Open Circuit Performance of Axial Air Gap Flux Switching Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Wind Energy Conversion: Modeling and Experimental Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. AFSPM for Wind Energy Conversion
2.1. Axial Flux vs. Radial Flux Machines
2.2. Flux Switching Machines (FSMs)
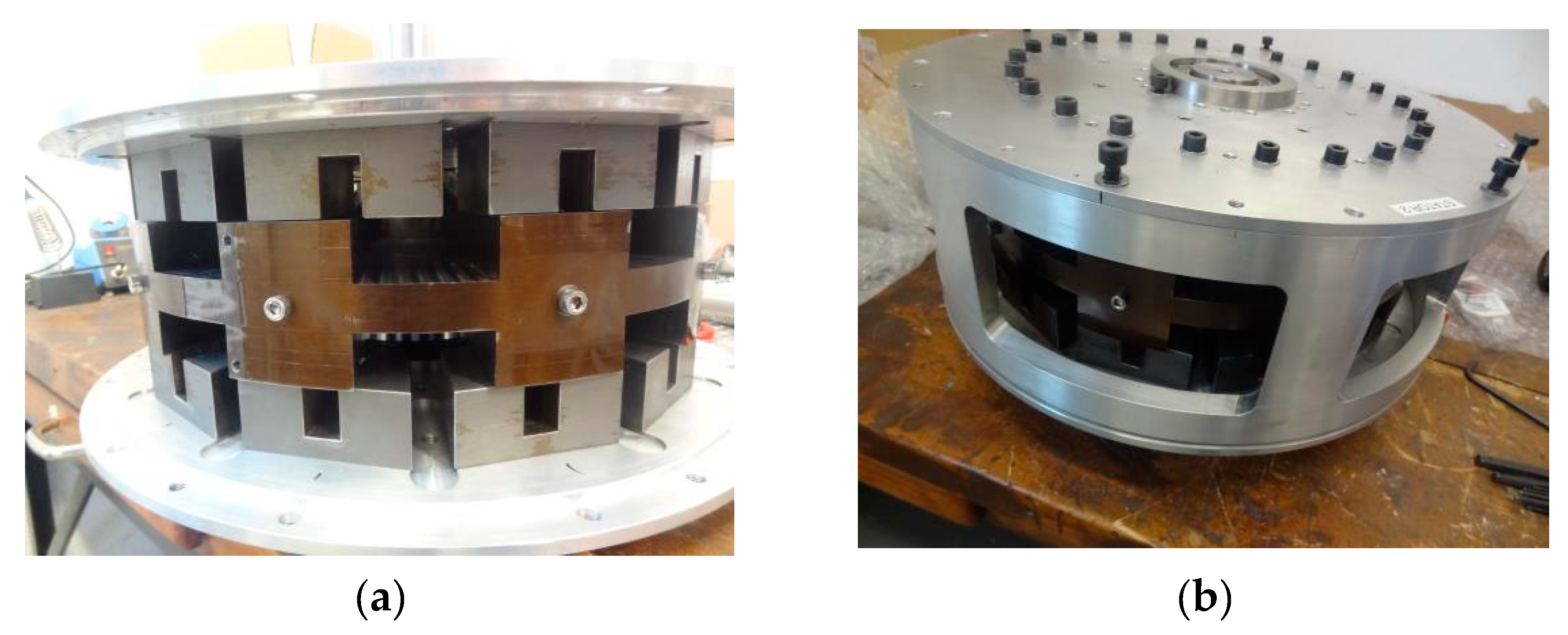
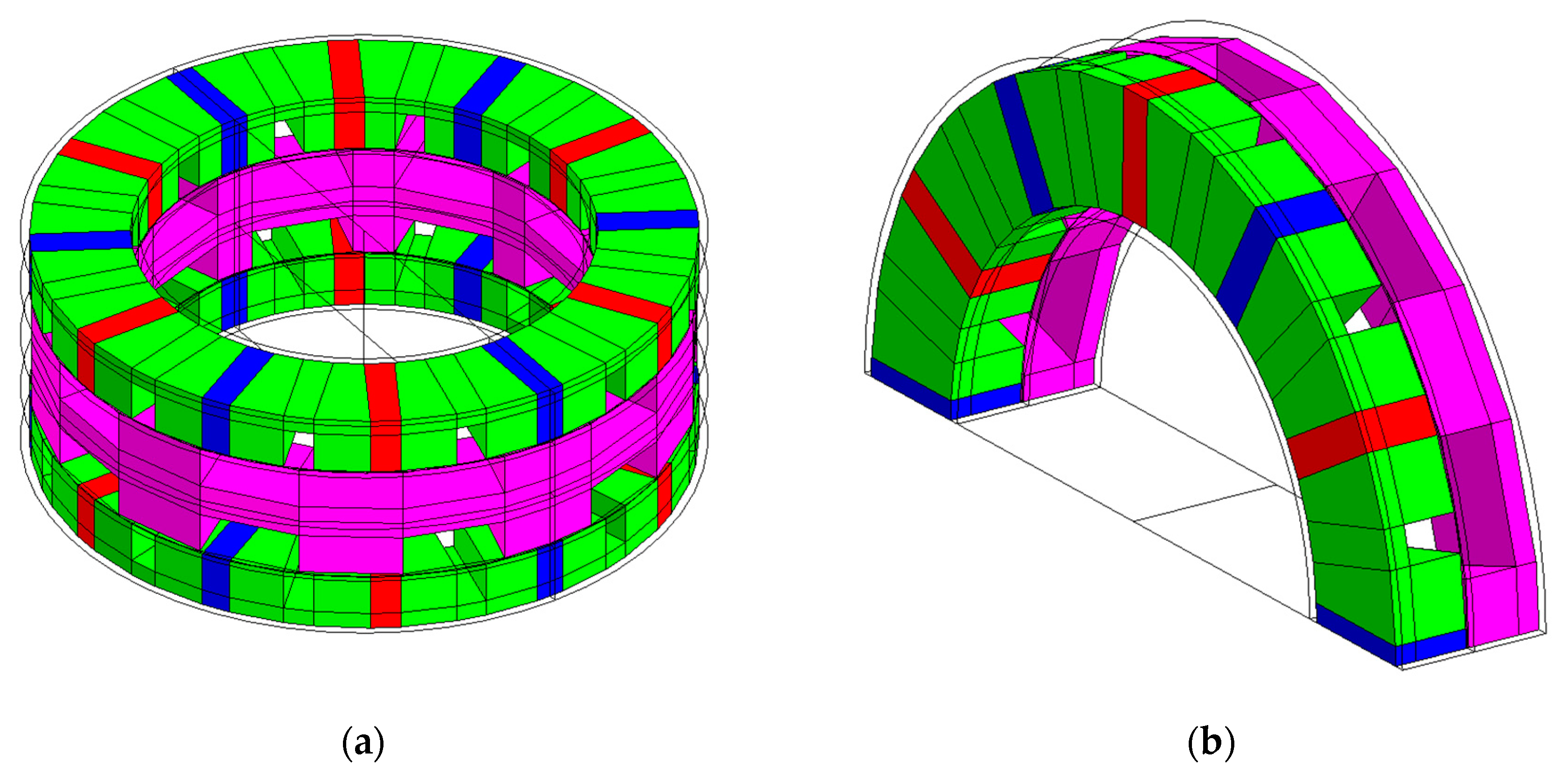
3. AFSPM Prototype Structure and Specifications
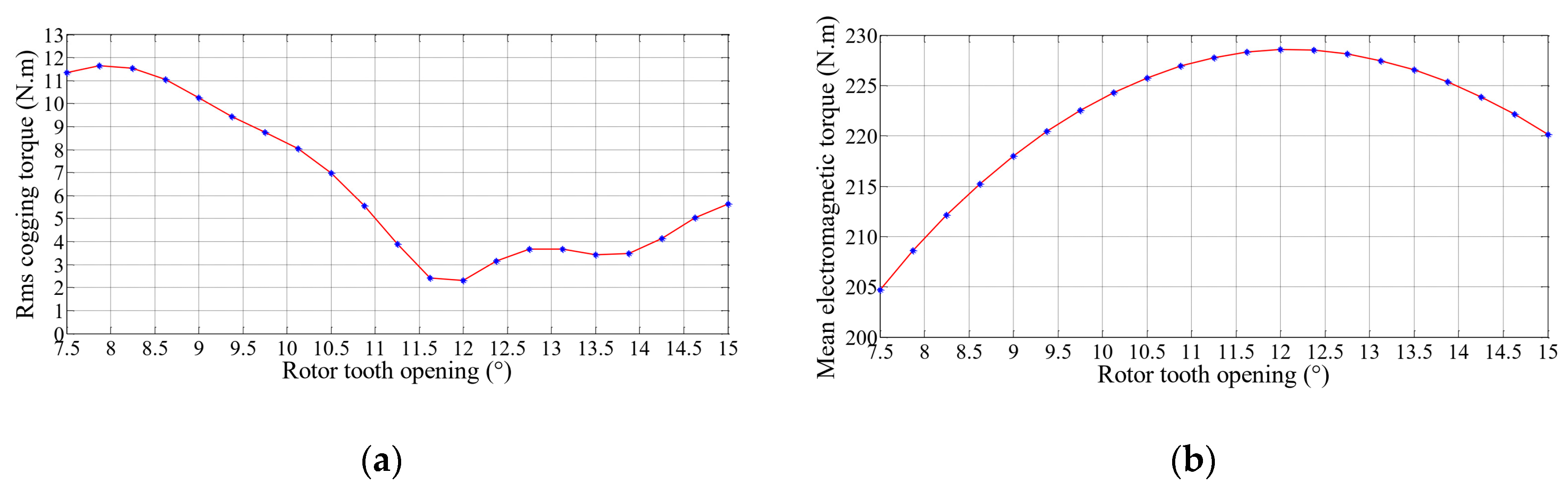
3.1. Choice of Design Parameters
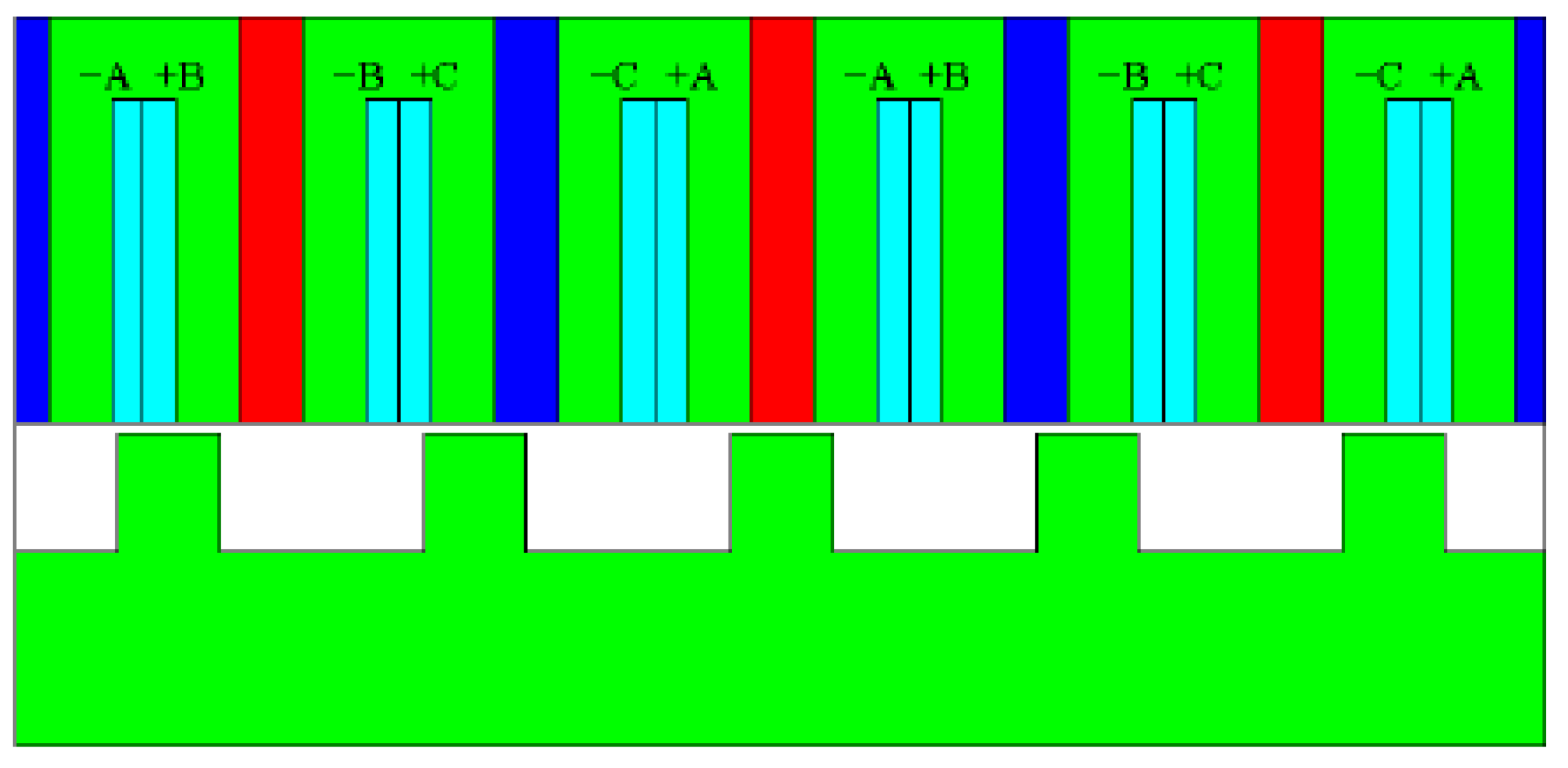
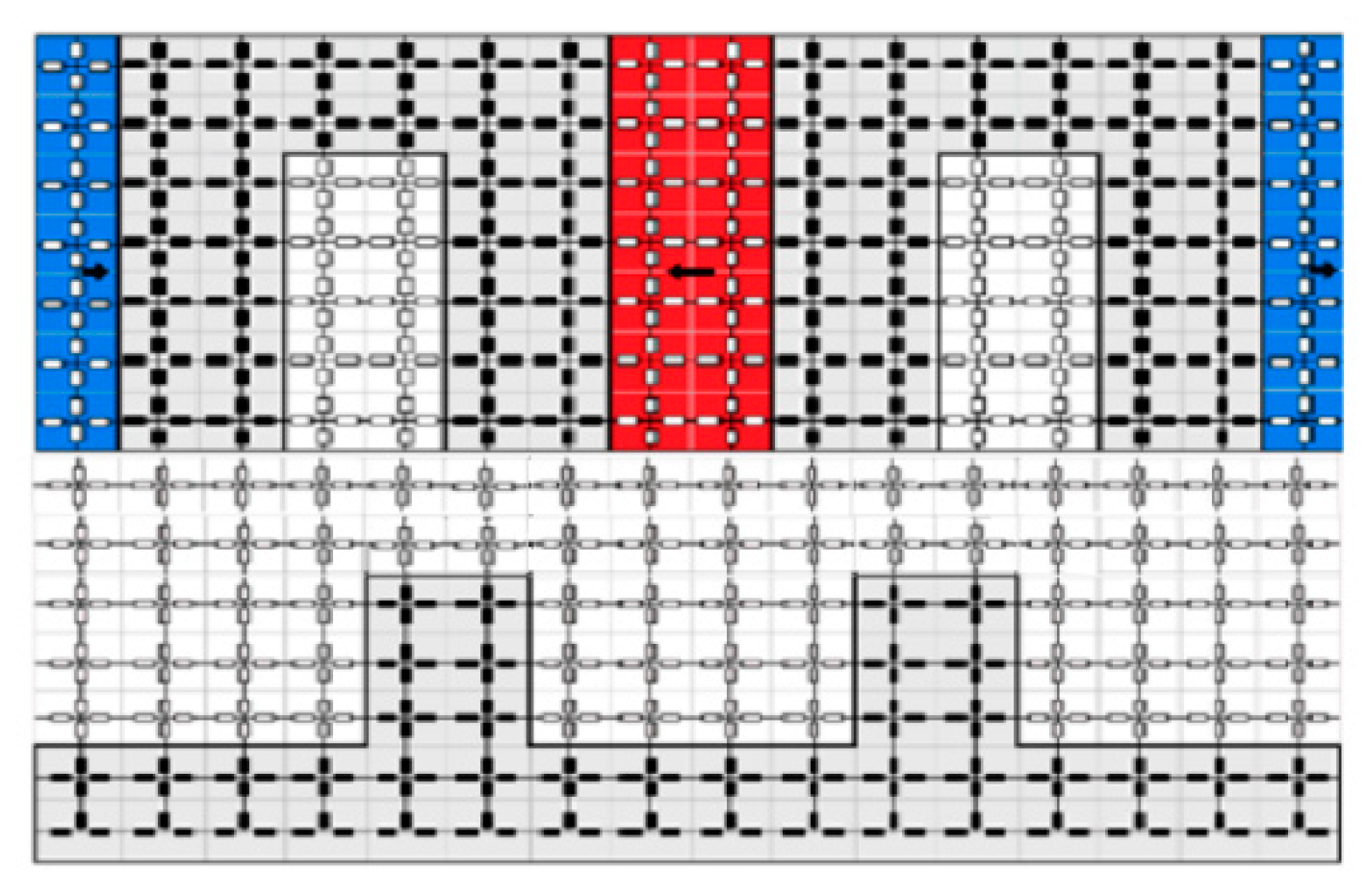
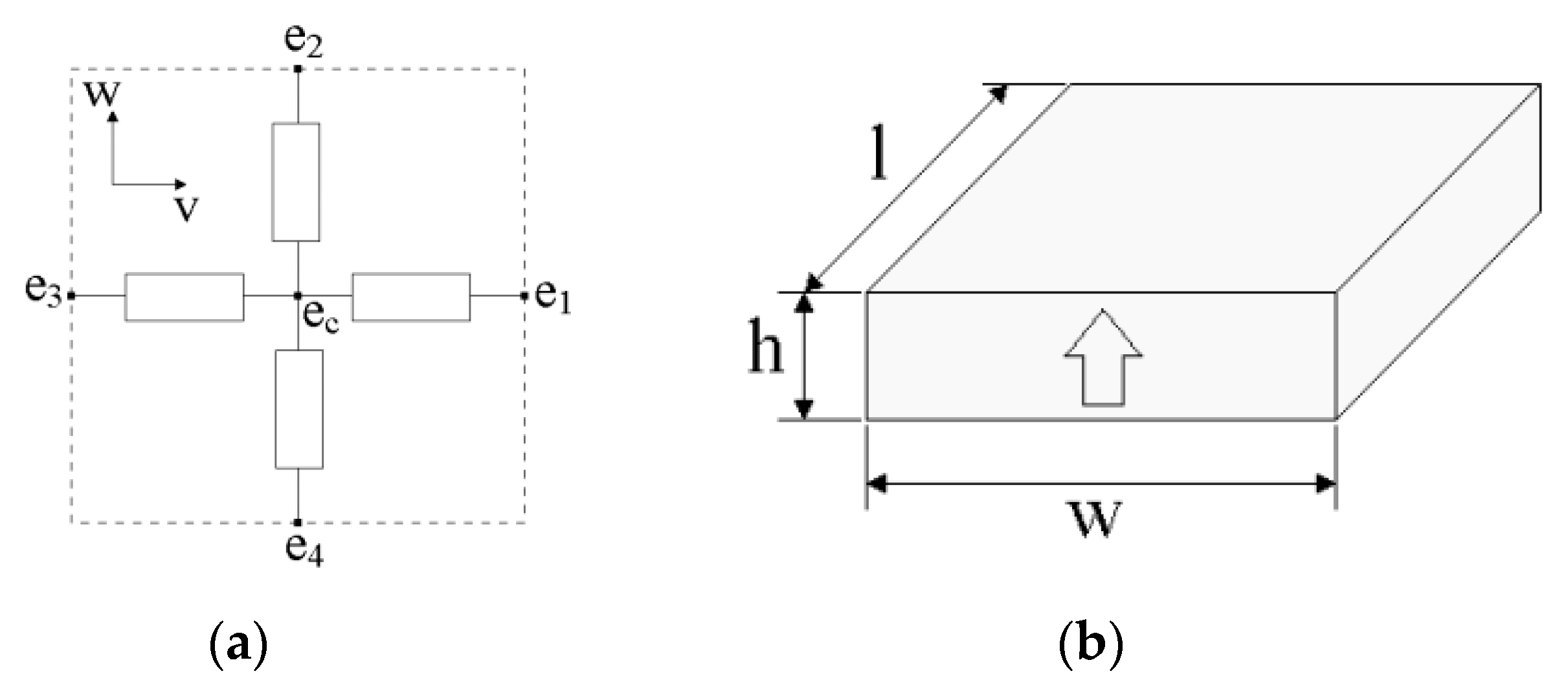
4. Reluctance Network Magnetic Model (RN)
4.1. Quantities Calculation
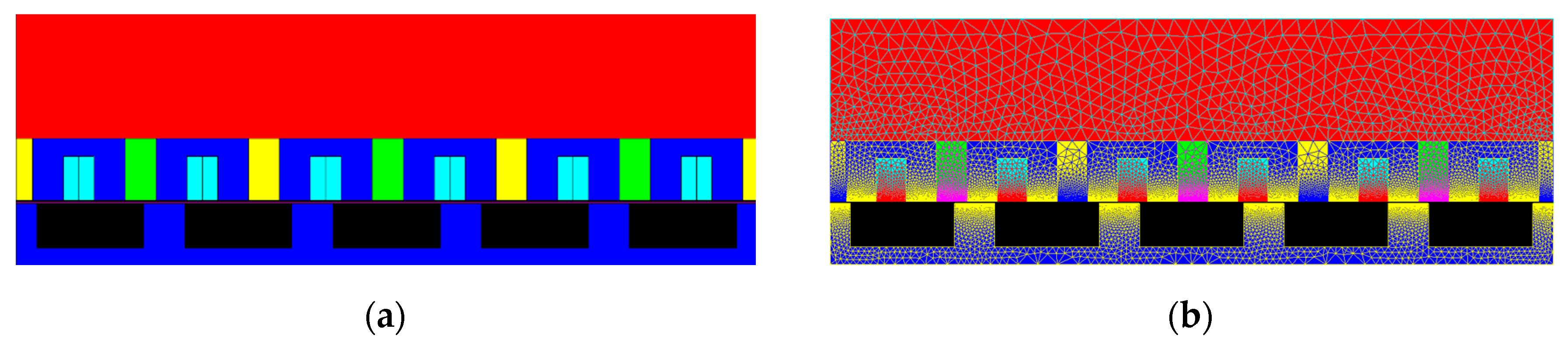
4.2. Finite Elements Method Model
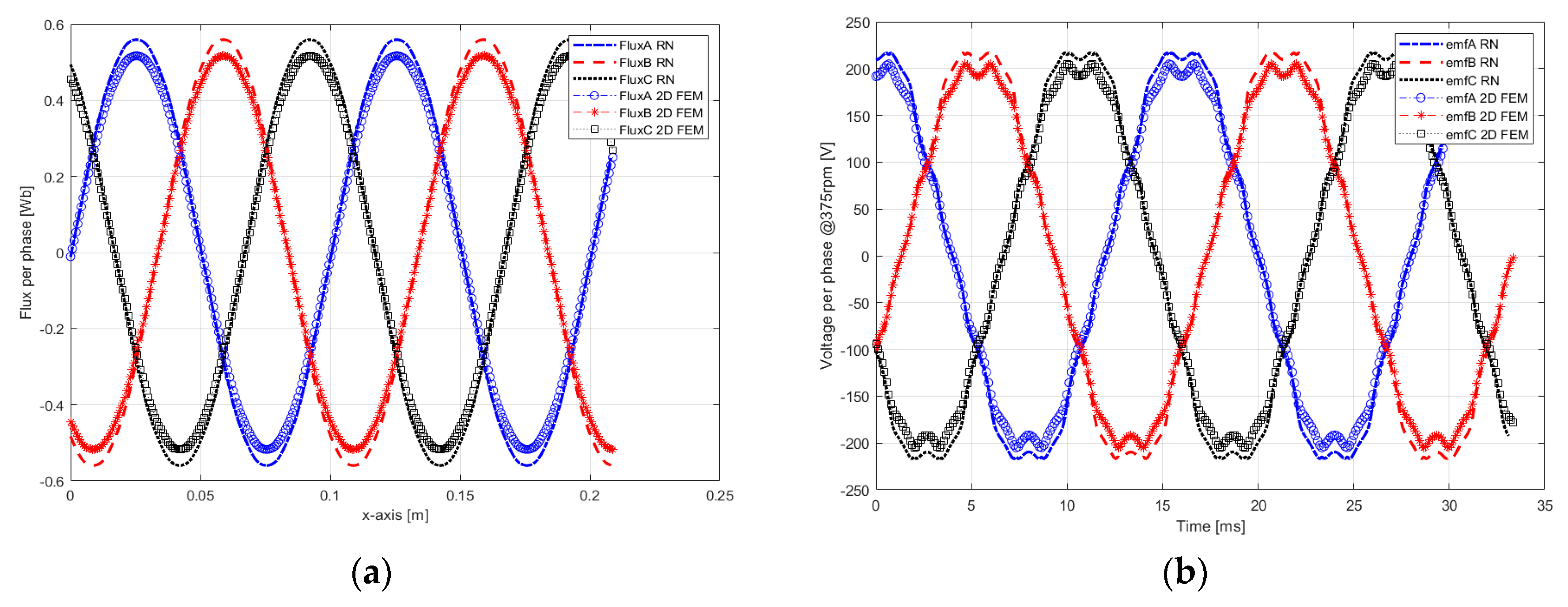
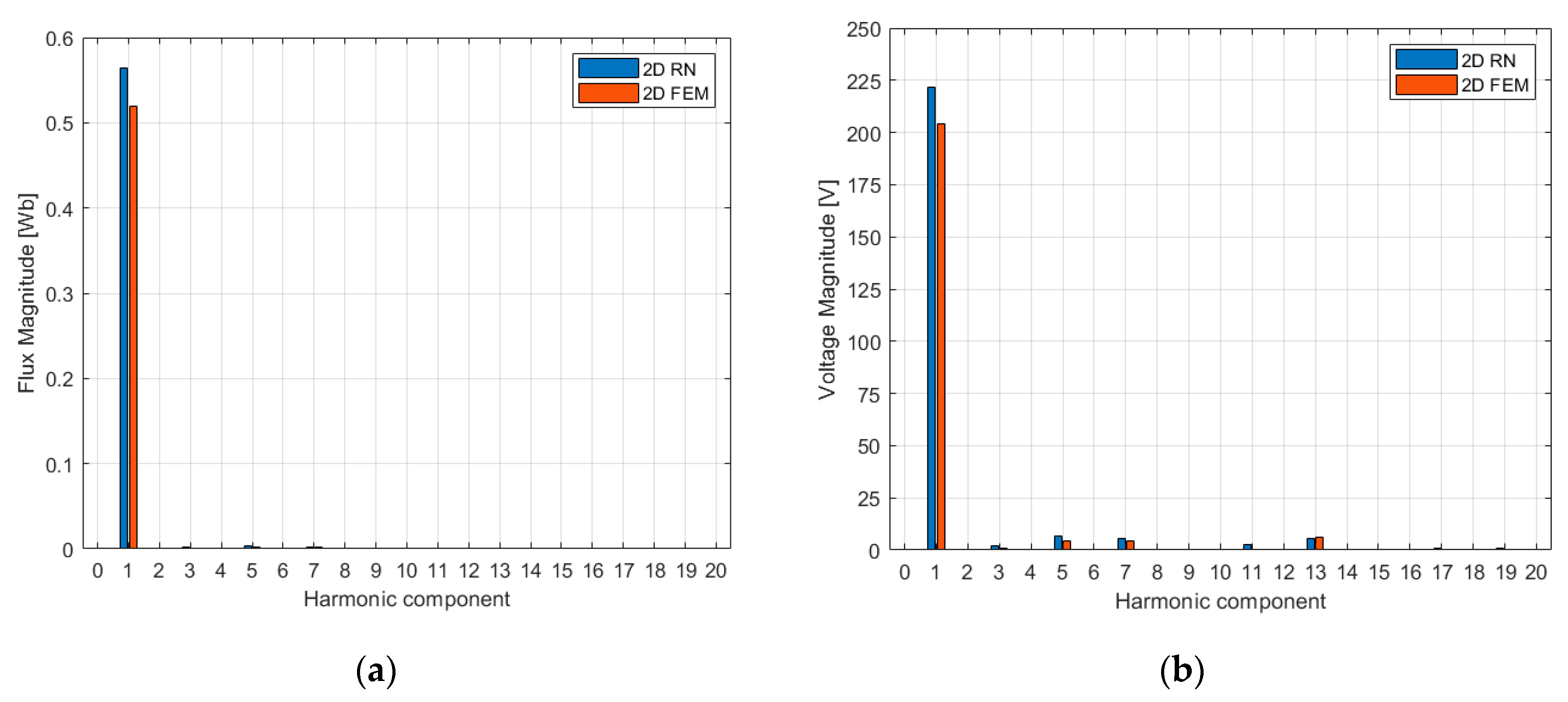
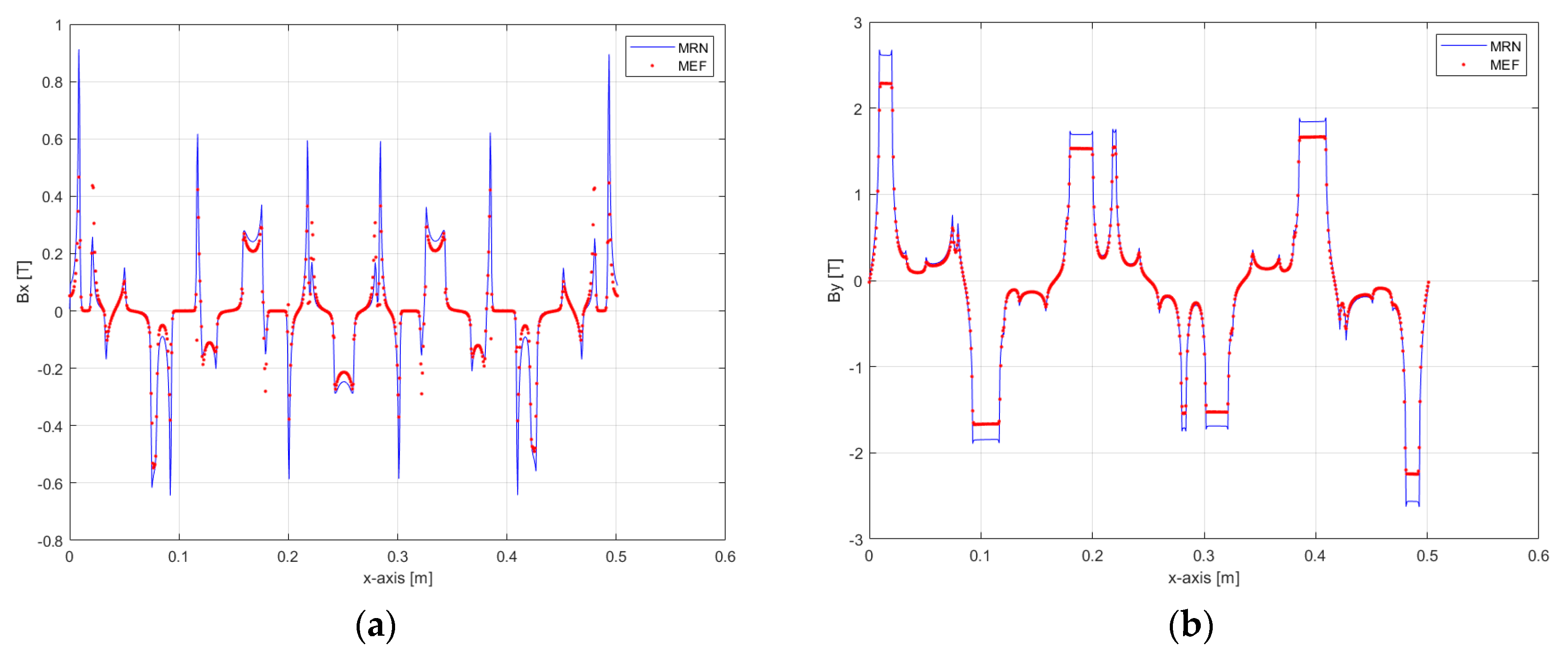
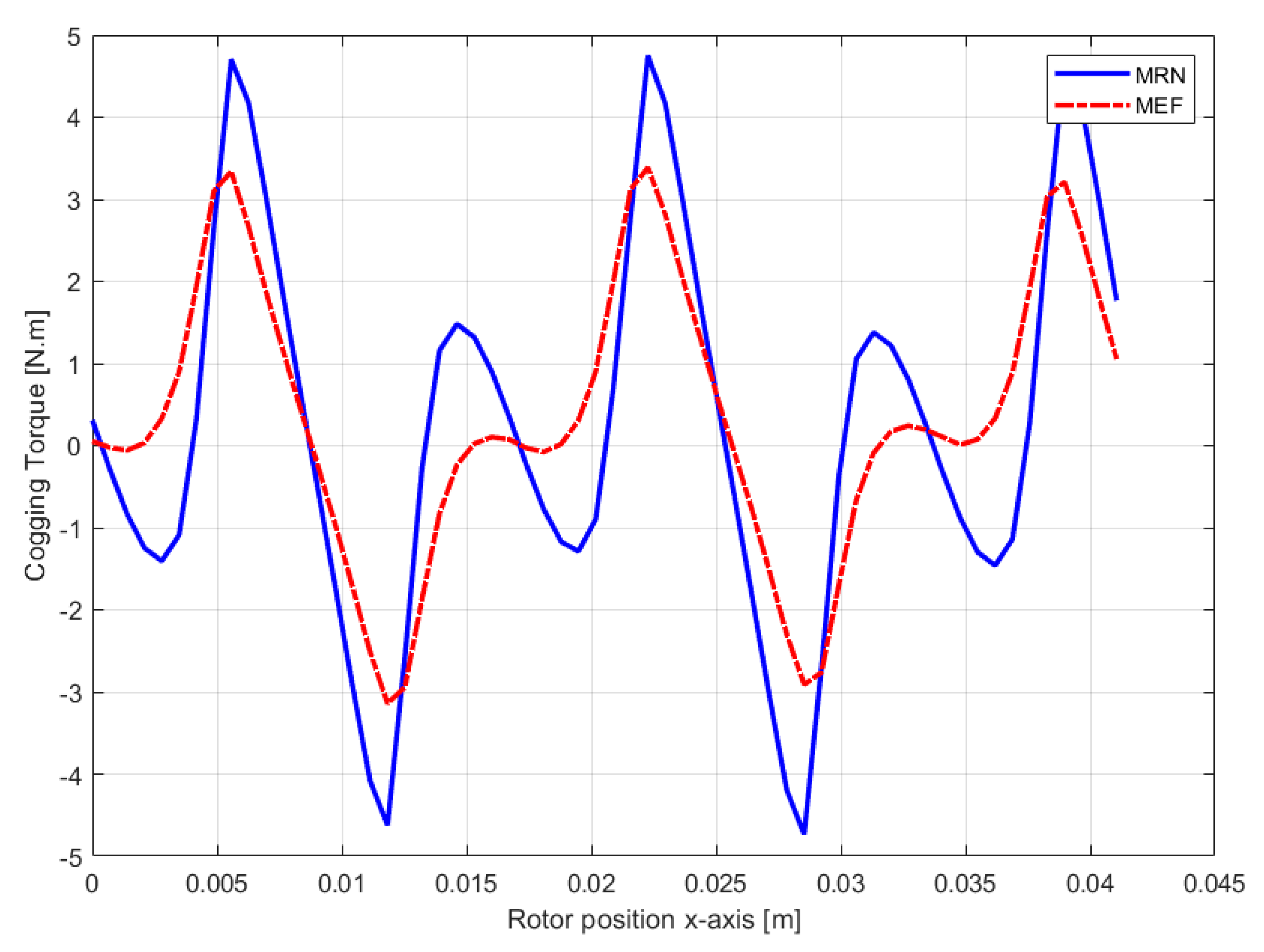
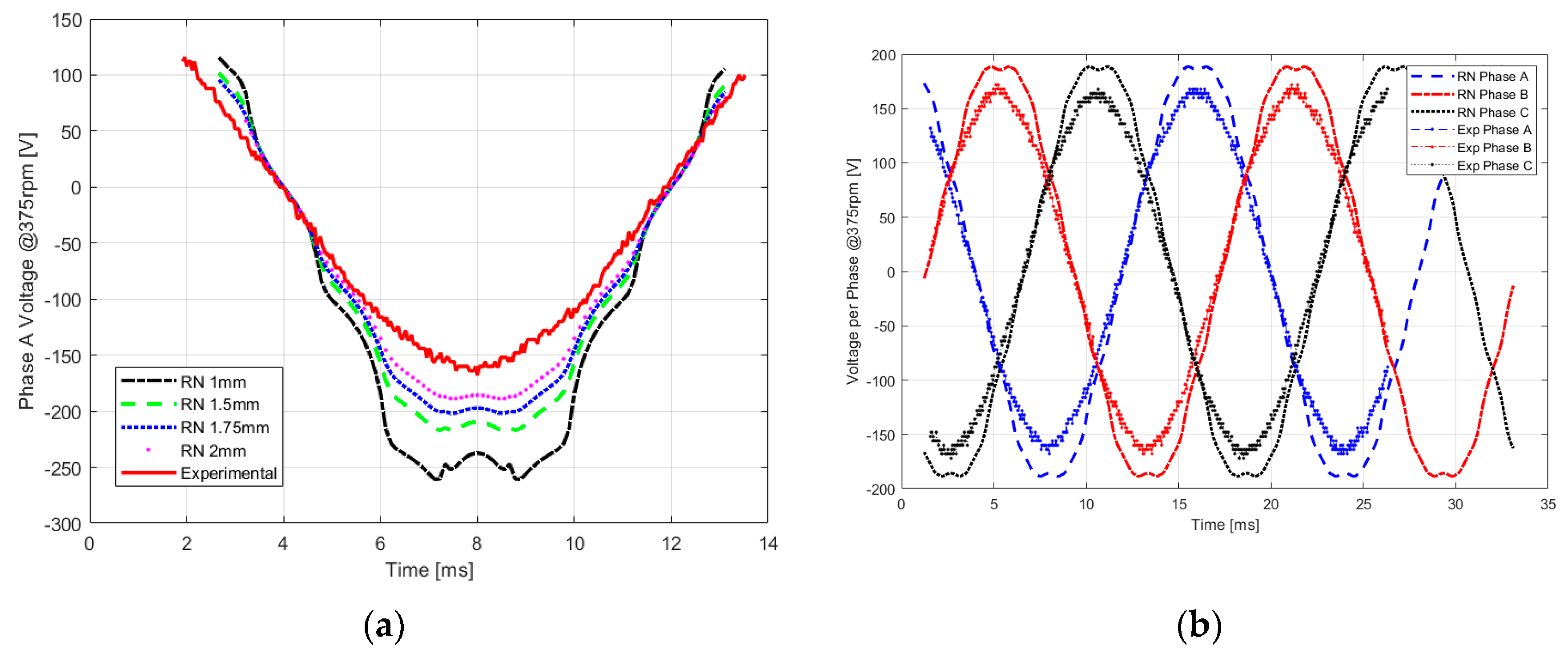
4.3. Results
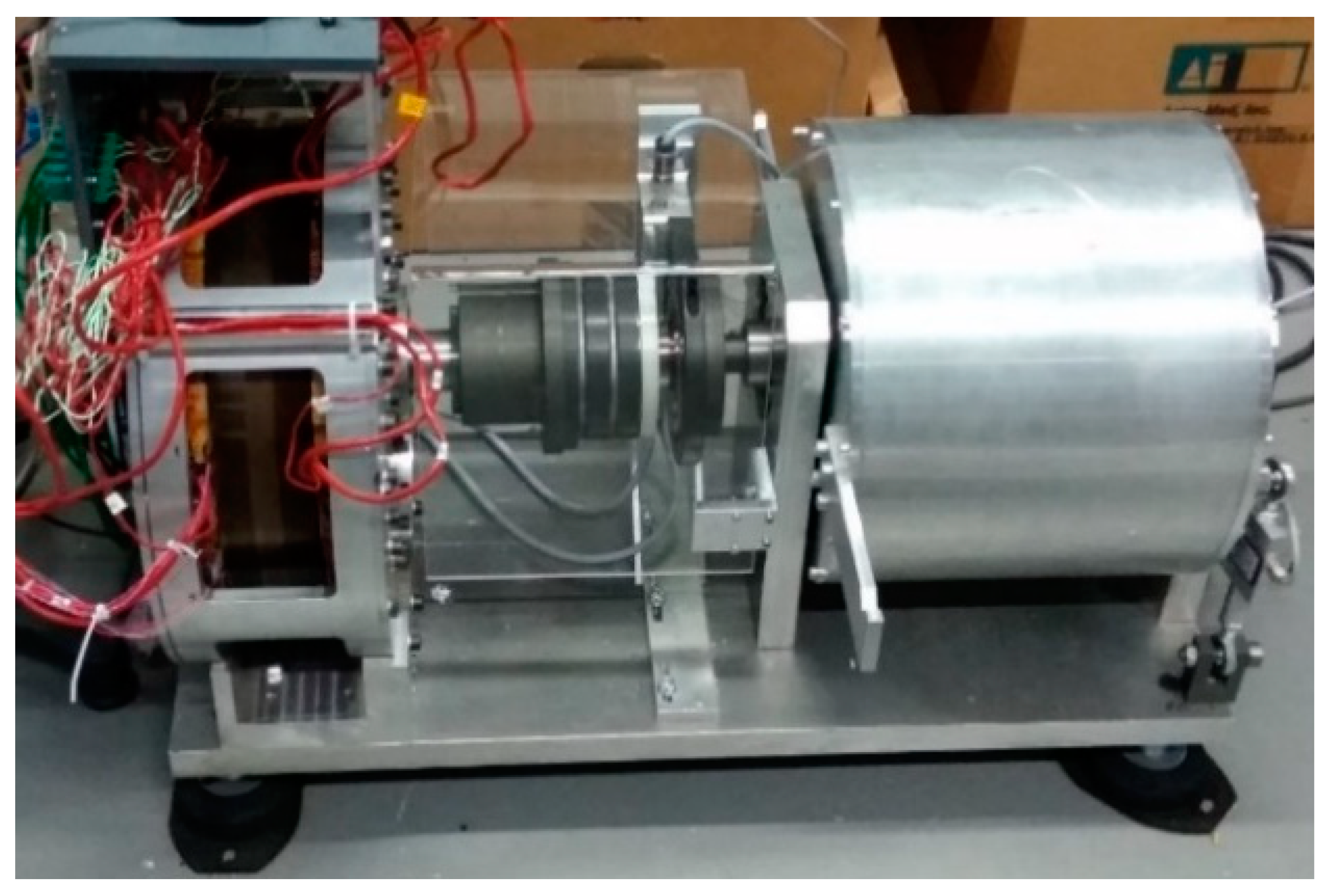
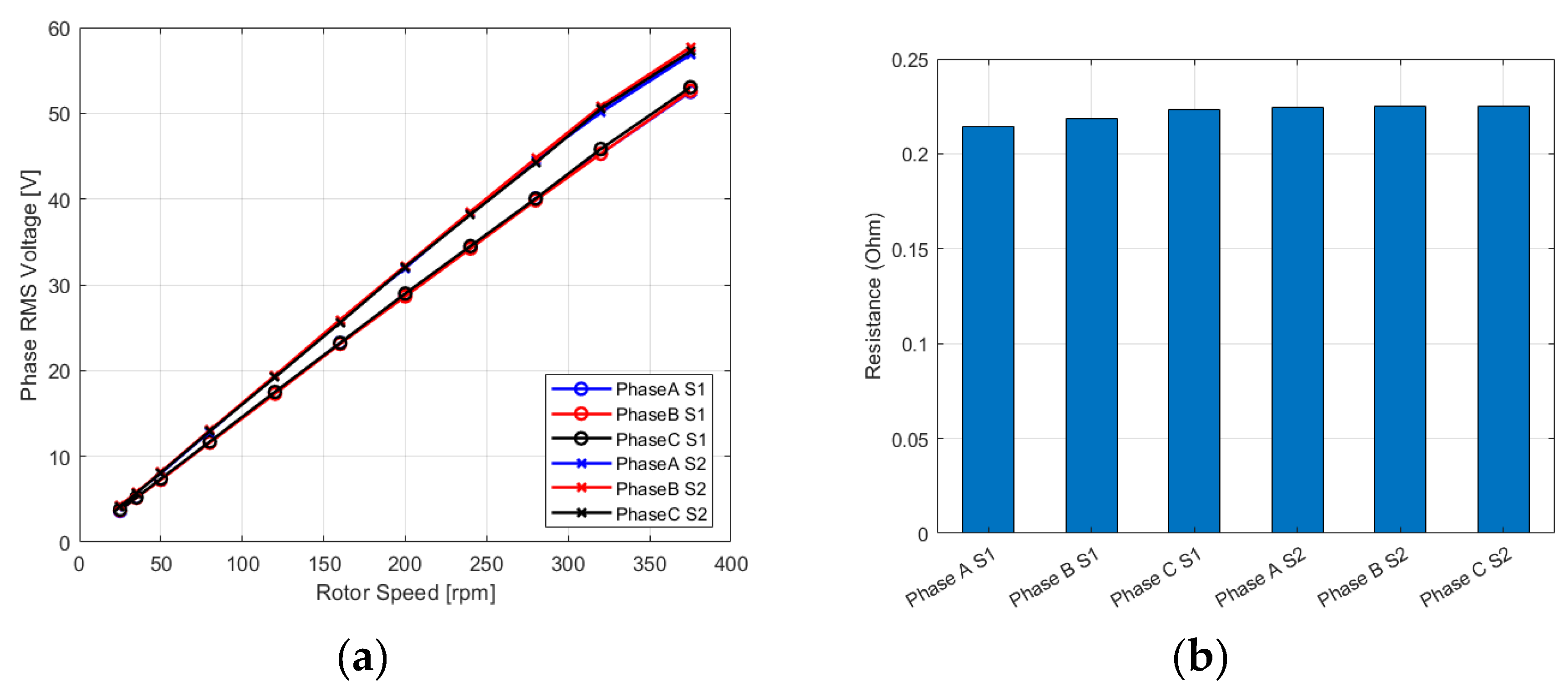
5. Experimental Study
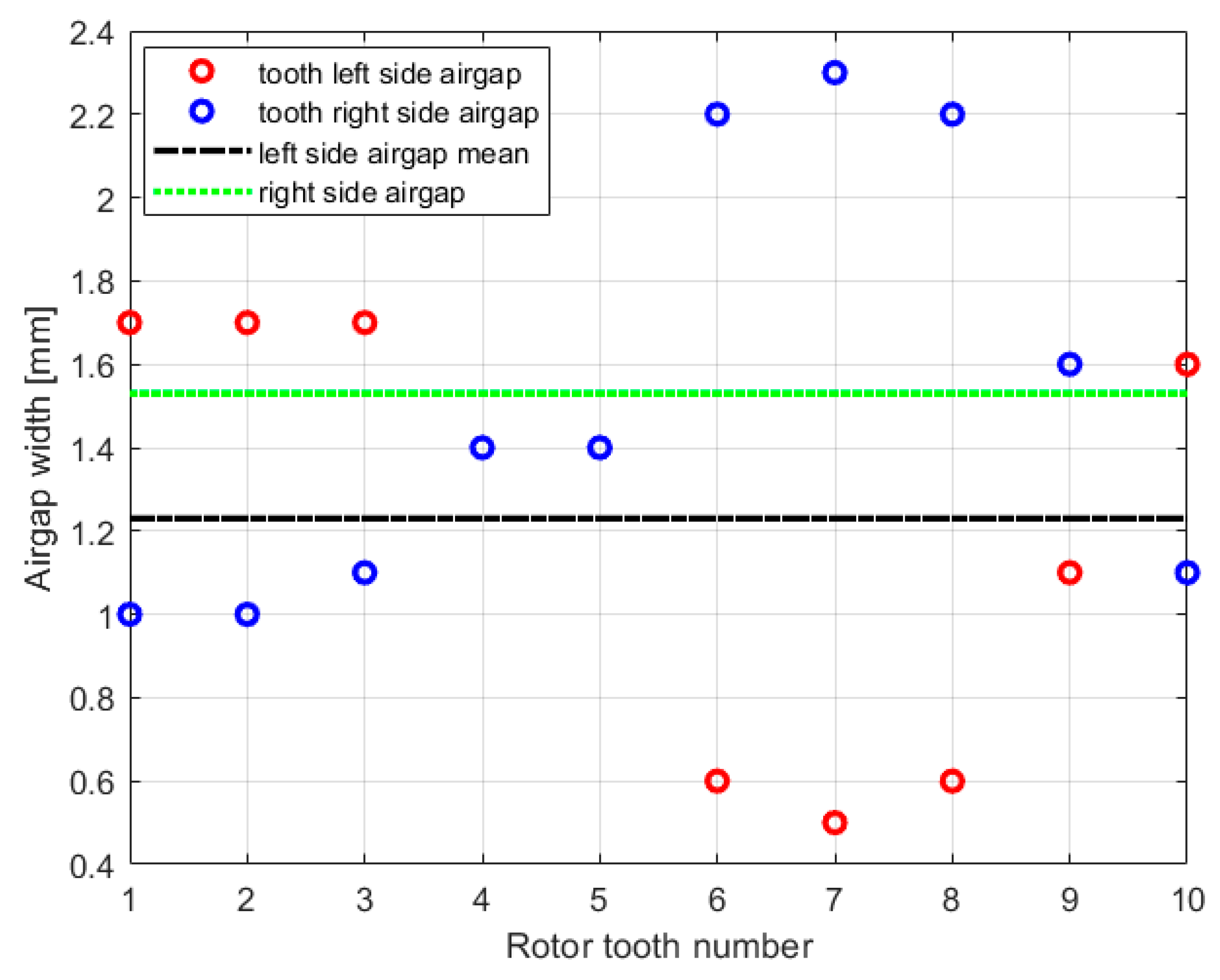
5.1. Airgap Estimation
5.2. Comparison between the AFSPM and the Axial Flux Surface Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Flux through a branch in a magnetic circuit | |
| Flux source in a permanent magnet | |
| Total flux for a certain phase | |
| Permanent magnet remanence | |
| Permanent magnet permeability | |
| Machine’s external radius | |
| Machine’s internal radius | |
| Reluctance of a branch in a magnetic circuit | |
| The magnetic scalar potential between the nodes of a branch in a magnetic circuit | |
| Free space magnetic permeability ( | |
| Permanent magnet relative permeability | |
| ha | Permanent magnet height |
| hcs | Stator yoke height |
| hdr | Rotor tooth height |
| hds | Stator tooth height |
| her | Rotor slot height |
| hes | Stator slot height |
| Lperiod | Machine’s period length in the circumferential direction (x-direction in 2D) |
| Ltotal | Machine’s total length in the circumferential direction (x-direction in 2D) |
| wa | Permanent magnet width |
| wdr | Rotor tooth width |
| wds | Stator tooth width |
| wer | Rotor slot width |
| wes | Stator slot width |
| Number of rotor teeth | |
| Number of stator slots |
Appendix A

References
- Andrada, P.; Martínez, F. Flux switching alternators for small wind generation. Renew. Energy Power Qual. J. 2016, 1, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lei, G. New Axial Laminated-Structure Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Machine With 6/7 Poles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 2823–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Chen, J.T. Advanced Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Brushless Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Jiang, S.Z.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Chan, C.C. Analytical Methods for Minimizing Cogging Torque in Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E.M.; Betz, R.E. Optimal torque per amp for brushless doubly fed reluctance machines. In Proceedings of the Fourtieth IAS Annual Meeting. Conference Record of the 2005 Industry Applications Conference, Hong Kong, China, 2–6 October 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1749–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Sitapati, K.; Krishnan, R. Performance comparisons of radial and axial field, permanent-magnet, brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 37, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.F.; Lai, L.L. An Axial-Flux Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generator for a Direct-Coupled Wind-Turbine System. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pillay, P.; Khan, A. PM Wind Generator Topologies. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parviainen, A.; Pyrhonen, J.; Kontkanen, P. Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Generator with Concentrated Winding for Small Wind Power Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electric Machines and Drives, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15 May 2005; pp. 1187–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Dhifli, M. Contribution au Développement de Structures Discoïdes de Machines Électriques à Aimants Permanents à Commutation de Flux Pour la L’éolien, Université du Havre; Normandie Université: Caen, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Azzouzi, J. Modeling and Optimisation of Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Wind Energy Application. Ph.D. Thesis, Université du Havre, Le Havre, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tiegna, H. Contribution à la Modélisation Analytique des Machines Synchrones à Aimants Permanents, à Flux Axial, à Entraînement Direct en Vue de Leur Dimensionnement: Application Aux Éoliennes; Université du Havre: Le Havre, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ennassiri, H. Magneto-Vibro-Acoustic Analysis of Synchronous Permanent Magnet Machines Dedicated to Electric Hybrid Vehicles. Ph.D. Thesis, Normandie Université, Caen, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Lin, M.; Li, W.; Luo, H.; Fu, X.; Jin, P. Novel Dual-Rotor Axial Field Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 4232–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q. Winding Configurations and Optimal Stator and Rotor Pole Combination of Flux-Switching PM Brushless AC Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.E.; Johnson, L.J. Design Principles of Flux-Switch Alternators [includes discussion]. Trans. Am. Inst. Electr. Eng. Part III Power Appar. Syst. 1955, 74, 4499226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, E.; Ben Ahmed, H.; Lucidarme, J. Switching flux permanent magnet polyphased synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the EPE 97, Trondheim, Norway, 8–10 September 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Boisson, J. Analytical Approach for Magnetic, Mechanical and Acoustic Modeling of Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet Motors: Application to Geometrical Optimization. Ph.D. Thesis, École normale supérieure de Cachan—ENS Cachan, Cachan, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- VEREZ, G. Contribution to the Study of Vibro-Acoustic Emissions of Electrical Machines. Case of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines for Automotive Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Université du Havre; Normandie Université, Caen, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.-X.; Fei, W.-Z. Permanent magnet flux switching machines – Topologies, analysis and optimization. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–17 May 2013; pp. 352–366. [Google Scholar]
- Ilhan, E.; Kremers, M.F.J.; Motoasca, E.T.; Paulides, J.J.H.; Lomonova, E.A. Sensitivity analysis for phase inductances in Flux-Switching PM machines. In Proceedings of the 2012 XXth International Conference on Electrical Machines, Marseille, France, 2–5 September 2012; pp. 763–768. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Lin, M.; Zhao, X.; Fu, X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Jin, P. Static Characteristics Analysis and Experimental Study of a Novel Axial Field Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Generator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 4212–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Stator and Rotor Pole Combinations for Multi-Tooth Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet Brushless AC Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 4659–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q. Comparison of All- and Alternate-Poles-Wound Flux-Switching PM Machines Having Different Stator and Rotor Pole Numbers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Zhu, Z.Q. Influence of the Rotor Pole Number on Optimal Parameters in Flux-Switching PM Brushless AC Machines by the Lumped-Parameter Magnetic Circuit Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, C.; Husain, I.; Ouyang, W. Cogging Torque Reduction in Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet Machines by Rotor Pole Shaping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3609–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Cheng, M.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Analysis and Optimization of Back-EMF Waveform of a Novel Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Motor. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference, Antalya, Turkey, 3–5 May 2007; pp. 1025–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Dhifli, M.; Ennassiri, H.; Amara, Y.; Barakat, G. Impact of the airgap magnetic field harmonics on the performances of a disc type flux switching machine for wind application. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 2431–2437. [Google Scholar]
- Sykulski, J.K. Computational Magnetics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; ISBN 978-94-011-1278-9. [Google Scholar]
- Aden, A.; Amara, Y.; Barakat, G.; Hlioui, S.; De La Barriere, O.; Gabsi, M. Modeling of a radial flux PM rotating machine using a new hybrid analytical model. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Electrical Sciences and Technologies in Maghreb (CISTEM), Tunis, Tunisia, 3–6 November 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Benhamida, M.A.; Ennassiri, H.; Amara, Y.; Barakat, G.; Debbah, N. Study of switching flux permanent magnet machines using interpolation based reluctance network model. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical Sciences and Technologies in Maghreb (CISTEM), Marrakech, Morocco, 26–28 October 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Marinescu, M.; Marinescu, N. Numerical computation of torques in permanent magnet motors by Maxwell stresses and energy method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1988, 24, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.N. An Introduction to the Finite Element Method, 3rd ed.; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, UK, 2006; p. 13. [Google Scholar]


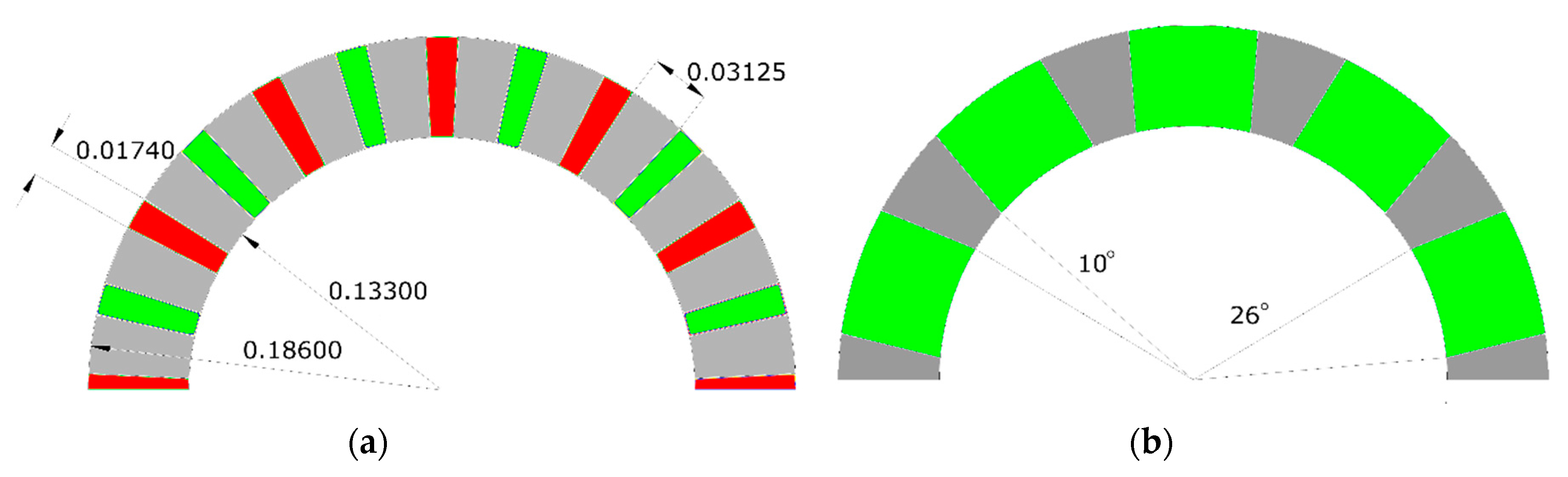





| Parameter Name | Value (Unit) | Parameter Name | Value [Unit] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Power | 10 (Kw) | Magnet height (ha) | 35 (mm) |
| Nominal rotation speed | 375 (rpm) | Stator slot width (wes) | 6.25 (°) |
| Structure | S-R-S | Stator slot height (hes) | 25 (mm) |
| No of stator slots/No of rotor teeth | 12/10 | Air gap at each side (e) | 1.5 (mm) |
| Magnets Type | NdFeB | Rotor teeth width (wdr) | 15 (°) |
| Remanence (Br) | 1.2 (T) | Rotor tooth height (hdr) | 35 (mm) |
| Stator interior radius (Rint) | 133 (mm) | Rotor slots (openings) width (wer) | 21 (°) |
| Stator exterior radius (Rext) | 186 (mm) | Rotor slot height (her) | 25 (mm) |
| Stator tooth height (hds) | 35 (mm) | Axial Length | 142 (mm) |
| Stator tooth width (wds) | 8.75 (°) | ||
| Stator yoke height (hcs) | 10 (mm) | Stator Material | Fer-Silicium M270-50A |
| Magnet width (wa) | 6.25 (°) | Rotor Material | M270-35A |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diab, H.; Amara, Y.; Barakat, G. Open Circuit Performance of Axial Air Gap Flux Switching Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Wind Energy Conversion: Modeling and Experimental Study. Energies 2020, 13, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040912
Diab H, Amara Y, Barakat G. Open Circuit Performance of Axial Air Gap Flux Switching Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Wind Energy Conversion: Modeling and Experimental Study. Energies. 2020; 13(4):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040912
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiab, Haidar, Yacine Amara, and Georges Barakat. 2020. "Open Circuit Performance of Axial Air Gap Flux Switching Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Wind Energy Conversion: Modeling and Experimental Study" Energies 13, no. 4: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040912
APA StyleDiab, H., Amara, Y., & Barakat, G. (2020). Open Circuit Performance of Axial Air Gap Flux Switching Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Wind Energy Conversion: Modeling and Experimental Study. Energies, 13(4), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040912






