Abstract
The paper presents mathematical modelling of steam condensation in the atmospheric air transonic flows. A single-fluid model was employed. The model was validated against the in-house experimental studies of internal flow in nozzles and against benchmark tests available in literature i.e., RAE2822 transonic airfoil. The impact of air relative humidity on the condensation process under transonic flow conditions was examined. The paper shows that the impact of the condensation process in air transonic flow is non-negligible and has to be taken under consideration in flow simulations. The presence of air contaminants in form of small particles was considered too. Their crucial role in the change of the transonic flow structure was numerically confirmed.
1. Introduction
Air is certainly one of the most popular working fluids in power and transport machinery and installations. Air that has not been dried always contains a certain amount of water in the form of vapour or small droplets, called humidity. Relative humidity indicates the ratio between the actual amount of water and the maximum amount the air can hold. Ambient humidity is conditioned by the geographical location. The areas of highest humidity are located in the equatorial zone, where the relative humidity is above 70%. In extreme conditions, air humidity can reach 90%. Therefore, it is reasonable to investigate the humidity influence on flow aerodynamics, for example, flow around an aerofoil [1], especially in the transonic regime.
The condensation can be divided, based on the triggering phenomenon, into homogenous and heterogeneous. The homogenous condensation process occurs spontaneously when the condensation nuclei of the critical size are formed. The suitable conditions for the homogenous condensation are, especially, behind the sonic line, where the pressure drops significantly. In moist air transonic flows, the condensation process can be very sudden, forming a so-called condensation wave, which, due to latent heat release, exerts a significant impact on the flow. Heterogeneous condensation is triggered by impurities that are present in the air and they play the role of nuclei of critical size. The most popular experimental studies of moist air transonic flow are the works of Schnerr et al. [2,3], who proposed a model based on the kinetic nucleation theory, and it has been successfully implemented to numerical solvers by many researchers. The valuable input was provided by Adam [4], who conducted numerous experimental and numerical studies of non-stationary condensation in internal flows. In terms of aviation, the condensation can take place in the compressor (or fan) inlet channels and compressor blade-to-blade channels [5]. In both cases, the transition from subsonic to supersonic is accompanied by shock waves.
The importance of condensation induced by spontaneous nucleation and air pollution has also encouraged scientists to investigate its influence regarding external flows [6,7]; however, the result presented by the authors indicate different effects of condensation on lift and drag forces acting on the airfoil in transonic flow regime. The discrepancy of results presented by different authors directs us to continue the research initiated by Schnerr over 30 years ago in the area of condensation.
The results presented in this paper were obtained through commercial CFD software, ANSYS Fluent. The condensation model was implemented using User Defined Functions (UDF’s). The models were validated based on experimental studies conducted in the Department of Power Engineering and Turbomachinery of Silesian University of Technology and based on experimental data available in the literature [4,8,9]. The implementation of the condensation into commercial software (including its validation) was one of the main aims of this study, as the commercial codes give a robust and reliable tool for a wide range of applications—their major advantage over specialized—dedicated for single application academic codes.
2. Numerical Model
The numerical studies presented herein were conducted using the commercial software ANSYS Fluent. The airflow conservation equations are formulated for the compressible flow using Unsteady Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (URANS) equations. The condensation model is implemented to the numerical solver employing UDFs. The inviscid and viscid models were considered. The turbulence effect is modelled using the kω-Shear Stress Transport (SST) model proposed by Menter [10]. The works by Dykas et al. [5,11,12,13] were taken as references for the numerical solver settings and used numerical techniques. The air parameters were computed based on the ideal gas model.
2.1. Homogenous Condensation
The homogenous condensation model, based on the Kinetic Gas Theory, is implemented to the ANSYS Fluent numerical solver by means of UDFs. In the model, the humid air with a liquid droplet phase is treated as a homogenous fluid. Thus, one set of the mass, momentum, and energy conservation equations for the single-fluid model are being solved. The fundamental condition for homogenous condensation is the formation and growth of nuclei in water vapour. Therefore, the nucleation rate is described based on classical nucleation theory [14], the critical radius, , is described by a form of Kelvin equation [12], assuming the perfect gas model, it takes the following form:
where is surface tension, is liquid density, is gas constant, is vapor temperature and are vapor and saturation pressure. The nucleation rate,, number of nuclei in time per kilogram, can be further calculated from following equation:
where is Kantrowitz correction [15], is water molecular mass, is vapour density, is Boltzmann constant. The droplet growth rate is based on the molecular kinetic droplet growth rate [14]:
where is time derivative. The droplet radius is further calculated as an average value base on the liquid water mass fraction and the number of droplets. Based on the nucleation and droplet growth equation the sources of mass, energy, and momentum can be derived.
Two additional conservation equations regarding mass fraction, and number of droplets, , with appropriate source terms are computed. These equations were introduced by use of a built-in solver function, User Defined Scalar, which allows to create additional conservation equation with the flux function based on the mass flow rate. These equation take the following form:
where and are time and space derivatives, denotes the considered scalar, in this case it is liquid mass fraction and number of droplets, is the directional component of the velocity vector. The S is the source terms, which, for liquid mass fraction and droplet numbers, have the following forms:
2.2. Heterogeneous Condensation
The heterogeneous condensation is based on the same physical phenomena that drives the droplet growth in homogenous condensation. However, the condensation occurs on the particles that are already present in the fluid, for example, pollution or dust. Thus, nucleation does not occur and the critical radius condition does not have to be met (see Equations (1) and (2)). The droplet growth rate is also based on the molecular kinetic droplet growth (see Equation (3)), and the droplet radius,, is computed as follows:
where the is the initial radius of suspended particles and is the particles number per kilogram. As the number of droplets is constant, to describe the phenomena of heterogeneous condensation, only single conservation equation for liquid water mass fraction is needed; it is implemented in the same manner as for homogenous condensation (see Equation 4). The source term takes a simplified (without nucleation term) form of the homogenous condensation source term:
It has to be pointed out that the assumption of suspended particle density equal to liquid water density is made. This assumption can be justified by the character of the droplet mass change with the radius growth. Doubling the diameter causes an eightfold increase of mass, with expected tenfold or higher droplet radius change, the initial mass of the particles is less than 0.1% of the final droplet mass; therefore, its initial density change can be neglected. Additionally, that assumption is justified in case of mist flow, i.e., flow through medium with suspended water droplets.
3. Internal Flow
3.1. Circular Nozzle
The experimental studies, regarding nozzle with a circular profile, with a diameter of 100 mm and throat of 20 mm, provide validation data for the condensation model. The supersonic outflow and subsonic outflow cases were taken into consideration. The subsonic outflow occurs when the backpressure is relatively high, the normal shock wave arises in the divergent section of the nozzle and the transition from supersonic to subsonic occurs. The mesh, depicted in Figure 1, which consists of 141 × 151 nodes, where the y+ is equal to ~1 and boundary layer growth ratio equal to 1.05 was used. The mesh number of elements was selected based on previous studies [11] and is considered as not affecting the solution.

Figure 1.
Nozzle numerical mesh.
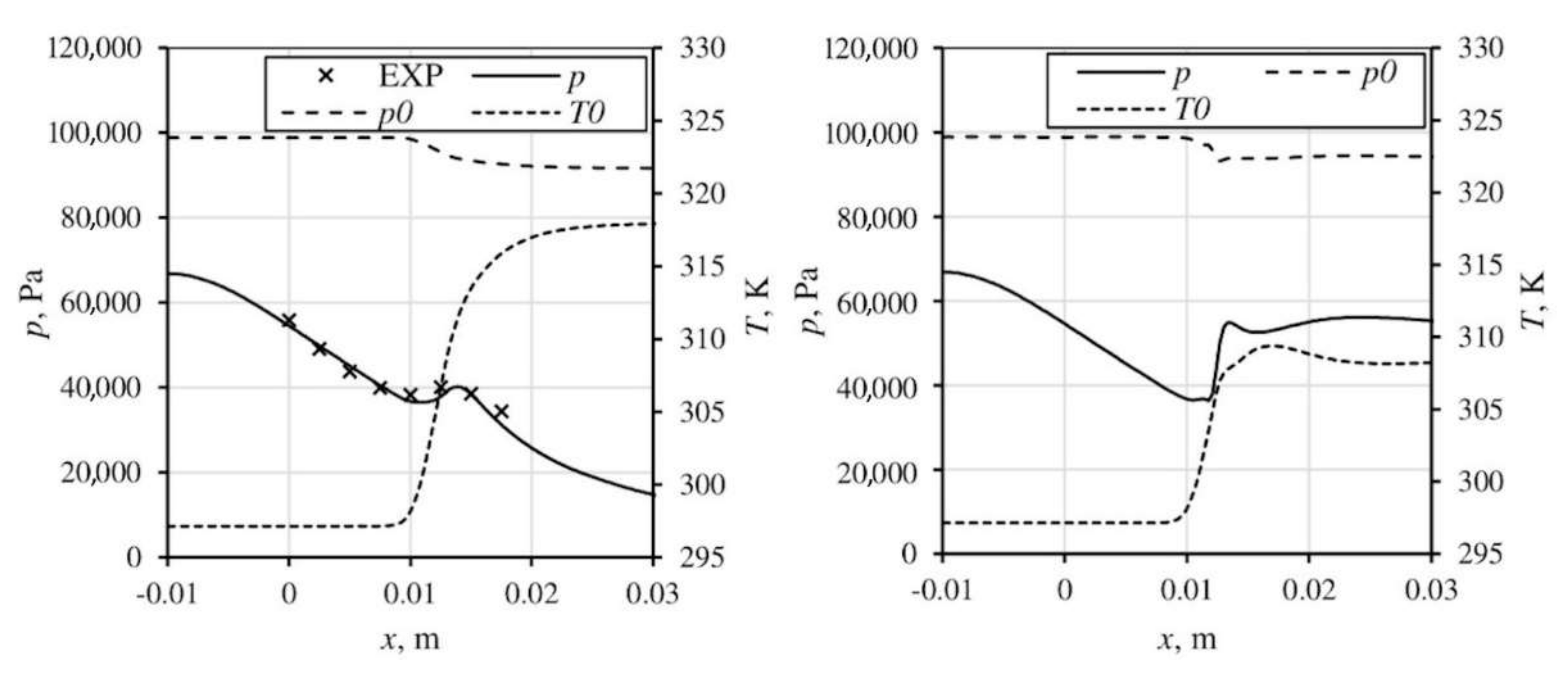
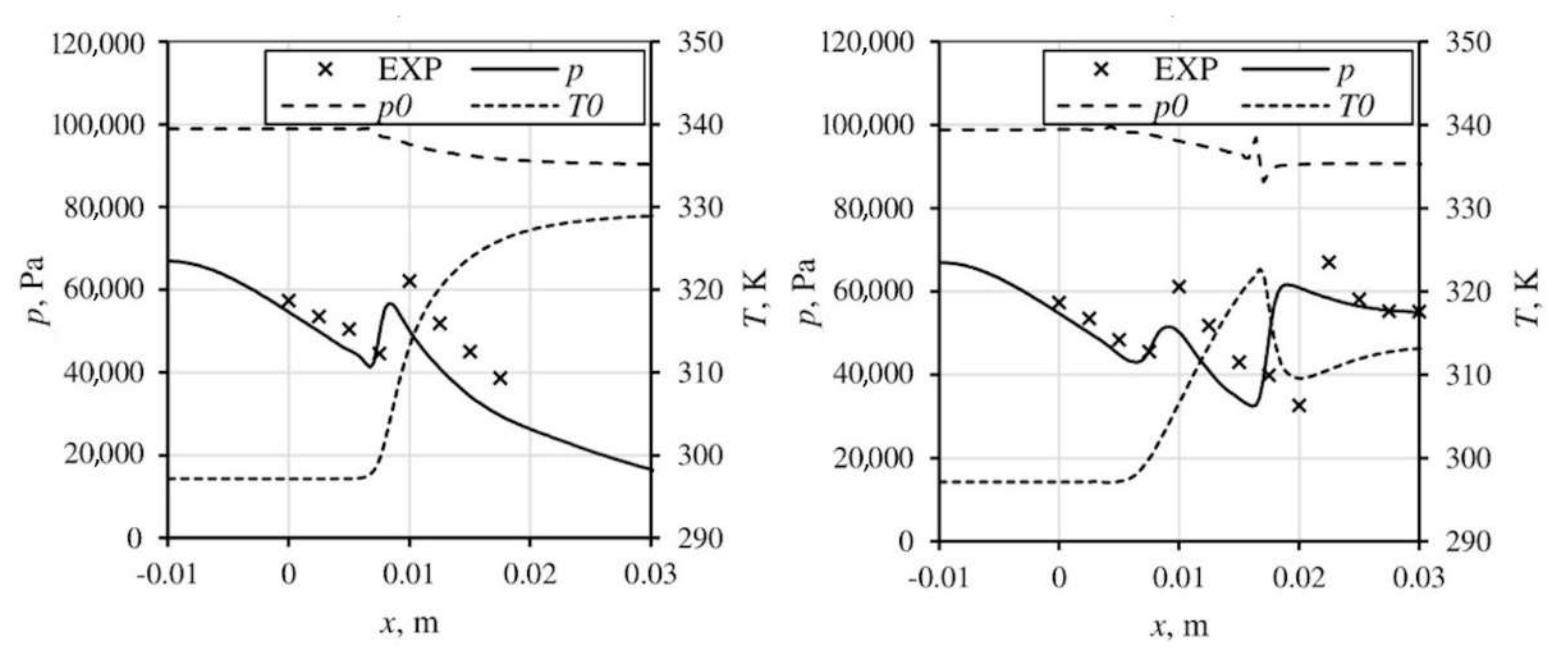
The calculations were performed for atmospheric air of total temperature equal to 297 K and total pressure equal to 98.8 kPa. The computations were performed for different air relative humidity of 0%, 43% and 68%. The outflow boundary conditions are supersonic outflow and outflow with backpressure equal to 55 kPa, which triggers a strong normal shock wave with Mach number drop from 1.45 to 0.8. Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the static and total parameters along the nozzle. The influence of latent heat release due to the condensation process is visible, it causes a significant drop of total pressure and increment of total temperature. The drop of total temperature on the shock wave is caused by the evaporation of water. The pressure increment drove by condensation delays the shock wave position, which is especially visible in Figure 3 (right).

Figure 2.
The experimental and numerical results for relative humidity equal to 43% (supersonic outlet—left, back pressure 55 kPa—right).

Figure 3.
The experimental and numerical results for relative humidity equal to 68% (supersonic outlet—left, back pressure 55 kPa—right).
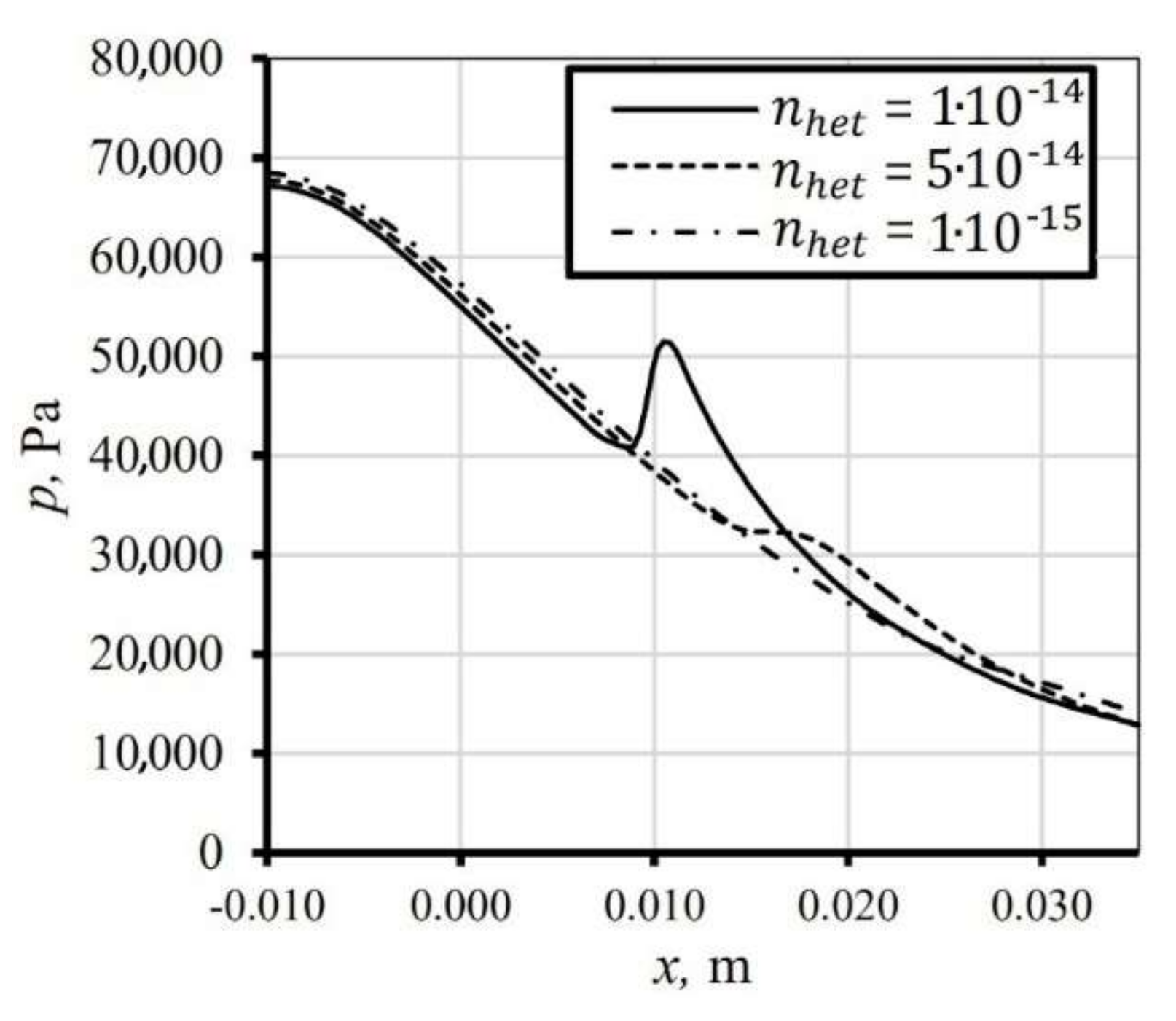
The air always contains a number of suspended particles; thus, the influence of the air impurities on the condensation phenomena was investigated. Figure 4 shows the influence of heterogeneous condensation on the flow character, the number of suspended particles () is based on the data available in literature [6]. As it is shown, the increment of the pollution number of particles flattens the pressure increment due to the condensation; it is caused because the nucleation importance decreases as the condensation occurs on the pollution particles. Another crucial aspect is the size of the contamination particles. In this study, we considered the polydisperse droplet size, which radius was equal to 10−8 m, which corresponds to diameter used by researchers in the literature data [6]. However, the size of the particles can differ significantly. The national standard of air pollution, which corresponds to World Health Organization recommendations regarding air pollution levels, is defined for fine (PM2.5) and coarse (PM10) particles, i.e., particles with a diameter up to 2.5 × 10−6 m and up to 10 × 10−6 m [16,17].

Figure 4.
The numerical results for condensing flow with different number of impurities content and relative humidity equal to 70%.
3.2. Parallel Nozzle
The nozzle with parallel outlet walls gives the possibility to perceive high instabilities of the condensation phenomenon yielding to symmetric or non-symmetric oscillations, depending on the humidity. Thus, the numerical studies were conducted based on the data from Adam studies [4].
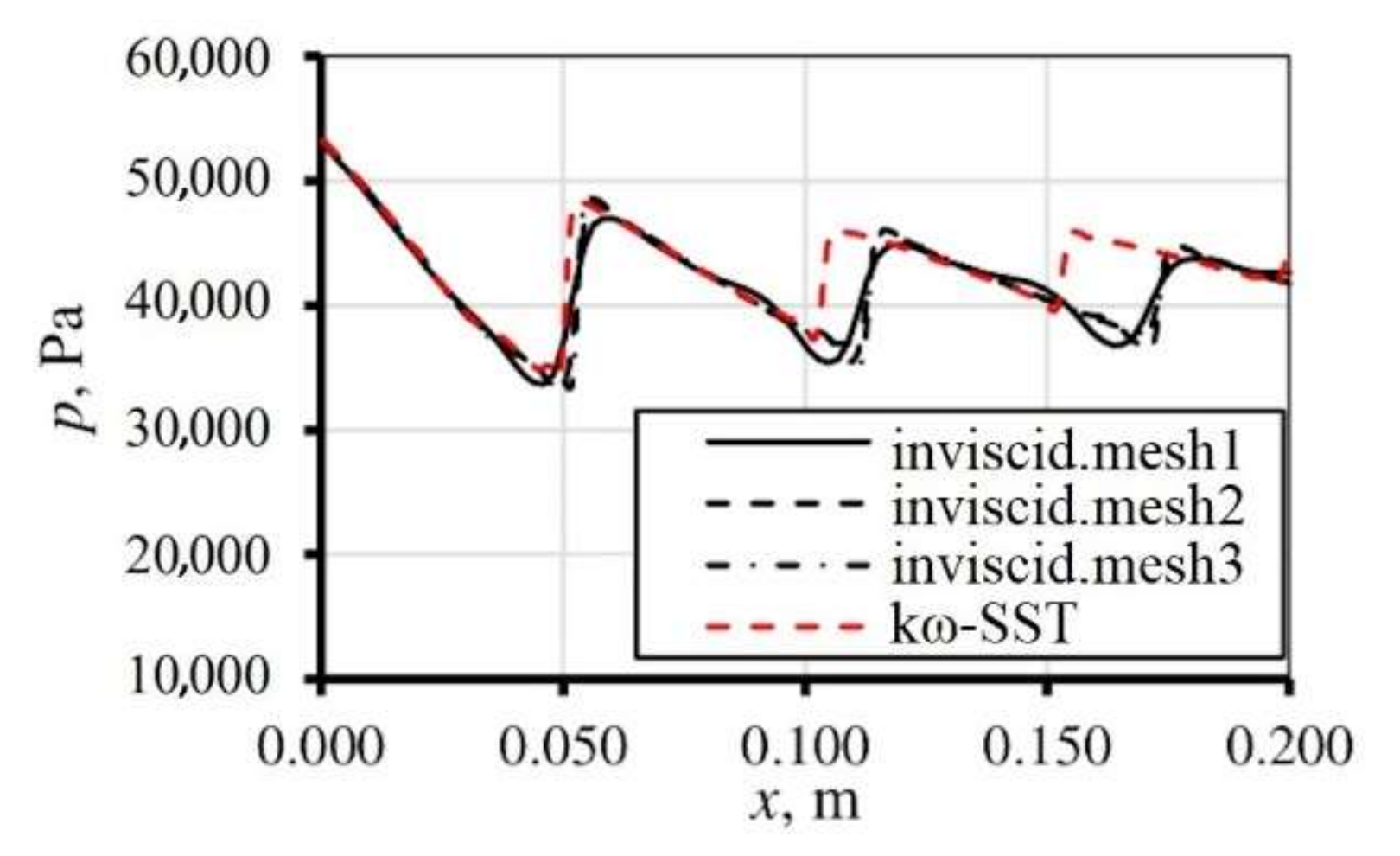
The calculations were done for inviscid and viscid flow models, where the kω-SST was used to describe the shear stresses. Using the inviscid model, the mesh dependence studies were conducted, the parameters of flow are described hereafter. Three meshes with the number of nodes equal to 51 × 141, 101 × 281, and 201 × 561 were tested. Figure 5 shows the influence of mesh number of elements onto the static pressure along the nozzle axis; it also shows the influence of the turbulence. The mesh with the number of elements 201 × 561 was considered to give the results, independent of further increments of elements numbers. For the viscid flow, the mesh in the boundary layer was compacted, the y+ function was kept on the level of ~1, and the boundary layers growth ratio was equal to 1.05, resulting with mesh that has 301 × 561 elements.

Figure 5.
Impact of mesh number of elements on the results.
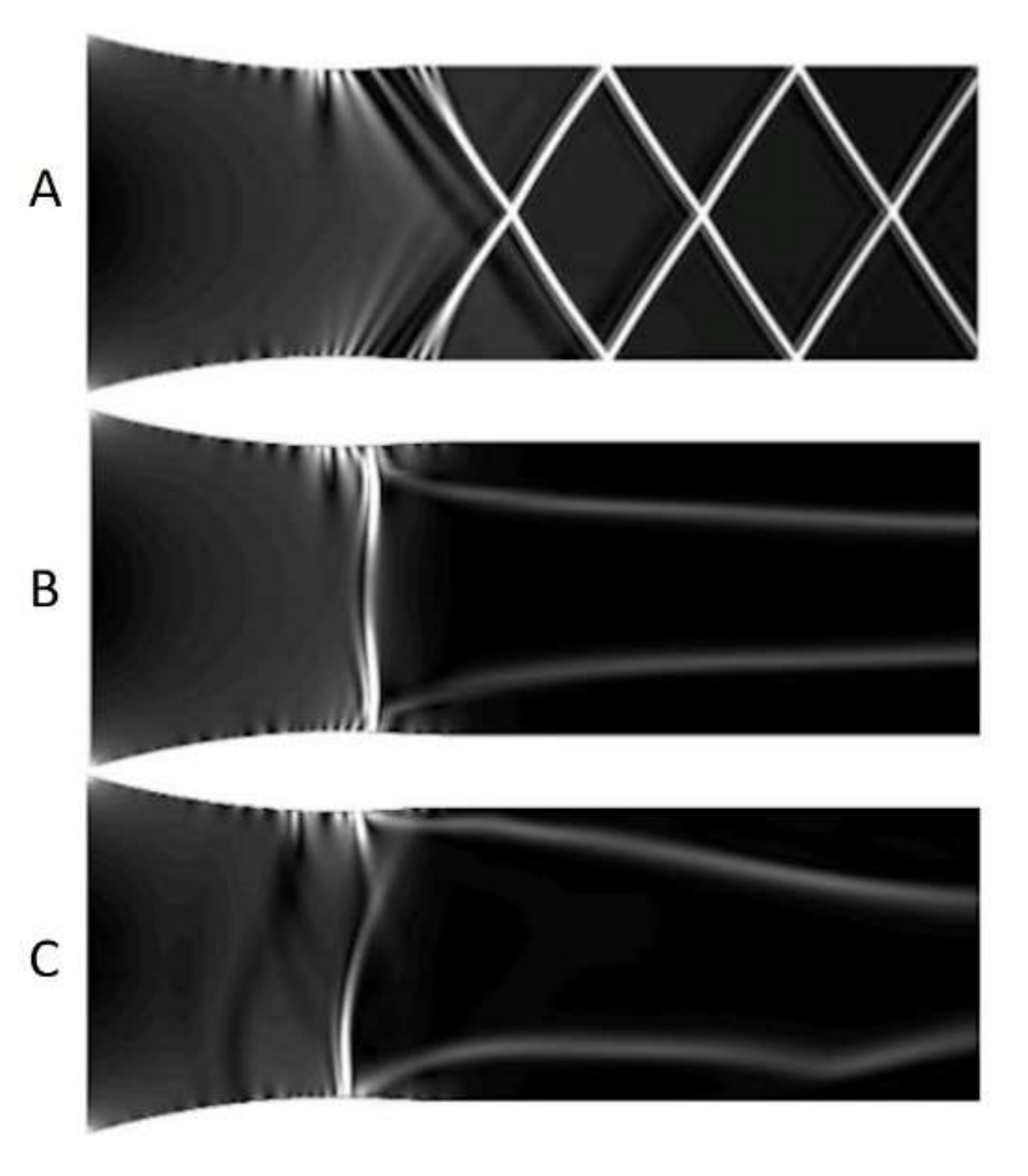
Furthermore, the studies were performed for atmospheric air, of stagnation temperature (T01) equal to 292.8 K and stagnation pressure (p01) equal to 98.8 kPa; three cases with humidity of 0%, 51.6%, and 82% were considered. Figure 6 shows the numerical Schlieren images for dry and humid airflow. In the case of dry airflow, the characteristic pattern of so-called shock diamonds or Mach disks appear, see Figure 6A.

Figure 6.
The numerical Schlieren for inviscid flow in parallel nozzle with humidity equal to (A) 0%, (B) 51.6%, (C) 82%.
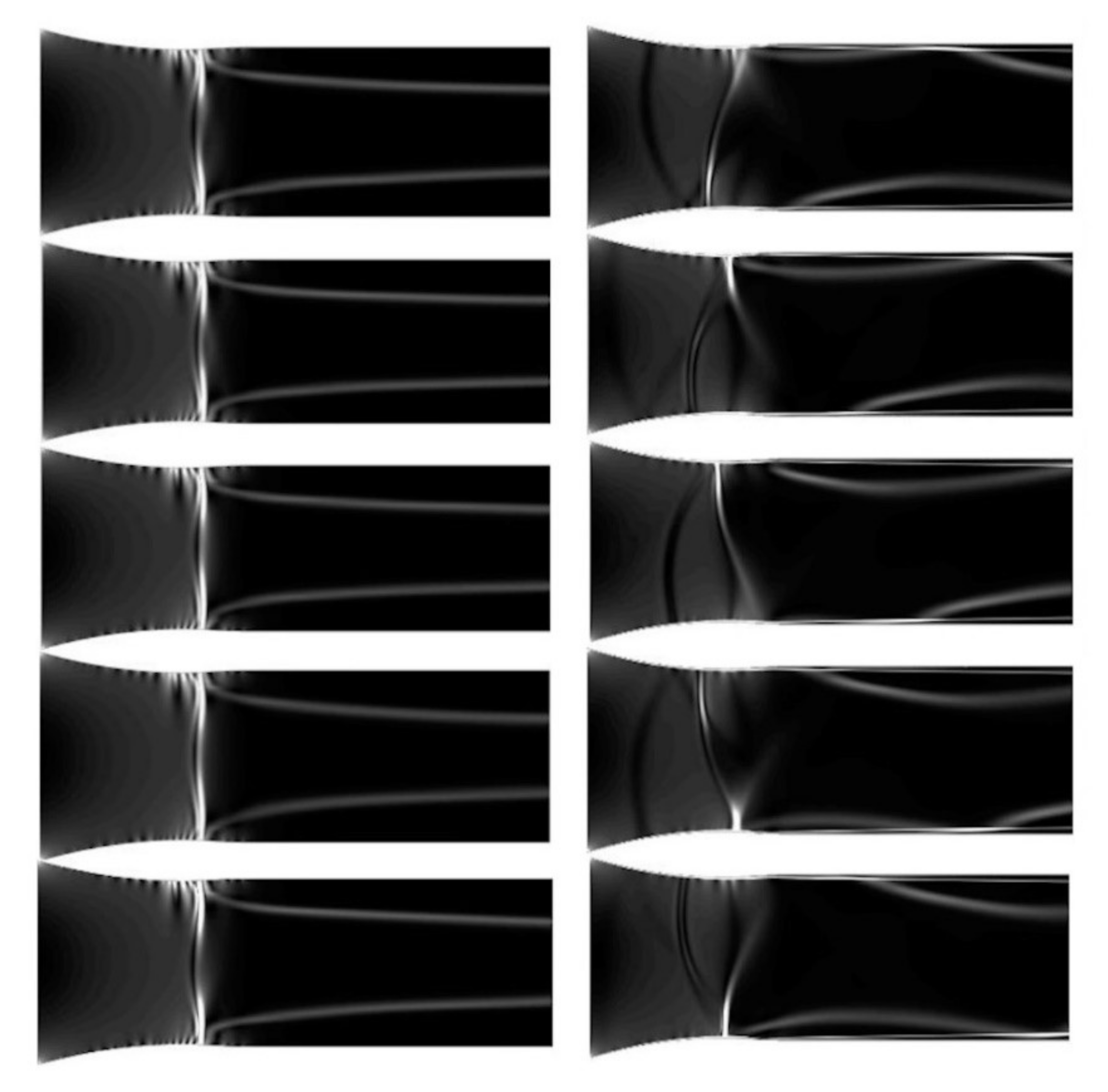
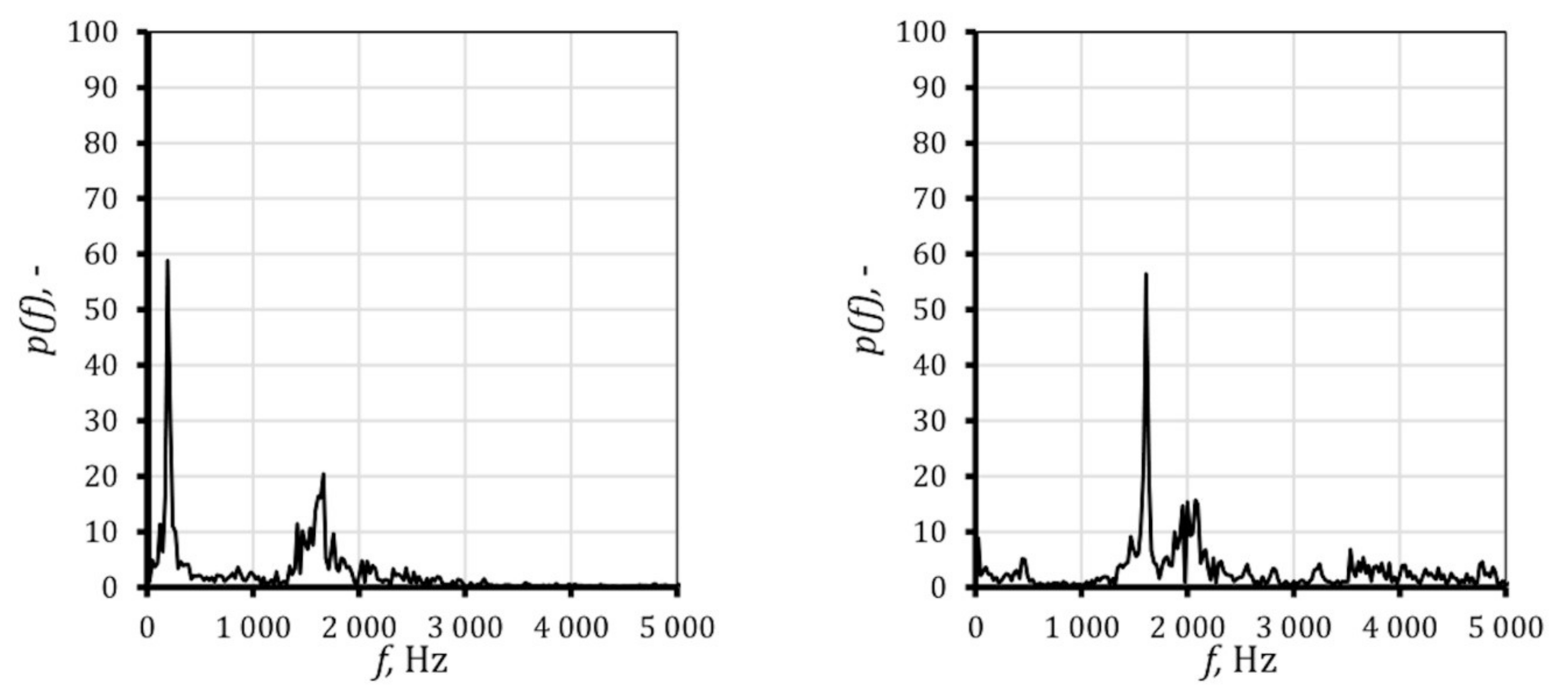
The Mach discs are the consecutive expansion and compressions waves. This phenomenon occurs when the flow is under-expanded; its pressure is lower than the ambient pressure, so the supersonic expansion process occurs to reach the ambient pressure. The flow has to be parallel to the nozzle centreline; thus, if the expansion shock is strong enough to reach the centreline, another expansion wave is created, and a region where the pressure drops below the ambient one is created. As the pressure drops below the ambient one, a compression shock appears. For viscid flow, the distance between consecutive shock drops significantly; it is caused by viscous losses. Figure 7 shows one full oscillation cycle (from up to bottom); the oscillation period for the low humidity case is 1/195 s and for high humidity case amounts to 1/984 s. It shows the influence of air humidity on the condensation wave character; the non-symmetrical oscillations appear for the high humidity case. Based on the obtained results, the Fast Fourier Transform was performed to distinguish the major oscillation frequency. The transform was performed on the 1024 data point, which cover 0.04 s of flow. This time is considered to give a reliable description, as it covers at least 10 full oscillation cycles. Figure 8 shows the pressure amplitude in function of frequency for the nozzle with relative humidity equal to 51.6%. The results distinguish two major frequencies for the inviscid method and one for the kω-SST turbulence model. The discrepancy between the numerical simulation and experimental studies is significant, additionally, the influence of turbulence description is non-negligible. However, such discrepancy was not observed in the simulation of higher relative humidity value, the frequencies in both models, inviscid and kω-SST, are consistent and show better convergent with the experimental results. The frequency of oscillations computed numerically and the experimental results for flow with relative humidity, φ, equal to 51.6% and 82%, are shown in Table 1. Theoretically, the shape of the nozzle contributes to the minimization of the viscous effects due to the very thin wall boundary layer. However, the interaction of the pressure waves with a wall boundary layer for viscous flow modelling has a visible effect on the flow field. The significant influence of turbulence modelling is driven by viscous forces. The experimental data and the numerical indicates the need for further studies; it is planned to perform a complex analysis of turbulence modelling influence on the oscillation phenomena.

Figure 7.
One oscillation cycle in a parallel nozzle for inviscid flow model with air relative humidity equal to 51.6% (left, ~Δt = 10−3 s) and 82% (right, ~Δt = 20−4 s).

Figure 8.
Oscillation frequency for parallel nozzle with air relative humidity equal to 51.6%, using inviscid (left) and kω-SST (right) modelling.

Table 1.
Experimental (fexp) and numerical (inviscid finvis, viscous fkω-SST) frequency of oscillations for flow with relative humidity, φ, equal to 51.6% and 82%.
4. External Flow
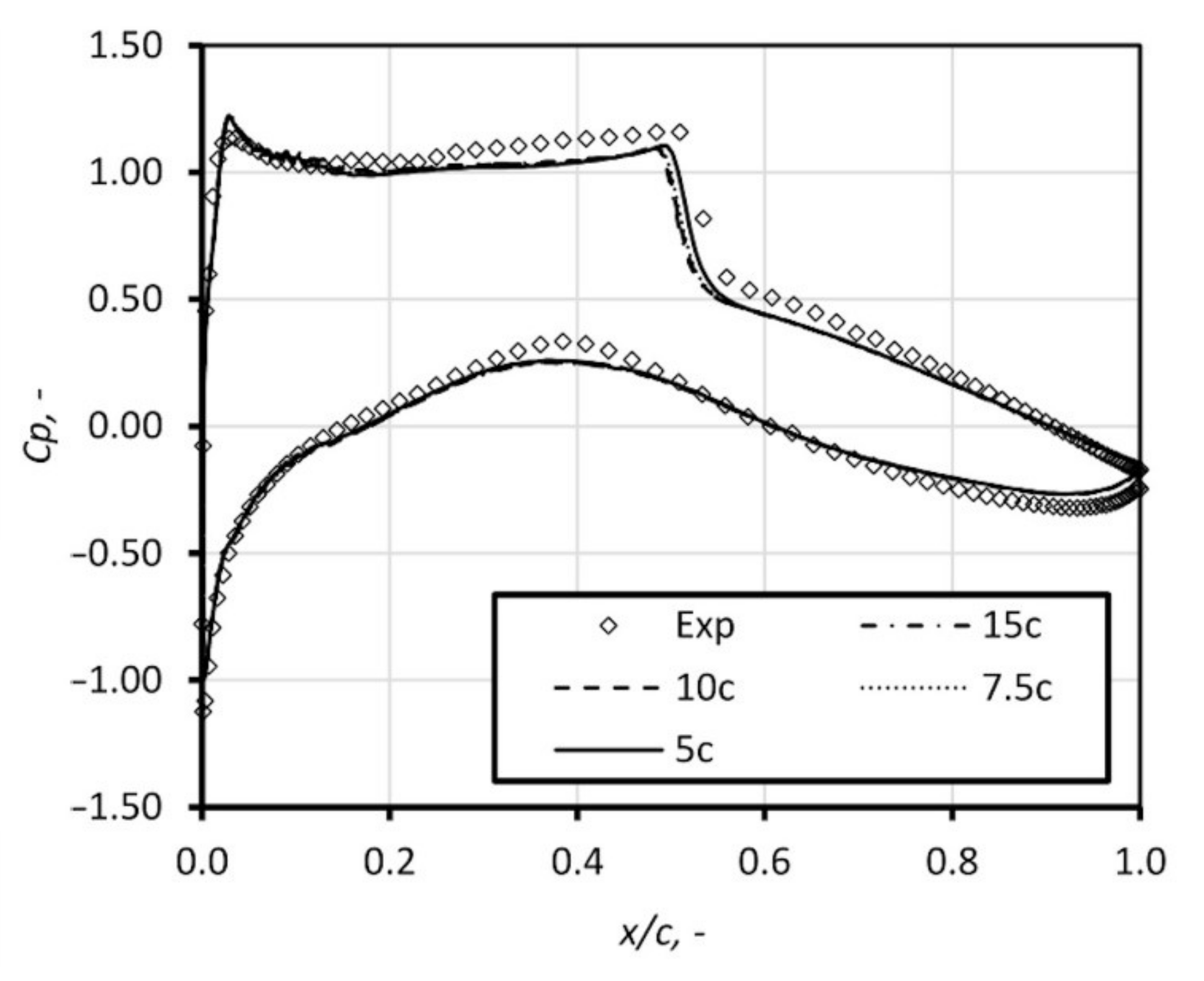
The condensation is in major importance during computations of external flow. The validation of the numerical code was performed based on the flow conditions available in the literature [9,18,19]. The flow conditions were set by the total pressure and the total temperature at the inlet boundary condition and by the static pressure at the outlet boundary condition. The air is assumed to be dry, i.e., the relative humidity is equal to 0%. The domain and the mesh are depicted in Figure 9. The mesh number of elements along the airfoil is equal to 500; the boundary layer was introduced to ensure the y+ value equal to ~1, the growth ratio is 1.05. The CFD domain influence studies were performed, see Figure 10. The domain of length, equal to 20 times chord length, and width equal to 25 times chord length, was considered to give results uninfluenced by the boundary conditions. As a result, the mesh with 123,065 elements was considered in further studies.

Figure 9.
Domain size and numerical mesh.

Figure 10.
The domain size influence on the pressure coefficient distribution on the airfoil surface.
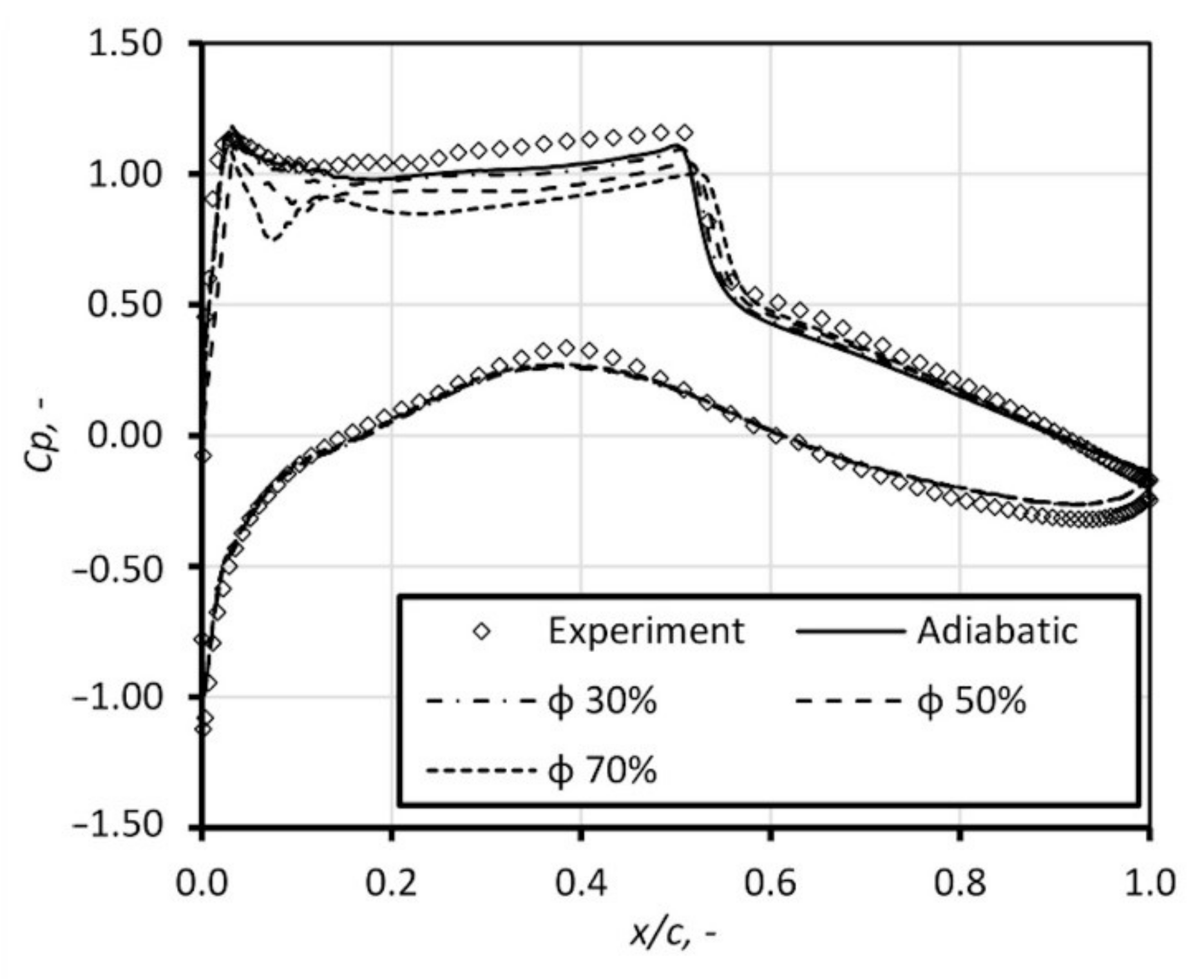
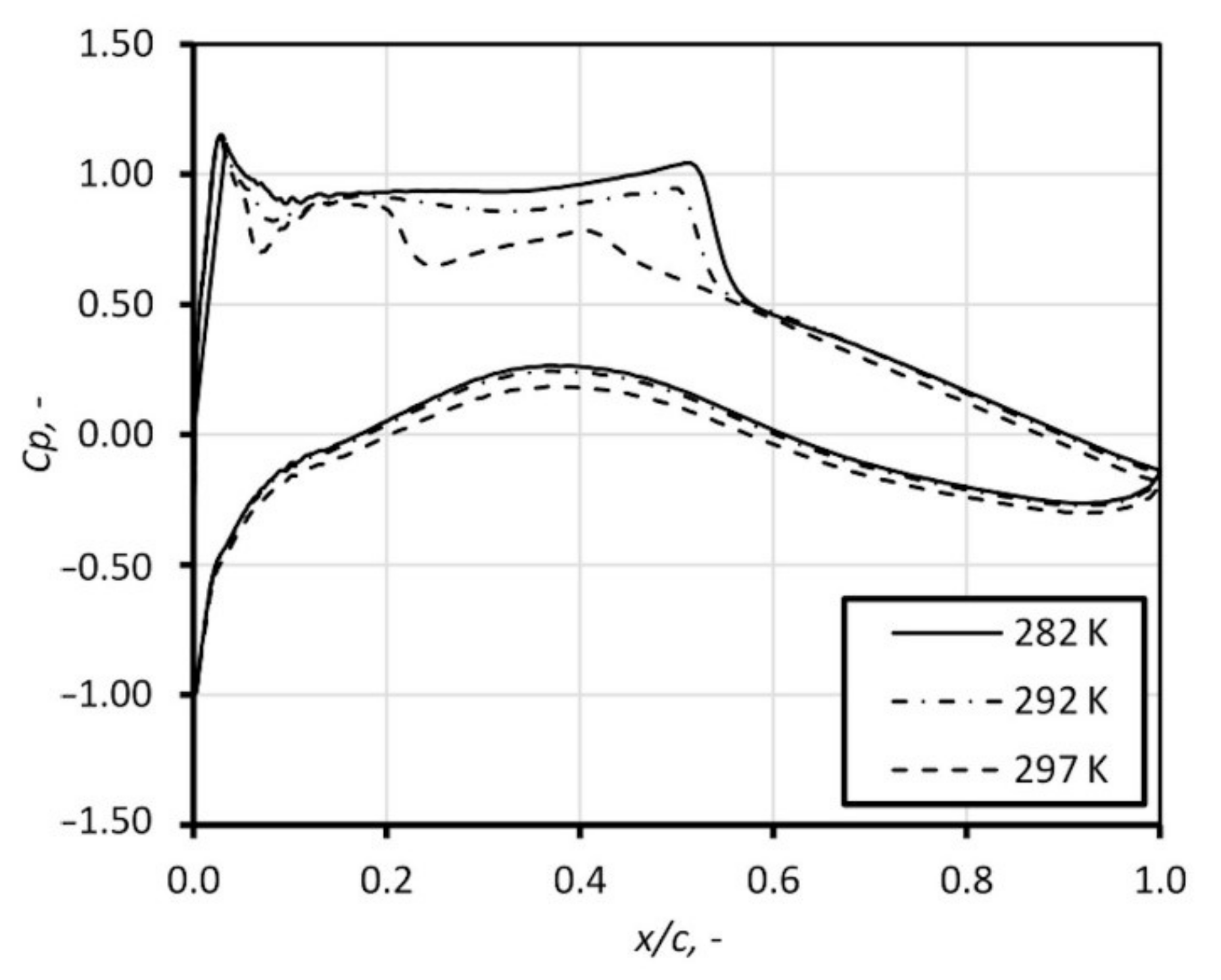
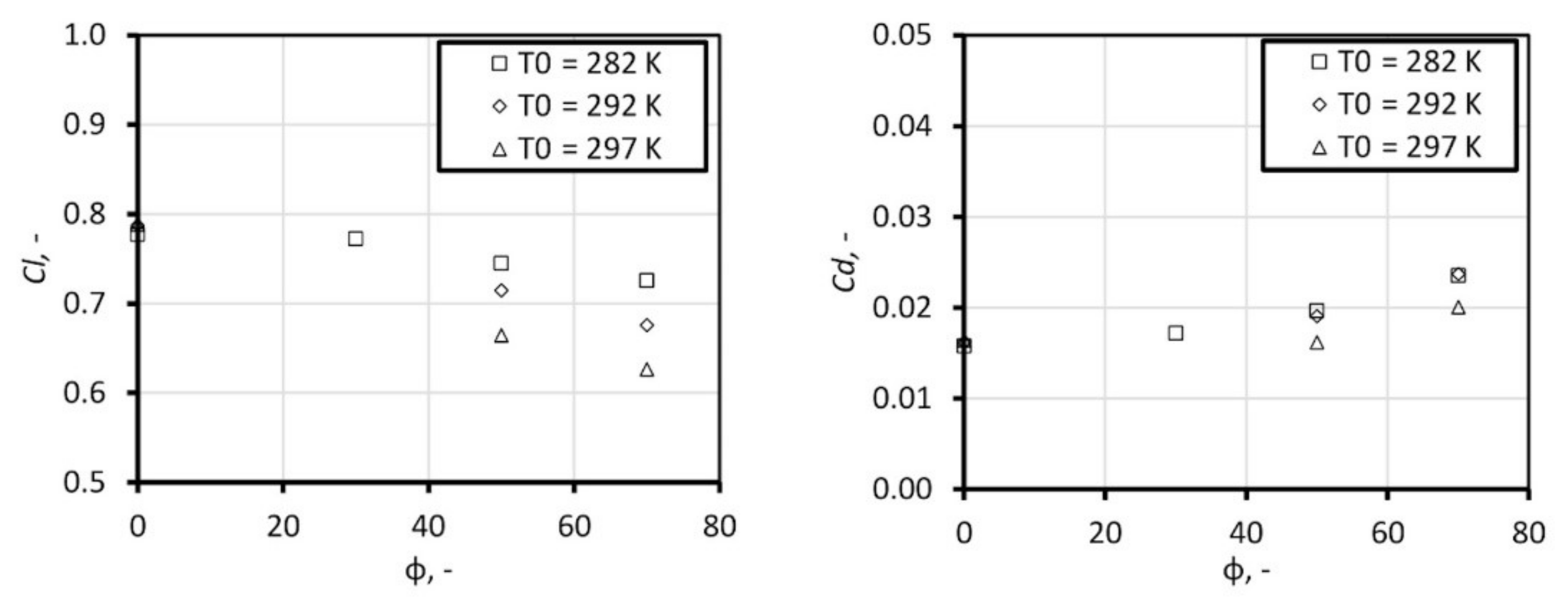
Firstly, the computation of dry airflow was performed. Further, the calculations for humid air with relative humidity, φ, equal to 30%, 50%, and 70% were performed. Figure 11 presents the static pressure distribution by means of pressure coefficient (, p is static pressure, is free stream pressure, is total pressure) along the airfoil obtained in numerical studies with comparison to the experimental results. The influence of air humidity is significant; the condensation process occurs at the suction surface of the airfoil, in the vicinity of the sonic region. This is accompanied by a sudden pressure rise in this region. The release of latent heat causes a drop of velocity, which moves the shock position downstream. Figure 12 and Figure 13 show the influence of the inlet total temperature. With increase of the total temperature, the mass of water contained in the air rises, which leads to increase of the latent heat release. The phenomena of condensation exerts significant influence on the airfoil characteristic; the drag and lift coefficient changes, shifting the ratio into a non-profitable area, see Figure 14.

Figure 11.
Pressure coefficient distribution on the airfoil for dry and humid airflow for total temperature of 282 K.

Figure 12.
Influence of the inlet total temperature on pressure coefficient distribution on the airfoil for humid air with relative humidity of 50%.

Figure 13.
Influence of the inlet total temperature on pressure coefficient distribution on the airfoil for humid air with relative humidity of 70%.

Figure 14.
Lift coefficient (left) and drag coefficient (right) change with the increase of relative humidity and total temperature.
5. Conclusions
In the paper, the results of the condensation model, which was implemented to commercial software, are shown. The presented model was validated, based on the experimental studies and benchmark tests available in the literature. Firstly, the influence of the condensation phenomenon onto the flow character in the transonic nozzle was investigated. As it was presented, the condensation phenomenon drives a rapid release of latent heat, which influences the pressure distribution along the nozzle, and the condensation wave occurs. The position of the condensation wave moves upwind the nozzle with the humidity increment. In case of flow with discontinuities in the form of shock waves, humidity impacts the position of the shock wave. The increment of pressure downwind the condensation wave delays the position of the shock. The heterogeneous condensation decreases the importance of nucleation phenomena; thus, with the increment of the number of suspended particles, the condensation waves weaken.
Further, the influence of condensation and turbulence modelling in the nozzle with a parallel outlet was investigated. The turbulence modelling has a significant impact on the results; the losses connected energy dissipation fluid viscosity is non-negligible. The viscosity of the flow has a significant impact on the oscillation frequency.
In sequence, the test of humidity influence on the external flow over an airfoil was modelled. The condensation phenomenon influences the pressure distribution along the profile and moves the shock wave position. The condensation phenomena exerts significant influence on the drag and lift coefficients, decreasing the airfoil performance. The influence of the condensation is strictly connected with the total temperature and relative humidity. With the increase of total temperature, the water content increases; thus, the amount of released heat during the condensation grows.
In conclusion, the condensation phenomenon has a significant impact on the flow character regarding internal and external flows within the transonic regime. The impact is strictly connected with the air relative humidity and its pollution. The results of this study show that it is reasonable and recommended to take into account the water conditions and air quality during the computations of transonic airflow.
Author Contributions
Data curation, P.W.; Investigation, P.W.; Methodology, P.W., S.D. and S.Y.; Resources, S.D.; Supervision, S.D. and S.Y.; Validation, P.W.; Writing—original draft, P.W.; Writing—review & editing, S.D. and S.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded within the Statutory Research Funds of the Silesian University of Technology and co-financed by the European Union through the European Social Fund (grant POWR.03.05.00-00-Z305).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yammamoto, S.; Hagari, H.; Murayama, M. Numerical simulation of condensation around the 3-D Wing. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2000, 42, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Schnerr, G.H.; Mundinger, G. Similarity, drag, and lift in transonic flow with given internal heat addition. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 1993, 12, 597–611. [Google Scholar]
- Schnerr, G.H.; Dohrmann, U. Transonic flow around airfoils with relaxation and energy supply by homogeneous condensation. AIAA J. 1990, 28, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, S. Numerische und Experimentelle Untersuchung Instationarer Dusenstromungen mit Energiezufuhr Durch Homogene Kondensation; Universität Karlsruhe: Karlsruhe, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dykas, S.; Majkut, M.; Smołka, K. Influence of air humidity on transonic flows with weak shock waves. J. Therm. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodheart, K.A. 3-D Transonic Flow Dynamics with Nonequilibrium Condensation Munich; Universitätsbibliothek der TU München: München, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Karabelas, S.J.; Markatos, N.C. Water vapor condensation in forced convection flow over an airfoil. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2008, 12, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykas, S. Badania Przepływów Transonicznych z Kondensacją Pary Wodnej; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, P.H.; McDonald, M.A.; Firmin, M.C. Aerofoil Rae 2822: Pressure Distributions, and Boundary Layer and Wake Measurements, Experimental Data Base for Computer Program Assessment; AGARD Report ar 138; AGARD: Neuilly sur Seine, France, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykas, S.; Majkut, M.; Smołka, K.; Strozik, M. Analiza Zjawisk Cieplno-Przepływowych W Okołodźwiękowych Przepływach Powietrza Wilgotnego w Dyszach; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dykas, S.; Majkut, M.; Smołka, K.; Strozik, M. Numerical analysis of the impact of pollutants on water vapour condensation in atmospheric air transonic flows. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 338, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykas, S.; Majkut, M.; Smołka, K.; Strozik, M. Comprehensive investigations into thermal and flow phenomena occurring in the atmospheric air two-phase flow through nozzles. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 114, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J. Kinetic Theory of Liquids; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz, A. Nucleaton in very rapid vapor expansions. J. Chem. Phys. 1951, 19, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Główny Inspektorat Ochrony Środowiska (Chief Inspectorate for Environmental Protection). 2020. Available online: https://powietrze.gios.gov.pl/pjp/content/annual_assessment_air_acceptable_level?lang=pl (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- World Health Organization. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- Chris, N.; Julianne, D. NPARC Alliance Validation Archive. 2008. Available online: https://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/wind/valid/raetaf/raetaf05/raetaf05.html (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- TU Berlin. Available online: https://www.cfd.tu-berlin.de/research/thermofluid/transport/node6.html (accessed on 27 April 2020).
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).