A Family of Transformerless Quadratic Boost High Gain DC-DC Converters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
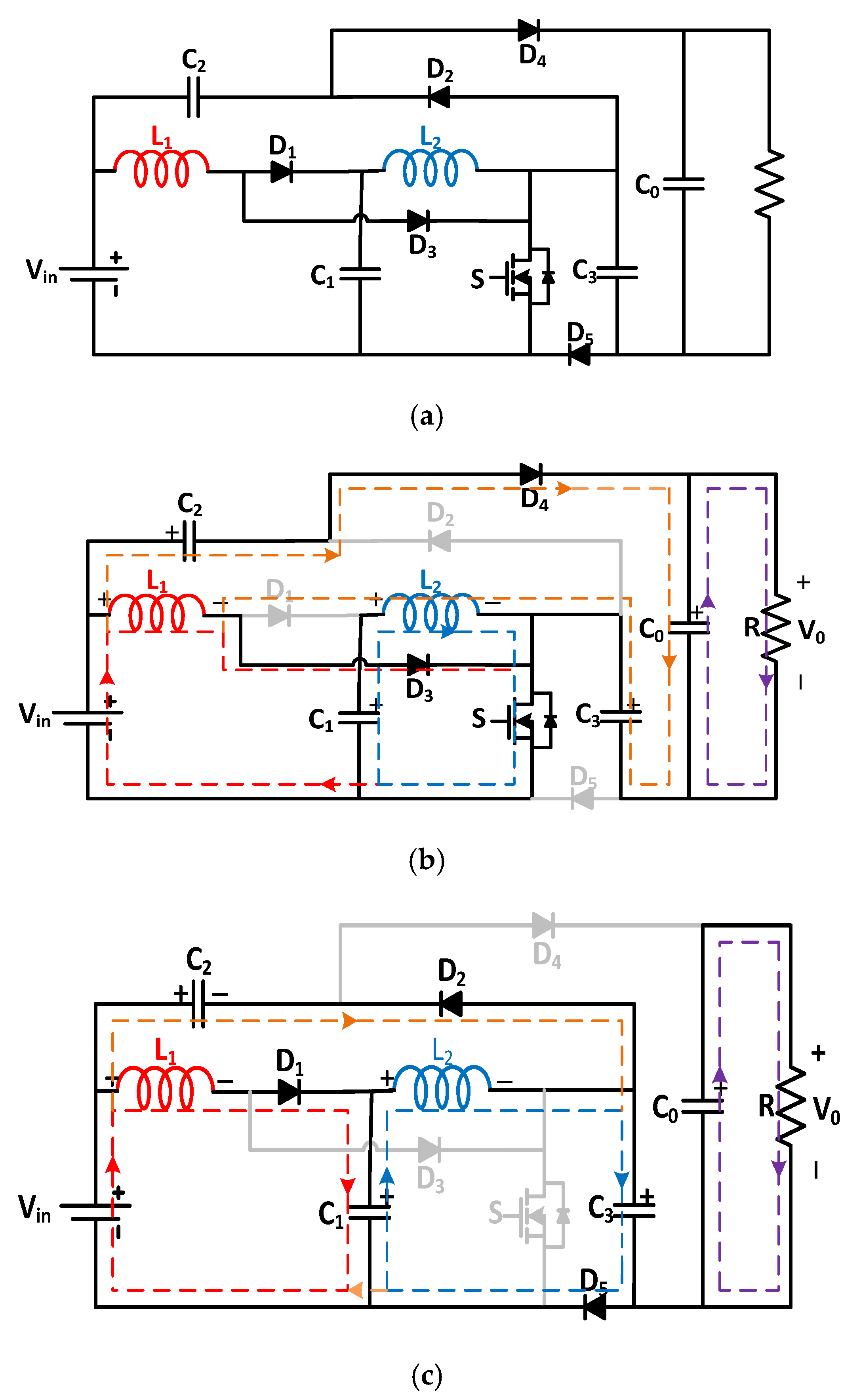
2. Proposed Converter I
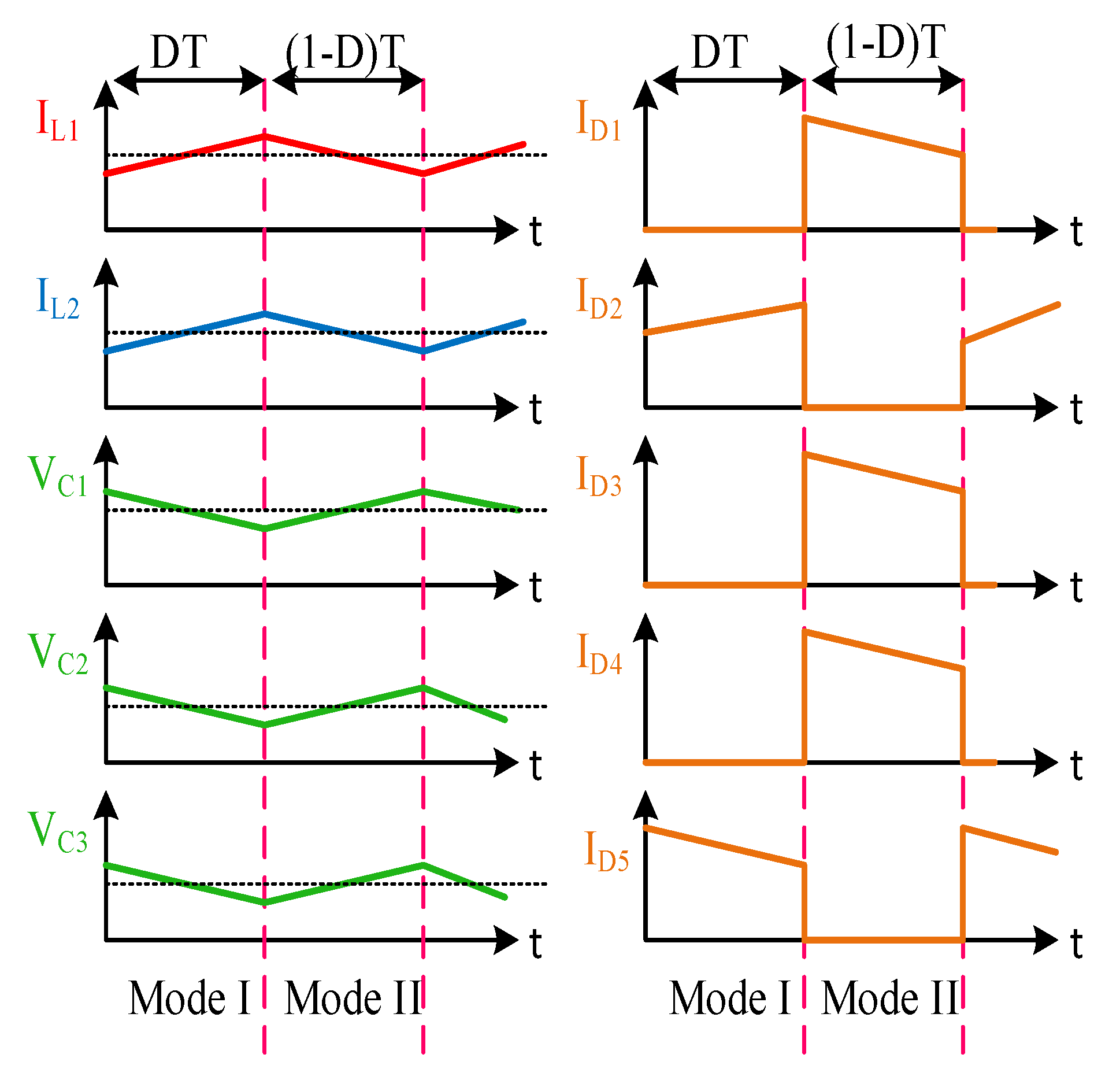
2.1. Analysis in CCM Mode
2.1.1. MODE I [0-DT]
2.1.2. MODE II [DT-T]
2.2. Passive Components Selection
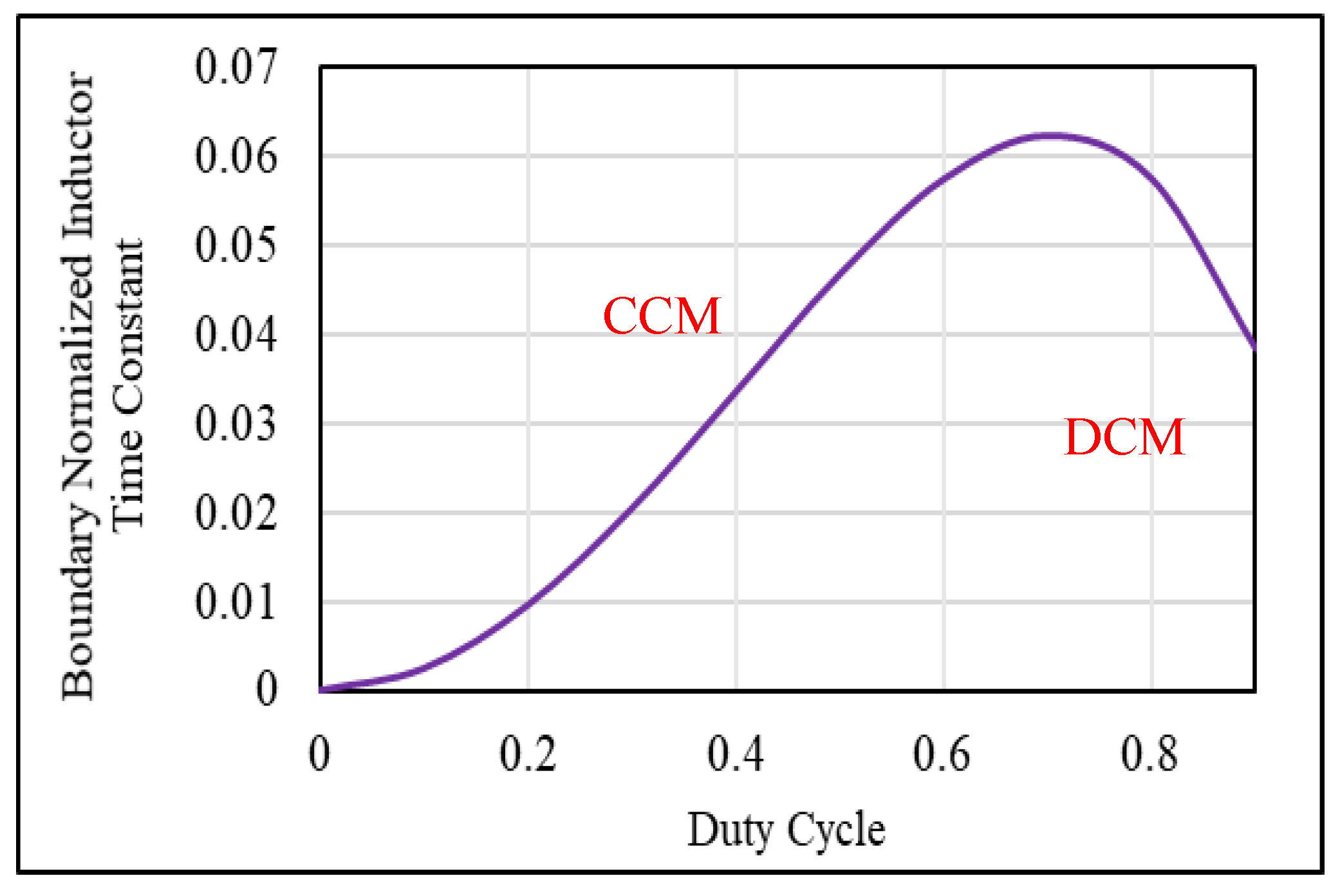
2.3. Boundary Condition Mode
3. Proposed Converter II
3.1. Analysis in CCM Mode
3.1.1. Mode I [0-DT]
3.1.2. Mode II [DT-T]
3.2. Passive Component Selection
3.3. Boundary Condition
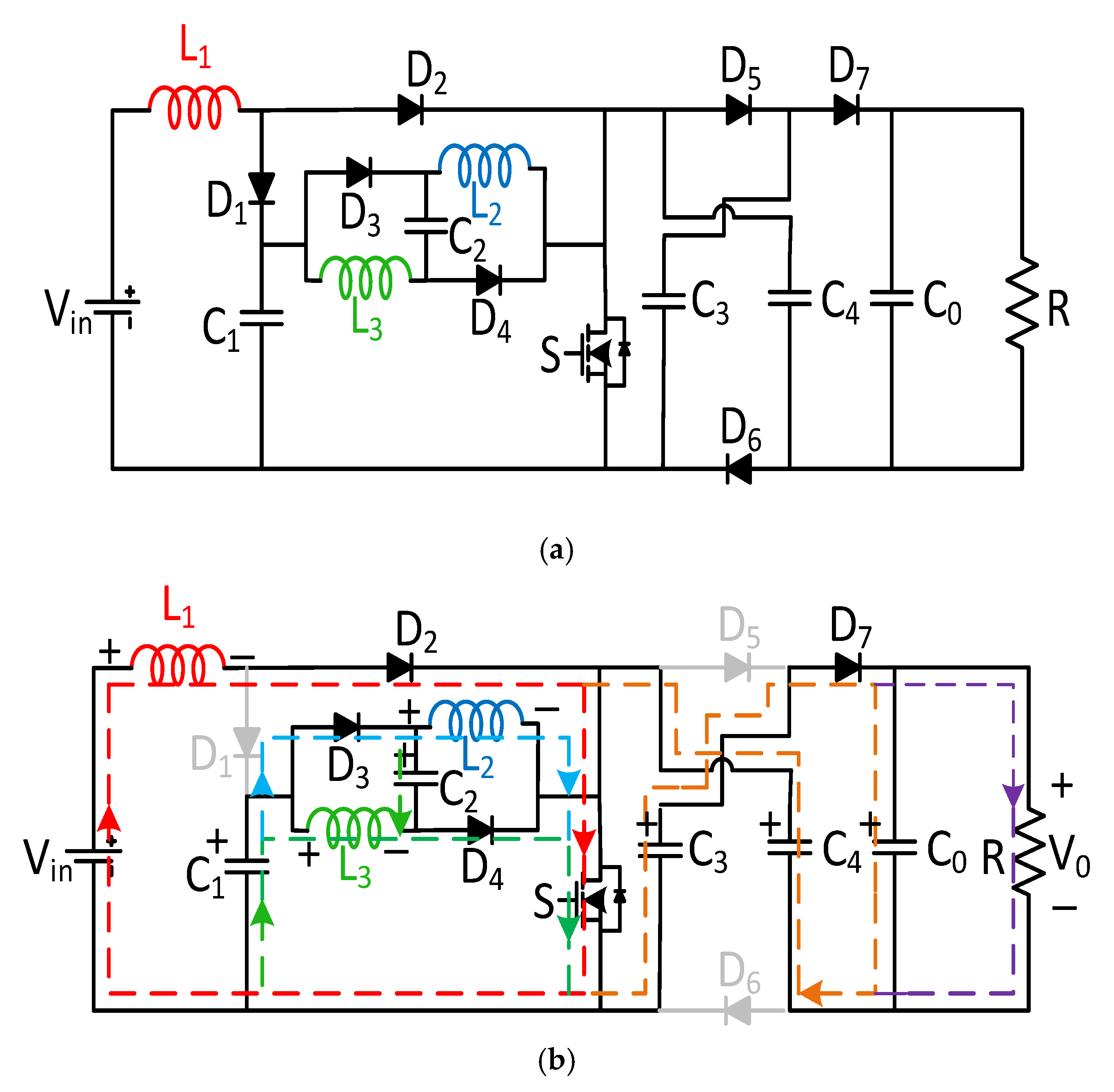
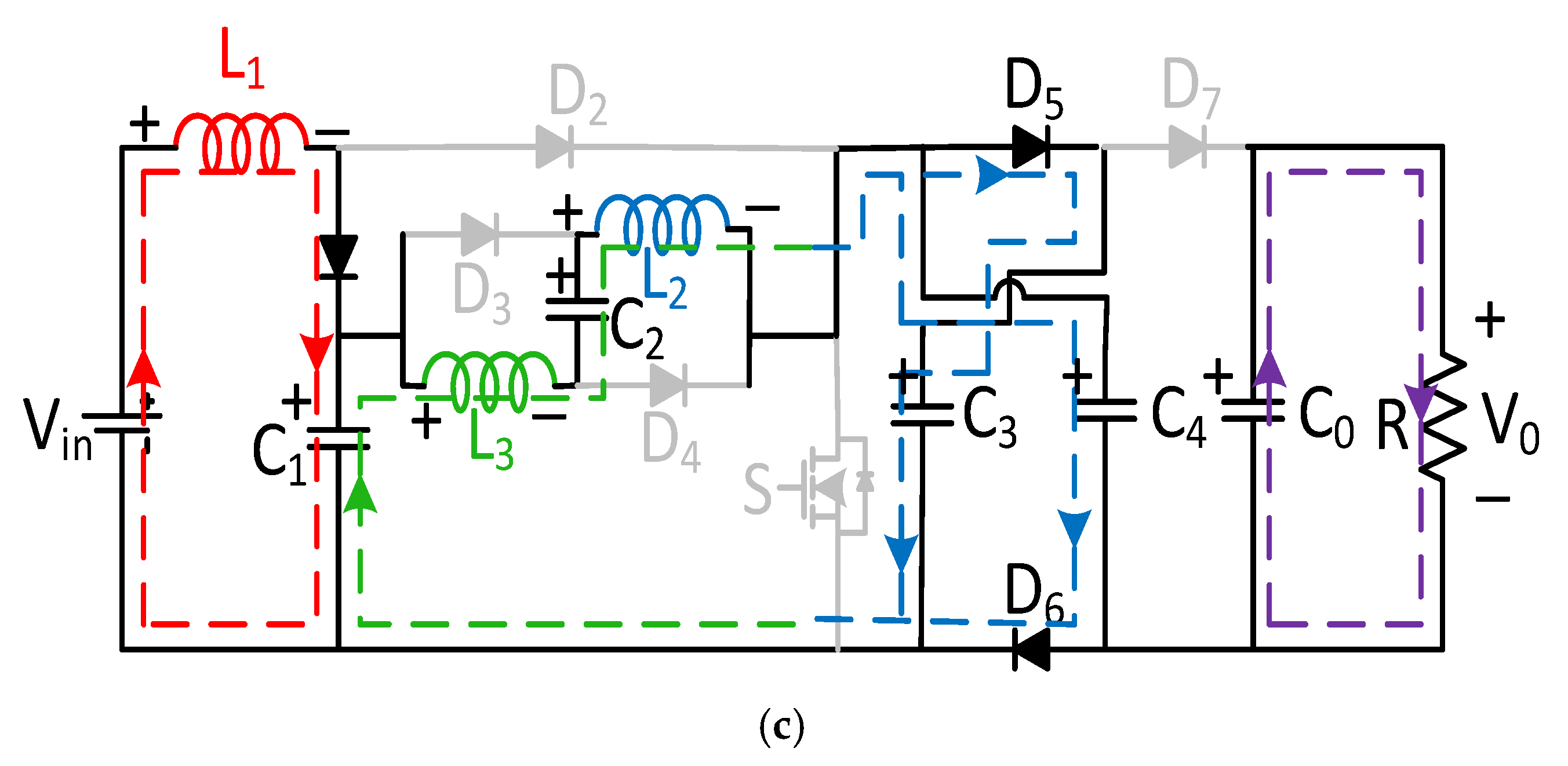
4. Proposed Converter III
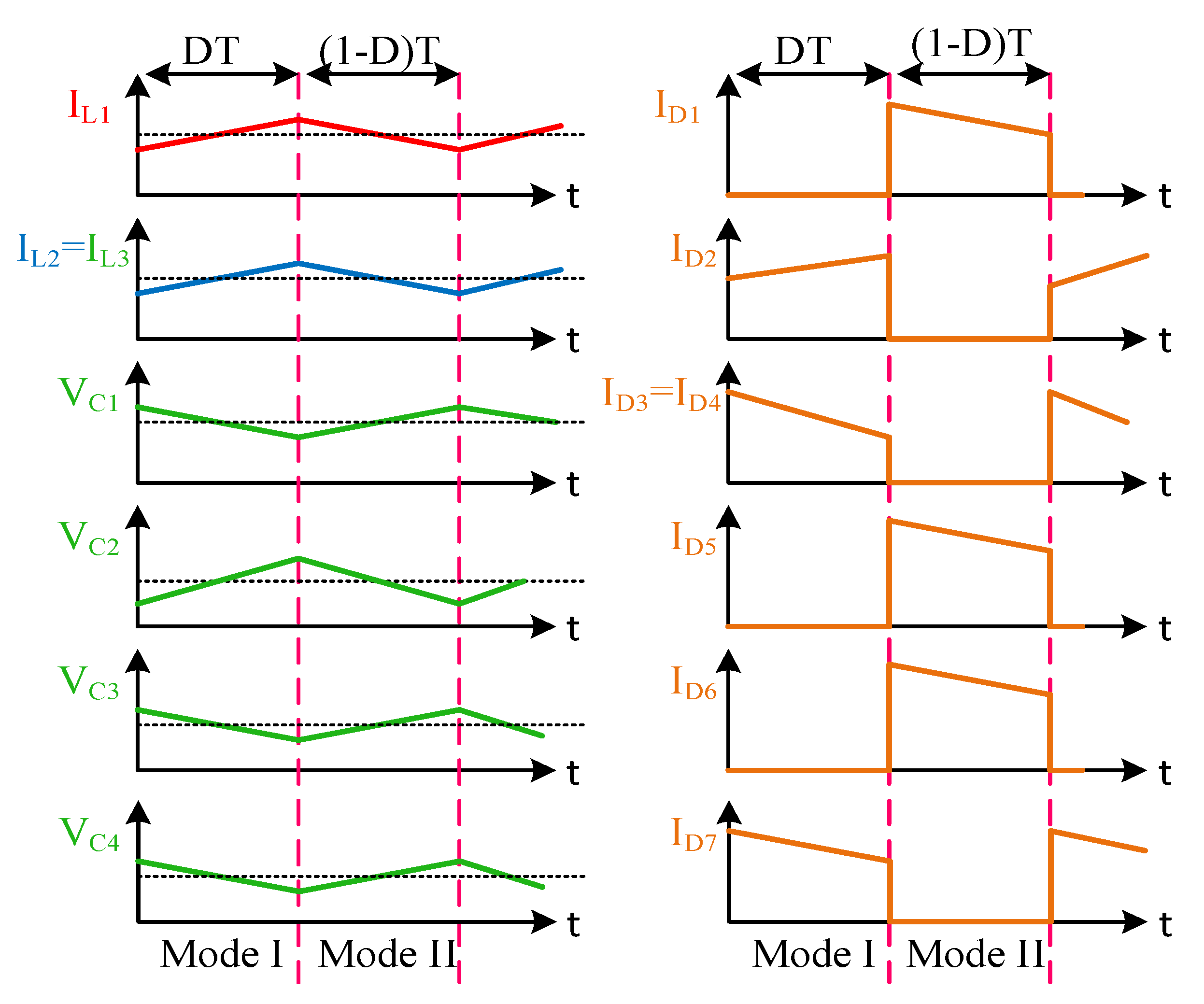
4.1. Analysis in CCM Mode
4.1.1. Mode I [0-DT]
4.1.2. Mode I [DT-T]
4.2. Passive Component Selection
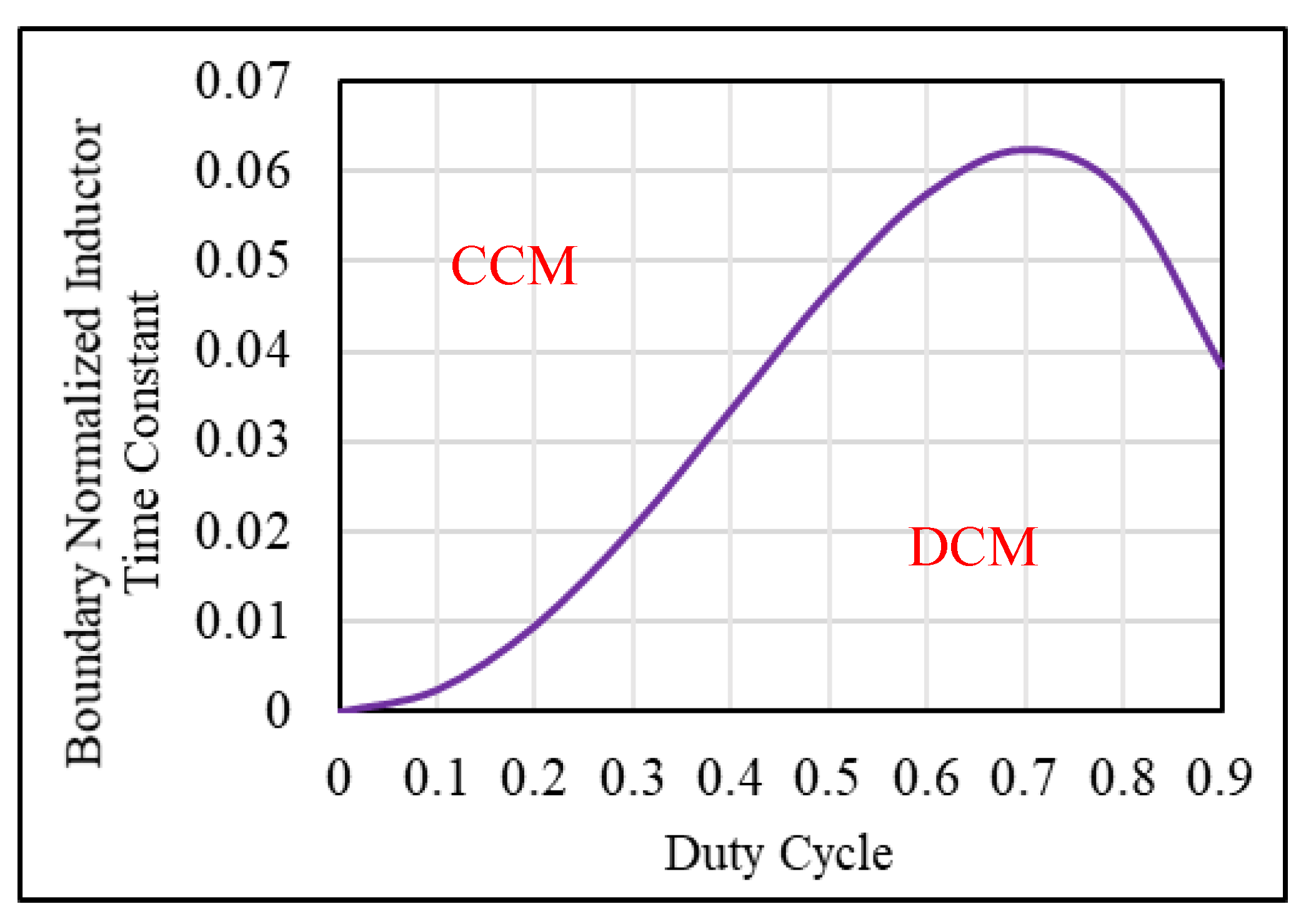
4.3. Boundary Condition
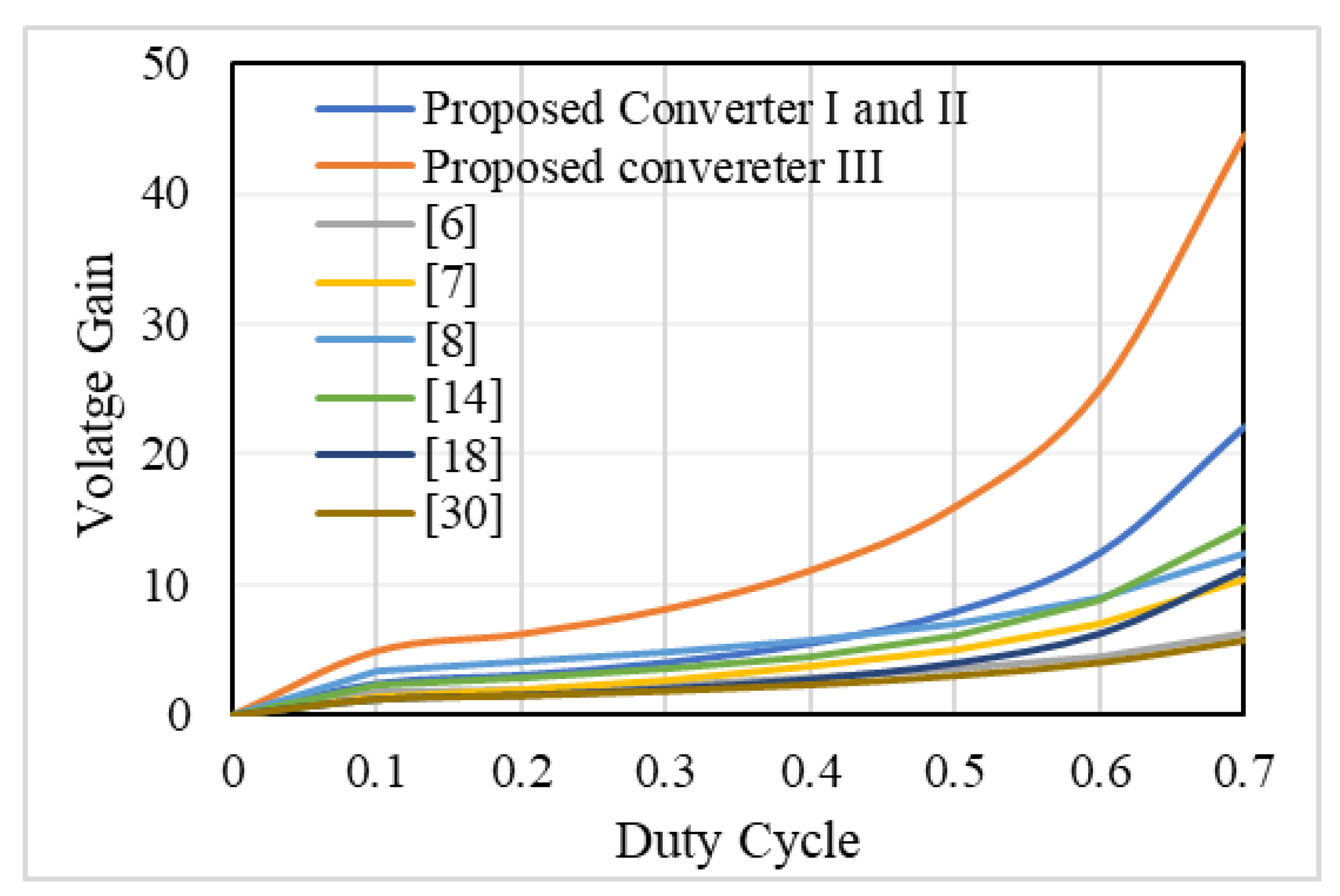
5. Comparison of the Proposed Topologies
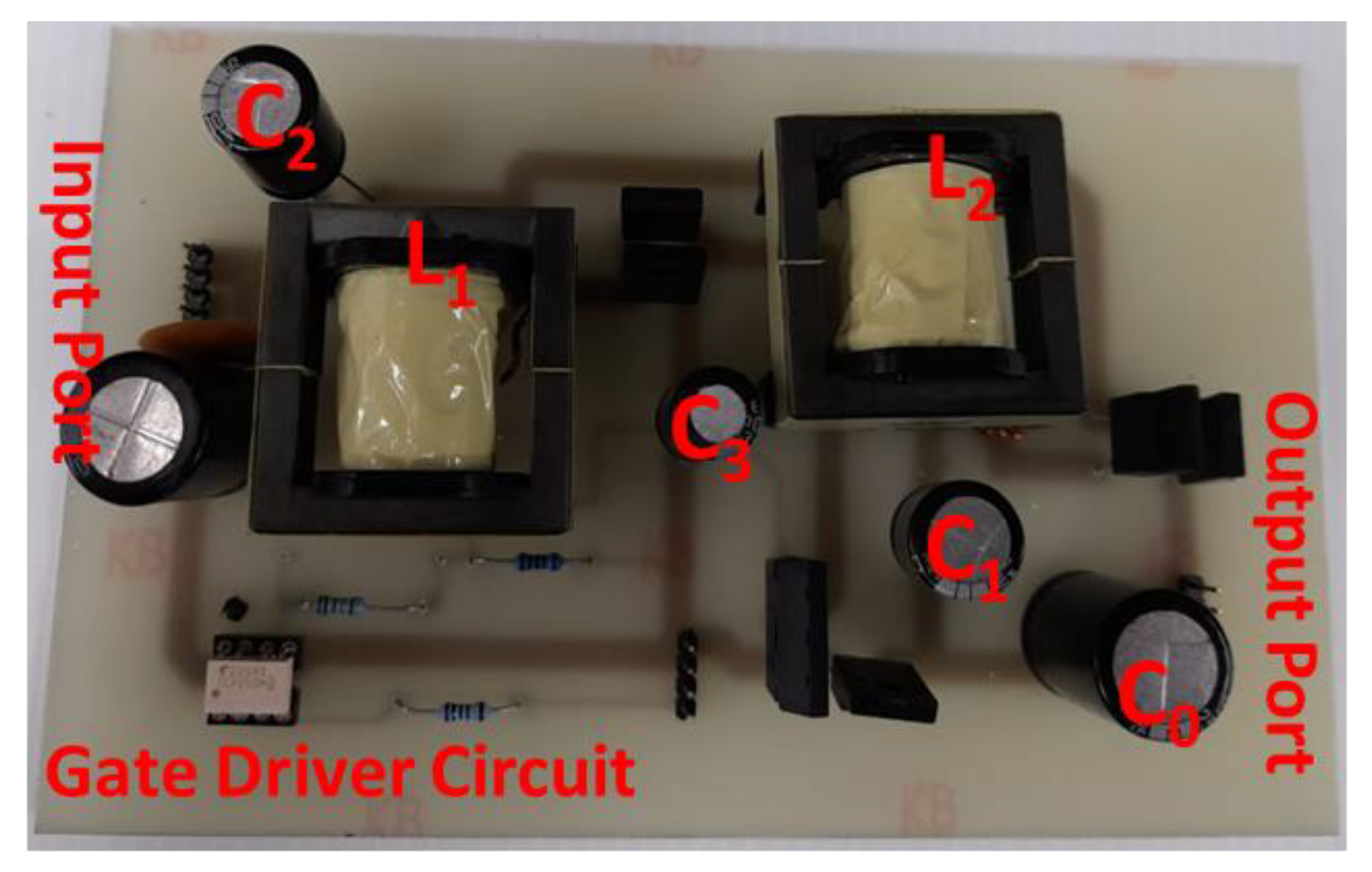
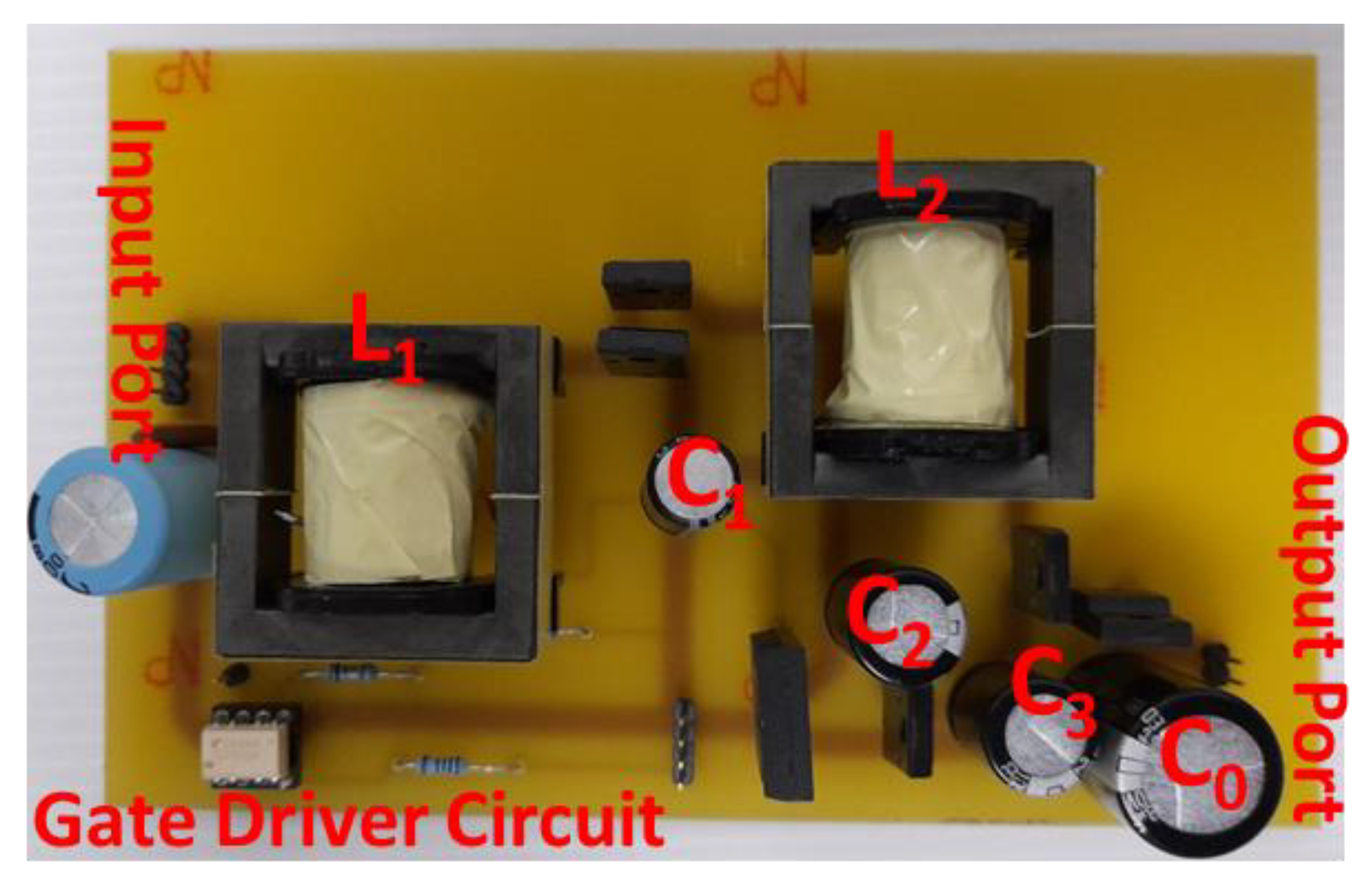
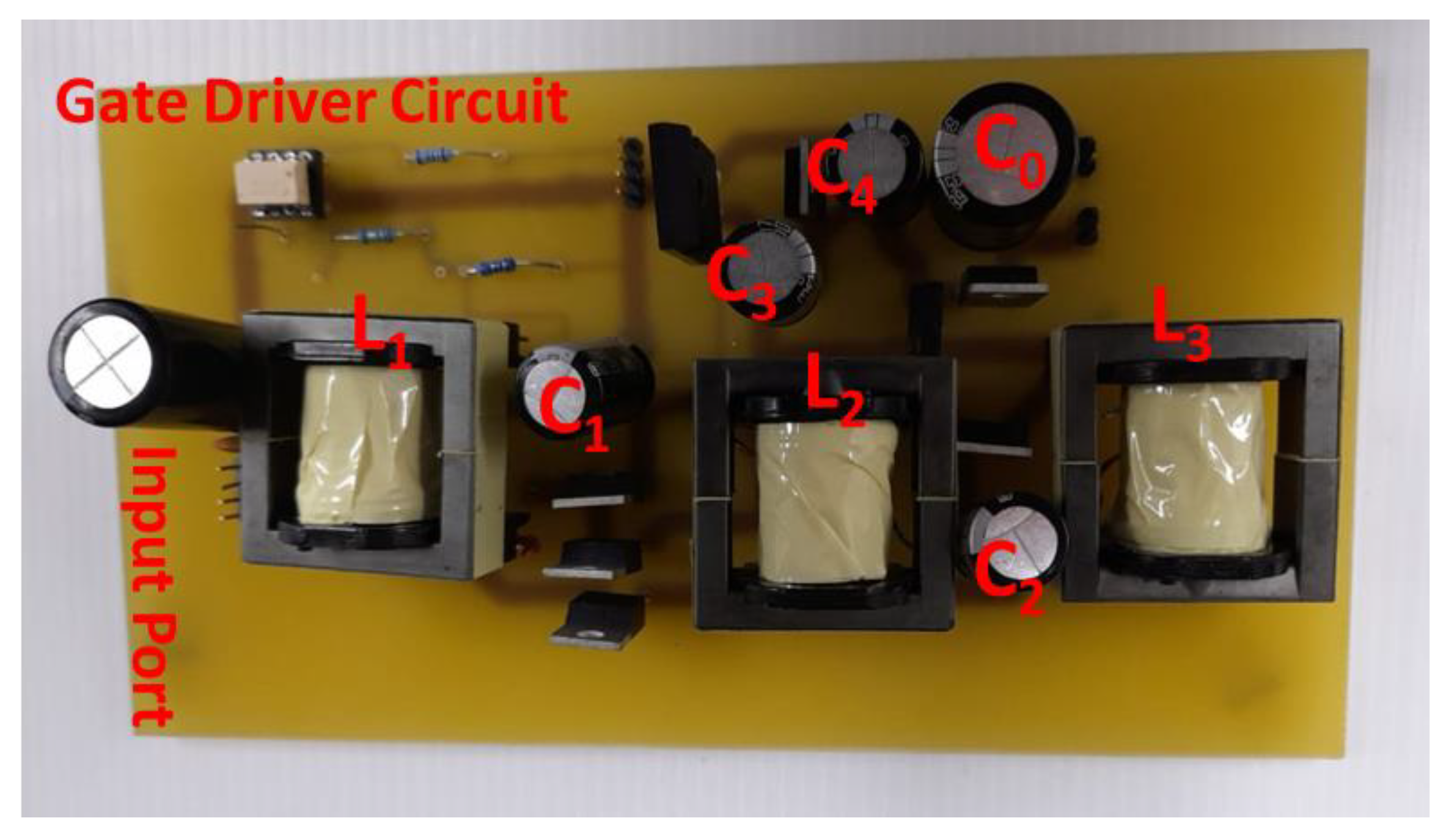
6. Experimental Verification of the Proposed Converters
6.1. Proposed Converter I
6.2. Proposed Converter II
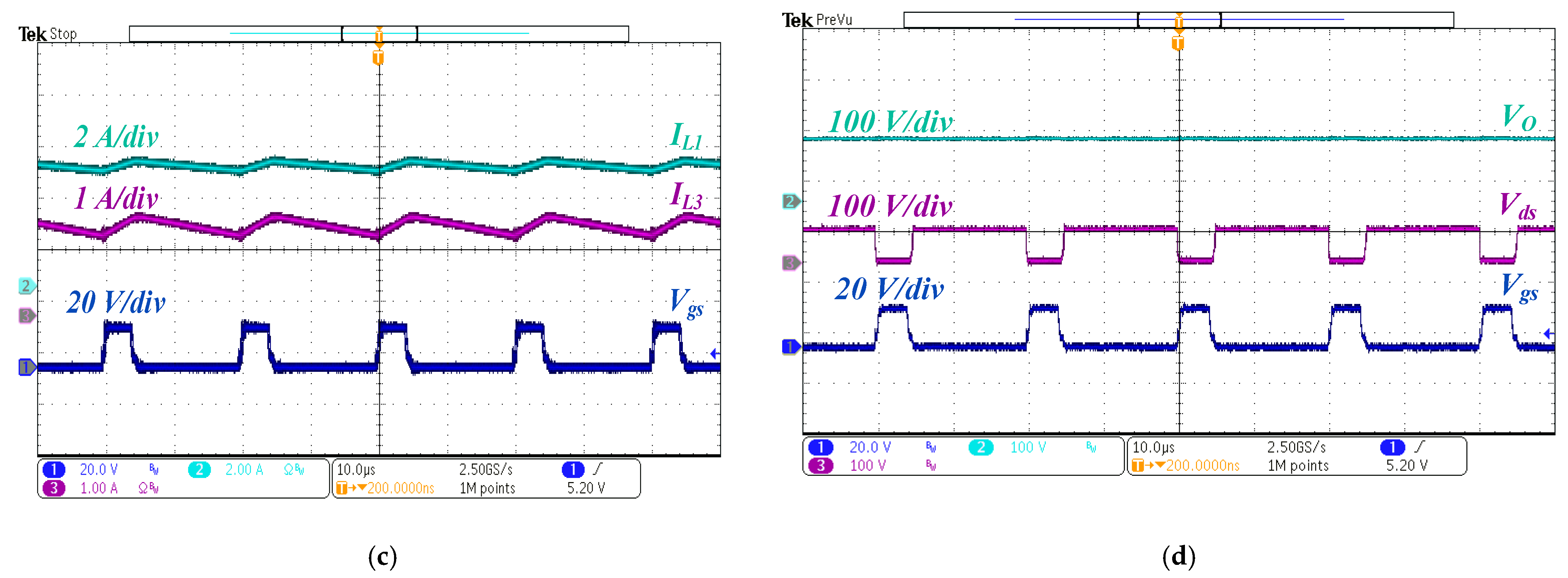
6.3. Proposed Converter III
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forouzesh, M.; Siwakoti, Y.P.; Gorji, S.A.; Blaabjerg, F.; Lehman, B. Step-Up DC–DC Converters: A Comprehensive Review of Voltage-Boosting Techniques, Topologies, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 9143–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroti, P.K.; Padmanaban, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Meraj, M.; Iqbal, A. A New Structure of High Voltage Gain SEPIC Converter for Renewable Energy Applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 89857–89868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayeghi, H.; Pourjafar, S.; Hashemzadeh, S.M. A switching capacitor based multi-port bidirectional DC–DC converter. IET Power Electron. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaf, S.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Meraj, M.; Iqbal, A.; Al-Emadi, N. A Novel Modified Switched Inductor Boost Converter With Reduced Switch Voltage Stress. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 1275–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahir, F.M.; Babaei, E.; Farsadi, M. Extended Topology for a Boost DC–DC Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Babu, N.R. Design and Development of Single Switch High Step-Up DC–DC Converter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 6, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Fu, D.; Wang, T.; Xu, Z. Hybrid Switched-Inductor Converters for High Step-Up Conversion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1480–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, T.; He, Y. A Switched-Capacitor-Based Active-Network Converter with High Voltage Gain. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumari, T.; Indragandhi, V.; Arunkumar, G.; Sanjeevikumar, P.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B. Implementation of a high-gain non-isolated DC-DC converter for PV-fed applications. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, T.; Prabha, S.U.; Sundaramoorthy, K. Non-isolated n-stage High Step-up DC-DC Converter for Low voltage DC Source Integration. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, S.; Baghramian, A.; Mojallali, H. Analysis and Modeling of a New Coupled-Inductor Buck–Boost DC–DC Converter for Renewable Energy Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 8088–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, S.; Siwakoti, Y.P.; Mostaan, A.; Blaabjerg, F. New Semiquadratic High Step-Up DC/DC Converter for Renewable Energy Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, R.; Tavakoli, A. A DC–DC boost converter with high voltage gain integrating three-winding coupled inductor with low input current ripple. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Do, H. Quadratic Boost DC–DC Converter with High Voltage Gain and Reduced Voltage Stresses. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Bian, Q.; Guan, Y.; Xu, D. A Single Switch Quadratic Boost High Step Up DC–DC Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 4387–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, M.S.; Almakhles, D.J.; Padmanaban, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Kumar, A.R.; Masebinu, S.O. Triple-Mode Active-Passive Parallel Intermediate Links Converter With High Voltage Gain and Flexibility in Selection of Duty Cycles. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 134716–134727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahim, O.; Funato, H.; Haruna, J. A comprehensive study of three high-gain DC-DC topologies based on Cockcroft-Walton voltage multiplier for reduced power PV applications. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 13, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi-Kangarlu, M.; Khiavi, A.M.; Neyshabouri, Y. A non-isolated single-input dual-output boost DC–DC converter. IET Power Electron. 2021, 14, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.; Ferdowsi, M.; Shamsi, P. A Family of Scalable Non-Isolated Interleaved DC-DC Boost Converters with Voltage Multiplier Cells. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 11707–11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraj, M.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Al-Emadi, N.; Rahman, S. Interleaved Multilevel Boost Converter with Minimal Voltage Multiplier Components for High-Voltage Step-Up Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 12816–12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Chuang, C.; Chu, C. A Novel Transformer-less Adaptable Voltage Quadrupler DC Converter with Low Switch Voltage Stress. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4787–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathi, P.; Natarajan, S. Single switch quasi Z-source based high voltage gain DC-DC converter. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinagh, F.A.A.; Yuan, J.; Yang, Y. Analysis and design of a high voltage-gain quasi-Z-source DC–DC converter. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, W.; Cortes, C.; Yamamoto, M.; Imaoka, J. Effect of inductor parasitic resistances on the voltage gain of high step-up DC–DC converters for electric vehicle applications. IET Power Electron. 2018, 11, 1628–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Zaid, M.; Sarwar, A.; Lin, C.-H.; Asim, M.; Yadav, R.K.; Tariq, M.; Satpathi, K.; Alamri, B. A New High-Gain DC-DC Converter with Continuous Input Current for DC Microgrid Applications. Energies 2021, 14, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Zaid, M.; Sarwar, A.; Tariq, M.; Sarwer, Z. A New Transformerless Quadratic Boost Converter with High Voltage Gain. Smart Sci. 2020, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilzadeh, T.; Rostami, N.; Babaei, E.; Maalandish, M. Non-Isolated Topology for High Step-Up DC-DC Converters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Yin, A.; Ghaderi, D. A transformer-less single-switch boost converter with high-voltage gain and mitigated-voltage stress applicable for photovoltaic utilizations. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, M.; Ahmad, J.; Sarwar, A.; Sarwer, Z.; Tariq, M.; Alam, A. A Transformerless Quadratic Boost High Gain DC-DC Converter. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), Jaipur, India, 16–19 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Maheri, H.M.; Sabahi, M.; Hosseini, S.H. Extendable Nonisolated High Gain DC-DC Converter Based on Active–Passive Inductor Cells. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9478–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Zaid, M.; Ahmad, J.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, S.; Sifat, Z.; Lin, C.-H.; Sarwar, A.; Tariq, M.; Alamri, B. A Non-Inverting High Gain DC-DC Converter with Continuous Input Current. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 54710–54721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



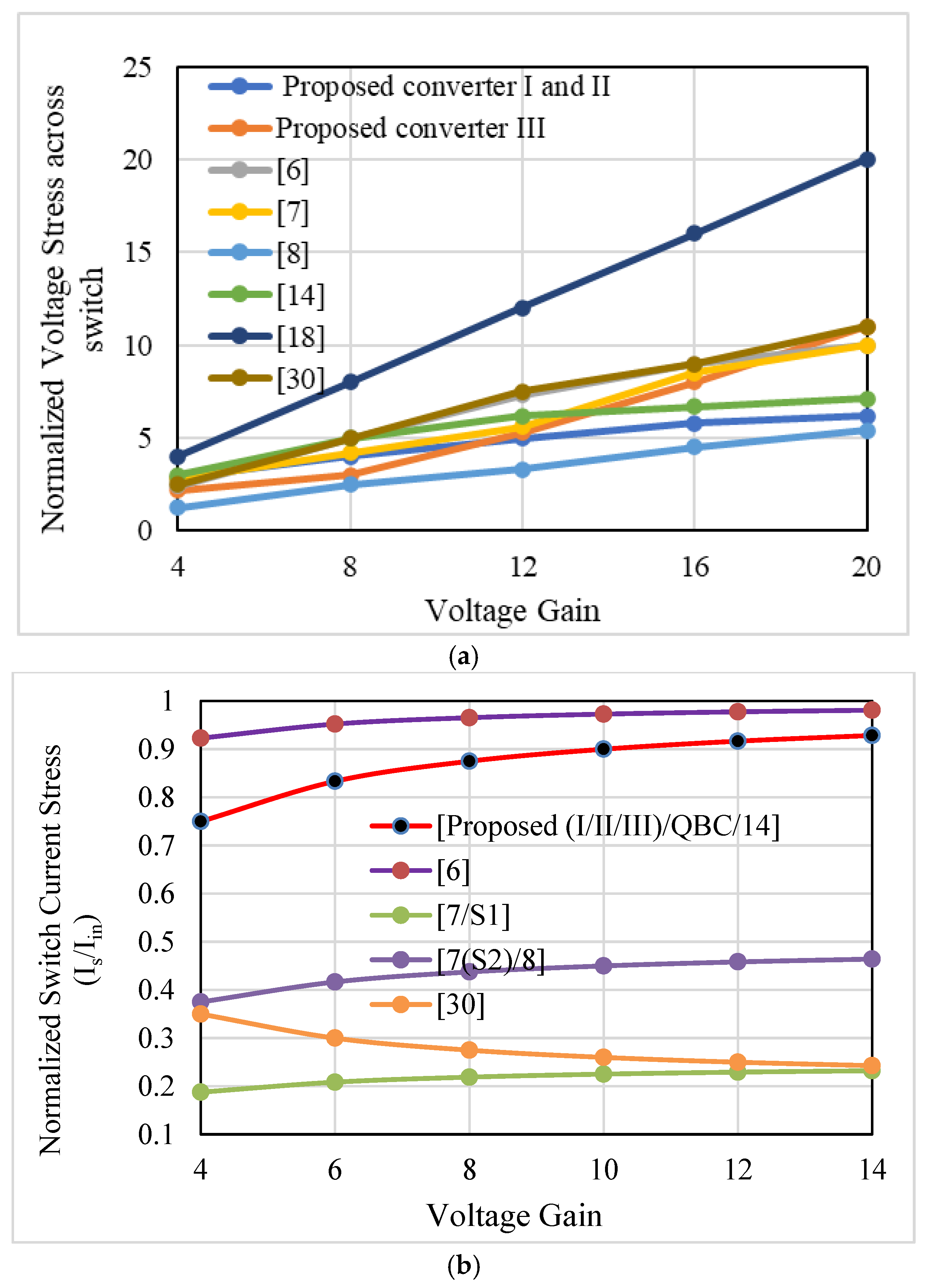

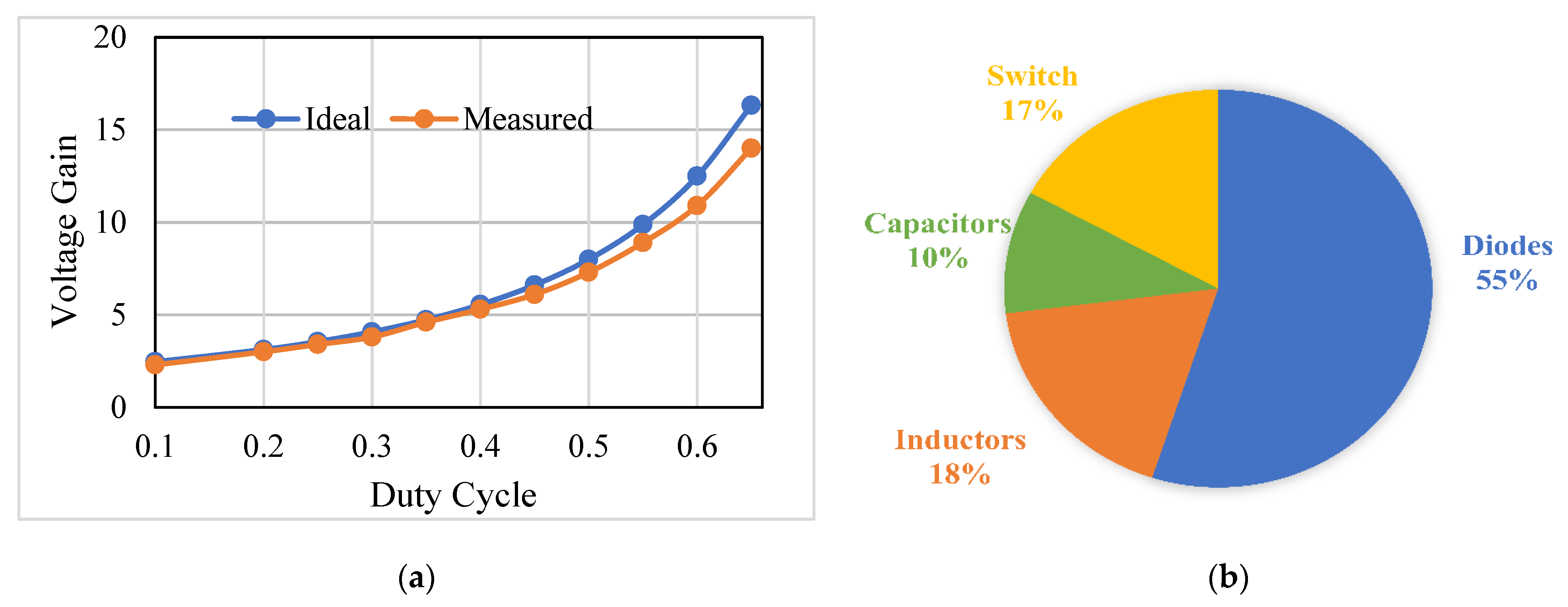




| Topology | Inductors | Capacitors | Switch | Diodes | Voltage Gain | Voltage across Switch | Common Ground |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [3] | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | Low | Yes | |
| [4] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | Low | Yes | |
| [5] | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | Low | Yes | |
| [6] | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | Low | Yes | |
| [7] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | Low | No | |
| [8] | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | Low | No | |
| [9] | 2 | 5 | 1 | 5 | Low | Yes | |
| [10] | 2 | 3 | 1 | 6 | Low | No | |
| [11] | 1 + 1 Coupled Inductor | 3 | 1 | 3 | High for a low value of n | Yes | |
| [14] | 1 + 1 Coupled Inductor | 3 | 1 | 5 | High | Yes | |
| [15] | 1 + 1 Transformer | 4 | 1 | 5 | Low | Yes | |
| [16] | n + 1 | n + 1 | n + 2 | n + 2 | n = no. of legs | Low | No |
| [17] | 2 | 4 | 1 | 6 | Low | No | |
| Conventional QBC | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | High | Yes | |
| [22] | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | Low | No | |
| [23] | 2 | 5 | 2 | 5 | Low | No | |
| [26] | 3 | 3 | 1 | 5 | High | Yes | |
| [27] | 3 | 6 | 2 | 5 | Low | No | |
| [28] | 3 | 6 | 1 | 6 | Low | No | |
| [29] | 3 | 4 | 1 | 6 | Low | Yes | |
| [30] | 8 | 1 | 4 | 17 | Low | Yes | |
| Proposed Converter I | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | Low | No | |
| Proposed Converter II | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | Low | No | |
| Proposed Converter III | 3 | 5 | 1 | 7 | Low | No |
| Topology | NL | NC | NSW | ND | MCCM | Average Switch Current Stress | MCCM at D = 0.5 | SCCM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | |||
| [7] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 5 | |||
| [8] | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 7 | |||
| [14] | 1 + 1 Coupled Inductor | 3 | 1 | 5 | 6 | |||
| QBC | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | |||
| [30] | 8 | 1 | 4 | 17 | 9 | |||
| Proposed Converter I | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 8 | |||
| Proposed Converter II | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 8 | |||
| Proposed Converter III | 3 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 16 |
| Elements | Specification |
|---|---|
| Maximum Power | 150 W |
| Input Voltage | 24 V |
| Switching Frequency | 50 kHz |
| Load Resistance | R = 200–400 Ω, Chroma electronic load simulator model 63202 |
| Inductors | L1 = L2 = 330 µH |
| Capacitors | C1 = 100 µF/63 V, C2 = C3 = 47 µF/200 V & CO = 68 µF/250 V |
| Power MOSFET | SPW52N50C3 |
| Diodes | SF8L60USM |
| Gate Drivers IC | TLP250H |
| Microcontroller | STM32 Nucleo H743ZI2, STM Microelectronics, Geneva, Switzerland |
| Elements | Specification |
|---|---|
| Maximum Power | 150 W |
| Input Voltage | 24 V |
| Switching Frequency | 50 kHz |
| Load Resistance | R = 350 Ω, Chroma electronic load simulator model 63202 |
| Inductors | L1 = L2 = 330 µH |
| Capacitors | C1 = 100 µF/63 V, C2 = C3 = 47 µF/200 V & CO = 68 µF/350 V |
| Power MOSFET | SPW52N50C3 |
| Diodes | SF8L60USM |
| Gate Drivers IC | TLP250H |
| Microcontroller | STM32 Nucleo H743ZI2, Microelectronics, Geneva Switzerland |
| Elements | Specification |
|---|---|
| Maximum Power | 150 W |
| Input Voltage | 24 V |
| Switching Frequency | 50 kHz |
| Load Resistance | R = 200 Ω, Chroma electronic load simulator model 63202 |
| Inductors | L1 = L 2= L3 = 330 µH |
| Capacitors | C1 = C2 = C3 = C4 = 47 µF/200 V CO = 68 µF/350 V |
| Power MOSFET | SPW52N50C3 |
| Diodes | SF8L60USM |
| Gate Drivers IC | TLP250H |
| Microcontroller | STM32 Nucleo H743ZI2 |
| Topology | Duty Ratio | Load Resistance | Capacitor Voltage | Inductor Current | Switch Stress | Output Voltage | Deviation from Ideal Voltage | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.4 | R = 200 Ω | 4.75% | 95.3% | ||||
| II | 0.4 | R = 350 Ω | 2.55% | 97.5% | ||||
| III | 0.2 | R = 200 Ω | 14.66% | 85.33% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaid, M.; Lin, C.-H.; Khan, S.; Ahmad, J.; Tariq, M.; Mahmood, A.; Sarwar, A.; Alamri, B.; Alahmadi, A. A Family of Transformerless Quadratic Boost High Gain DC-DC Converters. Energies 2021, 14, 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144372
Zaid M, Lin C-H, Khan S, Ahmad J, Tariq M, Mahmood A, Sarwar A, Alamri B, Alahmadi A. A Family of Transformerless Quadratic Boost High Gain DC-DC Converters. Energies. 2021; 14(14):4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144372
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaid, Mohammad, Chang-Hua Lin, Shahrukh Khan, Javed Ahmad, Mohd Tariq, Arshad Mahmood, Adil Sarwar, Basem Alamri, and Ahmad Alahmadi. 2021. "A Family of Transformerless Quadratic Boost High Gain DC-DC Converters" Energies 14, no. 14: 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144372
APA StyleZaid, M., Lin, C.-H., Khan, S., Ahmad, J., Tariq, M., Mahmood, A., Sarwar, A., Alamri, B., & Alahmadi, A. (2021). A Family of Transformerless Quadratic Boost High Gain DC-DC Converters. Energies, 14(14), 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144372










