Distributed Nonlinear AIMD Algorithms for Electric Bus Charging Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation and Objective
1.2. Literature Overview
1.3. Contributions
1.4. Outline of the Paper
2. Methodology and Preliminaries
2.1. AIMD Algorithm
2.2. NAIMD Algorithm
3. Charging Process and Bus Characteristics
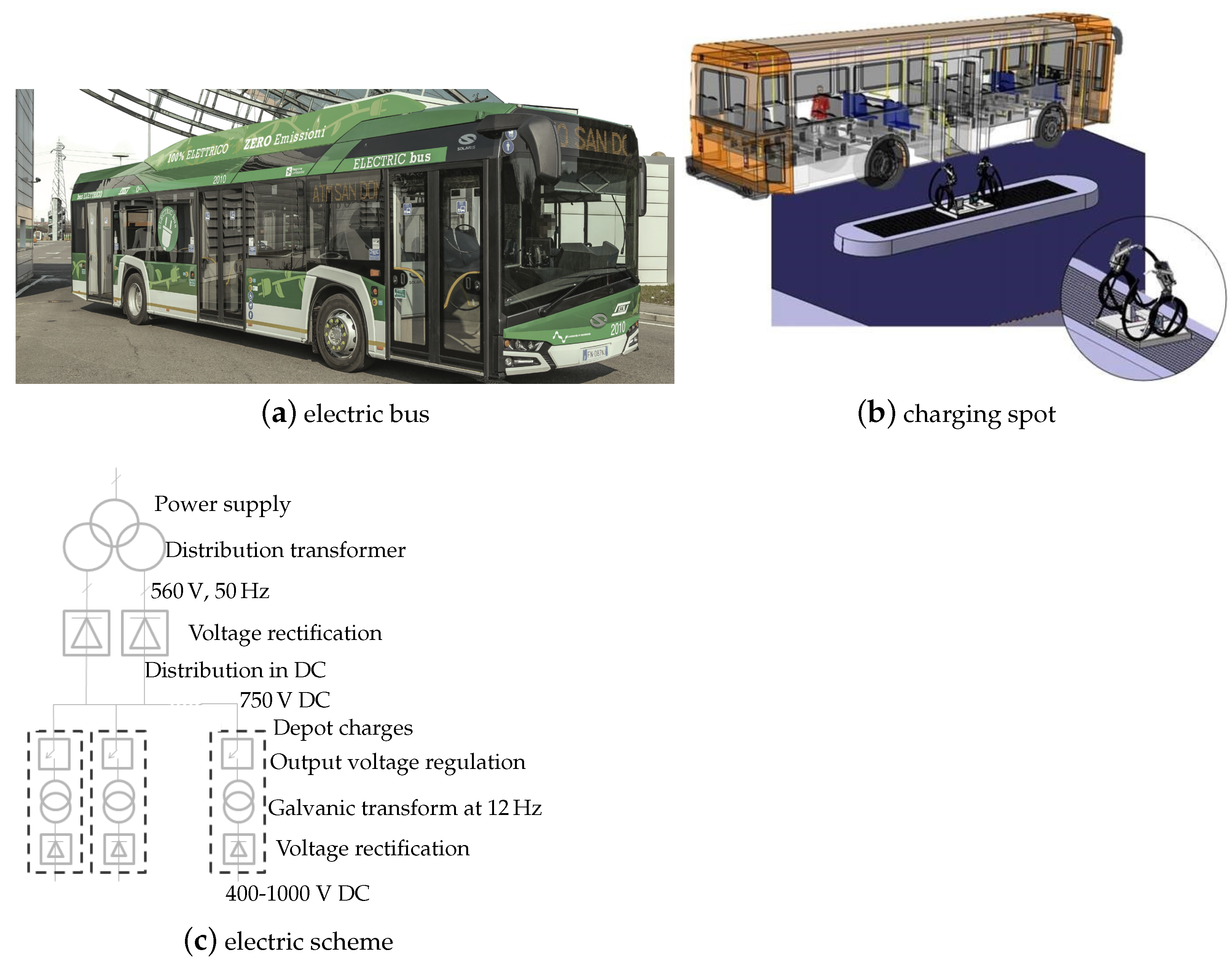
3.1. Power Plant and Depot Characteristics
- charging is executed after the service time when the buses are parked on the shunting area inside the depot;
- charging is also possible during the service time, by means of fast-charging spots at terminal stations.
3.2. Bus Characteristics
3.3. The Charging Rate Allocation Problem
4. The Adopted NAIMD Algorithm
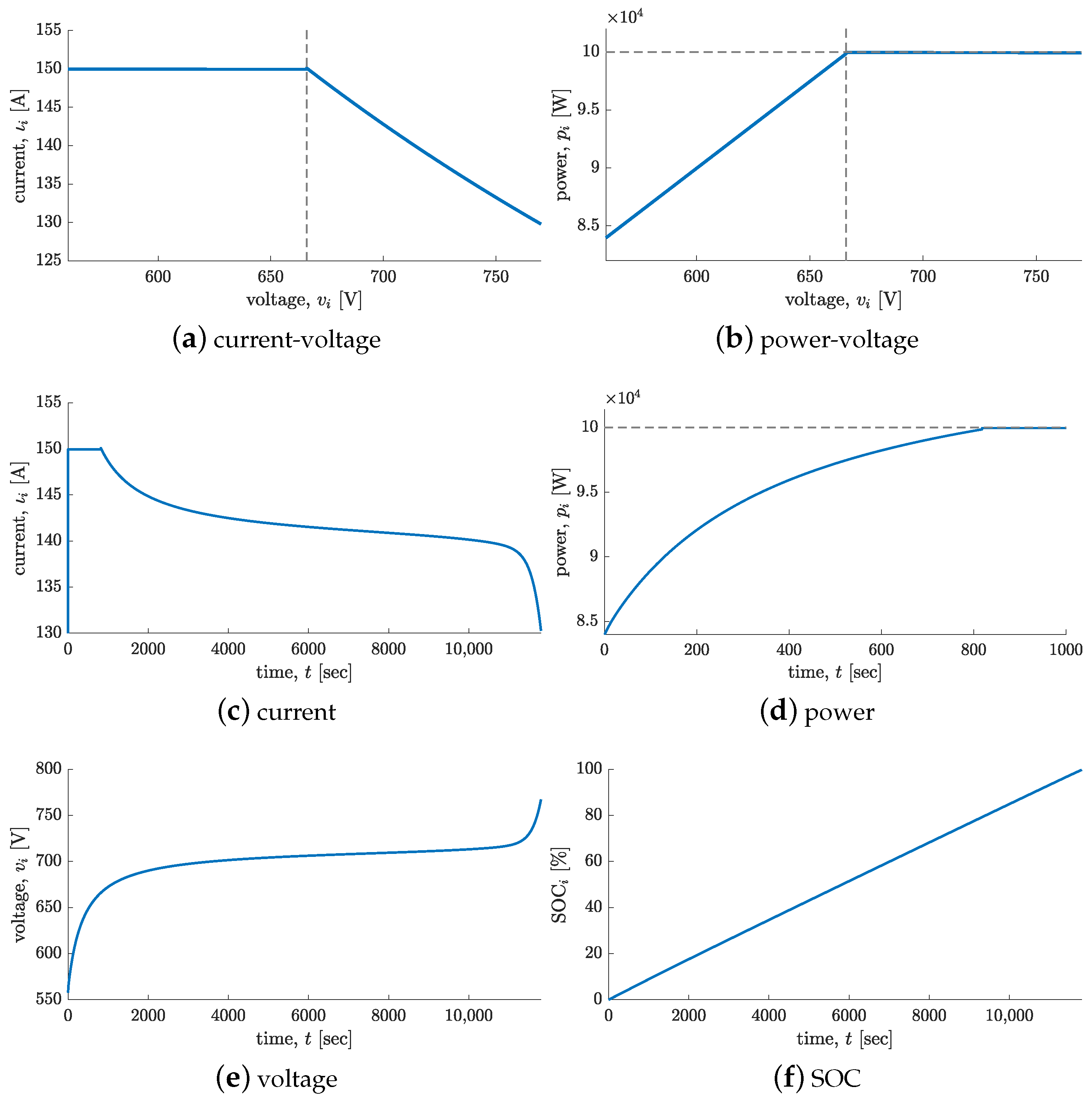
4.1. Recast of the Battery Model in the NAIMD Framework
4.2. Minimization of the Sum of Charging Times
4.3. The Proposed NAIMD Solution
4.4. Convergence Considerations
5. Case Studies
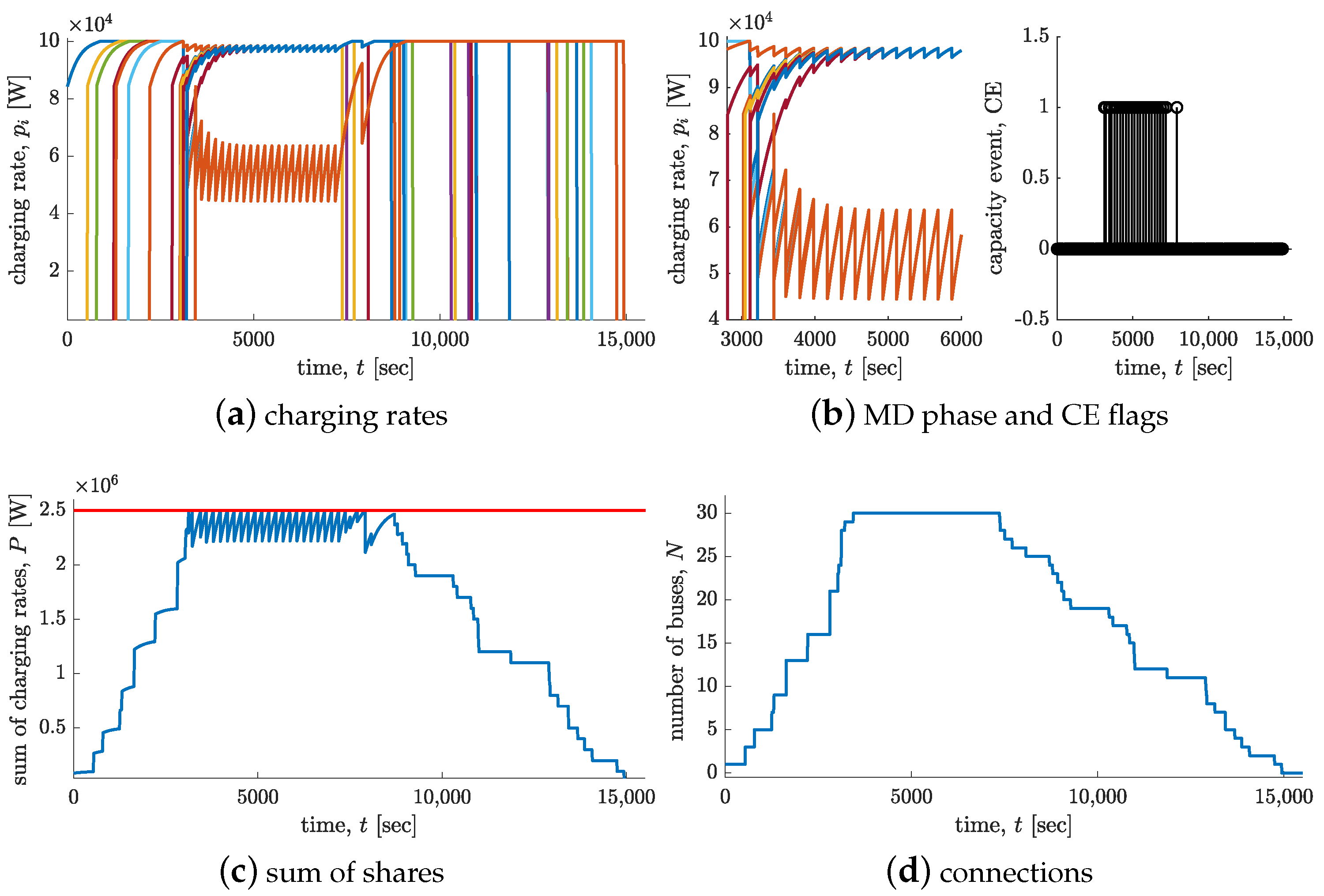
5.1. Case Study 1: Charging Rate Allocation of an Existing Plant
5.2. Case Study 2: Sizing of a Bus Charging Plant
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Additive Increase |
| AIMD | Additive Increase Multiplicative Decrease |
| CE | Capacity Event |
| EMS | Energy Management System |
| EV | Electric Vehicle |
| LS | Least Square |
| MD | Multiplicative Decrease |
| NAIMD | Nonlinear Additive Increase Multiplicative Decrease |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition |
References
- Sneha Angeline, P.; Newlin Rajkumar, M. Evolution of electric vehicle and its future scope. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 3930–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.; Tammi, K.; Kalita, K.; Mahanta, P. Impact of Electric Vehicle Charging Station Load on Distribution Network. Energies 2018, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouramdane, O.; Elbouchikhi, E.; Amirat, Y.; Sedgh Gooya, E. Optimal Sizing and Energy Management of Microgrids with Vehicle-to-Grid Technology: A Critical Review and Future Trends. Energies 2021, 14, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, J.; Dimitrova, Z.; Petit, M.; Dessante, P. Optimization and Coordination of Electric Vehicle Charging Process for Long-Distance Trips. Energies 2021, 14, 4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, W.; Wei, S.; Wang, Z. Optimization of an Energy Storage System for Electric Bus Fast-Charging Station. Energies 2021, 14, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Cheng, L.; Wen, L.; Lu, X.; Ding, T. A coordinated charging scheduling method for electric vehicles considering different charging demands. Energy 2020, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolaki-Iosifidou, E.; Codani, P.; Kempton, W. Measurement of power loss during electric vehicle charging and discharging. Energy 2017, 127, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bi, S.; Zhang, Y.J.A.; Huang, J. Electrical Vehicle Charging Station Profit Maximization: Admission, Pricing, and Online Scheduling. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Wang, L. Real-Time Charging Navigation of Electric Vehicles to Fast Charging Stations: A Hierarchical Game Approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yan, Z.; Feng, D.; Zhao, X. Decentralized charging control strategy of the electric vehicle aggregator based on augmented Lagrangian method. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 104, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, L.; Ouyang, M.; Wang, H.; Lu, L.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Optimal decentralized valley-filling charging strategy for electric vehicles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 78, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Hu, Z.; Song, Y.; Lu, N.; Xu, Z.; Jia, L. A probability transition matrix based decentralized electric vehicle charging method for load valley filling. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 125, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireshika, M.A.S.T.; Lliuyacc-Blas, R.; Kepplinger, P. Voltage-Based Droop Control of Electric Vehicles in Distribution Grids under Different Charging Power Levels. Energies 2021, 14, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, W.; Cao, D.; Dragičević, T.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. Electric Vehicle Charging Management Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. J. Modern Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corless, M.; King, C.; Shorten, R.; Wirth, F. AIMD Dynamics and Distributed Resource Allocation; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Stuedli, S.; Corless, M.; Middleton, R.; Shorten, R. On the AIMD Algorithm Under Saturation Constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 62, 6392–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studli, S.; Crisostomi, E.; Middleton, R.; Shorten, R. A flexible distributed framework for realising electric and plug-in hybrid vehicle charging policies. Int. J. Control 2012, 85, 1130–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studli, S.; Crisostomi, E.; Middleton, R.; Shorten, R. Optimal real-time distributed V2G and G2V management of electric vehicles. Int. J. Control 2014, 87, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisostomi, E.; Shorten, R.; Studli, S.; Wirth, F. Electric and Plug-in Hybrid Vehicle Networks: Optimization and Control; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nisar Shah, S.; Incremona, G.P.; Bolzern, P.; Colaneri, P. Optimization based AIMD saturated algorithms for public charging of electric vehicles. Eur. J. Control 2019, 47, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschella, M.; Murad, M.A.A.; Crisostomi, E.; Milano, F. Decentralized Charging of Plug-In Electric Vehicles and Impact on Transmission System Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasio, M. Optimization AIMD Algorithms for a Real Electric Bus Charging Plant. Master’s Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, D.M.; Jain, R. Analysis of the Increase and Decrease Algorithms for Congestion Avoidance in Computer Networks. Comput. Netw. Isdn Syst. 1989, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozzi, A.; Torchio, M.; Braatz, R.D.; Raimondo, D.M. Optimal charging of an electric vehicle battery pack: A real-time sensitivity-based model predictive control approach. J. Power Sources 2020, 461, 228133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houbbadi, A.; Trigui, R.; Pelissier, S.; Redondo-Iglesias, E.; Bouton, T. Optimal Scheduling to Manage an Electric Bus Fleet Overnight Charging. Energies 2019, 12, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Song, Z.; He, Y. Planning of Fast-Charging Stations for a Battery Electric Bus System under Energy Consumption Uncertainty. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Bus i | (s) | (kW h) | (h min) | (h min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 34.14 | 3 h 18 | 3 h 18 |
| 2 | 538 | 5.6 | 3 h 35 | 3 h 44 |
| 3 | 538 | 109.11 | 1 h 59 | 2 h 8 |
| 4 | 784 | 85.93 | 2 h 47 | 3 h |
| 5 | 784 | 124.737 | 1 h 50 | 2 h 3 |
| 6 | 1252 | 90.47 | 2 h 10 | 2 h 31 |
| 7 | 1252 | 118.51 | 1 h 54 | 2 h 14 |
| 8 | 1311 | 102.58 | 2 h 3 | 2 h 25 |
| 9 | 1311 | 100.27 | 2 h 4 | 2 h 26 |
| 10 | 1637 | 148.54 | 1 h 35 | 2 h 3 |
| 11 | 1637 | 145.03 | 1 h 38 | 1 h 5 |
| 12 | 1637 | 24.04 | 3 h 24 | 3 h 52 |
| 13 | 1637 | 50.82 | 3 h 28 | 3 h 36 |
| 14 | 2218 | 66.62 | 2 h 59 | 3 h 36 |
| 15 | 2218 | 45.24 | 3 h 12 | 3 h 49 |
| 16 | 2218 | 121.80 | 1 h 52 | 2 h 29 |
| 17 | 2809 | 76.50 | 2 h 53 | 3 h 40 |
| 18 | 2809 | 82.67 | 2 h 49 | 3 h 18 |
| 19 | 2809 | 68.85 | 2 h 57 | 3 h 44 |
| 20 | 2809 | 50.66 | 3 h 8 | 3 h 55 |
| 21 | 2809 | 87.33 | 2 h 14 | 3 h 1 |
| 22 | 3023 | 141.22 | 1 h 40 | 2 h 30 |
| 23 | 3023 | 32.51 | 3 h 19 | 4 h 10 |
| 24 | 3049 | 103.74 | 2 h 3 | 2 h 53 |
| 25 | 3117 | 108.50 | 1 h 59 | 2 h 55 |
| 26 | 3117 | 137.10 | 1 h 43 | 2 h 38 |
| 27 | 3117 | 89.24 | 2 h 11 | 3 h 7 |
| 28 | 3117 | 89.70 | 2 h 11 | 3 h 6 |
| 29 | 3215 | 92.32 | 2 h 9 | 2 h 3 |
| 30 | 3441 | 44.60 | 3 h 9 | 4 h 6 |
| (MW) | (h min) | (h min) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 h 11′ | 9 h 44′ |
| 1.5 | 3 h 55′ | 7 h 50′ |
| 2 | 3 h 26′ | 7 h 1′ |
| Bus i | 09:00 10:00 | 10:00 11:00 | 11:00 12:00 | 12:00 13:00 | 13:00 14:00 | 14:00 15:00 | 15:00 16:00 | 16:00 17:00 | 17:00 18:00 | 18:00 19:00 | 19:00 20:00 | 20:00 21:00 | 21:00 22:00 | 22:00 23:00 | 23:00 24:00 | 24:00 01:00 | 01:00 02:00 | 02:00 03:00 | 03:00 04:00 | 04:00 05:00 | 05:00 06:00 | 06:00 07:00 | 07:00 08:00 | 08:00 09:00 |
| 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 35 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 39 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 43 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 44 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 48 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 49 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50 |
| J (h) | # CEs | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 346.77 | 491 |
| 1.5 | 226.52 | 74 |
| 2 | 195.12 | 12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravasio, M.; Incremona, G.P.; Colaneri, P.; Dolcini, A.; Moia, P. Distributed Nonlinear AIMD Algorithms for Electric Bus Charging Plants. Energies 2021, 14, 4389. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154389
Ravasio M, Incremona GP, Colaneri P, Dolcini A, Moia P. Distributed Nonlinear AIMD Algorithms for Electric Bus Charging Plants. Energies. 2021; 14(15):4389. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154389
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavasio, Matteo, Gian Paolo Incremona, Patrizio Colaneri, Andrea Dolcini, and Piero Moia. 2021. "Distributed Nonlinear AIMD Algorithms for Electric Bus Charging Plants" Energies 14, no. 15: 4389. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154389
APA StyleRavasio, M., Incremona, G. P., Colaneri, P., Dolcini, A., & Moia, P. (2021). Distributed Nonlinear AIMD Algorithms for Electric Bus Charging Plants. Energies, 14(15), 4389. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154389






