Understanding Membrane Fouling in Electrically Driven Energy Conversion Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
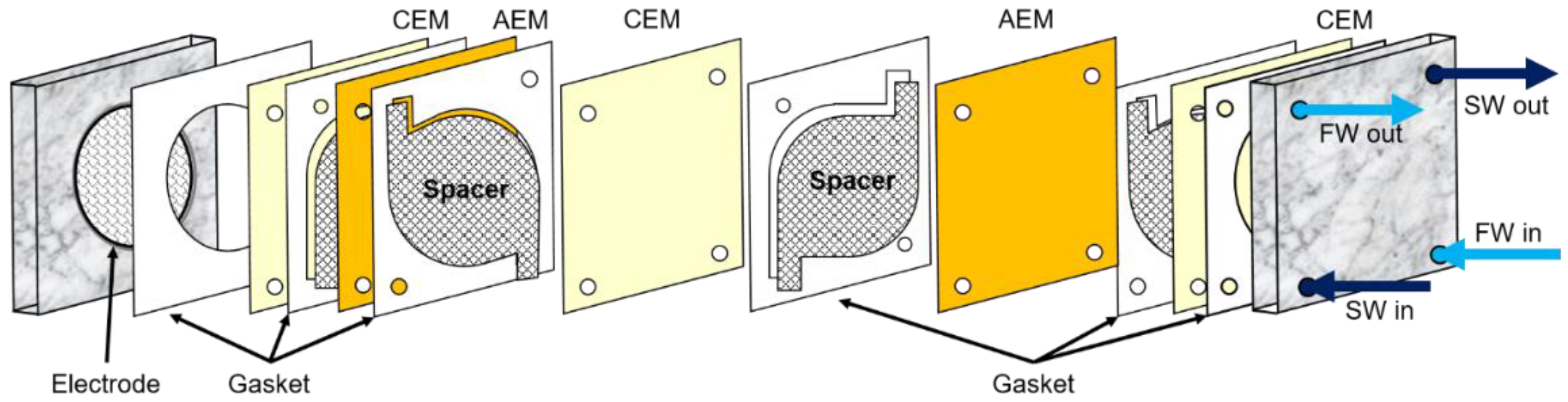
2. Materials and Methods
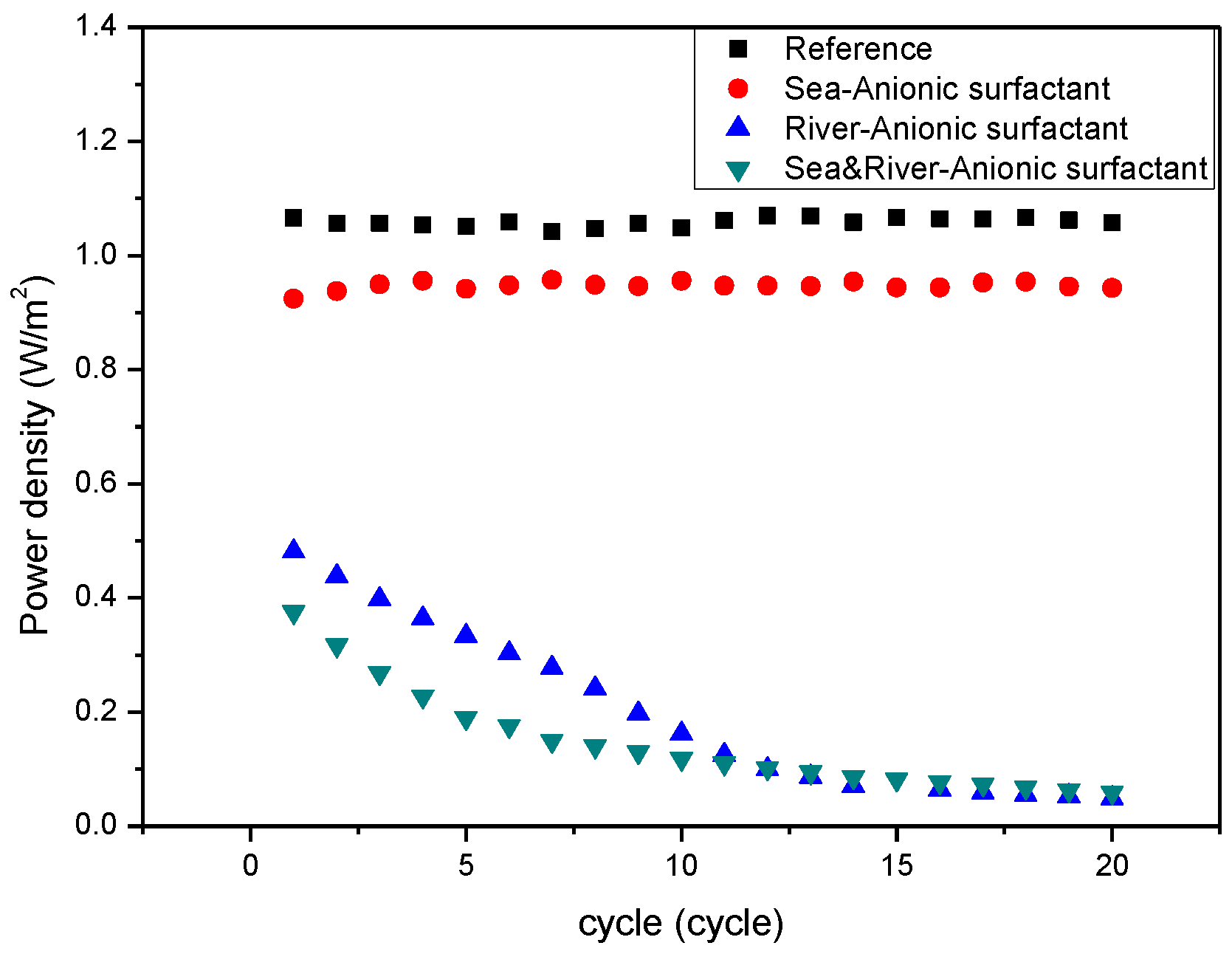
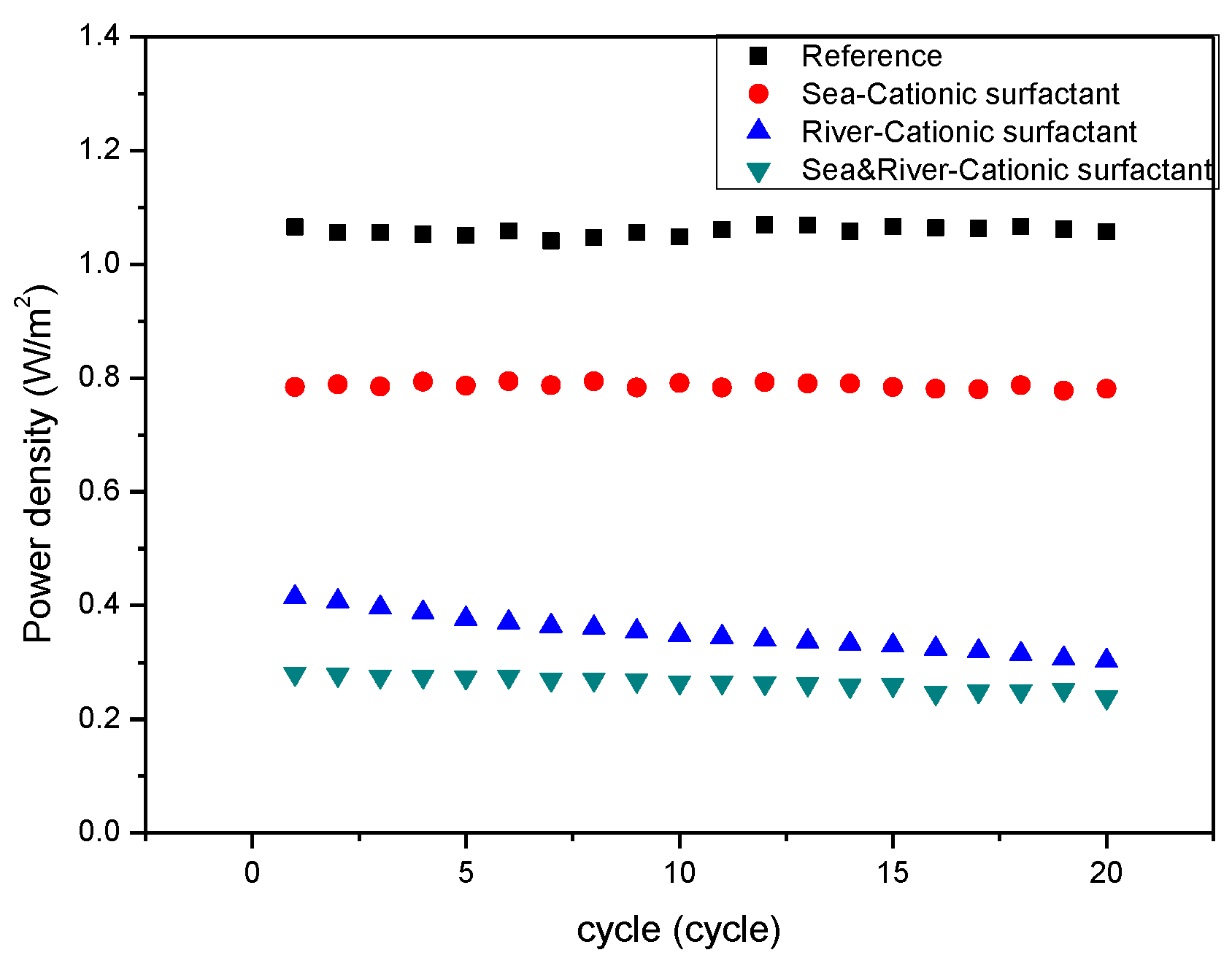
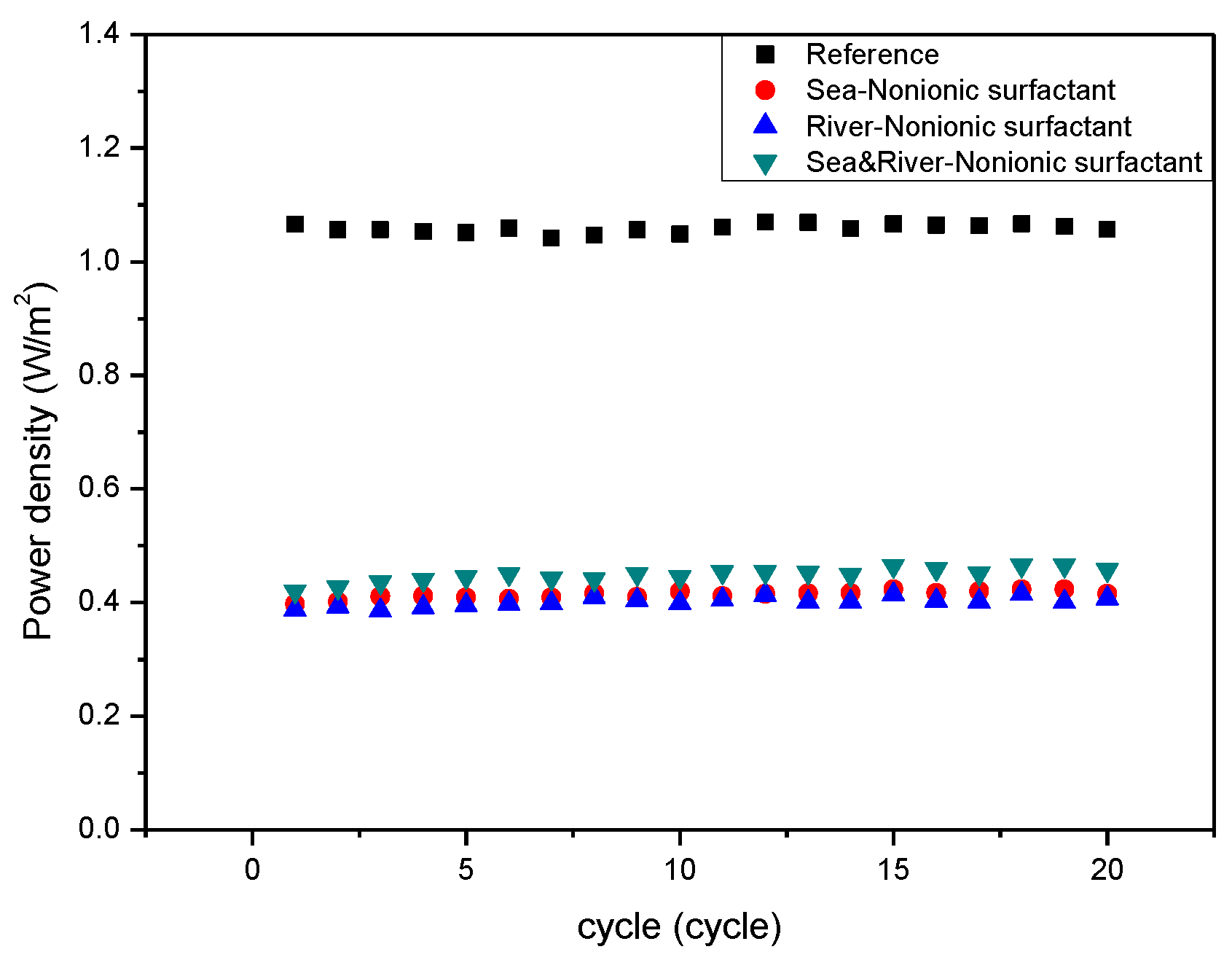
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krakhella, K.W.; Morales, M.; Bock, R.; Seland, F.; Burheim, O.S.; Einarsrud, K.E. Electrodialytic Energy Storage System: Permselectivity, Stack Measurements and Life-Cycle Analysis. Energies 2020, 13, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Shin, M.-S.; Park, J.-S. Anion-conducting Pore-filling Membranes with Optimization of Transport Number and Resistance for Reverse Electrodialysis. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerman, J. The Effect of the NaCl Bulk Concentration on the Resistance of Ion Exchange Membranes—Measuring and Modeling. Energies 2020, 13, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, A.; Castelló, R.C. Redox Flow Batteries: A Literature Review Oriented to Automatic Control. Energies 2020, 13, 4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Shin, M.-S.; Kim, C.-S. Proton exchange membranes for fuel cell operation at low relative humidity and intermediate temperature: An updated review. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 5, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.-K. Power Generation from Concentration Gradient by Reverse Electrodialysis in Anisotropic Nanoporous Anodic Aluminum Oxide Membranes. Energies 2020, 13, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Han, S.-J.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, H.; Han, J.-H.; Hwang, K.-S.; Jeong, N.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Chae, S. Effects of Divalent Cations on Electrical Membrane Resistance in Reverse Electrodialysis for Salinity Power Generation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 15803–15810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K.B.; Vidic, R.D.; Dzombak, D.A. Water Management Challenges Associated with the Production of Shale Gas by Hydraulic Fracturing. Elements 2011, 7, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Krantz, W.B.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Post, J.W.; Verliefde, A.R.; Tang, C.Y. A novel hybrid process of reverse electrodialysis and reverse osmosis for low energy seawater desalination and brine management. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, A.P.; Deshmukh, A.; Elimelech, M. Pressure-retarded osmosis for power generation from salinity gradients: Is it viable? Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakhella, K.W.; Bock, R.; Burheim, O.S.; Seland, F.; Einarsrud, K.E. Heat to H2: Using Waste Heat for Hydrogen Production through Reverse Electrodialysis. Energies 2019, 12, 3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, M.; Zhang, J.; Hatzell, M.C. Harvesting Natural Salinity Gradient Energy for Hydrogen Production Through Reverse Electrodialysis Power Generation. J. Electrochem. Energy Convers. Storage 2017, 14, 020702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzell, M.C.; Ivanov, I.; Cusick, R.D.; Zhu, X.; Logan, B.E. Comparison of hydrogen production and electrical power generation for energy capture in closed-loop ammonium bicarbonate reverse electrodialysis systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzell, M.C.; Zhu, X.; Logan, B.E. Simultaneous Hydrogen Generation and Waste Acid Neutralization in a Reverse Electrodialysis System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2211–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yasukawa, M.; Endo, N.; Kakihana, Y.; Futamura, H.; Inoue, K.; Miyake, H.; Usui, J.; Hayashi, A.; et al. Sustainable hydrogen production from seawater and sewage treated water using reverse electrodialysis technology. Water Pr. Technol. 2019, 14, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T. Storable hydrogen production by Reverse Electro-Electrodialysis (REED). J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Chae, S.; Yeon, K.-H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, C.-S.; Jeong, N.-J.; Park, J.-S. Porous carbon-coated graphite electrodes for energy production from salinity gradient using reverse electrodialysis. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2016, 91, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Moon, S.-H. A study on fouling mitigation using pulsing electric fields in electrodialysis of lactate containing BSA. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 19, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Kang, M.-S.; Moon, S.-H. Effects of silica sol on ion exchange membranes: Electrochemical characterization of anion exchange membranes in electrodialysis of silica sol containing-solutions. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, S.-J.; Geckeler, K.E.; Cho, J.; Moon, S.-H. Fouling mitigation of anion exchange membrane by zeta potential control. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 259, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Moon, S.-H. Determination of an optimum frequency of square wave power for fouling mitigation in desalting electrodialysis in the presence of humate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 30, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Chilcott, T.; Coster, H.; Moon, S.-H. Characterization of BSA-fouling of ion-exchange membrane systems using a subtraction technique for lumped data. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 246, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Choi, J.-H.; Yeon, K.-H.; Moon, S.-H. An approach to fouling characterization of an ion-exchange membrane using current–voltage relation and electrical impedance spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 294, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansima, M.; Makehelwala, M.; Jinadasa, K.; Wei, Y.; Nanayakkara, K.; Herath, A.C.; Weerasooriya, R. Fouling of ion exchange membranes used in the electrodialysis reversal advanced water treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Jeong, N.; Rho, H.; Nam, J.-Y.; Jwa, E.; Cho, J. Fouling characteristics of dissolved organic matter in fresh water and seawater compartments of reverse electrodialysis under natural water condtions. Desalination 2020, 496, 114478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shi, S.; Cao, H.; Li, Y.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Comparative studies on fouling of homogeneous anion exchange membranes by different structured organics in electrodialysis. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 77, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijnaarts, T.; Moreno, J.; Saakes, M.; De Vos, W.; Nijmeijer, K. Role of anion exchange membrane fouling in reverse electrodialysis using natural feed waters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.; Chen, G.Q.; Freeman, B.; Suarez, F.; Freckleton, A.; Bathurst, K.; Kentish, S.E. Fouling and in-situ cleaning of ion-exchange membranes during the electrodialysis of fresh acid and sweet whey. J. Food Eng. 2019, 246, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shi, S.; Cao, H.; Shan, B.; Sheng, Y. Property characterization and mechanism analysis on organic fouling of structurally different anion exchange membranes in electrodialysis. Desalination 2018, 428, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Fouling on ion-exchange membranes: Classification, characterization and strategies of prevention and control. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, G.A. Particulate Organic Matter in Sea Water. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1971, 8, 1–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.J.; Adams, H.E. Dissolved organic matter quantity and quality from freshwater and saltwater lakes in east-central Alberta. Biogeochem. 1995, 30, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion Exchange Membranes for Water Purification, Fujifilm Membrane Technology. Available online: https://www.fujifilmmembranes.com/images/IEM_brochure_1_1_-final_small_size.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2020).





| Fujifilm Membranes | AEM (Type 1) | CEM (Type 10) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | anion permselective | cation permselective |
| Reinforcement | polyolefin | polyolefin |
| Thickness (μm) | 125 | 135 |
| Resistance 1 (Ω cm2) | 1.3 | 2.0 |
| Permselectivity 2 (-) | 92 | 99 |
| Water permeation (mL bar−1 m−2 h−1) | 14 | 6.5 |
| Burst strength (kg cm−2) | 2.4 | 2.8 |
| pH stability | pH 2–10 | pH 1–13 |
| Temperature stability (°C) | - | 60 |
| Surfactants | Anionic Foulant | Cationic Foulant | Nonionic Foulant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) | cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) | polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400 |
| Molecular weight (g mol−1) | 288 | 340 | 380‒420 |
| Molecular formula | C12H25O4NaS | C21H38ClN | H(OCH2CH2)nOH |
| Chemical structure | 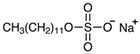 | 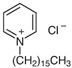 |  |
| Main Fouling Phenomena | Anionic Foulant | Cationic Foulant | Nonionic Foulant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seawater/River | Seawater/River | Seawater/River | |
| Adsorption by electromigration | strong AEM fouling /none | strong CEM fouling /none | none/none |
| Adsorption by electrostatic attraction | strong AEM fouling /weak AEM fouling | strong CEM fouling /weak CEM fouling | none/none |
| Adsorption by macromolecule interaction | none/none | none/none | IEM fouling /IEM fouling |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.-J.; Park, J.-S. Understanding Membrane Fouling in Electrically Driven Energy Conversion Devices. Energies 2021, 14, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010212
Han S-J, Park J-S. Understanding Membrane Fouling in Electrically Driven Energy Conversion Devices. Energies. 2021; 14(1):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010212
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Soo-Jin, and Jin-Soo Park. 2021. "Understanding Membrane Fouling in Electrically Driven Energy Conversion Devices" Energies 14, no. 1: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010212
APA StyleHan, S.-J., & Park, J.-S. (2021). Understanding Membrane Fouling in Electrically Driven Energy Conversion Devices. Energies, 14(1), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010212






