Heat Transfer Analysis of Timber Windows with Different Wood Species and Anatomical Direction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Purpose
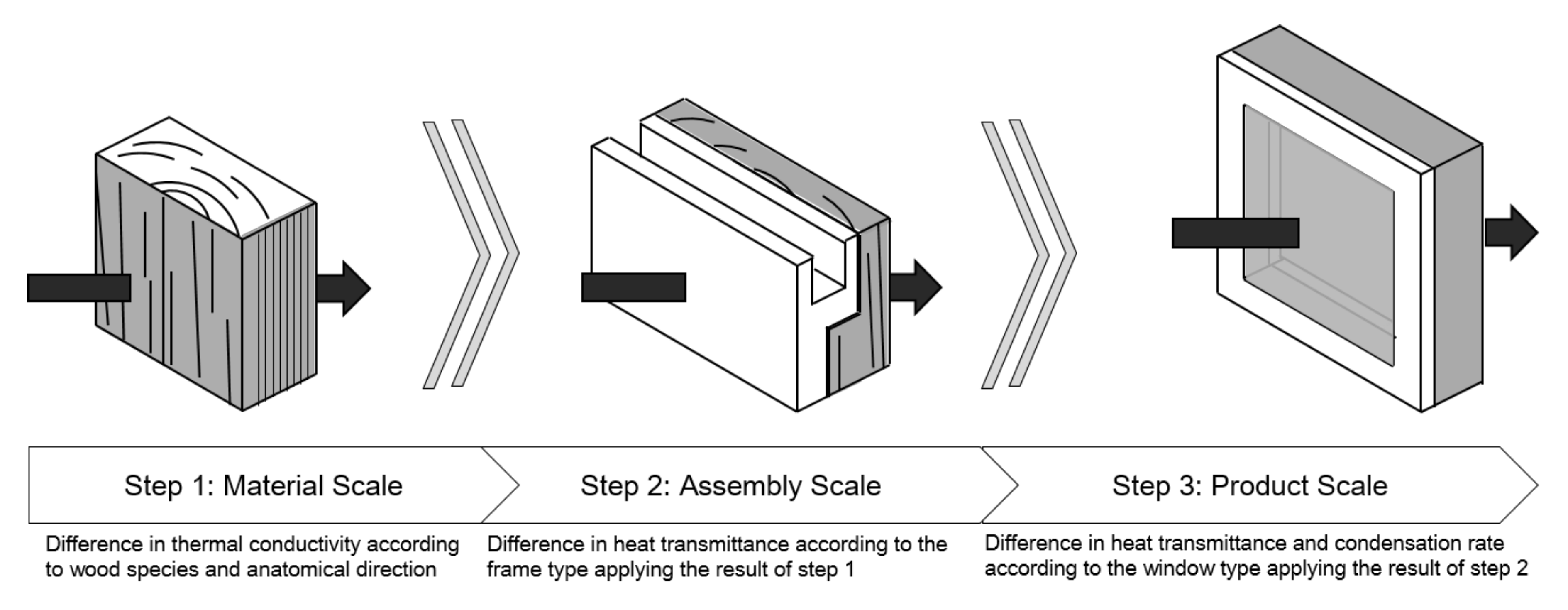
1.3. Scope
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Measurement of Thermal Conductivity
2.2.2. Calculation of Heat Transmittance of Window Frames
2.2.3. Calculation of Heat Transmittance (U-value) and Condensation Resistance (CR) of Windows
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Conductivity of Wood
3.2. Heat Transmittance of Window Frames
3.3. Heat Transmittance and Condensation Resistance of Windows
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Window and Door Market Trends & Opportunities. In Proceedings of the Window Door Manufacturers Association 2018 Technical & Manufacturing Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 19–21 June 2018. Available online: https://www.homeinnovation.com/-/media/Files/Market_Research/WDMA-Technical-Manufacturing-PPT-Home-Innovation.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Jeld-Wen 2018 Annual Report. Available online: https://investors.jeld-wen.com/financials/annual-reports/default.aspx (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- WWF-UK. Window of Opportunity. Available online: https://www.wwf.org.uk/sites/default/files/2017-06/windows_0305.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Asif, M.; Muneer, T.; Kubie, J. Sustainability Analysis of Window Frames. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2005, 26, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, S.V.; Zelinka, S.L. Moisture Relations and Physical Properties of Wood. In Wood Handbook: Wood As an Engineering Material: Chapter 4, Centennial ed.; General Technical Report FPL; GTR-190; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 2010; Volume 190, pp. 4.1–4.19. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H. Numerical Analysis on Temperature and Moisture Profiles of Wood Considering Crack Occurrence during High Temperature Drying. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yapici, F.; Ozcifci, A.; Esen, R.; Kurt, S. The Effect of Grain Angle and Species on Thermal Conductivity of Some Selected Wood Species. BioResources 2011, 6, 2757–2762. [Google Scholar]
- Asdrubali, F.; Ferracuti, B.; Lombardi, L.; Guattari, C.; Evangelisti, L.; Grazieschi, G. A Review of Structural, Thermo-Physical, Acoustical, and Environmental Properties of Wooden Materials for Building Applications. Build. Environ. 2017, 114, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggrey-Smith, S.; Preko, K.; Owusu, F.W. Study of Thermal Properties of Some Selected Tropical Hard Wood Species. Int. J. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2016, 5, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, A.; Kozokiewicz, P. Comparison of thermal properties of selected wood species intended to woodwork windows production. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci. SGGW For. Wood Technol. 2014, 85, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Tenwolde, A.; McNatt, J.D.; Krahn, L. Thermal Properties of Wood and Wood Panel Products for Use in Buildings; DOE/OR/21697-1; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 1988; p. 6059532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, J.D. Thermal conductivity of wood. Heat. Pip. Air Cond. 1941, 13, 380–391. [Google Scholar]
- Çavuş, V.; Şahin, S.; Esteves, B.; Ayata, U. Determination of Thermal Conductivity Properties in Some Wood Species Obtained from Turkey. BioResources 2019, 14, 6709–6715. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.; Kang, Y.; Kim, S. Wood Thermal Conductivity Database Construction for the Application of Building Energy Simulation. J. Korea Furnit. Soc. 2016, 27, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Yu, S.; Seo, J.; Kim, S. Thermal Performance of Wooden Building Envelope by Thermal Conductivity of Structural Members. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2013, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vay, O.; De Borst, K.; Hansmann, C.; Teischinger, A.; Müller, U. Thermal Conductivity of Wood at Angles to the Principal Anatomical Directions. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, N.; Park, S. Comparative Analysis of Heat Transmittance of Timber Window Frames with Different Wood Species and Anatomical Direction. In Proceedings of the Autumn Annual Conference of the Korean Society of Wood Science Technology, Daegu, Korea, 24–25 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, M.-S.; Rhee, K.-N.; Yu, J.-Y.; Jung, G.-J. Determination of Equivalent Thermal Conductivity of Window Spacers in Consideration of Condensation Prevention and Energy Saving Performance. Energies 2017, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Song, S.-Y. Evaluation of Alternatives for Improving the Thermal Resistance of Window Glazing Edges. Energies 2019, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hee, W.J.; Alghoul, M.A.; Bakhtyar, B.; Elayeb, O.; Shameri, M.A.; Alrubaih, M.S.; Sopian, K. The Role of Window Glazing on Daylighting and Energy Saving in Buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastines, M.; Correa, E.; Pattini, A. Window Frame Thermal Performance Simulation. Suitable Methods According to Climate and Technology. Revista de la Construcción 2018, 17, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, T.G. Considerations for the Condensation Resistance of Fenestration Assemblies. In Proceedings of the Building Enclosure Science & Technology 2 Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 12–14 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, H.; Lenz, J.; Sommer, P. Deconstructing the Window: Let’s Forget about the Center of Glass. In Proceedings of the Building Enclosure Science & Technology 5 Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 15–18 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, J.; Seo, J.; Kim, S. Building Materials Thermal Conductivity Measurement and Correlation with Heat Flow Meter, Laser Flash Analysis, and TCi. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 109, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Cha, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Huh, W. Development of the Thermal Performance of Wood-Flooring by Improving the Thermal Conductivity of Plywood. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2014, 8, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.-S.; Seo, J.-K.; Kim, S.-M. Suggestion of Thermal Environment Miniature for Evaluation of Heating Efficiency Based on Thermal Conductivity Measurement Method of Building Materials. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2011, 39, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BC Reference Procedure and Tools for Using THERM to Determine Window Performance Values for Use with PHPP. Available online: https://www.fen-bc.org/resource_details.php?id_resource=3 (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- NFRC. ANSI/NFRC 500-2020, Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product Condensation Index Ratings; National Fenetration Rating Council: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Beall, F.C. Specific Heat of Wood: Further Research Required to Obtain Meaningful Data: [With List of Literature Cited]; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 13061-1:2014, Physical and Mechanical Properties of Wood—Test Methods for Small Clear Wood Specimens—Part 1: Determination of Moisture Content for Physical and Mechanical Tests; International Organization for Strandardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- NFRC. ANSI/NFRC 100-2020, Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product U-factors; National Fenetration Rating Council: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 10077-2:2017, Thermal Performance of Windows, Door, and Shutters—Calculation of Thermal Transmittance—Part 2: Numerical Method for Frames; International Organization for Strandardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J.L. Using a 4th Surface Low-e Coating on Windows in a Cold Climate: Background, Observations, and Practical Strategies—White Paper. Available online: http://www.solarme.uwaterloo.ca/DownloadPDFs/FSWhitePaper_final.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2020).








| Window Type | Opening Type | Glazing Type | Graphical Representation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timber Window | Horizontal Slider | 22 mm Double Pane (5 cl+12 argon+5 lowE) |  |
| Aluminum-Clad Timber Window | Horizontal Slider | 28 mm Double Pane (6 cl+16 argon+6 lowE) |  |
| Timber-Clad Aluminum Window | Horizontal Slider | 43 mm Triple Pane (5 cl+14 argon+5 lowE+14 argon+5 lowE) |  |
| Wood Species | Moisture Content (%) | Density(kg/m3) | Specific Heat (cal/g∙C) 1 | Thermal Diffusivity (mm2/s) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m∙K) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radial | Tangential | Radial | Tangential | ||||
| Ash | 13.3 | 670 | 0.292 | 0.179 (±0.002) | 0.154 (±0.010) | 0.147 (±0.002) | 0.127 (±0.008) |
| Cherry | 12.4 | 697 | 0.291 | 0.221 (±0.010) | 0.157 (±0.002) | 0.181 (±0.008) | 0.129 (±0.001) |
| Maple | 13.2 | 732 | 0.292 | 0.190 (±0.006) | 0.149 (±0.003) | 0.156 (±0.005) | 0.122 (±0.002) |
| Oak, White | 13.8 | 884 | 0.293 | 0.206 (±0.010) | 0.165 (±0.001) | 0.169 (±0.008) | 0.136 (±0.001) |
| Walnut | 11.3 | 566 | 0.289 | 0.185 (±0.002) | 0.162 (±0.002) | 0.152 (±0.002) | 0.133 (±0.001) |
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m∙K) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 160 | ISO 10077-2 |
| EPDM (gasket) | 0.25 | ISO 10077-2 |
| Frame cavity | automatically calculated for each cavity within THERM | ISO 10077-2 |
| Frame cavity (slightly ventilated) | ||
| Mohair | 0.14 | ISO 10077-2 |
| Spacer | 0.01 | NFRC 100 |
| Steel | 50 | ISO 10077-2 |
| Wood | measured value | - |
| Urethane (thermal break) | 0.12 | NFRC |
| Window Type | Wood Species | Anatomical Direction | ID | U-value of Window Frame (W/m2·K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timber Window | Ash | Radial | T-AR | 1.908 |
| Tangential | T-AT | 1.764 | ||
| Cherry | Radial | T-CR | 2.124 | |
| Tangential | T-CT | 1.779 | ||
| Maple | Radial | T-MR | 1.969 | |
| Tangential | T-MT | 1.725 | ||
| Oak, White | Radial | T-OR | 2.052 | |
| Tangential | T-OT | 1.831 | ||
| Walnut | Radial | T-WR | 1.942 | |
| Tangential | T-WT | 1.809 | ||
| Aluminum-Clad Timber Window | Ash | Radial | AcT-AR | 2.422 |
| Tangential | AcT-AT | 2.316 | ||
| Cherry | Radial | AcT-CR | 2.566 | |
| Tangential | AcT-CT | 2.327 | ||
| Maple | Radial | AcT-MR | 2.465 | |
| Tangential | AcT-MT | 2.287 | ||
| Oak, White | Radial | AcT-OR | 2.516 | |
| Tangential | AcT-OT | 2.365 | ||
| Walnut | Radial | AcT-WR | 2.446 | |
| Tangential | AcT-WT | 2.409 | ||
| Timber-Clad Aluminum Window | Ash | Radial | TcA-AR | 2.219 |
| Tangential | TcA-AT | 2.146 | ||
| Cherry | Radial | TcA-CR | 2.317 | |
| Tangential | TcA-CT | 2.154 | ||
| Maple | Radial | TcA-MR | 2.248 | |
| Tangential | TcA-MT | 2.126 | ||
| Oak, White | Radial | TcA-OR | 2.285 | |
| Tangential | TcA-OT | 2.181 | ||
| Walnut | Radial | TcA-WR | 2.235 | |
| Tangential | TcA-WT | 2.170 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, N.; Park, S. Heat Transfer Analysis of Timber Windows with Different Wood Species and Anatomical Direction. Energies 2020, 13, 6050. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226050
Ahn N, Park S. Heat Transfer Analysis of Timber Windows with Different Wood Species and Anatomical Direction. Energies. 2020; 13(22):6050. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226050
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Namhyuck, and Sanghoon Park. 2020. "Heat Transfer Analysis of Timber Windows with Different Wood Species and Anatomical Direction" Energies 13, no. 22: 6050. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226050
APA StyleAhn, N., & Park, S. (2020). Heat Transfer Analysis of Timber Windows with Different Wood Species and Anatomical Direction. Energies, 13(22), 6050. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226050




