Reservoir Formation Model and Main Controlling Factors of the Carboniferous Volcanic Reservoir in the Hong-Che Fault Zone, Junggar Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Data and Methods
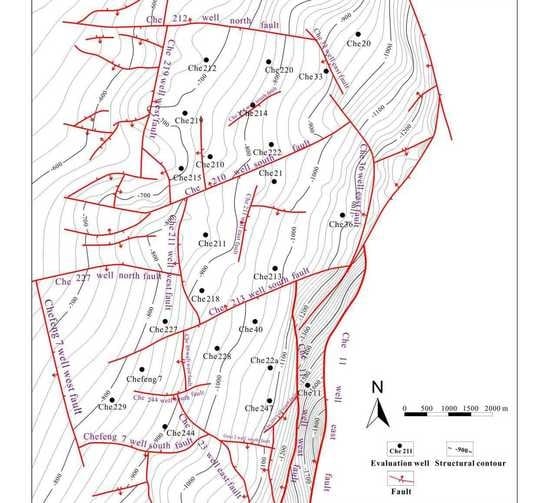
3.1. Structural characteristics
3.2. Characteristics of Volcanic Reservoirs
3.3. Reservoir Characteristics and Types
4. Analysis of Main Controlling Factors of Carboniferous Reservoir
4.1. Structure
4.2. Volcanic Lithofacies
4.3. Unconformity
4.4. Physical Properties
5. Reservoir Formation Model
6. Conclusions
- The Carboniferous volcanic reservoir in the Hong-Che Fault Zone is mainly distributed in the hanging wall of the fault zone and oil and gas has mainly accumulated in the high part of the structure. The reservoir is controlled by faults and lithofacies in the plane direction and is vertically distributed within 400 m from the top of the Carboniferous. The formation of the volcanic reservoir was mainly controlled by structures and was also controlled by volcanic lithofacies, unconformity surfaces, and physical properties.
- The physical reservoir properties of the eruptive facies in the Hong-Che Fault Zone are most favorable and are followed by overflow facies, while the volcanic sedimentary facies are least favorable.
- The Carboniferous portion of the Hong-Che Fault Zone has been exposed to the surface for a long period, has been subjected to weathering and leaching, and a weathering crust has developed. The vertical zonation characteristics of the weathering crust at the top of the Carboniferous in the area of the Che 210 well are obvious. A soil layer, corrosion zone, disintegration zone, and parent rock developed from top to bottom. Among them, the reservoirs with the best physical properties are developed in the corrosion zone, which are 30–350 m distant from the top of the Carboniferous.
- The reservoir space of the Carboniferous reservoir in the Hong-Che Fault Zone consists mainly of secondary pores and fractures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schutter, S.R. Occurrences of Hydrocarbons in and around Igneous Rocks. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2003, 214, 35–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petford, N.; McCaffrey, K. Hydrocarbons in crystalline rocks: An introduction. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2003, 214, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Shi, F.; Kou, Y.; Wang, L. Potential of global volcanics-hosted oil-gas resources. Resour. Ind. 2009, 11, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Meng, F.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y. Discussion on the formation mechanism of volcanic oil and gas reservoirs. Acta Pet. Sin. 2010, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y. Review and prospect of global volcanic reservoirs. Geol Chin. 2015, 42, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Zorin, Y.A. Geodynamics of the western part of the Mongolia-Okhotsk collisional belt, Trans-Baikal region (Russia) and Mongolia. Tectonophysics 1999, 306, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, C.; Zhao, W.; Jia, C.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, X. Formation and distribution of volcanic hydrocarbon reservoirs in sedimentary basins of China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2008, 35, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, B. Research status and exploration technology investigation of volcanic oil and gas reservoirs at home and abroad. Nat. Gas Explor. Dev. 1994, 16, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Lu, F.; Lin, C. Meso-Cenozoic Basin Evolution and Geodynamic Environments in Eastern China and Adjacent Areas; Publishing House of China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T.; Dai, J.; Niu, J. Effective reservoir recognition of paleogene trachyte in the middle part of the east sag of Liaohe Depression. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2007, 34, 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zou, C.; Li, J.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, G.; Hu, S.; Kuang, L.; Zhang, Y. Comparative study on volcanic hydrocarbon accumulations in western and eastern China and its significance. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2009, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Sun, M.; Yuan, C.; Xiao, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, K.; Li, J. Genesis of Carboniferous volcanic rocks in the eastern Junggar: Constraints on the closure of the Junggar Ocean. Acta Pet. Sinica 2006, 22, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Mei, H.; Yu, X.; Bai, Z.; Niu, H.; Cheng, F.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Q. Adakite volcanic related to plate subduction in Late Paleozoic island arc of northern margin Junggar: A product of partial melting of subducting slab. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2001, 46, 684–688. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, F.; Peng, P. Characteristics of volcanic rocks in Chinese basins and their relationship with oil-gas reservoir forming process. Acta Pet. Sinica 2010, 26, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y. The Gravitational and Magnetic Field Research of Carboniferous Volcanic Rocks in Western-Central Junggar Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, F. Tectonic Evolution and Its Relationship with Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Northwest Margin of Junggar Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 779–793. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Yin, C.; Du, S.; Shi, X.; Ma, H. Characteristics of structural segmentation of foreland thrust belts—A case study of the fault belts in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2004, 11, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Rao, G.; Wang, R. Mesozoic reactivated transpressional structures and multi-stage tectonic deformation along the Hong-Che fault zone in the northwestern Junggar Basin, NW China. Tectonophysics 2016, 679, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Bao, Z.; Xian, B.; Huang, Z. Structural Transform Zone and Its Control of Mesozoic Deposits in Northwestern Margin of Junggar Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2009, 30, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, J.; Guan, Y.; Yang, Z. Comparative analysis on the segmentation of tectonic characteristic in northwest Junggar Basin. Pet. Geol Eng. 2008, 22, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhi, D.; Xing, C.; Shi, J. Formation of Carboniferous Reservoir in Hongche Fault Belt, Northwestern Margin of Junggar Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2010, 21, 917–923. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, C.; Wu, K. Structural characteristics and reservoir forming control of Hongche fault zone in Junggar Basin. Compet. Hydropower Reserves 2018, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Guo, J.; Du, Y. Architecture of buried reverse fault zone in the sedimentary basin: A case study from the Hong-Che Fault Zone of the Junggar Basin. J. Struct. Geol. 2017, 105, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ji, J.; Song, B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. Late Paleozoic vertical growth of continental crust around the Junggar Basin, Xinjiang, China (Part I): Timing of post-collisional plutonism. Acta Pet. Sin. 2006, 22, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Tang, H.; Hou, G.; Liu, C. Geochemistry of aluminous A-type granites along Darabut tectonic belt in West Junggar, Xinjiang. Geochimica 2006, 35, 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Guo, Z.; Fang, S. A new insight into the thrust structures at the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2009, 16, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Wu, S.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, M.; Li, D.; Lu, Y. Tectono⁃Depositional Setting and Its Evolution during Permian to Triassic around Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2018, 39, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y. Geological Structure, Formation and Evolution of Chepaizi Uplift in Western Junggar Basin. Ph.D. Dissertation, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Kuang, L.; Cha, M.; Shao, Y.; Lei, D.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, C.; et al. Hydrocarbon Accumulation Mechanism and Exploration Technology of Volcanic Rocks: A Case Study of Junggar Basin; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Qin, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y. Structure characteristics and fracture development pattern of the Carboniferous in Hongche fracture belt. Spec. Oil Gas Reserves 2010, 17, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Structural Evolution and Dislocation Mechanism of Western Margin Chepaizi Uplift of Junggar Basin. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2015, 45, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Study on Hydrocarbon Accumulation Law for Volcanic Rock Reservoirs in Hongche Fault Belt, Junggar Basin. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum (East China), Dongying, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Pan, J.; Tan, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, D. Application of volcanic seismic reservoir to oil and gas exploration of Carboniferous in Hongche fault belt in Junggar Basin. Litho Reserves 2010, 22, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Song, W. Characteristics of the Carboniferous volcanic reservoir in the Hongche fault zone. Spec. Oil Gas Reserves 2011, 18, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Cai, Y.; Fan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Jiang, Q. Fracture characteristics of Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in Hongche fault belt of Junggar Basin. Litho Reserves 2011, 23, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Su, P.; Qin, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, F. Characteristics of Volcanic Reservoir Fractures in Upper Wall of HongChe Fault Belt. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2011, 32, 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Hao, F.; Tan, K.; Wei, P.; Ren, P.; Chen, Y.; Yin, L. Characteristics and accumulation of Paleozoic volcanic rock reservoirs in Hongche fault belt, Junggar Basin. Litho Reserves 2007, 19, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Guo, J.; Yao, W.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B. Analysis on the structure and accumulation differences of Hongche fault belt in Junggar Basin. Geol. Resour. 2019, 28, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, J. Modeling of Pool-Forming Dynamics for Jurassic in Che-Guai Area, Northwest Edge of Junggar Basin. Geol. Sci. Tech. Inform. 2010, 29, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, E.; Jin, Z.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, H. Study on physical simulation experiment for the controlling of faults to oil-Taking the Hongche faults in the northwest of Junggar Basin as an example. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2005, 27, 414–418. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Ran, Y.; Lu, J.; Wu, E. The geochemistry research on the sealing feature of fault in Hongche faults. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. (Sci. Tech. Ed.) 2008, 30, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Li, T. Cementing and sealing actions of Hongche Fault Belt in Zhongguai area of Northwest Margin of Junggar Basin. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2019, 38, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Guan, J.; Liang, Z.; Yao, W.; Shi, J. Reservoir-Forming Conditions and the Main Control Factors Analysis of Triassic System in Chepaizi Prominence, Junggar Basin. Xinjiang Geol. 2012, 30, 434–437. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K. Sealing Evaluation of Hongche Fault Zone in Cheguai Area, Junggar Basin, Northwest China. Xinjiang Geol. 2019, 37, 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Shi, L. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and time frame of hydrocarbon accumulation for volcanic reservoirs in Chepaizi Uplift. Fau-Block OilGas Fie 2020, 27, 545–550. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.; Zou, C.; Liu, L.; Wen, B.; Wu, X.; Wei, Y.; Mao, Z. Geologic essential elements for hydrocarbon accumulation within Carboniferous volcanic weathered crusts in northern Xinjiang, China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 533–540. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, A.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Hydrocarbon sources and accumulation modes of Hongche fault zone in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin. J. Xian Shiyou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 30, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Wu, K.; Huang, Y.; Ji, D.; Fu, X. Weathering Crust Characterization and Its Hydrocarbon Geology Significance in the Northwestern Junggar Basin. Spec. Oil Gas Reserves 2018, 25, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.; Hou, L.; Tao, S.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Pang, Z. Hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism and structure of large-scale volcanic weathering crust of the Carboniferous in northern Xinjiang, China. Sci. Chin. Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Zhao, X.; Mao, Z. Weathered volcanic crust and its petroleum geologic significance: A case study of the Carboniferous volcanic crust in northern Xinjiang. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zou, C.; Kuang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Kuang, J.; Liu, L. Discussion on controlling factors for Carboniferous hydrocarbon accumulation in the Ke-Bai fractured zone of the northwestern margin in Junggar Basin. Acta Pet. Sinica 2009, 30, 513–517. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, L.; Xue, X.; Zou, C.; Hou, L. Oil accumulation and concentration regularity of volcanic lithostratigraphic oil reservoir: A case from upper-plate Carboniferous of KA-BAI fracture zone, Junggar Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2007, 34, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Fei, J.; Xiang, K.; Qin, L.; Xi, W.; Zhu, L. Origin and accumulation process of heavy oil in Chepaizi area of Junggar Basin. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2014, 36, 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, L.; He, D.; Du, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Guan, S.; Yang, G. The reservoir formation model in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2005, 16, 460–463. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, X.M. Petroleum geology features and prospecting targets of Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin. Xinjiang Geol. 2009, 27, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; He, D.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tian, A. Tectono-stratigraphic sequence and basin evolution of Shawan Sag in the Junggar Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2018, 39, 943–954. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; He, D.; Zheng, M.; Liu, D.; Wu, H. Extensional structural feature and of Shawan sag, Junggar in the stage of tectonic evolution Carboniferous—Permian. Chin. J. Geol. 2018, 53, 185–206. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Y. Sedimentary facies analysis of the Lower Jurassic Badaowan Formation in Chepaizi Area, Junggar Basin. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 2019, 43, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Wu, S.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Liu, D.; Kong, Y.; Wu, H. The structural model in the transitional zone of Chepaizi uplift and Shawan sag. Chin. J. Geol. 2018, 53, 155–168. [Google Scholar]















| Country | Field Name | Basin | Type | Output | Reservoir Rock | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil (t/d) | Gas (104m3/d) | |||||
| Cuba | Cristales | South Cuba | oil | 3425 | basaltic tuff | |
| Brazil | Igarape Cuia | Amazonas | oil | 68–3425 | dolerite sill | |
| Vietnam | 15-2-RD 1X | Cuu Long | oil | 1370 | altered granite | |
| Argentina | YPF Palmar Largo | Noroeste | oil, gas | 550 | 3.4 | vuggy basalt |
| Georgia | Samgori | oil | 411 | laumontite tuff | ||
| United States | West Rozel | North Basin | oil | 296 | basalt, agglomerate | |
| Venezuela | Totumo | Maracaibo | oil | 288 | igneous rocks | |
| Argentina | Vega Grande | Neuquen | oil, gas | 224 | 1.1 | fractured andesite |
| New Zealand | Kora | Taranaki | oil | 160 | andesite tuffs, volcaniclastics | |
| Japan | Yoshii-Kashiwazaki | Niigata | gas | 49.5 | rhyolite | |
| Brazil | Barra Bonita | Parana | gas | 19.98 | flood basalt, dolerite sill | |
| Australia | Scotia | Bowen-Surat | gas | 17.8 | fractured andesite | |
| Indonesia | Jatibarang | NW Java | oil, gas | 85 | fractured basalt, andesitic tuff, tuff breccia | |
| Mexico | Furbero | Vera Cruz | oil | 9 | gabbro | |
| Azerbaijan | Muradkhanly | western | oil | 12–64 | andesite and basalt | |
| Basin | Region | Reservoir Name | Strata | Reservoir Rock |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bohai Bay | Jiyang Depression | Binnan oilfield | Paleogene | Basalt, andesitic basalt |
| Linpan lin 9 fault block | Paleogene, Neogene | Tuff | ||
| Shanghe 3 District | Paleogene, Neogene | Basalt, diabase | ||
| Jizhong Depression | Caojiawu Gas Reservoir | Paleogene | Diabase | |
| Huanghua Depression | Fenghuadian | Upper Jurassic | Andesite | |
| Liaohe Depression | Rehetai-Oulituozi | Paleogene | Trachyte | |
| Niuxintuo | Mesozoic | Rhyolite, andesite, breccia, and tuff | ||
| Sichuan | West Sichuan | Zhougongshan | Upper Permian | Basalt |
| Junggar | Northwestern Margin | Karamay Oilfield District 5, 8 | Carboniferous | Basalt |
| Hong-Che area | Carboniferous, Permian | Basalt, andesite, and volcanic breccia | ||
| Central Part | Shixi area | Carboniferous, Permian | Basalt, andesite, diabase, breccia, and tuff | |
| Kalameili area | Carboniferous | Basalt, andesite, breccia, and tuff | ||
| Eastern part | Wucaiwan area | Carboniferous | Basalt, andesite, rhyolite, volcanic breccia, tuff | |
| Subei | Dongtai Depression | Biandong structure | Paleogene | Basalt |
| Songliao | Xujiaweizi Fault Depression | Xingcheng | Cretaceous | Rhyolite |
| Changling Fault Depression | Haerjin structure | Cretaceous | Rhyolite | |
| Erlian | Manite Depression | Abei | Jurassic | Andesite |
| Santanghu | Malang Depression | Haerjiawu Formation | Carboniferous | Andesite |
| Hailar | Beier depression | Budate Group buried hill | Triassic | Altered basalt and andesite |
| Major Category | Volcanism Manner | Rock Type | Number of Samples | Thin Section Lithology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sedimentary rock | Sedimentary rocks | 37 | Sandstone | |
| Sandy conglomerate | ||||
| Conglomerate | ||||
| Mudstone | ||||
| Igneous rock | Extrusive rock (Igneous rock) | Pyroclastic sedimentary rocks | 47 | Tuffaceous glutenite |
| Tuffaceous sandstone | ||||
| Sedimentary pyroclastic rocks | 33 | Sedimentary tuff | ||
| Pyroclastic rocks (168) | 49 | Tuff | ||
| Basaltic tuff | ||||
| Andesitic tuff | ||||
| Acidic tuff | ||||
| 30 | Basaltic breccia tuff | |||
| Andesitic breccia tuff | ||||
| 89 | Basaltic tuffaceous volcanic breccia | |||
| Basaltic volcanic breccia | ||||
| Andesitic volcanic breccia | ||||
| Pyroclastic lava | 8 | Basaltic breccia lava | ||
| Basaltic tuff lava | ||||
| Basaltic andesitic breccia lava | ||||
| Volcanic lava | 104 | Basalt | ||
| Amygdaloidal basalt | ||||
| Andesite | ||||
| Intrusive rock (Plutonic rocks, hypabyssal rock) | Intermediate intrusive rocks | 7 | Diorite | |
| Fine diorite | ||||
| Amphibolite |
| Lithofacies | Effective Porosity/% | Horizontal Permeability/mD |
|---|---|---|
| Eruptive facies | 10.52 | 11.23 |
| Clastic sedimentary facies | 14.51 | 7.44 |
| Overflow facies | 8.93 | 2.83 |
| Volcanic sedimentary facies | 4.72 | 0.98 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, D.; Liu, X.; Guo, S. Reservoir Formation Model and Main Controlling Factors of the Carboniferous Volcanic Reservoir in the Hong-Che Fault Zone, Junggar Basin. Energies 2020, 13, 6114. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226114
Zhu D, Liu X, Guo S. Reservoir Formation Model and Main Controlling Factors of the Carboniferous Volcanic Reservoir in the Hong-Che Fault Zone, Junggar Basin. Energies. 2020; 13(22):6114. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226114
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Danping, Xuewei Liu, and Shaobin Guo. 2020. "Reservoir Formation Model and Main Controlling Factors of the Carboniferous Volcanic Reservoir in the Hong-Che Fault Zone, Junggar Basin" Energies 13, no. 22: 6114. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226114
APA StyleZhu, D., Liu, X., & Guo, S. (2020). Reservoir Formation Model and Main Controlling Factors of the Carboniferous Volcanic Reservoir in the Hong-Che Fault Zone, Junggar Basin. Energies, 13(22), 6114. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226114