Performance Enhancement of Direct Torque-Controlled Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with a Flexible Switching Table
Abstract
:1. Introduction
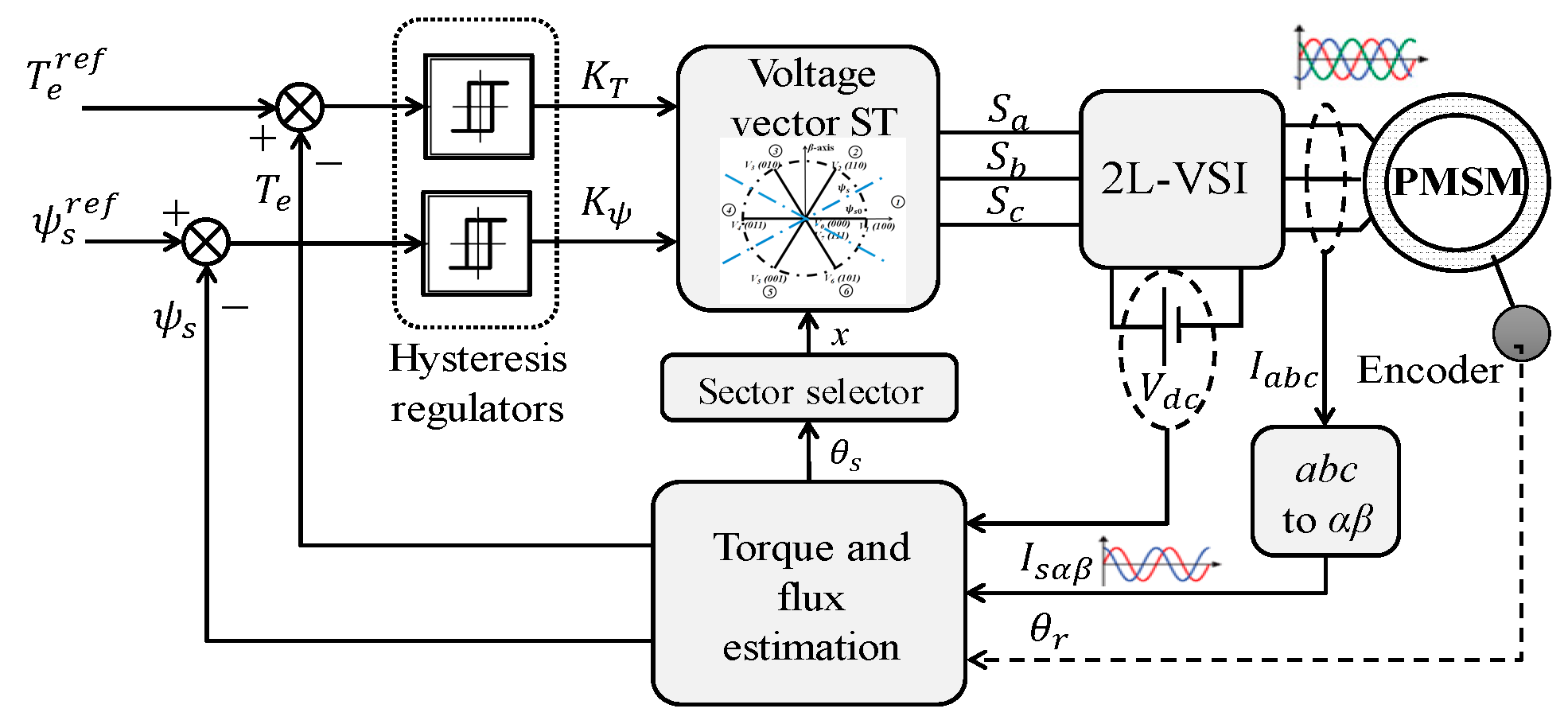
2. Analysis of DTC for PMSM
2.1. Machine Model and DTC Concept
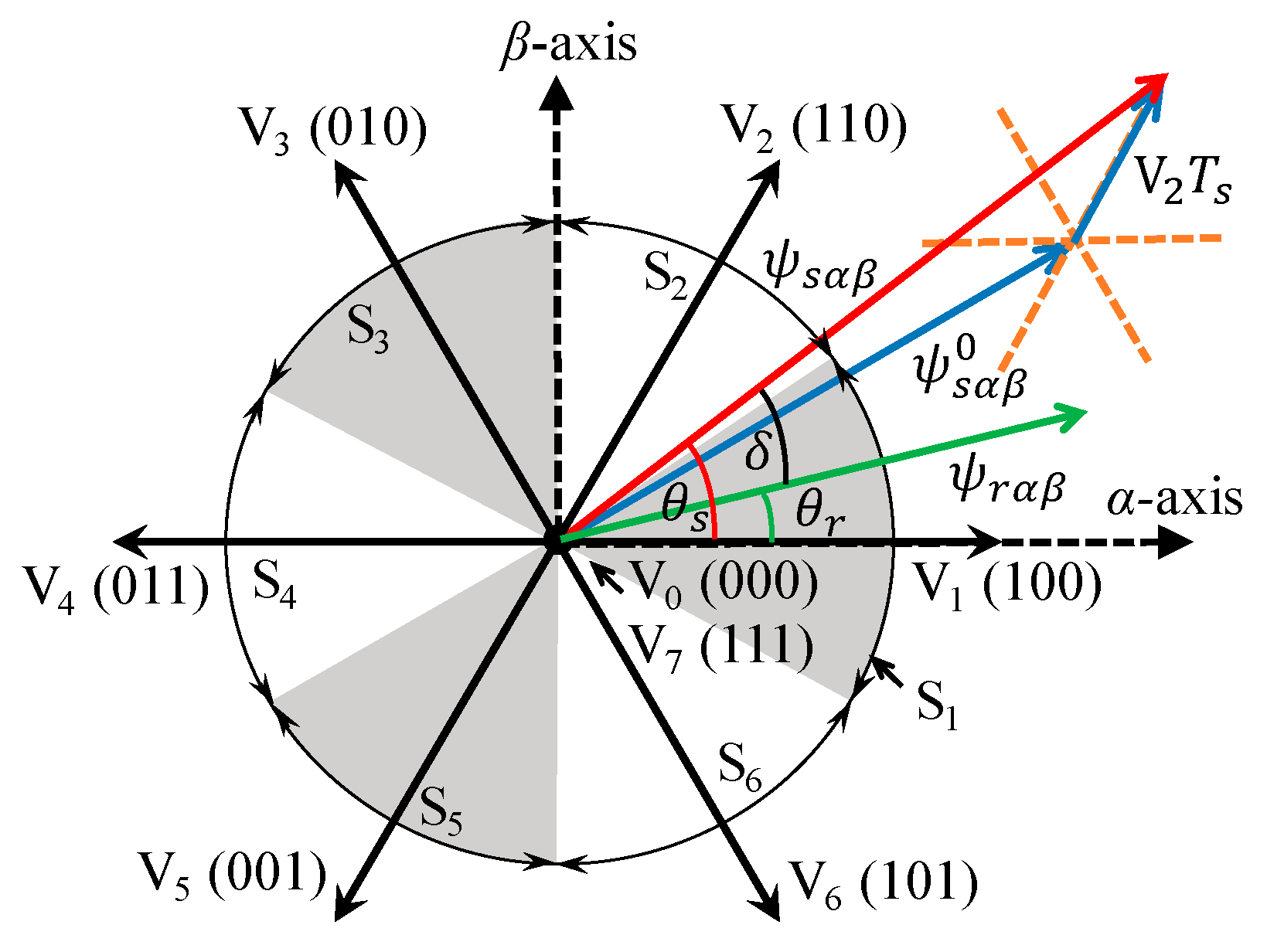
2.2. Conventional STs
2.3. Analyzing the Voltage Selection in the Conventional ST
3. Proposed Flexible ST and Voltage Selection Strategy
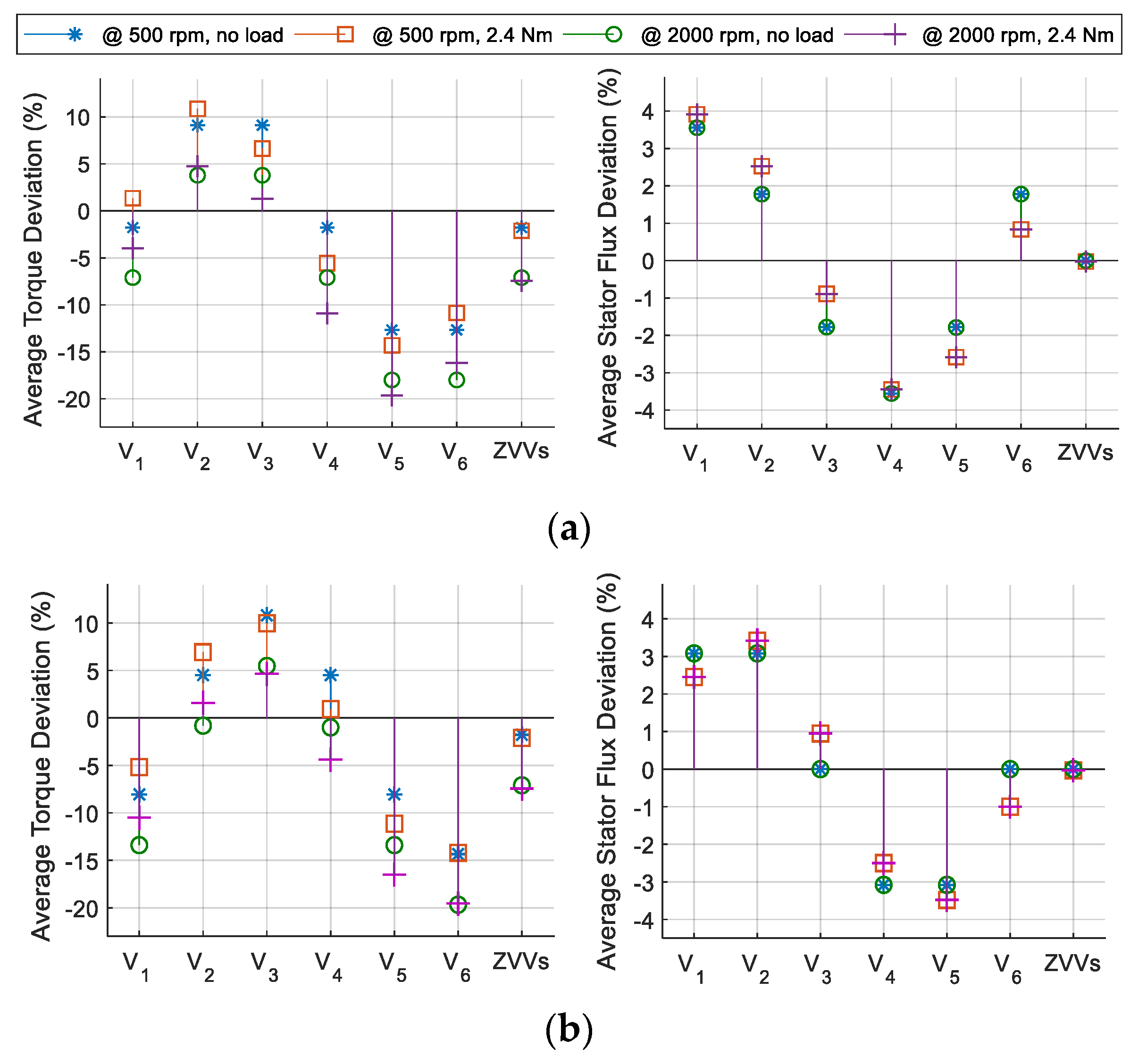
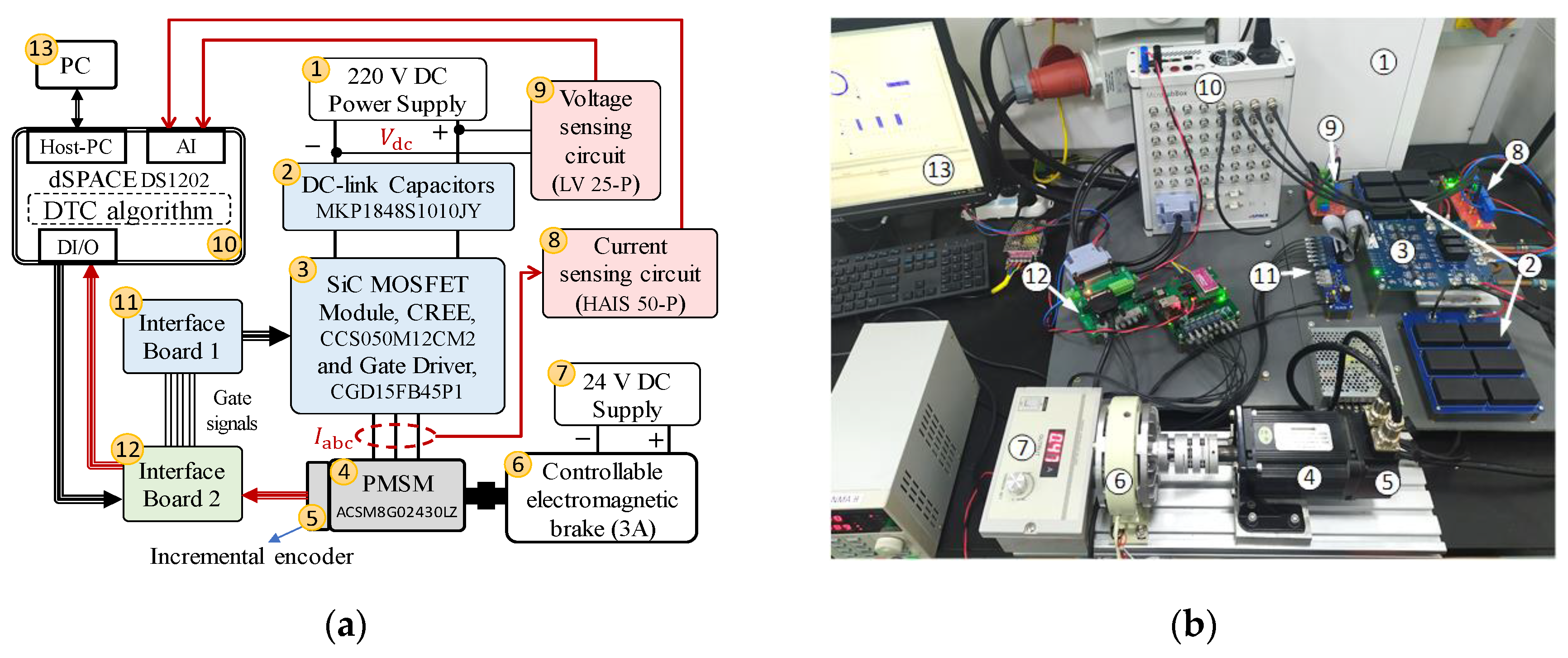
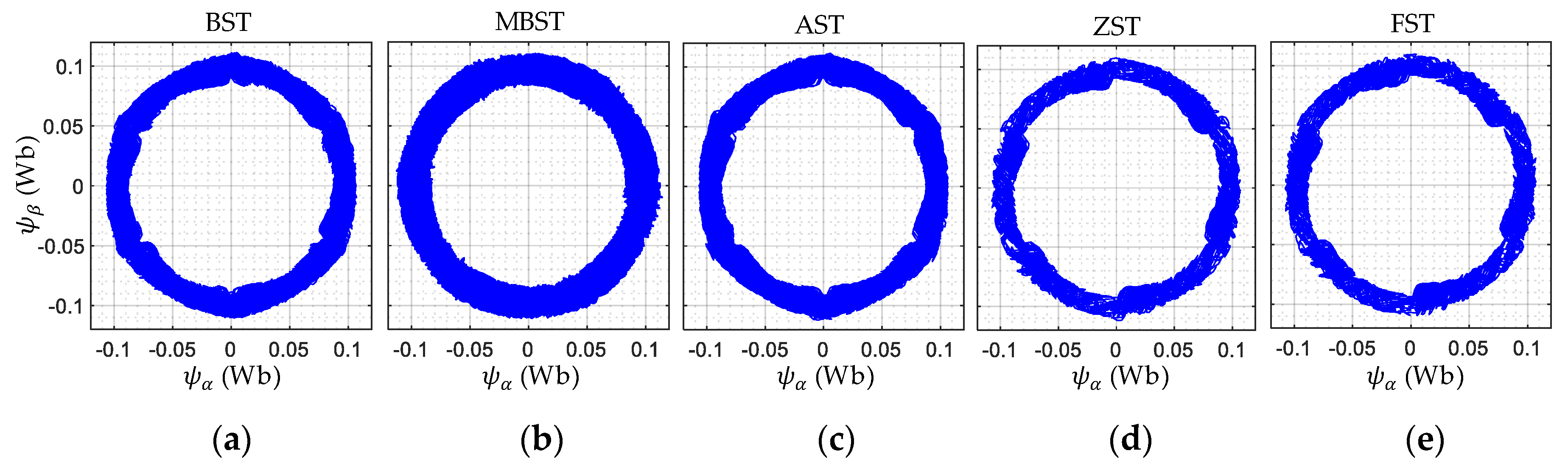
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Vsαβ, Isαβ | Stator voltage (V) and current (A) vectors in stationary reference frame |
| ψsαβ, ψrαβ | Stator and rotor flux vectors in stationary reference frame (Wb) |
| ψs, ψf | Stator and rotor (permanent magnet) flux amplitude (Wb) |
| θs, θr | Electrical angular position of the stator and rotor flux vectors (degree) |
| Te | Electromagnetic torque (Nm) |
| Rs, Ls | Stator winding resistance (Ω) and inductance (H) |
| Ts | Sampling period (s) |
| KT, Kψ | Digital indicators of the torque and flux deviation directions |
| δ | Electrical load angle (degree) |
| k | Sampling index |
| x (subscript) | Sector index |
| ref, 0 (superscript) | Reference value and initial value |
| err (superscript) | Error value |
| (superscript) | Conjugate of a complex space vector |
| Sa, Sb, Sc | Switching states of the inverter legs |
| div. | Division |
| ST | Switching table |
| DTC | Direct torque control |
| PMSM | Permanent magnet synchronous motor |
| CVC | Current vector control |
| MPC | Model predictive control |
| AVV | Active voltage vector |
| ZVV | Zero voltage vector |
| 2L-VSI | Two-level voltage source inverter |
| BST | Basic switching table in Reference [19] |
| MBST | Basic switching table with modified sector boundaries in Reference [20] |
| AST | Switching table with only active voltage vectors in Reference [18] |
| ZST | Switching table with zero voltage vector at one state in Reference [21] |
| FST | Flexible switching table (proposed) |
| SiC | Silicon carbide |
| MOSFET | Metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor |
| DC | Direct current |
| RMS | Root mean square |
Appendix A
| Machine Parameters | Value | Control Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator resistance (Rs) | 0.901 Ω | DC bus voltage (Vdc) | 220 V |
| Inductance (Ls) | 6.552 mH | Sampling frequency (fs) | 40 kHz |
| Number of pole pairs (p) | 4 | Torque hysteresis band (±) | ±2% of Trated |
| PM flux linkage () | 0.09427 Wb | Flux hysteresis band (±) | ±2% of |
| Rated current (Is) | 4.2 A (RMS) | ||
| Rated shaft output power | 0.75 kW | ||
| Rated speed | 3000 rpm | ||
| Rated torque (Trated) | 2.4 Nm | ||
| Inertia coefficient (J) | 1.2 kg·m2·10−4 |
References
- Abad, G. Power Electronics and Electric Drives for Traction Applications; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2017; p. 630. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Wang, B.; Babel, A.S.; Li, K.; Strangas, E.G. Comparative Evaluation of Direct Torque Control Strategies for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1408–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Cheng, M.; Chau, K.T. Field-Oriented Control. and Direct Torque Control. for Paralleled VSIs Fed PMSM Drives With Variable Switching Frequencies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Luo, Y. Overview of advanced control strategies for electric machines. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2017, 3, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, F.; Lian, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Gu, G. Study on a Novel Predictive Torque Control. Strategy Based on the Finite Control. Set for PMSM. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Che, C.; Xu, D. Direct Torque Control. for 2L-VSI PMSM Using Switching Instant Table. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9410–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.F.; Zhong, L.; Haque, M.E.; Rahman, M.A. A direct torque-controlled interior permanent-magnet synchronous motor drive without a speed sensor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2003, 18, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Wang, S.; Gu, X.; Yan, Y.; Shi, T. Direct Torque Control. for VSI-PMSM Using Vector Evaluation Factor Table. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4571–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Reduction of Both Harmonic Current and Torque Ripple for Dual Three-Phase Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine Using Modified Switching-Table-Based Direct Torque Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6671–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liu, J. Direct Torque Control of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives With a Simple Duty Ratio Regulator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5249–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hameyer, K. Torque Ripple Minimization for Direct Torque Control of PMSM With Modified FCSMPC. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 4855–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijie, L.; Dongliang, L.; Qiuxuan, W.; Lili, C.; Xiaodan, Z. A novel deadbeat-direct torque and flux control of IPMSM with parameter identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’16 ECCE Europe), Karlsruhe, Germany, 5–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zanma, T.; Kawasaki, M.; Liu, K.; Hagino, M.; Imura, A. Model Predictive Direct Torque Control for PMSM with Discrete Voltage Vectors. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2014, 3, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandre-Hernandez, O.; Rangel-Magdaleno, J.; Morales-Caporal, R. A Comparison on Finite-Set Model Predictive Torque Control Schemes for PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8838–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahideh, A.; Rahideh, A.; Karimi, M.; Shakeri, A.; Azadi, M. High Performance Direct Torque Control of a PMSM using Fuzzy Logic and Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference, Antalya, Turkey, 3–5 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Li, K.; Wang, Y. Direct Torque Control for Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines Based on Duty Ratio Modulation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6160–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, I.; Noguchi, T. A New Quick-Response and High-Efficiency Control Strategy of an Induction Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1986, IA-22, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Rahman, M.F.; Hu, W.Y.; Lim, K.W. Analysis of direct torque control in permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1997, 12, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwen, H.; Cun, T.; Yikang, G.; Zhiqing, Y.; Tang, L.X.; Rahman, M.F. In-depth research on direct torque control of permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2002 28th Annual Conference of the Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 02), Sevilla, Spain, 5–8 November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Toufouti, R.; Meziane, S.; Benalla, H. Direct Torque Control Strategy of Induction Motors. J. Acta Electrotech. Et Inform. 2007, 7, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yaohua, L.; Gerling, D.; Weiguo, L. A novel switching table using zero voltage vectors for direct torque control in permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the 2008 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines, Vilamoura, Portugal, 6–9 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J. A Novel Duty Cycle Control Strategy to Reduce Both Torque and Flux Ripples for DTC of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives With Switching Frequency Reduction. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3055–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, A.; Inoue, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. Comparison of stator flux linkage estimators for PWM-based direct torque controlled PMSM drives. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 11th International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems, Sydney, Australia, 9–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]





| Voltage Selection | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BST | MBST | AST | ZST | ||
| 1 | 1 | Vx + 1 | Vx + 1 | Vx + 1 | Vx + 1 |
| 0 | ZVV | ZVV | - | - | |
| −1 | Vx − 1 | Vx | Vx − 1 | Vx − 1 | |
| −1 | 1 | Vx + 2 | Vx + 3 | Vx + 2 | Vx + 2 |
| 0 | ZVV | ZVV | - | - | |
| −1 | Vx − 2 | Vx − 2 | Vx − 2 | ZVV | |
| Voltage Selection | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Vx + 1 | |
| ZVV | |||
| −1 | Vx − 1 | ||
| −1 | 1 | Vx + 2 | |
| −1 | Vx − 2 | ||
| ZVV | |||
| Index | Speed (rpm) | Switching Tables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BST | MBST | AST | ZST | FST | ||
| (Nm) | 500 | 0.272 | 0.255 | 0.307 | 0.209 | 0.208 |
| 1000 | 0.279 | 0.264 | 0.305 | 0.244 | 0.246 | |
| 2000 | 0.274 | 0.431 | 0.299 | 0.263 | 0.263 | |
| (mWb) | 500 | 3.672 | 4.848 | 3.714 | 3.251 | 3.252 |
| 1000 | 3.715 | 4.704 | 3.828 | 3.311 | 3.311 | |
| 2000 | 3.794 | 4.562 | 3.975 | 3.682 | 3.682 | |
| fav (kHz) | 500 | 10.27 | 9.08 | 9.85 | 4.58 | 4.31 |
| 1000 | 9.49 | 8.44 | 9.20 | 5.96 | 5.73 | |
| 2000 | 8.61 | 8.15 | 8.43 | 6.42 | 6.13 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasr, A.; Gu, C.; Bozhko, S.; Gerada, C. Performance Enhancement of Direct Torque-Controlled Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with a Flexible Switching Table. Energies 2020, 13, 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13081907
Nasr A, Gu C, Bozhko S, Gerada C. Performance Enhancement of Direct Torque-Controlled Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with a Flexible Switching Table. Energies. 2020; 13(8):1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13081907
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasr, Ahmed, Chunyang Gu, Serhiy Bozhko, and Chris Gerada. 2020. "Performance Enhancement of Direct Torque-Controlled Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with a Flexible Switching Table" Energies 13, no. 8: 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13081907
APA StyleNasr, A., Gu, C., Bozhko, S., & Gerada, C. (2020). Performance Enhancement of Direct Torque-Controlled Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with a Flexible Switching Table. Energies, 13(8), 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13081907






