Abstract
Passive water transport through thin-surface wicks made of heat conducting material is important for developing thermal management devices such as heat pipes and spreaders. In this study, we demonstrated the hydrophilic coating of a Cu particle monolayer wick for enhanced water transport. We fabricated a Cu particle monolayer using Cu powder with a nominal particle diameter of 100 μm and determined the particle size distribution using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). We observed a remarkable change in the water contact angle on the application of a hydrophilic coating, which demonstrated the enhanced passive water transport. The elemental mapping of Cu, O, and Si obtained by electron probe microanalysis confirmed the deposition of the SiO2-based coating material on each Cu particle. Although the Cu particles were only partially covered by SiO2, a remarkable enhancement in wettability was achieved. Finally, we conducted a rate-of-rise experiment to quantitatively characterize the water transport performance of the coated Cu particle monolayer. Thus, we propose hydrophilic coating as a simple and effective method to enhance passive water transport through Cu particle monolayer wicks.
1. Introduction
The recent increase in the power density and reduced sizes of electronic devices necessitates small-scale thermal management [1]. Thus, the heat pipes and spreaders that are used to dissipate heat from such miniaturized devices are getting smaller and thinner; recently, there is increasing demand for heat pipes with thicknesses below 0.6 mm [2]. Accordingly, their components—namely the evaporator and condenser—should also be realized in a thin space on the surface.
The evaporator is an essential component of heat pipes/spreaders, which utilize the latent heat of the working fluid. Wick function, which enables passive liquid transport via capillary force, is required for continuous evaporator operation. Thin-film surface wicks have been investigated by using microstructured Si surface developed via semiconductor processing [3]. As Si surface wicks offer the advantages of flexible design and precise manufacturing of microstructures, the wick performance (capillary force) of various microstructures is being investigated [4]. However, semiconductor processing is a high-cost approach that requires expensive facilities and vacuum procedures. Hence, other promising low-cost approaches have attracted attention, such as the use of Cu for manufacturing thin-surface wicks.
Cu is widely used in heat transfer devices because of its high thermal conductivity (~400 W/(m·K) at room temperature) and reasonable cost. However, Cu surfaces lose their hydrophilicity property upon exposure to ambient air [5,6]; therefore, Cu requires special treatment for the enhancement of its wettability. For example, Cu surface treatment using the piranha solution (H2SO4 + H2O2) has been reported [7]; however, owing to its safety concerns and operational cost, this method requires a safer and simpler replacement.
The Cu particle monolayer has been proposed as a promising surface wick [8,9]; however, because of the abovementioned surface-wettability problem, its liquid transport function was evaluated using methanol instead of water [6]. Moreover, as the Cu surface easily loses its hydrophilicity, there is room for improvement in its wick performance. Therefore, it is desirable to enhance the hydrophilicity of a Cu surface using a simple surface-treatment process.
In this study, we demonstrated the hydrophilic coating of a Cu particle monolayer to enhance its surface wettability. For this, we fabricated a Cu particle monolayer using Cu powder, and then applied a hydrophilic coating over it. The surface structure of the Cu particle wick was investigated by electron microscopy and the deposition of the hydrophilic coating material was confirmed by surface chemistry analysis. To demonstrate the effect of the hydrophilic coating on water wettability, the water contact angle and wick performance were measured.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Cu Particle Monolayer
We used Cu powder with a nominal particle diameter of 100 µm and 99.8% purity (Nilaco, Japan). The as-received powder comprised a broad particle size range; therefore, sieving was performed to control the particle size distribution: two stainless-steel sieves with 90 and 106 µm openings (conforming to ISO 3310-1 criteria) were used to obtain the powder particles of a small size range. Both the as-received (sample #1) and sieved (sample #2) powders were used to prepare wick samples, and the water transport performance of the two was compared.
The fabrication process of the particle monolayer wick is illustrated in Figure 1. The prepared Cu powder was distributed over the water–air interface to form the particle monolayer, which was then transferred onto a Cu plate of dimensions 50 × 10 mm. Monodispersed particles with a diameter of tens of micrometers can form a monolayer at the water–air interface [10]. The dry Cu particles were supplied to the water–air interface from the air side, so the gravity acting on a particle was balanced with the interfacial tension. Also, the floating Cu particles at the water–air interface were subjected to the lateral force, which resulted in planar accumulation of particles at the water–air interface. After forming a Cu particle monolayer on the surface of water, water was pumped out from the beaker. As the water level decreased, the particles were transferred to a Cu plate immersed in the water. Thin liquid films of water remained in between Cu particles on the Cu plate, which enabled the monolayer structure to be transferred stably due to the lateral force acting on the particles. Next, the Cu particles were sintered in an electric furnace at 800 °C. A constant flow of a nitrogen and hydrogen gas mixture was supplied during heating to prevent the oxidation of Cu.
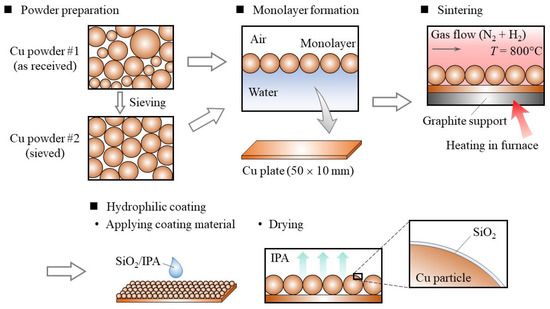
Figure 1.
Schematic of sample preparation process.
After the fabrication, a hydrophilic coating was applied on the Cu particle monolayer to enhance its wettability. For this, we used a commercial coating material consisting of SiO2 and isopropanol (Selface Coat PX-10, Marusho Sangyo, Japan). This coating material has been designed for versatile materials including glasses, metals, and plastics. A thin film of SiO2 can be prepared by the sol-gel process [11], and the coating material used here was a sol with 1.3 wt% SiO2 in isopropanol. We applied 70 μL of this coating material to our sample, and it immediately spread over the Cu particle monolayer because of the capillary force. When we applied too much of the coating material, we found that the pore of Cu monolayer was filled with SiO2.
We followed the coating instructions provided by the supplier to apply the coatings on a Cu plate and a Cu particle monolater wick.
2.2. Characterization of Particle Monolayer Structure
The surface structure of the prepared samples was observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) S-4700 (Hitachi, Japan). To determine the particle size distribution, the obtained SEM images were analyzed using the ImageJ software [12].
To evaluate the wetting behavior, we measured the water contact angle at the surface: a water droplet (5 μL) was deposited on the sample surface and a side-view image was captured using a CMOS camera 3R-MSUSB401 (3R Solution, Japan). Then, the obtained images were analyzed to determine the contact angle [13,14].
To confirm the deposition of the coating material on the Cu particle monolayer wick, we performed elemental mapping using an electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA)—EPMA-1720 (Shimadzu, Japan). Since SiO2 is the main component of the coating material, we obtained the elemental distributions of Si, O, and Cu.
2.3. Rate-of-Rise Experiment
The wick performance of the Cu particle monolayer with hydrophilic coating was evaluated through the rate-of-rise experiment [6,15,16]. The experimental setup is schematically shown in Figure 2. The sample was vertically suspended using a clamp above a water reservoir and irradiated with halogen light. As the transparency of the distilled water that was used in the experiment made it difficult to observe the liquid film propagation, we added a synthetic dye (methylene blue) to enhance visibility.
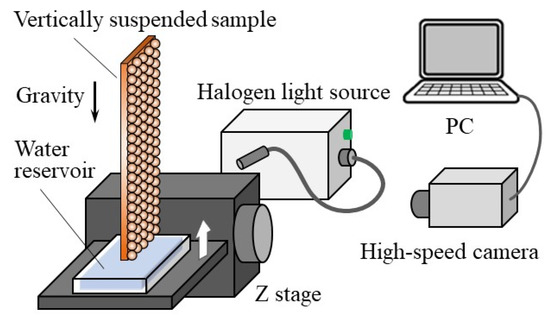
Figure 2.
Schematic of rate-of-rise experiment setup.
The water reservoir was placed on a z stage, so that it could vertically approach the bottom of the sample. The passive water transport was initiated immediately after water surface made contact with the bottom of the sample. The time variation of the water propagation front was determined using a monochromatic high-speed camera HAS-U2M (DITECT, Japan). The obtained images were analyzed to quantitatively evaluate the rate of rise.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cu Particle Size Distribution
As described in Section 2.1, we used two Cu powder samples. To clarify the difference between the two, we observed the Cu particle wick samples using an SEM: Figure 3a,b shows the SEM images of the prepared wick samples #1 and #2, respectively. Clearly, the as-received sample (#1) has a broad particle size range, while the sieved one (#2) has a narrow size range. The plain substrate surface was observable under each Cu particle as shown in the SEM images (Figure 3), so we were able to confirm the particle monolayer formation on a plain Cu plate.
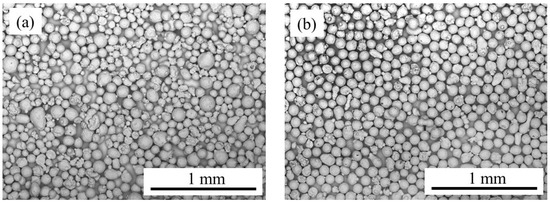
Figure 3.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of Cu particle monolayer wicks: (a) sample #1 (as-received powder) and (b) sample #2 (sieved powder).
To quantitatively evaluate the particle size distribution, we performed image analysis. Because the shape of the Cu particles is not an ideal sphere, the SEM image of each particle could not be represented by a simple circle. Therefore, we used the Heywood diameter dH, which is the diameter of a circle with equivalent projected area [17]. The results are summarized in Figure 4: Figure 4a confirms the broad particle size range of the as-received Cu powder, with the peak at 70–80 µm; the average diameter was 77 µm. On the other hand, the sieved powder exhibited a narrow particle size distribution with the peak at 90–100 µm, as shown in Figure 4b, which is consistent with the size of the sieve opening (described in Section 2.1); the average diameter was 96 µm.
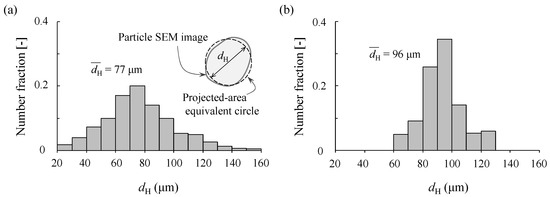
Figure 4.
Particle size distribution: (a) sample #1 (as-received powder) and (b) sample #2 (sieved powder).
Thus, we demonstrated the fabrication of the Cu particle monolayer wick with a controlled particle size range. Next, we examined the application of a hydrophilic coating to the prepared wick samples.
3.2. Contact Angle Measurement
The effect of the hydrophilic coating on surface wettability can be evaluated by the change in the contact angle θc of the water droplets. We measured the water contact angles on a Cu plate and a Cu particle monolayer, as shown in Figure 5. We used a flat Cu plate to examine the hydrophilic coating procedure and observe the intrinsic effect of the coating on the water contact angle. While the uncoated Cu plate exhibited a contact angle of 98° (Figure 5a), it was remarkably reduced to 28° after applying the hydrophilic coating (Figure 5b), which reflects the enhanced surface wettability.
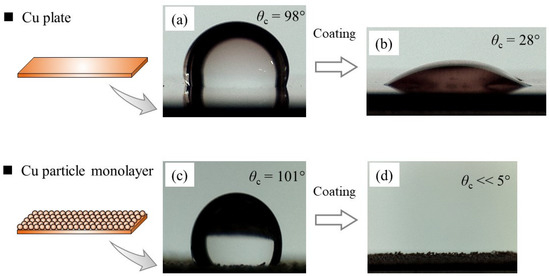
Figure 5.
Contact angle measurement using a water droplet: (a) Cu flat plate, (b) coated Cu flat plate, (c) Cu particle monolayer, and (d) coated Cu particle monolayer.
Then, we conducted the same experiment using a Cu particle monolayer sample. Before coating, the contact angle was 101° (Figure 5c), which is consistent with the previous report [6]; the water contact angle was increased because the surface wick structure has enhanced its hydrophobic surface behavior. After coating, the deposited water droplet was observed to rapidly spread over the surface, such that the contact angle was too small to be determined (θc < 5°), as shown in Figure 5d. As surface roughness is known to increase the wettability of hydrophilic materials [14,18], the results suggested that the Cu particles were coated well enough to exhibit enhanced wettability. For a detailed observation of the hydrophilic coating condition, we next performed a microscopic investigation.
3.3. Coating Condition
The coated and uncoated Cu particle monolayers were observed using SEM, and the results were compared. Figure 6a,b shows a Cu particle before and after coating, respectively. The uncoated particle exhibits a smooth surface with no specific texture, whereas disordered dark spots are observed on the surface of the coated Cu particle. We presumed that these dark spots were caused by the deposition of the coating material; hence, we performed EPMA to clarify the surface chemical composition. In general, an SiO2 sol is prepared from its precursor in solution and the aggregates of SiO2 develop [11]. The size of SiO2 was much smaller than that of the Cu particles, so it appeared to form a thin layer on each Cu particle.
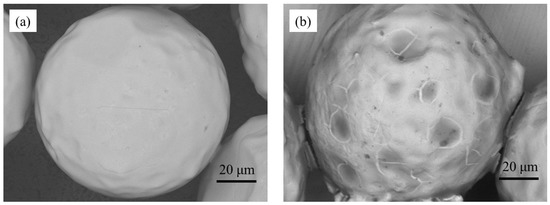
Figure 6.
SEM images of Cu particles: (a) uncoated and (b) coated.
The EPMA results are summarized in Figure 7. An SEM image of a coated Cu particle shows nonuniform surface texture (top left in Figure 7), as observed in Figure 6b. The elemental mapping of Cu indicates that there are some spots where Cu is covered by other elements (bottom left in Figure 7). The elemental mapping of O shows its existence over the dark spots in the Cu map. In addition, the Si map largely matches with the O map, indicating that this area is covered by SiO2. EPMA can be used in quantitative chemical analysis [19], and the difference between the Si and O mappings in Figure 7 appears to reflect the composition of SiO2. Although we successfully analyzed the upper hemisphere of a particle, a cross-sectional analysis might be an interesting future work to investigate the lower-hemisphere surface of a particle; however, we need to avoid any experimental artifact due to the cutting process of the sample. It should be noted that the resulting SiO2 thin film was not uniform and different from our initial expectation schematically shown in Figure 1.
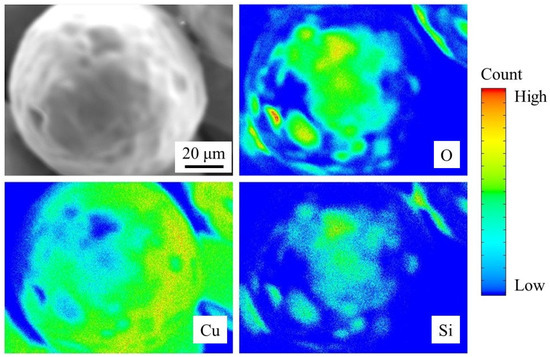
Figure 7.
Electron probe microanalysis results of coated Cu particles.
Despite the nonuniform deposition of the coating material (SiO2) over the Cu sphere, the effect of the coating causes a remarkable change in the water contact angle, which suggests promise for enhanced passive water transport. Consequently, we performed an experiment using water to evaluate the wick performance of the coated Cu particle monolayer.
3.4. Wick Performance
The hydrophilic coating of the Cu particle monolayer allowed the use of water as the working fluid in the rate-of-rise experiment, unlike in a previous study where methanol had to be used instead [6]. As the surface of a plain Cu plate improved its hydrophilicity due to the coating (Figure 5b), we consider that the hydrophilicity change of each coated Cu particle surface (Figure 7) made the Cu particle monolayer wick perform better for passive water transport.
Figure 8 shows the results of the rate-of-rise experiment. Exemplary snapshots of the bottom part of the Cu particle monolayer wick are shown in Figure 8a: the gravity is in the negative z direction, and the water propagation can be visualized by the changes in the image contrast. The series of images were analyzed to determine the location of water propagation front as a function of time. The resulting data for samples #1 (as-received) and #2 (sieved) are shown in Figure 8b,c. The functional form of the fitting curve was determined as described below.
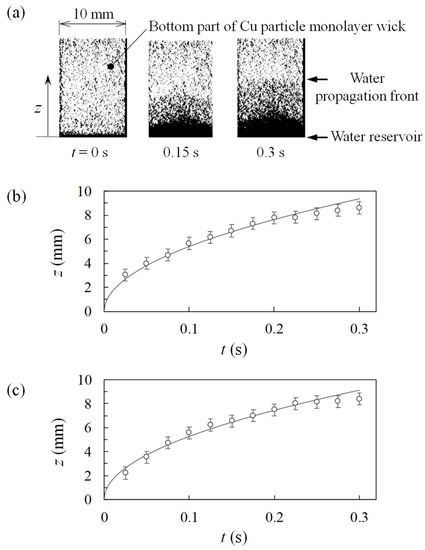
Figure 8.
Rate-of-rise experiment results. (a) Snapshots of high-speed-camera images. Time variation of water propagation front: (b) sample #1 and (c) sample #2.
In the rate-of-rise experiment, the water was wicked by the Cu particle monolayer and did not flood over the Cu particles; therefore, the water flow took place inside the porous structure. Water transport in a porous medium is expressed by the following one-dimensional (z direction) Darcy equation [20]:
where p is the pressure, μ is the viscosity of water, K is the permeability of the porous medium, and uf is the filtration velocity in the z direction. Integrating Equation (1) from the bottom to the water propagation front, under the assumption that uf is constant throughout the flow, the following relation is obtained:
where ∆p is the pressure difference causing the water transport and is defined as the sum of the capillary pressure (∆pc) and hydrostatic pressure.
The capillary pressure is calculated using the Young–Laplace equation: ∆pc = 2σ/re, where σ is the surface tension of water and re is the effective radius of the porous structure. As the uf is equal to the time variation of the water front dz/dt, Equation (2) is rearranged as follows:
where ρ is the density of water and g is the gravitational acceleration. Under the condition: 2σ/re ≫ ρgz, the right-hand side of Equation (3) is constant (z-dependence can be neglected) and the differential equation has the following solution:
where G is the propagation coefficient [16] and is given by:
We determined the propagation coefficient for each wick sample using Figure 8b,c. The propagation coefficients of samples #1 and #2 are 17.1 mm/s0.5 and 16.7 mm/s0.5, respectively. We observed that sample #1 exhibits a slightly larger propagation coefficient, indicating a larger capillary force. The average Heywood diameter of sample #1 is smaller than that of sample #2, and moreover, sample #1 contains a greater number of small particles, as shown in Figure 4a. Considering the Young–Laplace equation, we observed that the smaller effective radius of the porous structure caused the larger capillary pressure in sample #1. Nevertheless, despite the significant difference in their particle size distribution (Figure 4), both wicks exhibited a similar performance in terms of water transport. This result suggests that powder sieving is not essential for wick performance and omitting this process would lead to a simple and low-cost fabrication.
Figure 9 shows the plot between the obtained propagation coefficients and the characteristic length. The propagation coefficients of a Si micropillar wick have also been included for comparison: a broad value range is shown because of the various geometrical parameters that have been reported [16]. The characteristic length lc is the diameter of the particle or cylindrical pillar. Considering the Young–Laplace equation, a smaller characteristic length would lead to larger capillary force. Hence, the greater G of the Cu particle monolayer wick compared with the Si micropillar wicks seems to be affected by the difference in their permeability. Thus, we demonstrated the excellent water transport performance of the Cu particle monolayer with the hydrophilic coating.
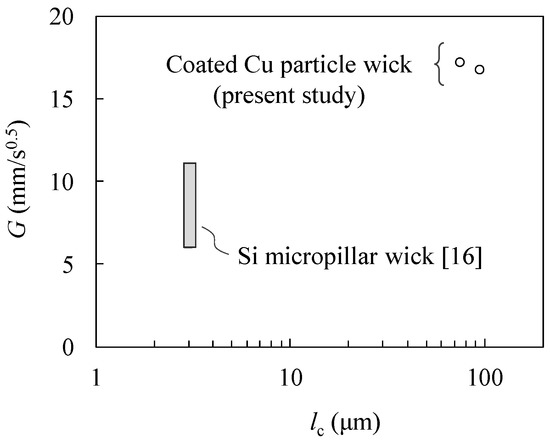
Figure 9.
Comparison of the propagation coefficients: coated Cu particle wick and Si micropillar wick with experimental data [16].
4. Conclusions
We demonstrated the effect of hydrophilic coating on a Cu particle monolayer wick for enhanced water transport. The coating enabled the use of water in the rate-of-rise experiment without which the Cu surface would easily become hydrophobic. Although the Cu particles were only partially covered by the SiO2-based coating material, a remarkable change was observed in wettability. Furthermore, the dependence of the Cu particle size distribution on wick performance was small, which is promising for the low-cost fabrication of Cu particle monolayer wicks. The proposed hydrophilic coating could be useful as a simple and effective method to enhance water transport in a Cu particle monolayer wick.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.K.; methodology, Y.K.; formal analysis, Y.K. and Y.A.; investigation, Y.K., R.O. and Y.A.; writing—review and editing, Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 20K05406 (Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C)).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Massoud Kaviany (University of Michigan) for suggesting the fabrication process of the copper particle monolayer wick.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, X.; Ye, H.; Fan, X.; Ren, T.; Zhang, G. A review of small heat pipes for electronics. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 96, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Tang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, W.; Lu, L.; Li, Y.; Tang, K. Review of applications and developments of ultra-thin micro heat pipes for electronic cooling. Appl. Energy 2018, 223, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; He, B.; Liang, Q.; Somasundaram, S.; Tan, C.S.; Wang, E.N. Optimization and thermal characterization of uniform silicon micropillar based evaporators. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 127, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Patel, A.; Garimella, S.V.; Murthy, J.Y. Wicking and thermal characteristics of micropillared structures for use in passive heat spreaders. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazy, M.R.; Blais, S.; Fréchette, L.G. Mechanism of wettability transition in copper metal foams: From superhydrophilic to hydrophobic. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6416–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.; Nam, Y.; Fleming, E.; Dussinger, P.; Ju, Y.S.; Kaviany, M. Multi-artery heat pipe spreader: Experiment. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 2662–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, J.A.; Garimella, S.V.; North, M.T. Characterization of evaporation and boiling from sintered powder wicks fed by capillary action. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 4204–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kaviany, M. Multi-artery heat-pipe spreader: Monolayer-wick receding meniscus transitions and optimal performance. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 112, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kaviany, M. Flow-boiling canopy wick for extreme heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 117, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.-J.; Kappl, M. Surface and Interfacial Forces 2e; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameya, Y. Wettability modification of polydimethylsiloxane surface by fabricating micropillar and microhole arrays. Mater. Lett. 2017, 196, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameya, Y.; Yabe, H. Optical and Superhydrophilic Characteristics of TiO2 Coating with Subwavelength Surface Structure Consisting of Spherical Nanoparticle Aggregates. Coatings 2019, 9, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, B.; Faghri, A. Permeability and effective pore radius measurements for heat pipe and fuel cell applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Enright, R.; Wang, E.N. Prediction and Optimization of Liquid Propagation in Micropillar Arrays. Langmuir 2010, 26, 15070–15075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Di Guida, O.A. Comparison of sizing small particles using different technologies. Powder Technol. 2003, 132, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P.-G.; Brochard-Wyart, F.; Quéré, D. Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena: Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, R.; Llovet, X. Electron Probe Microanalysis: A Review of the Past, Present, and Future. Microsc. Microanal. 2015, 21, 1053–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaviany, M. Principles of Heat Transfer in Porous Media; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).