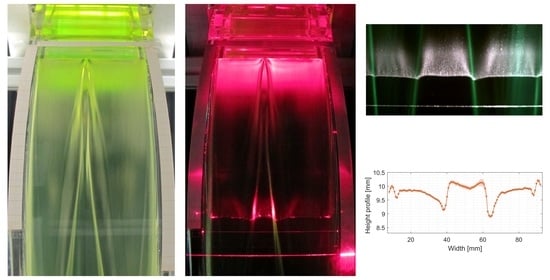
Wake Shape and Height Profile Measurements in a Concave Open Channel Flow regarding the Target in DONES
Abstract
:1. Introduction
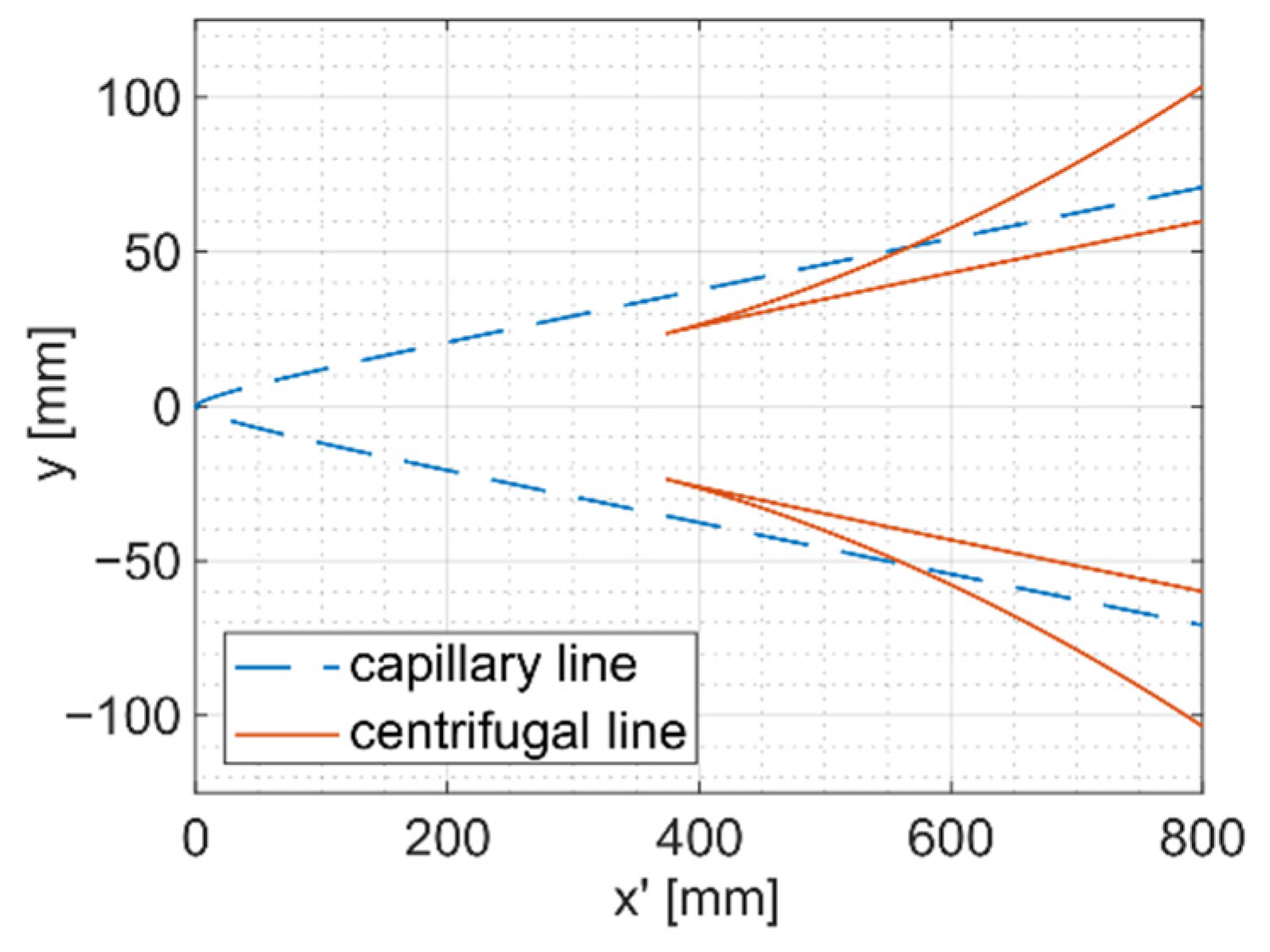
2. Analytical Wake Equations
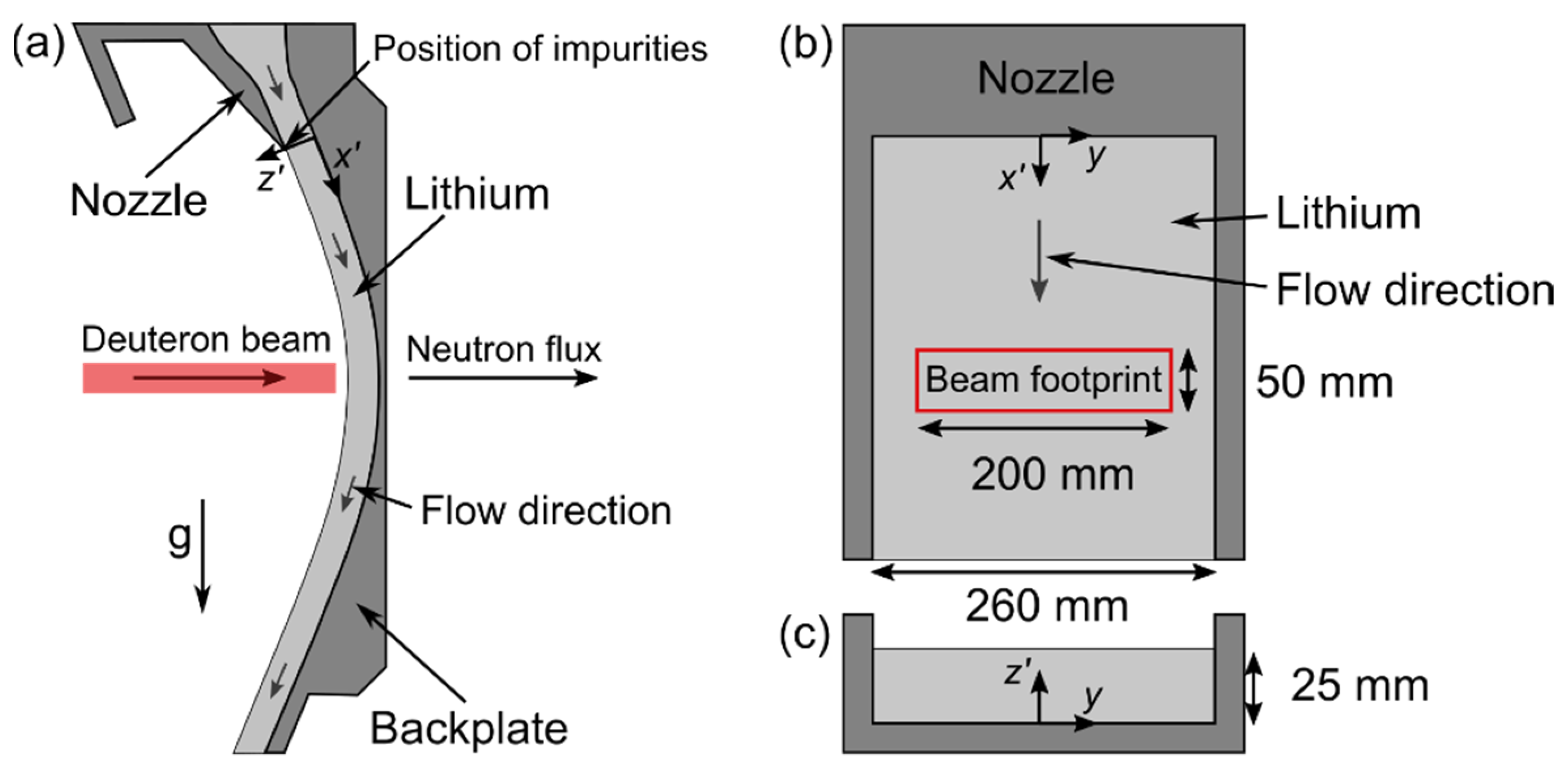
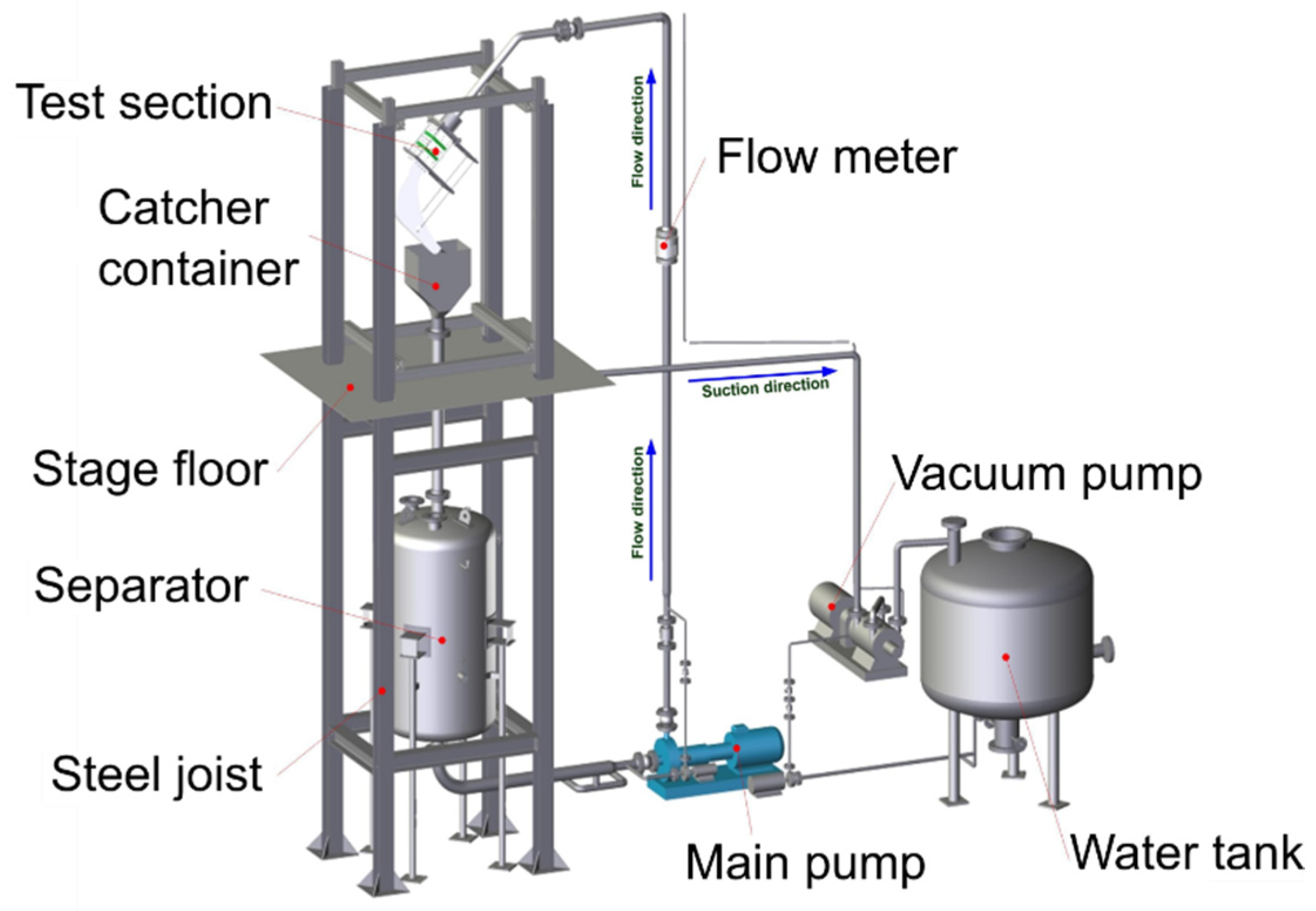
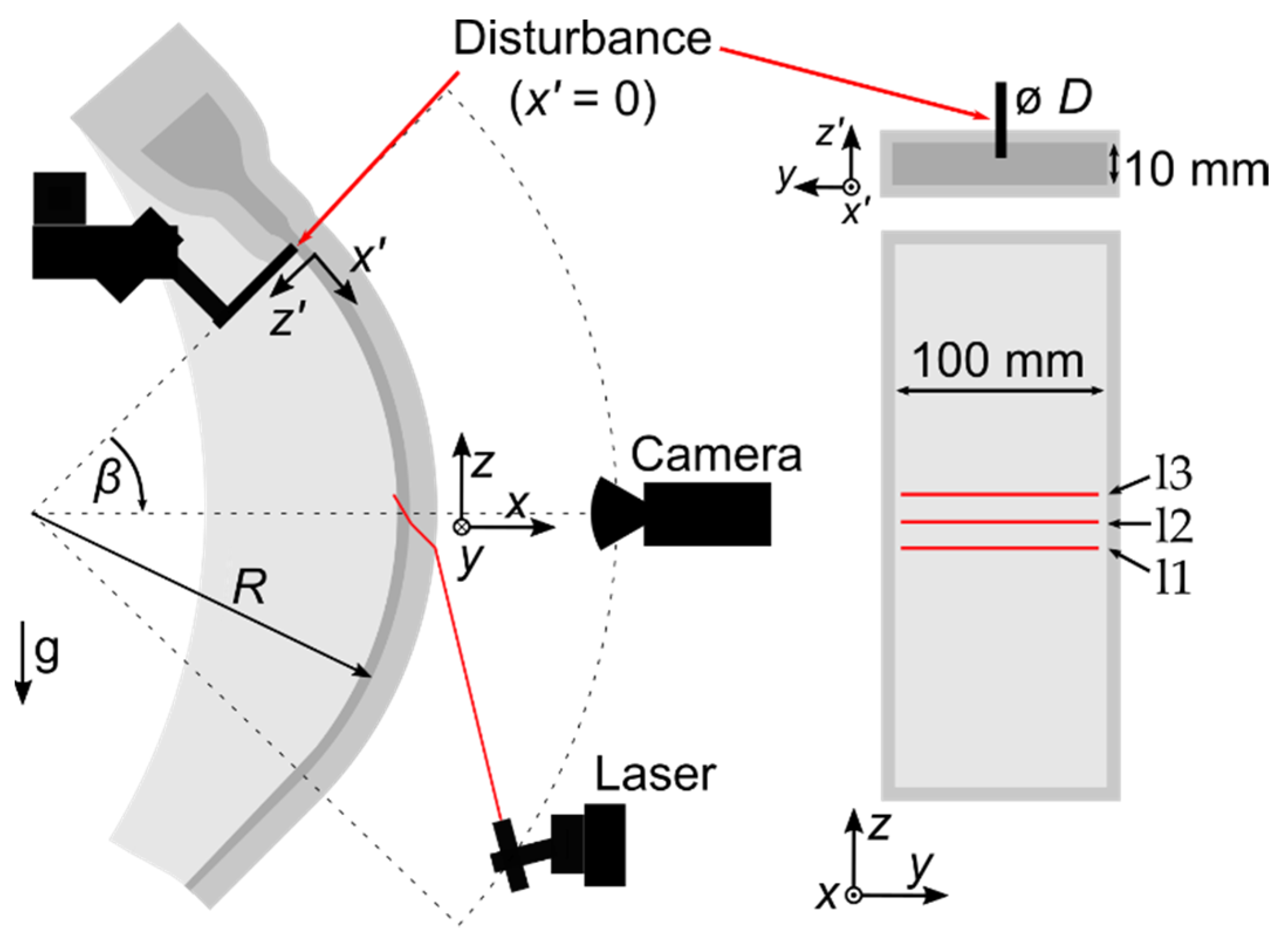
3. Experimental Setup
4. Experimental Results
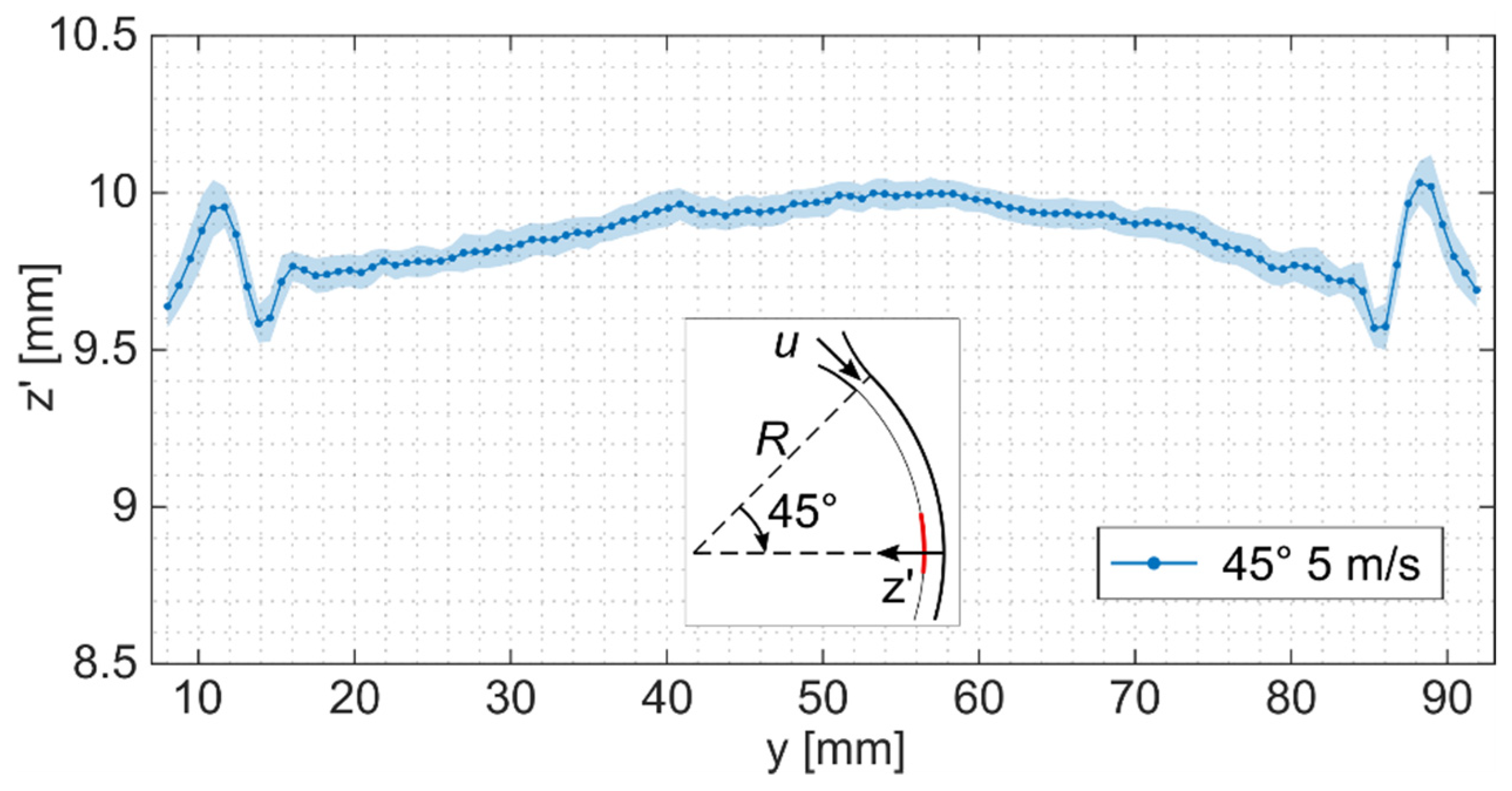
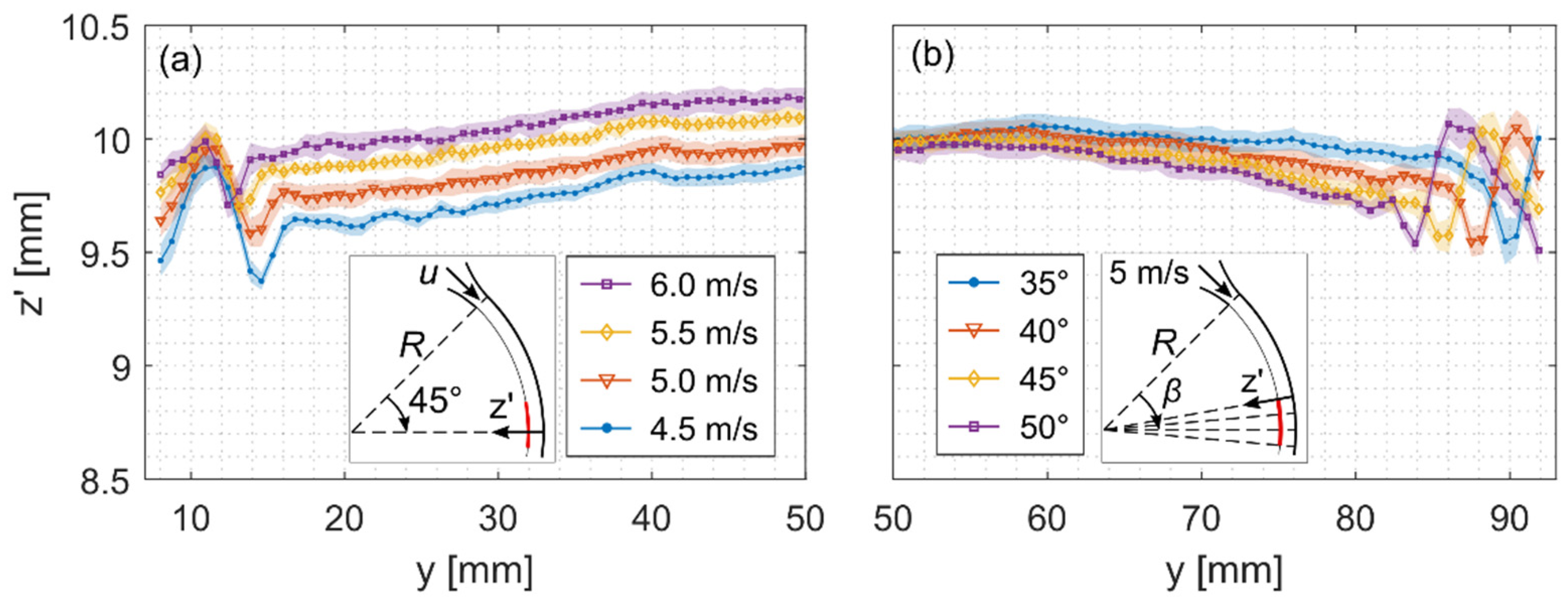
4.1. Undisturbed Height Profile Measurements
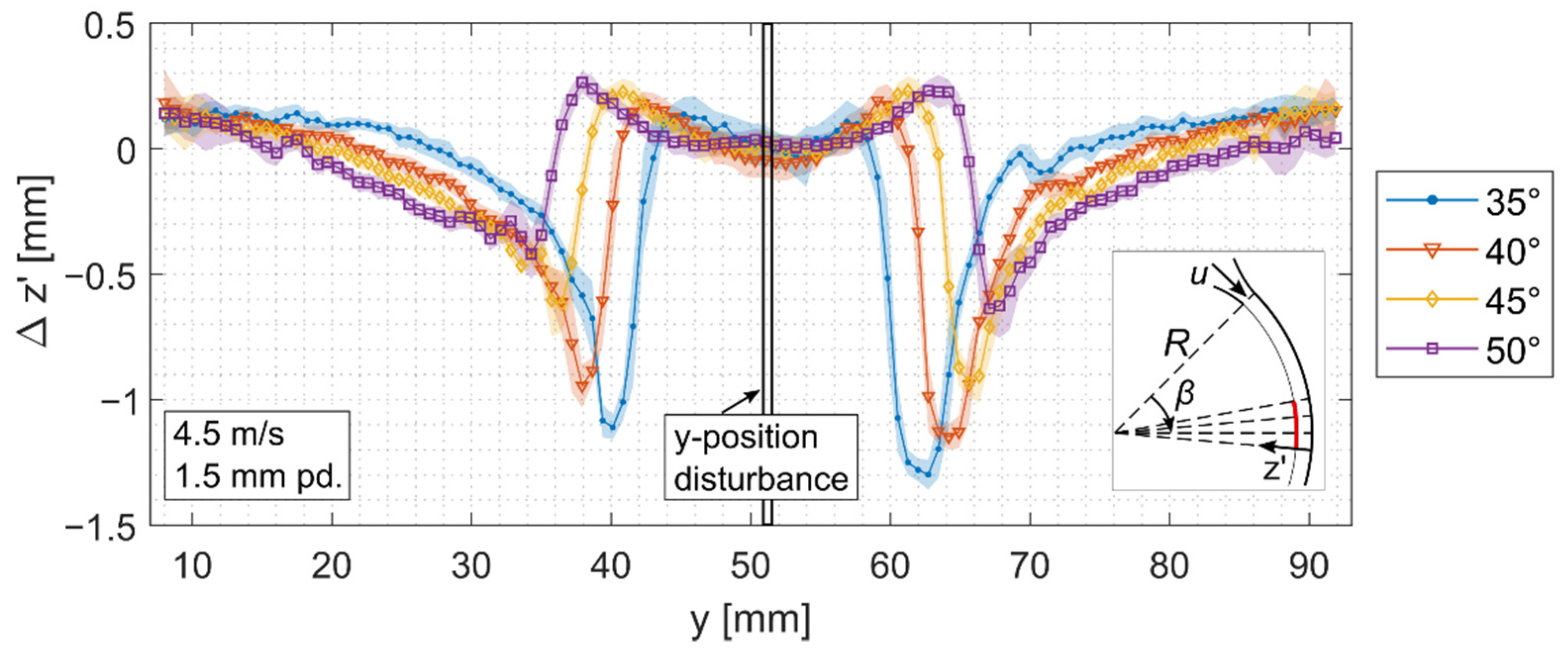
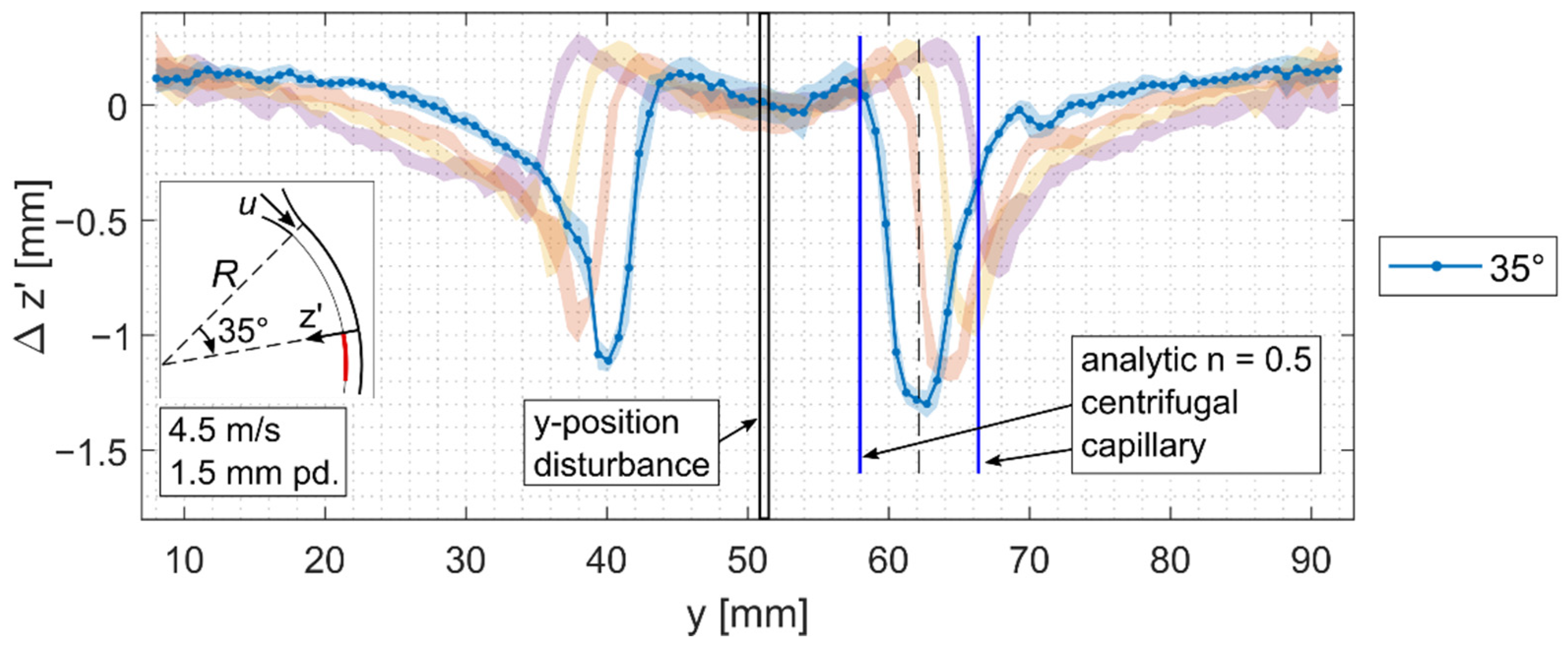
4.2. Disturbance Induced Wake Profile Measurements
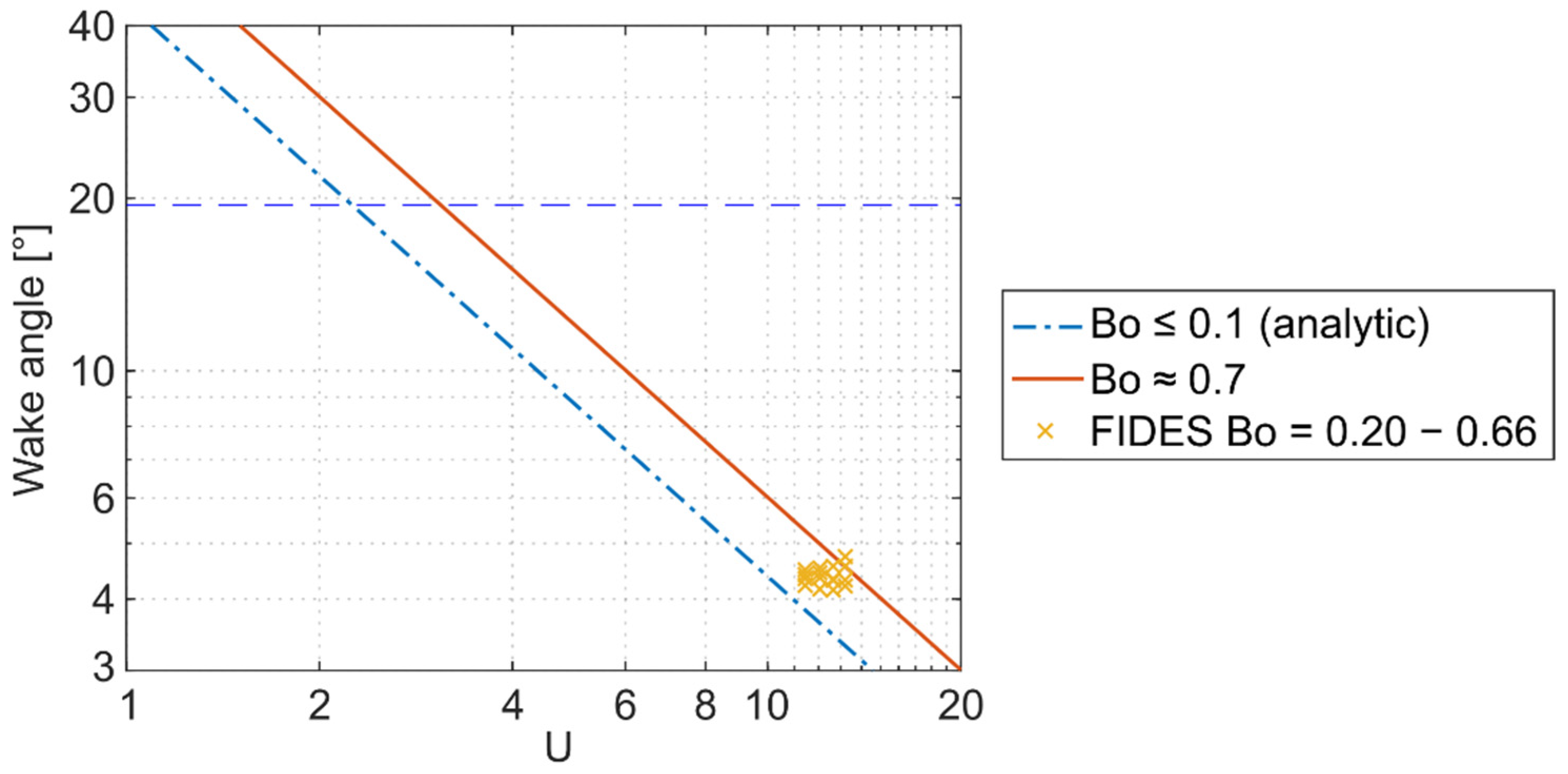
4.3. Wake Angle Evaluation
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knaster, J.; Moeslang, A.; Muroga, T. Materials research for fusion. Nat. Phys. 2016, 12, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, M.; Nakamura, H.; Nakamura, H.; Nakamura, H.; Ezato, K.; Takeuchi, H. Thermal-hydraulic characteristics of IFMIF liquid lithium target. Fusion Eng. Des. 2002, 63–64, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Fujisato, A.; Yamaoka, N.; Inoue, S.; Miyamoto, S.; Sato, F.; Iida, T.; Horiike, H.; Matushita, I.; Ida, M.; et al. High speed lithium flow experiments for IFMIF target. J. Nucl. Mater. A 2004, 329–333, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Kanemura, T.; Furukawa, T.; Hirakawa, Y.; Wakai, E.; Knaster, J. Validation of liquid lithium target stability for an intense neutron source. Nucl. Fusion 2017, 57, 066008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemura, T.; Kondo, H.; Furukawa, T.; Hirakawa, Y.; Hoashi, E.; Yoshihashi, S.; Horiike, H.; Wakai, E. Measurement of lithium target surface velocity in the IFMIF/EVEDA lithium test loop. Fusion Eng. Des. 2016, 109–111, 1682–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Kanemura, T.; Yamaoka, N.; Miyamoto, S.; Ida, M.; Nakamura, H.; Matushita, I.; Muroga, T.; Horiike, H. Measurement of free surface of liquid metal lithium jet for IFMIF target. Fusion Eng. Des. 2007, 82, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaud, M.; Moisy, F. Ship Wakes: Kelvin or Mach Angle? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 214503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, H. Hydrodynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1916. [Google Scholar]
- Darmon, A.; Benzaquen, M.; Raphaël, E. Kelvin wake pattern at large Froude numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 738, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moisy, F.; Rabaud, M. Mach-like capillary-gravity wakes. Phys. Rev. 2014, E90, 023009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pethiyagoda, R.; Moroney, T.; Lustri, C.; McCue, S. Kelvin wake pattern at small Froude numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 915, A126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblesse, F.; He, J.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, R.; Yang, C. Why can ship wakes appear narrower than Kelvin’s angle? Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2014, 46, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageorges, V.; Peixinho, J.; Perret, G. Flow and air entrainment around partially submerged vertical cylinders. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2019, 4, 064801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaplin, J.R.; Teigen, P. Steady flow past a vertical surface-piercing circular cylinder. J. Fluids Struct. 2003, 18, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.; Yang, J.; Yeon, S.M.; Stern, F. Reynolds and froude number effect on the flow past an interface-piercing circular cylinder. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2014, 6, 529–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bestehorn, M. Hydrodynamik und Strukturbildung; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lighthill, J. Waves in Fluids; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- acA2040-55uc—Basler Ace. Basler AG, 22926 Ahrensburg, Germany. Available online: https://www.baslerweb.com/de/produkte/kameras/flaechenkameras/ace/aca2040-55uc/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- KOWA LM16JC3M2. Kowa Optimed Deutschland GmbH, 40233 Düsseldorf, Germany. Available online: https://www.kowa-lenses.com/lm16jc3m2-3mp-industrieobjektiv-c-mount (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- MATLAB R. The MathWorks Inc., Natick, Massachusetts 01760, USA. 2019. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Confocal Displacement Sensor CL-3000. KEYENCE DEUTSCHLAND GmbH, 63263 Neu-Isenburg, Germany. Available online: https://www.keyence.de/products/measure/laser-1d/cl-3000/models/cl-3000/ (accessed on 22 September 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brenneis, B.; Gordeev, S.; Ruck, S.; Stoppel, L.; Hering, W. Wake Shape and Height Profile Measurements in a Concave Open Channel Flow regarding the Target in DONES. Energies 2021, 14, 6506. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206506
Brenneis B, Gordeev S, Ruck S, Stoppel L, Hering W. Wake Shape and Height Profile Measurements in a Concave Open Channel Flow regarding the Target in DONES. Energies. 2021; 14(20):6506. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206506
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrenneis, Björn, Sergej Gordeev, Sebastian Ruck, Leonid Stoppel, and Wolfgang Hering. 2021. "Wake Shape and Height Profile Measurements in a Concave Open Channel Flow regarding the Target in DONES" Energies 14, no. 20: 6506. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206506
APA StyleBrenneis, B., Gordeev, S., Ruck, S., Stoppel, L., & Hering, W. (2021). Wake Shape and Height Profile Measurements in a Concave Open Channel Flow regarding the Target in DONES. Energies, 14(20), 6506. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206506