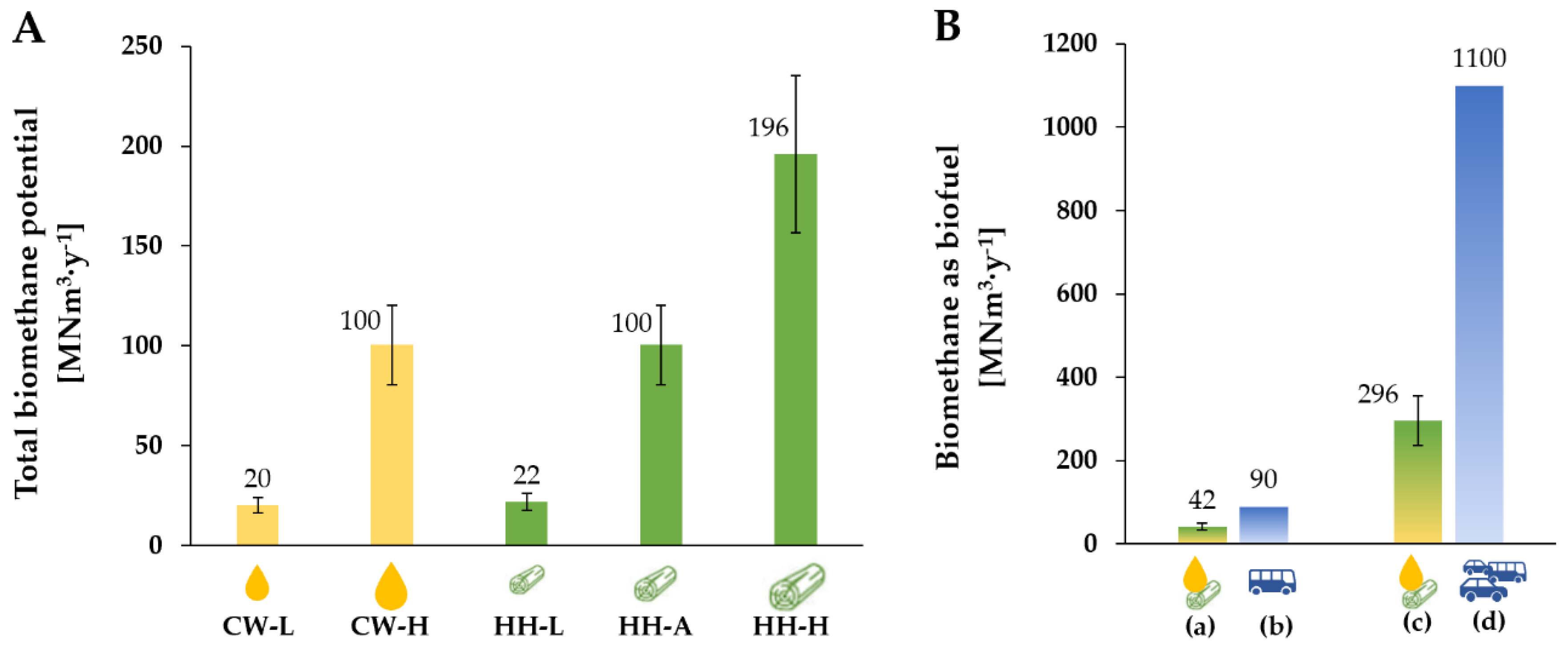
3.4. Preliminary Techno-Economic Assessment of Bioenergy Valorization of Hemp Hurds with and without Cheese Whey
3.5. The Overall Biomethane Potential from Cheese Whey and Hemp Hurds in Italy: A Future Outlook for the Transportation Sector
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bio-Waste in Europe—European Compost Network. Available online: https://www.compostnetwork.info/policy/biowaste-in-europe/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Making the EU Climate-Neutral by 2050. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/IP_20_335 (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Eriksson, M.; Strid, I.; Hansson, P.-A. Carbon footprint of food waste management options in the waste hierarchy—A Swedish case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 93, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, J.; De Mulder, T.; Matassa, S.; Zhou, J.; Angenent, L.T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Stochasticity in microbiology: Managing unpredictability to reach the Sustainable Development Goals. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 0, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlas, M.; Dvořáček, J.; Pitschke, T.; Peche, R. Biowaste Treatment and Waste-To-Energy—Environmental Benefits. Energies 2020, 13, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, H.; Castro, L.; Amaya, M.; Jaimes, L.; Estévez, J.J. Anaerobic digestion of cheese whey: Energetic and nutritional potential for the dairy sector in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.D.F.N.; Prazeres, A.R.; Rivas, J. Cheese whey wastewater: Characterization and treatment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 445, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prazeres, A.R.; Carvalho, M.F.; Rivas, J.; Carvalho, M.D.F.N. Cheese whey management: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzipaschali, A.A.; Stamatis, A. Biotechnological Utilization with a Focus on Anaerobic Treatment of Cheese Whey: Current Status and Prospects. Energies 2012, 5, 3492–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaducci, S.; Scordia, D.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, H.; Testa, G.; Cosentino, S.L. Key cultivation techniques for hemp in Europe and China. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 68, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Struik, P.; Yin, X.; Thouminot, C.; Bjelková, M.; Stramkale, V.; Amaducci, S. Comparing hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivars for dual-purpose production under contrasting environments. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 87, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cas, M.D.; Casagni, E.; Saccardo, A.; Arnoldi, S.; Young, C.; Scotti, S.; De Manicor, E.V.; Gambaro, V.; Roda, G. The Italian panorama of cannabis light preparation: Determination of cannabinoids by LC-UV. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 307, 110113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovic, A.; Dubrovskis, V.; Platače, R. Productivity of industrial hemp and its utilisation for anaerobic digestion. Quest Sustain. Energy 2014, 190, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuger, E.; Prade, T.; Escobar, F.; Svensson, S.-E.; Englund, J.-E.; Björnsson, L. Anaerobic digestion of industrial hemp–Effect of harvest time on methane energy yield per hectare. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review on analysis in pretreatment of lignocelluloses: Degree of polymerization, adsorption/desorption, and accessibility. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, G.; Papirio, S.; Lens, P.N.; Esposito, G. A Preliminary Study of the Effect of Bioavailable Fe and Co on the Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw. Energies 2019, 12, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshat, S.A.; Mohammadi, M.; Najafpour-Darzi, G.; Lahijani, P. Anaerobic co-digestion of animal manures and lignocellulosic residues as a potent approach for sustainable biogas production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussoline, W.; Esposito, G.; Lens, P.N.; Spagni, A.; Giordano, A. Enhanced methane production from rice straw co-digested with anaerobic sludge from pulp and paper mill treatment process. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Güiza, M.; Vila, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Simon, F.-G.; Astals, S. The role of additives on anaerobic digestion: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papirio, S. Coupling acid pretreatment and dosing of Ni and Se enhances the biomethane potential of hazelnut skin. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Continuous anaerobic co-digestion of Ulva biomass and cheese whey at varying substrate mixing ratios: Different responses in two reactors with different operating regimes. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanand, V.; Mulat, D.G.; Eijsink, V.G.; Horn, S.J. Synergistic effects of anaerobic co-digestion of whey, manure and fish ensilage. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Monteverde, G.; Race, M.; Papirio, S.; Esposito, G. Comparing performances, costs and energy balance of ex situ remediation processes for PAH-contaminated marine sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19363–19374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gusovius, H.-J.; Lühr, C.; Musio, S.; Uhrlaub, B.; Amaducci, S.; Müssig, J. Assessment system to characterise and compare different hemp varieties based on a developed lab-scaled decortication system. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 117, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Race, M.; Papirio, S.; Esposito, G. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during anaerobic biostimulation of marine sediments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 709, 136141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AWWA-WEF, A.P.H.A. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Edición 2005, 21, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cucchiella, F.; D’Adamo, I.; Gastaldi, M. Sustainable Italian Cities: The Added Value of Biomethane from Organic Waste. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.; Liu, E.; Saeed, A.; Williams, D.W.; Hu, H.; Li, C.; Ray, A.E.; Shi, J. Industrial hemp as a potential bioenergy crop in comparison with kenaf, switchgrass and biomass sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluttenhofer, C.; Yuan, L. Challenges towards Revitalizing Hemp: A Multifaceted Crop. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.; Li, W.; Dodge, L.A.; Stevens, J.C.; Williams, D.W.; Hu, H.; Li, C.; Ray, A.E.; Shi, J. Comparative Evaluation of Industrial Hemp Cultivars: Agronomical Practices, Feedstock Characterization, and Potential for Biofuels and Bioproducts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 6200–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prade, T.; Svensson, S.-E.; Andersson, A.; Mattsson, J.E. Biomass and energy yield of industrial hemp grown for biogas and solid fuel. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, F.; Carletto, R.A.; Marmo, L. An Integrated Cheese Whey Valorization Process. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2018, 64, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiermann, M.; Plöchl, M.; Linke, B.; Schelle, H.; Herrmann, C. Biogas Crops—Part I: Specifications and Suitability of Field Crops for Anaerobic Digestion. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2009, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Števulová, N.; Cigasova, J.; Estokova, A.; Terpáková, E.; Geffert, A.; Kačík, F.; Singovszka, E.; Holub, M. Properties Characterization of Chemically Modified Hemp Hurds. Materials 2014, 7, 8131–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagos, K.; Zong, J.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Lu, X. Anaerobic co-digestion process for biogas production: Progress, challenges and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astals, S.; Batstone, D.J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Jensen, P. Identification of synergistic impacts during anaerobic co-digestion of organic wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imeni, S.M.; Pelaz, L.; Corchado-Lopo, C.; Busquets, A.M.; Ponsá, S.; Colón, J. Techno-economic assessment of anaerobic co-digestion of livestock manure and cheese whey (Cow, Goat & Sheep) at small to medium dairy farms. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labatut, R.A.; Angenent, L.T.; Scott, N.R. Biochemical methane potential and biodegradability of complex organic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atasoy, M.; Eyice, O.; Cetecioglu, Z. A Comprehensive Study of Volatile Fatty Acids Production from the Batch Reactor to Anaerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor by Using Cheese Processing Wastewater. Bioresour Technol. 2020, 311, 123529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, G.; Papirio, S.; Lens, P.N.; Esposito, G. Solvent Pretreatments of Lignocellulosic Materials to Enhance Biogas Production: A Review. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 1892–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gioannis, G.; Friargiu, M.; Massi, E.; Muntoni, A.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Spiga, D. Biohydrogen production from dark fermentation of cheese whey: Influence of pH. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 20930–20941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaducci, S. Hemp Production in Italy. J. Ind. Hemp 2005, 10, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consorzio Italiano Biogas e Gassificazione 2018. pp. 1–119. Available online: https://www.consorziobiogas.it/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/Biogas-INFORMA-24-Speciale-Biometano.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- EU Science Hub Renewable Energy—Recast to 2030 (RED II)_EU Science Hub. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/jec/renewable-energy-recast-2030-red-ii (accessed on 14 May 2020).

| Parameter | Cheese Whey | Hemp Hurds | Inoculum |
|---|---|---|---|
| TS [%] | 5.93 ± 0.63 | 89.66 ± 0.19 | 6.65 ± 0.08 |
| VS [%] | 5.00 ± 0.63 | 85.77 ± 0.50 | 4.51 ± 0.02 |
| tCOD [g·L−1] | 47.50 ± 0.46 | n.a. | n.a. |
| N-NH4+ [g·L−1] | 0.07 ± 0.01 | n.a. | 1.12 ± 0.05 |
| NTOT [g·L−1] | 0.48 ± 0.05 | n.a. | 1.39 ± 0.04 1 |
| pH | 4.75 ± 0.08 | n.a. | 8.57 ± 0.02 1 |
| Experimental Condition | Initial vs. [g] | BMPexp [mL CH4·g VS−1] | BMPcalc [mL CH4·g VS−1] | Δ [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW | HH | ||||
| 100% CW | 0.90 | - | 446 ± 66 | ||
| 70% CW + 30% HH | 0.63 | 0.27 | 426 ± 31 | 385 | +10.7% |
| 30% CW + 70% HH | 0.27 | 0.63 | 257 ± 34 | 303 | −15.2% |
| 100% HH | - | 0.90 | 242 ± 13 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papirio, S.; Matassa, S.; Pirozzi, F.; Esposito, G. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cheese Whey and Industrial Hemp Residues Opens New Perspectives for the Valorization of Agri-Food Waste. Energies 2020, 13, 2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13112820
Papirio S, Matassa S, Pirozzi F, Esposito G. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cheese Whey and Industrial Hemp Residues Opens New Perspectives for the Valorization of Agri-Food Waste. Energies. 2020; 13(11):2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13112820
Chicago/Turabian StylePapirio, Stefano, Silvio Matassa, Francesco Pirozzi, and Giovanni Esposito. 2020. "Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cheese Whey and Industrial Hemp Residues Opens New Perspectives for the Valorization of Agri-Food Waste" Energies 13, no. 11: 2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13112820
APA StylePapirio, S., Matassa, S., Pirozzi, F., & Esposito, G. (2020). Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cheese Whey and Industrial Hemp Residues Opens New Perspectives for the Valorization of Agri-Food Waste. Energies, 13(11), 2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13112820








