Experimental Vortex Flow Patterns in the Primary and Secondary Pump Intakes of a Model Underground Pumping Station
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- 1)
- How are the vortices distributed in the underground pumping station?
- 2)
- What is the mechanism of the complex flow pattern in the underground pumping station?
- 3)
- What are the influencing parameters of the vortices in the underground pumping station?
2. Experimental Setup
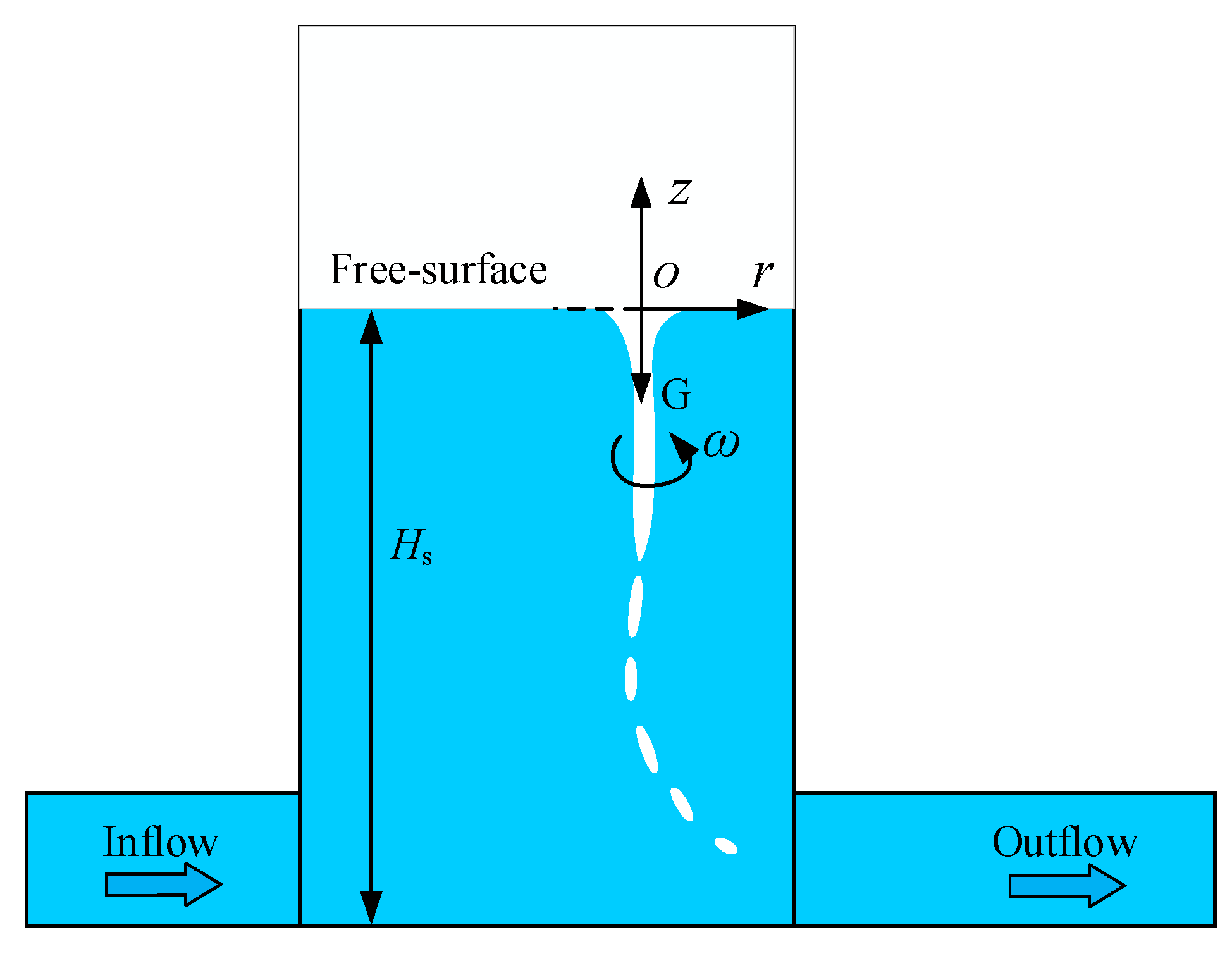
2.1. Nondimensional Parameters Influencing Vortex Flows in Pump Intake
2.2. Normalized Geometric Parameters of the Experimental Facility
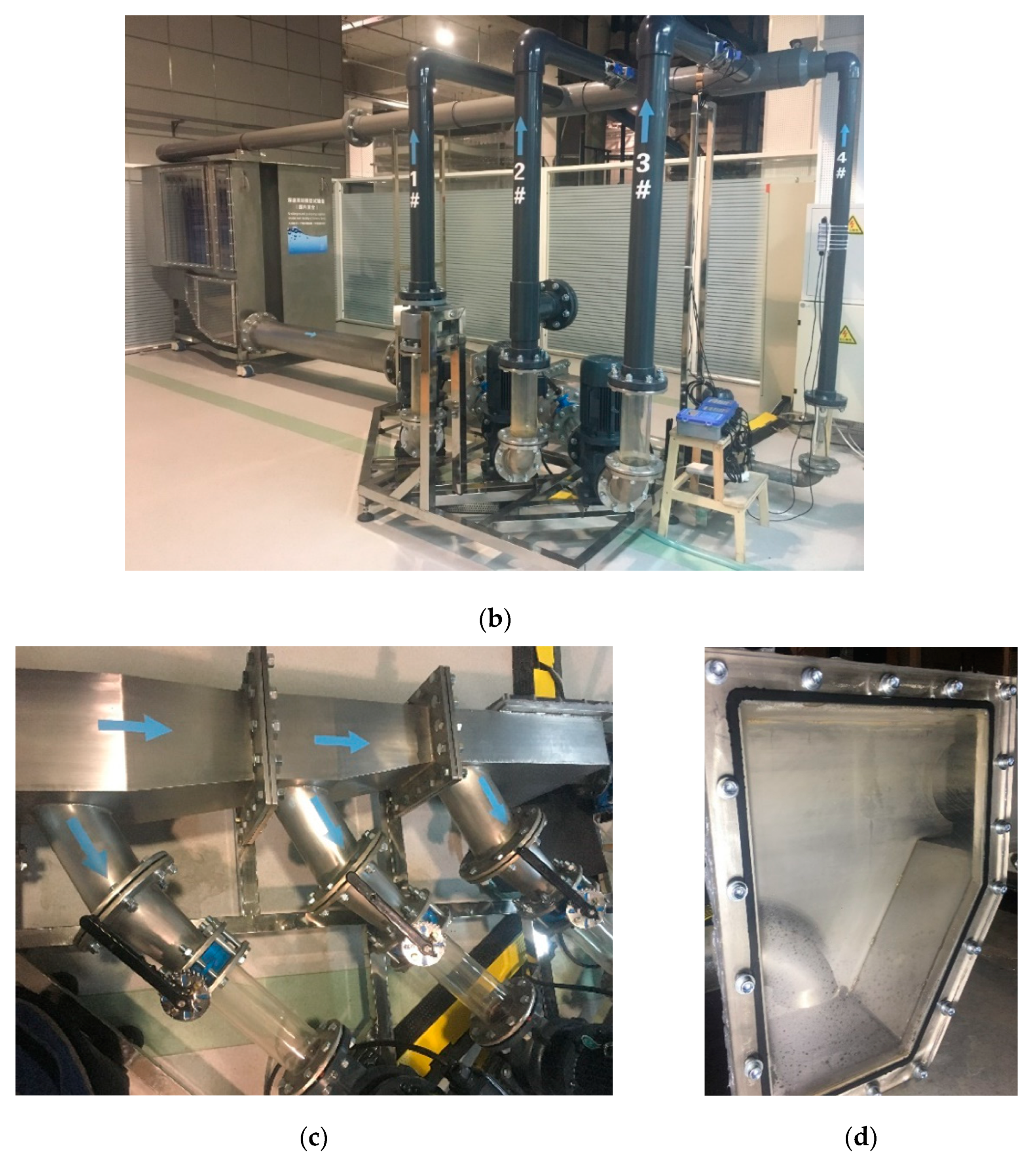
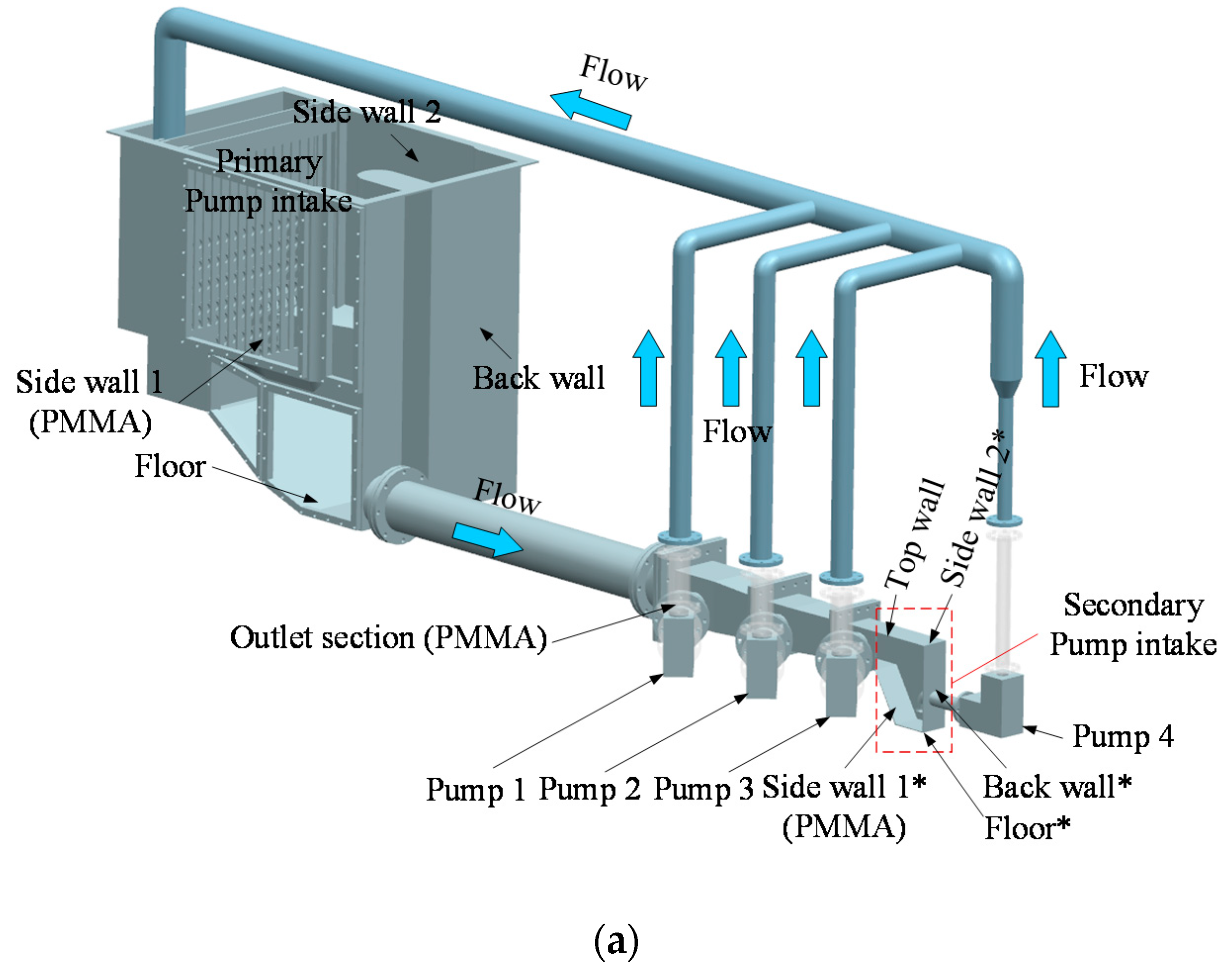
2.3. Experimental Facility
2.4. Experimental Process
3. Results and Analysis
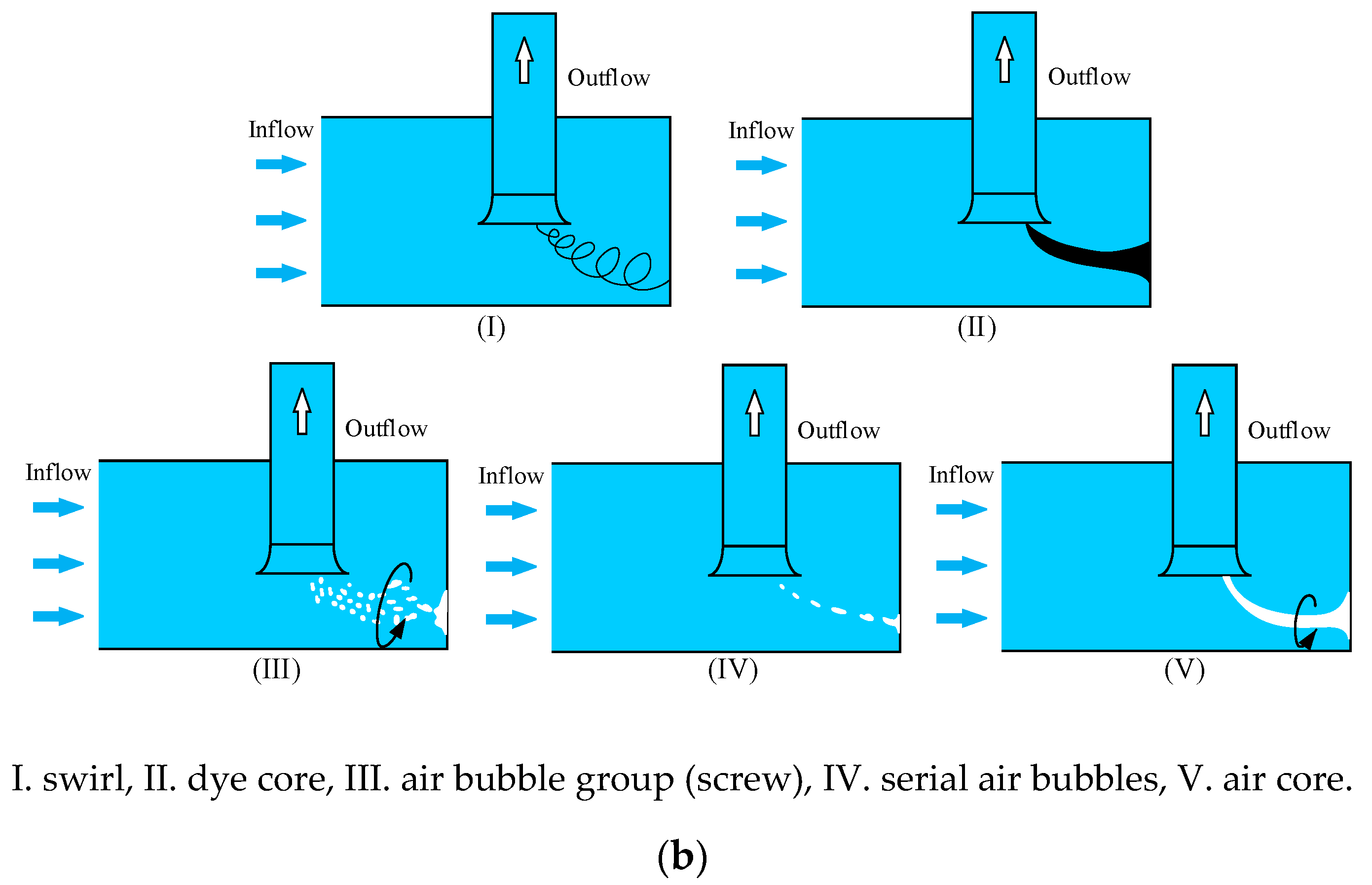
3.1. Classification of Free- and Sub-Surface Vortex
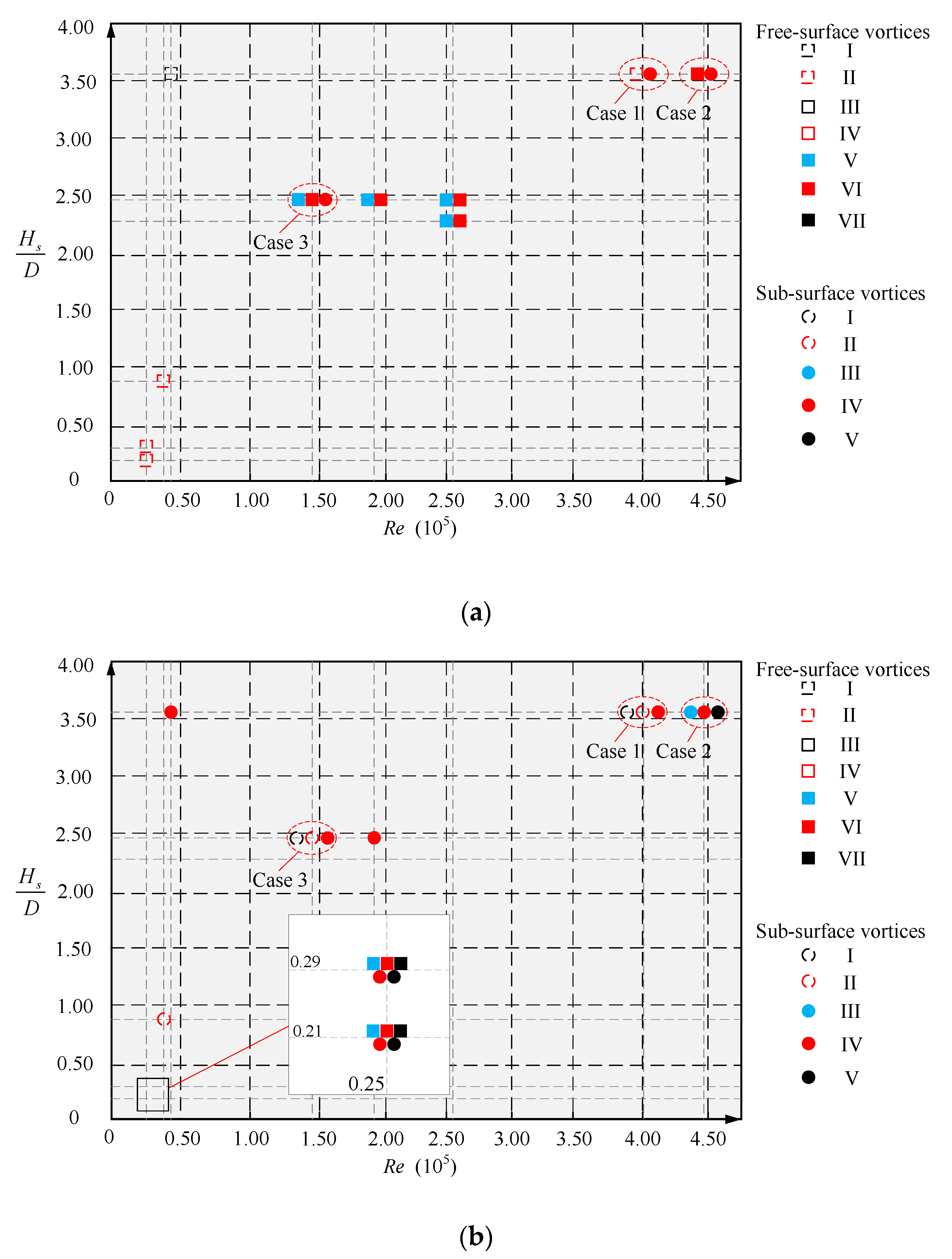
3.2. Vortex Distribution Phase Diagram
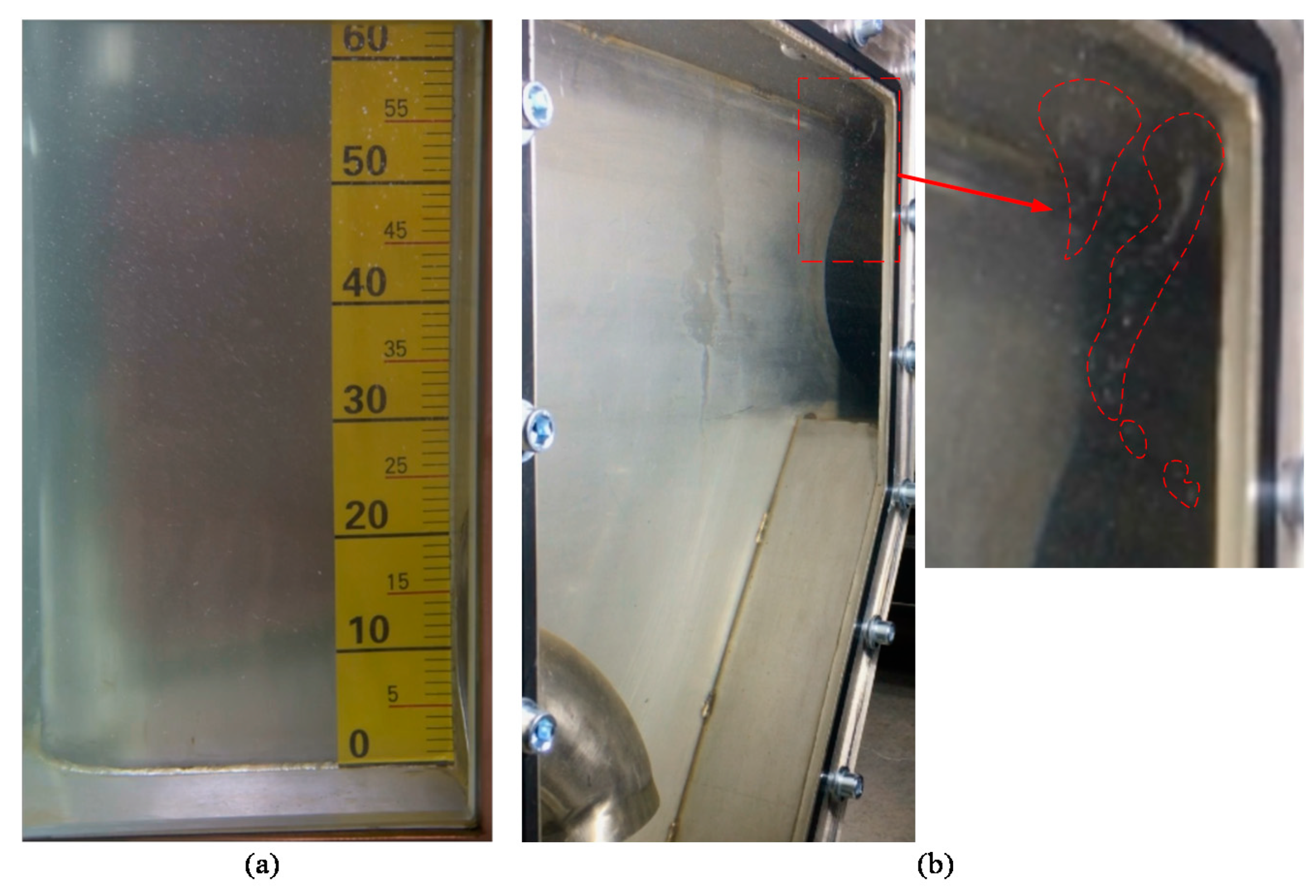
3.3. Case Study
3.3.1. Case 1: Re = 4.01 × 105 and
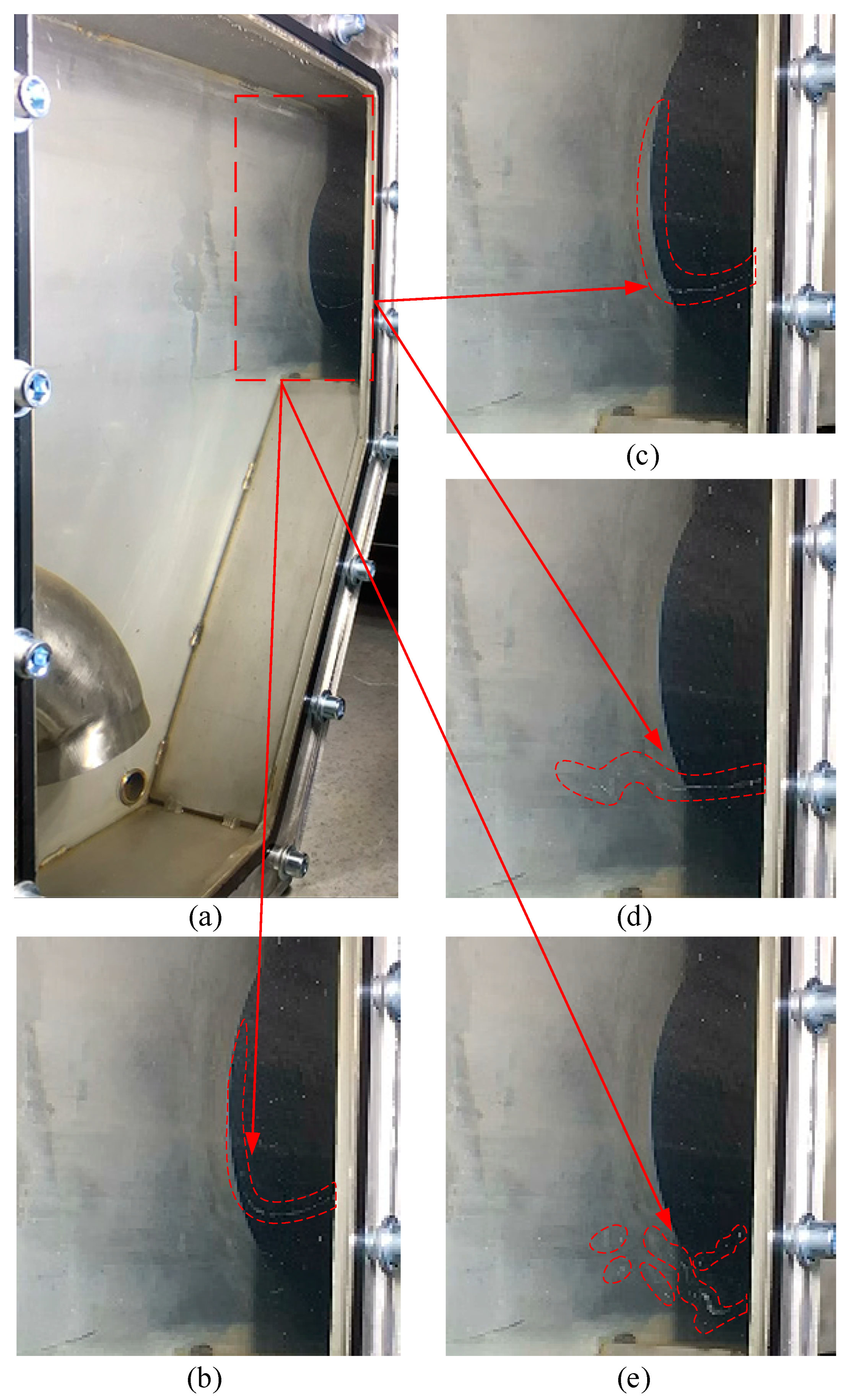
3.3.2. Case 2: Re = 4.45 × 105 and
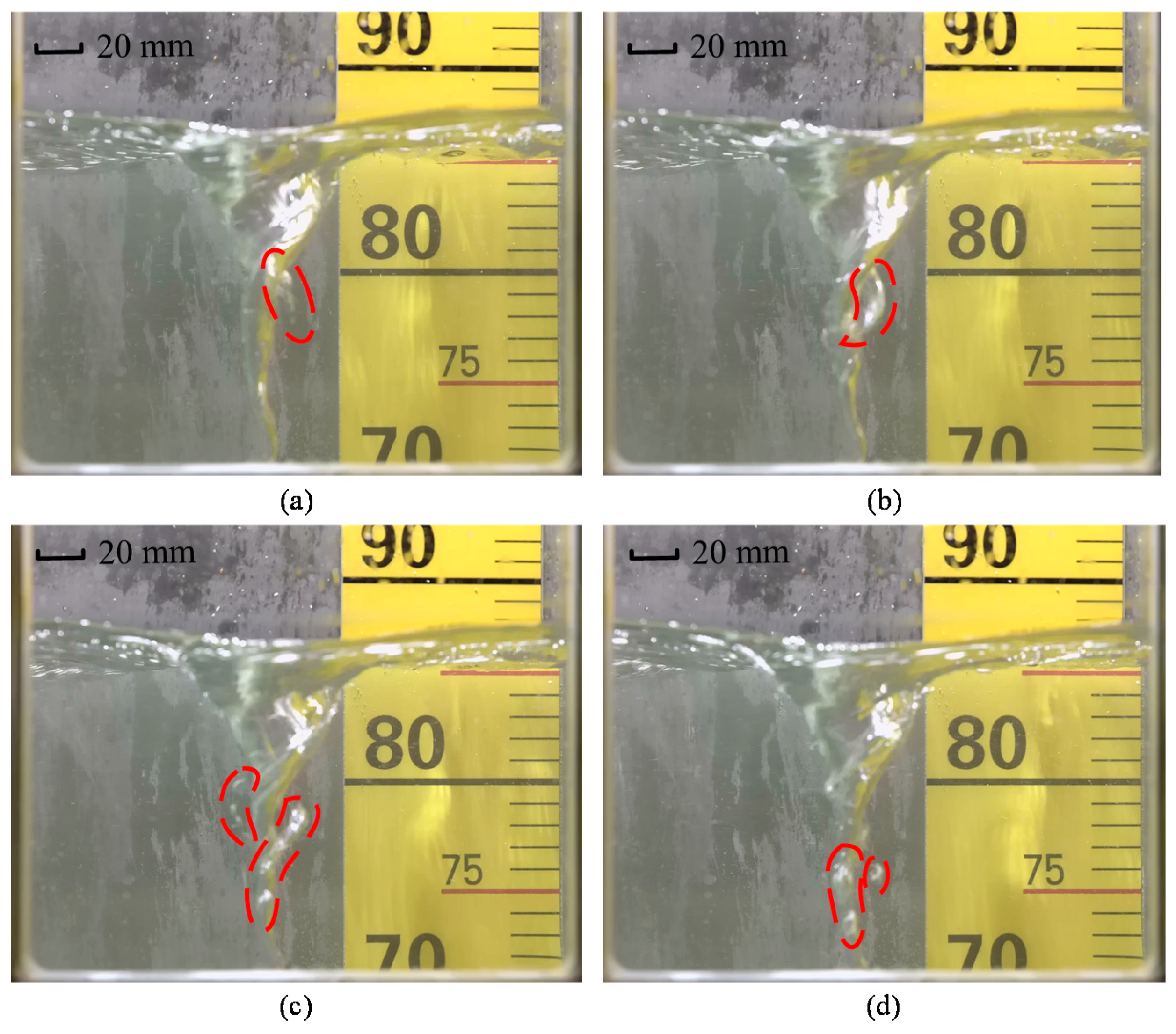
3.3.3. Case 3: Re = 1.43 × 105 and
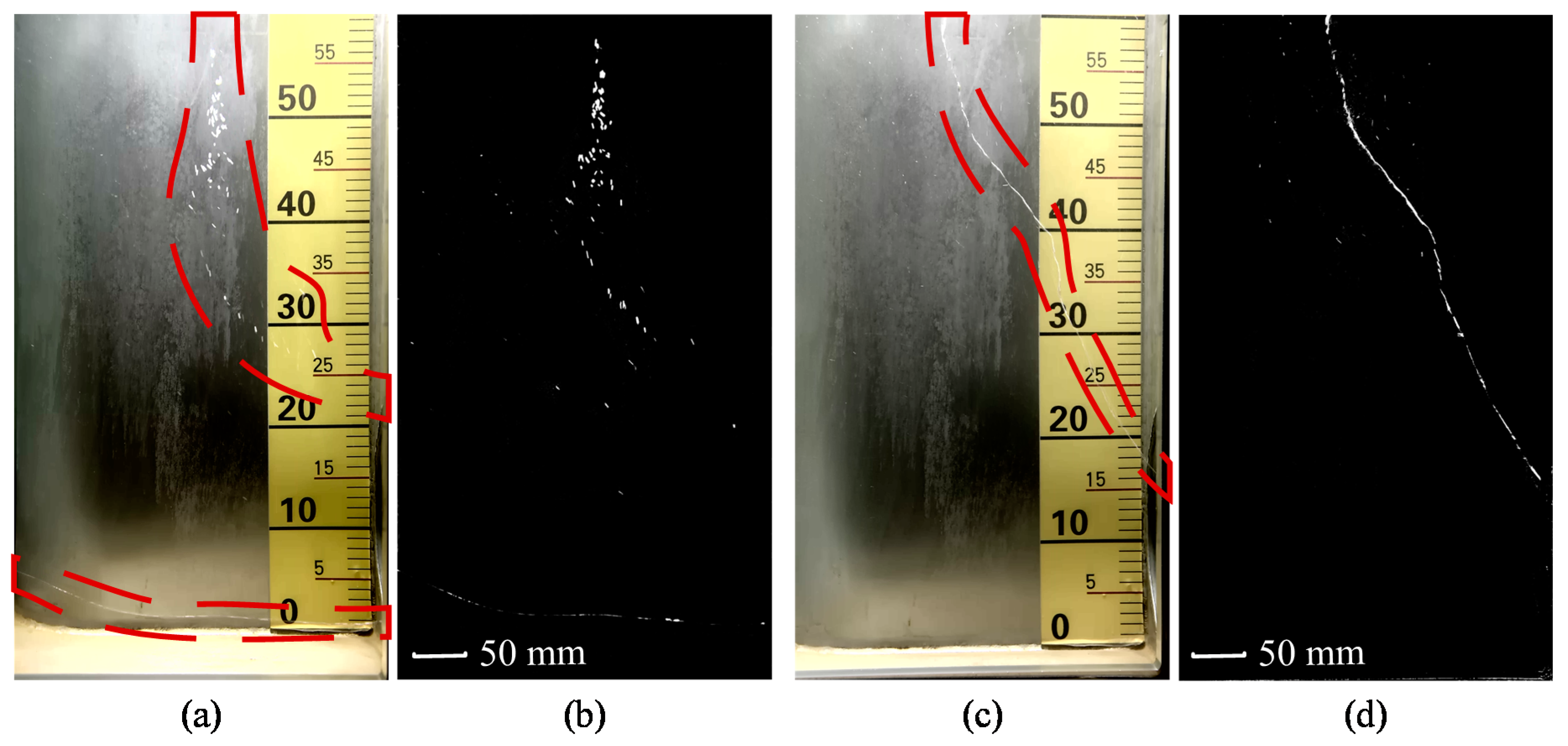
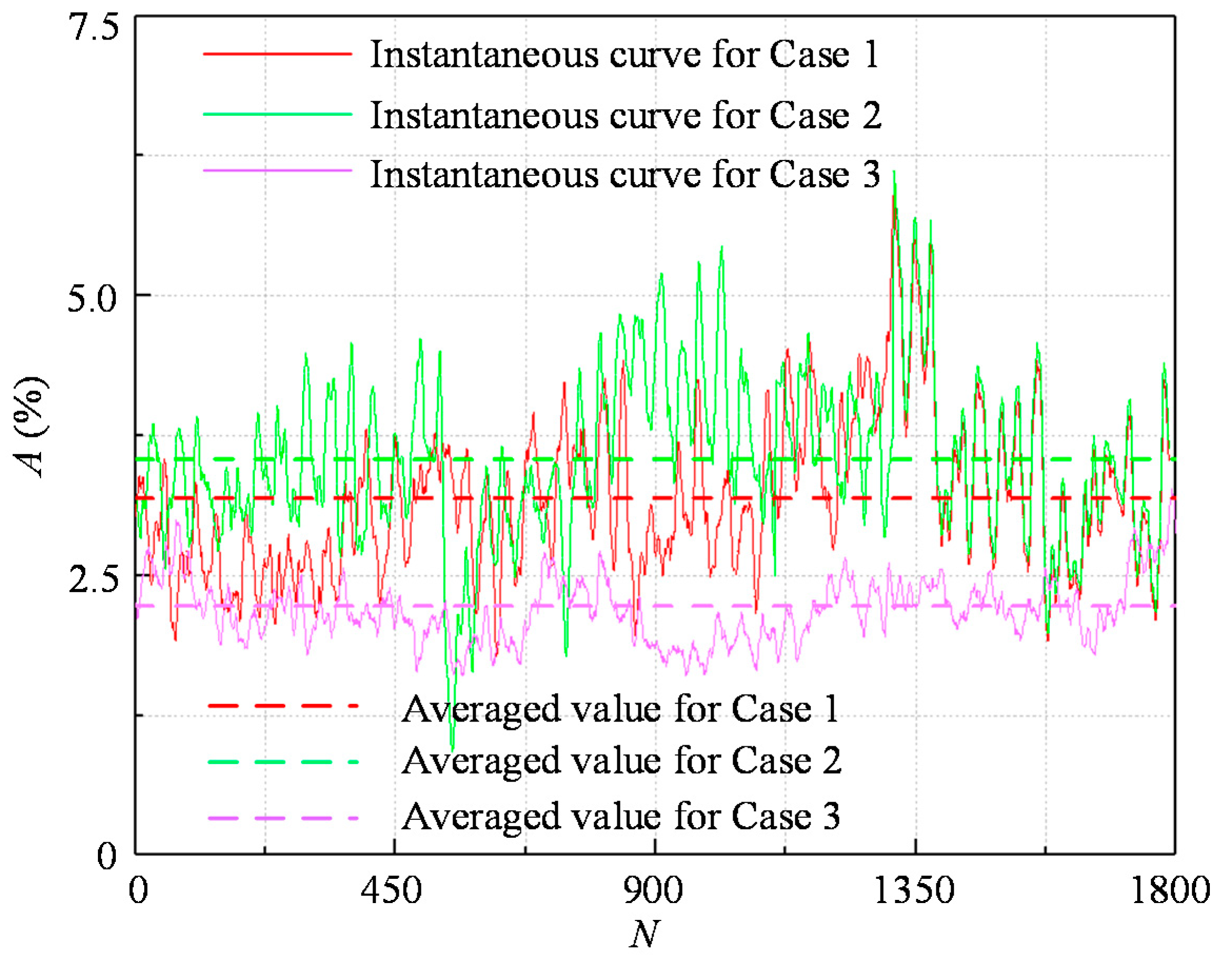
3.4. Vortex Area Evolution Diagram
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wongkaew, K.; Owyang, M.S. Seismic design of a gargantuan underground pump station. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. Inc. Trenchless Technol. Res. 2004, 19, 512. [Google Scholar]
- Mostkov, V.M.; Kubetskii, V.L. Underground pumping station. Hydrotech. Constr. 1997, 31, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.N.; Twala, B. Improving single classifiers prediction accuracy for underground water pump station in a gold mine using ensemble techniques. In Proceedings of the IEEE EUROCON 2015—International Conference on Computer as a Tool (EUROCON), Salamanca, Spain, 8–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Samarajiva, P.; Gosain, N. Investigation and Failure Analysis of Deep Underground Sewage Pump Station; Structures Congress, ASCE: Orlando, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan, M.; George, E.H. Scale effects in pump sump models. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 1540–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Tang, X.L.; Su, Y.W.; Wang, F.J.; Li, X.Q. Applications of three-dimensional LBM-LES combined model for pump intakes. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2018, 1, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yildirim, N.; Kocabas, F. Critical submergence for intakes in open channel flow. J. Hydrau. Eng. 1995, 121, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansa, K.; Wu, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. Flow measurement in the model pump suction sump with baffle by means of LDV and PIV. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2003, 51, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, V.P.; Patel, V.C. Measurement of vortices in a model pump-intake bay by PIV. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2000, 126, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.O.; Weller, J.A.; Amphlett, M.B. Similarity of free-vortex at horizontal intake. J. Hydraul. Res. 1978, 16, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echavez, G.; McCann, E. An experimental study on the free surface vertical vortex. Exp. Fluids 2002, 33, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.; Bohr, T.; Stenum, B.; Rasmussen, J.J.; Lautrup, B. Anatomy of a bathtub vortex. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 104502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.W.; Choi, Y.D.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, Y.H. Flow uniformity in a multi-intake pump sump model. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofano, L.; Nobili, M.; Caruso, G. Experimental Study on Unstable Free Surface Vortices and Gas Entrainment Onset Conditions. Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci. 2014, 42, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.G.; Kim, B.H.; Bang, B.H.; Lee, Y.H. Experimental and CFD Analysis for Prediction of Vortex and Swirl Angle in the Pump Sump Station Model. IOP Conference Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 72, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, A. Experimental and Numerical Analyses of Water-Pump Intakes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi, Y.; Tanaka, N. Experimental study on scale effect on gas entrainment at free surface. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1994, 146, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, K.; Hellmann, D.H. Optimization of Approach Flow Conditions of Vertical Pumping System by Computational Analysis and Physical Model Investigation. In Proceedings of the ASME 2010 3rd Joint US-European Fluids Engineering Summer Meeting and 8th International Conference on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels, Montreal, MO, Canada, 1–5 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kirst, K.; Hellmann, D.H.; Kothe, B.; Springer, P. Physical Model Investigation of a Compact Waste Water Pumping Station. Int. J. Fluid Mach. Syst. 2010, 3, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.Y. Characteristic analysis of rock mass quality surrounding underground plant cavern at pumping storage hudropower station. J. Eng. Geol. 2009, 17, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.P.; Liu, L.P.; Zhao, L.X.; Zhang, Y. Stability Analysis of an Underground Pumping Station Group of China. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2017, 865, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydraulic Institute. American National Standard for Pump Intake Design; ANSI-HI 9.8-1998 Pump Intake Design; Hydraulic Institute: Horsholm, Denmark, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Knauss, J. Swirling Flow Problems at Intakes; A. A. Balkema: Rotterdam, Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ansar, M. Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Pump-Approach Flow Distributions at Water Intakes. Ph.D. Thesis, The university of Iowa, owa City, IA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Möller, G.; Detert, M.; Robert, M.B. Vortex-Induced Air Entrainment Rates at Intakes. J. Hydraul. Res. 2015, 141, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Möller, G.; Robert, M.B. PIV measurements of air-core intake vortices. Flow. Meas. Instrum. 2014, 40, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Z.; Ma, H.Y.; Zhou, M.D. Vorticity and Vortex Dynamics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Wu, C.; Ye, M.; Ju, X.M. Hydraulic characteristics of vertical vortex at hydraulic intakes. J. Hydrodyn. 2007, 19, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanyants, Y.A.; Yeoh, G.H. Stationary bathtub vortices and a critical regime of liquid discharge. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 604, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odgaard, A.J. Free Surface Air Core Vortex. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1986, 112, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ministry of Water Resource of People’s Republic of China. Specification for Normal Hydraulic Model Test; SL 155-2012; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- The Ministry of Water Resource of People’s Republic of China. Design Code for Pumping Station; GB/T 50265-2010; China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shanghai Municipal Engineering Design Institute (Group) Co., LTD. Specification for Design of Drainage Pumping Station in Municipality; DGJ08-22-2003; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2003. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers. Standard Method for Model Testing the Performance of a Pump Sump; S004-1984; Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers: Tokyo, Japan, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.C.; Zuo, Z.G.; Mørch, K.A.; Liu, S.H. Thermodynamic effects on Venturi cavitation characteristics. Phys. Fluids. 2019, 31, 097107. [Google Scholar]




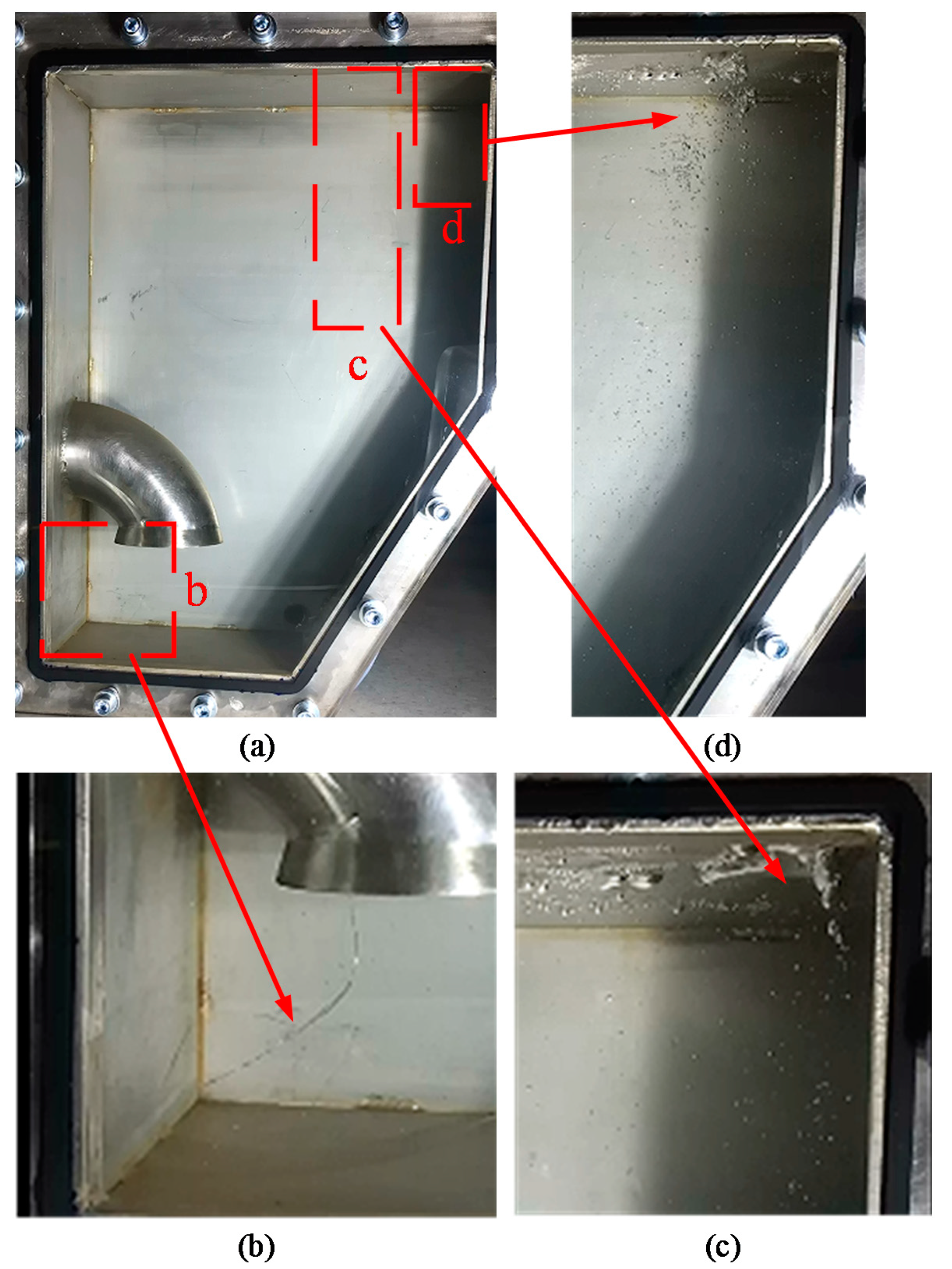

| Case | Re | Fr | We |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.01 × 105 | 1.46 × 10−2 | 1.44 × 104 |
| 2 | 4.44 × 105 | 0.16 × 10−2 | 1.79 × 104 |
| 3 | 1.43 × 105 | 0.75 × 10−2 | 3.16 × 103 |
| Dimensionless Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Length of test bench L* | 21.89 |
| Width of test bench W* | 12.72 |
| Height of test bench H* | 12.68 |
| Main pipe diameter D* | 1.00 |
| Branch diameter d* | 0.59 |
| Height of test bench HP* | 32.25 |
| Maximum flowrate Qmax* | 774 |
| Case | Q* (Q/Q4) | Hs/D |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.98 × 3 = 8.94 | 3.51 |
| 2 | 2.98 × 3 + 1.0 = 9.94 | 3.51 |
| 3 | 1.06 × 3 + 1.0 = 4.18 | 2.43 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, S.; Zou, H.; Chen, B.; Li, D. Experimental Vortex Flow Patterns in the Primary and Secondary Pump Intakes of a Model Underground Pumping Station. Energies 2020, 13, 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071790
Guo M, Zuo Z, Liu S, Zou H, Chen B, Li D. Experimental Vortex Flow Patterns in the Primary and Secondary Pump Intakes of a Model Underground Pumping Station. Energies. 2020; 13(7):1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071790
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Miao, Zhigang Zuo, Shuhong Liu, Huijun Zou, Baoyu Chen, and Deyou Li. 2020. "Experimental Vortex Flow Patterns in the Primary and Secondary Pump Intakes of a Model Underground Pumping Station" Energies 13, no. 7: 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071790
APA StyleGuo, M., Zuo, Z., Liu, S., Zou, H., Chen, B., & Li, D. (2020). Experimental Vortex Flow Patterns in the Primary and Secondary Pump Intakes of a Model Underground Pumping Station. Energies, 13(7), 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071790







