Modelling and Measurement of a Moving Magnet Linear Motor for Linear Compressor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. FEA Model
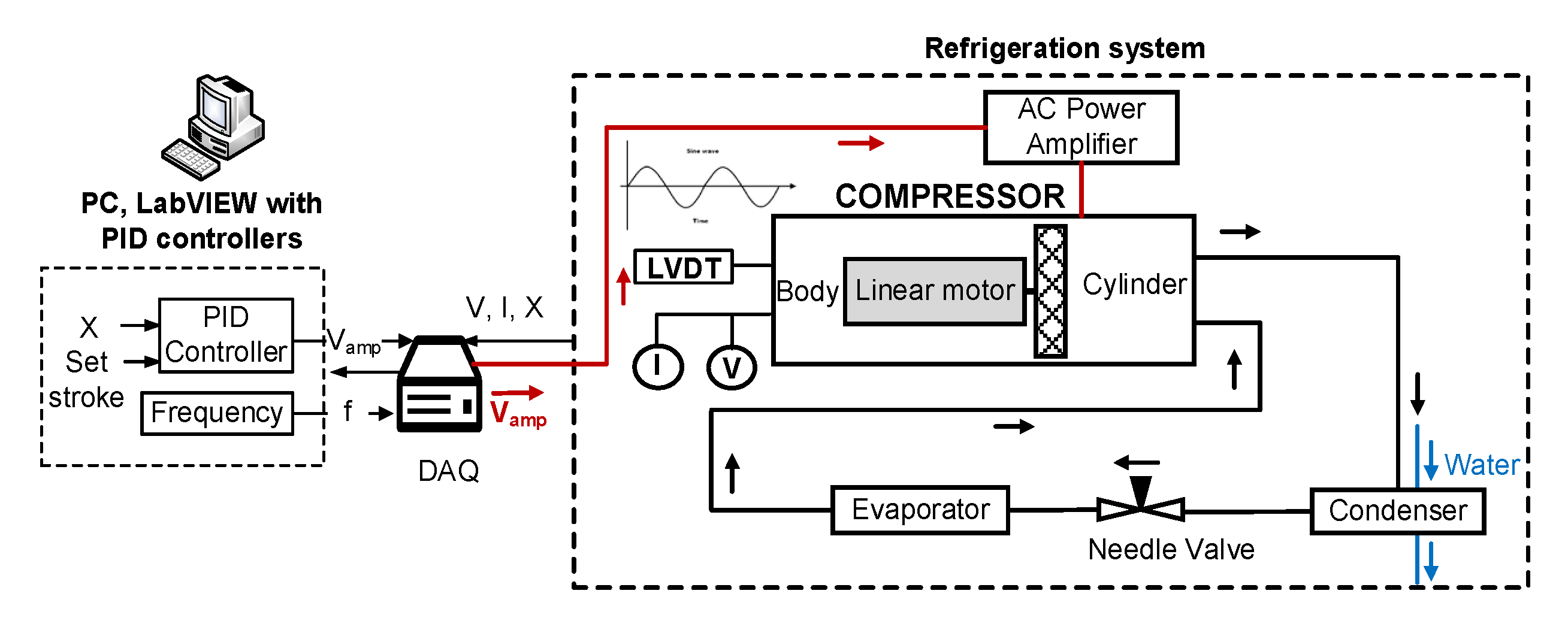
3. Experimental Setup
4. Results and Discussions
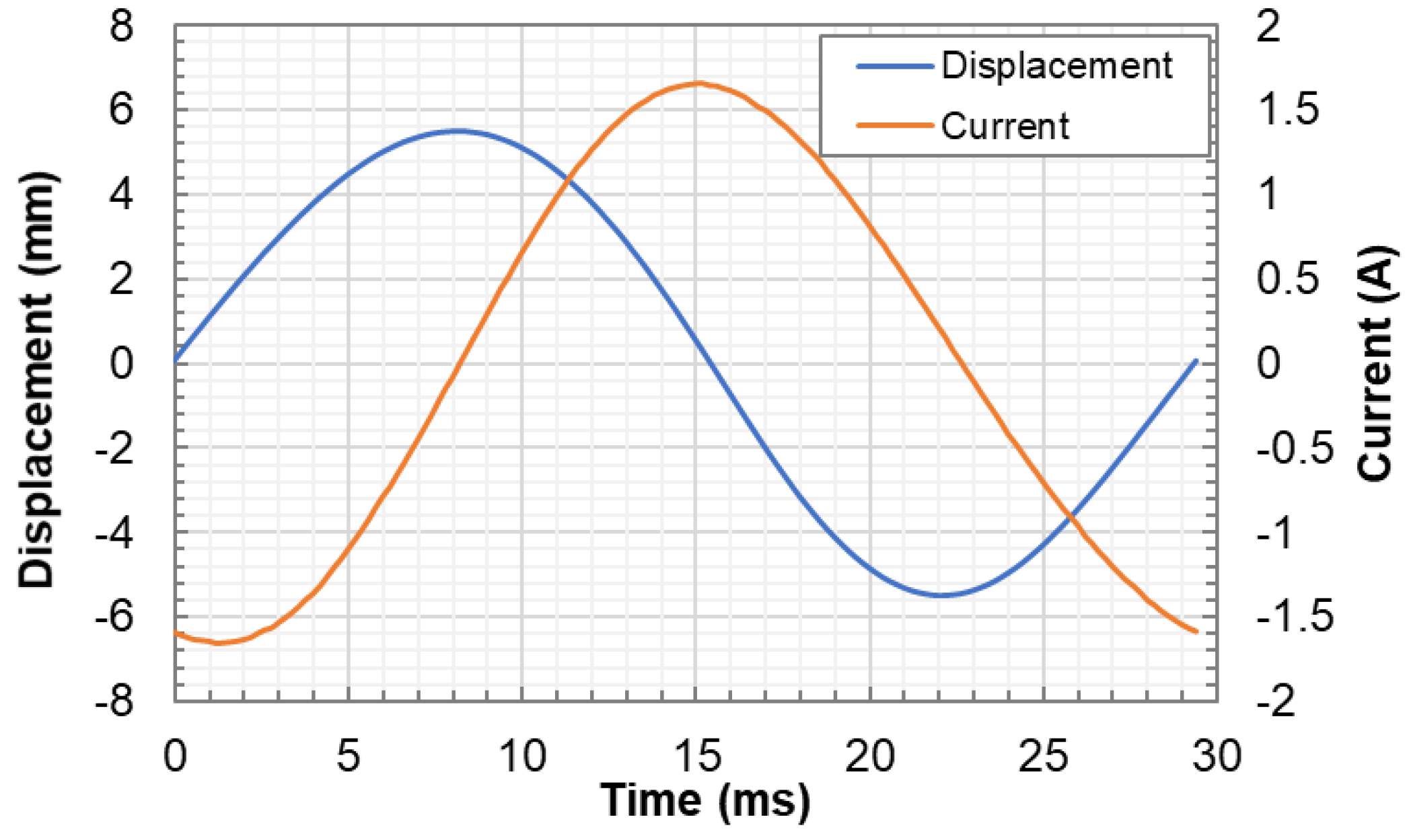
4.1. Voltage and Current
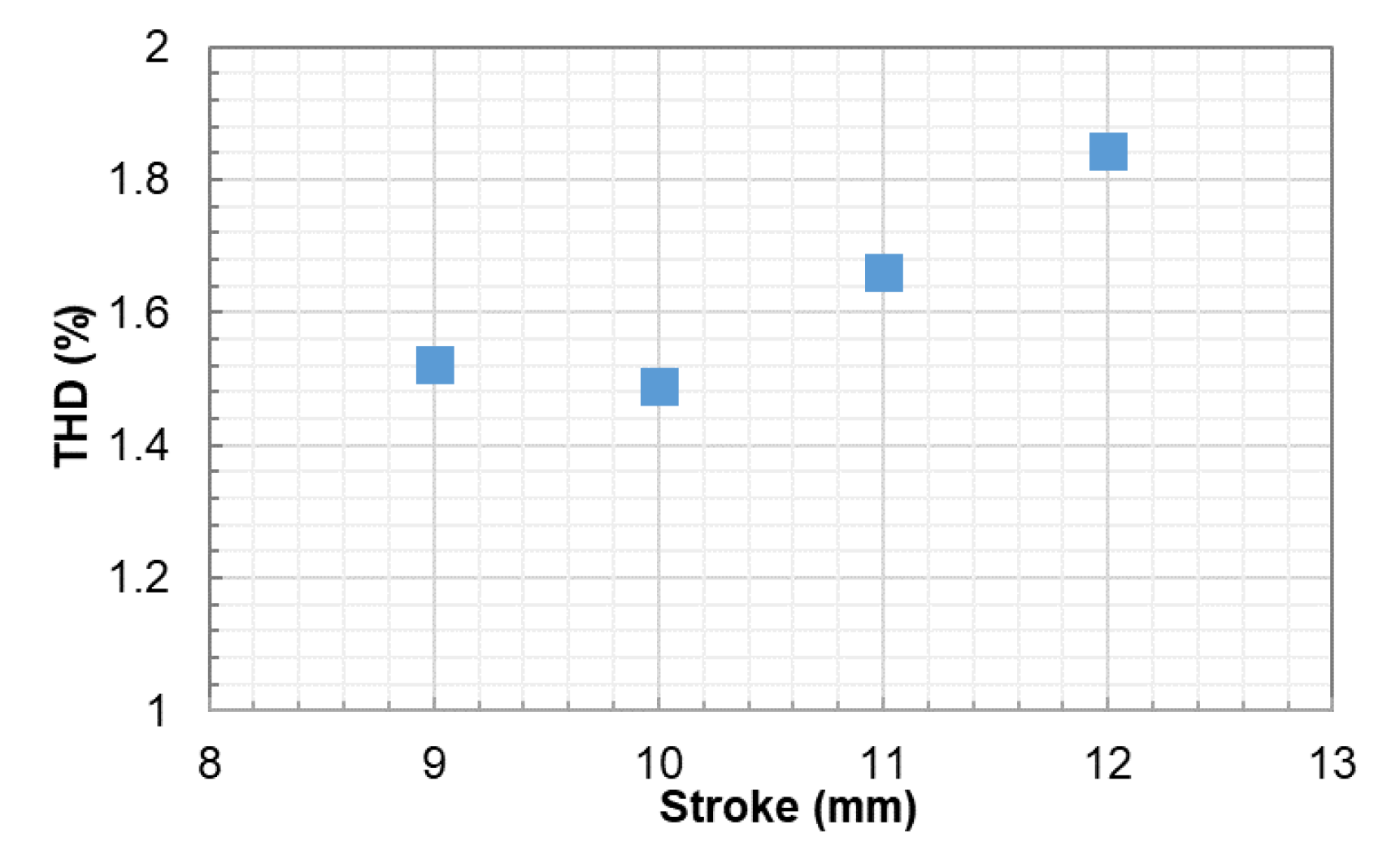
4.2. THD
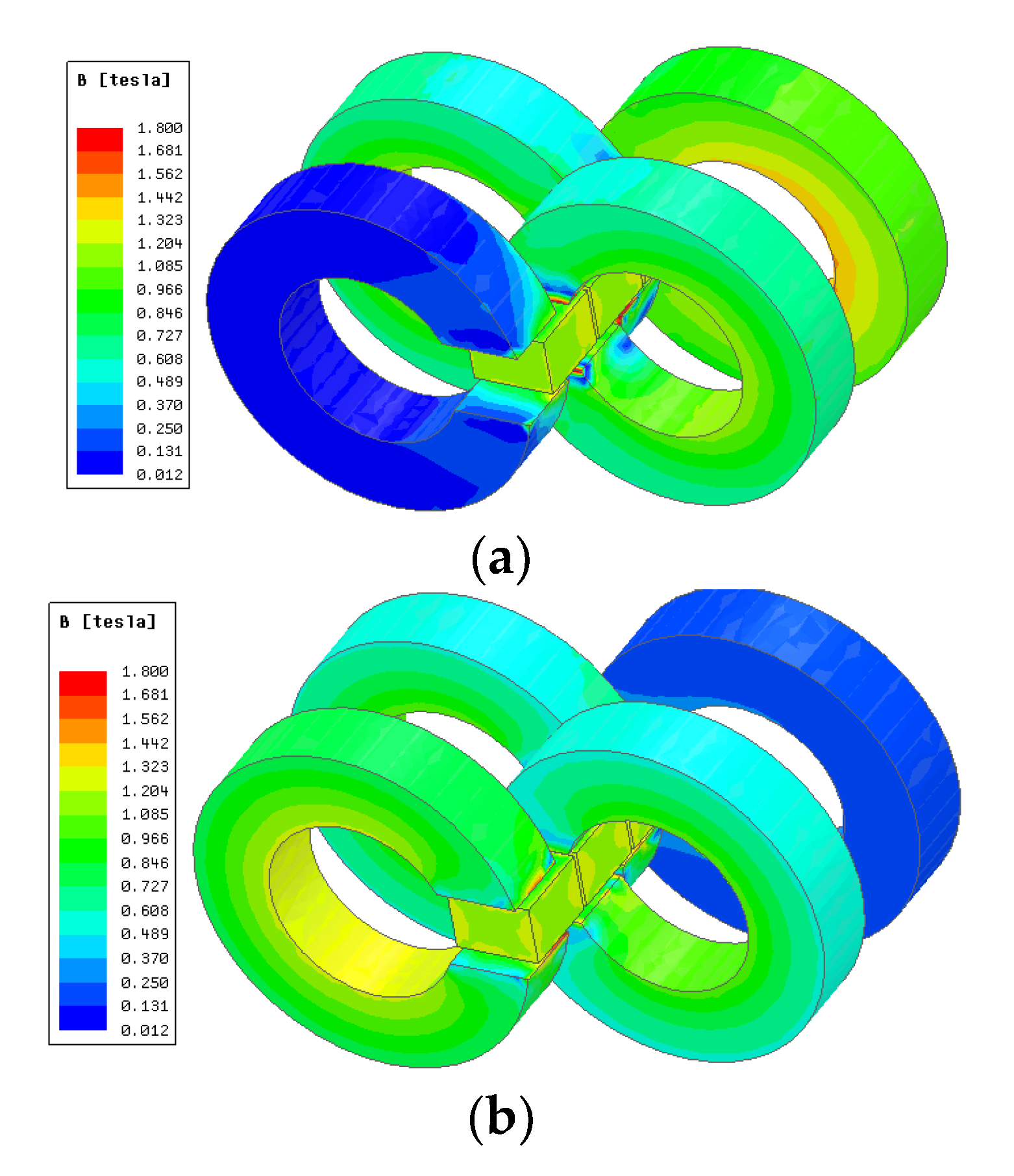
4.3. Flux Density
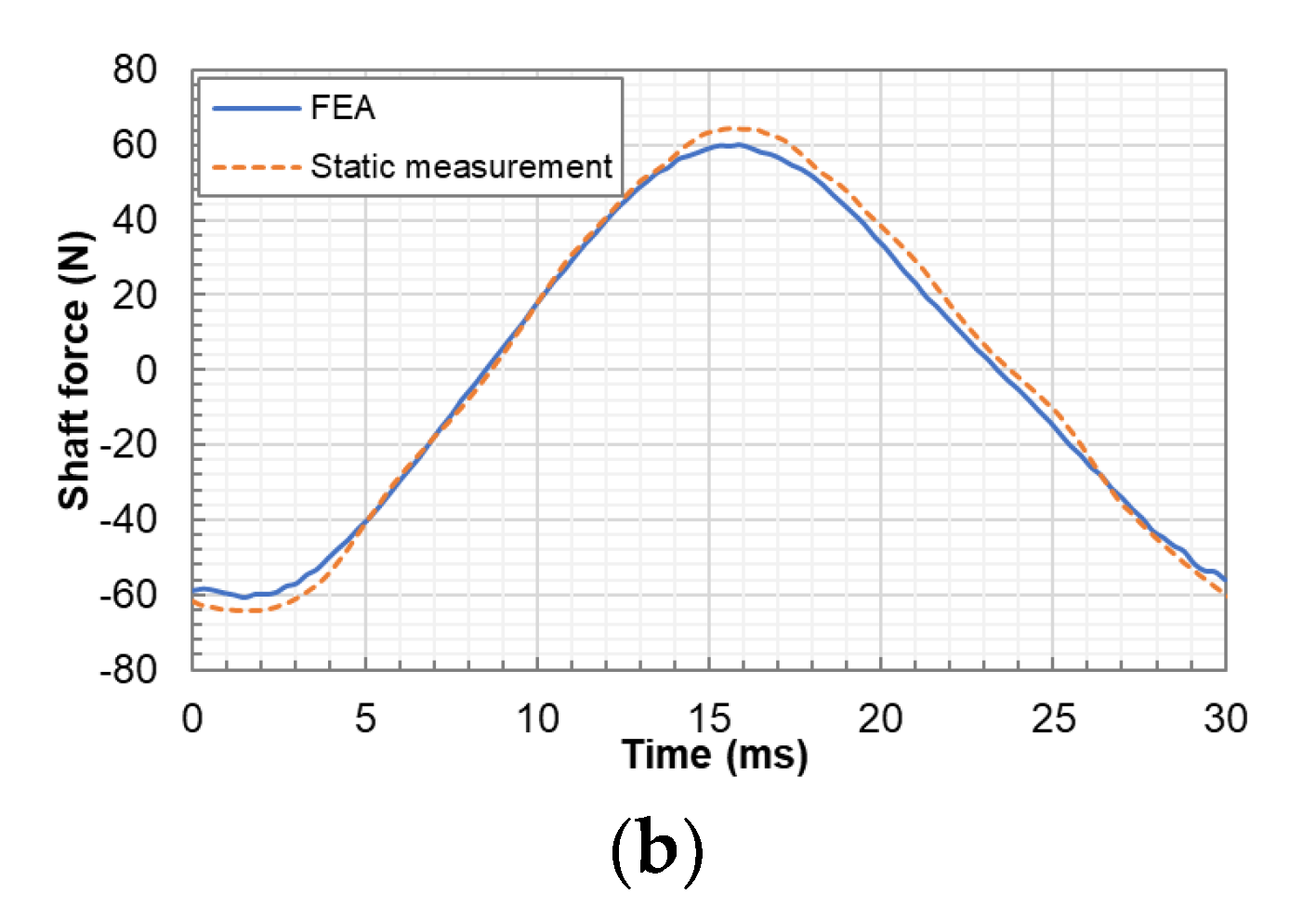
4.4. Transient Motor Force
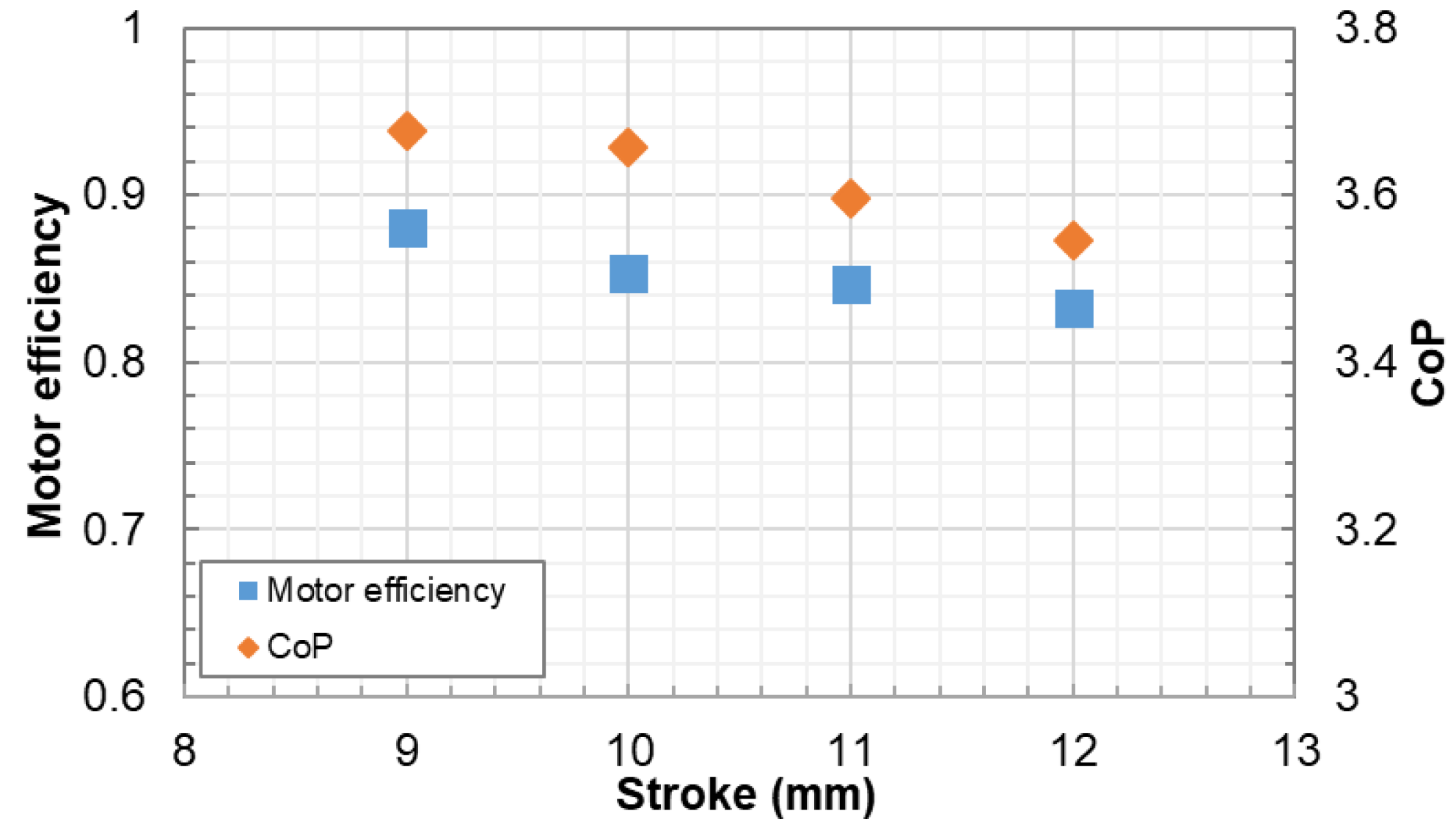
4.5. Motor Efficiency
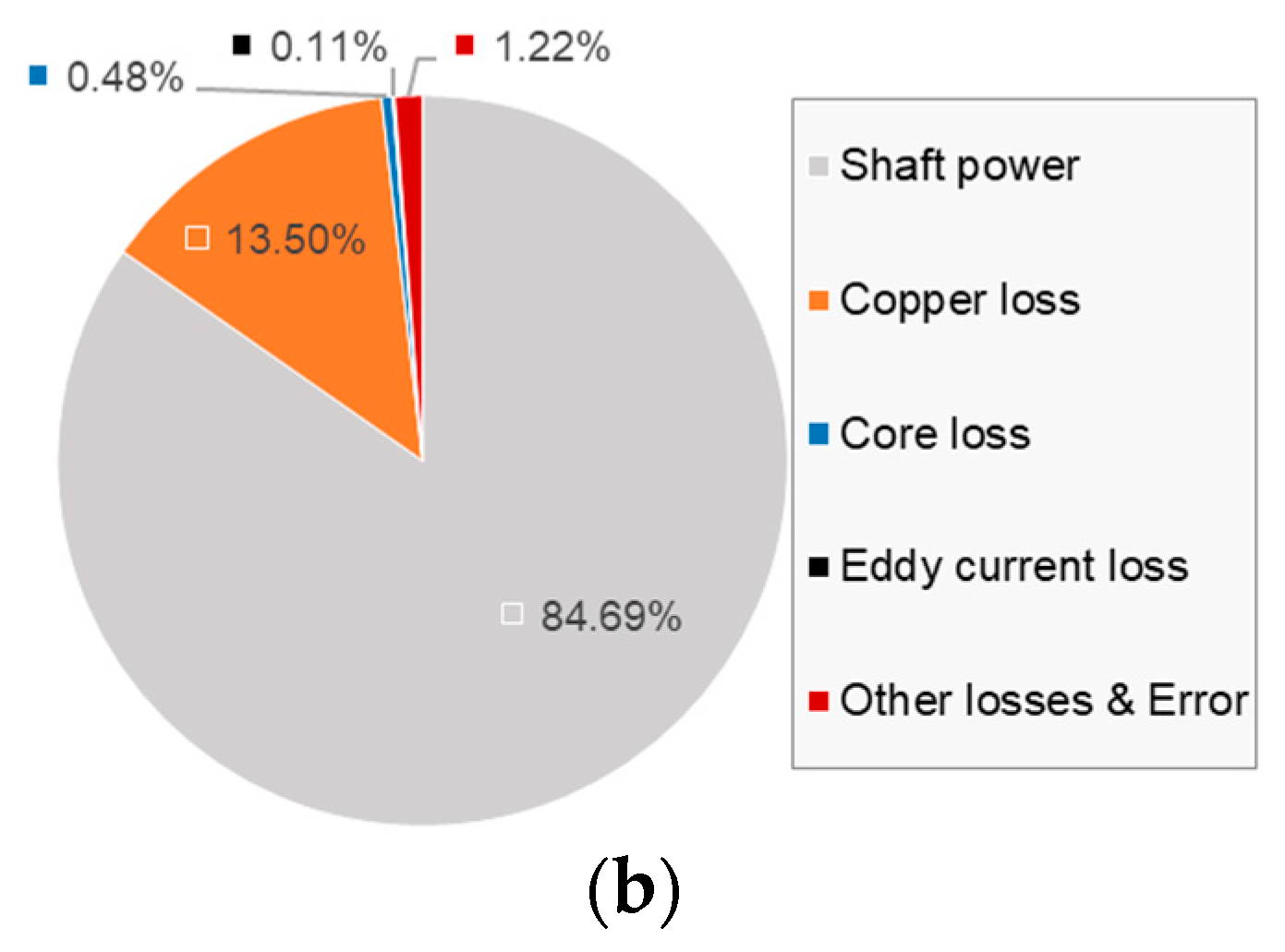
4.6. Motor Losses
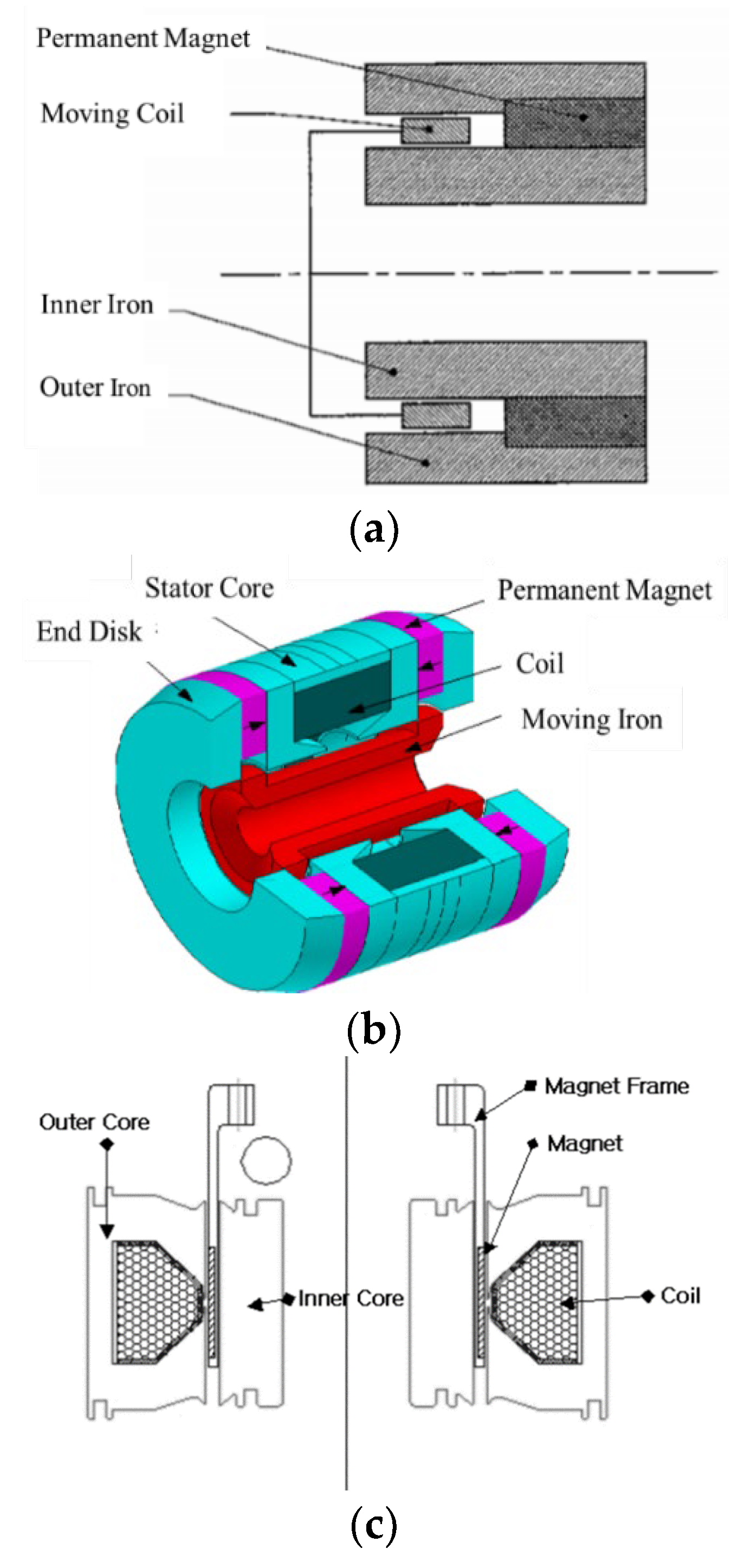
5. Comparisons with Moving Coil Linear Motor
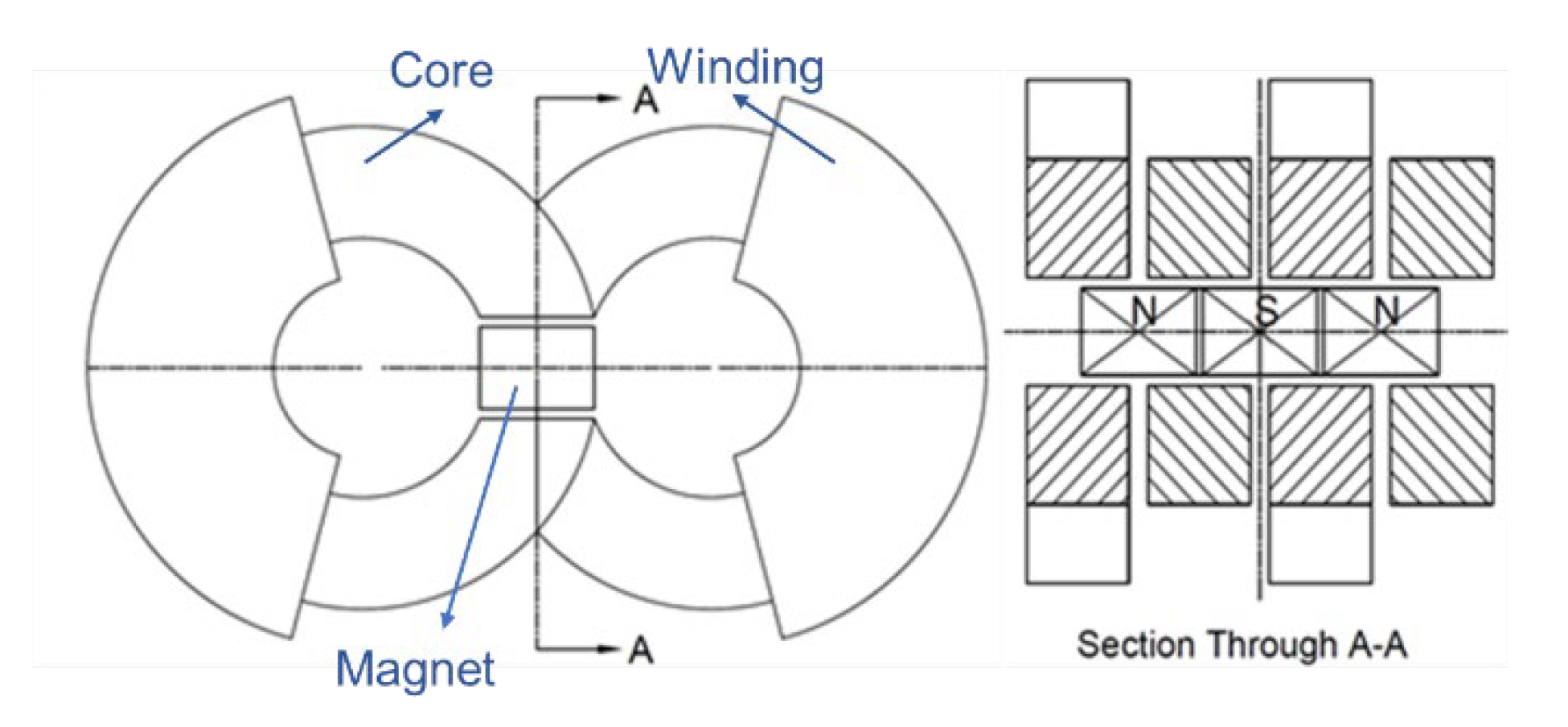
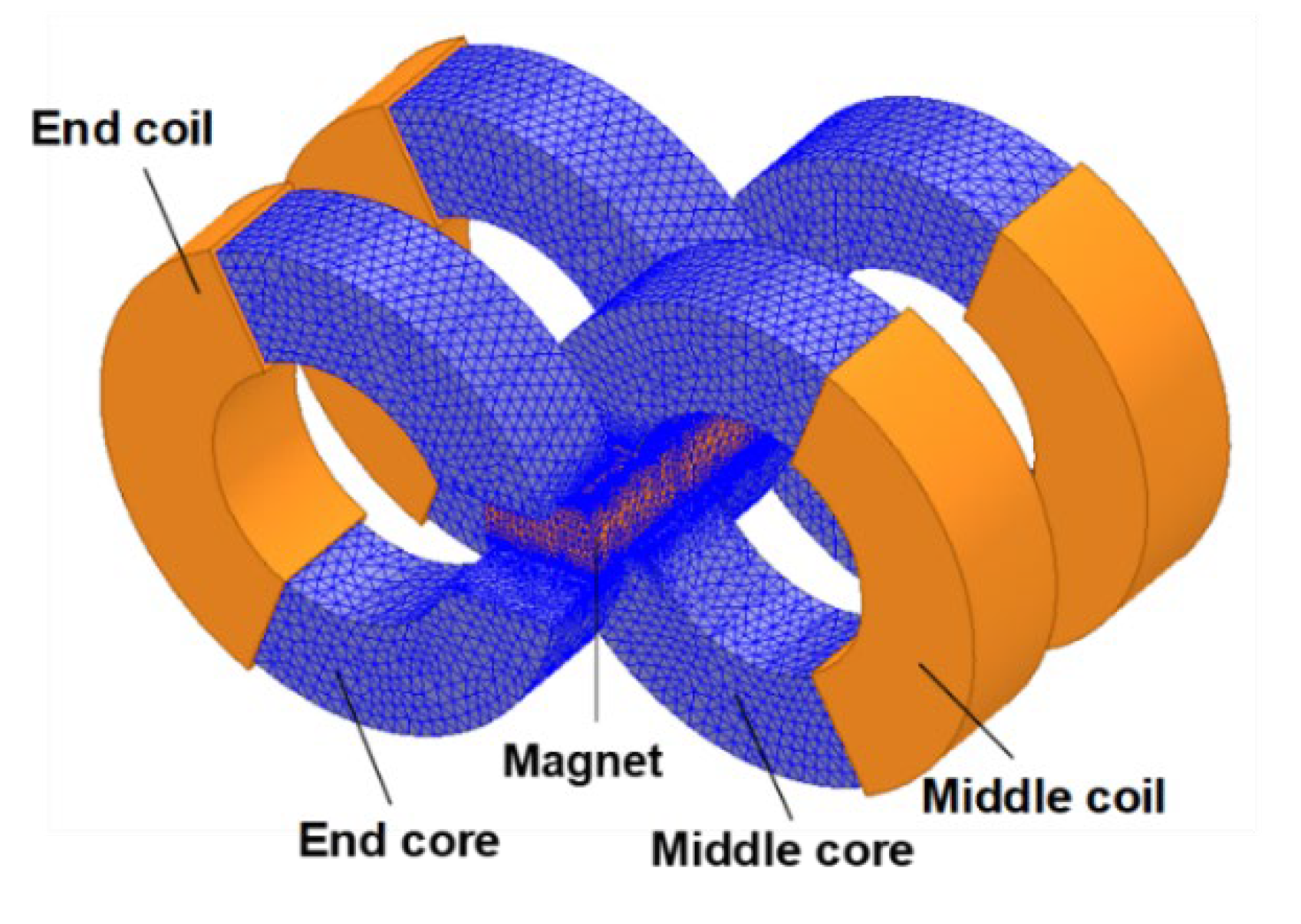
6. Comparisons with Other Moving Magnet Linear Motors
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- The transient shaft force varies almost sinusoidally in one cycle, and the shaft force peaks at zero displacement. Close agreements are shown between the transient shaft force from the FEA model and the interpolation results from the static shaft force.
- (2)
- The THDs of voltage were below 2%, which indicates the harmonic deviation is within the acceptable range.
- (3)
- Copper loss of the windings is the major loss of the linear motor, which occupies about 90% of the total loss.
- (4)
- From the comparisons between the moving magnet and moving coil linear motors, the moving magnet type is suggested for scaling up in terms of motor efficiency and superior heat dissipation for coils.
- (5)
- Compared with other moving magnet designs, the present linear motor provides fair motor efficiency with simple structure and low manufacturing difficulties. Part load efficiency is particularly high.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coulomb, D.; Dupont, J.L.; Pichard, A. 29th Informatory note on refrigeration technologies. In The Role of Refrigeration in the Global Economy; IIR document; IIR (International Institute of Refrigeration): Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Jewell, G.W.; Howe, D. A general framework for the analysis and design of tubular linear permanent magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 1986–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Yu, M.; Ye, Y. A novel transverse-flux moving-magnet linear oscillatory actuator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldea, I.; Nasar, S.A. Linear electric actuators and generators. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1999, 14, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Howe, D.; Lin, Z.Y. Comparative studies on linear motor topologies for reciprocating vapor compressors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference, Antalya, Turkey, 3–5 May 2007; pp. 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.K.; Park, K.B.; Park, J.S.; Hong, E.P. Linear Motor and Linear Compressor Using the Same. U.S. Patent US2007152516, 25 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Beers, D.; Barito, T.H.; Gregory, W. Linear Compressor. U.S. Patent US20150226200, 13 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.Y. Spring supporting structure of linear compressor. U.S. Patent US6435842B2, 20 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Noboru, K.; Hiroaki, S.; Kensaku, K. Linear oscillatory actuator. U.S. Patent US8373315B2, 12 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Z.; Wang, T.; Yan, L. Design of a tubular linear oscillating motor with a novel compound halbach magnet array. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2017, 22, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Chen, X. Analysis of an e-core interior permanent magnet linear oscillating actuator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 4384–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Howe, D.; Lin, J. Development of transverse flux linear motor with permanent-magnet excitation for direct drive applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 1936–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, K.; Stone, R.; Hancock, W.; Dadd, M.; Bailey, P. Comparison between a crank-drive reciprocating compressor and a novel oil-free linear compressor. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 45, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, R.; Unger, R.; van der Walt, N. Linear compressor: Motor configuration, modulation and system. In Proceedings of the International Compressor Engineering Conference, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 23–26 July 1996; Purdue: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1996; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, T.; Wang, J.; Howe, D.; Nor, N.M. Design and optimization of a moving-iron linear permanent magnet motor for reciprocating compressors using finite element analysis. Int. J. Elect. Comput. Sci. 2010, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Wang, S.; Park, K. Iron loss analysis of linear motor for linear compressor. In Proceedings of the International Compressor Engineering Conference, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 12–15 July 2004; Purdue: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2004; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lubin, T.; Mezani, S.; Rezzoug, A. Development of a 2D analytical model for the electromagnetic computation of axial-field magnetic gears. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 5507–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiegna, H.; Amara, Y.; Barakat, G. Overview of analytical models of permanent magnet electrical machines for analysis and design purposes. Math. Comput. Simul. 2013, 90, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liang, K.; Li, Z. Characteristics of a novel moving magnet linear motor for linear compressor. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 121, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Y. Study on static and dynamic characteristics of moving magnet linear compressors. Cryogenics 2007, 47, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, W.; Ye, C.; Boldea, I. Comparative study of transversal-flux permanent-magnetic linear oscillatory machines for compressor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7437–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, I.I.; Ibrahim, T.; Nor, N.B.M. Development and optimization of a moving-magnet tubular linear permanent magnet motor for use in a reciprocating compressor of household refrigerators. Int. J. Elect. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 77, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Choi, J.; Jang, S.; Choi, J. Analysis of eddy current losses in cylindrical linear oscillatory actuator with Halbach permanent magnet array mover. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07B547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, I.I.; Ibrahim, T.; Nor, N.B.M. Minimization of eddy-current loss in a permanent-magnet tubular linear motor. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2017, 7, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansys Maxwell, ANSYS, Inc. Available online: http://www.ansys.com/ (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Associated Power Technologies. Total Harmonic Distortion and Effects in Electrical Power Systems; Associated Power Technologies: Lake Forest, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Std. IEEE Recommended Practices and Requirements for Harmonic Control in Electrical Power Systems; IEEE Std: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 519–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.C.; Edey, K. Influence of manufacturing processes on iron losses. In Proceedings of the 1995 Seventh International Conference on Electrical Machines and Drives, Durham, UK, 11–13 September 1995; pp. 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Sun, J.; Zou, H.; Cai, J. Effects of the driving voltage waveform on the performance of vapor compression cycle system driven by the moving coil oil-free linear compressor. Int. J. Refrig. 2019, 108, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Li, J.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zha, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, H.; Xue, R. Theoretical modeling and experimental verification of the motor design for a 500 g micro moving-coil linear compressor operating at 90–140 Hz. Int. J. Refrig. 2019, 104, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H. Development of high performance moving-coil linear compressors for space Stirling-type pulse tube cryocoolers. Cryogenics 2015, 68, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Song, G.; Park, J.; Hong, E.; Jung, W. Development of the linear compressor for a household refrigerator. In Proceedings of the International Compressor Engineering Conference, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 25–28 July 2000; Purdue: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2000; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Howe, D.; Lin, Z. Design optimization of short-stroke single-phase tubular permanent-magnet motor for refrigeration applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijanzad, A.; Hassan, A.; Lazoglu, I.; Kerpicci, H. Development of a new moving magnet linear compressor. Part A: Design and modeling. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 113, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijanzad, A.; Hassan, A.; Lazoglu, I.; Kerpicci, H. Development of a new moving magnet linear compressor. Part B: Performance analysis. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 113, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Moving Magnet | Moving Coil |
|---|---|---|
| Moving mass (kg) | 0.66 | 0.313 |
| Resistance of motor coil (Ω) | 3.5 | 2.62 |
| Stroke (mm) | 11.5 | 8 |
| THD of current (%) | >50 | 5.2 |
| Copper loss (W) | 5.6 | 7.1 |
| Motor efficiency (%) | 84 | 82 (only considered copper loss) |
| Motor constant (N/A) | 31 | 28.5 |
| CoP | 3.56 | 3.22 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Liang, K. Modelling and Measurement of a Moving Magnet Linear Motor for Linear Compressor. Energies 2020, 13, 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13154030
Chen X, Jiang H, Li Z, Liang K. Modelling and Measurement of a Moving Magnet Linear Motor for Linear Compressor. Energies. 2020; 13(15):4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13154030
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xinwen, Hanying Jiang, Zhaohua Li, and Kun Liang. 2020. "Modelling and Measurement of a Moving Magnet Linear Motor for Linear Compressor" Energies 13, no. 15: 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13154030
APA StyleChen, X., Jiang, H., Li, Z., & Liang, K. (2020). Modelling and Measurement of a Moving Magnet Linear Motor for Linear Compressor. Energies, 13(15), 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13154030




