Experimental Investigation of the Heat Transfer Characteristics of Plate Heat Exchangers Using LiBr/Water as Working Fluid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
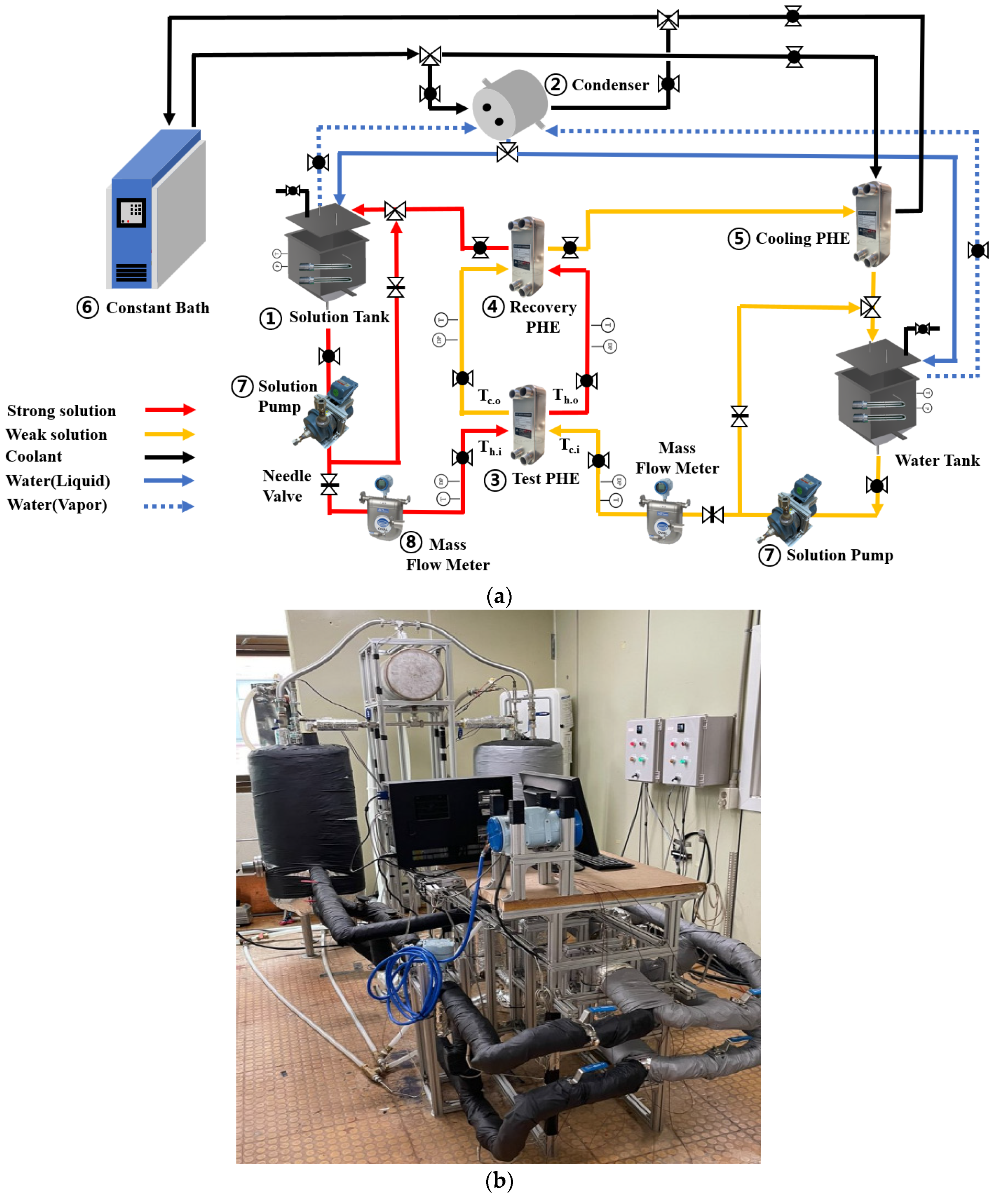
2.1. Experimental Apparatus
2.2. Data Reduction
2.2.1. Heat Transfer Analysis
2.2.2. Uncertainty Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of Heat Transfer Performances of Water and LiBr
3.2. Development of Nu Correlation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamamoto, T.; Ozaki, A.; Lee, M. Optimal air conditioner placement using a simple thermal environment analysis method for continuous large spaces with predominant advection. Energies 2021, 14, 4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garc, Y.; Best, R.; Hugo, G.; Vargas, A.; Rivera, W.; Jim, C. A Cascade Proportional Integral Derivative Control for a Plate-Heat-Exchanger-Based Solar Absorption Cooling System. Energies 2021, 14, 4058. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Fu, L.; Zhang, S. A review of working fluids of absorption cycles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruta, P.; Bujok, T.; Mika, Ł.; Sztekler, K. Adsorbents, Working Pairs and Coated Beds for Natural Refrigerants in Adsorption Chillers—State of the Art. Energies 2021, 14, 4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinnia, S.M.; Naghashzadegan, M.; Kouhikamali, R. CFD simulation of adiabatic water vapor absorption in large drops of water-LiBr solution. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 102, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfand, F.; Stiriba, Y.; Bourouis, M. CFD simulation to investigate heat and mass transfer processes in a membrane-based absorber for water-LiBr absorption cooling systems. Energy 2015, 91, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Xie, X.; Jiang, Y. Numerical research on flow characteristics in a plate type falling film heat exchanger for a LiBr-H2O absorption heat pump. Procedia Eng. 2017, 205, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edreis, E.; Petrov, A. Types of heat exchangers in industry, their advantages and disadvantages, and the study of their parameters. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 963, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Elmaaty, T.M.; Kabeel, A.E.; Mahgoub, M. Corrugated plate heat exchanger review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.S.; Khan, M.S.; Chyu, M.C.; Ayub, Z.H. Experimental investigation of single phase convective heat transfer coefficient in a corrugated plate heat exchanger for multiple plate configurations. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attalla, M.; Maghrabie, H.M. Investigation of effectiveness and pumping power of plate heat exchanger with rough surface. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 211, 115277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegarian, R.; Moraveji, M.K.; Aloueyan, A. Experimental investigation on heat transfer characteristics and pressure drop of BPHE (brazed plate heat exchanger) using TiO2–water nanoflu. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2016, 74, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, B.; Sundar, L.S. Experimental study on heat transfer, friction factor, entropy and exergy efficiency analyses of a corrugated plate heat exchanger using Ni/water nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 165, 106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wu, Z.; Sunden, B. Pressure drop and convective heat transfer of Al2O3/water and MWCNT/water nanofluids in a chevron plate heat exchanger. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 89, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrangzade, A.; Heyhat, M.M. The effect of using nano-silver dispersed water based nanofluid as a passive method for energy efficiency enhancement in a plate heat exchanger. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 102, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vega, M.; Almendros-Ibañez, J.A.; Ruiz, G. Performance of a LiBr-water absorption chiller operating with plate heat exchangers. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 3393–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Hong, H.K.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, Y.T. Impact of plate design on the performance of welded type plate heat exchangers for sorption cycles. Int. J. Refrig. 2009, 32, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, S.S.; Kang, Y.T. Heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of plate heat exchanger for absorption application. Proceedings SAREK Conference. 2005, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, O.K.; Cha, D.A.; Yun, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Performance evaluation of plate heat exchanger with chevron angle variations. Trans. Korean Soc. Mech. Eng. B 2009, 33, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Kang, Y.T. Comparisons of Nu correlations for H2O/LiBr solution in plate heat exchanger for triple effect absorption chiller application. Energy 2019, 172, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kang, Y.T. Heat transfer and frictional pressure drop characteristics of H2O/LiBr solution in plate heat exchangers for triple-effect absorption application. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 189, 116730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulcerations, P.F. Heat exchanger development for compact water/LiBr sorption systems 200 DRAFT Proceedings of IMECE2006. In Proceedings of the 6 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–10 November 2006; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.; Garimella, S. Falling-film and droplet mode heat and mass transfer in a horizontal tube LiBr/water absorber. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 1445–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killion, J.D.; Garimella, S. A review of experimental investigations of absorption of water vapor in liquid films falling over horizontal tubes. HVAC R Res. 2003, 9, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.J.; Best, R.; Cerezo, J.; Barrera, M.A.; Lezama, F.R. Experimental study of a bubble mode absorption with an inner vapor distributor in a plate heat exchanger-type absorber with NH3-LiNO3. Energies 2018, 11, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Haglind, F. Relationship between inclination angle and friction factor of chevron-type plate heat exchangers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 162, 120370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Seara, J.; Uhía, F.J.; Sieres, J.; Campo, A. A general review of the Wilson plot method and its modifications to determine convection coefficients in heat exchange devices. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alzahran, S.; Islam, M.; Saha, S. A thermo-hydraulic characteristics investigation in corrugated plate heat exchanger. Energy Procedia 2019, 160, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Baleta, J.; Sundén, B. Performance analysis of a plate heat exchanger using various nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 158, 119993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetzel, W.; Das, S.K.; Luo, X. Measurement of the heat transfer coefficient in plate heat exchangers using a temperature oscillation technique. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1994, 37, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjević, E.; Kabelac, S.; Šerbanović, S. Heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop during refrigerant R-134a condensation in a plate heat exchanger. Chem. Pap. 2008, 62, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focke, W.W.; Zachariades, J.; Olivier, I. The effect of the corrugation inclination angle on the thermohydraulic performance of plate heat exchangers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1985, 28, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, G.A.; Zilio, C. Condensation of the low GWP refrigerant HFC1234yf inside a brazed plate heat exchanger. Int. J. Refrig. 2013, 36, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Dimension |
|---|---|
| Plate width, Lw | 0.108 m |
| Plate length, L | 0.203 m |
| Plate thickness, twall | 0.0005 m |
| Corrugation depth, b | 0.002 m |
| Corrugation pitch, λ | 0.007 m |
| Chevron angle, α | 60° |
| Number of plates, N | 20 |
| Number of channels, Nch | 9 |
| Port diameter, Dpart | 0.025 m |
| Type | Item | Cold Side | Hot Side |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water/water | Inlet fluid temperature, °C | 40 | 80 |
| Mass flow rate, kg/h | 300 | 200–700 | |
| Reynolds number | 250.4–289.7 | 210.9–832.1 | |
| LiBr/water | LiBr concentration, % | - | 56, 58, 60, 62 |
| Inlet fluid temperature, °C | 40 | 80 | |
| Mass flow rate, kg/h | 300 | 200–700 | |
| Reynolds number | 238–275.6 | 22.5–140.6 |
| Measurements | Model | Range | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature, °C | RTD PT100 | −50–400 | ±0.5 °C |
| Mass flow rate, kg/h | ALT mass type U | 0–1200 | ±0.1% |
| Pressure, kPa | UNIK 5000 | 0–20 | ±0.1% |
| Density, g/mL | ALT mass type U | 0.32–2 | ±0.0005 g/mL |
| Measurements | Uncertainty |
|---|---|
| Heat transfer rate | ±2.4% |
| Heat transfer coefficient | ±1.76% |
| Nusselt number | ±3.37% |
| Reference | A | B | C | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roetzel et al. [30] | 0.371 | 0.703 | 1/3 | |
| Donowski and Kandlikar. [31] | 0.2875 | 0.78 | 1/3 | |
| Focke et al. [32] | 0.77 | 0.54 | 1/3 | - |
| Longo and zilio. [33] | 0.277 | 0.766 | 0.333 |
| Reference | Chevron Angle, ° | Plate Width, m | Plate Length, m | Corrugation Depth, m | Corrugation Pitch, m | Plate Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim et al. [18] | 30, 45, 63 | 0.192 | 0.519 | 0.0025 | - | 80 |
| Kwon et al. [19] | 120, 60, 60 × 120 | 0.119 | 0.289 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 20 |
| Song et al. [21] | 55.7, 78.5 | 0.111 | 0.4315 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 20 |
| Present study | 60 | 0.108 | 0.203 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 20 |
| Reference | Item | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xh, % | xc, % | mh, kg/h | mc, kg/h | Th, °C | Tc, °C | |
| Kim et al. [18] | 62.5 | 53.2 | 5688–11,808 | 4140–11,088 | 125–160 | 80–95 |
| Kwon et al. [19] | 62.5 | 58.5 | 150–550 | 380 | 135–165 | 70 |
| Song et al. [21] | 50.21–64.92 | 181.8–1,063.8 | 75–154.7 | 26.24–125.6 | ||
| Present study | 58–62 | 0 | 200–700 | 300 (Water) | 80 | 40 |
| LiBr Concentration, % | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 56 | 0.28 | 0.677 | 1/3 |
| 58 | 0.282 | 0.671 | 1/3 |
| 60 | 0.3 | 0.654 | 1/3 |
| 62 | 0.324 | 0.644 | 1/3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yong, J.; Ham, J.; Kwon, O.; Cho, H. Experimental Investigation of the Heat Transfer Characteristics of Plate Heat Exchangers Using LiBr/Water as Working Fluid. Energies 2021, 14, 6761. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206761
Yong J, Ham J, Kwon O, Cho H. Experimental Investigation of the Heat Transfer Characteristics of Plate Heat Exchangers Using LiBr/Water as Working Fluid. Energies. 2021; 14(20):6761. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206761
Chicago/Turabian StyleYong, Junhyeok, Junggyun Ham, Ohkyung Kwon, and Honghyun Cho. 2021. "Experimental Investigation of the Heat Transfer Characteristics of Plate Heat Exchangers Using LiBr/Water as Working Fluid" Energies 14, no. 20: 6761. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206761
APA StyleYong, J., Ham, J., Kwon, O., & Cho, H. (2021). Experimental Investigation of the Heat Transfer Characteristics of Plate Heat Exchangers Using LiBr/Water as Working Fluid. Energies, 14(20), 6761. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206761






