Driving Factors for the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Technical Efficiency of China’s New Energy Industry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
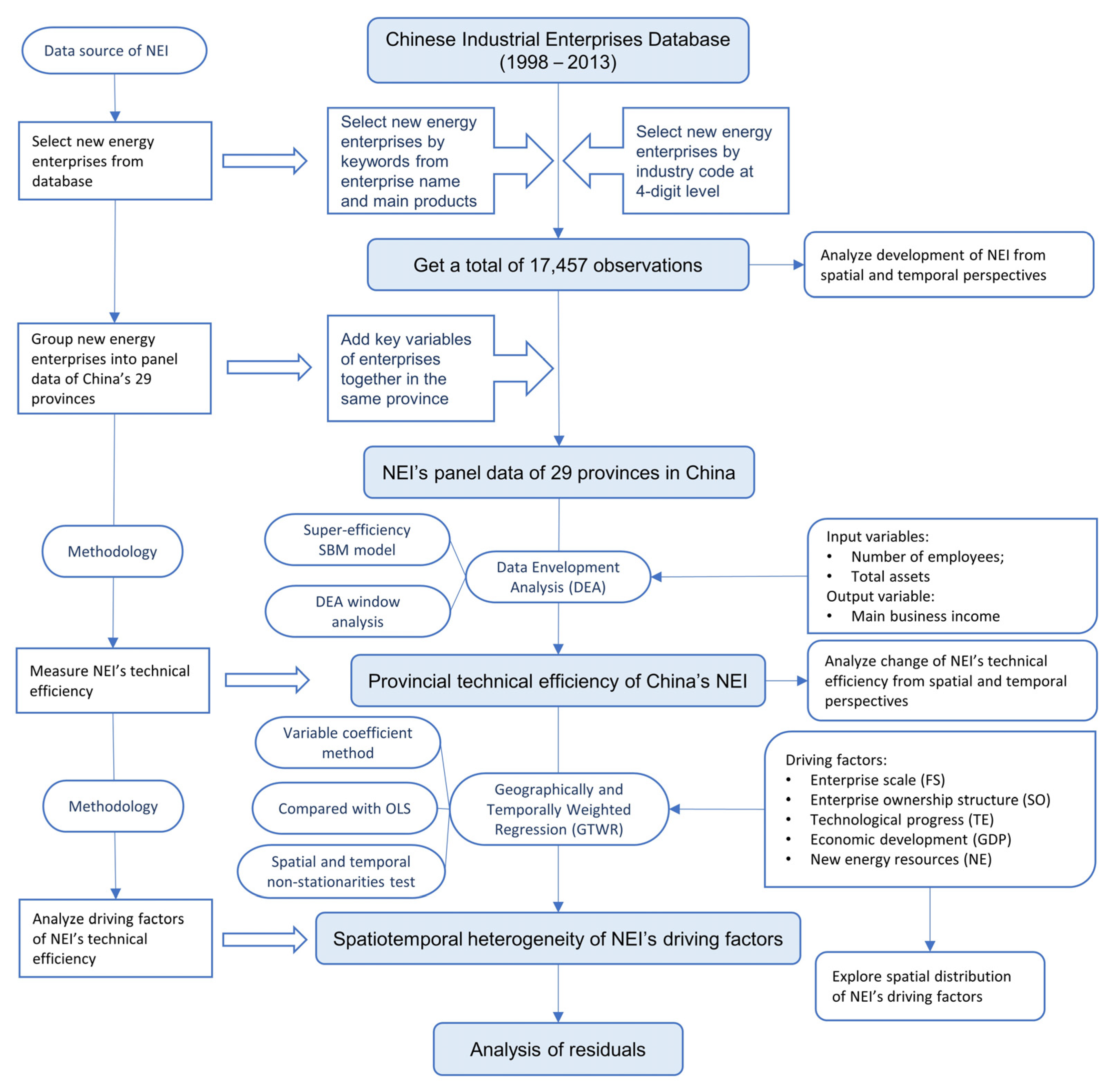
2. Methodology and Data
2.1. Methodology
2.1.1. Super-Efficiency SBM Model
2.1.2. GTWR Model
2.2. Variables
2.2.1. Input-Output Variables of Technical Efficiency Measurement
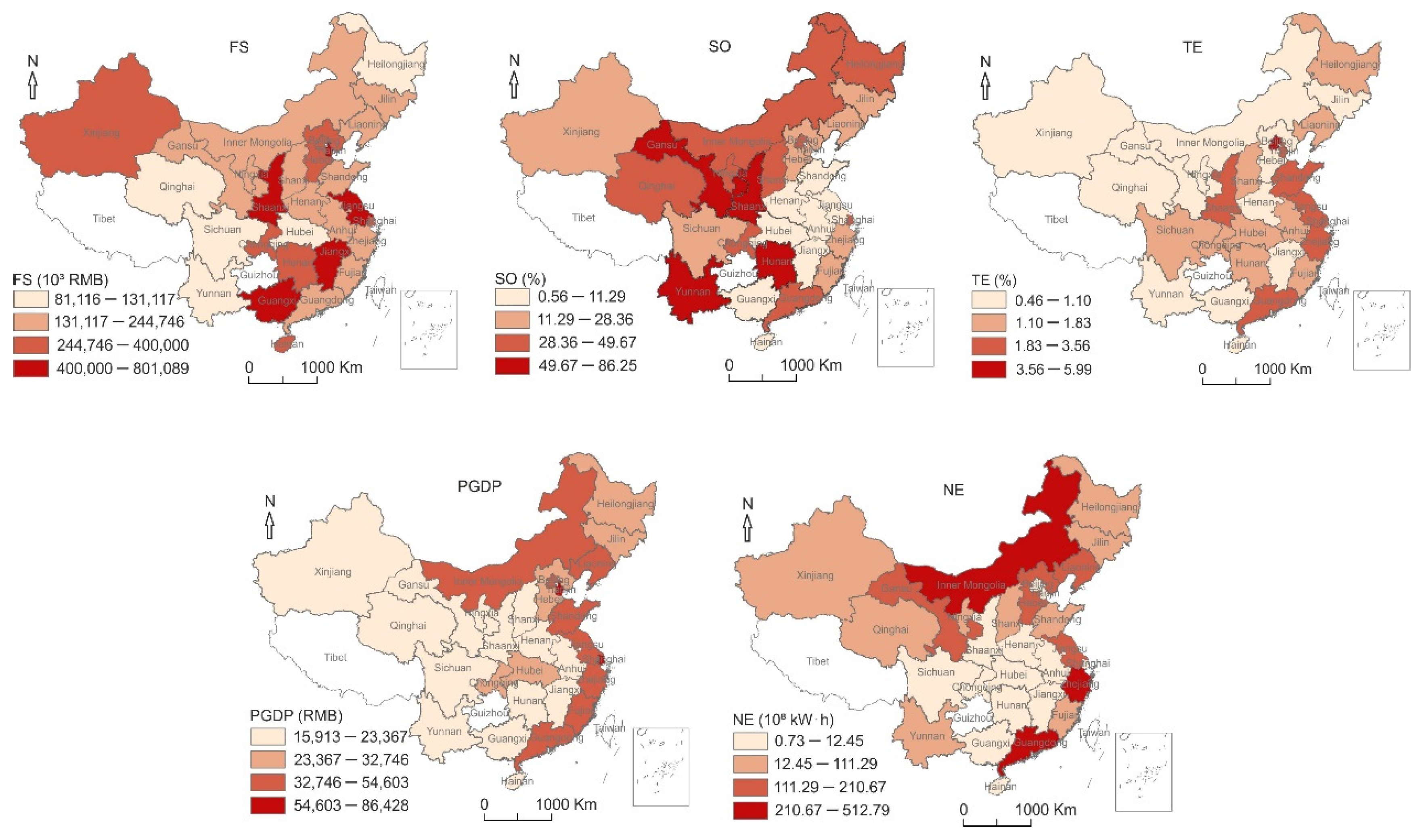
2.2.2. Driving Factors of Technical Efficiency
2.3. Data Source and Processing
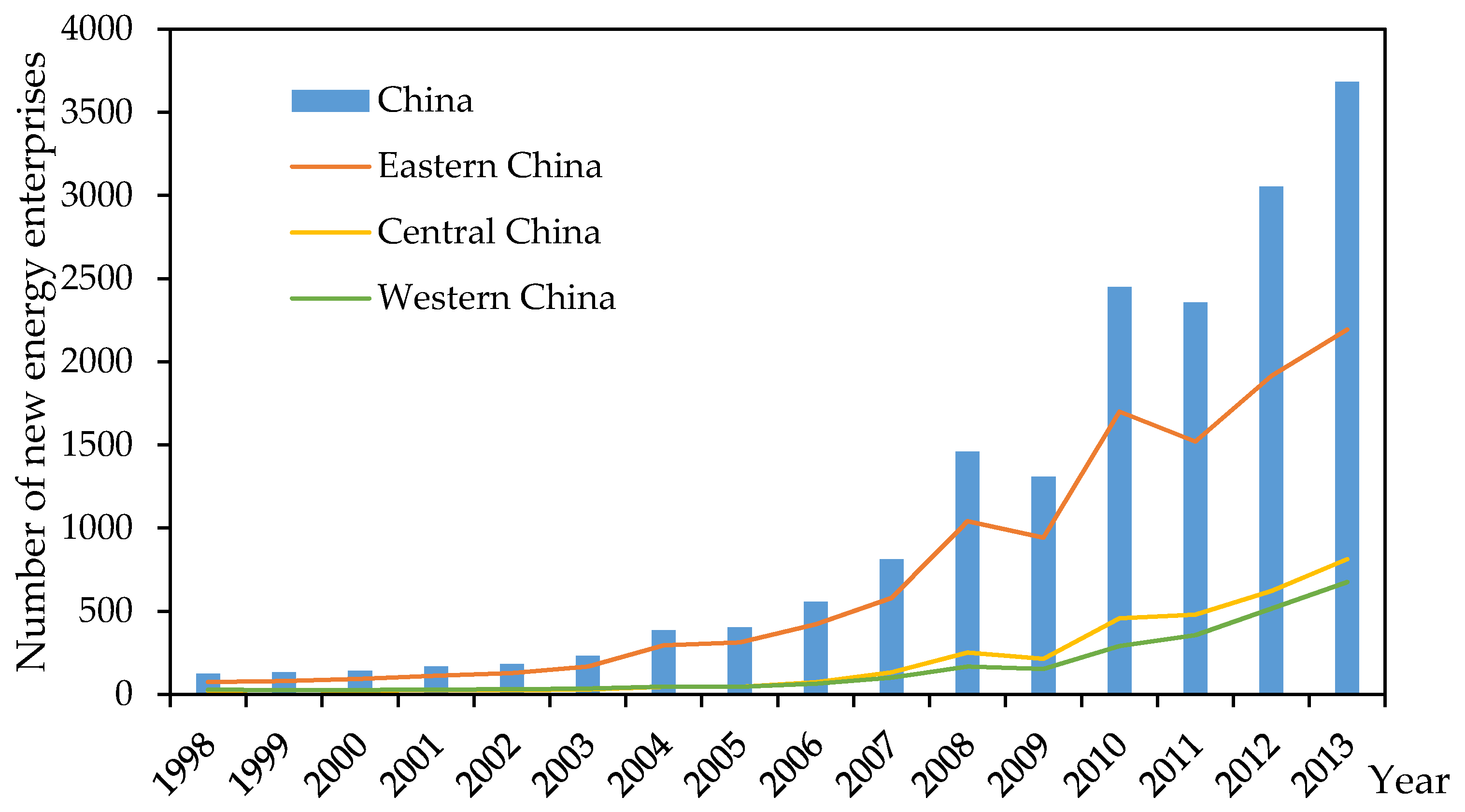
2.4. Data Description
3. Results and Discussion
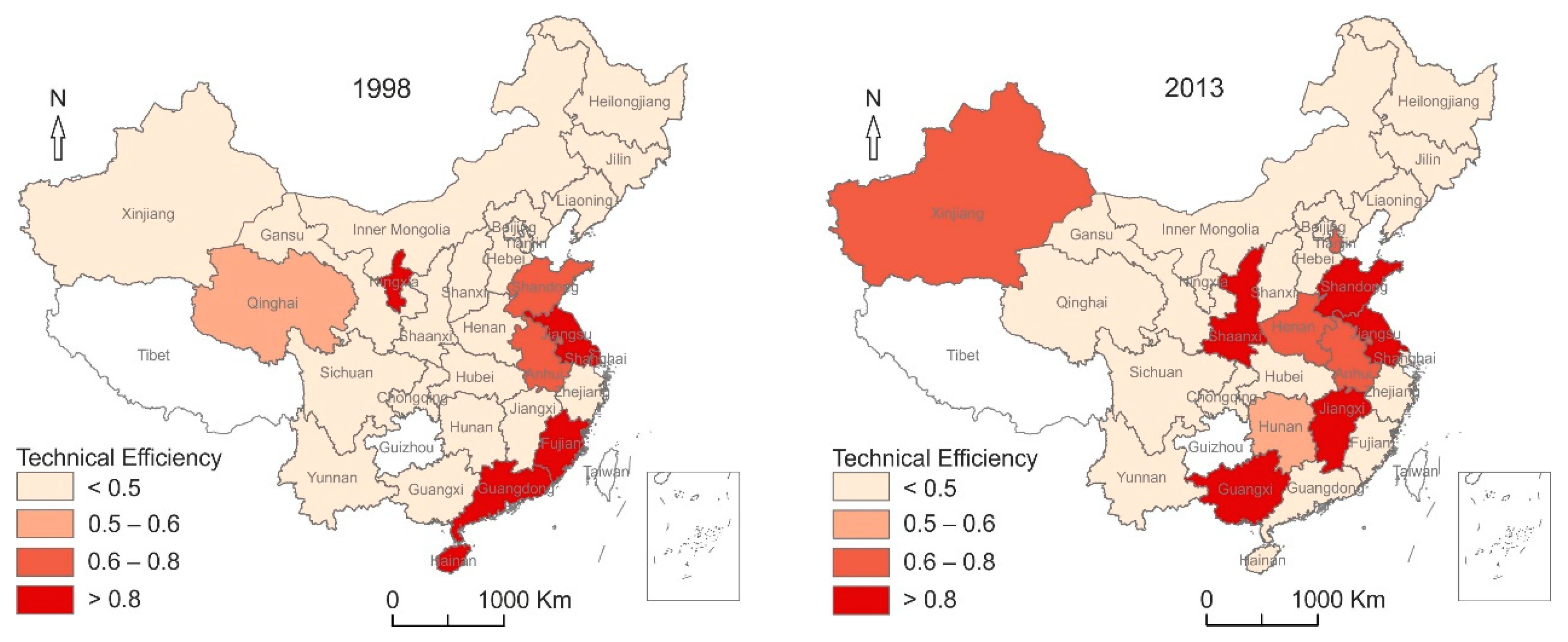
3.1. The Spatiotemporal Analysis of NEI’s Technical Efficiency
3.2. Performance of GTWR Model
3.3. Driving Factors for the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Technical Efficiency
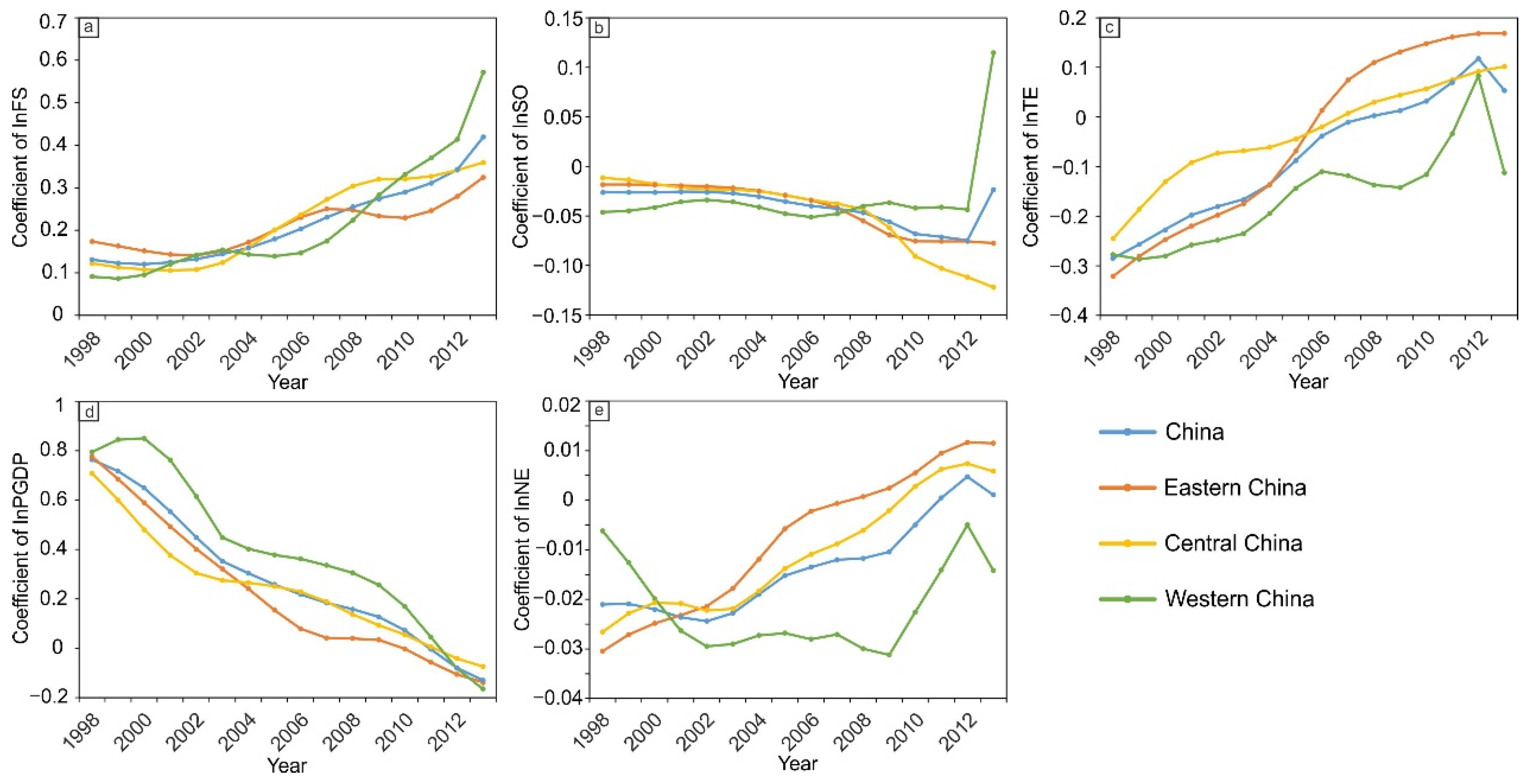
3.3.1. Enterprise Scale Effect
3.3.2. Enterprise Ownership Structure Effect
3.3.3. Technological Progress Effect
3.3.4. Economic Development Effect
3.3.5. New Energy Resources Effect
3.4. Policy Implications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NEI | New energy industry |
| DEA | Data envelopment analysis |
| GTWR | Geographically and temporally weighted regression |
| SFA | Stochastic frontier analysis |
| SBM | Slacks-based measure |
| DMUs | Decision making units |
| CRS | Constant returns to scale |
| VRS | Variable returns to scale |
| E | Technical efficiency |
| FS | Enterprise scale |
| SO | Enterprise ownership structure |
| TE | Technological progress |
| PGDP | Economic development (per capita GDP) |
| NE | New energy resources |
| GWR | Geographically weighted regression |
| AIC | Akaike information criterion |
| R&D | Research and development |
| RDI | R&D expenditure intensity |
| OLS | Ordinary least squares |
| SE | Standard error |
References
- Engels, A. Understanding how China is championing climate change mitigation. Palgrave Commun. 2018, 4, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gi, K.; Sano, F.; Akimoto, K.; Hiwatari, R.; Tobita, K. Potential contribution of fusion power generation to low-carbon development under the Paris Agreement and associated uncertainties. Energy Strategy Rev. 2020, 27, 100432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D.; Bazilian, M.D.; Wagner, N.; Gorini, R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.Y.; Hultman, N.; Cui, D.; McJeon, H.; Yu, S.; Edwards, M.R.; Sen, A.; Song, K.; Bowman, C.; Clarke, L.; et al. A plant-by-plant strategy for high-ambition coal power phaseout in China. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, K.; Bertram, C.; Harmsen, M.; Kriegler, E.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Wang, S.; Fujimori, S.; Tavoni, M. Assessing China’s efforts to pursue the 1.5 °C warming limit. Science 2021, 372, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Yao, X. The Economic Effects of the Development of the Renewable Energy Industry in China. Energies 2019, 12, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bu, Y.; Wang, E.; Bai, J.; Shi, Q. Spatial pattern and driving factors for interprovincial natural gas consumption in China: Based on SNA and LMDI. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Bu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, Z. Natural Gas Security in China: A Simulation of Evolutionary Trajectory and Obstacle Degree Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, B.Q.; Bin, X. How to promote the growth of new energy industry at different stages? Energy Policy 2018, 118, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Q.; Moubarak, M. Renewable energy consumption—Economic growth nexus for China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Q.; Chen, Y.F. Does electricity price matter for innovation in renewable energy technologies in China? Energy Econ. 2019, 78, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BP, Statistical Review of World Energy. 2020. Available online: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2020-full-report.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Lin, B.; Luan, R. Do government subsidies promote efficiency in technological innovation of China’s photovoltaic enterprises? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Q.; Luan, R.R. Are government subsidies effective in improving innovation efficiency? Based on the research of China’s wind power industry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Yang, Y.; Campana, P.E.; He, J. City-level analysis of subsidy-free solar photovoltaic electricity price, profits and grid parity in China. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W. Who drives China’s renewable energy policies? Understanding the role of industrial corporations. Environ. Dev. 2017, 21, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.-G.; Li, P.-L.; Zhou, Y. Which policy can promote renewable energy to achieve grid parity? Feed-in tariff vs. renewable portfolio standards. Renew. Energy 2020, 162, 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Du, H.; Brown, M.A.; Mao, G. Large-scale PV power generation in China: A grid parity and techno-economic analysis. Energy 2017, 134, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clack, C.T.M.; Qvist, S.A.; Apt, J.; Bazilian, M.; Brandt, A.R.; Caldeira, K.; Davis, S.J.; Diakov, V.; Handschy, M.A.; Hines, P.D.H.; et al. Evaluation of a proposal for reliable low-cost grid power with 100% wind, water, and solar. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6722–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrell, M.J. The Measurement of Productive Efficiency. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 1957, 120, 253–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelli, T.J.; Rao, D.S.P.; Battese, G.E. An Introduction to Efficiency and Productivity Analysis; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.G.; Zhen, W. The technical efficiency of China’s wind power list enterprises: An estimation based on DEA method and micro-data. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 470–479. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wen, H.; Fu, Z.; Li, X. Operating performance, industry agglomeration and its spatial characteristics of Chinese photovoltaic industry. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Z. Two-stage innovation efficiency of new energy enterprises in China: A non-radial DEA approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2016, 112, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Jiang, C.; Ma, C.; Su, B. Investment efficiency of the new energy industry in China. Energy Econ. 2018, 70, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-L.; Chen, H.H. Examining the efficiency of biomass energy: Evidence from the Chinese recycling industry. Energy Policy 2018, 119, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.-G. The industrial performance of wind power industry in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adom, P.K.; Amakye, K.; Abrokwa, K.K.; Quaidoo, C. Estimate of transient and persistent energy efficiency in Africa: A stochastic frontier approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 166, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, R.; Natarajan, R.; Zhang, D. Two-stage estimation of the impact of contextual variables in stochastic frontier production function models using Data Envelopment Analysis: Second stage OLS versus bootstrap approaches. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 278, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorca, M.; Baños, J.; Somoza, J.; Arbués, P. A Stochastic Frontier Analysis Approach for Estimating Energy Demand and Efficiency in the Transport Sector of Latin America and the Caribbean. Energy J. 2017, 38, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Streimikiene, D.; Jusoh, A.; Khoshnoudi, M. A comprehensive review of data envelopment analysis (DEA) approach in energy efficiency. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 1298–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Yuan, Y.; Goto, M. A literature study for DEA applied to energy and environment. Energy Econ. 2017, 62, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J. Data envelopment analysis application in sustainability: The origins, development and future directions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 264, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics, N.B.o. Chinese Industrial Enterprises Database 1998–2013. In Beijing, 2018.
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring efficiency of decision-making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Ang, B.; Poh, K. A survey of data envelopment analysis in energy and environmental studies. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 189, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulina, M.; Detotto, C.; Paba, A. An investigation into the relationship between size and efficiency of the Italian hospitality sector: A window DEA approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 204, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Liang, H.; Gao, Z.; Luo, X.; Ren, J. Spatial distribution of China’s renewable energy industry: Regional features and implications for a harmonious development future. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B.Q. Do we really understand the development of China’s new energy industry? Energy Econ. 2018, 74, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Wan, Y.; Yuan, J.; Yin, J.; Baležentis, T.; Streimikiene, D. Economic and Technical Efficiency of the Biomass Industry in China: A Network Data Envelopment Analysis Model Involving Externalities. Energies 2017, 10, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.; Brunsdon, C. The geography of parameter space: An investigation of spatial non-stationarity. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1996, 10, 605–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillen, D.P. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2004, 86, 554–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Crespo, R.; Yao, J. Geographical and Temporal Weighted Regression (GTWR). Geogr. Anal. 2015, 47, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, W.; Yvrande-Billon, A. Ownership, contractual practices and technical efficiency: The case of urban public transport in France. J. Transp. Econ. Policy 2007, 41, 257–282. [Google Scholar]
- Walheer, B.; He, M. Technical efficiency and technology gap of the manufacturing industry in China: Does firm ownership matter? World Dev. 2020, 127, 104769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, R. A study of the R&D efficiency and productivity of Chinese firms. J. Comp. Econ. 2003, 31, 444–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Ming, Z.; Peng, L.; Liu, X.; Bo, L.; Duan, J. China’s new energy development: Status, constraints and reforms. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B.Q. Assessing the development of China’s new energy industry. Energy Econ. 2018, 70, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sheng, Y. Productivity Spillovers from Foreign Direct Investment: Firm-Level Evidence from China. World Dev. 2012, 40, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, G.H.; Rawski, T.G.; Zhang, Y. Productivity growth and convergence across China’s industrial economy. J. Chin. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2008, 6, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics, N.B.o. China Statistical Yearbook on Science and Technology; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Statistics, N.B.o. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Statistics, N.B.o. China Energy Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Board, C.E.P.Y.E. China Electric Power Yearbook; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Kammen, D.M. Where, when and how much wind is available? A provincial-scale wind resource assessment for China. Energy Policy 2014, 74, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Kammen, D.M. Where, when and how much solar is available? A provincial-scale solar resource assessment for China. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, C.-E.; Li, D.D.; Tao, Z.; Wang, Y. A Multitask Theory of State Enterprise Reform. J. Comp. Econ. 2000, 28, 716–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shayegh, S.; Sanchez, D.L.; Caldeira, K. Evaluating relative benefits of different types of R&D for clean energy technologies. Energy Policy 2017, 107, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, M.; Abdul-Rahim, A.; Mohd-Shahwahid, H. Determinants of technical efficiency in the bioenergy industry in the EU28 region. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 1331–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Russell, R.R. Technological change, technological catch-up, and capital deepening: Relative contributions to growth and convergence. Am. Econ. Rev. 2002, 92, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Teo, T.S.H.; Zhou, F.; Lim, M.K.; Chen, H. Does industrial green transformation successfully facilitate a decrease in carbon intensity in China? An environmental regulation perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Andrews-Speed, P.; Zhao, X.; He, Y. Interactions between renewable energy policy and renewable energy industrial policy: A critical analysis of China’s policy approach to renewable energies. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Objective | Industry | Scale | Data Sources | Methodology | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhao et al. [22] | Delineate the technical efficiency of China’s wind power industry | Wind power industry | Enterprise-level | 28 wind power listed enterprise | Four-stage DEA method |
| Lin et al. [14] | Analyze the impact of government subsidies on innovation efficiency of China’s wind power industry | Wind power industry | Enterprise-level | 40 wind power listed enterprises | Stochastic frontier analysis |
| Lin et al. [13] | Analyze the impact of government subsidies on innovation efficiency of China’s photovoltaic industry | Photovoltaic industry | Enterprise-level | 44 photovoltaic listed enterprises | DEA method; Tobit model |
| Zhang et al. [23] | Analyze the operating performance, industry agglomeration and spatial characteristics of China’s photovoltaic industry | Photovoltaic industry | Enterprise-level | 58 photovoltaic listed enterprises | DEA method; spatial autocorrelation analysis |
| Wang et al. [24] | Evaluate the innovation efficiency of China’s new energy industry | Solar, wind and nuclear power industries | Enterprise-level | 38 listed enterprises | DEA method |
| Zeng et al. [25] | Evaluate the investment efficiency of China’s new energy industry and investigates driving factors | New energy industry | Enterprise-level | 74 listed enterprises | Four-stage DEA method |
| Xu et al. [26] | Conduct an empirical analysis for the technical efficiency of biomass energy in China | Biomass energy | Industry-level; Provincial level | Data from recycling industry | Stochastic frontier analysis |
| Region | Province | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern China | Beijing | 0.412 | 0.596 | 0.782 | 0.653 | 0.513 | 0.637 | 0.499 | 0.402 | 0.345 | 0.319 | 0.331 | 0.652 | 1.248 | 0.520 | 0.315 | 0.292 |
| Tianjin | 0.458 | 0.458 | 0.550 | 0.819 | 0.578 | 0.368 | 0.798 | 1.103 | 0.930 | 0.966 | 1.166 | 0.972 | 1.002 | 0.715 | 0.670 | 0.769 | |
| Hebei | 0.388 | 0.726 | 0.719 | 0.769 | 0.909 | 1.192 | 0.754 | 0.728 | 0.797 | 0.743 | 0.731 | 0.767 | 0.797 | 0.634 | 0.464 | 0.437 | |
| Shanghai | 1.260 | 0.361 | 0.311 | 0.449 | 0.438 | 0.380 | 0.455 | 0.480 | 0.692 | 0.456 | 0.962 | 0.593 | 0.922 | 0.732 | 0.551 | 0.437 | |
| Jiangsu | 0.836 | 1.067 | 0.615 | 0.720 | 0.773 | 0.683 | 1.301 | 1.115 | 1.200 | 0.790 | 0.913 | 0.994 | 0.956 | 1.050 | 0.871 | 1.000 | |
| Zhejiang | 0.340 | 0.280 | 0.550 | 0.597 | 0.460 | 0.503 | 0.665 | 0.625 | 0.544 | 0.446 | 0.567 | 0.506 | 0.690 | 0.544 | 0.466 | 0.409 | |
| Fujian | 0.871 | 1.037 | 0.509 | 0.403 | 0.249 | 0.288 | 0.231 | 0.185 | 0.386 | 0.241 | 0.253 | 0.418 | 0.319 | 0.523 | 0.512 | 0.334 | |
| Shandong | 0.660 | 1.073 | 1.134 | 1.055 | 1.349 | 1.000 | 0.552 | 0.807 | 0.714 | 0.729 | 0.918 | 1.174 | 0.875 | 0.983 | 1.010 | 1.035 | |
| Guangdong | 0.893 | 1.232 | 0.916 | 1.096 | 0.826 | 1.723 | 1.009 | 0.842 | 0.671 | 0.502 | 0.386 | 0.511 | 0.527 | 0.478 | 0.405 | 0.368 | |
| Hainan | 1.055 | 1.009 | 0.976 | 0.961 | 0.870 | 0.860 | 1.153 | 0.638 | 0.837 | 0.907 | 0.869 | 1.794 | 0.262 | 0.452 | 0.442 | 0.486 | |
| Liaoning | 0.151 | 0.145 | 0.155 | 0.195 | 0.187 | 0.166 | 0.228 | 0.280 | 0.488 | 0.631 | 0.322 | 0.436 | 0.650 | 0.543 | 0.564 | 0.417 | |
| Average | 0.666 | 0.726 | 0.656 | 0.701 | 0.650 | 0.709 | 0.695 | 0.655 | 0.691 | 0.612 | 0.674 | 0.802 | 0.750 | 0.652 | 0.570 | 0.544 | |
| Central China | Shanxi | 0.086 | 0.086 | 0.083 | 0.453 | 0.700 | 0.194 | 0.523 | 0.729 | 0.262 | 0.687 | 1.198 | 0.940 | 0.428 | 0.503 | 0.462 | 0.249 |
| Anhui | 0.601 | 0.269 | 1.602 | 0.237 | 0.303 | 0.127 | 0.158 | 0.138 | 0.549 | 0.511 | 0.479 | 0.516 | 0.613 | 0.648 | 0.635 | 0.601 | |
| Jiangxi | 0.189 | 0.189 | 2.006 | 0.779 | 1.653 | 0.458 | 0.225 | 0.296 | 0.489 | 0.327 | 0.598 | 0.498 | 0.614 | 1.115 | 0.876 | 0.957 | |
| Henan | 0.166 | 0.189 | 0.272 | 0.221 | 0.202 | 0.210 | 0.276 | 0.300 | 0.366 | 0.639 | 0.570 | 0.568 | 0.666 | 0.680 | 0.680 | 0.705 | |
| Hubei | 0.086 | 0.102 | 0.362 | 0.418 | 0.542 | 0.449 | 0.906 | 0.312 | 0.860 | 0.367 | 0.376 | 0.340 | 0.297 | 0.393 | 0.349 | 0.415 | |
| Hunan | 0.406 | 0.246 | 0.185 | 0.198 | 0.247 | 0.773 | 1.278 | 0.577 | 0.617 | 0.453 | 0.612 | 1.091 | 0.758 | 0.685 | 0.637 | 0.588 | |
| Jilin | 0.166 | 0.191 | 0.197 | 0.312 | 0.258 | 0.859 | 0.408 | 0.324 | 0.124 | 0.142 | 0.146 | 0.428 | 0.361 | 0.516 | 0.497 | 0.419 | |
| Heilongjiang | 0.381 | 0.134 | 0.228 | 0.181 | 0.303 | 0.291 | 0.139 | 0.209 | 0.177 | 0.162 | 0.189 | 0.214 | 0.227 | 0.236 | 0.333 | 0.303 | |
| Average | 0.260 | 0.176 | 0.617 | 0.350 | 0.526 | 0.420 | 0.489 | 0.361 | 0.431 | 0.411 | 0.521 | 0.574 | 0.496 | 0.597 | 0.559 | 0.530 | |
| Western China | Inner Mongolia | 0.176 | 0.466 | 0.306 | 0.338 | 0.380 | 0.278 | 0.262 | 0.293 | 0.156 | 0.202 | 0.273 | 0.354 | 0.351 | 0.499 | 0.451 | 0.399 |
| Guangxi | 0.210 | 0.423 | 0.376 | 0.463 | 0.503 | 0.894 | 0.652 | 1.375 | 0.862 | 0.415 | 0.411 | 0.546 | 0.600 | 0.596 | 1.234 | 1.027 | |
| Chongqing | 0.200 | 0.177 | 0.148 | 0.374 | 0.519 | 0.637 | 0.194 | 0.312 | 0.275 | 0.408 | 0.387 | 0.693 | 0.715 | 0.795 | 0.696 | 0.498 | |
| Sichuan | 0.248 | 0.257 | 0.238 | 0.161 | 0.191 | 0.271 | 0.355 | 0.420 | 0.355 | 0.269 | 0.252 | 0.273 | 0.336 | 0.471 | 0.399 | 0.218 | |
| Yunnan | 0.234 | 0.250 | 0.369 | 0.300 | 0.855 | 0.284 | 0.295 | 0.342 | 0.344 | 0.376 | 0.383 | 0.252 | 0.328 | 0.371 | 0.292 | 0.267 | |
| Shaanxi | 0.204 | 0.182 | 0.229 | 0.168 | 0.167 | 0.281 | 0.240 | 0.253 | 0.318 | 0.431 | 0.419 | 0.507 | 0.447 | 0.430 | 0.567 | 1.036 | |
| Gansu | 0.216 | 0.216 | 0.277 | 0.165 | 0.138 | 0.342 | 0.219 | 0.147 | 0.131 | 0.160 | 0.132 | 0.090 | 0.409 | 0.524 | 0.526 | 0.306 | |
| Qinghai | 0.569 | 0.569 | 0.569 | 0.569 | 0.560 | 0.398 | 0.683 | 0.762 | 0.751 | 0.962 | 1.156 | 0.643 | 1.000 | 0.825 | 0.442 | 0.259 | |
| Ningxia | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.237 | 0.075 | 0.593 | 0.471 | 0.507 | 0.821 | 0.477 | 0.366 | 0.237 | 0.237 | |
| Xinjiang | 0.328 | 0.244 | 0.262 | 0.281 | 0.255 | 0.529 | 0.779 | 0.702 | 1.030 | 0.893 | 0.795 | 1.884 | 0.781 | 0.843 | 0.734 | 0.684 | |
| Average | 0.338 | 0.378 | 0.377 | 0.382 | 0.457 | 0.491 | 0.492 | 0.468 | 0.482 | 0.459 | 0.472 | 0.606 | 0.544 | 0.572 | 0.558 | 0.493 | |
| China | Average | 0.441 | 0.454 | 0.549 | 0.494 | 0.549 | 0.554 | 0.568 | 0.509 | 0.547 | 0.504 | 0.562 | 0.672 | 0.609 | 0.609 | 0.563 | 0.522 |
| R2 | Adjusted R2 | AICc | Residual Squares | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | 0.257 | 0.249 | 751.687 | 133.775 |
| GTWR | 0.627 | 0.623 | 636.751 | 67.297 |
| Variables | 2 × SE (OLS) | Interquartile (1998) | Interquartile (2006) | Interquartile (2013) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnFS | 0.046 | 0.136 | 0.187 | 0.127 |
| lnSO | 0.012 | 0.019 | 0.064 | 0.080 |
| lnTE | 0.092 | 0.128 | 0.287 | 0.215 |
| lnPGDP | 0.117 | 0.231 | 0.339 | 0.378 |
| lnNE | 0.013 | 0.034 | 0.020 | 0.041 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yan, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Bu, Y. Driving Factors for the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Technical Efficiency of China’s New Energy Industry. Energies 2021, 14, 4151. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144151
Liu H, Yan X, Cheng J, Zhang J, Bu Y. Driving Factors for the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Technical Efficiency of China’s New Energy Industry. Energies. 2021; 14(14):4151. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144151
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongli, Xiaoyu Yan, Jinhua Cheng, Jun Zhang, and Yan Bu. 2021. "Driving Factors for the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Technical Efficiency of China’s New Energy Industry" Energies 14, no. 14: 4151. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144151
APA StyleLiu, H., Yan, X., Cheng, J., Zhang, J., & Bu, Y. (2021). Driving Factors for the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Technical Efficiency of China’s New Energy Industry. Energies, 14(14), 4151. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144151






